If you encounter an error message while using Data Transmission Service (DTS), see Common errors for a solution. If you do not receive a specific error message, find your issue in the categories below.
Issue categories
Common issues fall into the following categories:
Billing issues
How does DTS billing work?
DTS offers two billing methods: subscription and pay-as-you-go. For more information, see Billing overview.
How do I view my DTS bill?
For instructions on how to view your DTS bill, see View bills.
Am I still charged after pausing a DTS instance?
Migration instances are not billed while paused.
You are still charged for a data synchronization instance when it is paused, regardless of whether the databases can be connected. This is because DTS only pauses writing data to the destination database. It still consumes resources, such as CPU and memory, to continuously connect to the databases and pull logs from the source database. This allows the instance to resume quickly when restarted.
Why is data synchronization priced higher than data migration?
Data synchronization is priced higher because it includes advanced features, such as online adjustment of synchronization objects and bidirectional synchronization between MySQL databases. Additionally, data synchronization uses internal network transmission, which ensures lower network latency.
What happens if my account has an overdue payment?
For more information about the impact of overdue payments, see Expiration or overdue payment.
How do I release a subscription-based task early?
To do this, you must first convert the subscription task to a pay-as-you-go task and then unsubscribe. For more information about the conversion, see Switch between billing methods.
Can I convert a subscription task to pay-as-you-go?
Yes, you can. For more information, see Switch between billing methods.
Can I convert a pay-as-you-go task to subscription?
You can switch the billing method for data synchronization or tracking tasks. For more information, see Switch between billing methods.
Data migration tasks support only the pay-as-you-go billing method.
Why did my DTS task suddenly start incurring charges?
Your free trial period may have expired. DTS offers a limited-time free trial for tasks that use Alibaba Cloud proprietary database engines as the destination. After the free trial ends, charges are automatically incurred.
Why am I still being charged for a released task?
DTS bills pay-as-you-go tasks on a daily basis. If you used a DTS task on the day you released it, you are charged for that day's usage.
How does pay-as-you-go billing work?
DTS incurs charges only during the normal operation of incremental tasks (including pauses during incremental synchronization, but excluding pauses during incremental migration). For more information, see Billing methods.
Does DTS charge for data transfer?
Some DTS tasks incur public network and data transfer fees, regardless of the source and destination regions. Migration tasks incur public network traffic fees if the destination database Access Method is set to Public IP Address. Full validation tasks using the Full field validation by row sampling mode incur data transfer fees based on the validated data volume. For more information, see Billing items.
Performance and specification issues
What are the differences between instance specifications?
For more information about the differences between instance specifications, see Data migration link specification and Data synchronization link specification.
Can I upgrade my instance specification?
Yes, you can. For more information, see Upgrade instance link specification.
Can I downgrade my instance specification?
Currently, only sync instances are supported. For more information, see Instance link downgrade specifications.
Can DTS tasks be downgraded (lowered specification)?
Eligible DTS tasks support downgrades (reduced link specification). For details, see Downgrade instance link specification.
Can DTS tasks be downgraded below the medium specification?
Not supported.
How long does data synchronization or migration take?
The performance of a DTS task depends on multiple factors, such as the internal processing of DTS, the loads on the source and destination databases, the data volume, whether incremental tasks are running, and network conditions. Therefore, the exact duration of a task cannot be estimated. If you require high performance, select an instance with higher specifications. For more information about specifications, see Data migration link specification and Data synchronization link specification.
How do I view performance metrics for data migration or synchronization tasks?
For instructions on how to view performance metrics, see View incremental migration link status and performance or View synchronization link status and performance.
Why can't I find a specific DTS instance in the console?
Possible cause: The subscription DTS instance has expired and been released.
The selected resource group is incorrect. Select All resources under account.
You may have selected the wrong region. Make sure that the selected region is the one where the destination instance resides.
This can occur if you select the wrong task type. Verify that you are viewing the correct task list page. For example, synchronization instances only appear in the Data Synchronization Tasks list.
The instance is released due to expiration or an overdue payment. When a DTS instance expires or incurs an overdue payment, its data transmission task stops. If you do not add funds to your account within 7 days, the system releases and deletes the instance. For more information, see Expiration and Overdue Payments.
Precheck issues
Why does the Redis eviction policy precheck show an alert?
If the eviction policy (maxmemory-policy) of the destination database is set to a value other than noeviction, data inconsistency may occur between the source and destination databases. For more information about eviction policies, see Redis data eviction policy introduction.
How do I handle Binlog-related precheck failures during incremental data migration?
Check whether the binary logs of the source database are enabled and working as expected. For more information, see Source database binary log check.
Database connection issues
How do I handle source database connection failures?
Check whether the information and settings of the source database are correctly configured. For more information, see Source database connectivity check.
How do I handle destination database connection failures?
Check whether the information and settings of the destination database are correctly configured. For more information, see Destination database connectivity check.
How do I migrate or synchronize data when the source or destination instance is in a region not yet supported by DTS?
For data migration tasks, obtain a public IP address for your database instance (such as RDS MySQL) and use the public IP to connect to the instance. Select a DTS-supported region for the instance and add the corresponding DTS server IP ranges to your instance's whitelist. For the required IP addresses, see Add DTS server IP addresses to whitelist.
For data synchronization tasks, DTS does not support synchronization in these regions because synchronization currently does not support connecting database instances via public IP.
Data synchronization issues
Which database instances does DTS support for synchronization?
DTS supports data synchronization between various data sources, including relational database management systems (RDBMS), NoSQL databases, and online analytical processing (OLAP) databases. For more information about the supported database instances, see Synchronization scenarios overview.
What's the difference between data migration and data synchronization?
The following table describes the differences between data migration and data synchronization.
Self-managed database: When configuring a DTS instance, a database instance whose Access Method is not Alibaba Cloud Instance. Self-managed databases include third-party cloud databases, on-premises databases, and databases deployed on ECS instances.
Comparison item | Data migration | Data synchronization |
Use case | Primarily used for cloud migration. For example, you can migrate on-premises databases, self-managed databases on ECS instances, or third-party cloud databases to Alibaba Cloud databases. | Primarily used for real-time data synchronization between two data sources. This is suitable for scenarios such as active geo-redundancy, data disaster recovery, cross-border data synchronization, query and reporting offloading, cloud business intelligence (BI), and real-time data warehouses. |
Supported databases | For more information, see Migration scenarios overview. Note For some databases that are not supported by data synchronization, you can use data migration to achieve synchronization. Examples include standalone MongoDB databases and OceanBase (MySQL mode) databases. | For more information, see Synchronization scenarios overview. |
Supported database deployment locations (connection types) |
|
Note Data synchronization uses internal network transmission, which ensures lower network latency. |
Feature differences |
|
|
Billing method | Supports only the pay-as-you-go billing method. | Supports both the pay-as-you-go and subscription billing methods. |
Is it billed? | Only migration instances with incremental migration tasks incur charges. | Yes. Synchronization instances include incremental synchronization by default, so they always incur charges. |
Billing rules | Charges are incurred only when an incremental data migration task is running. Paused tasks are not billed. No charges are incurred during schema migration or full data migration. |
|
How does data synchronization work?
For more information about how data synchronization works, see Service architecture and functional principles.
How is synchronization latency calculated?
Synchronization latency is the time difference in milliseconds between the timestamp of the latest data entry synchronized to the destination database and the current timestamp of the source database.
Normal latency is less than 1,000 milliseconds.
Can I modify synchronization objects in a running synchronization task?
Yes, you can. For instructions on how to modify synchronization objects, see Add synchronization objects and Remove synchronization objects.
Can I add new tables to an existing synchronization task?
Yes, you can. For instructions on how to add new tables, see Add synchronization objects.
How do I modify tables and fields in a running synchronization task?
You can modify synchronization objects after the full synchronization phase is complete and the task enters the incremental synchronization phase. For instructions, see Add synchronization objects and Remove synchronization objects.
Will pausing and later restarting a synchronization task cause data inconsistency?
If data in the source database is modified while the task is paused, data inconsistency may occur between the source and destination databases. After you restart the task and the incremental data is synchronized, the data in the destination database becomes consistent with the data in the source database.
If I delete data from the source database of an incremental synchronization task, will the synchronized data in the destination database be deleted?
If the DML operations to be synchronized do not include delete, no data will be deleted in the destination. Otherwise, the corresponding data in the destination will be deleted.
During Redis-to-Redis synchronization, will data in the destination Redis instance be overwritten?
Yes, data with the same key is overwritten. DTS checks the destination database during the precheck and reports an error if the destination database contains existing data.
Can synchronization tasks filter specific fields or data?
Yes, you can. You can use the object name mapping feature to filter out columns that you do not want to synchronize. You can also specify SQL WHERE conditions to filter the data that you want to synchronize. For more information, see Synchronize or migrate specific columns and Filter task data using SQL conditions.
Can a synchronization task be converted to a migration task?
No, you cannot. You cannot convert a task of one type to another.
Can I synchronize only data without synchronizing the schema?
Yes, you can clear the Schema synchronization option when configuring the synchronization task.
What might cause data inconsistency between source and destination in a data synchronization instance?
The following are possible causes of data inconsistency:
The destination database was not cleared before the task was configured, and existing data was present in the destination database.
Only incremental synchronization was selected during task configuration, without full synchronization.
Only full synchronization was selected during task configuration, without incremental synchronization, and the source data changed after the task was complete.
Data was written to the destination database from sources other than the DTS task.
Incremental writes are delayed, and not all incremental data has been written to the destination database.
Can I rename the source database in the destination during synchronization?
Yes, you can. For instructions on how to rename the source database in the destination database, see Set names of synchronization objects in destination instance.
Does DTS support real-time synchronization of DML or DDL operations?
Yes, it does. Data synchronization between relational databases supports Data Manipulation Language (DML) operations, such as INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, and Data Definition Language (DDL) operations, such as CREATE, DROP, ALTER, RENAME, and TRUNCATE.
The supported DML or DDL operations vary based on the scenario. In Synchronization scenarios overview, select the link that matches your business scenario and check the supported DML or DDL operations in the specific link configuration documentation.
Can a read-only instance serve as the source for a synchronization task?
Synchronization tasks include incremental data synchronization by default. This results in two scenarios:
Read-only instances that record transaction logs, such as RDS for MySQL 5.7 or 8.0, can serve as the source.
Read-only instances that do not record transaction logs, such as RDS for MySQL 5.6, cannot serve as the source.
Does DTS support sharded database and table synchronization?
Yes, it does. For example, you can synchronize sharded databases and tables from a MySQL or PolarDB for MySQL database to an AnalyticDB for MySQL database to merge multiple tables.
Why is the data volume in the destination instance smaller than in the source after synchronization?
If you filtered data during the synchronization or if the source instance contained significant table fragmentation, the data volume in the destination instance may be smaller than that in the source instance after the migration is complete.
Does cross-account data synchronization support bidirectional synchronization?
Currently, bidirectional cross-account synchronization is supported only between RDS MySQL instances, between PolarDB for MySQL clusters, between Tair (Enterprise Edition) instances, between ApsaraDB for MongoDB (ReplicaSet architecture) instances, and between ApsaraDB for MongoDB (sharded cluster architecture) instances.
Does reverse synchronization in bidirectional synchronization support DDL synchronization?
No, it does not. Only forward synchronization tasks (from source to destination) support DDL synchronization. Reverse synchronization tasks (from destination to source) do not support DDL synchronization and automatically filter out DDL operations.
To synchronize DDL operations in the current reverse synchronization task, you can try to reverse the direction of the bidirectional synchronization instance if your business allows.
Do I need to manually configure the reverse synchronization task?
Required. Wait until the forward sync task completes initial synchronization (until the Status is Running), then navigate to the reverse sync task and click Configure Task to configure it.
We recommend that you configure the reverse synchronization task only after the forward synchronization task has no delay (0 milliseconds).
Does DTS support cross-border bidirectional synchronization tasks?
Not supported.
Why doesn't a record added to one database in a bidirectional synchronization task appear in the other database?
This may be because the reverse task is not configured.
Why doesn't the incremental synchronization percentage ever reach 100%?
An incremental synchronization task continuously synchronizes real-time data changes from the source database to the destination database and does not automatically end. Therefore, the completion progress never reaches 100%. If you do not require continuous real-time synchronization, you can manually end the task in the DTS console.
Why can't an incremental synchronization task synchronize data?
If a DTS instance is configured for only incremental synchronization, DTS synchronizes only the data generated after the task starts. Existing data is not synchronized. To ensure data consistency, we recommend that you select Incremental synchronization, Schema synchronization, and Full synchronization when you configure the task.
Does full data synchronization from RDS affect source RDS performance?
Yes, it affects the query performance of the source database. To reduce the impact of the DTS task on the source database, you can use one of the following methods:
Increase the specification of the source database instance.
Temporarily pause the DTS task and restart it after the load on the source database decreases.
Reduce the rate of the DTS task. For instructions, see Adjust full migration rate.
Why doesn't a synchronization instance with PolarDB-X 1.0 as the source display latency?
Instances with PolarDB-X 1.0 as the source are distributed tasks, and DTS monitoring metrics exist only in subtasks. Therefore, latency information is not displayed for PolarDB-X 1.0 source instances. Click the instance ID and view latency information in the Task Management section under Subtask Details.
Why does a multi-table merge task report error DTS-071001?
During the execution of a multi-table merge task, online DDL operations might have modified the source table structure without corresponding manual modifications in the destination database.
How do I handle whitelist addition failures when configuring tasks in the Legacy Console?
You can use the new console to configure tasks.
How do I handle task failures caused by DDL operations on the source database during DTS data synchronization?
You can manually execute the same DDL operations on the destination database that were executed on the source database, and then restart the task. During data synchronization, do not use tools such as pt-online-schema-change to perform online DDL changes on synchronization objects in the source database. This can cause the synchronization to fail. If no data other than the data from DTS has been written to the destination database, you can use Data Management (DMS) to perform online DDL changes, or remove the affected tables from the synchronization objects. For instructions on how to remove tables, see Remove synchronization objects.
How do I handle task failures caused by DDL operations on the destination database during DTS data synchronization?
If a database or table is deleted from the destination database during DTS incremental synchronization, which causes task exceptions, you can use one of the following solutions:
Method 1: Reconfigure the task and exclude the database or table that caused the failure from the synchronization objects.
Method 2: Modify the synchronization objects to remove the problematic database or table. For instructions, see Remove synchronization objects.
Can a released synchronization task be restored? Can data consistency be guaranteed when reconfiguring the task?
Released synchronization tasks cannot be restored. If you reconfigure a task without selecting Full synchronization, data generated between the task release and the new task startup will not be synchronized to the destination database, compromising data consistency. If your business requires precise data, delete the data in the destination database and then reconfigure the synchronization task. In the Task Steps, select Schema synchronization and Full synchronization (with Incremental synchronization selected by default).
How do I handle a DTS full synchronization task that shows no progress for a long time?
If a table that you want to synchronize does not have a primary key, the full synchronization will be very slow. We recommend that you add a primary key to the source table before you start the synchronization.
When synchronizing tables with the same name, does DTS support transferring source table data only when it doesn't exist in the destination table?
Yes. During task configuration, you can set Handling mode for existing tables in destination to Ignore errors and continue. If the table structures match, during a full synchronization, a source record is not synchronized if a record with the same primary key value already exists in the destination.
How do I configure a cross-account synchronization task?
First, you need to identify the scenarios for cross-account tasks. Then, use the Alibaba Cloud account that owns the database instance to configure RAM authorization for cross-account tasks. Finally, you can configure cross-account tasks.
How do I handle inability to select a DMS LogicDB instance?
Make sure that you have selected the correct region for the instance. If you still cannot select the instance, there might be only one instance available. You can continue to configure other parameters.
Does a synchronization task with SQL Server as the source support synchronizing functions?
No, it does not. When synchronization objects are selected at the table granularity, other objects, such as views, triggers, and stored procedures, are not synchronized to the destination database.
How do I handle synchronization task errors?
Based on the error message, check Common errors for solutions.
How do I enable hot spot merging in a synchronization task?
Set the trans.hot.merge.enable parameter to true. For more information, see Modify parameter values.
How do I handle synchronization when triggers exist in the source database?
When you synchronize an entire database and triggers (TRIGGER) in the database update a table within the same database, data inconsistency between the source and destination databases may occur. For more information about the synchronization procedure, see How to configure synchronization or migration jobs when triggers exist in the source database.
Does DTS support synchronizing the sys database and system databases?
No, it does not.
Does DTS support synchronizing MongoDB's admin and local databases?
No, it does not. DTS does not support using the admin and local databases of MongoDB as the source or destination.
When can I configure the reverse task for a bidirectional synchronization task?
You can configure the reverse task for a bidirectional synchronization task only after the forward incremental task has zero latency.
Does a synchronization task with PolarDB-X 1.0 as the source support scaling nodes?
No, it does not. If node scaling occurs on the PolarDB-X 1.0 source, you must reconfigure the task.
Can DTS guarantee uniqueness for data synchronized to Kafka?
No, it cannot. Because data written to Kafka is appended, duplicate data may occur when the DTS task restarts or re-pulls source logs. DTS guarantees data idempotence. This means that data is ordered sequentially, and the latest value of duplicate data appears last.
Does DTS support synchronizing from RDS MySQL to AnalyticDB for MySQL?
Yes, it does. For configuration instructions, see Synchronize from RDS MySQL to AnalyticDB for MySQL 3.0.
Why doesn't Redis-to-Redis synchronization display full synchronization?
Redis-to-Redis synchronization supports both full and incremental data synchronization, and is displayed as Incremental synchronization.
Can I skip full synchronization?
Yes, you can. Skipping full synchronization allows incremental synchronization to continue, but errors may occur. We recommend that you do not skip full synchronization.
Does DTS support scheduled automatic synchronization?
DTS does not support scheduled startup of data synchronization tasks.
Does synchronization transfer table fragmentation space along with the data?
No, it does not.
What should I note when synchronizing from MySQL 8.0 to MySQL 5.6?
You must create the database in MySQL 5.6 before you start the synchronization. We recommend that you keep the source and destination versions consistent or synchronize data from a lower version to a higher version to ensure compatibility. Synchronizing data from a higher version to a lower version may cause compatibility issues.
Can I synchronize accounts from the source database to the destination database?
Currently, only synchronization tasks between RDS for MySQL instances support account synchronization. Other synchronization tasks do not support this feature.
Can I configure cross-account bidirectional synchronization tasks?
Currently, bidirectional cross-account synchronization is supported only between RDS MySQL instances, between PolarDB for MySQL clusters, between Tair (Enterprise Edition) instances, between ApsaraDB for MongoDB (ReplicaSet architecture) instances, and between ApsaraDB for MongoDB (sharded cluster architecture) instances.
For tasks that do not have the Replicate Data Across Alibaba Cloud Accounts configuration option, you can use CEN to implement cross-account bidirectional synchronization. For more information, see Access database resources across Alibaba Cloud accounts or regions.
How do I configure parameters when Message Queue for Apache Kafka is the destination?
You can configure the parameters as needed. For more information about special parameter configuration methods, see Configure parameters for Message Queue for Apache Kafka instances.
When using DTS for Redis data synchronization or migration tasks, how do I handle the error ERR invalid DB index?
Cause: The ERR invalid DB index error occurs when the destination database executes the SELECT DB operation. This error is usually caused by an insufficient number of databases in the destination database. If the destination database uses a proxy, check whether the proxy can remove the restrictions on the number of databases.
Solution: Modify the databases configuration of the destination database. We recommend that you expand it to match the source database, and then restart the DTS task. You can use the following command to query the databases configuration of the destination database:
CONFIG GET databases;When synchronizing or migrating SQL Server data to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, how do I handle the error IDENTIFIER CLUSTERED?
Cause: When you synchronize or migrate SQL Server data to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, the task fails because the CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX command is not supported.
Solution: After you confirm that no other DDL statements exist during the lag period, modify the instance parameter sink.ignore.failed.ddl to true to skip the execution of all DDL statements. After the incremental synchronization or migration offset advances, reset the sink.ignore.failed.ddl parameter to false.
When extending the expiration time of keys in the destination database during Redis synchronization or migration tasks, does it have practical effect?
Yes, it does. To prevent keys from expiring during full data synchronization, you can extend the expiration time of keys in the destination database. For DTS tasks that include incremental synchronization or migration, if a key expires and is deleted in the source database, the corresponding key in the destination database is also released.
After setting an extended expiration time for keys in the destination database, if a key expires in the source database, will the key in the destination be immediately released?
No, keys in the destination database are not necessarily released immediately. The corresponding key in the destination database is released only after the key expires and is cleared from the source database.
For example, if a key in the source database has an expiration time of 5 seconds and the expiration time of the destination key is extended to 30 seconds, the destination key is immediately released when the source key expires and is automatically cleared after 5 seconds. When the source key expires and is automatically cleared, the system adds a deletion operation to the AOF file. This operation is synchronized to and executed in the destination database.
When using DTS to synchronize to SelectDB, how do I handle the error column_name[xxx], the length of input string is too long than vec schema?
Detailed error:
Reason: column_name[xxx], the length of input string is too long than vec schema. first 32 bytes of input str: [01a954b4-xxx-xxx-xxx-95b675b9] schema length: 2147483643; limit length: 1048576; actual length: 7241898; . src line [];Cause: The incremental size of the xxx field in the source has exceeded the length limit of the xxx field type in the destination.
Solution: If the field is of the
STRINGtype, you can increase the value of the string_type_length_soft_limit_bytes parameter in the SelectDB console to a value greater than theactual length(7241898).
When using DTS to synchronize to SelectDB, how do I handle the error column(xxx) values is null while columns is not nullable.?
Detailed error:
Reason: column(xxx) values is null while columns is not nullable. src line [ xxx ];Cause: The xxx field in the destination is
NOT NULL, butNULLvalues are being written.NoteCommon scenario: Illegal date format data such as
0000-0000-0000is written to the source, which causes DTS to automatically convert it toNULLand triggers the error.Solution:
Adjust the destination field type to allow NULL values.
Modify the synchronization objects: Remove the problematic table, correct the source data, and then delete the table in the destination database. Re-add the table to the synchronization objects and re-execute full and incremental synchronization.
Data migration issues
After executing a data migration task, does the source database data still exist?
DTS migrates and synchronizes data from a source database to a destination database without affecting the source data.
Which database instances does DTS support for migration?
DTS supports data migration between various data sources, including relational database management systems (RDBMS), NoSQL databases, and online analytical processing (OLAP) databases. For more information about the supported migration instances, see Migration scenarios overview.
How does data migration work?
For more information about how data migration works, see Service architecture and functional principles.
Can I modify migration objects in a running migration task?
No, you cannot.
Can I add new tables to an existing migration task?
No, you cannot.
How do I modify tables and fields in a running migration task?
Data migration tasks do not support modifying migration objects.
Will pausing and later restarting a migration task cause data inconsistency?
If data in the source database is modified while the task is paused, data inconsistency may occur between the source and destination databases. After you restart the task and the incremental data is migrated, the data in the destination database becomes consistent with the data in the source database.
Can a migration task be converted to a synchronization task?
No, you cannot. You cannot convert a task of one type to another.
Can I migrate only data without migrating the schema?
Yes, you can. When configuring the migration task, clear the Schema migration option.
What might cause data inconsistency between source and destination in a data migration instance?
The following are possible causes of data inconsistency:
The destination database was not cleared before the task was configured, and existing data was present in the destination database.
Only incremental migration was selected during task configuration, without full migration.
Only full migration was selected during task configuration, without incremental migration, and the source data changed after the task was complete.
Data was written to the destination database from sources other than the DTS task.
Incremental writes are delayed, and not all incremental data has been written to the destination database.
Can I rename the source database in the destination during migration?
Yes, you can. For instructions on how to rename the source database in the destination database, see Database, table, and column mapping.
Does DTS support data migration within the same instance?
Yes, it does. For instructions on how to perform same-instance data migration, see Data synchronization or migration between different database names.
Does DTS support real-time migration of DML or DDL operations?
Yes, it does. Data migration between relational databases supports DML operations, such as INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, and DDL operations, such as CREATE, DROP, ALTER, RENAME, and TRUNCATE.
The supported DML or DDL operations vary based on the scenario. In Migration scenarios overview, select the link that matches your business scenario and check the supported DML or DDL operations in the specific link configuration documentation.
Can a read-only instance serve as the source for a migration task?
If the migration task does not require incremental data migration, a read-only instance can serve as the source. If incremental data migration is required, two scenarios are possible:
Read-only instances that record transaction logs, such as RDS for MySQL 5.7 or 8.0, can serve as the source.
Read-only instances that do not record transaction logs, such as RDS for MySQL 5.6, cannot serve as the source.
Does DTS support sharded database and table migration?
Yes, it does. For example, you can migrate sharded databases and tables from a MySQL or PolarDB for MySQL database to an AnalyticDB for MySQL database to merge multiple tables.
Can migration tasks filter specific fields or data?
Yes, you can. You can use the object name mapping feature to filter out columns that you do not want to migrate. You can also specify SQL WHERE conditions to filter the data that you want to migrate. For more information, see Synchronize or migrate specific columns and Filter data to be migrated.
Why is the data volume in the destination instance smaller than in the source after migration?
If you filtered data during the migration or if the source instance contained significant table fragmentation, the data volume in the destination instance may be smaller than that in the source instance after the migration is complete.
Why does the completed value exceed the total after migration task completion?
The displayed total is an estimate. After the migration task is complete, the total is adjusted to the accurate value.
What is the purpose of the increment_trx table created in the destination database during data migration?
During data migration, DTS creates an `increment_trx` table in the destination instance. This table serves as a checkpoint table for incremental migration. It records incremental migration checkpoints to support resuming from breakpoints after a task fails. Do not delete this table during the migration. Otherwise, the migration task will fail.
Does DTS support resuming from breakpoints during the full migration phase?
Yes, it does. If you pause and then restart a task during the full migration phase, the task resumes from where it left off instead of restarting from the beginning.
How do I migrate non-Alibaba Cloud instances to Alibaba Cloud?
For instructions on how to migrate non-Alibaba Cloud instances to Alibaba Cloud, see Migrate from third-party cloud to Alibaba Cloud.
How do I migrate a local Oracle database to PolarDB?
For instructions on how to migrate an on-premises Oracle database to PolarDB, see Migrate self-managed Oracle to PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle).
Can I pause a data migration task before full migration completes?
Yes, you can.
How do I migrate partial data from RDS MySQL to self-managed MySQL?
During task configuration, you can select the objects to migrate in Source Objects or filter them in Selected Objects as needed. The process for a MySQL-to-MySQL migration is similar. For more information, see Migrate self-managed MySQL to RDS MySQL.
How do I migrate between RDS instances under the same Alibaba Cloud account?
DTS supports migration and synchronization between RDS instances. For more information about the configuration methods, see the relevant configuration documentation in Migration scenarios overview.
After starting a migration task, the source database shows IOPS alerts. How can I ensure source database stability?
If the load on the source database instance is high when a DTS task is running, you can use one of the following methods to reduce the impact of the DTS task on the source database:
Increase the specification of the source database instance.
Temporarily pause the DTS task and restart it after the load on the source database decreases.
Reduce the rate of the DTS task. For instructions, see Adjust full migration rate.
Why can't I select a database named test for data migration?
DTS data migration does not support the migration of system databases. You must select a user-created database for migration.
Why doesn't a migration instance with PolarDB-X 1.0 as the source display latency?
Instances with PolarDB-X 1.0 as the source are distributed tasks, and DTS monitoring metrics exist only in subtasks. Therefore, latency information is not displayed for PolarDB-X 1.0 source instances. Click the instance ID and view latency information in the Task Management section under Subtask Details.
Why can't DTS migrate MongoDB databases?
The database to be migrated might be a local or admin database. DTS does not support using the admin and local databases of MongoDB as the source or destination.
Why does a multi-table merge task report error DTS-071001?
During the execution of a multi-table merge task, online DDL operations might have modified the source table structure without corresponding manual modifications in the destination database.
How do I handle whitelist addition failures when configuring tasks in the Legacy Console?
You can use the new console to configure tasks.
How do I handle task failures caused by DDL operations on the source database during DTS data migration?
You can manually execute the same DDL operations on the destination database that were executed on the source database, and then restart the task. During data migration, do not use tools such as pt-online-schema-change to perform online DDL changes on migration objects in the source database. This can cause the migration to fail. If no data other than the data from DTS has been written to the destination database, you can use Data Management (DMS) to perform online DDL changes.
How do I handle task failures caused by DDL operations on the destination database during DTS data migration?
If a database or table is deleted from the destination database during DTS incremental migration, which causes task exceptions, you must reconfigure the task and exclude the database or table that caused the failure from the migration objects.
Can a released migration task be restored? Can data consistency be guaranteed when reconfiguring the task?
You cannot restore a released migration task. If you reconfigure a task without selecting Full migration, data generated between the task release and the start of the new task is not migrated to the destination database. This compromises data consistency. If your business requires high data accuracy, delete the data from the destination database, and then reconfigure the migration task. In the Task Steps section, select Schema migration, Incremental migration, and Full migration.
How do I handle a DTS full migration task that shows no progress for a long time?
If a table that you want to migrate does not have a primary key, the full migration will be very slow. We recommend that you add a primary key to the source table before you start the migration.
When migrating tables with the same name, does DTS support transferring source table data only when it doesn't exist in the destination table?
Yes. During task configuration, set Handling mode for existing tables in destination to Ignore errors and continue. When the table structures match, a source record is not migrated during a full migration if the destination already contains a record with the same primary key value.
How do I configure a cross-account migration task?
First, you need to understand the scenarios of cross-account tasks. Then, use the Alibaba Cloud account that owns the database instance to configure RAM authorization for cross-account tasks. Finally, you can configure the cross-account task.
How do I connect to a local database for data migration tasks?
Set Connection Type to Public IP to configure the migration task. For more information, see Migrate self-managed MySQL to RDS MySQL.
How do I handle data migration failure with error DTS-31008?
Click View Reason or check Common errors to find a solution for the error message.
How do I handle network connectivity issues when using leased lines to connect to self-managed databases?
Check whether the leased line correctly configures the DTS-related IP whitelist. For more information about the required IP address ranges, see Add DTS server IP address ranges to self-managed database IP whitelist.
Does a migration task with SQL Server as the source support migrating functions?
No, it does not. When migration objects are selected at the table granularity, other objects, such as views, triggers, and stored procedures, are not migrated to the destination database.
How do I handle slow DTS full migration speed?
The migration may take some time because the data volume can be large. You can check the migration progress on the task details page in the Task Management section under Full Migration.
How do I handle schema migration errors?
Click the instance ID to go to the task details page. Check the specific error messages in the Task Management section for the schema migration, and then resolve the errors. For common error solutions, see Common errors.
Are schema migration and full migration billed?
No, they are not. For more information about billing, see Billing items.
During Redis-to-Redis data migration, will zset data in the destination be overwritten?
The destination zset is overwritten. If the destination database already contains a key that is identical to a key in the source database, DTS first deletes the corresponding zset in the destination database, and then adds each object from the source zset collection to the destination database.
What impact does full migration have on the source database?
The DTS full migration process first slices the data, and then reads and writes data within each slice range. For the source database, slicing increases IOPS. Reading data within slice ranges affects IOPS, CachePool, and outbound bandwidth. Based on DTS practical experience, these impacts are negligible.
Does a migration task with PolarDB-X 1.0 as the source support scaling nodes?
No, it does not. If node scaling occurs on the PolarDB-X 1.0 source, you must reconfigure the task.
Can DTS guarantee uniqueness for data migrated to Kafka?
No, it cannot. Because data written to Kafka is appended, duplicate data may occur when the DTS task restarts or re-pulls source logs. DTS guarantees data idempotence. This means that data is ordered sequentially, and the latest value of duplicate data appears last.
If I configure a full migration task first, then configure an incremental data migration task, will data inconsistency occur?
Yes, data inconsistency may occur. If you configure an incremental data migration task separately, the data migration starts only after the incremental migration task begins. Data that was generated in the source instance before the incremental migration task started is not synchronized to the destination instance. For zero-downtime migration, we recommend that you select schema migration, full data migration, and incremental data migration when you configure the task.
When configuring an incremental migration task, should I select schema migration?
Schema migration transfers object definitions, such as the definition of Table A, to the destination instance before the data migration begins. To ensure data consistency for incremental migration, we recommend that you select schema migration, full data migration, and incremental data migration.
Why does RDS use more storage space than the source database during self-managed database to RDS migration?
DTS performs logical migration. This means that the data to be migrated is packaged as SQL statements and then migrated to the destination RDS instance. This process generates binary log (binlog) data in the destination RDS instance. Therefore, the RDS instance may use more storage space than the source database during the migration.
Does DTS support migrating MongoDB in VPC networks?
Yes, it does. DTS supports using a VPC-based ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance as the source database for migration.
What happens to migrated data if the source database changes during data migration?
If the migration task is configured with schema migration, full migration, and incremental migration, all data changes in the source database during the migration are migrated to the destination database by DTS.
Will releasing a completed migration task affect the migrated database's usage?
No. After the migration task completes (Running Status shows Completed), you can safely release the migration task.
Does DTS support MongoDB incremental migration?
Yes, it does. For configuration examples, see Migration scenarios overview.
What's the difference between using an RDS instance and a self-managed database with public IP as the source instance for migration tasks?
When you configure migration tasks with RDS instances, DTS automatically adapts to changes such as DNS modifications or network type switches in the RDS instances. This ensures link reliability.
Does DTS support migrating self-managed databases on ECS in VPC to RDS instances?
Supported.
If the source ECS instance and the destination RDS instance are in the same region, DTS can directly access the self-managed database on the ECS instance in the VPC.
If the source ECS instance and the destination RDS instance are in different regions, the ECS instance requires an Elastic IP address. When you configure the migration task, you can select the ECS instance as the source, and DTS automatically uses the Elastic IP address of the ECS instance to access the database.
Does DTS lock tables during migration? Does it affect the source database?
No, DTS does not lock tables in the source database during either full or incremental data migration. The tables in the source database remain readable and writable during the migration.
When performing RDS migration, does DTS pull data from the RDS primary or secondary database?
DTS pulls data from the primary RDS database during data migration.
Does DTS support scheduled automatic migration?
DTS does not support scheduled startup of data migration tasks.
Does DTS support data migration for RDS instances in VPC mode?
Yes. To configure a migration task, you only need to provide the RDS instance ID.
For same-account or cross-account migration/synchronization, does DTS use internal or public network for ECS/RDS instances? Are traffic fees charged?
For synchronization or migration tasks, the network used (internal or public) is unrelated to whether the accounts are cross-account. Traffic fees depend on the task type.
Network used
Migration tasks: For same-region migration, DTS uses the internal network to connect to ECS and RDS instances. For cross-region migration, DTS uses the public network to connect to the source instance (ECS or RDS) and the internal network to connect to the destination RDS instance.
Sync tasks use a private network.
Traffic fees
For migration tasks, you are charged for public network outbound traffic if the Access Method of the destination database instance is Public IP Address. Traffic fees are not charged for other DTS instance types.
Synchronization tasks: No traffic fees are charged.
When using DTS for data migration, will source database data be deleted after migration?
No, it will not. DTS copies data from the source database to the destination database without affecting the data in the source database.
When performing data migration between RDS instances, can I specify the destination database name?
Yes, you can. When you perform data migration between RDS instances, you can use the database name mapping feature of DTS to specify the destination database name. For more information, see Data synchronization or migration between different database names.
How do I handle DTS migration task source unable to connect to ECS instances?
The ECS instance might not have a public IP address enabled. You can bind an Elastic IP address to the ECS instance and retry. For more information about how to bind an Elastic IP address, see Elastic IP Address.
Why doesn't Redis-to-Redis migration display full migration?
Redis-to-Redis migration supports both full and incremental data migration, which are displayed together as Incremental migration.
Can I skip full migration?
Yes, you can. Skipping full migration allows incremental migration to continue, but errors may occur. We recommend that you do not skip full migration.
Does Redis Cluster Edition support public IP connection to DTS?
No, it does not. Currently, only Redis Basic Edition supports public IP connection to DTS migration instances.
What should I note when migrating from MySQL 8.0 to MySQL 5.6?
You must create the database in MySQL 5.6 before you start the migration. We recommend that you keep the source and destination versions consistent or migrate data from a lower version to a higher version to ensure compatibility. Migrating data from a higher version to a lower version may cause compatibility issues.
Can I migrate accounts from the source database to the destination database?
Currently, only migration tasks between RDS for MySQL instances support account migration. Other migration tasks do not support this feature.
How do I configure parameters when Message Queue for Apache Kafka is the destination?
You can configure the parameters as needed. For more information about special parameter configuration methods, see Configure parameters for Message Queue for Apache Kafka instances.
How do I schedule full migration?
You can use the scheduling strategy in data integration to periodically migrate the schema and historical data of the source database to the destination database. For more information, see Configure data integration tasks between RDS MySQL instances.
Does DTS support migrating ECS self-managed SQL Server to local self-managed SQL Server?
Yes, it does. The on-premises self-managed SQL Server needs to be connected to Alibaba Cloud. For more information, see Preparations overview.
Does DTS support migrating PostgreSQL databases from other clouds?
When PostgreSQL databases from other clouds allow DTS public network access, DTS supports data migration.
If the PostgreSQL version is earlier than 10.0, incremental migration is not supported.
Change tracking issues
How does change tracking work?
For more information, see Service architecture and features.
After a change tracking task expires, are consumer groups deleted?
After a DTS change tracking task expires, the related data consumer groups are retained for seven days. If the instance is not renewed within seven days after it expires, the instance is released and the corresponding consumer groups are deleted.
Can a read-only instance serve as the source for a subscription task?
Two scenarios are possible:
Read-only instances that record transaction logs, such as RDS for MySQL 5.7 or 8.0, can serve as the source.
Read-only instances that do not record transaction logs, such as RDS for MySQL 5.6, cannot serve as the source.
How do I consume subscribed data?
For more information, see Consume subscribed data.
Why does date data format change after using change tracking to transfer data?
DTS stores date data in the default format YYYY:MM:DD. Although YYYY-MM-DD is the display format, the actual storage format is YYYY:MM:DD. Therefore, regardless of the input format, the data is converted to the default format.
How do I troubleshoot subscription task issues?
For more information about troubleshooting methods for subscription tasks, see Troubleshoot subscription tasks.
SDK normal data download suddenly pauses and can't subscribe to data. How do I handle this?
Check whether your SDK code calls the `ackAsConsumed` interface to report consumption checkpoints. If the `ackAsConsumed` interface is not called to report checkpoints, the record cache space in the SDK is not cleared. When the cache is full, new data cannot be pulled. This causes the SDK to pause and stop subscribing to data.
After restarting the SDK, I can't successfully subscribe to data. How do I handle this?
Before you start the SDK, you must modify the consumption checkpoint to make sure that it is within the data range. For more information about modification methods, see Save and query consumption checkpoints.
How can the client specify a time point for data consumption?
When you consume subscribed data, you can use the initCheckpoint parameter to specify the time point. For more information, see Use SDK sample code to consume subscribed data.
DTS subscription task has accumulated data. How do I reset the checkpoint?
Open the corresponding code file based on your SDK client usage mode. For example, DTSConsumerAssignDemo.java or DTSConsumerSubscribeDemo.java.
NoteFor more information, see Use SDK sample code to consume subscribed data.
In the subscription task list, check the modifiable checkpoint range for the target subscription instance in the Data Range column.
Select a new consumption checkpoint as needed and convert it to a Unix timestamp.
Replace the old consumption checkpoint (initCheckpoint parameter) in the code file with the new one.
Restart the client.
Client can't connect using the subscription task's VPC address. How do I handle this?
The client machine might not be in the VPC that was specified during the subscription task configuration, for example, due to a VPC replacement. You need to reconfigure the task.
Why is the consumption checkpoint in the console larger than the maximum data range value?
The data range of a subscription channel is updated every minute, while the consumption checkpoint is updated every 10 seconds. Therefore, with real-time consumption, the consumption checkpoint value might exceed the maximum value of the subscription channel data range.
How does DTS ensure SDK receives complete transactions?
Based on the provided consumption checkpoint, the server searches for the complete transaction that corresponds to this checkpoint and distributes data starting from the BEGIN statement of the transaction. This ensures that the complete content of the transaction is received.
How do I confirm data is being consumed normally?
If data is consumed normally, the consumption checkpoint in the Data Transmission Service console advances as expected.
What does usePublicIp=true mean in the change tracking SDK?
Setting usePublicIp=true in the change tracking SDK configuration means that the SDK accesses the DTS subscription channel over the public network.
Will RDS primary-secondary switchover or primary restart affect business during change tracking tasks?
For RDS for MySQL, RDS for PostgreSQL, PolarDB for MySQL, PolarDB for PostgreSQL, and PolarDB-X 1.0 (with RDS for MySQL storage type) instances, DTS automatically adapts to primary-secondary switchover or restarts without affecting your business.
Can RDS automatically download Binlog to a local server?
DTS change tracking supports real-time subscription to RDS binlogs. You can enable the DTS change tracking service and use the DTS SDK to subscribe to RDS binlog data and synchronize it in real time to a local server.
Does real-time incremental data in change tracking refer only to new data or include modified data?
DTS change tracking can subscribe to incremental data that includes all inserts, deletes, updates, and schema changes (DDL).
Why does the SDK receive duplicate data after restart when one record wasn't ACKed in the change tracking task?
If the SDK has a message that has not been acknowledged (ACKed), the server pushes all messages in the buffer. After this process is complete, the SDK cannot receive new messages. The server saves the consumption checkpoint as the checkpoint of the last message before the unacknowledged message. When the SDK restarts, the server re-pushes data starting from the checkpoint before the unacknowledged message to prevent message loss. This causes the SDK to receive duplicate data.
How often does the change tracking SDK update consumption checkpoints? Why do I sometimes receive duplicate data when restarting the SDK?
After consuming each message, the change tracking SDK must call `ackAsConsumed` to send an ACK reply to the server. After the server receives the ACK, it updates the consumption checkpoint in memory and persists it every 10 seconds. If the SDK restarts before the latest ACK is persisted, the server pushes messages starting from the last persisted checkpoint to prevent message loss. This causes the SDK to receive duplicate messages.
Can one change tracking instance subscribe to multiple RDS instances?
No, it cannot. One change tracking instance can subscribe to only one RDS instance.
Do change tracking instances experience data inconsistency?
No, it cannot. Change tracking tasks only capture source database changes and do not involve data inconsistency. If the consumed data differs from your expectations, you must troubleshoot the issue independently.
How do I handle UserRecordGenerator when consuming subscription data?
When you consume subscription data, if you see messages such as UserRecordGenerator: haven't receive records from generator for 5s, check whether the consumption checkpoint is within the checkpoint range of the incremental data collection module and make sure that the consumer is running as expected.
Can one Topic create multiple partitions?
No, it cannot. To ensure global message ordering, each subscription topic has only one partition, which is fixed to partition 0.
Does the change tracking SDK support Go language?
Sample code is available at dts-subscribe-demo.
Does the change tracking SDK support Python language?
For sample code, see dts-subscribe-demo.
Does flink-dts-connector support multi-threaded concurrent consumption of subscription data?
No, it does not.
Data validation issues
What are common causes of data inconsistency in data validation tasks?
The following are common causes:
Migration or synchronization tasks have delays.
The source database executed a column addition with default values, and the task has delays.
Data was written to the destination database from sources other than DTS.
DDL operations were executed on the source database of tasks with multi-table merge enabled.
Migration or synchronization tasks used the database, table, and column name mapping features.
Why does schema validation detect isRelHasoids differences?
PostgreSQL versions earlier than 12 support adding a globally unique object identifier (OID) field by specifying WITH OIDS when you create a table. If you specify WITH OIDS when you create a table in the source database, and the destination database is a later PostgreSQL version that does not support WITH OIDS, `isRelHasoids` differences are detected.
Should I be concerned about isRelHasoids differences detected in schema validation tasks?
No, you should not.
Does DTS synchronize or migrate object identifier (OID) fields?
No, it does not. Object identifier (OID) fields are automatically generated when you specify WITH OIDS. DTS does not synchronize or migrate this data, regardless of whether the destination database supports this field.
How do I check if a table has object identifier (OID) fields?
Replace <table_name> in the commands with the name of the table that you want to query.
SQL command:
SELECT relname AS table_name, relhasoids AS has_oids FROM pg_class WHERE relname = '<table_name>' AND relkind = 'r';Client command:
\d+ <table_name>
Other issues
What happens if I modify destination database data during data synchronization or migration tasks?
Modifying data in the destination database may cause the DTS task to fail. During migration or synchronization, operations on destination objects might cause primary key conflicts or missing update records, which can cause the DTS task to fail. However, operations that do not interrupt DTS tasks are allowed, such as creating and writing data to a table in the destination instance that is not a migration or synchronization object.
Because DTS reads data from the source instance and migrates or synchronizes the full data, schema data, and incremental data to the destination instance, modifications made to the destination data during the task may be overwritten by data from the source.
Can both source and destination databases be written to simultaneously during data synchronization or migration tasks?
Yes, they can. However, if other data sources write to the destination database besides DTS during task execution, the destination data or DTS instances might become abnormal.
What happens if I change the source or destination database password while a DTS instance is running?
If a DTS instance reports an error, the task is interrupted. To resolve the issue, click the instance ID to open the instance details. On the Basic Information tab, modify the password for the source or destination account. Then, navigate to the Task Management tab, locate the failed task, and restart it from the Basic Information section.
Why don't some source or destination databases have public IP as a connection option?
This depends on the connection type of the source or destination database, the task type, and the database type. For example, for MySQL database sources, migration and subscription tasks can use a public IP connection, but synchronization tasks do not support public IP connections.
Does DTS support cross-account data migration or synchronization?
Yes, it does. For more information about the configuration methods, see Configure cross-Alibaba Cloud account tasks.
Can the source and destination databases be the same database instance?
Yes, they can. If your source and destination databases are the same instance, we recommend that you use the mapping feature to isolate and distinguish data to prevent DTS instance failure or data loss. For more information, see Database, table, and column name mapping.
Why does a task with Redis as the destination report "OOM command not allowed when used memory > 'maxmemory'"?
The storage space of the destination Redis instance might be insufficient. If the destination Redis instance uses a cluster architecture, one shard might have reached its memory limit. You need to upgrade the specification of the destination instance.
What is the AliyunDTSRolePolicy permission policy and what is it used for?
The AliyunDTSRolePolicy policy grants current or cross-account access to cloud resources such as RDS and ECS under Alibaba Cloud accounts. It is invoked when you configure a data migration, synchronization, or subscription task to access relevant cloud resource information. For more information, see Grant DTS access to cloud resources.
How do I perform RAM role authorization?
When you first log in to the console, DTS prompts you to authorize the AliyunDTSDefaultRole role. You can follow the prompts in the console to go to the RAM authorization page for authorization. For more information, see Grant DTS access to cloud resources.
You need to log in to the console using your Alibaba Cloud account (primary account).
Can I modify the account password entered for DTS tasks?
Yes, you can click the instance ID to go to the instance details. On the Basic Information tab, click Modify Password to change the password for the source or destination account.
The passwords of DTS task system accounts cannot be modified.
Why do MaxCompute tables have a _base suffix?
Initial schema synchronization
DTS synchronizes the schema definitions of the tables to be synchronized from the source database to MaxCompute. During initialization, DTS adds the `_base` suffix to the table names. For example, if the source table is `customer`, the table in MaxCompute is `customer_base`.
Initial full data synchronization
DTS synchronizes all historical data from the tables to be synchronized in the source database to the destination tables (ending in `_base`) in MaxCompute. For example, data is synchronized from the `customer` table in the source database to the `customer_base` table in MaxCompute. This data serves as the baseline for subsequent incremental data synchronization.
NoteThis table is also known as the full baseline table.
Incremental data synchronization
DTS creates an incremental log table in MaxCompute. The name of this table is formed by adding the `_log` suffix to the destination table name, for example, `customer_log`. DTS then synchronizes incremental data from the source database to this table in real time.
NoteFor more information about the structure of the incremental log table, see Schema of an incremental log table.
Can't get Kafka topics. How do I handle this?
The currently configured Kafka broker might not have topic information. You can check the topic broker distribution using the following command:
./bin/kafka-topics.sh --describe --zookeeper zk01:2181/kafka --topic topic_nameCan I set up a local MySQL instance as a replica of an RDS instance?
Yes, you can. You can use the data migration feature of DTS to configure real-time synchronization from an RDS instance to an on-premises self-managed MySQL instance. This implements a master-slave architecture.
How do I copy data from an RDS instance to a newly created RDS instance?
You can use DTS data migration with the migration types selected as schema migration, full migration, and incremental migration. For more information about the configuration methods, see Data migration between RDS instances.
Does DTS support copying a database within one RDS instance that's identical except for the database name?
Yes, it does. The object name mapping feature of DTS can copy a database within one RDS instance that is identical except for the database name.
DTS instance always shows latency. How do I handle this?
The following are possible causes:
Multiple DTS tasks were created with different accounts on the same source database instance, which causes a high instance load. You can use the same account to create tasks.
The destination database instance has insufficient memory. After you arrange your business operations, you can restart the destination instance. If the problem persists, you can upgrade the specification of the destination instance or perform a primary-secondary switchover.
NoteA primary-secondary switchover might cause transient network disconnections. Make sure that your application has an automatic reconnection mechanism.
When synchronizing or migrating to the destination database using the Legacy Console, fields are all lowercase. How do I handle this?
You can use the new console to configure tasks and use the destination database object name case sensitivity policy feature. For more information, see Destination database object name case sensitivity policy.
Can a paused DTS task be resumed?
In most cases, DTS tasks that have been paused for less than 24 hours can be resumed. For tasks with smaller data volumes, tasks that have been paused for less than seven days can be resumed. We recommend that you do not pause a task for more than six hours.
Why does progress start from 0 after restarting a paused task?
After a task is restarted, DTS re-queries the completed data and continues to process the remaining data. During this process, the task progress might differ from the actual progress due to delays.
What's the principle behind lockless DDL changes?
For more information about the main principles of lockless DDL changes, see Main principles.
Does DTS support pausing synchronization or migration for specific tables?
No, it does not.
If a task fails, do I need to repurchase?
No, you do not. You can reconfigure the original task.
What happens if multiple tasks write data to the same destination?
Data inconsistency may occur.
Why is the instance still locked after renewal?
After you renew a locked DTS instance, it takes some time for the instance to unlock. Please be patient.
Can I modify the resource group for a DTS instance?
Yes, you can. Go to the instance's Basic Information page. In the Basic Information section, click Modify next to Resource Group Name to make changes.
Does DTS have a Binlog analysis tool?
DTS does not have a binlog analysis tool.
Incremental tasks always show 95%. Is this normal?
Yes, it is. Incremental tasks run continuously and never complete, so the progress never reaches 100%.
Why hasn't my DTS task been released after 7 days?
Frozen tasks are occasionally saved for more than seven days.
Can I modify the port for an already created task?
Not supported.
Can I downgrade the RDS MySQL instances attached under PolarDB-X 1.0 in DTS tasks?
This is not recommended. Downgrading triggers a primary-secondary switchover, which might cause data loss.
Can I upgrade or downgrade source or destination instances while DTS tasks are running?
Upgrading or downgrading source or destination instances while a DTS task is running may cause task delays or data loss. We recommend that you do not change instance specifications while a task is running.
What impact do DTS tasks have on source and destination instances?
Full data initialization consumes the read and write resources of both the source and destination databases, which can increase the database load. We recommend that you run full data initialization tasks during off-peak hours.
What's the typical latency for DTS tasks?
The latency of a DTS task cannot be estimated because it depends on multiple factors, including the source instance load, network bandwidth, network latency, and destination instance write performance.
If the data transmission console automatically redirects to the Data Management (DMS) console, how do I return to the legacy data transmission console?
In the Data Management (DMS) console, you can click the  icon in the bottom-right corner, and then click the
icon in the bottom-right corner, and then click the  icon to return to the legacy Data Transmission Service console.
icon to return to the legacy Data Transmission Service console.
Does DTS support data encryption?
DTS supports secure access to source or destination databases using SSL encryption for reading data from the source or writing data to the destination. However, DTS does not support data encryption during transmission.
Does DTS support ClickHouse as source or destination?
No, it does not.
Does DTS support AnalyticDB for MySQL 2.0 as source or destination?
AnalyticDB for MySQL 2.0 is supported only as the destination. Solutions with AnalyticDB for MySQL 2.0 as the destination have not been launched in the new console and can be configured only in the legacy console.
Why can't I see newly created tasks in the console?
You might have selected the wrong task list or applied filters. You can select the correct filter options in the appropriate task list, such as the correct region and resource group.
Can I modify disabled configuration items in created tasks?
Not supported.
How do I configure latency alerts and thresholds?
DTS provides monitoring and alerting features. You can set alert rules for important monitoring metrics in the console to stay informed about the running status. For more information about the configuration methods, see Configure monitoring.
For tasks that failed a long time ago, can I view the failure reason?
No, you cannot. If a task fails for a long time, such as more than seven days, the related logs are cleared and the failure reason cannot be viewed.
Can I restore tasks that failed a long time ago?
No, you cannot. If a task fails for a long time, such as more than seven days, the related logs are cleared and cannot be restored. You need to reconfigure the task.
What is the rdsdt_dtsacct account?
If you did not create the rdsdt_dtsacct account, it might have been created by DTS. DTS creates the built-in account rdsdt_dtsacct in some database instances to connect to the source and destination database instances.
How do I check for heap tables, tables without primary keys, compressed tables, tables with computed columns, and tables with sparse columns in SQL Server?
You can execute the following SQL statements to check whether your source database contains tables with these characteristics:
Check for heap tables in the source database:
SELECT s.name AS schema_name, t.name AS table_name FROM sys.schemas s INNER JOIN sys.tables t ON s.schema_id = t.schema_id AND t.type = 'U' AND s.name NOT IN ('cdc', 'sys') AND t.name NOT IN ('systranschemas') AND t.object_id IN (SELECT object_id FROM sys.indexes WHERE index_id = 0);Check for tables without primary keys:
SELECT s.name AS schema_name, t.name AS table_name FROM sys.schemas s INNER JOIN sys.tables t ON s.schema_id = t.schema_id AND t.type = 'U' AND s.name NOT IN ('cdc', 'sys') AND t.name NOT IN ('systranschemas') AND t.object_id NOT IN (SELECT parent_object_id FROM sys.objects WHERE type = 'PK');Check for primary key columns that are not included in clustered index columns in the source database:
SELECT s.name schema_name, t.name table_name FROM sys.schemas s INNER JOIN sys.tables t ON s.schema_id = t.schema_id WHERE t.type = 'U' AND s.name NOT IN('cdc', 'sys') AND t.name NOT IN('systranschemas') AND t.object_id IN ( SELECT pk_colums_counter.object_id AS object_id FROM (select pk_colums.object_id, sum(pk_colums.column_id) column_id_counter from (select sic.object_id object_id, sic.column_id FROM sys.index_columns sic, sys.indexes sis WHERE sic.object_id = sis.object_id AND sic.index_id = sis.index_id AND sis.is_primary_key = 'true') pk_colums group by object_id) pk_colums_counter inner JOIN ( select cluster_colums.object_id, sum(cluster_colums.column_id) column_id_counter from (SELECT sic.object_id object_id, sic.column_id FROM sys.index_columns sic, sys.indexes sis WHERE sic.object_id = sis.object_id AND sic.index_id = sis.index_id AND sis.index_id = 1) cluster_colums group by object_id ) cluster_colums_counter ON pk_colums_counter.object_id = cluster_colums_counter.object_id and pk_colums_counter.column_id_counter != cluster_colums_counter.column_id_counter);Check for compressed tables in the source database:
SELECT s.name AS schema_name, t.name AS table_name FROM sys.objects t, sys.schemas s, sys.partitions p WHERE s.schema_id = t.schema_id AND t.type = 'U' AND s.name NOT IN ('cdc', 'sys') AND t.name NOT IN ('systranschemas') AND t.object_id = p.object_id AND p.data_compression != 0;Check for tables that contain computed columns:
SELECT s.name AS schema_name, t.name AS table_name FROM sys.schemas s INNER JOIN sys.tables t ON s.schema_id = t.schema_id AND t.type = 'U' AND s.name NOT IN ('cdc', 'sys') AND t.name NOT IN ('systranschemas') AND t.object_id IN (SELECT object_id FROM sys.columns WHERE is_computed = 1);Check for tables that contain sparse columns:
SELECT s.name AS schema_name, t.name AS table_name FROM sys.schemas s INNER JOIN sys.tables t ON s.schema_id = t.schema_id AND t.type = 'U' AND s.name NOT IN ('cdc', 'sys') AND t.name NOT IN ('systranschemas') AND t.object_id IN (SELECT object_id FROM sys.columns WHERE is_sparse = 1);
How do I handle schema inconsistencies between source and destination?
You can try to use the mapping feature to establish column mapping relationships between the source and destination. For more information, see Database, table, and column name mapping.
Modifying column types is not supported.
Does database, table, and column mapping support modifying column types?
No, it does not.
Does DTS support limiting source database read speed?
No, it does not. Before you execute a task, you must evaluate the performance of the source database, such as whether the IOPS and network bandwidth meet the requirements. We also recommend that you run tasks during off-peak hours.
How do I clean up orphaned documents in MongoDB (sharded cluster architecture)?
Check for orphaned documents
Connect to the MongoDB sharded cluster instance using Mongo Shell.
For more information about how to connect to an ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance, see Connect to MongoDB sharded cluster instance using Mongo Shell.
Execute the following command to switch to the target database.
use <db_name>Run the following command to check for orphaned documents.
db.<coll_name>.find().explain("executionStats")NoteCheck the
chunkSkipsfield in theSHARDING_FILTERstage ofexecutionStatsfor each shard. If the value of this field is not 0, orphaned documents exist on that shard.In the following example, before the
SHARDING_FILTERstage, theFETCHstage returned 102 documents ("nReturned": 102). Then, theSHARDING_FILTERstage filtered two orphaned documents ("chunkSkips": 2), resulting in 100 documents being returned ("nReturned": 100)."stage" : "SHARDING_FILTER", "nReturned" : 100, ...... "chunkSkips" : 2, "inputStage" : { "stage" : "FETCH", "nReturned" : 102,For more information about the
SHARDING_FILTERstage, see the MongoDB Manual.
Clean up orphaned documents
If you have multiple databases, you must clean up the orphaned documents for each database.
ApsaraDB for MongoDB
An error is reported if you run a cleanup script on an instance that runs a major version earlier than MongoDB 4.2 or a minor version earlier than 4.0.6. To view the current version of your instance, see Minor version release notes. To upgrade the major or minor version, see Upgrade the major version of a database and Upgrade the minor version of a database.
To clean up orphaned documents, you can use the cleanupOrphaned command. The method for using this command varies slightly between MongoDB 4.4 or later and MongoDB 4.2 or earlier. The following sections describe the required operations.
MongoDB 4.4 and later
On a server that can connect to the sharded cluster instance, create a JavaScript (JS) script to clean up orphaned documents and name the script
cleanupOrphaned.js.NoteThis script cleans up orphaned documents from all collections in multiple databases across multiple shard nodes. To clean up orphaned documents from a specific collection, you can modify the JS script.
// List of shard instance names var shardNames = ["shardName1", "shardName2"]; // List of databases var databasesToProcess = ["database1", "database2", "database3"]; shardNames.forEach(function(shardName) { // Traverse the specified list of databases databasesToProcess.forEach(function(dbName) { var dbInstance = db.getSiblingDB(dbName); // Get the names of all collections in the database instance var collectionNames = dbInstance.getCollectionNames(); // Traverse each collection collectionNames.forEach(function(collectionName) { // The full name of the collection var fullCollectionName = dbName + "." + collectionName; // Build the cleanupOrphaned command var command = { runCommandOnShard: shardName, command: { cleanupOrphaned: fullCollectionName } }; // Execute the command var result = db.adminCommand(command); if (result.ok) { print("Cleaned up orphaned documents for collection " + fullCollectionName + " on shard " + shardName); printjson(result); } else { print("Failed to clean up orphaned documents for collection " + fullCollectionName + " on shard " + shardName); } }); }); });You must modify the values of the
shardNamesanddatabasesToProcessparameters in the script. The following list describes the parameters:shardNames: An array of IDs for the shard nodes from which you want to clean up orphaned documents. You can obtain the IDs from the Shard List section of the instance details page. Example:d-bp15a3796d3a****.databasesToProcess: An array of names for the databases from which you want to clean up orphaned documents.
In the directory where the
cleanupOrphaned.jsscript is located, run the following command to clean up orphaned documents.mongo --host <Mongoshost> --port <Primaryport> --authenticationDatabase <database> -u <username> -p <password> cleanupOrphaned.js > output.txtThe following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
<Mongoshost>The endpoint of the Mongos node of the sharded cluster instance. Format:
s-bp14423a2a51****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com.<Primaryport>The port number of the Mongos node of the sharded cluster instance. The default value is 3717.
<database>The name of the authentication database. This is the database to which the database account belongs.
<username>The database account.
<password>The password of the database account.
output.txtThe execution results are saved to the output file.
MongoDB 4.2 and earlier
On a server that can connect to the sharded cluster instance, create a JS script to clean up orphaned documents and name the script
cleanupOrphaned.js.NoteThis script cleans up orphaned documents from a specified collection in a specified database across multiple shard nodes. To clean up orphaned documents from multiple collections in a database, you can modify the
fullCollectionNameparameter and run the script multiple times. You can also modify the script to run in a loop.function cleanupOrphanedOnShard(shardName, fullCollectionName) { var nextKey = { }; var result; while ( nextKey != null ) { var command = { runCommandOnShard: shardName, command: { cleanupOrphaned: fullCollectionName, startingFromKey: nextKey } }; result = db.adminCommand(command); printjson(result); if (result.ok != 1 || !(result.results.hasOwnProperty(shardName)) || result.results[shardName].ok != 1 ) { print("Unable to complete at this time: failure or timeout.") break } nextKey = result.results[shardName].stoppedAtKey; } print("cleanupOrphaned done for coll: " + fullCollectionName + " on shard: " + shardName) } var shardNames = ["shardName1", "shardName2", "shardName3"] var fullCollectionName = "database.collection" shardNames.forEach(function(shardName) { cleanupOrphanedOnShard(shardName, fullCollectionName); });You must modify the values of the
shardNamesandfullCollectionNameparameters in the script. The following list describes the parameters:shardNames: An array of IDs for the shard nodes from which you want to clean up orphaned documents. You can obtain the IDs from the Shard List section of the instance details page. Example:d-bp15a3796d3a****.fullCollectionName: Replace this with the name of the collection from which you want to clean up orphaned documents. Use thedatabase_name.collection_nameformat.
In the directory where the
cleanupOrphaned.jsscript is located, run the following command to clean up orphaned documents.mongo --host <Mongoshost> --port <Primaryport> --authenticationDatabase <database> -u <username> -p <password> cleanupOrphaned.js > output.txtThe following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
<Mongoshost>The endpoint of the Mongos node of the sharded cluster instance. Format:
s-bp14423a2a51****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com.<Primaryport>The port number of the Mongos node of the sharded cluster instance. The default value is 3717.
<database>The name of the authentication database. This is the database to which the database account belongs.
<username>The database account.
<password>The password of the database account.
output.txtThe execution results are saved to the output file.
Self-managed MongoDB
On a server that can connect to the self-managed MongoDB database, download the cleanupOrphaned.js script file.
wget "https://docs-aliyun.cn-hangzhou.oss.aliyun-inc.com/assets/attach/120562/cn_zh/1564451237979/cleanupOrphaned.js"Modify the cleanupOrphaned.js script file. Replace
testwith the name of the database from which you want to clean up orphaned documents.ImportantIf you have multiple databases, you must repeat Step 2 and Step 3.
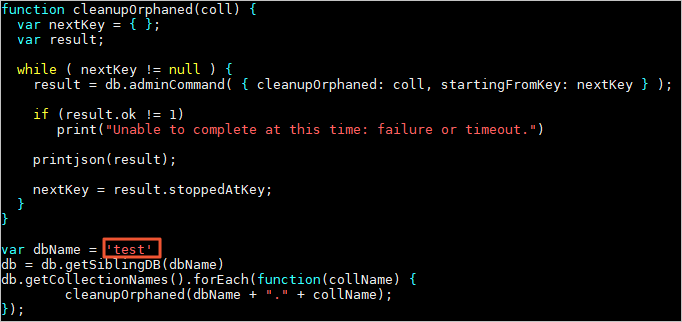
Run the following command to clean up the orphaned documents from all collections in the specified database on a shard node.
NoteYou must repeat this step for each shard node to clean up orphaned documents.
mongo --host <Shardhost> --port <Primaryport> --authenticationDatabase <database> -u <username> -p <password> cleanupOrphaned.jsNote<Shardhost>: The IP address of the shard node.
<Primaryport>: The service port of the primary node in the shard.
<database>: The name of the authentication database. This is the database to which the database account belongs.
<username>: The account used to log on to the database.
<password>: The password of the database account.
Example:
In this example, the self-managed MongoDB database has three shard nodes. You must clean up the orphaned documents for each of these three nodes.
mongo --host 172.16.1.10 --port 27018 --authenticationDatabase admin -u dtstest -p 'Test123456' cleanupOrphaned.jsmongo --host 172.16.1.11 --port 27021 --authenticationDatabase admin -u dtstest -p 'Test123456' cleanupOrphaned.jsmongo --host 172.16.1.12 --port 27024 --authenticationDatabase admin -u dtstest -p 'Test123456' cleanupOrphaned.js
Exception handling
If idle cursors exist on the namespace that corresponds to the orphaned documents, the cleanup process might never complete. The corresponding mongod log for orphaned documents contains the following information:
Deletion of DATABASE.COLLECTION range [{ KEY: VALUE1 }, { KEY: VALUE2 }) will be scheduled after all possibly dependent queries finishYou can connect to mongod using Mongo Shell and execute the following command to check whether idle cursors exist on the current shard. If they do, you need to either restart mongod or use the killCursors command to clean up all idle cursors. Then, you can re-attempt to clean up the orphaned documents. For more information, see the JIRA ticket.
db.getSiblingDB("admin").aggregate( [{ $currentOp : { allUsers: true, idleCursors: true } },{ $match : { type: "idleCursor" } }] )How do I handle uneven data distribution in MongoDB sharded cluster architecture?
You can enable the Balancer feature and perform pre-sharding to resolve the issue where most data is written to a single shard (data skew).
Enable Balancer
If the Balancer is disabled or has not reached the Balancer window period, you can enable it or temporarily cancel the Balancer window to start data balancing immediately.
Connect to the MongoDB sharded cluster instance.
In the mongos node command window, switch to the config database.
use configExecute the following commands as needed.
Enable the Balancer feature
sh.setBalancerState(true)Temporarily cancel the Balancer window period
db.settings.updateOne( { _id : "balancer" }, { $unset : { activeWindow : true } } )
Pre-sharding
MongoDB supports range sharding and hash sharding. Pre-sharding helps distribute chunk values across multiple shard nodes as evenly as possible. This achieves a balanced load during DTS data synchronization or migration.
Hash sharding
You can use the numInitialChunks parameter for convenient and quick pre-sharding. The default value is number of shards × 2, and the maximum value is number of shards × 8192. For more information, see sh.shardCollection().
sh.shardCollection("phonebook.contacts", { last_name: "hashed" }, false, {numInitialChunks: 16384})Range sharding
If the source MongoDB database is also a sharded cluster, you can use data from
config.chunksto obtain the chunk ranges for the corresponding sharded tables in the source MongoDB database. You can use these as reference values for<split_value>in subsequent pre-sharding commands.If the source MongoDB database is a replica set, you can only use the
findcommand to determine the specific range of the shard key, and then design reasonable split points.# Get minimum value of shard key db.<coll>.find().sort({<shardKey>:1}).limit(1) # Get maximum value of shard key db.<coll>.find().sort({<shardKey>:-1).limit(1)
Command format
The splitAt command is used as an example. For more information, see sh.splitAt(), sh.splitFind(), and Split Chunks in a Sharded Cluster.
sh.splitAt("<db>.<coll>", {"<shardKey>":<split_value>})Example statements
sh.splitAt("test.test", {"id":0})
sh.splitAt("test.test", {"id":50000})
sh.splitAt("test.test", {"id":75000})After you complete the pre-sharding operations, you can execute the sh.status() command on the mongos node to confirm the pre-sharding effect.
How do I set the number of instances displayed per page in the console task list?
This procedure uses synchronization instances as an example.
Go to the data synchronization task list page in the destination region. You can do this in one of two ways.
DTS console
Log on to the DTS console.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Data Synchronization.
In the upper-left corner of the page, select the region where the synchronization instance is located.
DMS console
NoteThe actual steps may vary depending on the mode and layout of the DMS console. For more information, see Simple mode console and Customize the layout and style of the DMS console.
Log on to the DMS console.
In the top menu bar, choose .
To the right of Data Synchronization Tasks, select the region of the synchronization instance.
On the right side of the page, drag the scrollbar to the bottom of the page.
In the bottom-right corner of the page, select Items per page.
NoteThe available values for Items per page are 10, 20, or 50.
How do I handle ZooKeeper connection timeout errors in DTS instances?
You can try to restart the instance to see if it recovers. For instructions on how to restart an instance, see Start DTS instance.
After deleting DTS network segments in CEN, why are they automatically re-added?
You might be using Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN) Basic Edition transit routers to connect your database to DTS. If you create a DTS instance using this database, DTS automatically adds the IP address ranges of the server to the corresponding router even if you delete the DTS network segments in CEN.
Does DTS support task export?
No, it does not.
How do I call OpenAPI using Java?
The process for calling an OpenAPI with Java is similar to that with Python. For a Python example, see the Python SDK calling example. To find the Java sample code, go to the Data Transmission Service DTS SDK page and select your programming language under All languages.
How do I configure ETL functionality for synchronization or migration tasks using API?
In the API operation's `Reserve` parameter, you can configure the functionality using common parameters, such as etlOperatorCtl and etlOperatorSetting. For more information, see ConfigureDtsJob and Reserve parameter description.
Does DTS support Azure SQL Database?
Yes. When using Azure SQL Database as the source database, you must set the SQL Server Incremental Synchronization Mode to Polling and querying CDC instances for incremental synchronization.
After DTS synchronization or migration completes, is source database data retained?
Yes, it is. DTS does not delete data from the source database. If you do not need to retain the data in the source database, you must delete it yourself.
Can I adjust the rate after synchronization or migration instances start running?
Supported. For more information, see Adjust migration rate.
Does DTS support time-range sampling for synchronization or migration?
No, it does not.
When synchronizing or migrating data, do I need to manually create data tables in the destination database?
For DTS instances that support schema tasks (schema synchronization or schema migration), you do not need to manually create data tables in the destination database if you set Synchronization Types to Schema Synchronization or Migration Types to Schema Migration.
When synchronizing or migrating data, do I need to connect the source and destination databases' networks?
No, you do not.
When configuring cross-account DTS tasks using public network, do I need to configure RAM authorization?
No. When you configure a DTS task, set the Access Method for the database instance to Public IP Address.
Data synchronization tasks do not support connecting to database instances via Public IP Address.
When using DTS for data synchronization or migration, will existing data in the destination be overwritten?
Using data synchronization as an example, the default behavior of DTS and related parameters are as follows:
DTS default behavior
If a primary key or unique key conflict occurs during the execution of a synchronization task:
If the table schemas are consistent and a record in the destination database has the same primary key or unique key value as a record in the source database:
During full data synchronization, DTS retains the destination record and skips the source record.
During incremental synchronization, DTS overwrites the destination record with the source record.
If the table schemas are inconsistent, data initialization may fail. This can result in only partial data synchronization or a complete synchronization failure. Use with caution.
Related parameters
During task configuration, you can manage data handling through the Processing Mode of Conflicting Tables parameter.
Precheck and Report Errors: Checks for tables with the same names in the destination database. If any tables with the same names are found, an error is reported during the precheck and the data synchronization task does not start. Otherwise, the precheck is successful.
NoteIf you cannot delete or rename the table with the same name in the destination database, you can map it to a different name in the destination. For more information, see Database Table Column Name Mapping.
Ignore Errors and Proceed: Skips the check for tables with the same name in the destination database.
WarningSelecting Ignore Errors and Proceed may cause data inconsistency and put your business at risk. For example:
If the table schemas are consistent and a record in the destination database has the same primary key or unique key value as a record in the source database:
During full data synchronization, DTS retains the destination record and skips the source record.
During incremental synchronization, DTS overwrites the destination record with the source record.
If the table schemas are inconsistent, data initialization may fail. This can result in only partial data synchronization or a complete synchronization failure. Use with caution.
Recommendation
To ensure data consistency, we recommend that you delete the destination table and reconfigure the DTS task if your business allows.