This topic describes how to view and manage the endpoints and ports of an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance in the ApsaraDB RDS console.
Basic Edition and High-availability Edition instances
Different types of endpoints are provided for RDS instances that run RDS Basic Edition and RDS High-availability Edition. You can view and change the endpoints based on your connection requirements. The following table describes the types of the endpoints.
Address type | Description | View and modify method |
Instance endpoint | The internal and public endpoints of the instance are provided.
| You can view and modify internal and public IP addresses and ports below. |
Database proxy endpoint | If the database proxy feature is enabled for your RDS instance (supported for RDS High-availability Edition but not for RDS Basic Edition), we recommend that you use the database proxy endpoint to connect to your RDS instance. This maximizes the read/write splitting performance and reduces the load on the primary instance. |
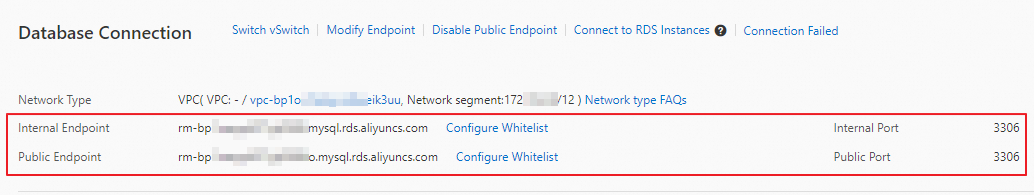
View the internal and public endpoints and port numbers of an RDS instance
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
On the Basic Information page, click View Details in the Basic Information section.
NoteThe public endpoint is displayed only after you apply for a public endpoint.
Change the internal and public endpoints and port numbers
If you have enabled Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption for the internal or public endpoint of your RDS instance, you must disable SSL encryption before you can change the internal or public endpoint. When you disable SSL encryption, your RDS instance is restarted. We recommend that you perform this operation during off-peak hours.
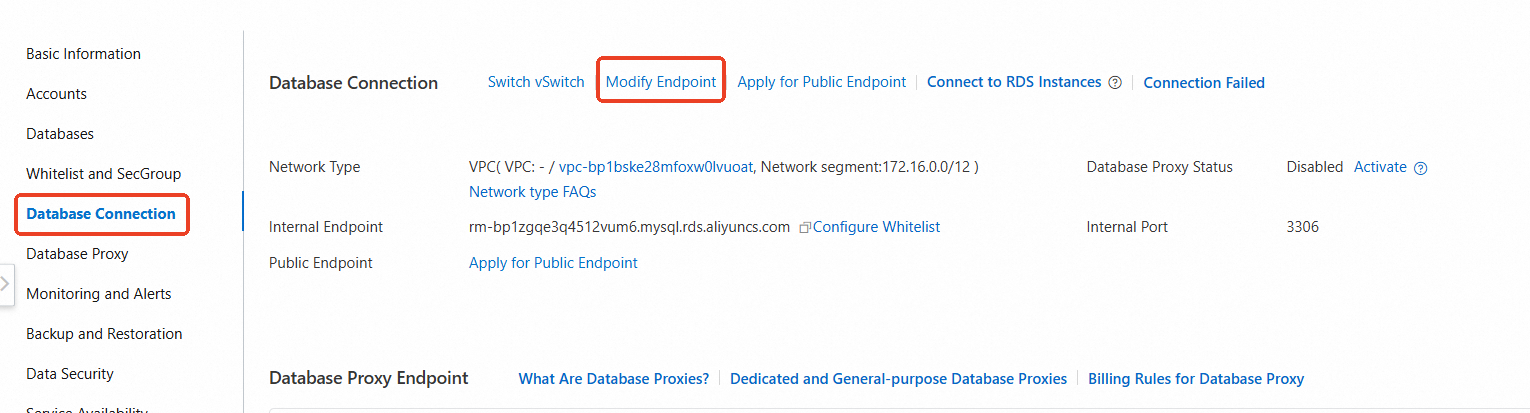
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Database Connection.
Click Modify Connection Address.
In the dialog box that appears, set the prefix and port number for the internal or public endpoint, and then click OK.
NoteThe prefix is globally unique and cannot be configured or modified to the prefix of an existing endpoint.
Cluster Edition instances
ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instances that run RDS Cluster Edition provide read/write endpoints, read-only endpoints, direct node connection endpoints, and database proxy endpoints. You can view or modify these endpoints based on your connection requirements:
Address type | Description | View and modify method |
Read/write endpoint | Each RDS cluster has only one read/write endpoint that connects to the primary node of the RDS cluster. The read/write endpoint supports read and write operations. Each read/write endpoint contains an internal endpoint that is automatically generated and a public endpoint that you must manually apply for.
| |
Read-only endpoint | You can configure up to one read-only endpoint for an RDS cluster. The read-only endpoint connects to the secondary nodes of the RDS cluster and supports load balancing. Each read-only endpoint contains an internal endpoint that is automatically generated during the creation of a read-only endpoint and a public endpoint that you must manually apply for. The number of secondary nodes that are added to the read-only endpoint is always the same as the user-defined number of secondary nodes to ensure availability:
| |
Direct node connection endpoint | You can use the direct node connection endpoint to connect to a node in an RDS cluster. If you connect to a primary node, read and write operations are supported. If you connect to a secondary node, only read operations are supported. Each direct node connection endpoint contains an internal endpoint that is automatically generated during the creation of a direct node connection endpoint and a public endpoint that you must manually apply for. | |
Database proxy endpoint | RDS Cluster Edition instances have the general-purpose database proxy feature enabled by default. You can configure a proxy endpoint as read/write or read-only:
|
Read/write endpoint
The read/write endpoint consists of the internal and public endpoints. After an RDS cluster is created, an internal endpoint is automatically generated. You can apply for a public endpoint based on your business requirements.
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
On the Basic Information page, in the section, view and modify the read/write endpoint, and apply for a public endpoint.
View the read/write endpoint: Hover your mouse over the read/write connection box to view the read/write endpoint in the dialog box that appears.
Modify the read/write endpoint and apply for a public endpoint: Click Edit. In the dialog box that appears, you can Change Endpoint, Change VPC, and Apply for a public endpoint.

Read-only endpoint
Create, view, and delete the read-only endpoint
When you create or delete the read-only endpoint of an RDS cluster, the read/write endpoint of the RDS cluster is not affected.
After you delete the read-only endpoint of an RDS cluster, the internal and public endpoints of the read-only endpoint are released, and the connections that are established by using the read-only endpoint are interrupted.
You can configure up to one read-only endpoint for an RDS cluster. You can use the read-only endpoint for multiple secondary nodes in the RDS cluster to implement load balancing.
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
On the Basic Information page, in the section, select:
Add an endpoint
Click Add Endpoint. In the dialog box that appears, enter or select the internal endpoint prefix, internal endpoint port, internal endpoint VPC, and internal endpoint VSwitch. Add the secondary nodes that you want to access, and then click OK.
Delete address
In the target read-only connection box, click Delete. In the dialog box that appears, click OK.
View the read-only endpoint: On the Basic Information page, in the section, hover your mouse over the read-only connection box to view the read-only endpoint in the dialog box that appears.

Adjust the settings of the nodes added to the read-only endpoint
Add secondary nodes or adjust node weights: Existing database connections are not affected. New connections that are established by using the read-only endpoint are load balanced based on the new node settings.
Remove secondary nodes: At least one secondary node must be retained. The database connections on the removed node are interrupted for 30 to 120 seconds. Other nodes are not affected.
When you adjust the weights of secondary nodes in an RDS cluster, make sure that the weight of at least one secondary node is greater than 0.
The node settings of the read-only endpoint of an RDS cluster take effect on both the internal and public endpoints of the read-only endpoint.
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
On the Basic Information page, in the section, click Edit in the read-only connection box:

Add nodes and adjust weights: Select the secondary nodes that you want to add to the endpoint, and click the
 icon. Adjust the node weights, and then click OK.
icon. Adjust the node weights, and then click OK.Remove nodes: Select the nodes that you want to remove, click the
 icon, and then click OK.
icon, and then click OK.

Direct node connection endpoint
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
On the Basic Information page, in the section, create, view, and modify the direct connection endpoints of cluster nodes, and apply for public endpoints.
Create a cluster node endpoint: In the target node section, click Create Node Endpoint. Configure the internal information, and then click OK.
View and modify the direct connection endpoint of a cluster node, and apply for a public endpoint: Click Manage. In the dialog box that appears, you can Change Endpoint, Change VPC, and Apply for a public endpoint.

FAQ
Related API operations
API operation | Description |
CreateDBInstanceEndpoint - Create an endpoint for an instance | Creates an endpoint for an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance that runs RDS Cluster Edition. |
DeleteDBInstanceEndpoint - Delete an endpoint of an instance | Deletes an endpoint of an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance that runs RDS Cluster Edition. |
ModifyDBInstanceEndpointAddress - Modify information about the endpoint of an instance | Modifies the information about the endpoint of an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance that runs RDS Cluster Edition. |