To handle high-concurrency database read requests and improve overall system throughput, you can create a read-only instance for efficient read/write splitting. A read-only instance is a replica of the primary database instance. Any data changes in the primary instance are automatically synchronized to all associated read-only instances. This reduces the read load on the primary instance and ensures that the data in the read-only instances remains consistent with the primary instance.
To create read-only instances for other database engines, see the following documents:
Prerequisites
The primary RDS for MySQL instance must meet the following conditions:
The RDS instance runs MySQL 8.0, MySQL 5.7, or MySQL 5.6.
The RDS instance uses the subscription or pay-as-you-go billing method. Serverless RDS instances do not support read-only RDS instances.
The RDS instance runs RDS High-availability Edition.
You can go to the Basic Information page of your RDS instance to obtain the preceding information.
You can create read-only RDS instances that run RDS High-availability Edition or RDS Basic Edition. A read-only RDS instance that runs RDS High-availability Edition includes a primary instance and a secondary instance that work in HA mode. For more information, see RDS High-availability Edition.
Precautions
You can only create read-only instances from a primary instance. You cannot convert an existing instance into a read-only instance.
Creating a read-only instance does not affect the primary instance because data is copied from the secondary node of the primary instance.
If the primary instance is released, subscription read-only instances are automatically refunded and released. Pay-as-you-go read-only instances are released immediately.
The parameters of a read-only instance do not inherit the parameter settings of the primary instance. Instead, default parameter values are used. You can modify these parameters in the console of the read-only instance.
The storage class of the read-only instance must be the same as that of the primary instance.
Because the primary instance already has backups, read-only instances only support setting a local log retention policy. They do not support setting an automatic backup policy or initiating manual backups.
Storage space:
Disk-based instances: The storage space of a read-only instance cannot be smaller than that of the primary instance. If the memory of the primary instance is larger than that of the read-only instance, the read-only instance restarts when you change the specifications of the primary instance.
Local disk-based instances: The storage space of a read-only instance cannot be smaller than that of the primary instance.
You can create a maximum of 10 read-only instances.
Billing method: The billing method can be subscription or pay-as-you-go. For pricing details, see Read-only instance types.
The VPCs you can select when creating a read-only instance are limited.
Create a read-only instance
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
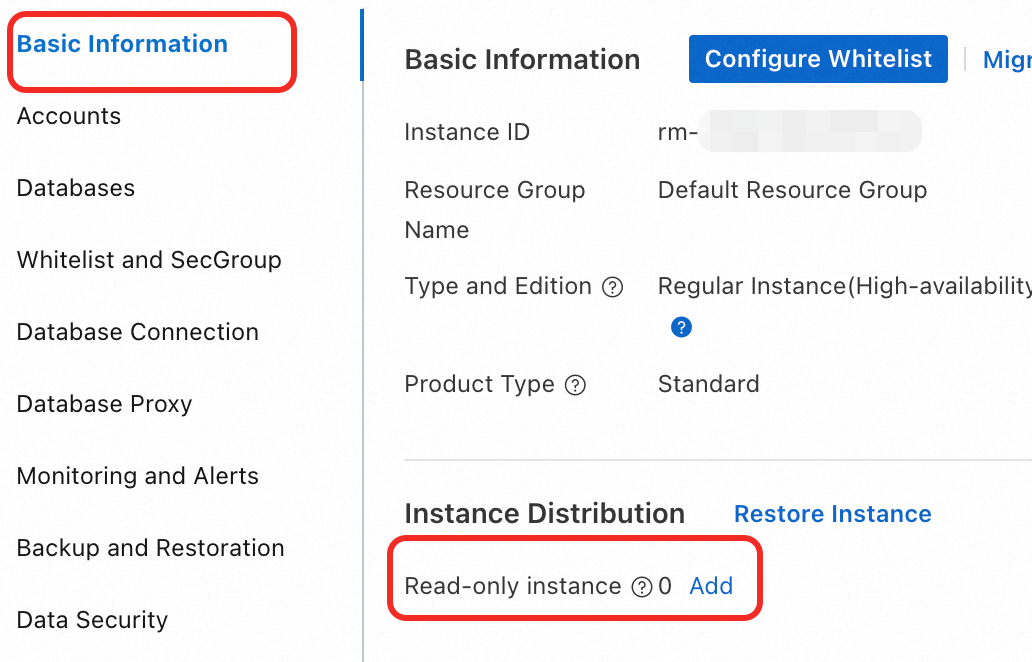
On the Basic Information page, in the Instance Distribution section, click the Add button to the right of Read-only Instance.
 Note
NoteIf the Add button is not displayed, check whether the instance meets the prerequisites.
Configure the basic resources for the read-only instance.
Parameter
Description
Billing Method
Subscription: This is a subscription billing method. You must pay for resources before you use them. This billing method is suitable for long-term use and is more cost-effective than pay-as-you-go. The longer the subscription duration, the higher the discount.
Pay-As-You-Go: This is a pay-as-you-go billing method. You are charged for resources on an hourly basis. This billing method is suitable for short-term use. You can release the instance at any time to save costs.
Edition
Basic Edition: A single-node read-only instance that is cost-effective and suitable for learning or testing. It takes a long time to recover from a fault or restart.
NoteThis option is available only when the storage class of the primary instance is cloud disk.
High-availability Edition (Default): This series provides a primary node and a secondary node to ensure high availability for the read-only instance. It is suitable for production environments and meets the requirements of more than 80% of user scenarios.
NoteIf you select the High-availability series, you must also configure the primary zone, deployment solution (multi-zone or single-zone deployment), and secondary zone.
Product Type
You can select Yitian Edition only when the Storage Class of the primary instance is ESSD, .
For more information about Standard and Yitian , see Product types.
Zone
This parameter applies only to read-only instances of the Basic Edition. A zone is an independent physical area within a region. There is no substantial difference between zones. An instance of the Basic Edition is a single-node instance and uses single-zone deployment by default.
Zone of Primary Node
Deployment Method
Zone of Secondary Node
This parameter applies only to read-only instances of the High-availability series. A zone is an independent physical area within a region. There is no substantial difference between zones. For an instance of the High-availability series, you must also select a deployment solution:
Single-zone Deployment: The primary and secondary nodes are in the same zone. You only need to set the primary zone.
Multi-zone Deployment: The primary and secondary nodes are in different zones. This provides cross-zone disaster recovery at no extra charge. You need to set the primary and secondary zones.
Instance Type
General-purpose Instance Types: A general-purpose instance type. It exclusively uses the allocated memory and I/O resources, and shares CPU and storage resources with other general-purpose instances on the same server.
Dedicated Instance Types: A dedicated or exclusive instance type. A dedicated instance exclusively uses the allocated CPU, memory, storage, and I/O resources. An exclusive instance is the top-tier dedicated type, exclusively occupying the entire server's CPU, memory, storage, and I/O resources.
NoteEach instance type has a corresponding number of CPU cores, memory, maximum connections, and maximum IOPS.
Database Proxy
If a database proxy is not enabled for the primary instance, you can choose to enable the free general-purpose database proxy when you create a read-only instance. The system automatically deploys the proxy based on the recommended specifications and enables the proxy feature for the primary instance at the same time. The proxy supports advanced features such as read/write splitting, connection pools, transaction splitting, persistent connections, and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption. After the proxy is enabled, you can flexibly change the proxy specifications and type or manually shut down the database proxy as needed.
NoteIf the proxy is already enabled for the primary instance, the proxy feature for the read-only instance is enabled by default. You do not need to enable it manually.
You can also enable the database proxy after the read-only instance is created.
Storage Capacity
Storage space includes data space, system file space, log file space, and transaction file space. The minimum increment for adjusting storage space is 5 GB.
NoteThe storage space of a read-only instance must be greater than or equal to the storage space of its primary instance.
Click Next: Instance Configuration.
Parameter
Description
VPC
By default, this is the same as the VPC of the primary instance. No configuration is required.
VSwitch of Primary Node
You can select a primary vSwitch or use the default one.
vSwitch of Secondary Node
The secondary vSwitch is automatically allocated. No configuration is required.
Port
The default value is 3306. You can change it as needed.
Release Protection
This parameter applies only to pay-as-you-go instances. Enable instance release protection for it to prevent accidental release of the pay-as-you-go instance.
Resource Group
By default, this is the same as the resource group of the primary instance. No configuration is required.
Instance Name
Customize the instance description for easy identification. This parameter is optional.
Tags
If you have many instances, you can bind tags to them for categorization and management. This parameter is optional.
Click Next: Confirm Order. Confirm the Parameter Configuration, and select the Quantity and Subscription Duration (for subscription instances only). Then, click Confirm Order and complete the payment.
NoteWhen you purchase a subscription read-only instance for a subscription primary instance, you can select the Align With Primary Instance checkbox next to Subscription Duration to align the lifecycle of the read-only instance with that of the primary instance.
If the primary instance is a subscription instance and you change the billing method of a read-only instance from pay-as-you-go to subscription, you cannot select Align With Primary Instance for Subscription Duration. This setting is available only for newly purchased read-only instances. We recommend that you first release the pay-as-you-go read-only instance and then purchase a new subscription read-only instance.
For subscription instances, we recommend that you select Auto-renewal. This prevents service interruptions caused by a forgotten renewal and eliminates the need for you to manually renew the instance.
View the read-only instance and its endpoint
Log on to the ApsaraDB RDS console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Instances. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the instance list, find the primary instance and click the arrow on the left to view the read-only instances under it.
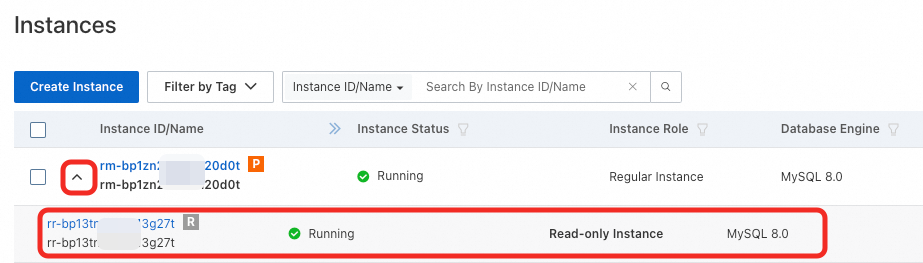
You can also click the primary instance ID to go to the details page. The read-only instances are displayed in the section.
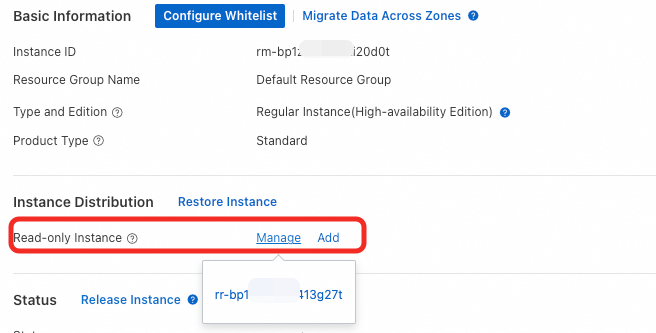
View the endpoint of the read-only instance: Each read-only instance has its own endpoint. To obtain the endpoint, you can click the read-only instance ID to go to its details page. Then, in the section, click View Details.

View the replication delay of a read-only instance
A replication delay may occur when a read-only instance synchronizes data from the primary instance. You can view the delay on the Basic Information page of the read-only instance. For more information, see Causes and solutions for replication delays of ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL read-only instances.
Configure read/write splitting (using read-only instances)
After you add a read-only instance, you can manually configure read/write splitting in your application, or enable the database proxy to automatically split read and write requests. For more information, see What is a database proxy?, What is read/write splitting?, and Enable the database proxy.
The general-purpose database proxy and persistent connection features are free of charge. For more information, see [New Features/Specifications] RDS for MySQL supports free general-purpose database proxy and free persistent connection features.
Best practice: Take a read-only instance offline without service interruption using the database proxy
Assume that you have a read/write splitting environment with one primary instance A and two read-only instances B and C. To take read-only instance C offline without service interruptions, perform the following steps.
Go to the RDS Instances page, select the region where instance A is located, and then click the ID of instance A.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Database Proxy. In the Connection Topology Management section, click Modify Configuration.

In the Modify Proxy Endpoint (Terminal) Configuration dialog box, set the read weight to 0 for read-only node C.

Go to the Monitoring and Alerts page for read-only instance C. In the Session Connection section, monitor the active_session metric and wait for it to drop to 0.
 Note
NoteCheck whether the value of active_session is 0. If the value does not drop to 0 after a long period, you can kill the session.
On the Database Proxy tab for primary instance A, remove read-only instance C from the database proxy endpoint.
FAQ
Creation
Q: Why can't I select a specific zone when creating a read-only instance?
A: If a zone is unavailable for selection, it means that resources are unavailable in that zone. You can select another zone. This does not affect the functionality of the read-only instance.
Q: Can I select a different VPC for the read-only instance than the one used by the primary instance?
A:
If the primary instance is in a classic network, you can select any VPC for the read-only instance.
If the primary instance is in a VPC, the options for the read-only instance's VPC are as follows:
If the storage class is local SSD, you can select any VPC for the read-only instance.
If the storage class is cloud disk, the VPC of the read-only instance must be the same as that of the primary instance.
Q: Does creating a read-only instance affect the primary instance?
A: During the creation of a read-only instance, you cannot perform operations such as changing the specifications of the primary instance. You must wait until the read-only instance is created. Apart from this restriction, the primary instance is not affected.
Q: Can I add a read-only instance to an RDS for MySQL instance of the Basic Edition to implement read/write splitting?
A: You cannot directly add a read-only instance to an RDS for MySQL instance of the Basic Edition. You can upgrade an RDS for MySQL 8.0 or 5.7 instance of the Basic Edition to the High-availability Edition, add a read-only instance, and then enable and configure the database proxy to implement read/write splitting. You can also upgrade the Basic Edition instance to the Cluster Edition and use the primary and secondary nodes of the Cluster Edition to implement read/write splitting.
For information about how to upgrade an instance from the Basic Edition to the High-availability Edition, see Upgrade an instance from Basic Edition to High-availability Edition.
For information about how to upgrade an instance from the Basic Edition to the Cluster Edition, see Upgrade an instance from Basic Edition to Cluster Edition.
For information about how to enable and configure the database proxy, see Enable the database proxy and Configure an access policy for a database proxy endpoint.
Q: Can I select primary and secondary zones when I create a read-only instance of the High-availability series?
A: You can select primary and secondary zones if the primary instance is a disk-based instance with a Milvus version of 20210430 or later. Otherwise, you cannot select primary and secondary zones.
Data synchronization and replication delay
Q: How long does data synchronization for a read-only instance take?
A: Under normal circumstances, synchronization is in real time. However, a replication delay may occur during large transactions or DDL operations. The actual delay varies depending on the circumstances.
Q: How can I determine if replication is normal based on the replication delay of a read-only instance?
A: Typically, the replication delay of a read-only instance is within 1 second. If the delay exceeds 1 second, this indicates a data synchronization delay. In extreme cases, the connection may break.
Q: What are the common causes of replication delay?
A: For information about common causes of and solutions for replication delays, see Causes and solutions for replication delays of ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL read-only instances.
Q: Do read-only instances support parallel replication?
A: Yes, read-only instances support parallel replication.
Connection and routing
Q: How can I force requests to be processed by the primary database/primary instance?
A: There are three ways to force requests to be sent to the primary instance for processing:
Connect directly to the internal or public endpoint of the primary instance to send requests directly to the primary instance for processing.
If the database proxy is enabled and transaction splitting is not, you can encapsulate requests within a transaction. Operations within a transaction are sent to the primary instance by default.
Use Hint syntax to route requests to the primary instance. For more information, see Hint syntax.
Q: Does a read-only instance have a separate endpoint? Can I connect to a read-only instance separately?
A: A read-only instance has a separate connection address, which is listed in the Basic Information section of the instance's details page.
Instance O&M
Q: I added a read-only instance to my RDS for MySQL instance. After a period, its storage usage (both total storage and data files) is higher than the primary instance. Is this normal?
A: Yes, this is expected behavior. The space inconsistency is caused by differences in the primary/secondary data synchronization mechanism:
Primary instance: Executes the original user SQL statements (such as
INSERTandUPDATE).Read-only instance: Completes synchronization by replaying row-based binary logging events.
This difference in InnoDB page writing mechanisms may cause page splits or more internal storage fragmentation on the read-only instance. Therefore, even if the data is completely consistent, the physical files of the read-only instance may be larger than those of the primary instance. In scenarios with frequent updates, deletions, or large transactions, the ibdata1 file, undo log, or temporary files of the read-only instance may grow faster, making the space difference more pronounced.
Solution: You need to recreate the read-only instance. After enabling read/write splitting with the database proxy, create a new read-only node. After the new read-only node is running as expected, delete the old read-only node.
Q: If a read-only instance is of the High-availability series and has primary and secondary nodes, how do I set parameters for these two nodes?
A: You only need to set parameters on the primary node of the read-only instance. The secondary node of the read-only instance automatically synchronizes the parameter values from the primary node. You cannot directly modify the parameters of the secondary node.
Q: Can a read-only instance be converted into a regular instance?
A: This feature is not supported.
Q: Can I back up the data of a read-only instance? Can automatic backups be performed on the read-only instance?
A: You do not need to back up the read-only instance. Backups are performed on the primary instance. Because snapshot backups are used, there is no performance overhead on the primary instance.
Q: How are transaction logs purged?
A: The binary logs of an RDS for MySQL instance are automatically or manually deleted based on rules.
Q: Do changing the configuration, releasing, or changing the billing method of a read-only instance affect the primary instance?
A: No, they do not.
Billing
Q: Can the billing method of a read-only instance be changed?
A: Yes, it can. For more information, see Change the billing method from pay-as-you-go to subscription or Change the billing method from subscription to pay-as-you-go.
Q: How can I estimate the cost of a read-only instance?
A: Log on to the ApsaraDB RDS console, go to the page for creating a read-only instance, and configure parameters such as the instance type and storage space according to your requirements. The fees displayed on the page provide a cost estimate.
Related API operations
API | Description |
Creates an RDS read-only instance |