This topic provides answers to some frequently asked questions about Data Disaster Recovery.
Billing FAQ
What are the billable items of a backup schedule?
Type: You must pay for the specifications when you purchase a subscription backup schedule. The backup and restoration performance, free quota for data backup, and unit price vary based on the backup schedule type. For more information, see Backup fees.
Storage: optional. If you set the storage type to DBS Storage for a subscription backup schedule, you are charged storage fees based on the storage space that you use and the storage duration in Data Disaster Recovery. For more information, see Storage fees.
Backup: optional. If the amount of data that is backed up by using a backup schedule exceeds the free quota for data backup in the current specifications, the excess backup data is charged. For more information about the free quota for data backup and the billing of excess backup data for each type of backup schedule, see Backup fees.
Sandbox: optional. Data Disaster Recovery allows you to create sandbox instances for the disaster recovery of self-managed MySQL databases.
After you enable the sandbox feature, Data Disaster Recovery charges you sandbox storage fees based on the volume of the data stored in the sandbox storage.
After you create a sandbox instance, Data Disaster Recovery charges you sandbox instance fees based on the specifications and usage duration of the sandbox instance. For more information, see Pricing.
You cannot create a pay-as-you-go backup schedule.
Which fees for billable items can be offset by Data Disaster Recovery storage plans and network plans?
Storage plans
The following table describes the two types of Data Disaster Recovery storage plans. Each plan comes with a variety of storage sizes (such as 100 GB, 500 GB, 1 TB, and 500 TB) and subscription periods (such as one month, six months, and one year.) If your storage exceeds your storage plan quota, you will be charged for your excess storage on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Plan type | Offset object |
Storage plans for CDM sandbox instances | These storage plans can be used to offset the fees incurred for your account when you use sandbox storage. For pricing details, see Sandbox fees. |
Storage plans for backup schedule instances | Offsets storage usage for backup schedule instances within the same Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see Built-in storage and OSS. |
Network plans
Offset object | Description |
Network traffic for cross-region backups | Data Disaster Recovery network plans can be used in all regions worldwide. After you purchase a network plan, you can use the network plan to offset the network traffic consumed by cross-region backups of ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL, ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server, PolarDB for MySQL, PolarDB for PostgreSQL, and ApsaraDB for MongoDB databases in all regions. The network traffic is offset by the network plan based on the offset factors in different regions. |
Network traffic for backup set downloads | Data Disaster Recovery network plans can be used in all regions worldwide. After you purchase a network plan, you can use the network plan to offset network traffic consumed by backup set downloads of ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL, and ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server databases in all regions. The network traffic is offset by the network plan based on the offset factors in different regions. |
For more information about the offset rules, offset factors, offset examples, and purchase methods, see Use storage plans and Use network plans.
Am I charged for a pay-as-you-go or subscription backup schedule that is not used?
Even if a pay-as-you-go or subscription backup schedule is not used to generate backup sets, historical backup sets still occupy storage resources. Therefore, you are still charged storage fees.
For more information about how to release a backup schedule or reduce the size of backup files, see View and reduce the size of backup data, Delete backup files or reduce the size of backup files, and Use the backup for deleted instances feature.
Pay-as-you-go: If you do not use a pay-as-you-go backup schedule for an extended period of time, we recommend that you release the backup schedule after you save relevant data and download historical backup sets. After the backup schedule is released, no backup or storage fees are charged. For more information, see Release or unsubscribe from a backup schedule.
Subscription: If you do not use a subscription backup schedule for an extended period of time but want to retain historical backup sets, we recommend that you pause the backup schedule. For more information, see Pause or start a backup schedule. After the backup schedule is paused, no backup fees are charged. However, you are still charged storage fees if the storage type of the backup schedule is DBS Storage.
After you pause a subscription backup schedule in the Running state, the subscription duration of the backup schedule does not change.
You are charged storage fees only for backup schedules whose storage type is DBS Storage.
Can I switch the billing method of an instance between subscription and pay-as-you-go?
No, you cannot change the billing method of a backup schedule from pay-as-you-go to subscription or from subscription to pay-as-you-go.
Can I release a pay-as-you-go backup schedule?
Yes, you can release a pay-as-you-go backup schedule. For more information, see Release or unsubscribe from a backup schedule.
Can I unsubscribe from a subscription backup schedule?
No, you cannot release a subscription backup schedule.
You cannot unsubscribe from a backup schedule.
For more information, see Unsubscribe from billable features.
What are the impacts if a storage plan or network plan expires?
Storage plans and network plans are subscription resource plans provided by Data Disaster Recovery. Storage plans and network plans become invalid after they expire. Expired plans cannot be used to offset storage fees and network traffic fees. This does not affect your backup schedules or existing backup data.
What are the impacts if a backup schedule expires or the payment is overdue?
For more information, see Service expiration and overdue payments.
How do I reduce the costs of a subscription backup schedule?
You can purchase storage plans to offset the built-in storage fees for backup schedules within the same Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see Built-in storage and OSS.
What are the billable items in a bill if I have not used the backup feature in the console?
Data Disaster Recovery provides the backup and restoration features for ApsaraDB RDS, PolarDB, ApsaraDB for MongoDB, Redis, Tair, and AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL. You can check whether you are charged fees for the billable items because you use the backup and restoration features for these services. For more information, see Pricing.
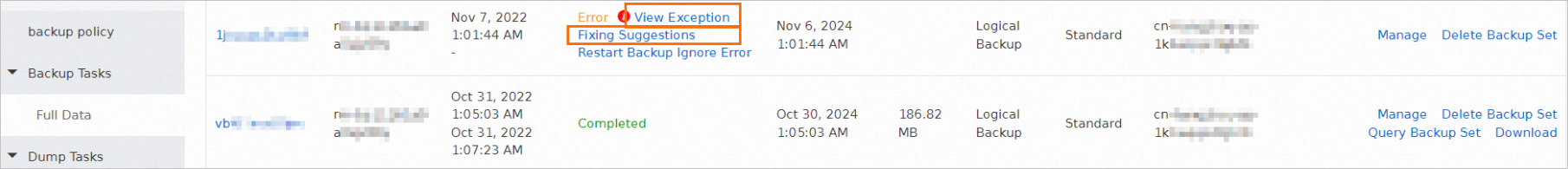
How do I fix errors for an abnormal backup schedule?
Description
A backup schedule is abnormal on the Backup Schedules page.
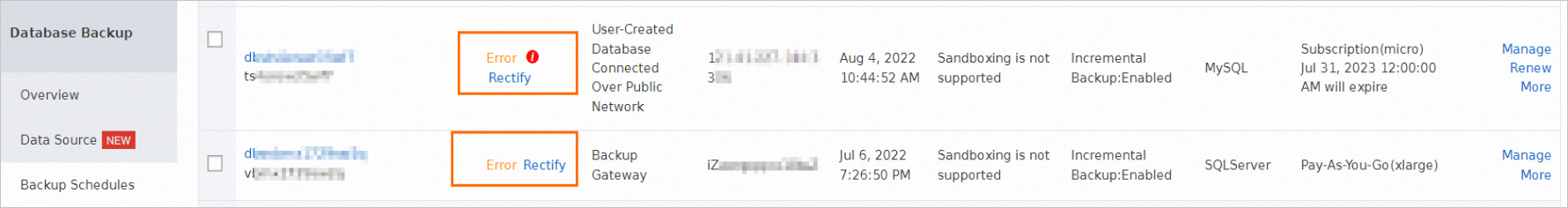
Cause
If your backup schedule is abnormal, at least one task becomes abnormal in the backup schedule. In most cases, the abnormal task may be a full backup task or an incremental backup task. The abnormal task may also be a task of other types.
If an error occurs in a task, Data Disaster Recovery does not directly start the abnormal task. This prevents your business from being affected.
To ensure that your business can run as expected, we recommend that you troubleshoot the error that occurs in your backup schedule at the earliest opportunity. If the error persists after you troubleshoot the error by referring to the solutions provided in this topic, contact technical support in the DingTalk group (ID: 35585947).
Solutions
The following table describes the solutions provided by Data Disaster Recovery to help you fix errors for abnormal tasks in a backup schedule.
Scenario and solution | Precautions |
If you have identified the cause of the error that occurs in an abnormal task and fixed the error, you can restart the abnormal task. For example, if a backup error is caused by the shutdown of the source instance, you can restart the backup task after you start the source instance. |
|
If you have identified the cause of the error that occurs in an abnormal task and fixed the error, you can ignore the error. For example, if a backup error is caused by the shutdown of the source instance or service exceptions, and the source instance is started or services become normal, you can ignore the error. The backup will be performed in the next backup window. | If the error is fixed, the state of the abnormal task changes to Completed after you ignore the error. In this case, if only one abnormal task exists in your backup schedule, the state of the backup schedule changes to Running. If the backup schedule is still abnormal, check whether other abnormal tasks exist in the backup schedule. |
If you cannot determine the cause of the error that occurs in an abnormal task or the solution to the error, you can move the pointer over the exclamation point (!) icon to view the error information. Then, search for the error that you want to fix in the Common errors and troubleshooting for Data Disaster Recovery topic. | If the error is not described in the "Common errors and troubleshooting for Data Disaster Recovery" topic, or your issue persists after you refer to the solutions provided in the topic, contact technical support in the DingTalk group (ID: 35585947). |
Procedure
In the left-side navigation pane, click Backup Schedules. On the Backup Schedules page, find the abnormal backup schedule and click Rectify in the Status column. You are navigated to the task list page based on the type of the abnormal task in the backup schedule.
If the abnormal task is a full backup task, you are navigated to the Full Data page. If the abnormal task is an incremental backup task, you are navigated to the Incremental Data page.
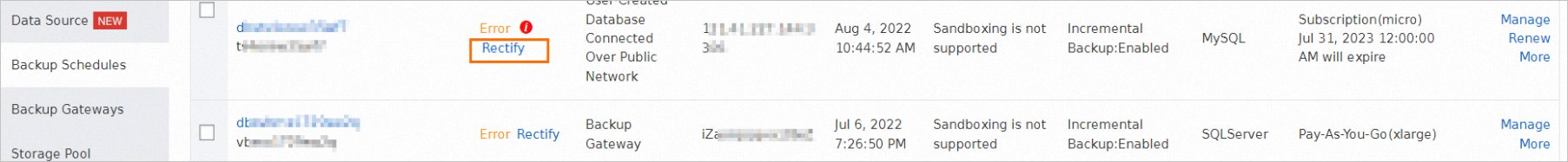
Select a solution based on the abnormal task and your business requirements.
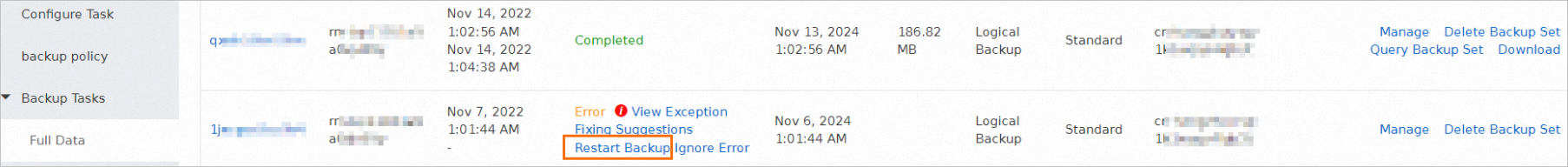
If you want to restart an abnormal backup task, find the task and click Restart Backup in the Status column.
NoteIf you perform full backup, evaluate the impact of full backup on the source database before you restart the abnormal backup task. We recommend that you restart the abnormal backup task during off-peak hours.
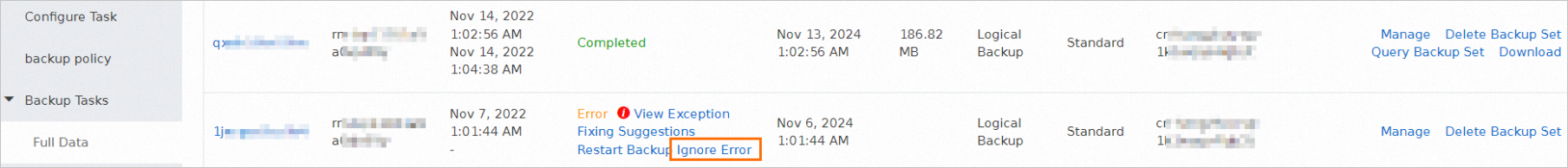
If you want to ignore errors for an abnormal task, find the task and click Ignore Error in the Status column.
If you want to fix errors for an abnormal full backup task, find the task and move the pointer over the exclamation point (!) icon in the Status column to view the error information. Then, click View Exception Fixing Suggestions in the Status column. If you want to fix errors for an abnormal incremental backup task, click View Incremental Exception Fixing Suggestions in the upper part of the Incremental Data page. You are navigated to the Common errors and troubleshooting for Data Disaster Recovery topic. Search for the error that you want to fix in the "Common Errors and Troubleshooting for Data Disaster Recovery" topic and try to fix the error based on the solutions provided in the topic.
NoteIf the error that you want to fix is not described in the "Common errors and troubleshooting for Data Disaster Recovery" topic, the error may be caused by an abnormal task of other types. In this case, contact technical support in the DingTalk group (ID: 35585947).
How do I activate Data Disaster Recovery?
If you use Data Disaster Recovery for the first time, you must assign the AliyunDBSDefaultRole role to Data Disaster Recovery and activate Object Storage Service (OSS) to allow Data Disaster Recovery to access, query, and manage your databases and back up your databases to OSS in real time. This authorization operation ensures that the backup and restoration features of Data Disaster Recovery run as expected without affecting the performance of your backup schedules.
Step 1: Assign the AliyunServiceRoleForDBS role to Data Disaster Recovery
The AliyunServiceRoleForDBS role is a Resource Access Management (RAM) role that allows Data Disaster Recovery to access other cloud services. Before Data Disaster Recovery accesses Alibaba Cloud databases that you purchase, such as ApsaraDB RDS instances, ApsaraDB for MongoDB instances, Redis instances, and PolarDB clusters, or self-managed databases hosted on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances, the AliyunServiceRoleForDBS role must be assigned to Before Data Disaster Recovery. For more information, see Service-linked roles.
If you use Data Disaster Recovery for the first time, you must assign the AliyunServiceRoleForDBS role to Data Disaster Recovery. For more information about the permissions of the role, see the AliyunServiceRoleForDBS section of the topic.
- Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
In the top navigation bar, choose Security and Specifications (DBS) > Disaster Recovery for Data (DBS) > Disaster Recovery Data Source.
NoteIf you use the DMS console in simple mode, move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose All Features > Security and Specifications (DBS) > Disaster Recovery for Data (DBS) > Disaster Recovery Data Source.
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose All Features > Security and Specifications (DBS) > Disaster Recovery for Data (DBS) > Disaster Recovery Data Source. In the dialog box that appears, click Authorize DBS SLR.
NoteIf the Information dialog box does not appear after you log on to the Data Disaster Recovery console, you can skip the subsequent steps and create a backup schedule. For more information, see Manage a backup by using a disaster recovery data source or Create a backup by using a backup schedule list.
Click OK.
The AliyunServiceRoleForDBS role is created for Data Disaster Recovery. You can delete the role based on your business requirements. For more information, see Delete a RAM role.
Step 2: Activate OSS
You are not charged for activating OSS. After you activate OSS, the backup data generated by Data Disaster Recovery can be stored in OSS.
Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
In the top navigation bar, choose Security and Specifications (DBS) > Disaster Recovery for Data (DBS) > Backup Plan.
NoteIf you use the DMS console in simple mode, move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose All Features > Security and Specifications (DBS) > Disaster Recovery for Data (DBS) > Backup Plan.
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose All Features > Security and Specifications (DBS) > Disaster Recovery for Data (DBS) > Backup Plan. In the dialog box that appears, click Activate OSS Now.
In the dialog box that appears, click Activate Now.
On the OSS page, read and agree to the service agreement by selecting the check box and click Activate Now.
Data Disaster Recovery is activated.
AliyunServiceRoleForDBS
Role name: AliyunServiceRoleForDBS
Policy attached to the role: AliyunServiceRolePolicyForDBS
Permissions:
{
"Version": "1",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"rds:DescribeDBInstanceNetInfo",
"rds:DescribeDBInstanceNetInfoForChannel",
"rds:DescribeTasks",
"rds:DescribeDBInstances",
"rds:DescribeFilesForSQLServer",
"rds:DescribeImportsForSQLServer",
"rds:DescribeSlowLogRecords",
"rds:DescribeBinlogFiles",
"rds:DescribeSQLLogRecords",
"rds:DescribeParameters",
"rds:DescribeParameterTemplates",
"rds:DescribeDBInstanceAttribute",
"rds:DescribeDatabases",
"rds:DescribeAccounts",
"rds:DescribeSecurityIPList",
"rds:DescribeSecurityIps",
"rds:DescribeDBInstanceIPArray",
"rds:DescribeDBInstanceIPArrayList",
"rds:DescribeDBInstanceSSL",
"rds:DescribeDBInstanceTDE",
"rds:CreateDBInstance",
"rds:CreateAccount",
"rds:CreateDatabase",
"rds:ModifySecurityIps",
"rds:GrantAccountPrivilege",
"rds:CreateMigrateTask",
"rds:CreateOnlineDatabaseTask",
"rds:DescribeMigrateTasks",
"rds:DescribeOssDownloads",
"rds:CreateBackup",
"rds:DescribeBackups",
"rds:DescribeBackupPolicy",
"rds:ModifyBackupPolicy",
"rds:DescribeBackupTasks",
"rds:DescribeBinlogFiles"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"ecs:DescribeInstance",
"ecs:DescribeInstances",
"ecs:DescribeVpcs",
"ecs:DescribeSecurityGroups",
"ecs:DescribeSecurityGroupAttribute",
"ecs:AuthorizeSecurityGroup",
"ecs:JoinSecurityGroup",
"ecs:RevokerSecurityGroup"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"kms:ListKeys"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"cms:PutEventRule",
"cms:PutEventTargets",
"cms:ListEventRules",
"cms:ListEventTargetsByRule",
"cms:DeleteEventRule",
"cms:DeleteEventTargets"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"polardb:DescribeDBClusterIPArrayList",
"polardb:DescribeDBClusterNetInfo",
"polardb:DescribeDBClusters",
"polardb:ModifySecurityIps",
"polardb:DescribeDBClusterEndpoints",
"polardb:DescribeDBClusterAccessWhitelist",
"polardb:ModifyDBClusterAccessWhitelist"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"dds:DescribeDBInstanceAttribute",
"dds:DescribeReplicaSetRole",
"dds:DescribeSecurityIps",
"dds:DescribeDBInstances",
"dds:ModifySecurityIps"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"kvstore:DescribeSecurityIps",
"kvstore:DescribeInstances",
"kvstore:DescribeAccounts",
"kvstore:DescribeDBInstanceNetInfo",
"kvstore:CreateAccount",
"kvstore:ModifySecurityIps",
"kvstore:DescribeInstanceAttribute",
"kvstore:AllocateInstancePrivateConnection",
"kvstore:DescribeLogicInstanceTopology"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"drds:DescribeDrdsDB",
"drds:DescribeDrdsDBs",
"drds:DescribeDrdsDbInstance",
"drds:DescribeDrdsDbInstances",
"drds:DescribeDrdsDBIpWhiteList",
"drds:DescribeDrdsInstances",
"drds:ModifyDrdsIpWhiteList",
"drds:CreateDrdsDB",
"drds:DescribeTable",
"drds:DescribeTables",
"drds:ModifyRdsReadWeight",
"drds:ChangeAccountPassword",
"drds:CreateDrdsInstance",
"drds:CreateInstanceAccount",
"drds:CreateInstanceInternetAddress",
"drds:DescribeInstanceAccounts"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"vpc:DescribeVpcs"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"bssapi:QueryResourcePackageInstances"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": "hdm:AddHDMInstance",
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": "ram:DeleteServiceLinkedRole",
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"ram:ServiceName": "dbs.aliyuncs.com"
}
}
}
]
}Required permissions for different types of database accounts
MySQL databases
Feature | Required permissions |
Backup |
|
Restoration | SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, DROP, INDEX, ALTER, CREATE VIEW, SHOW VIEW, CREATE ROUTINE, ALTER ROUTINE, EVENT, and TRIGGER |
To perform incremental backup in MySQL databases, Data Disaster Recovery must execute the
show binary logsstatement. For MySQL 5.5.24 and earlier versions, theSUPERpermission is required to execute the statement. For MySQL 5.5.25 and later versions, only theREPLICATION CLIENTpermission is required to execute the statement.The permissions required to back up or restore RDS databases are determined based on your business requirements. Read-only permissions are required for backup, and read and write permissions are required for backup and restoration.
SQL Server databases
Feature | Required permissions |
Backup | SELECT and VIEW DEFINITION |
Restoration | SELECT, INSERT, ALTER Database, REFERENCES, and VIEW DEFINITION |
PostgreSQL databases
Feature | Required permissions |
Backup | SELECT and SUPER |
Restoration | CREATE, INSERT, USAGE, REFERENCES, and TRIGGER |
How do I ensure the consistency of restored data?
To minimize the impact of a full backup that uses the logical backup method on database performance, Data Disaster Recovery pulls data from the source database in parallel and backs up the data to OSS in a lock-free manner.
Backup data is generated for different points in time. During data restoration, Data Disaster Recovery restores full backup data and then incremental log backup data, and ensures the consistency of restored data based on the idempotence of incremental log backup.
Incremental backup | Consistency of restored data |
Enabled | Supported |
Disabled | Not supported |
How do I manage the lifecycle rules of backup sets?
Lifecycle rules
The lifecycle of a backup set ranges from seven days to 3,650 days (10 years). Data Disaster Recovery automatically deletes the expired backup sets from a backup schedule
if the backup schedule contains more than three full backup sets. If this condition is not met, Data Disaster Recovery does not delete the expired backup sets.
You can wait for the next scheduled backup or manually back up data based on your business requirements. If the number of full backup sets exceeds three, the cleanup policy is triggered. For more information about manual backup, see Manually initiate a backup task.
If you continue to manually delete full backup sets and the number of full backup sets is less than or equal to three, the cleanup policy for backup sets is not triggered. This causes that incremental backup sets are continuously stored in Data Disaster Recovery, which occupies storage space. If you no longer need incremental backup, you can manually disable this feature. For more information, see Enable or disable incremental log backup.
If you modify the lifecycle of a backup schedule after the backup schedule is created, the new lifecycle rules apply to new backup sets and existing backup sets.
Modify and apply lifecycle rules
For more information, see Modify the backup policy of a backup schedule or Modify the lifecycle of a backup schedule.
Related operations
For more information about how to view the backup size and reduce the number of data backups, see Delete backup sets or reduce the backup frequency.
FAQ
Q: The lifecycle of my backup schedule is set to seven days. Why are backup sets not deleted after they expire?
A: If the number of full backup sets in a backup schedule is less than or equal to three, the cleanup policy for backup sets is not triggered. In this case, expired backup sets are not automatically deleted.
Q: Why does an expired incremental backup still occupy storage space?
A: You may have manually deleted full backup sets. As a result, the number of full backup sets is less than or equal to three, and the cleanup policy is not triggered. For more information, see the Lifecycle rules section of this topic.
What is the backup data size?
Backup data size refers to the actual volume of the data that has been transmitted over the Data Disaster Recovery server.
Concepts
Database backup scenarios involve the following concepts: database disk space, data file size, backup data size, and storage data size.
Data amount | Description |
Database disk space | The total space consumed by data files, logs, operating system files, and the available space of the operating system of the server where the database resides. Note
|
Data file size | The amount of disk space occupied by database data files on the server where the database resides. You can perform the following operations to view the data file size of a database:
|
Backup data size | The amount of data backed up by using Data Disaster Recovery. This size depends on a variety of factors such as the database type, backup mode, and backup granularity. |
Storage data size | The volume of data stored in the storage system. This size depends on a variety of factors such as the backup data size, the storage format of backup data, and the compression algorithm. |
The following space sizes are in descending order: database disk space > data file size > backup data size > storage data size.
You can reduce the backup data size by modifying configuration items provided by Data Disaster Recovery, such as the backup granularity and backup cycle, to reduce the Data Disaster Recovery cost. You can use the compact storage format, compression methods, and automatic dumping and cleaning policies provided by Data Disaster Recovery to reduce the storage data size and in turn the OSS cost.
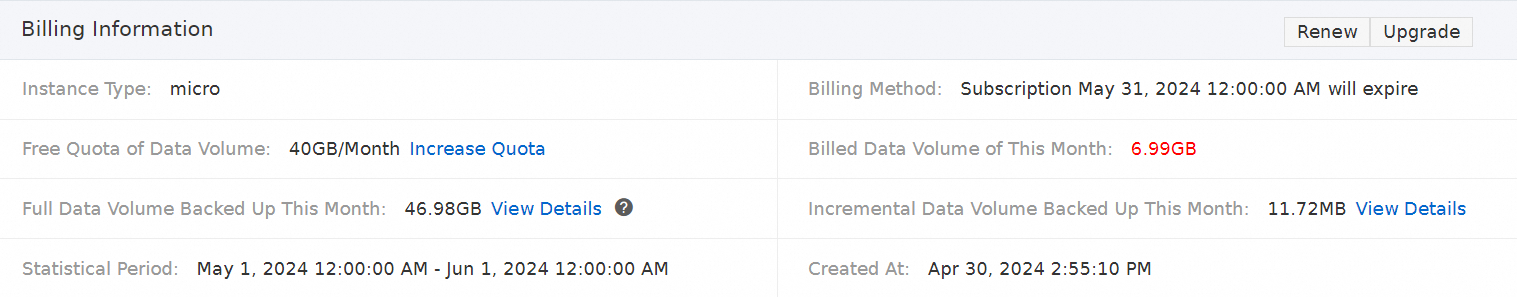
How do I view the backup data volume?
Click Manage in the Actions column of the backup schedule.
In the Billing Information section of the schedule details page, view the backup data volume. The following table describes the parameters in this section.
Field
Description
Instance Type
Data Disaster Recovery provides various backup schedule types, including serverless, micro, small, medium, large, and xlarge. For more information, see Select a backup schedule type.
Billing Method
Data Disaster Recovery supports the pay-as-you-go and subscription billing methods. For more information, see Pricing.
Free Quota of Data Volume
The free quota for data backup, unit price, and backup and restoration performance vary based on the backup schedule type. The backup and restoration performance is measured by the amount of time required for backup and restoration. For more information, see Pricing.
NoteYou can upgrade a backup schedule to increase the free quota for data backup. For more information, see Upgrade a backup schedule and Select a backup schedule type.
Billed Data Volume of This Month
You are charged for the amount of data that exceeds the free quota. A backup schedule type with higher specifications offers higher backup and restoration performance at a lower unit price.
Full Data Volume Backed Up This Month
The backup data volume of full backup tasks in the current month.
Incremental Data Volume Backed Up This Month
The backup data volume of incremental backup tasks in the current month.
Statistical Period
The backup data volume is calculated every calendar month.
Created At
The point in time when the backup schedule was created.
How do I modify the backup source database?
Scenarios
The original backup source database is migrated to another environment or is no longer in use. You want to change the backup source database to another database.
After testing is complete, you want to change the backup source database used in the testing to a production database.
The account and password that are configured to connect to the backup source database are improper, and the database account does not have sufficient permissions. You want to change the database account and password of the backup source database.
The tables of the backup source database change. You want to change the backup objects.
Procedure
Change database account and password or backup objects
Prerequisites
The backup schedule uses the logical backup method.
The database account of the backup source has the permissions to back up and restore data. For more information, see Account permissions.
Procedure
Find the backup schedule that you want to manage and click Manage in the Actions column. The Configure Task page appears.
In the Basic Information section, click Edit Backup Source. For more information about how to configure the backup source for different databases, see Configure a backup schedule and restore data.

Configure the information about the new backup source. After the backup source passes the connection test, click Next.
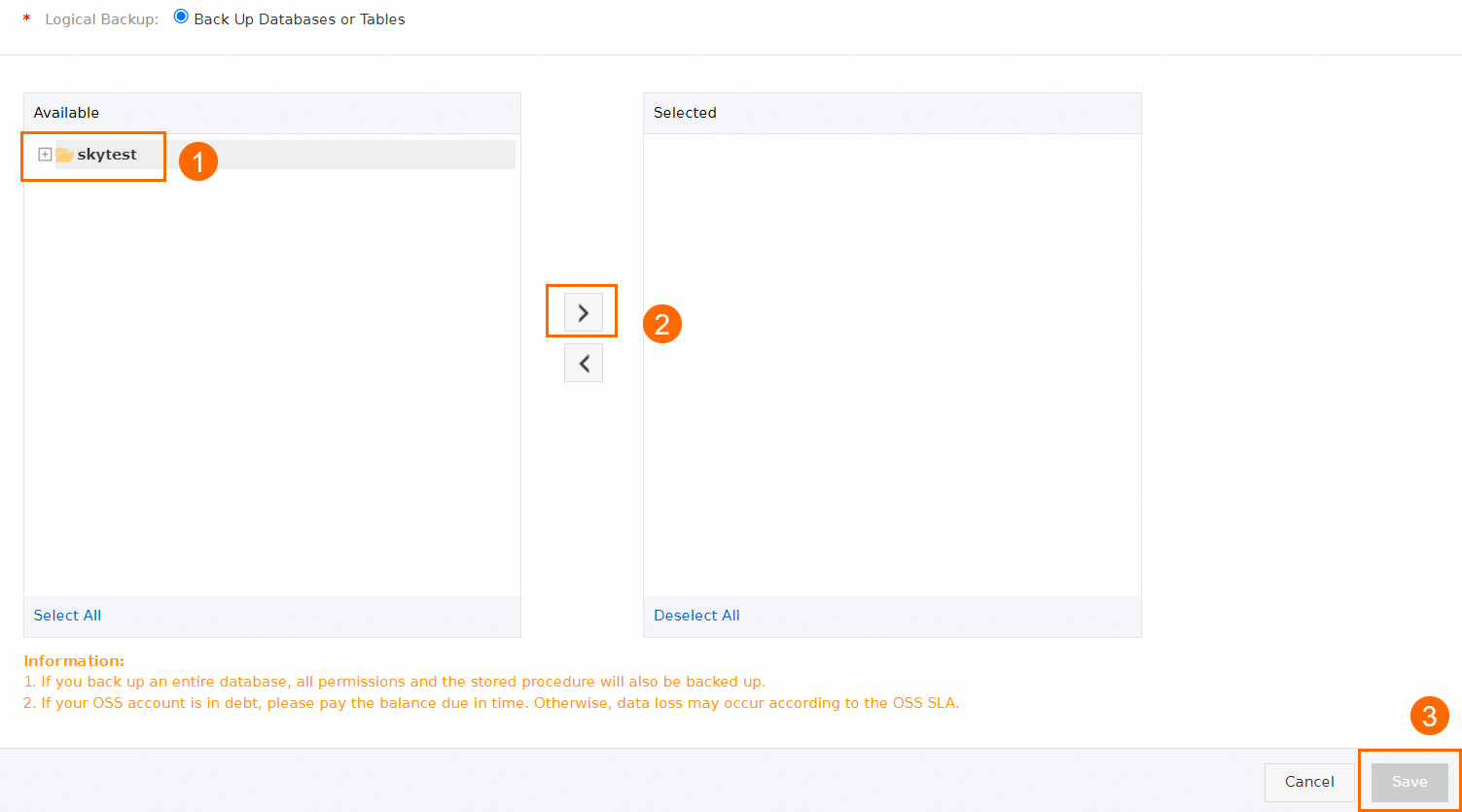
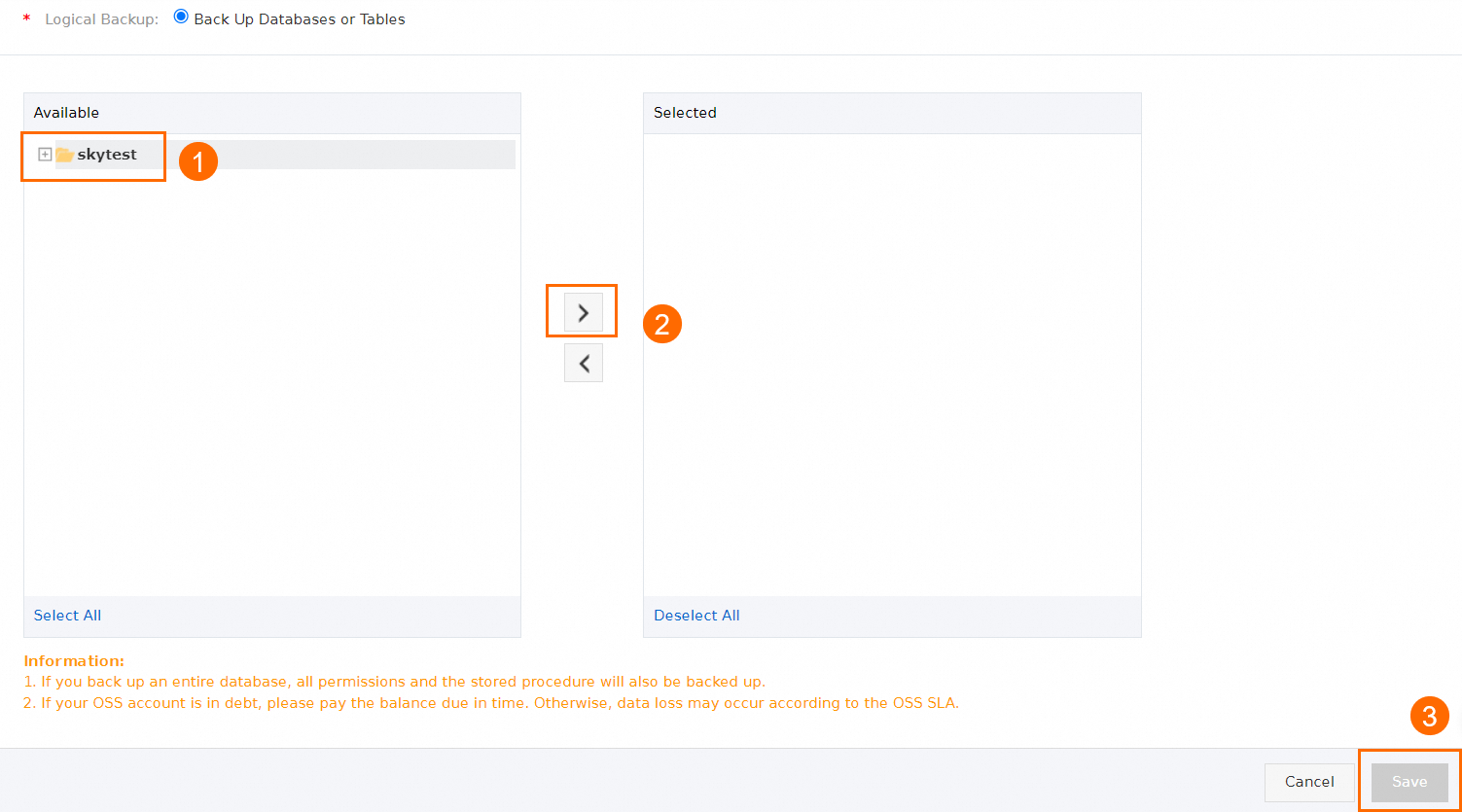
Configure the database objects to be backed up and click Save.
To add a new source database, select the database in the Available section and click the
 icon.
icon. To delete a selected database, select the database in the Selected section and click the
 icon.
icon.
After the precheck is passed, click Start Task. The new backup source is configured.
NoteIf an existing incremental backup task is running based on the backup schedule, the incremental backup task is ended after you click Start Task. The system schedules and starts a new incremental backup task by using the new account and password.
If no full backup task is running based on the backup schedule, the system immediately starts a full backup task after you click Start Task. To minimize the impact on the backup source database, we recommend that you modify the backup configurations during off-peak hours.
If an existing full backup task is running based on the backup schedule, the configurations of the backup task are not updated after you click Start Task. The system performs a full backup based on the latest configurations only when a new full backup task is scheduled or started the next time.
Change only backup objects
Find the backup schedule that you want to manage and click Manage in the Actions column. The Configure Task page appears.
In the Basic Information section, click Edit Backup Objects.

Modify the backup objects and click Save.
To add a new source database, select the database in the Available section and click the
 icon.
icon. To delete a selected database, select the database in the Selected section and click the
 icon.
icon.
In the Start Full Data Backup message, click OK or Close.
If you click OK, a full backup task starts in about one minute to back up the objects that are specified in the backup schedule. To minimize the impact on the backup source database, we recommend that you perform this operation during off-peak hours.
If you click Close, the modified configurations are saved, but the system does not immediately perform a full backup. The system performs a full backup based on the latest configurations only when a new full backup task is scheduled the next time.
What is the backup schedule generated by enabling the cross-region backup feature for an RDS instance?
If you enable the cross-region backup feature for an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server, or ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance in the ApsaraDB RDS console, Data Disaster Recovery transfers and backs up the data of the instance across regions by using Express Connect. A backup schedule used to dump the data of the instance is generated in the Data Disaster Recovery console. You can view the information about the source database on the details page of the backup schedule.
For more information about the cross-region backup feature and billing of this feature, see the following topics:
FAQ
Q: How do I stop a backup schedule generated by enabling the cross-region backup feature for an RDS instance?
A: After you disable the cross-region backup feature for an RDS instance in the ApsaraDB RDS console, Data Disaster Recovery automatically stops the corresponding backup schedule.
Q: After I disable the cross-region backup feature for an RDS instance, why am I still charged fees?
A: After you disable the cross-region backup feature for an RDS instance, no new backup files are generated and no traffic is generated for cross-region transfer of backup files. However, you are still charged for the storage of the existing backup files within the specified backup retention period. The existing backup files are retained for at least seven days. You can set the backup retention period to seven days. After seven days, the existing backup files are automatically deleted and you are no longer charged for the storage of the backup files. For more information, see Use the cross-region backup feature.
Q: Can I switch the billing method of a backup schedule generated by enabling the cross-region backup feature for an RDS instance to subscription?
A: No, you cannot switch the billing method to subscription. By default, the billing method of a backup schedule generated by enabling the cross-region backup feature for an RDS instance is pay-as-you-go.
Q: After I disable the cross-region backup feature for an RDS instance in the ApsaraDB RDS console, why does the corresponding backup schedule still exist in the Data Disaster Recovery console?
A: The backup schedule is not deleted in the Data Disaster Recovery console. However, no fees are charged.
What is the impact of backup on databases?
When Data Disaster Recovery performs a backup task on a database, the database performance is affected. Therefore, we recommend that you perform backup tasks during off-peak hours.
Backup principle and impact
Item | Logical backup | Physical backup |
Full backup | Data Disaster Recovery splits the data of all tables in a database and executes SQL statements on the database to read the data in multiple threads in parallel. | A backup gateway is installed on the server of a database for database backups. |
Incremental backup | Data Disaster Recovery incrementally backs up logs stored in the memory of a database in real time. This prevents the sudden I/O performance drop that may occur when a large amount of data is backed up at a time. | |
Impact on databases | Data is read from a database instance, which affects the database performance. However, no tables are locked during a logical backup. | Data is read from the disks of a database, which affects the I/O performance of the database. However, no tables are locked during a physical backup. |
How do I configure the binlog_format variable of a MySQL database to be backed up?
Data Disaster Recovery provides various features, such as full backup, incremental backup, and data restoration. To ensure the smooth backup of a database, you must configure the database and database account as required when you configure the backup schedule.
Scenario
In the precheck step of configuring a backup schedule in the Data Disaster Recovery console, information about precheck failure is displayed, which indicates that the precheck failed because the value of the binlog_format variable of the source database is not ROW. For more information, see Back up a on-premise database or cloud database from a third-party provider.
Usage notes
You must set the
binlog_formatvariable to ROW. In ROW mode, the images of the involved rows before and after DML operations are performed are logged. This facilitates data restoration.We recommend that you do not set the
binlog_formatvariable to STATEMENT OT MIXED. ROW mode is more stable and reliable.If you set the
binlog_formatvariable to ROW, only the binary logs are changed and the database queries are not affected. However, we recommend that you kill all current database connections to ensure that ROW mode takes effect for all database connections.
Procedure
Use a privileged account to run the following command in the source database to set
binlog_formattoROW.SET GLOBAL binlog_format = 'ROW';You can run the following command to query the value of binlog_format of a MySQL database:
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'binlog_format';Kill all connections to the database. Otherwise, connected processes may continue to write data in non-ROW mode, which results in inconsistent incremental data.
How do I back up a read-only RDS instance?
Prerequisites
A backup schedule is purchased. For more information, see Create a backup schedule.
NoteWhen you purchase a backup schedule, set the Data Source Type parameter to MySQL and the Backup Method parameter to Logical Backup.
A read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance is created. For more information, see Create a read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
Method 1: Configure a backup schedule for a read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance by using its public endpoint
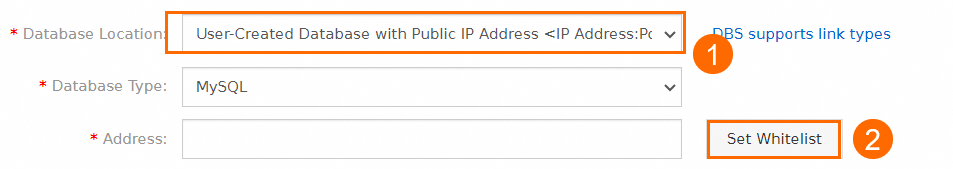
The public endpoint of the read-only instance is obtained. For more information, see View and manage instance endpoints and ports.
The CIDR blocks of the Data Disaster Recovery server are added to the whitelist of the read-only instance. For more information, see Configure an IP address whitelist.
NoteWhen you configure a backup schedule, you can set the Database Location parameter to User-Created Database with Public IP Address <IP Address:Port Number> and click Set Whitelist to obtain the CIDR blocks of the Data Disaster Recovery server.
Method 2: Configure a backup schedule for a read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance by using its internal endpoint
The internal endpoint of the read-only instance is obtained. A real-time internal IP address is obtained by running the ping command on your local device.
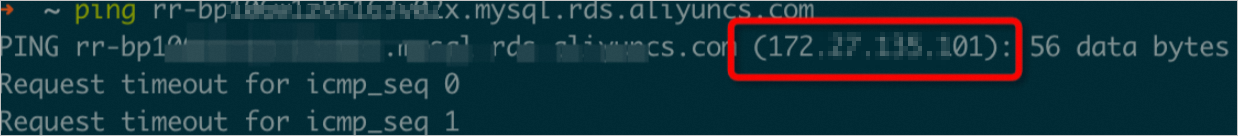 Important
ImportantThe internal IP address that you obtain may change in some scenarios. If the new internal IP address of the read-only instance differs from the internal IP address that is configured in the backup schedule, the backup fails. For more information, see What is the impact of backup on databases?
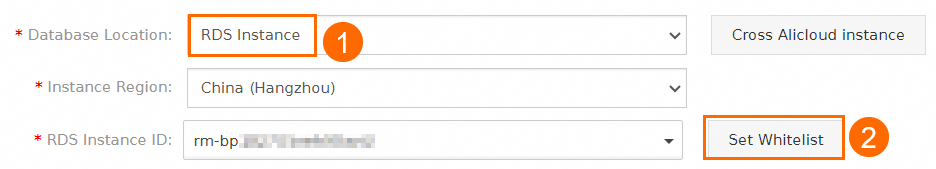
The CIDR blocks of the Data Disaster Recovery server are added to the whitelist of the read-only instance. For more information, see Configure an IP address whitelist.
NoteWhen you configure a backup schedule, you can set the Database Location parameter to RDS Instance and click Set Whitelist to obtain the CIDR blocks of the Data Disaster Recovery server.
Precautions
If you perform a backup over the public endpoint, the binary logs may be delayed. We recommend that you set the Retention Period parameter to a relatively large value on the Backup and Restoration page of the read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. This parameter indicates the retention period of local logs. Default value: 18. Unit: hours.
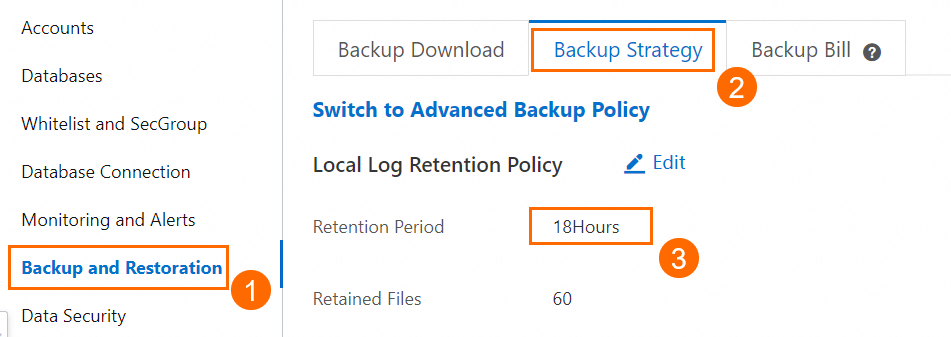
If you use the internal endpoint to configure a backup schedule and you clone the read-only instance, migrate the instance to another zone, or change the VPC or vSwitch of the instance, the real-time internal IP address that you obtain may change. In this case, the instance fails to be connected, and the backup fails.
To resolve this issue, you can obtain a new real-time internal IP address and reconfigure a backup schedule. For more information, see the Prerequisites section of this topic and How do I modify the backup source?
Procedure
When you configure a backup schedule for a read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, you can set the Database Location parameter to User-Created Database with Public IP Address <IP Address:Port Number> or Express Connect DB/VPN Gateway/Intelligent Gateway.
Method 1: Configure a backup schedule for a read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance by using its public endpoint
On the Backup Schedules page, find the ID of the backup schedule that you want to configure and click Configure Backup Schedule in the Actions column.

In the Configure Backup Source and Destination step of the Configure Backup Schedule wizard, configure the backup source and destination. Then, click Next in the lower-right corner of the page.
NoteSet the Database Location parameter to User-Created Database with Public IP Address <IP Address:Port Number>.
Set the Address parameter to the public endpoint of the read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. For more information, see View and manage instance endpoints and ports.
For more information about how to configure other parameters, see Manage a backup schedule.
In the Edit Backup Objects step, find the database or table that you want to back up and add it to the Selected section. Then, click Next.
NoteIf you selected Logical Backup when you purchased a backup schedule, Data Disaster Recovery allows you to specify the databases and tables to be backed up during full backups. You can back up a single table, a single database, multiple databases, or an entire database instance for some types of databases during full backups. Data Disaster Recovery supports incremental backups only for some types of databases. By default, all the incremental data is backed up during incremental backups.
You can click Select All in the lower-left corner of the Available section to back up the entire database. The database objects that can be backed up and the backup granularity vary based on the database type. For more information, see Supported database types and features.
By default, a backup schedule cannot be used to back up a database that is created after the backup schedule is configured. To back up the database, you can add the database to the backup schedule on the Edit Backup Objects page of the backup schedule. For more information, see Modify backup objects.
If you selected Physical Backup when you purchased a backup schedule, you must back up an entire database instance.
In the Configure Backup Time step, configure the parameters that are described in the following table and click Next.
Parameter
Description
Full-scale Backup Frequency
The frequency of the backup schedule. Valid values: Periodic Backup and Single Backup.
NoteIn scenarios in which incremental data needs to be restored, we recommend that you select Periodic Backup and perform a full backup at least once a week. Otherwise, a large number of binary logs must be replayed during restoration. This process is prone to errors and may result in a prolonged recovery time objective (RTO).
Full Data Backup Recurrence
This parameter is required if you set the Full-scale Backup Frequency parameter to Periodic Backup. You can select the days of the week on which Data Disaster Recovery runs the backup schedule. Select at least one day of the week.
Start At
This parameter is required if you set the Full-scale Backup Frequency parameter to Periodic Backup. We recommend that you set a point in time within off-peak hours. Example: 01:00.
NoteIf a previous full data backup is not complete at the start time of the next backup, Data Disaster Recovery skips the next backup.
Incremental Backup
Specifies whether to enable incremental backup. If you enable incremental backup, make sure that the binary logging feature is enabled for the database that you want to back up.
NoteThis parameter is displayed only when you set the Full-scale Backup Frequency parameter to Periodic Backup.
By default, the binary logging feature is enabled for an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. If you use a self-managed database, you must manually enable the binary logging feature.
Maximum Concurrent Threads for Full Data Backup
The maximum number of concurrent threads that are available for a full backup. You can configure this parameter to adjust the backup speed. For example, you can reduce the number of backup threads to minimize impacts on the database.
Backup network speed limit
The limit on the network bandwidth. Unit: MB/s. You can set the limit based on your business requirements. The default value 0 indicates that the network bandwidth is unlimited.
NoteThis parameter is displayed only when you configure a backup schedule for a MySQL database.
In the Edit Lifecycle step, configure the lifecycle for full backup data in the Configure Full Data Backup Lifecycle section.
NoteIf you set the Incremental Backup parameter to Enable, you must configure the lifecycle for incremental backup data.
After the configurations are complete, click Precheck in the lower-right corner of the page.
If the Precheck Passed message appears, click Start Task.
NoteIf the state of the backup schedule changes to Running, the backup schedule takes effect.
If an exception or error occurs when you start the backup schedule, troubleshoot the exception or error at the earliest opportunity. For more information, see How do I fix errors for an abnormal backup schedule? If your issue persists after you use the solution that is provided in the preceding topic, contact technical support in the DingTalk group (ID: 35585947).
Method 2: Configure a backup schedule for a read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance by using its internal endpoint
On the Backup Schedules page, find the ID of the backup schedule that you want to configure and click Configure Backup Schedule in the Actions column.

In the Configure Backup Source and Destination step of the Configure Backup Schedule wizard, configure the backup source and destination. Then, click Next in the lower-right corner of the page.
 Note
NoteSet the Database Location parameter to Express Connect DB/VPN Gateway/Intelligent Gateway.
Set the Peer VPC parameter to the VPC in which the read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance is deployed.
Set the Address parameter to the internal IP address that you obtain. For more information, see the Prerequisites section of this topic.
Set the Port Number parameter to the port number of the read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
For more information about how to configure other parameters, see Manage a backup schedule.
In the Edit Backup Objects step, find the database or table that you want to back up and add it to the Selected section. Then, click Next.
NoteIf you selected Logical Backup when you purchased a backup schedule, Data Disaster Recovery allows you to specify the databases and tables to be backed up during full backups. You can back up a single table, a single database, multiple databases, or an entire database instance for some types of databases during full backups. Data Disaster Recovery supports incremental backups only for some types of databases. By default, all the incremental data is backed up during incremental backups.
You can click Select All in the lower-left corner of the Available section to back up the entire database. The database objects that can be backed up and the backup granularity vary based on the database type. For more information, see Supported database types and features.
By default, a backup schedule cannot be used to back up a database that is created after the backup schedule is configured. To back up the database, you can add the database to the backup schedule on the Edit Backup Objects page of the backup schedule. For more information, see Modify backup objects.
If you selected Physical Backup when you purchased a backup schedule, you must back up an entire database instance.
In the Configure Backup Time step, configure the parameters that are described in the following table and click Next.
Parameter
Description
Full-scale Backup Frequency
The frequency of the backup schedule. Valid values: Periodic Backup and Single Backup.
NoteIn scenarios in which incremental data needs to be restored, we recommend that you select Periodic Backup and perform a full backup at least once a week. Otherwise, a large number of binary logs must be replayed during restoration. This process is prone to errors and may result in a prolonged recovery time objective (RTO).
Full Data Backup Recurrence
This parameter is required if you set the Full-scale Backup Frequency parameter to Periodic Backup. You can select the days of the week on which Data Disaster Recovery runs the backup schedule. Select at least one day of the week.
Start At
This parameter is required if you set the Full-scale Backup Frequency parameter to Periodic Backup. We recommend that you set a point in time within off-peak hours. Example: 01:00.
NoteIf a previous full data backup is not complete at the start time of the next backup, Data Disaster Recovery skips the next backup.
Incremental Backup
Specifies whether to enable incremental backup. If you enable incremental backup, make sure that the binary logging feature is enabled for the database that you want to back up.
NoteThis parameter is displayed only when you set the Full-scale Backup Frequency parameter to Periodic Backup.
By default, the binary logging feature is enabled for an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. If you use a self-managed database, you must manually enable the binary logging feature.
Maximum Concurrent Threads for Full Data Backup
The maximum number of concurrent threads that are available for a full backup. You can configure this parameter to adjust the backup speed. For example, you can reduce the number of backup threads to minimize impacts on the database.
Backup network speed limit
The limit on the network bandwidth. Unit: MB/s. You can set the limit based on your business requirements. The default value 0 indicates that the network bandwidth is unlimited.
NoteThis parameter is displayed only when you configure a backup schedule for a MySQL database.
In the Edit Lifecycle step, configure the lifecycle for full backup data in the Configure Full Data Backup Lifecycle section.
NoteIf you set the Incremental Backup parameter to Enable, you must configure the lifecycle for incremental backup data.
After the configurations are complete, click Precheck in the lower-right corner of the page.
If the Precheck Passed message appears, click Start Task.
NoteIf the state of the backup schedule changes to Running, the backup schedule takes effect.
If an exception or error occurs when you start the backup schedule, troubleshoot the exception or error at the earliest opportunity. For more information, see How do I fix errors for an abnormal backup schedule? If your issue persists after you use the solution that is provided in the preceding topic, contact technical support in the DingTalk group (ID: 35585947).
How do I obtain the internal and public endpoints of a read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance?
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
On the Basic Information page, click View Details next to the Network Type parameter to obtain the internal and public endpoints of the read-only ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
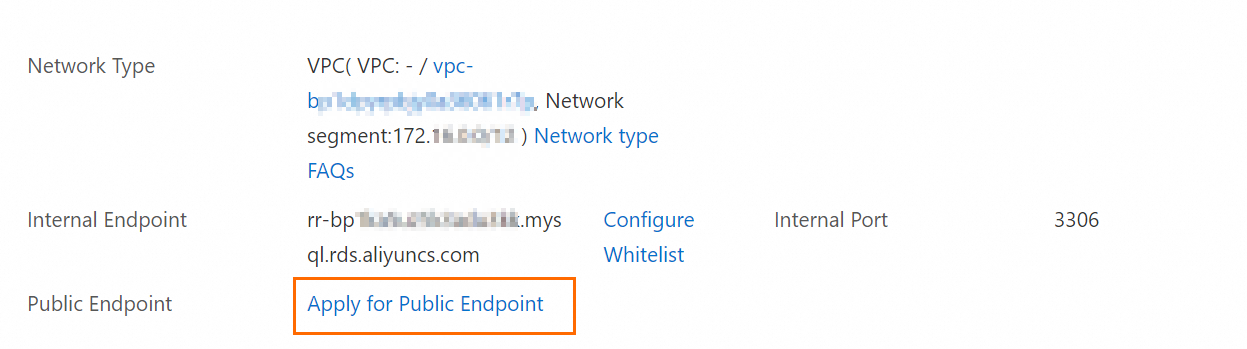
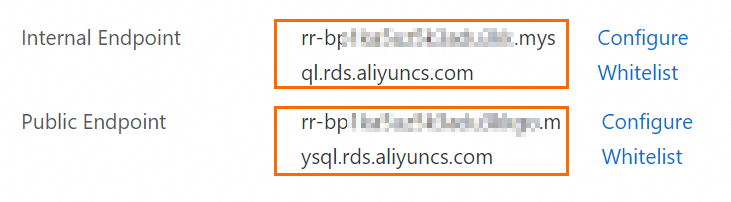 Note
NoteIf you have not applied for a public endpoint for the read-only instance, click Apply for Public Endpoint > OK to apply for a public endpoint. After the public endpoint is applied for, you can obtain the public endpoint.
FAQ
Q: What are the possible causes and solutions if the source instance fails to be connected when I configure a backup schedule for the instance by using its internal endpoint?
A: Possible cause: The internal IP address obtained in Method 2 is a real-time internal IP address. If you clone the source read-only instance, migrate the instance to another zone, or change the VPC or vSwitch of the instance, the real-time internal IP address may change. In this case, the source instance fails to be connected, and the backup fails.
Solution: You can use the internal endpoint of the read-only instance and run the ping command on your local device to obtain a new real-time internal IP address. Then, modify the backup source database and save the configurations.

Q: Can Data Disaster Recovery back up full data and incremental data of a read-only instance?
A: Yes.
What are the differences between Data Disaster Recovery and RDS backup?
Data Disaster Recovery provides dump backup and logical backup for RDS databases to meet the cross-region backup and flexible backup requirements.
RDS provides physical backup for RDS databases to meet the local backup and fast restoration requirements.
What is the value of dump backup provided by Data Disaster Recovery?
Cross-region backup
Data is backed up over a VPC that is secure and stable.
The physical backup data and logs of RDS instances are dumped without the need to initiate additional backup.
Backup sets can be restored to RDS with one click.
Backup sets can be retained for up to five years. Even after you release the RDS instance, the backup sets are still retained based on the specified retention period.
The storage is automatically scaled up.
Flexible backup
Data Disaster Recovery backs up core tables in real time. Data Disaster Recovery performs the full backup and real-time incremental backup on individual tables and provides a recovery point objective (RPO) accurate to seconds. Data can be restored to a specified point in time.
Data Disaster Recovery can restore an individual table from the entire backup set. The restoration duration is only related to the actual amount of data to be restored. Data can be restored within minutes.
Data Disaster Recovery provides the schema mapping feature. You can restore data to the original database instance without the need to purchase an additional database instance. You can manually rename and restore databases and tables. If object names are in conflict, Data Disaster Recovery automatically renames databases and tables that have the same name while retaining the original data in the destination database.
Data Disaster Recovery is integrated with DMS and you can back up and restore RDS databases by choosing Security and Specifications (DBS) > Disaster Recovery for Data (DBS) in the DMS console.
How do I view the backup files that are stored in OSS?
Data Disaster Recovery allows you to back up database instances to an OSS bucket that you create. When you back up data to your OSS bucket, Data Disaster Recovery automatically creates backup folders in the OSS bucket. You do not need to manually create the folders. A backup file is named in the following format: <Backup schedule ID>/<Backup type>/<Full or incremental backup task ID>/<Specific data>.
On the Backup Schedules page, find the backup schedule that you want to manage and click Manage in the Actions column.
On the Configure Task page, find Destination OSS Bucket and click the bucket name.
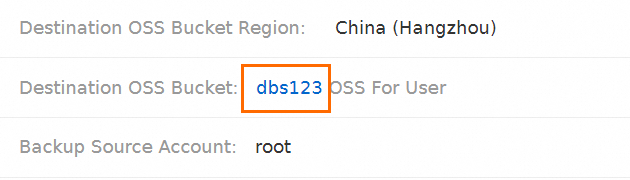
You are navigated to the details page of the destination bucket in the OSS console. The following figure shows the
fullandcontinuousfolders in the destination OSS bucket, which are used to store full backup files and incremental backup files. For more information about OSS, see Get started with OSS.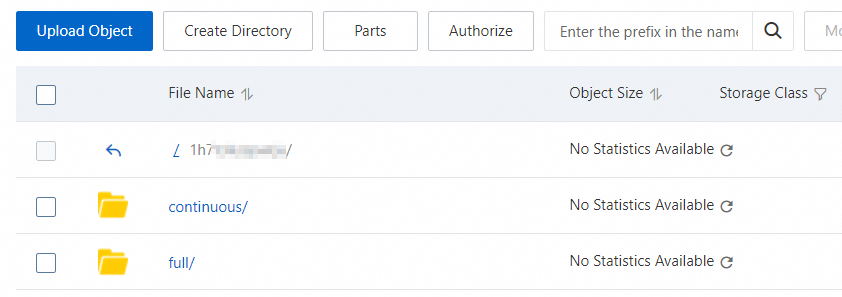
Why is the running time of backup SQL statements in the Data Disaster Recovery console different from the time displayed in the ApsaraDB RDS console?
To ensure the reliability of backup data, Data Disaster Recovery uses the UTC+0 time zone when Data Disaster Recovery executes a backup SQL statement during a logical backup. However, ApsaraDB RDS uses the UTC+8 time zone in SQL audit logs for the same backup SQL statement. As a result, the running time of the backup SQL statement displayed in the ApsaraDB RDS console is 8 hours different from the actual running time. The actual running time of the backup SQL statement is subject to the time displayed in the console.
What is the impact of backup on databases?
When Data Disaster Recovery performs a backup task on a database, the database performance is affected. Therefore, we recommend that you perform backup tasks during off-peak hours.
Item | Logical backup | Physical backup |
Full backup | Data Disaster Recovery splits the data of all tables in a database and executes SQL statements on the database to read the data in multiple threads in parallel. | A backup gateway is installed on the server of a database for database backups. |
Incremental backup | Data Disaster Recovery incrementally backs up logs stored in the memory of a database in real time. This prevents the sudden I/O performance drop that may occur when a large amount of data is backed up at a time. | |
Impact on databases | Data is read from a database instance, which affects the database performance. However, no tables are locked during a logical backup. | Data is read from the disks of a database, which affects the I/O performance of the database. However, no tables are locked during a physical backup. |