A cross table displays summary values for a field and merges homogeneous data. It features one group of data listed down the left side as rows and another group across the top as columns. At the intersection of rows and columns, you can perform various summary calculations, such as sum, average, count, maximum, and minimum. This topic describes how to add data to and configure styles for a cross table.
Overview
Scenarios
Multi-dimensional analysis: Analyze the relationship between province, product type, and profit amount.
Decision support: Support business decisions by cross-comparing measures such as order amount and shipping cost.
Complex calculation requirements: For scenarios that require quick access to period-over-period, cumulative, or percentage ranking values.
Benefits
Calculation capabilities: Configure advanced calculations with one click, such as period-over-period comparisons, cumulative calculations, percentages, rankings, TopN, percentiles, and totals/subtotals.
Visualization effects: Table themes, tree-like display, freezing, line breaks, column width, and more.
Annotation capabilities: Customize remarks and endnotes with text and measures. You can also set custom external link paths to enable interaction between data and other systems.
Event capability: Submit a data feedback event.
Conditional formatting: Make data more readable with formats such as text, background, icons, color scales, and data bars.
Interactive operations: Dimension/measure filtering, in-table filtering, and more.
Example effect diagram
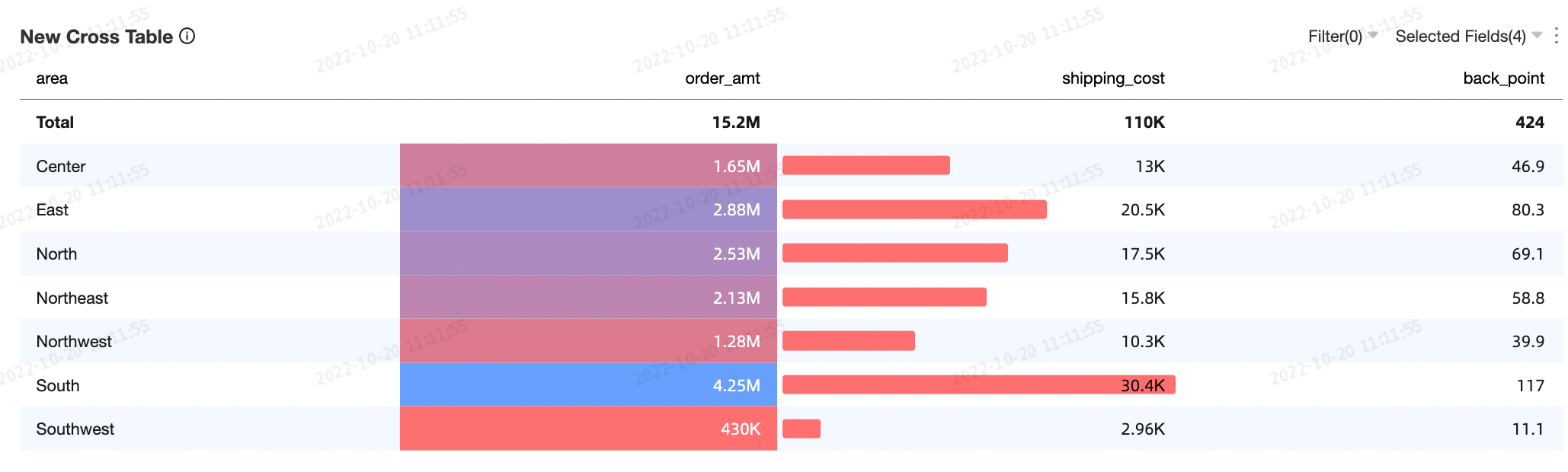
Limits
Prerequisites: You have created a dashboard. For more information, see Create a dashboard.
A cross table consists of Rows and Columns.
Rows are determined by the dimensions of the data, such as province and product type.
Columns are determined by the measures of the data, such as order quantity and profit amount.
NoteThe number of dimensions and measures for the rows and columns of a cross table is not limited.
You can export a maximum of 10,000 rows of data from a cross table. The time required to export the data varies based on your computer's configuration and the data volume. For more information, see Export controls.
Configure Chart Data
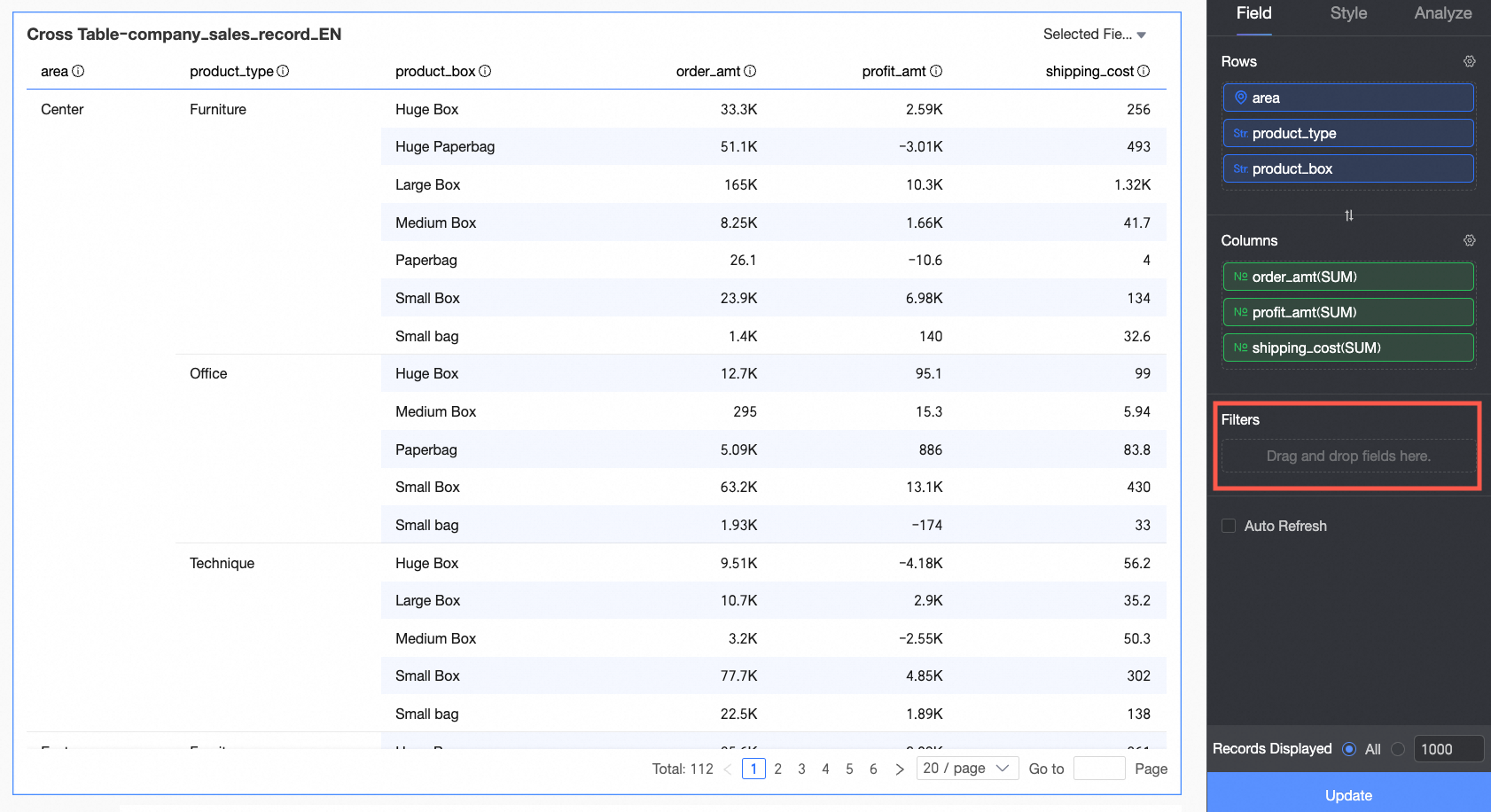
You can add dimension and measure fields to the rows and columns of a cross table.
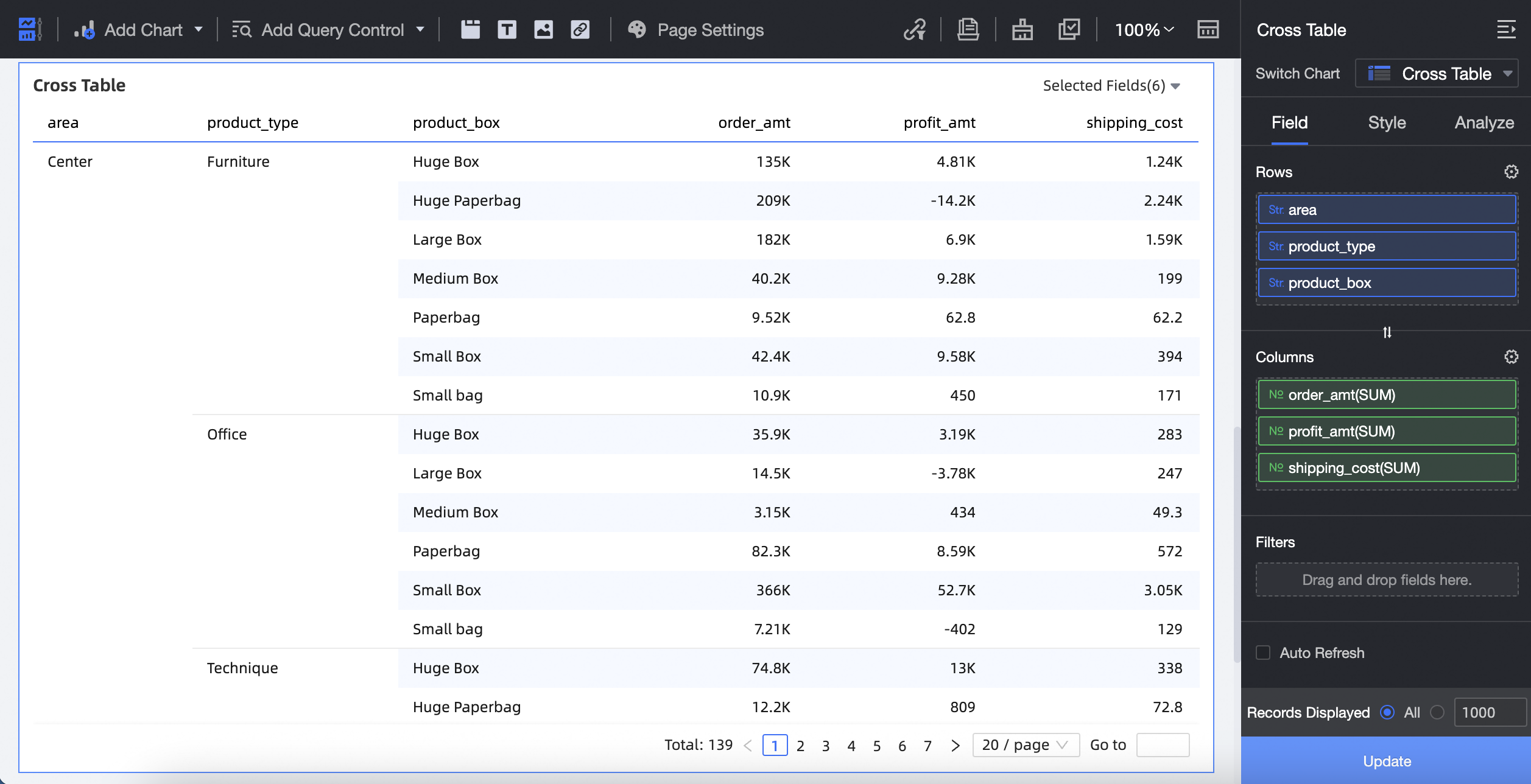
You can add dimension fields to Rows and measure fields to Columns as follows:
On the Data tab, select the required dimension and measure fields:
From the Dimensions list, double-click or drag area, product_type, and product_package to the Rows area.
In the Measures list, find order _amount, shipping_cost, and profit_amount. You can double-click or drag them to the Columns area.
Click Update. The system automatically updates the chart.
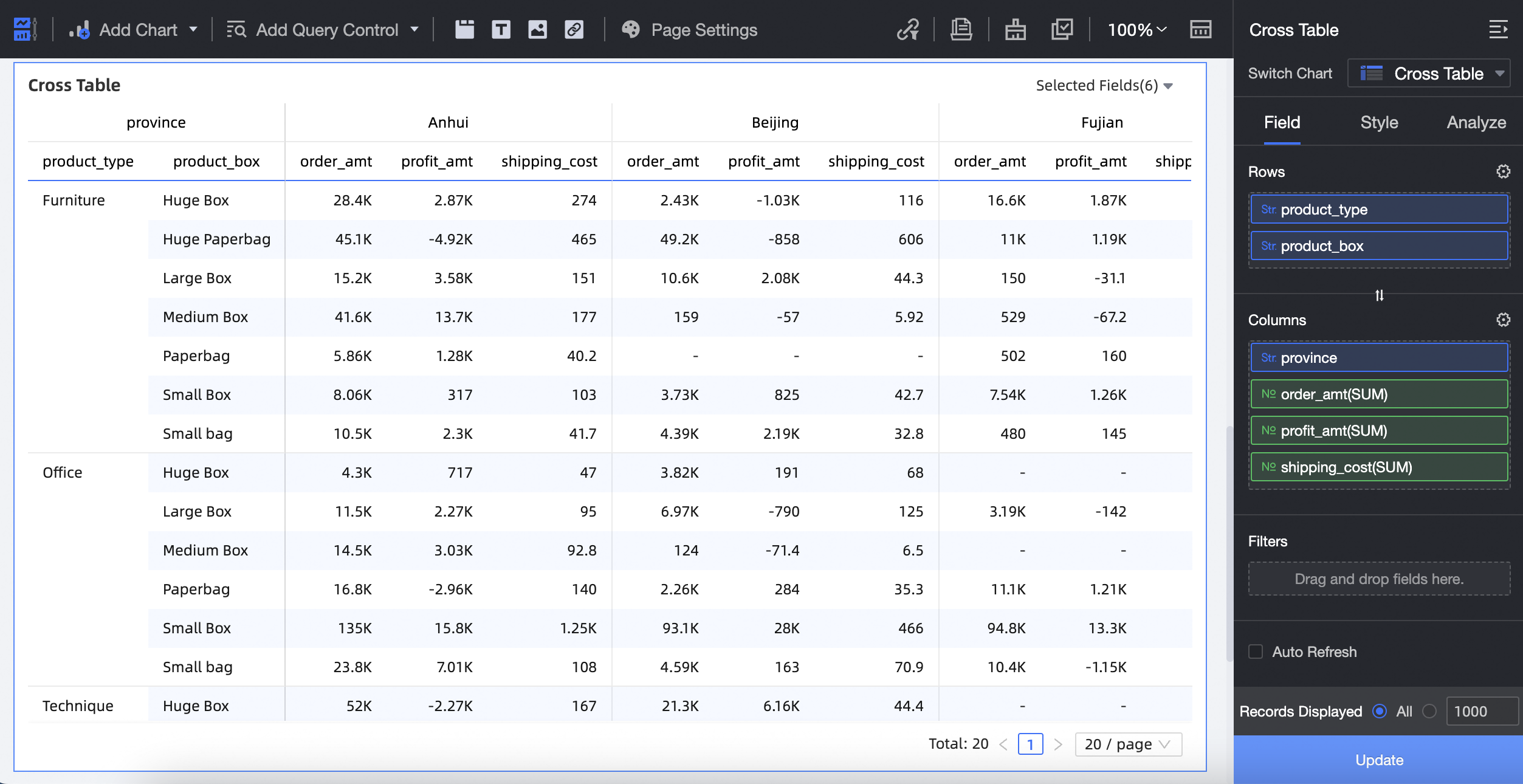
Add dimension fields to the Rows control and add measure or dimension fields to the Columns control as follows:
On the Data tab, select the required dimension and measure fields:
In the Dimensions list, locate product_type and product_package. You can double-click either item or drag it to the Rows area.
In the Dimensions list, drag province to the Columns area.
In the Measures list, find order _amount, shipping_cost, and profit_amount. Double-click or drag them to the Columns area.
Click Update. The system automatically updates the chart.
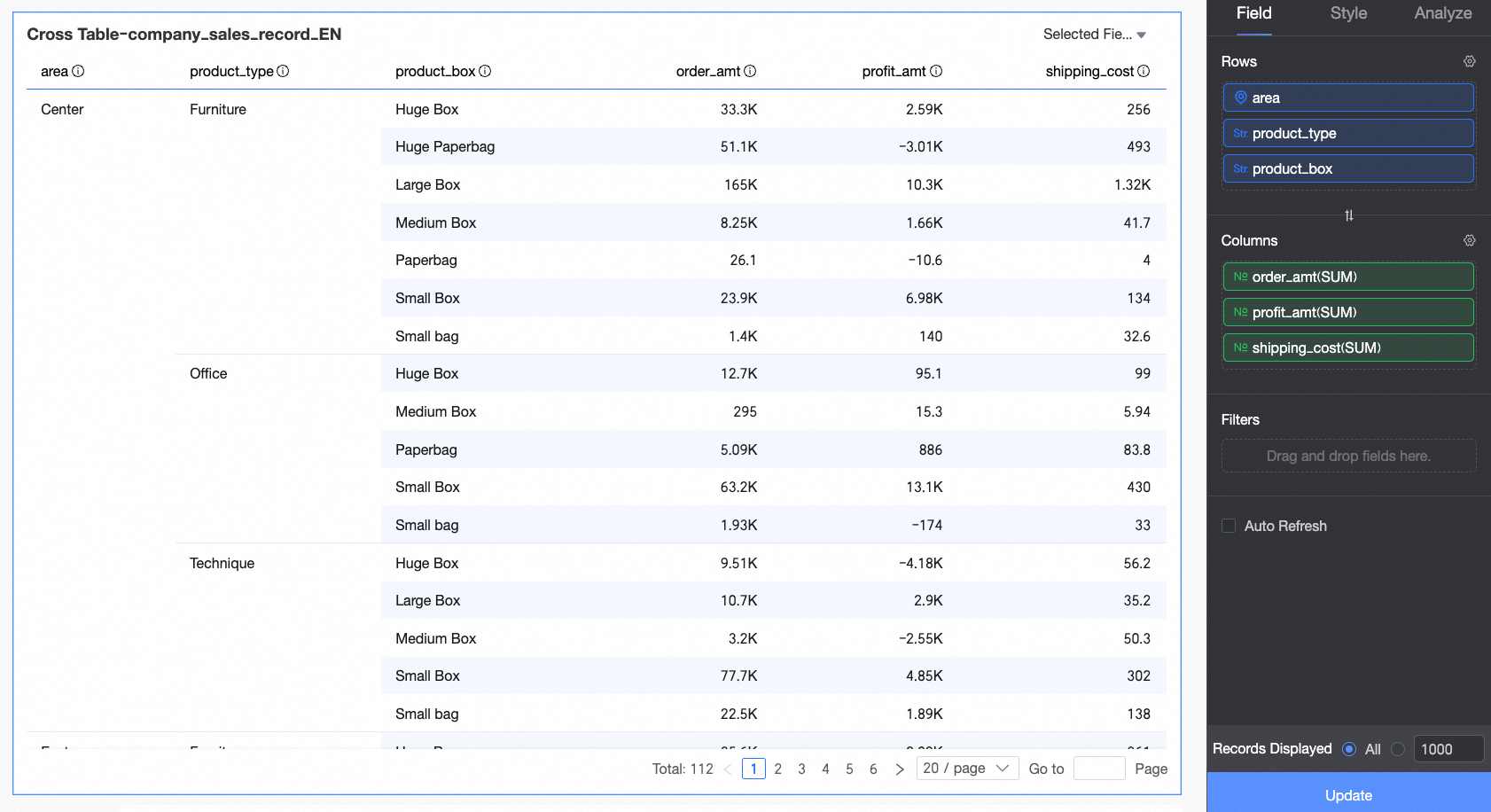
Add measure fields to Rows and dimension fields to Columns as follows:
On the Data tab, select the required dimension and measure fields:
From the Dimensions list, drag area, province, and product_type to the Columns area.
In the Measures list, locate order_amount, shipping_cost, and profit_amount. Then drag them to the Rows area.
Click Update. The system automatically updates the chart.
The number of dimensions and measures for the rows and columns of a cross table is not limited.
You can export a maximum of 10,000 rows of data from a cross table. The time required to export the data varies based on your computer's configuration and the data volume. For more information, see Export Data.
If a field is an image type, you can set its display size. On mobile devices, the image width and height default to half the size set for the PC.
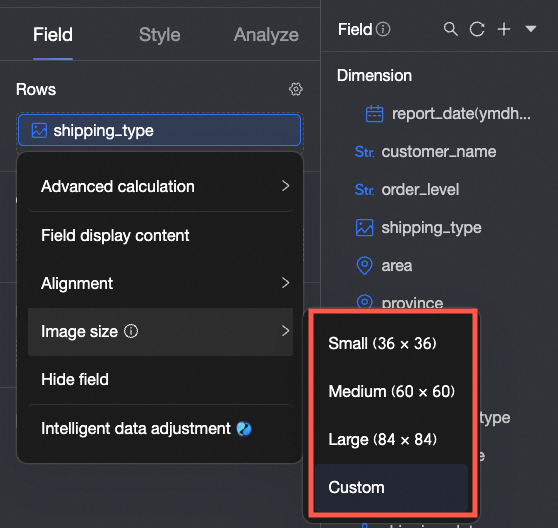
In the Filter section, you can set filter conditions. For more information, see Filter fields.
Configure the Data Panel
You can perform the following operations on the data panel:
Add fields in batches
Hold down Shift/Command and click the target fields to add them to the target area as a batch.
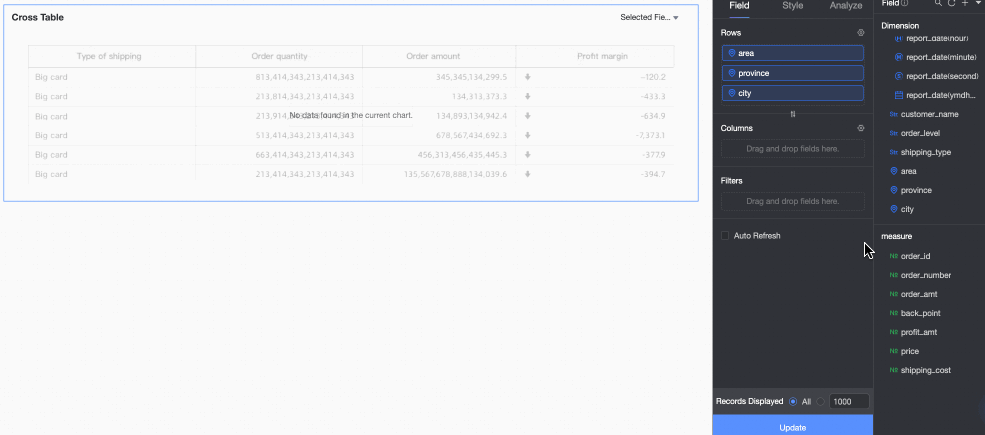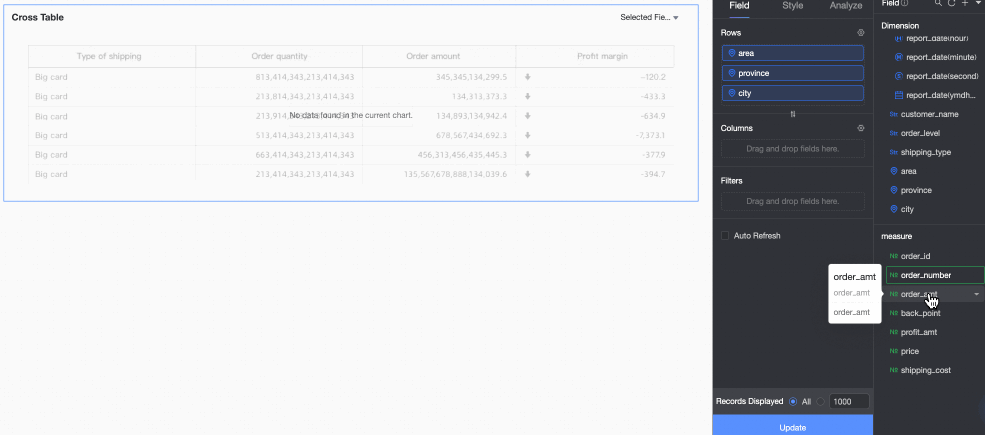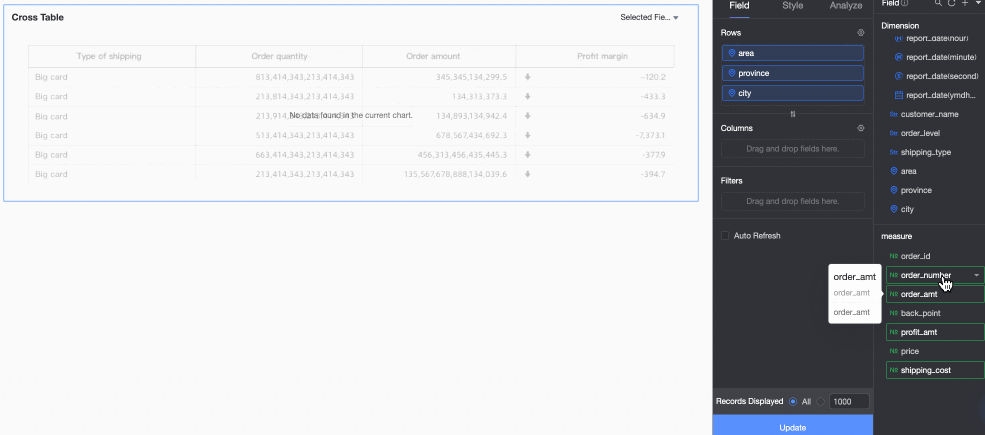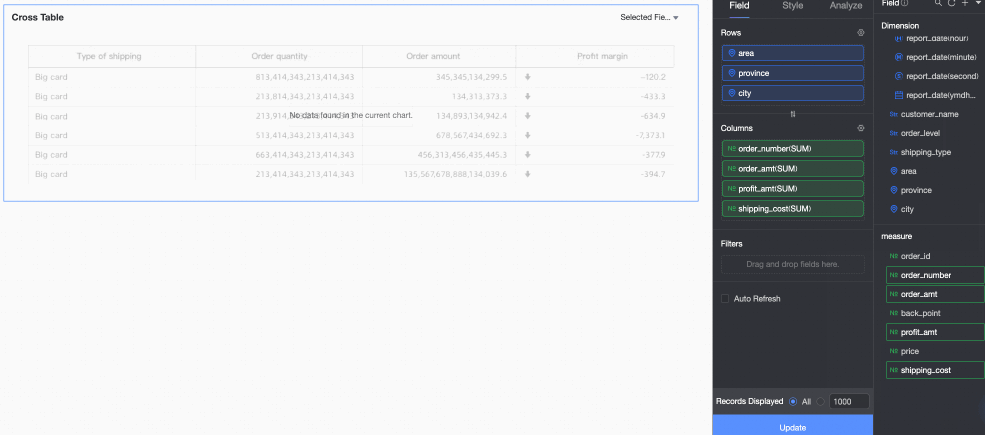
Hidden field.
You can hide measures in both rows and columns. There are four ways to quickly hide fields: hide a measure field on the editing page (①), enable field content filtering in the Filter section of the Style panel (②), add a query control (③), or use a filter (④) to filter data for related fields.
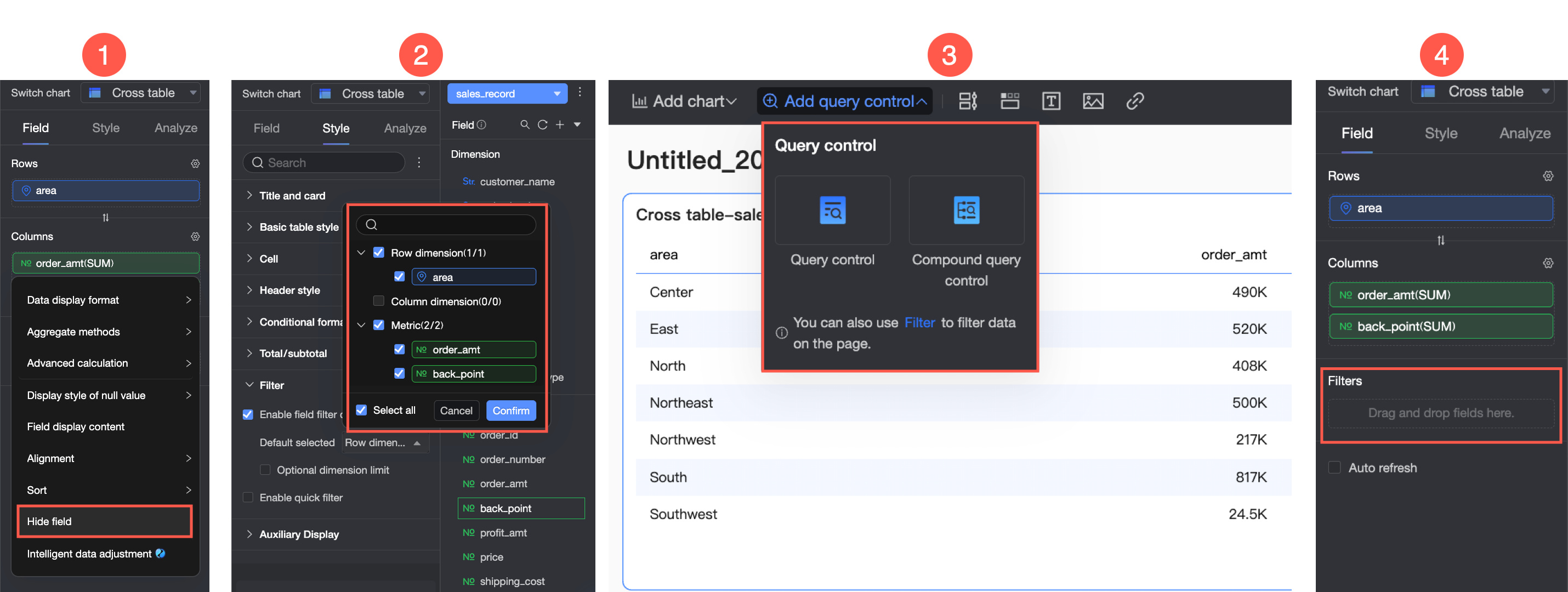
Note:
If you hide a dimension field in the Rows area, the field is not displayed in the chart but is included in grouping and calculations.
If you hide a dimension field in the Columns area, the field is not displayed in the chart but is included in total calculations.
Alignment.
For horizontal alignment, you can select left, center, right, or automatic.
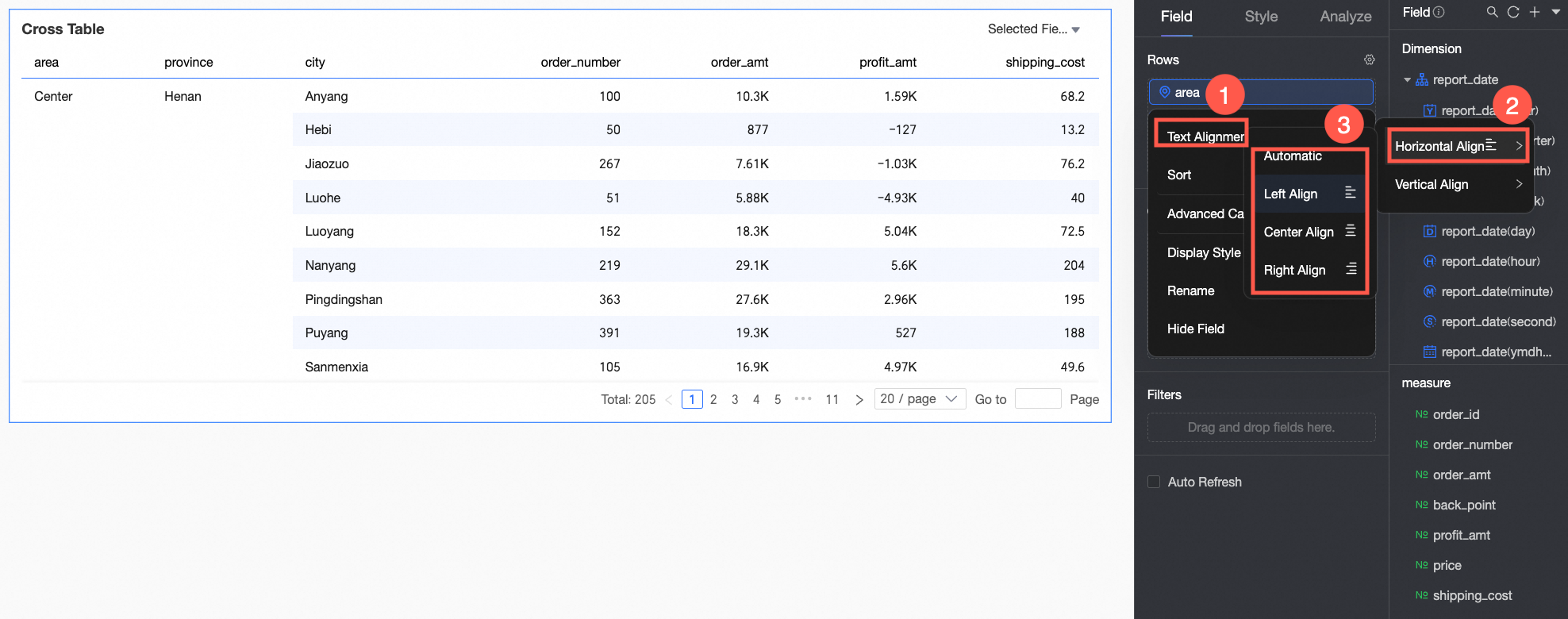
For vertical alignment, you can select top, middle, bottom, or automatic.
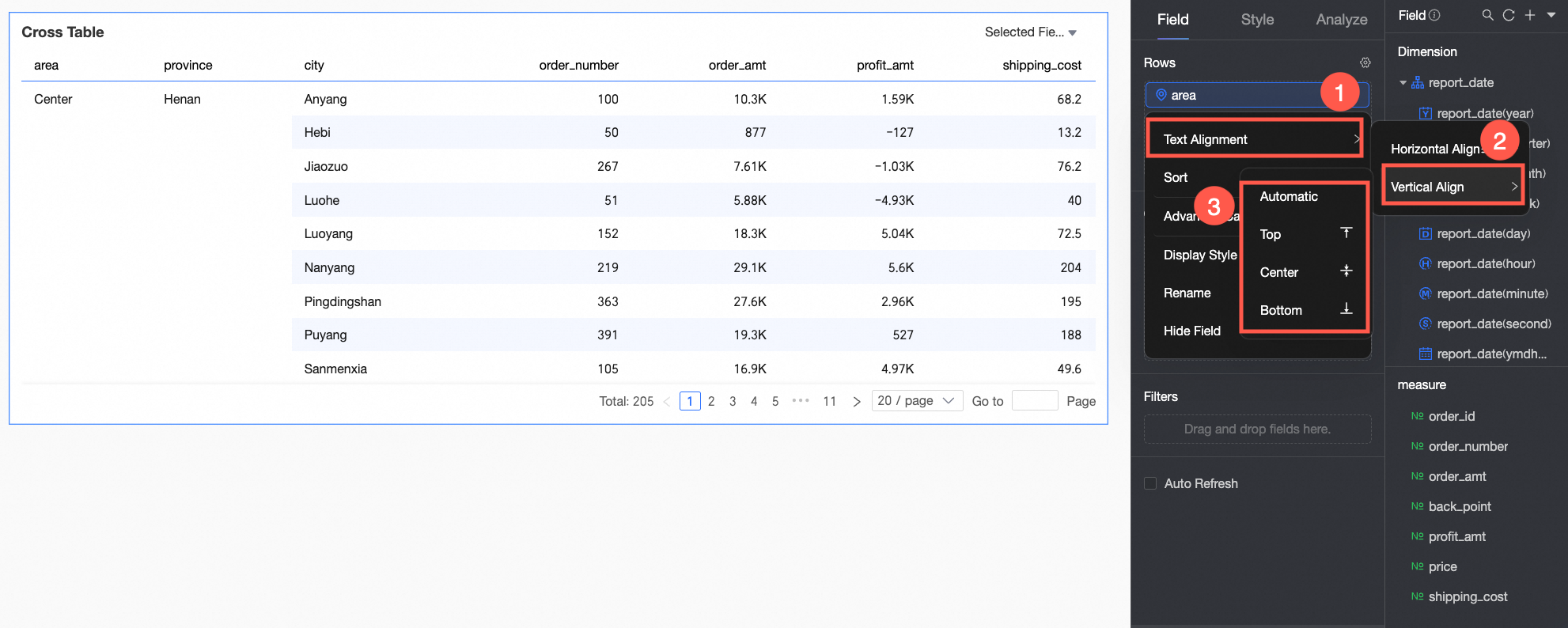
To align fields in batches, click the
 icon in the field panel. In the field configuration dialog box, select the fields and the alignment method.
icon in the field panel. In the field configuration dialog box, select the fields and the alignment method.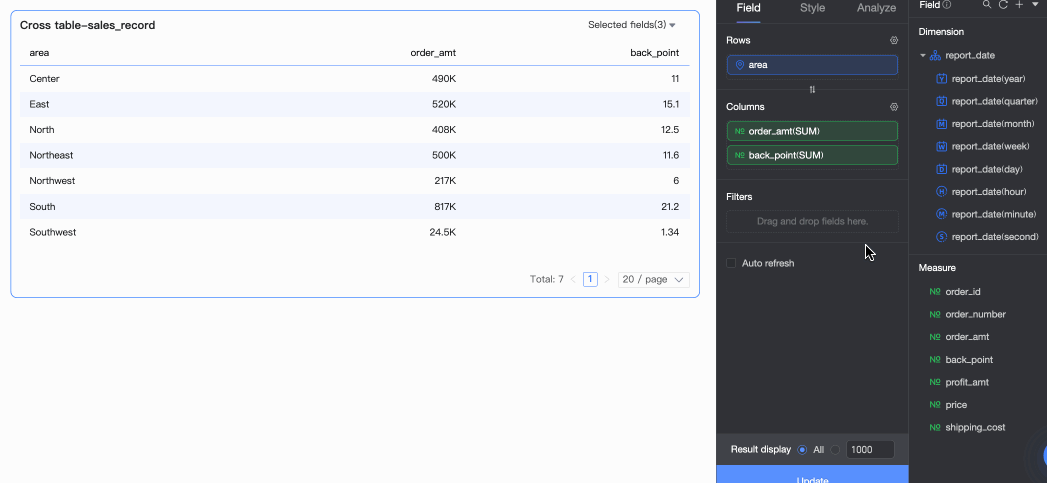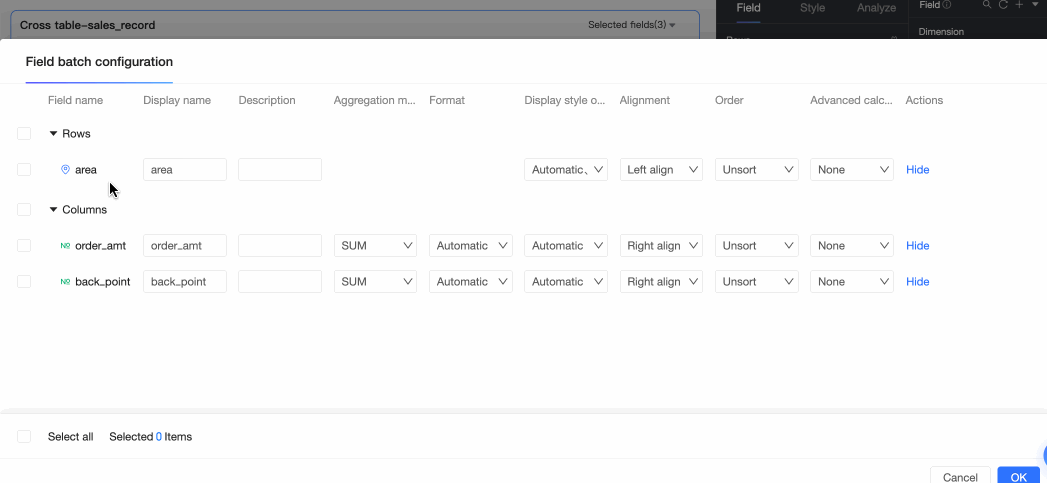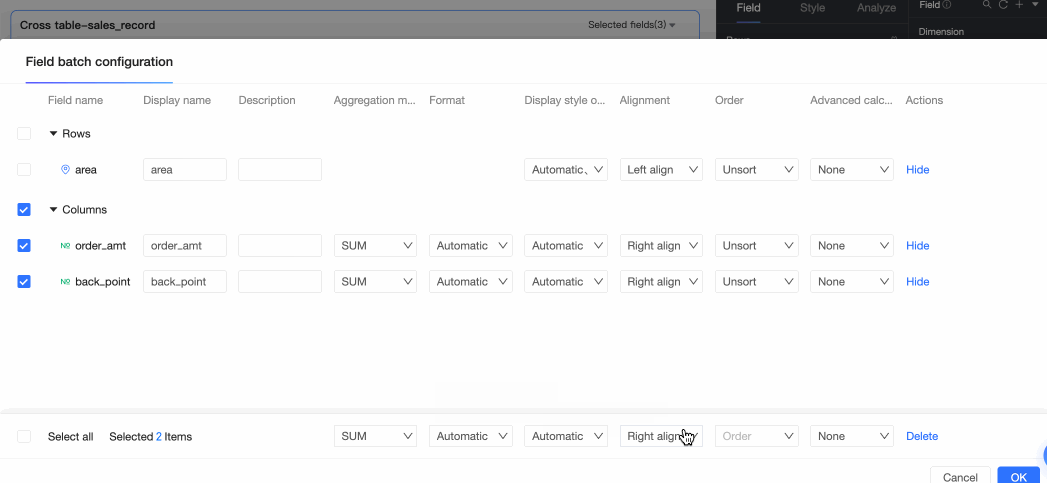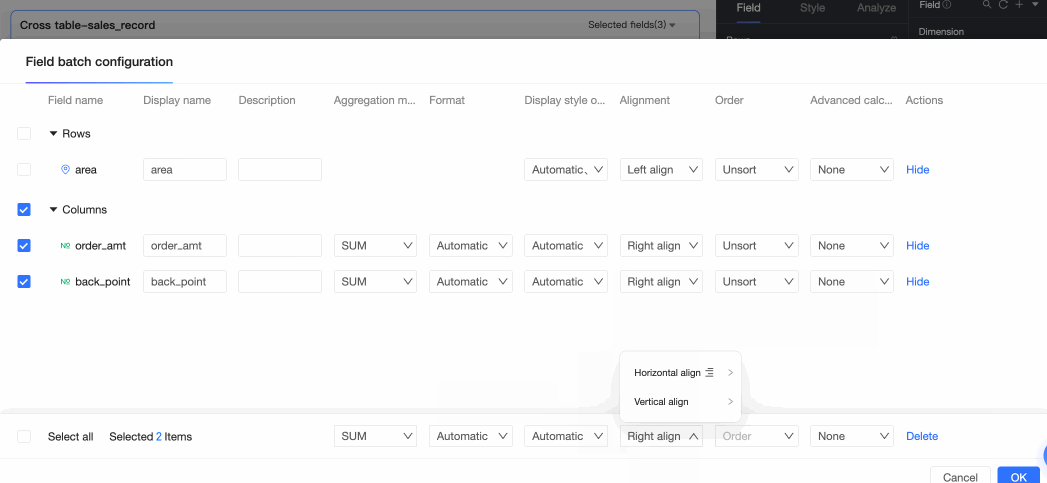
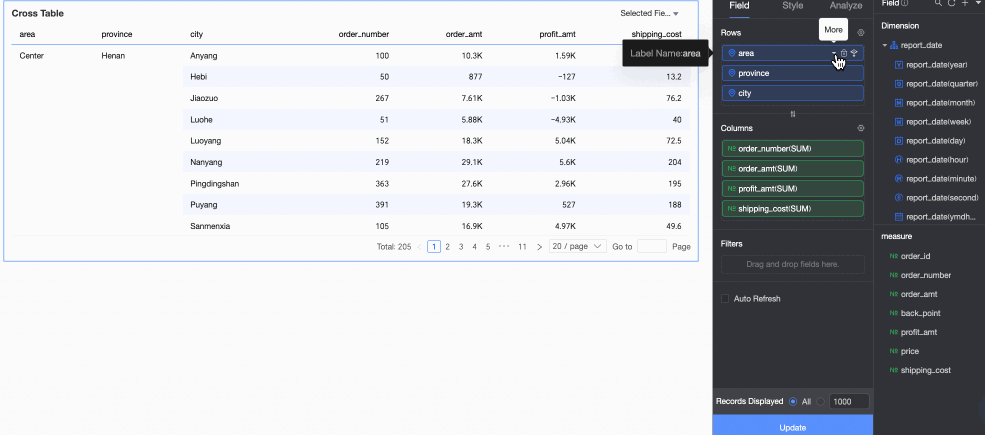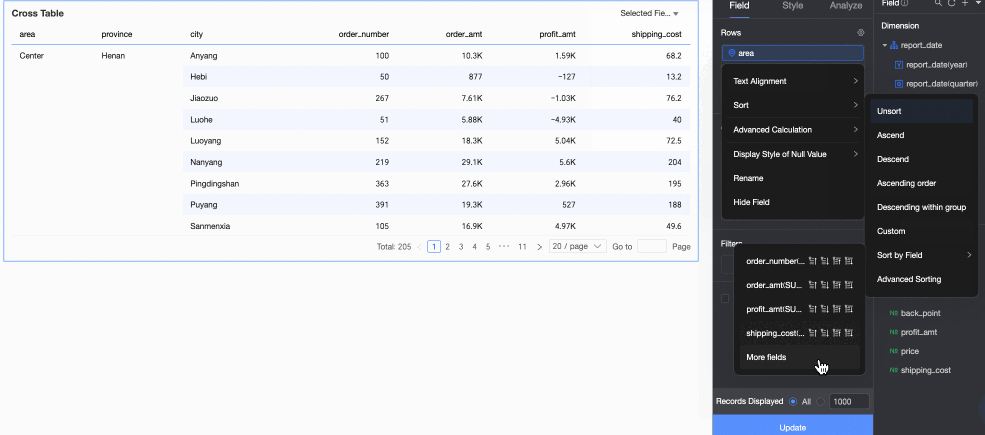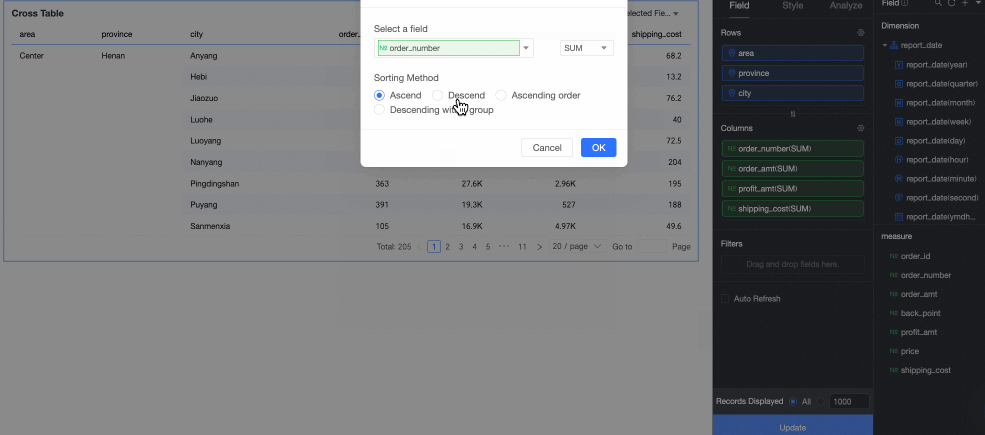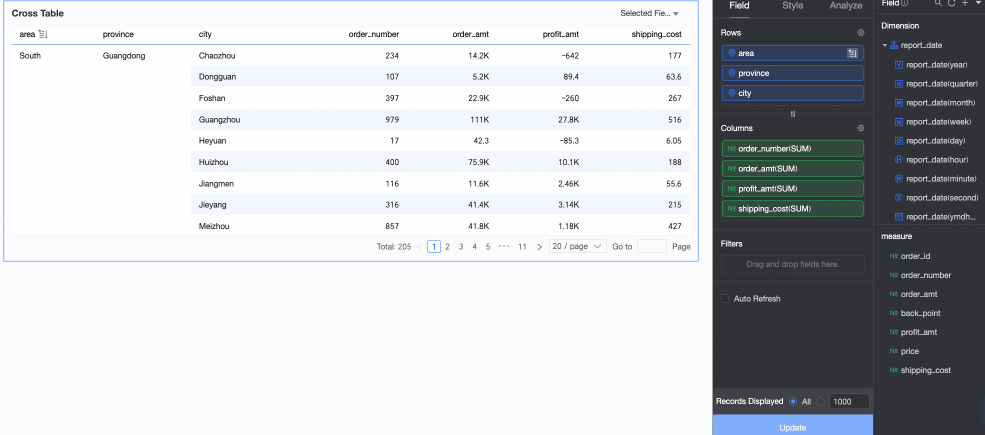
Sorting
You can choose no sorting, ascending, descending, ascending within a group, descending within a group, custom, field sorting, or advanced sorting. For more information, see Sort data.
Field sorting: You can sort row dimension fields by a measure or another dimension.
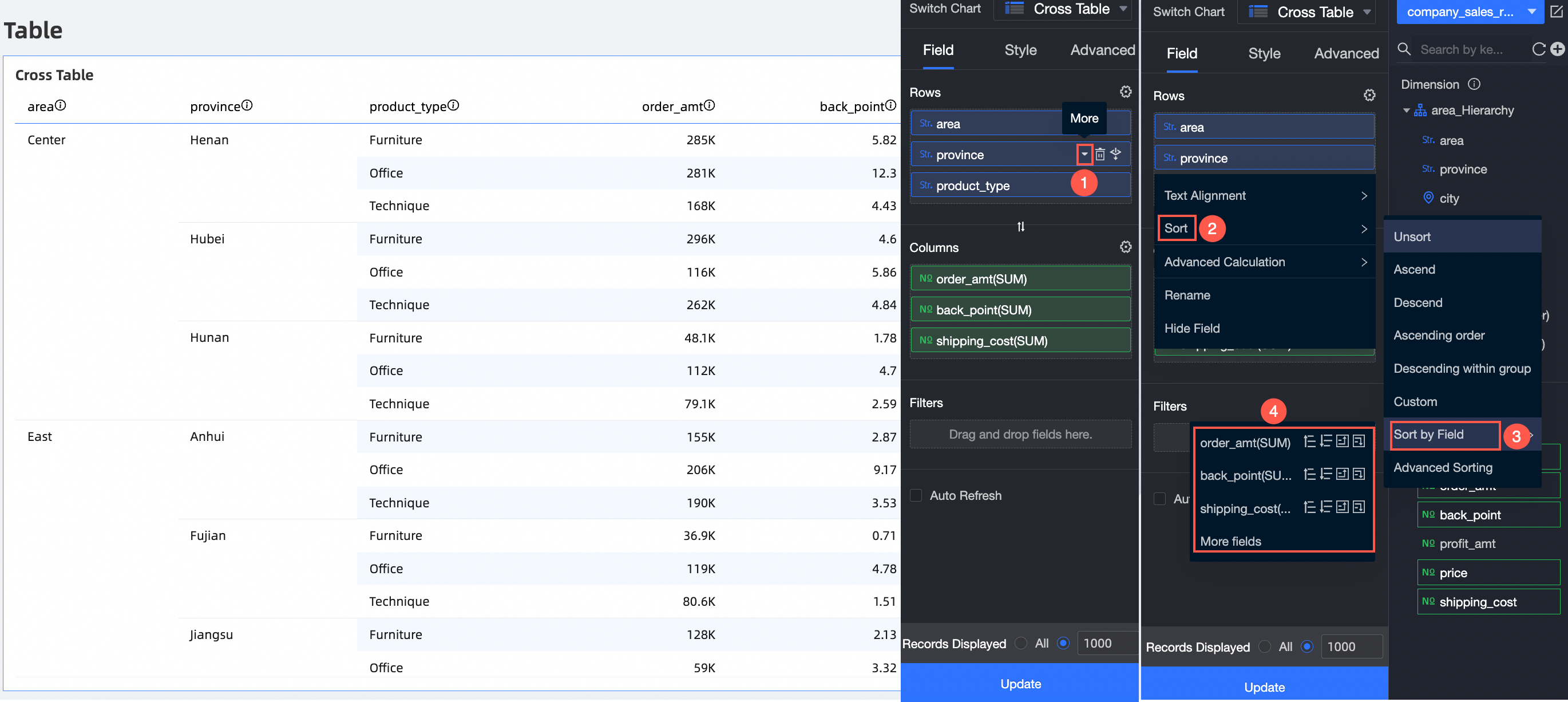
You can sort based on a measure field that has been added to the data panel.
① Select a measure field that has been added.
② Select a sorting method. From left to right, the options are ascending, descending, ascending within a group, and descending within a group.
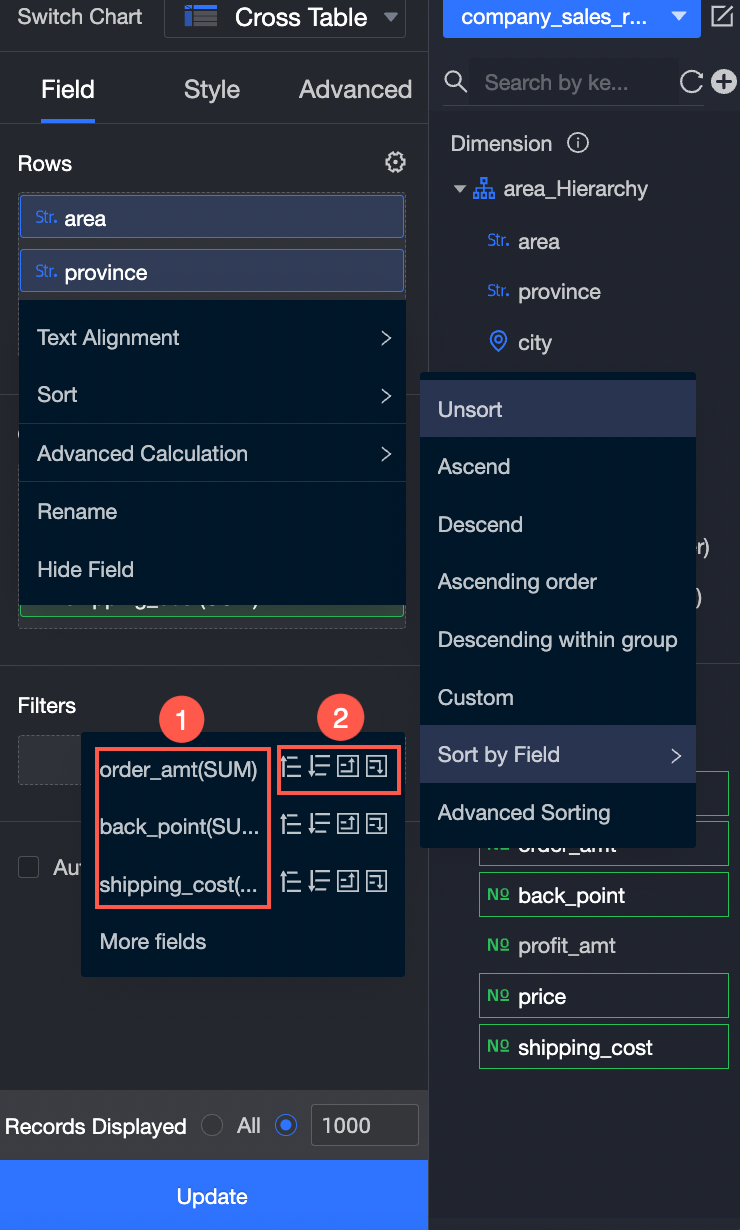
You can sort based on a measure or dimension field in the dataset.
The following figure shows how to sort by profit_amount.
NoteYou can configure field sorting only for dimension fields.
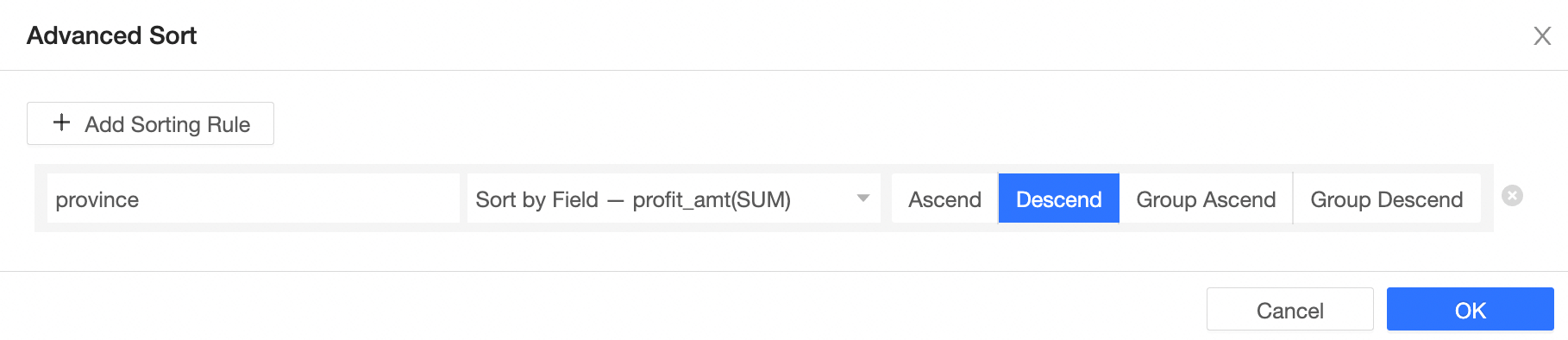
Advanced sorting: Advanced sorting is typically used for aggregate and detail tables.
You can apply advanced sorting to fields in both rows and columns.
Aggregation: Supports sum, average, count, distinct count, maximum, minimum, population standard deviation, sample standard deviation, population variance, sample variance, start time point, and last time point.
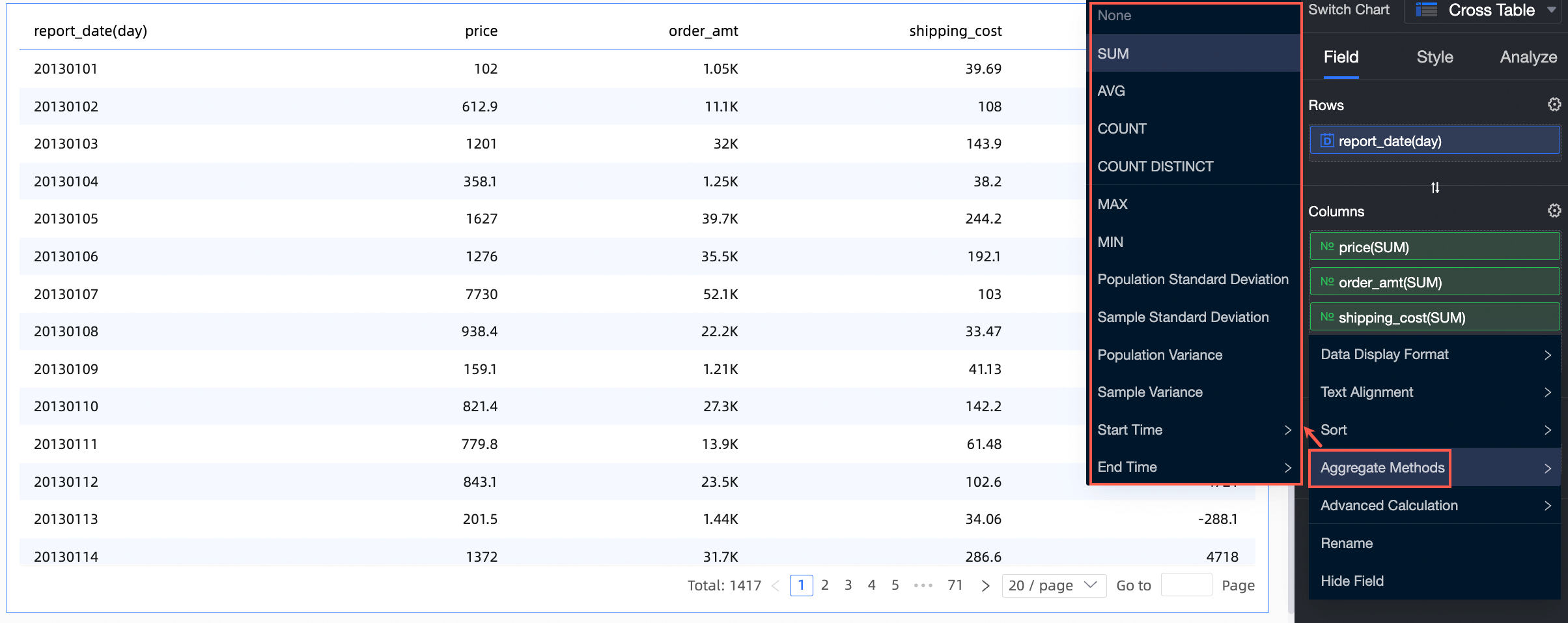
Start time point: You can set the aggregation method for a column field to Start time point and select the corresponding date field. After configuration, the field displays the aggregated data for the start time point in the cross table.
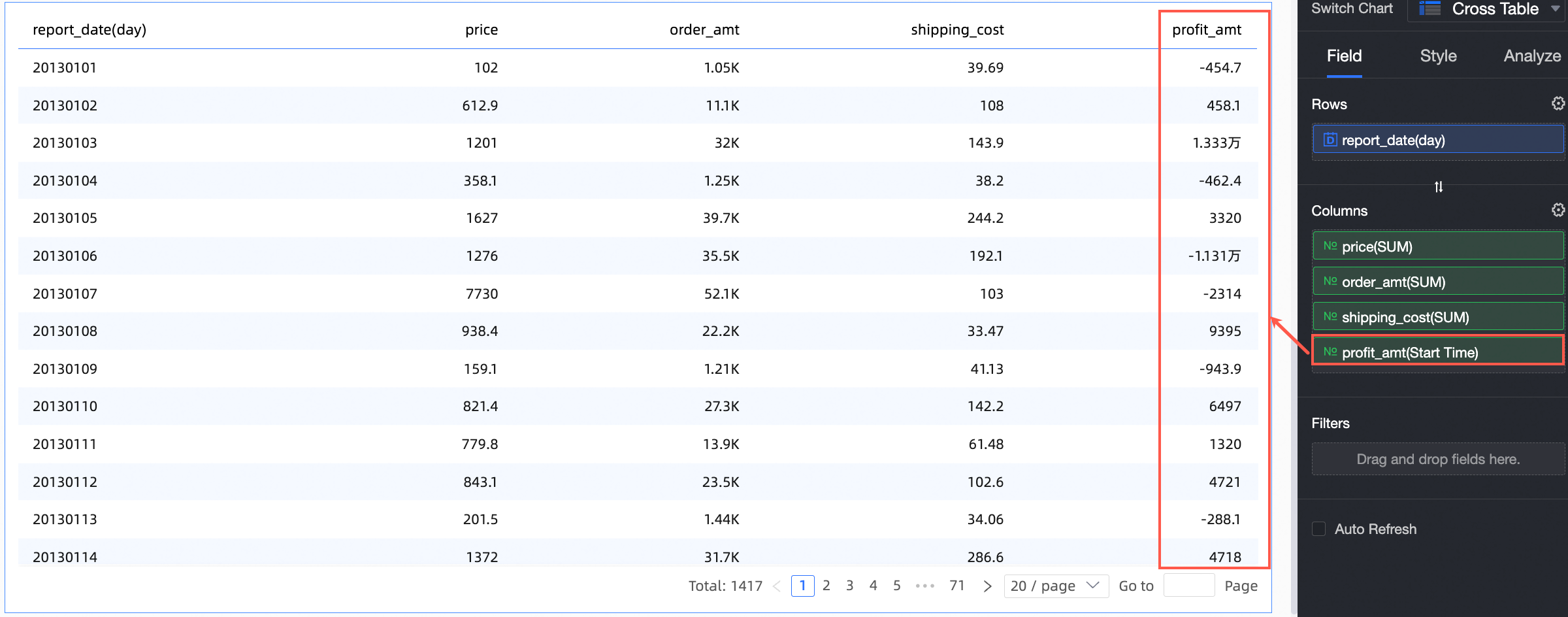
Advanced calculations include cumulative by date, cumulative calculation, percentage, ranking, TopN, percentile, and period-over-period comparison.
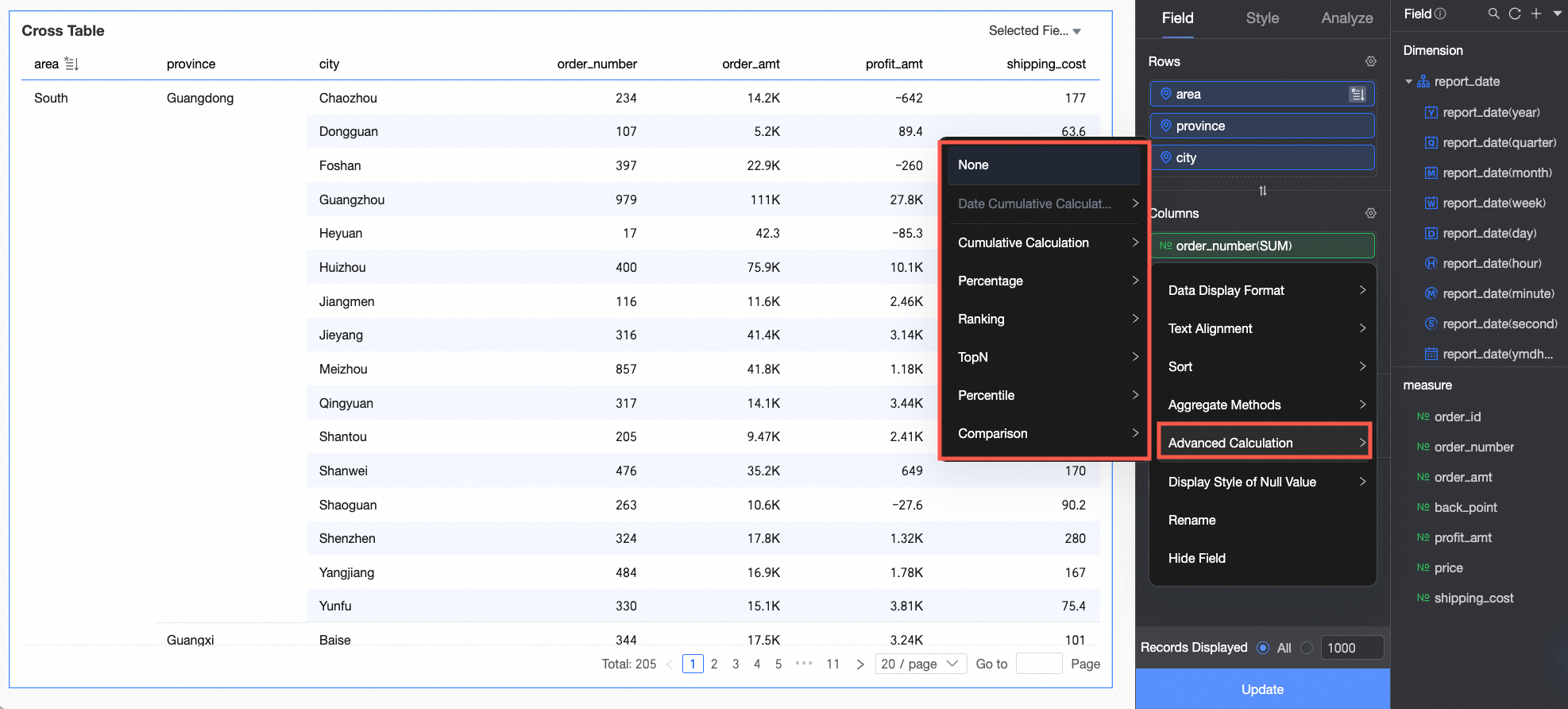
Cumulative by date calculates the sum of data from the initial date to the current date. For more information, see Cumulative by date.
Cumulative calculation progressively accumulates the data results. For more information, see Cumulative calculation.
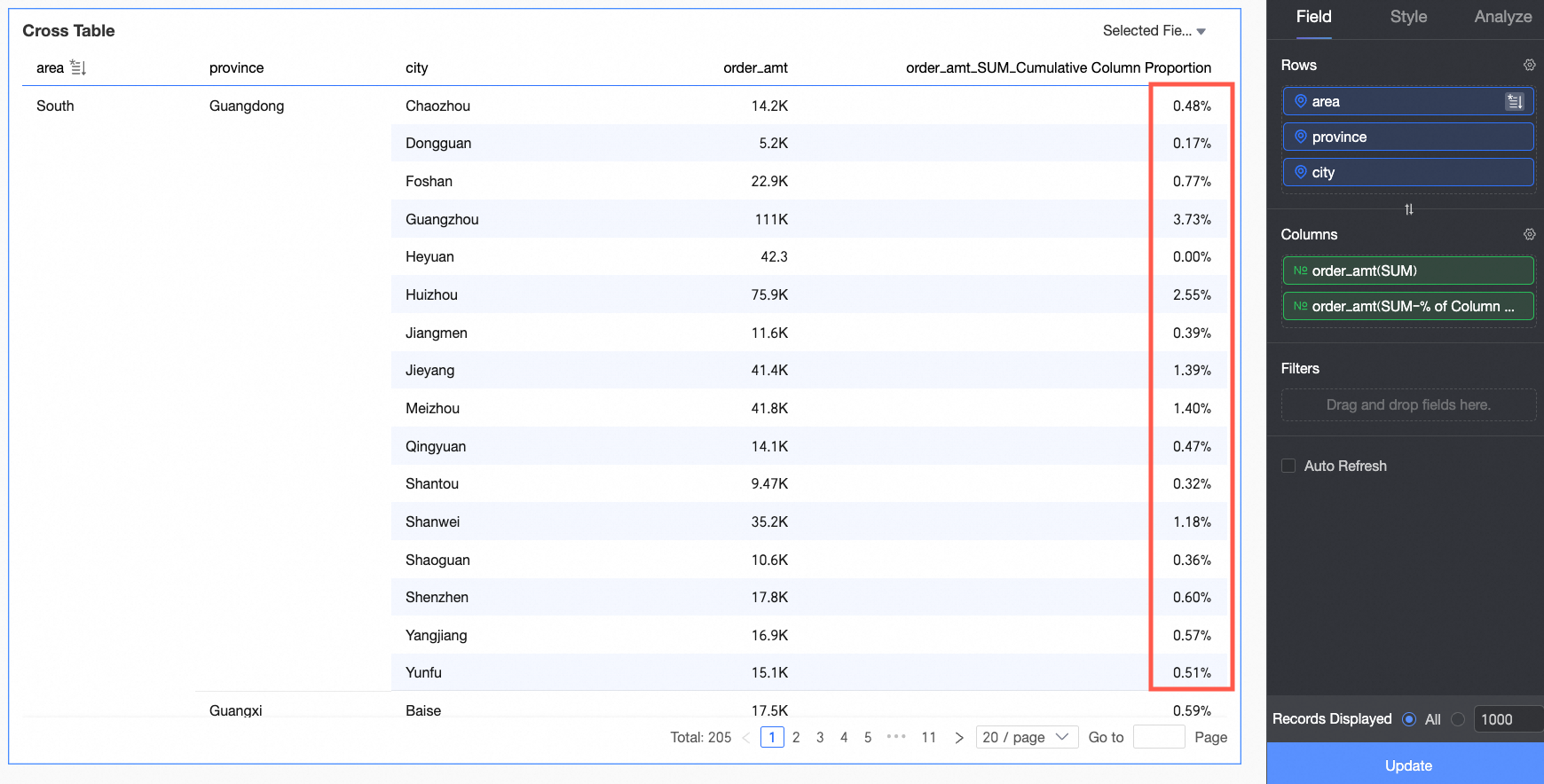
Percentage: You can configure data percentages to view the proportion of each item.
For example, to view the percentage of order amounts for each province, see the result in the following figure:
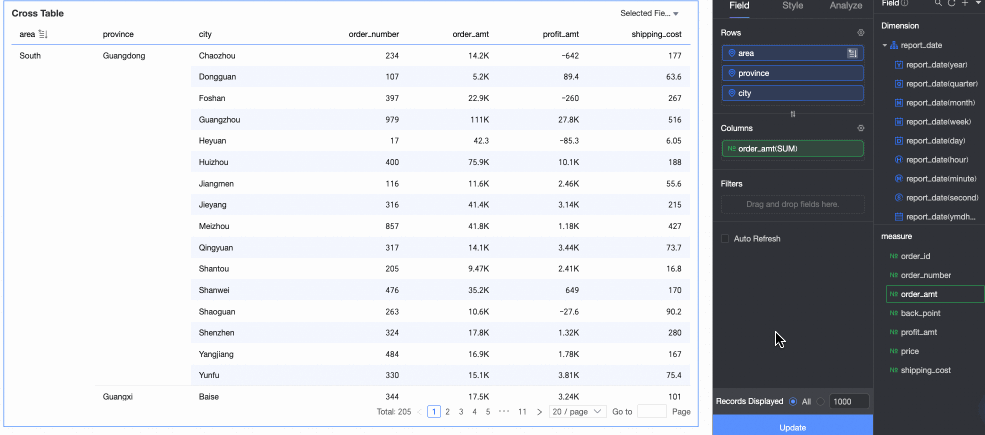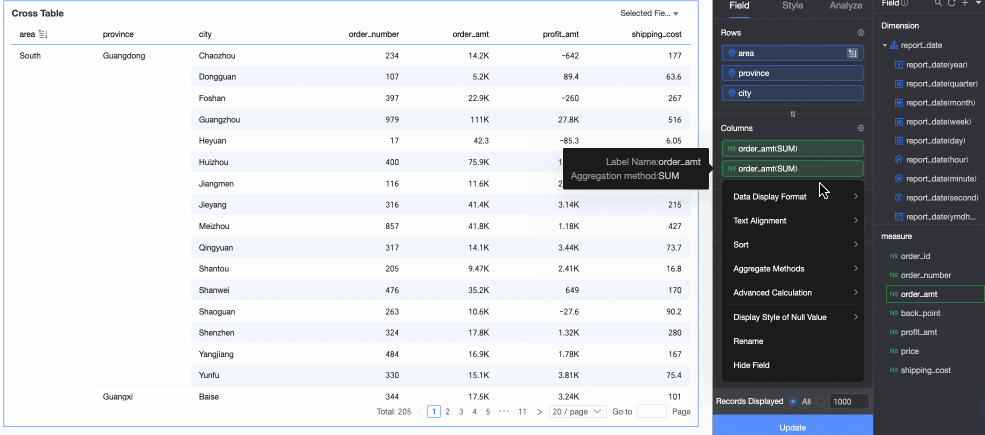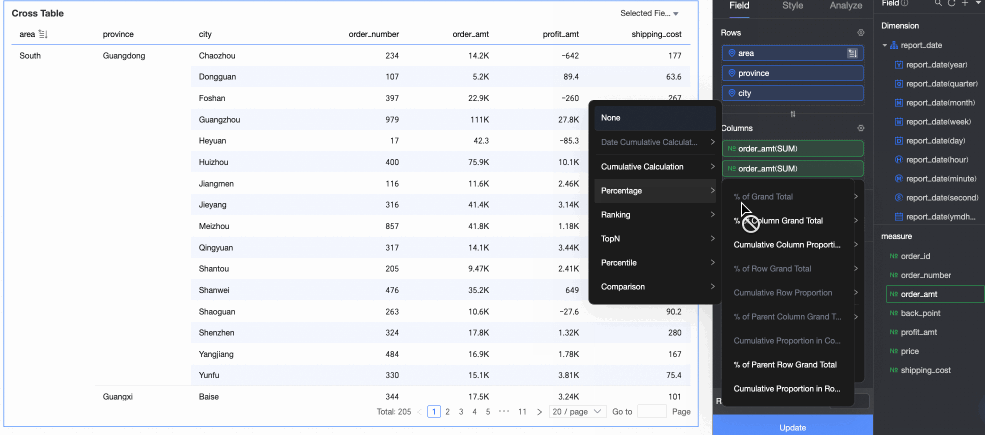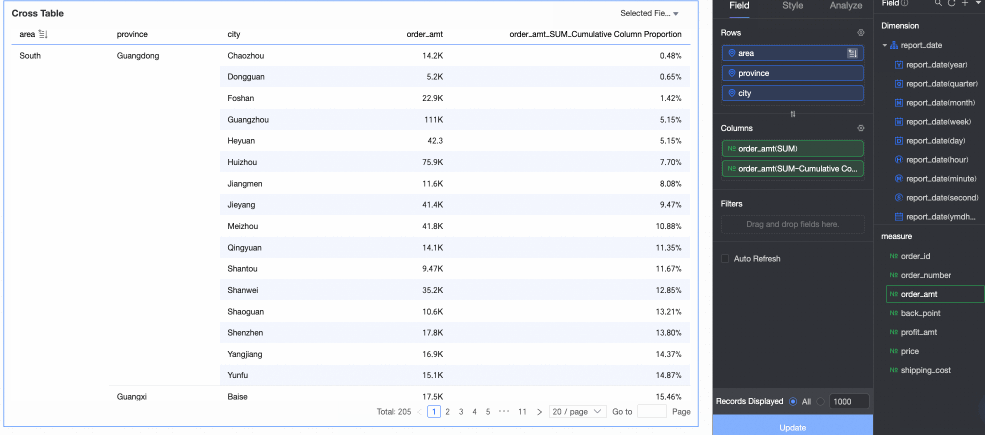
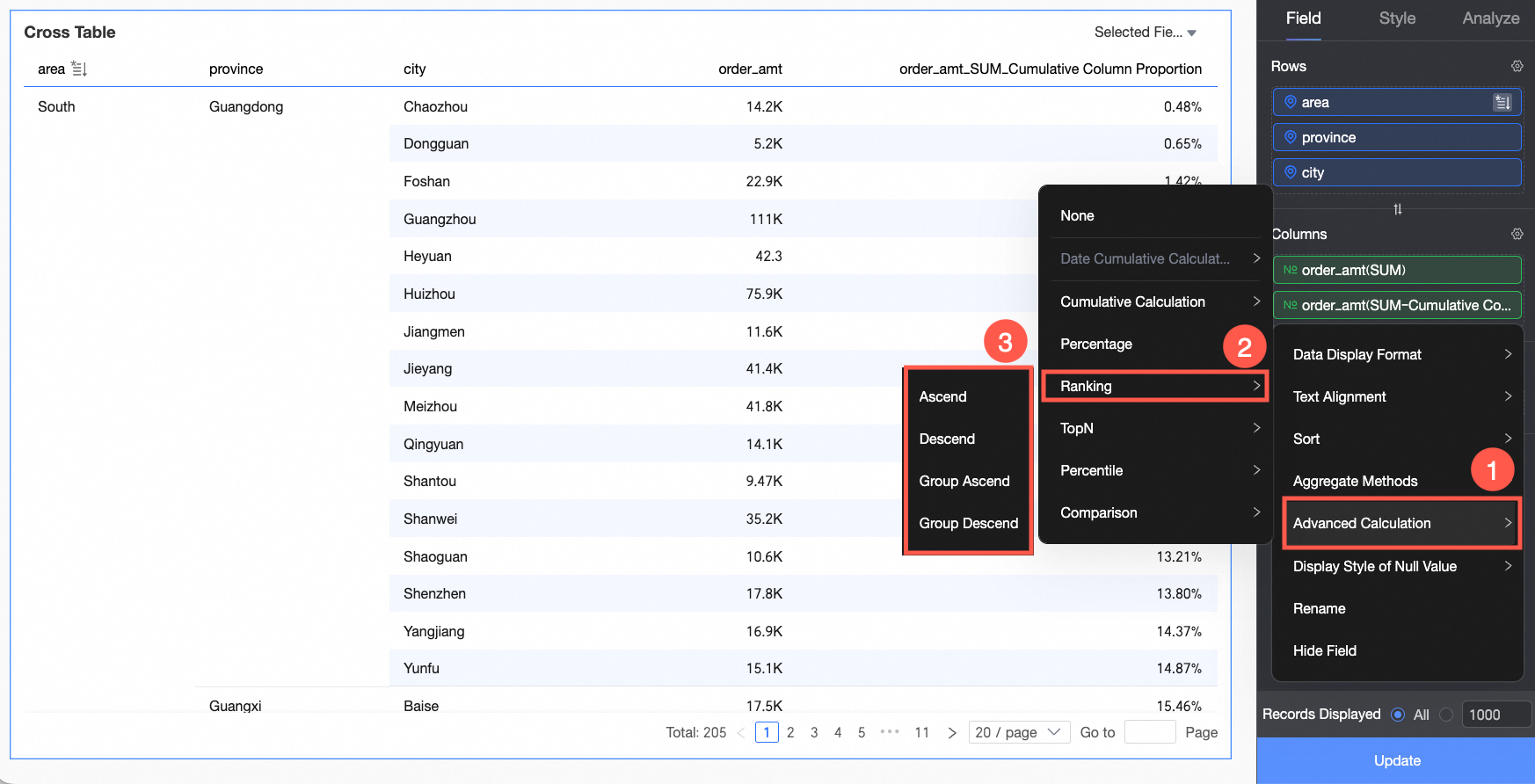
Data ranking: Ranking sorts the numerical values of grouped measures, which makes it easier to compare data sizes.
For more information, see Data ranking.
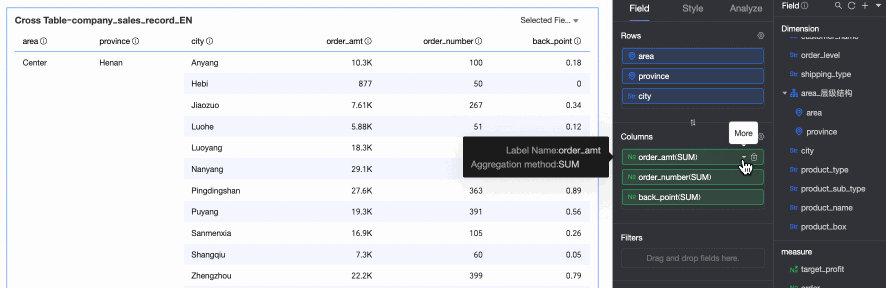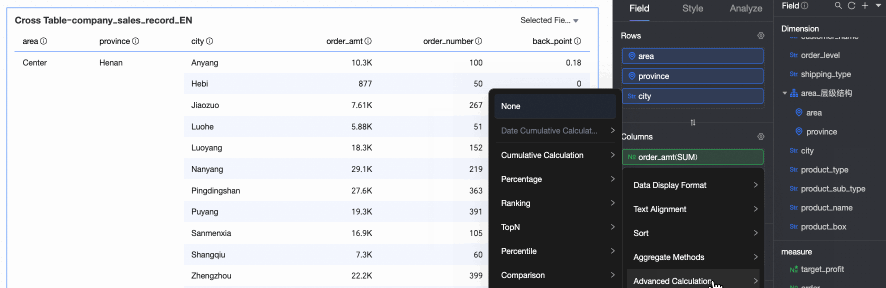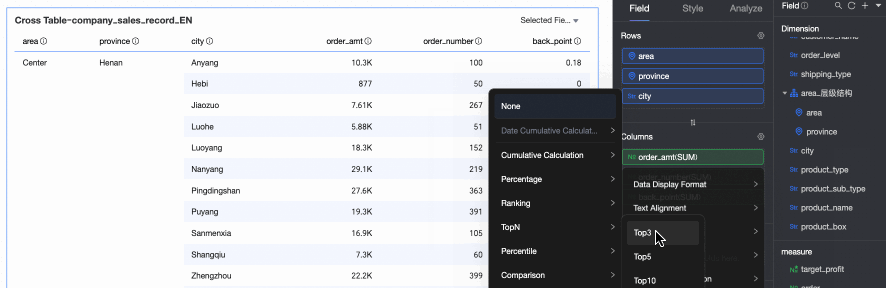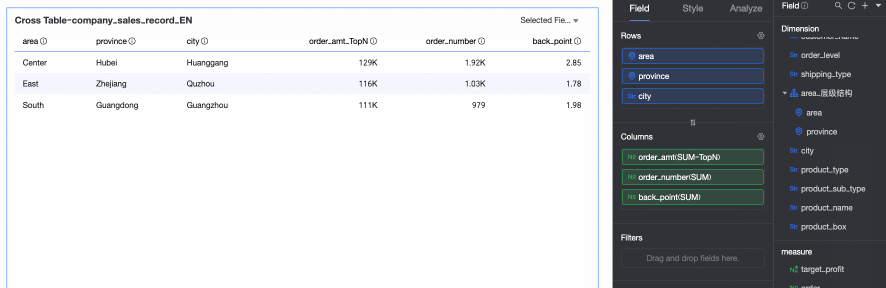
TopN: Retains the top N data entries. For example, if you select Top5, the top 5 data entries are retained. You can also customize the ranking method and the value of N. For more information, see TopN.
Percentile calculation ranks the data results in percentile form, which helps you observe the position of a specific data point within the entire dataset. For more information, see Percentile.
Period-over-period comparison: You can set up period-over-period comparisons for measures. For more information, see Period-over-period comparison.
NoteWhen you create a calculated field in a dataset, if the field needs to be based on the result of an advanced calculation (such as a percentage), you cannot directly reference the advanced calculation field. You must first obtain the required result using a custom SQL query and then create a new field in the dataset to reference this result.
Configure Chart Styles
This section describes the style settings for the chart. For information about common style settings, see Configure the chart title area.
You can enter keywords in the search box at the top of the configuration area to quickly find configuration items. You can also click the ![]() icon on the right to Expand/Collapse all categories.
icon on the right to Expand/Collapse all categories.
In the Basic Table Styles section, you can set the style of the cross table.
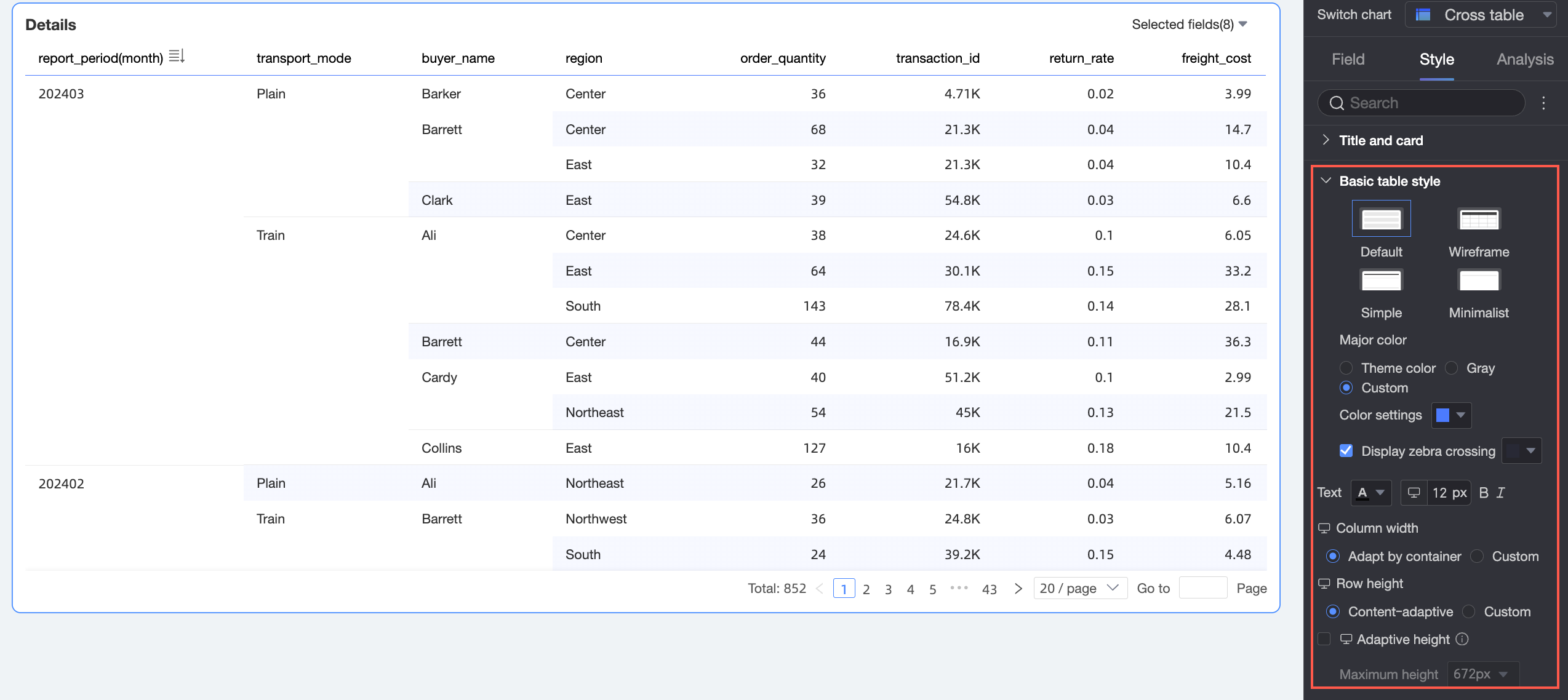
Chart configuration item
Description
Custom table theme
Set the appearance style of the cross table.
Theme style: You can select Default, Wireframe, Simple, or Minimalist.
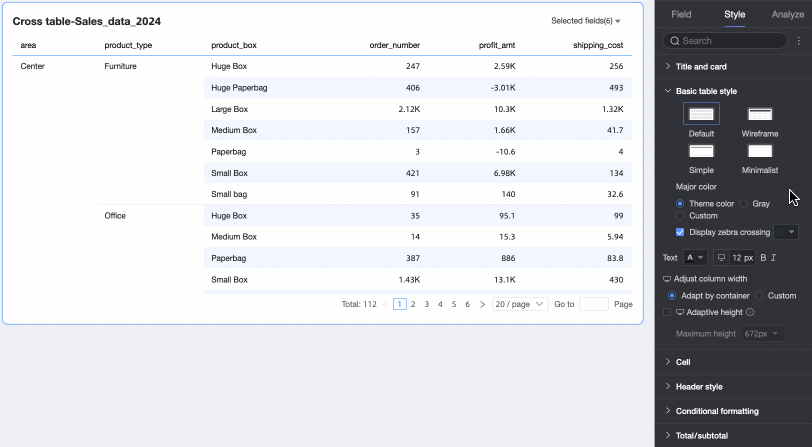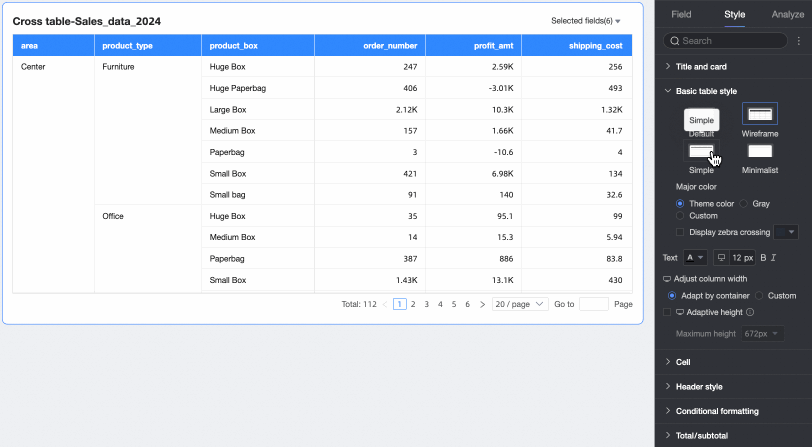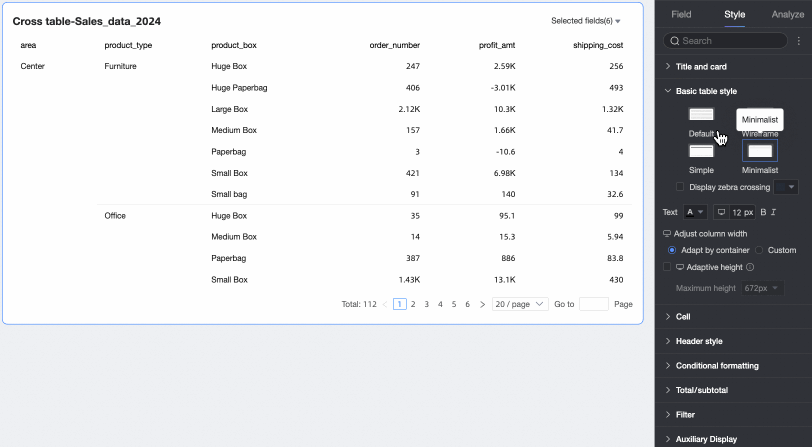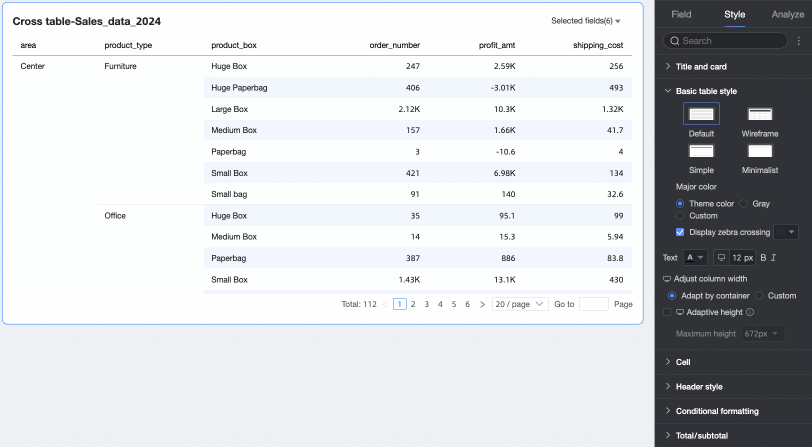
Primary color scheme: When the table's theme style is Default, Wireframe, or Simple, you can select the primary color scheme for the cross table. You can choose to follow the Theme Color, Gray, or Custom.

Show zebra stripes: Choose whether to display zebra stripes in the cross table and select their color.
Text
Set the text style for the cross table.
Column width, Row height
Set the Column width and Row height of the cross table. You can choose between Automatic and Custom.
Automatic: The system automatically allocates column width based on the available space in the chart container. It also automatically allocates row height based on the actual text content in the chart cells to ensure reasonable use of space and complete display of all text. This method is suitable for scenarios where the table needs to adapt flexibly to different displays and achieve automatic layout.
Custom: Enter custom values for column width and row height to configure the table layout as needed. This method is suitable for scenarios with high precision requirements for table layout. After selecting custom mode, row height and column width default to automatic. Deselect automatic to configure specific pixel values.
If you are unsure of the specific row height value to set and want to visually adjust it first, you can manually drag the table's row height to preview and quickly confirm the best display effect.
You can drag the header row height and the data area row height separately. After dragging, the row height in that area will be uniformly adjusted, and the specific row height value will be automatically filled into the corresponding setting box.
NoteThe column width and row height settings for PC and mobile are independent. You can set them separately as needed.
Dynamic table height adaptation, Maximum height
Table height settings support two policies: "Fixed height" and "Adaptive height".
Fixed height: The table height defaults to the "Fixed height" policy. You can manually set the table container height by dragging.
Adaptive height: Enable dynamic table height adaptation, and the table container height will automatically adjust based on the data content. You can also set the maximum table height, which is the total height of the header and data rows. After setting the maximum height, the table's height will not exceed the set value during dynamic adaptation.
The selectable maximum heights include the following: 192px (about 5 rows), 352px (about 10 rows), 672px (about 20 rows), 1632px (about 50 rows), and Custom.
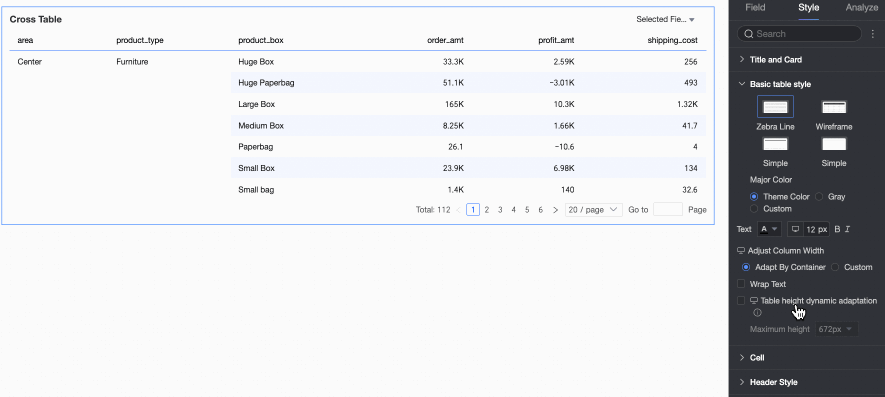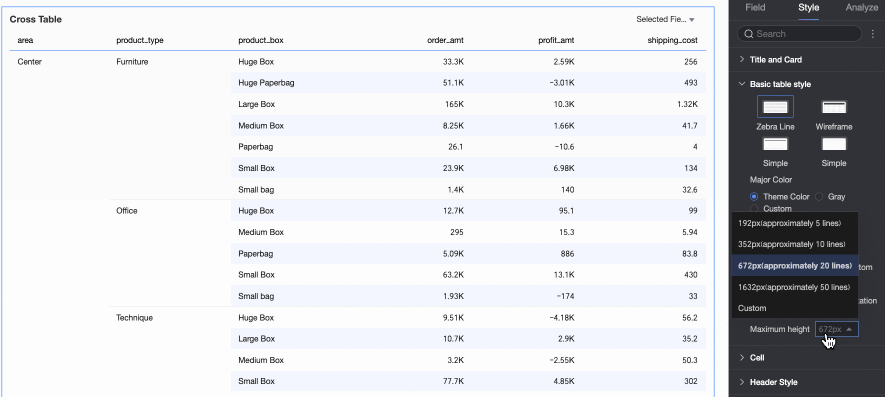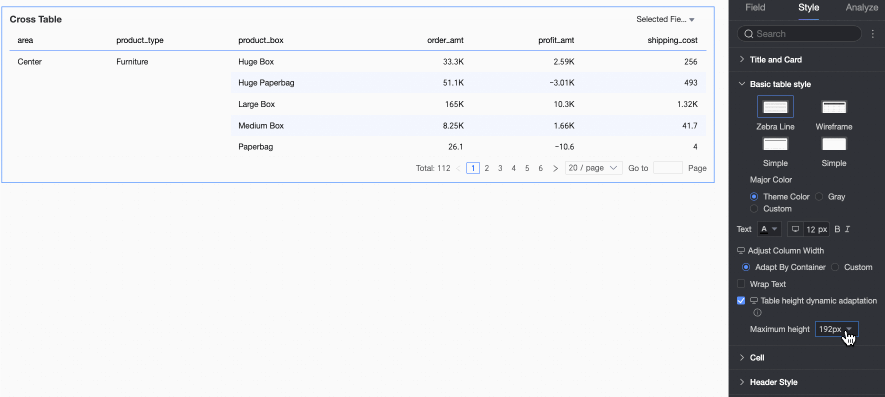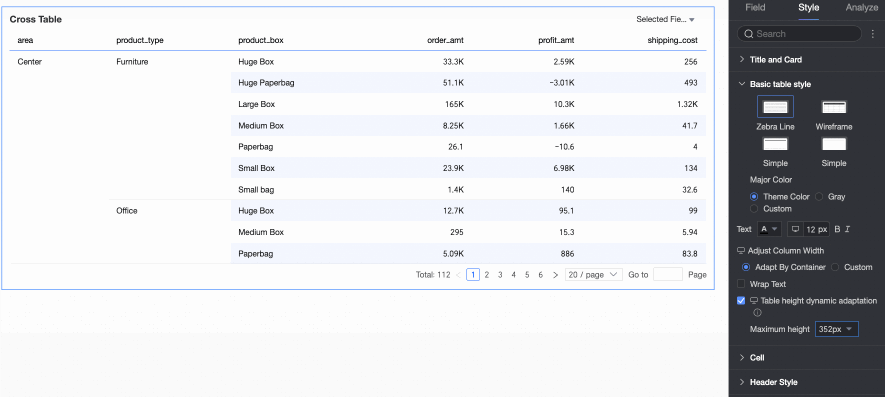
NoteWhen row height is set to Custom mode, Dynamic table height adaptation will only support custom. Set the maximum table height according to the desired effect.
You can switch the
 icon at the top of the page to configure height adaptation settings for PC and mobile separately.
icon at the top of the page to configure height adaptation settings for PC and mobile separately.Dynamic table height adaptation is enabled by default on mobile. You can only adjust the maximum table height value.
This feature may affect the overall layout of the report. Enable it based on your actual needs.
In the Cell section, you can configure the cell display, sorting, and other settings.

Chart configuration item
Configuration Item Description
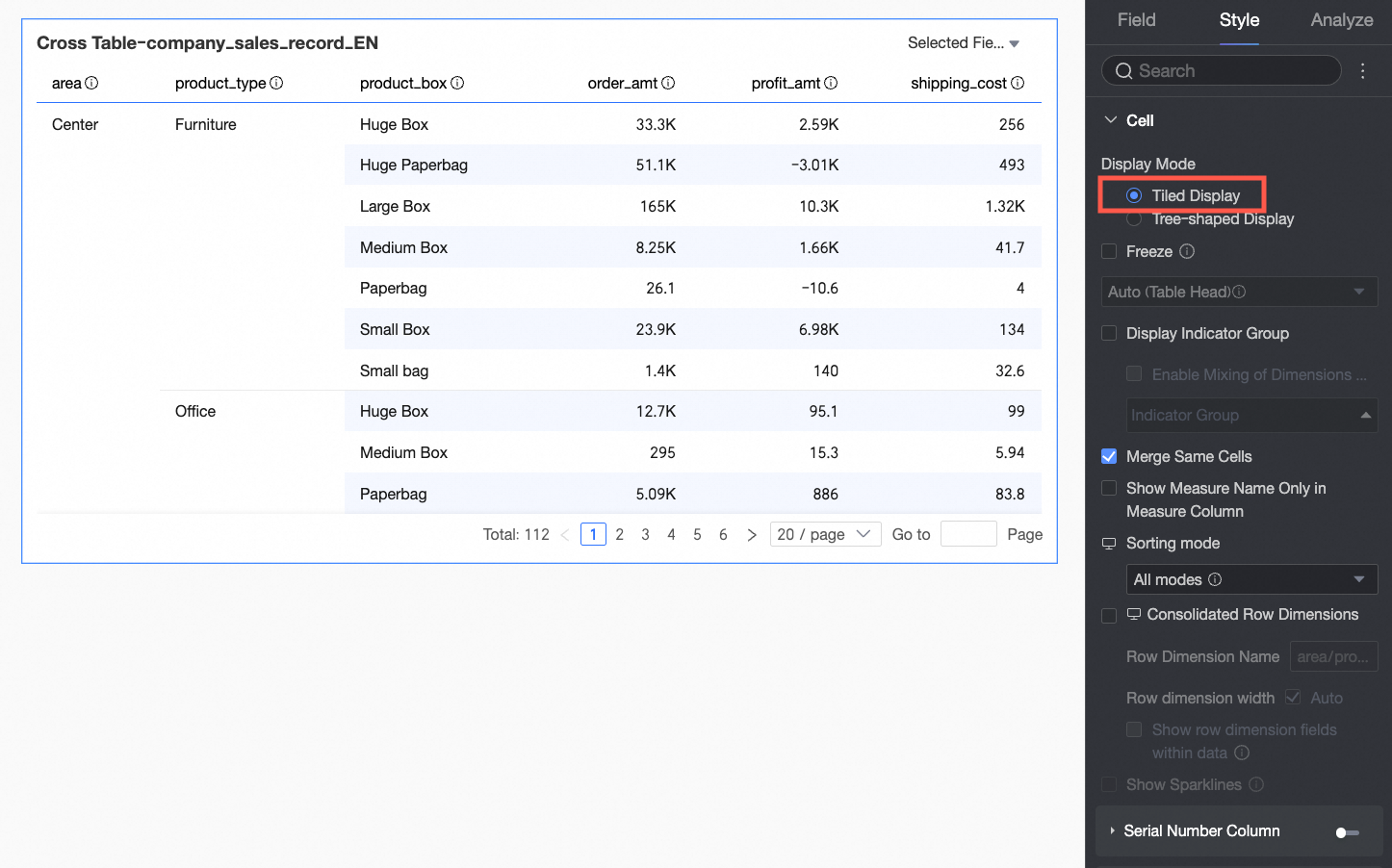
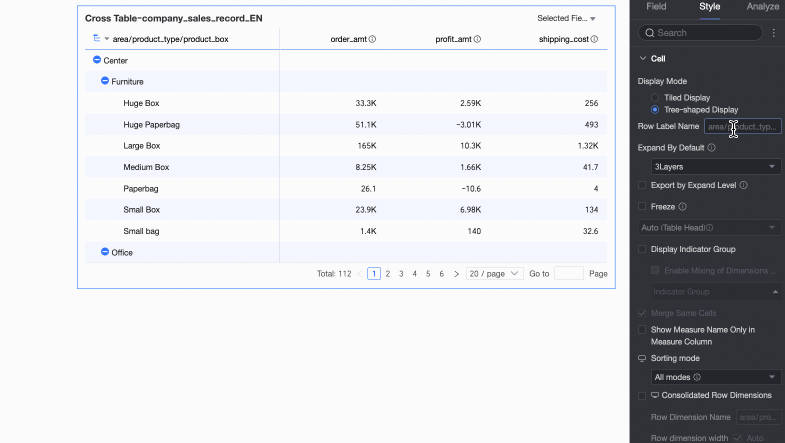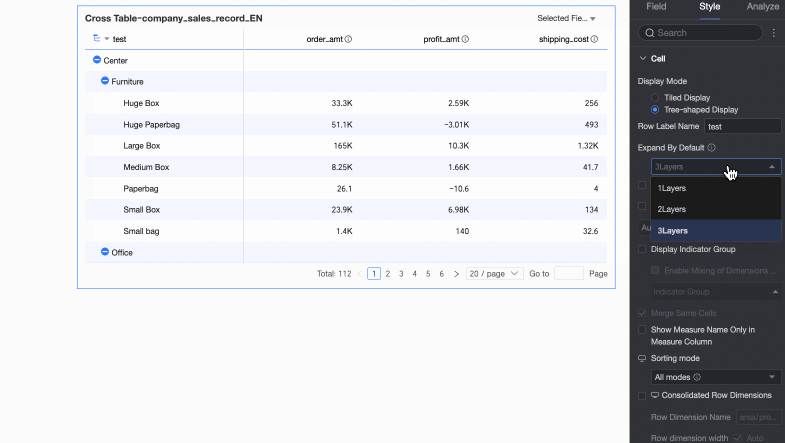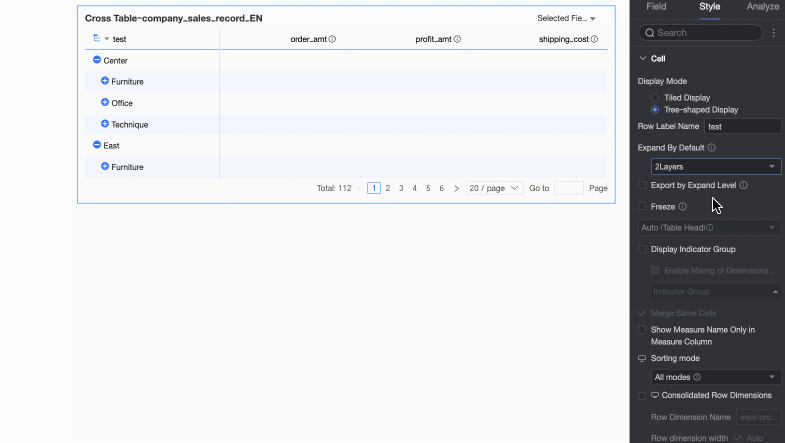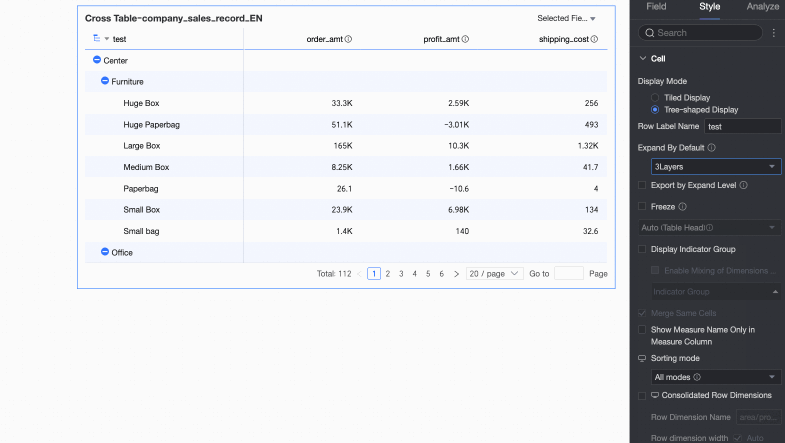
Display Mode
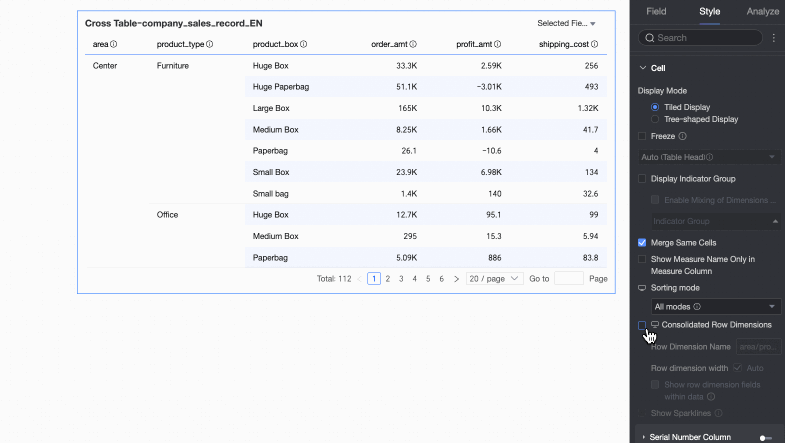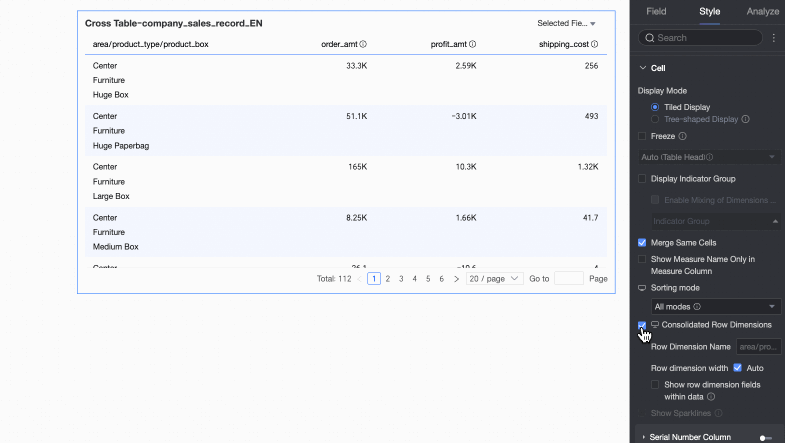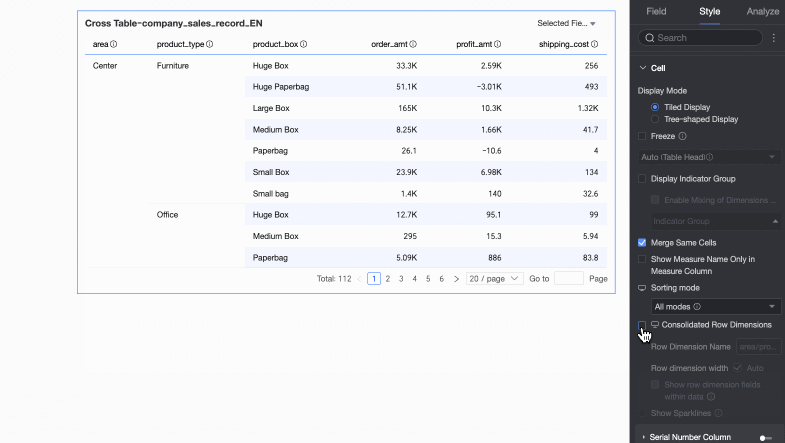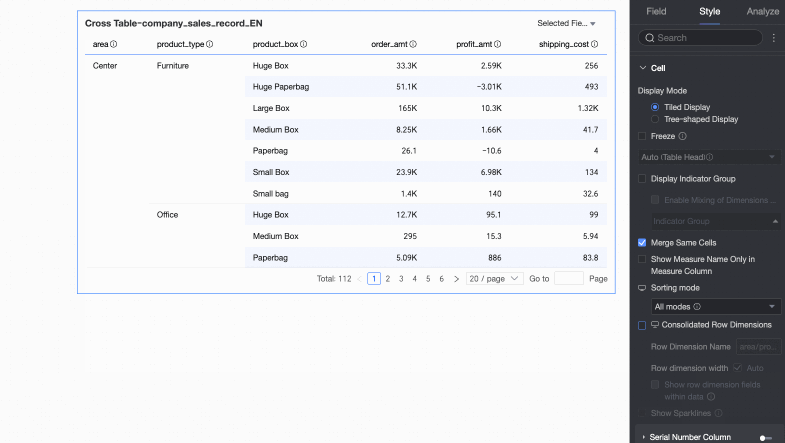
Supports Tiled Display and Tree-like Display modes.
If you select Tiled Display, the cross table is presented in a flat, two-dimensional format.
If you select Tree-like Display, dimension fields can be displayed in a hierarchical tree structure.
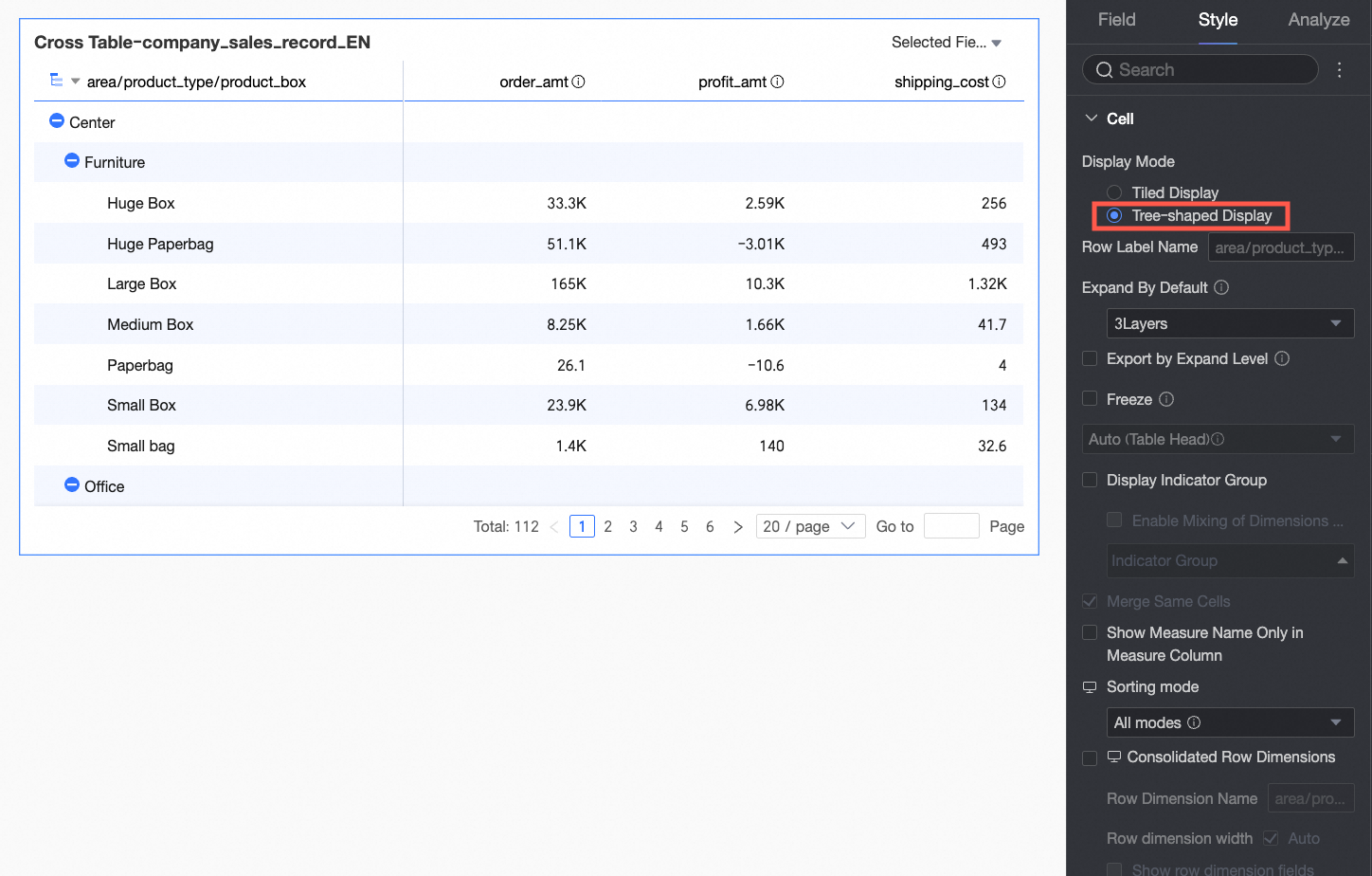
You can customize the Row label name and the Display level.
Export by expanded level
If you select this option, exporting with format will export to Excel based on the current tree expansion state on the page.
For example, if the expansion level is set to 3, the data exported to the local file will be within 3 levels.
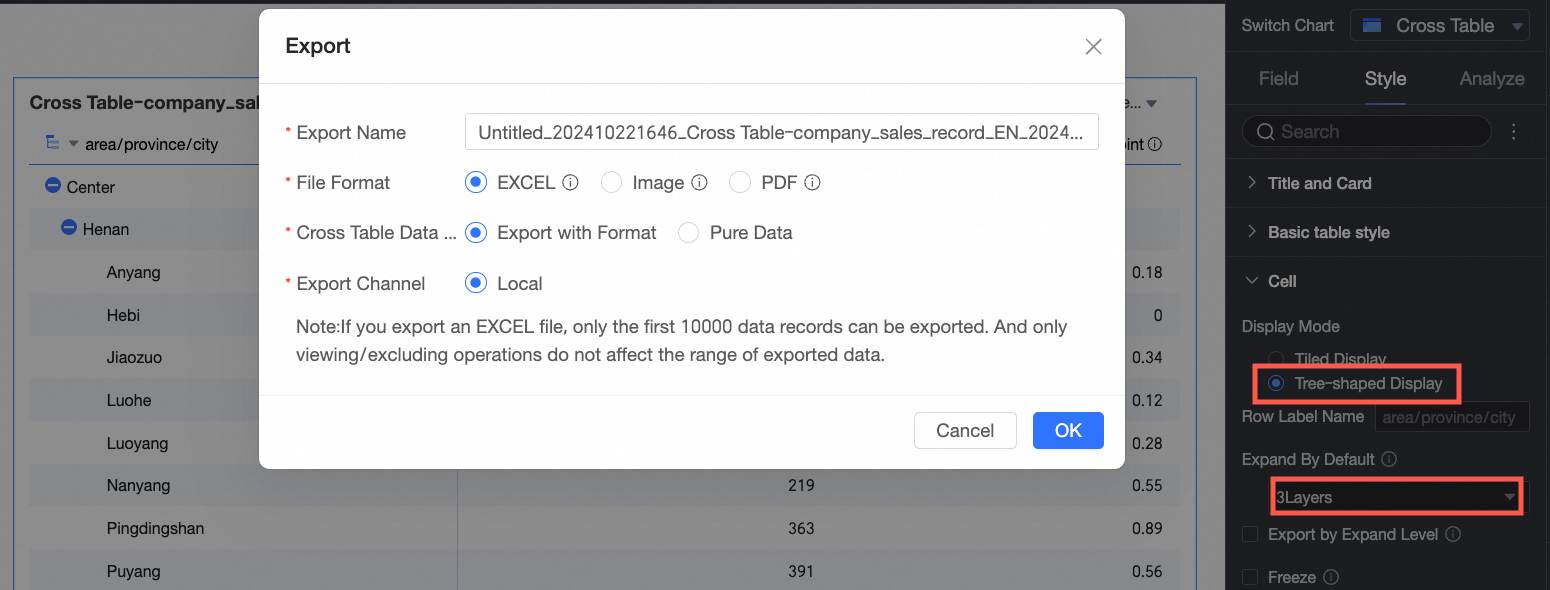 Note
NoteIf Paging is set for the cross table, only the current page can be exported. To resolve this, you can turn off paging or increase the number of rows displayed per page.
If the exported cross table does not have Subtotals set, the parent level will not display data.
Freeze
Set whether to freeze the Header or Columns.
NoteWhen setting to freeze Columns, ensure the frozen column width is less than 60% of the total table width.
Metric display grouping
Supports setting Metric display grouping. After you enable Dimension/Measure mixed layout, dimension fields can also be grouped. You can also set field descriptions for groups.
Merge cells with the same value
You can choose whether to merge cells with the same value.
Auto wrap
If you select this option, the table content supports automatic line breaks.
NoteThe cross table recognizes line feed characters in fields. You can also use line feed characters to customize the line break effect.
Image field display mode
When an image field is in the chart, you can set its display mode. Options include Scale to fit while maintaining aspect ratio, Crop to fit area while maintaining aspect ratio, and Stretch to fit area.
NoteYou can use the Image Field only when the dataset contains an image field and the field type is an image type (
 ).
). Display metric name for single-metric columns
In a mixed dimension-measure column layout, you can set whether to display the name of a single measure.
Sorting Mode
PC:
Sets the Sorting Mode for the cross table.
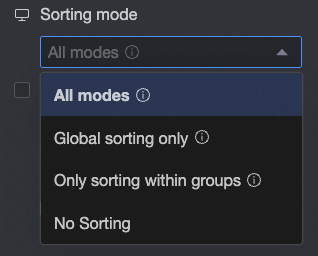
All methods: Displays all sorting methods in a dropdown list. The list shows the current sorting method, and you can manually switch to other methods.
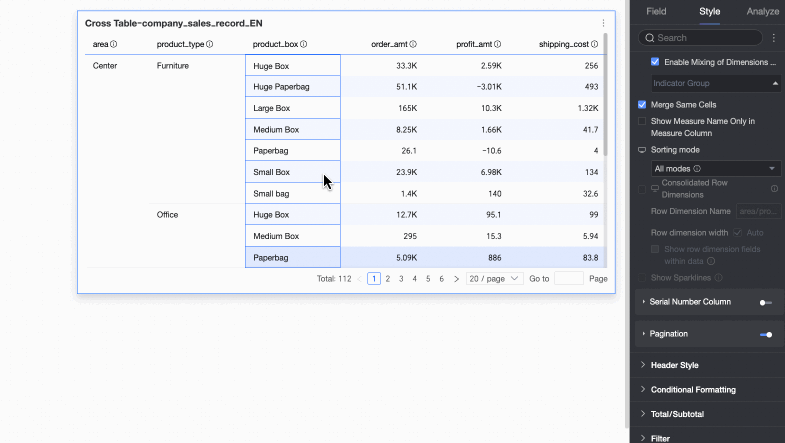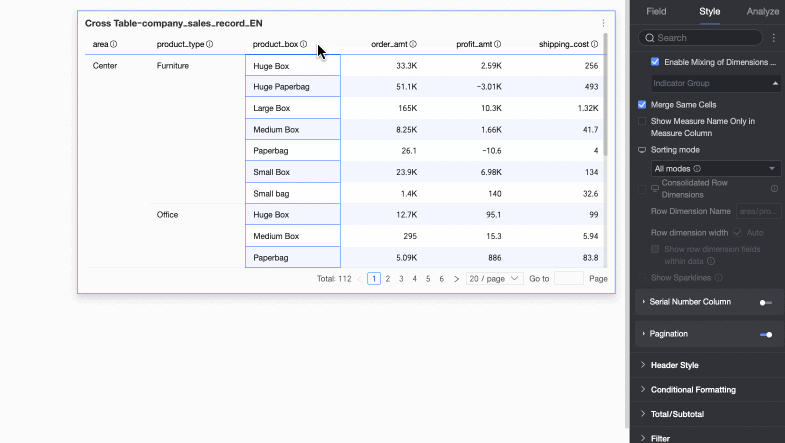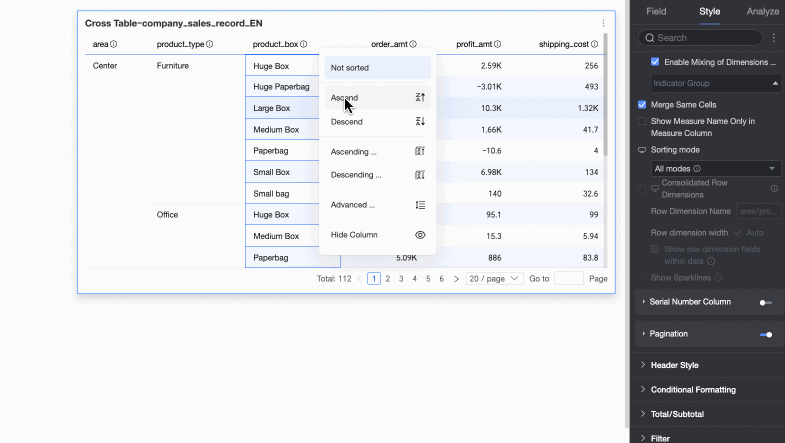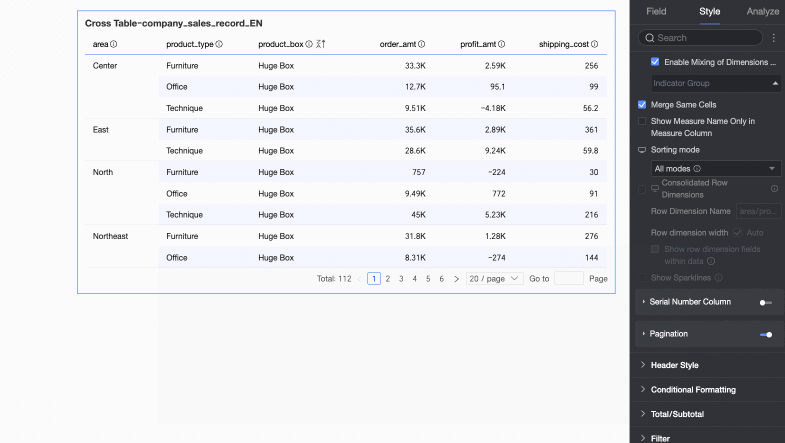
Global sorting only: If only global sorting is required, you can set this option to reduce unnecessary steps. Report viewers can then click the up and down arrows
 to perform global ascending, global descending, and no sorting operations.
to perform global ascending, global descending, and no sorting operations.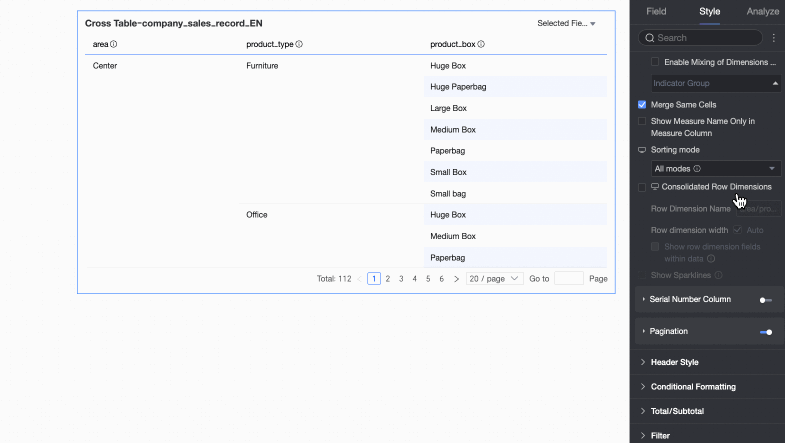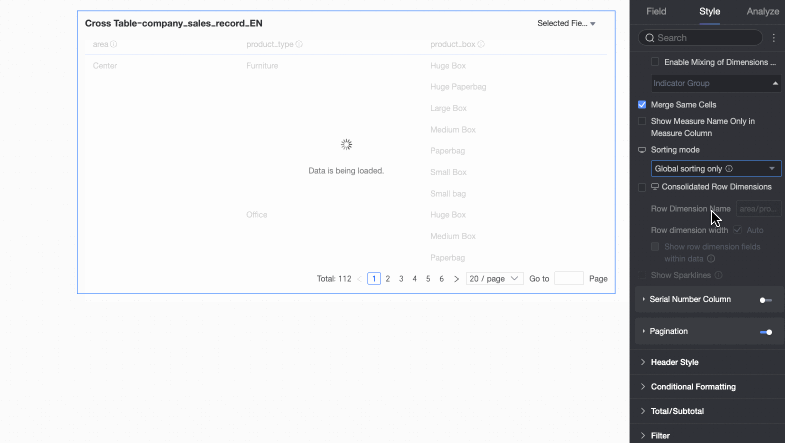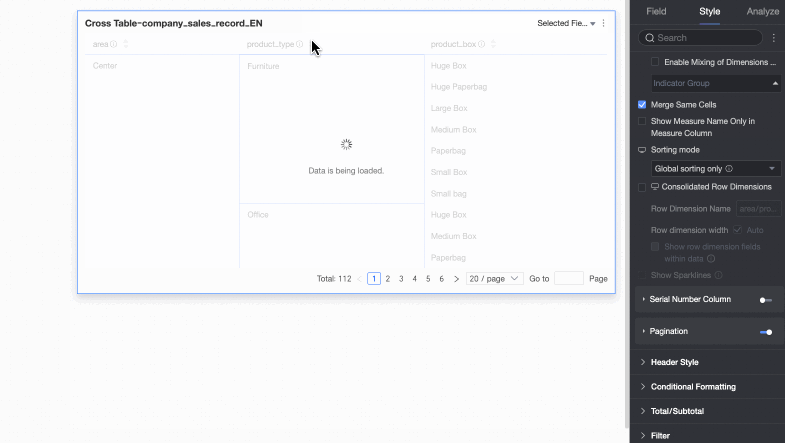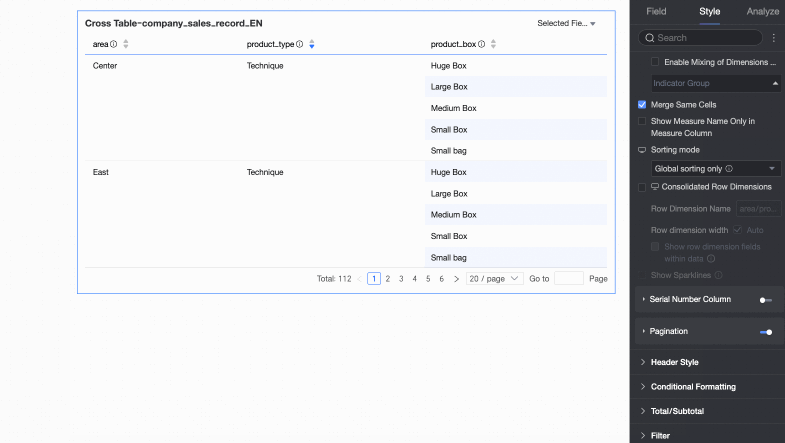
In-group sorting only: If only in-group sorting is required, you can set this option. Report viewers can then click the up and down arrows
 to perform in-group ascending, in-group descending, and no sorting operations.
to perform in-group ascending, in-group descending, and no sorting operations.
No sorting: If you select this mode, no sorting is performed.
Mobile:
Supports All methods, Global sorting only, In-group sorting only, and No sorting. The sorting logic is the same as on a PC.
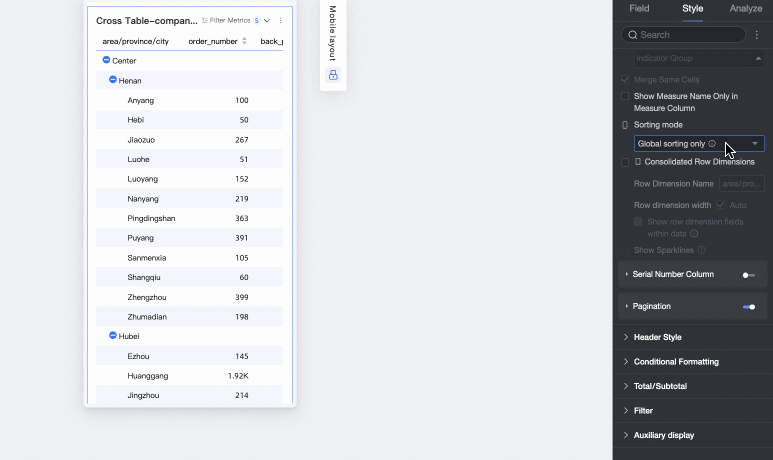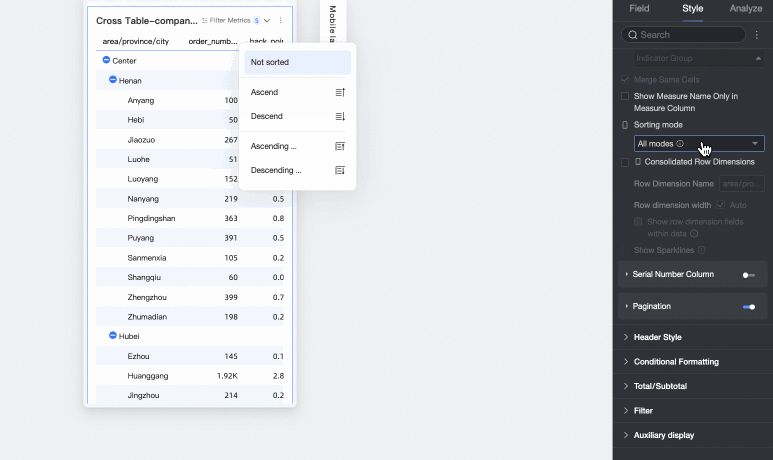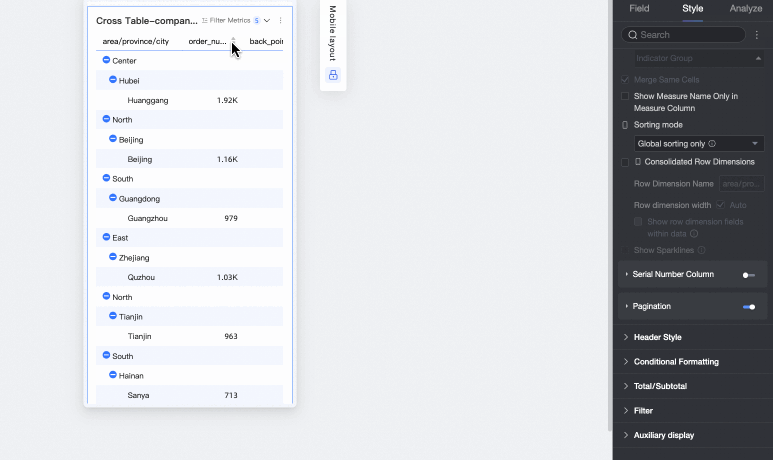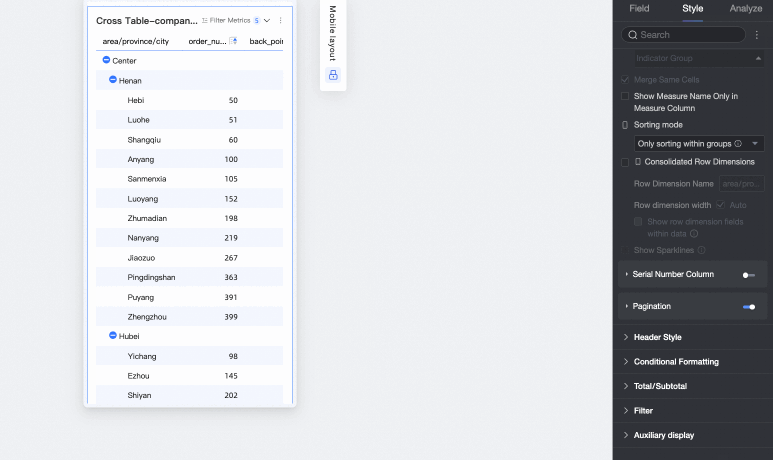
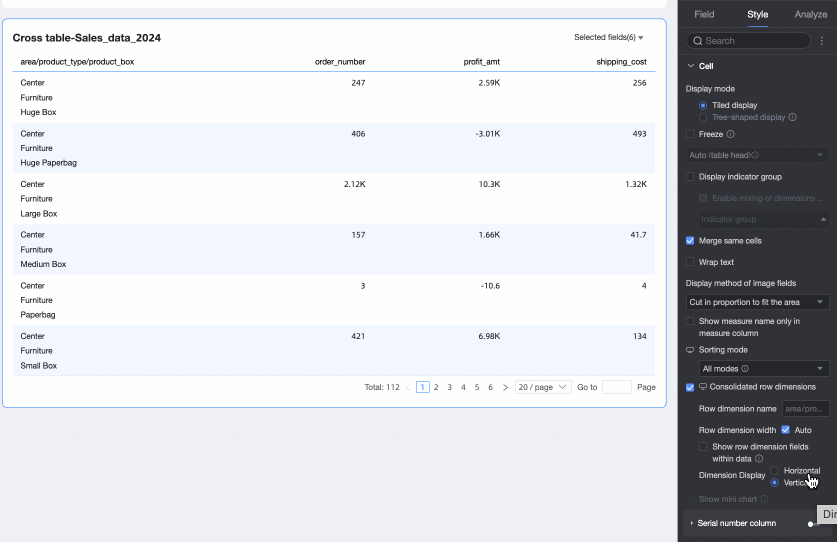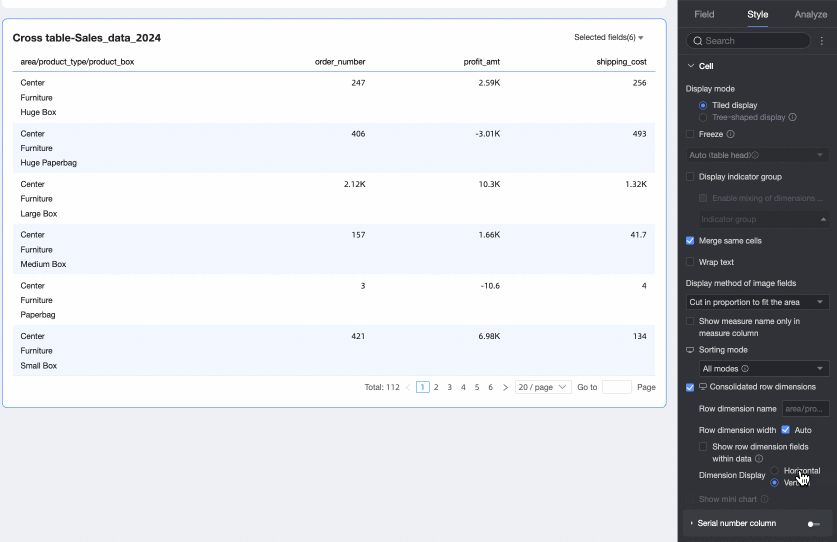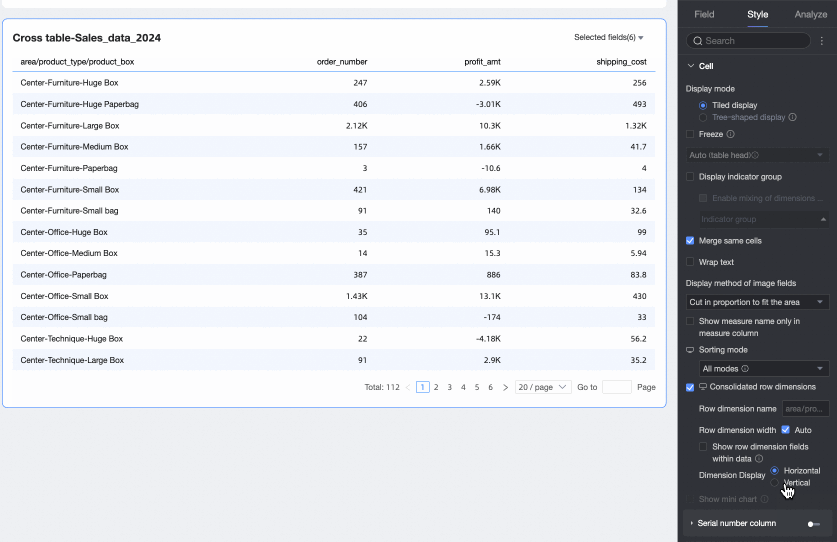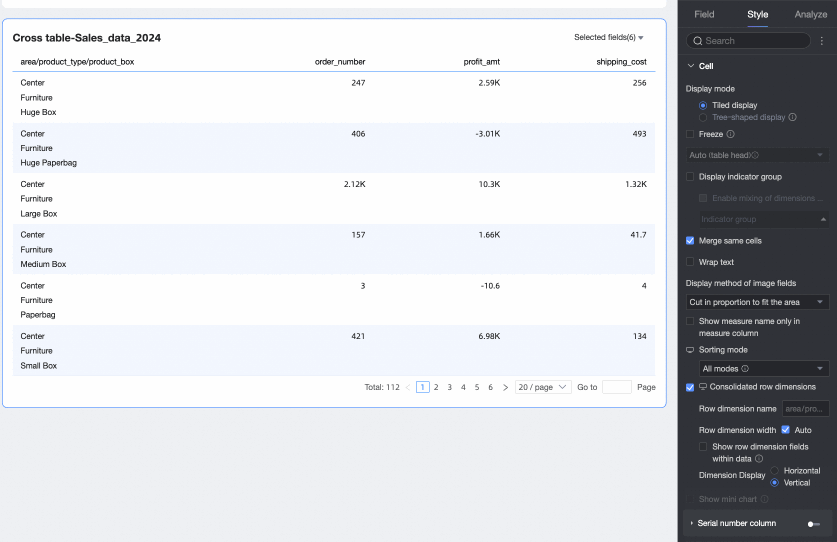
Merge row dimensions
Sets whether to merge row dimensions. If you select this option, the cross table merges dimension information into a single column, displayed by row. You can also configure the following settings.
Row dimension name: Enter the name for the merged row dimension.
Row dimension width: Sets the width of the row dimension column. You can choose to adapt the width automatically to the interface or enter a fixed custom column width.
Display row dimension field in data: If you select this option, the name of the row dimension field is displayed.
Dimension arrangement: Sets the text arrangement after merging row dimensions. You can choose horizontal or portrait.
NoteYou can configure the merging of row dimensions for PC and mobile separately by clicking the
 icon at the top of the page.
icon at the top of the page.Show sparkline
When the Columns area contains a date field and the Rows area contains a measure, you can choose to enable sparklines. If enabled, you can customize the sparkline name based on its business meaning.
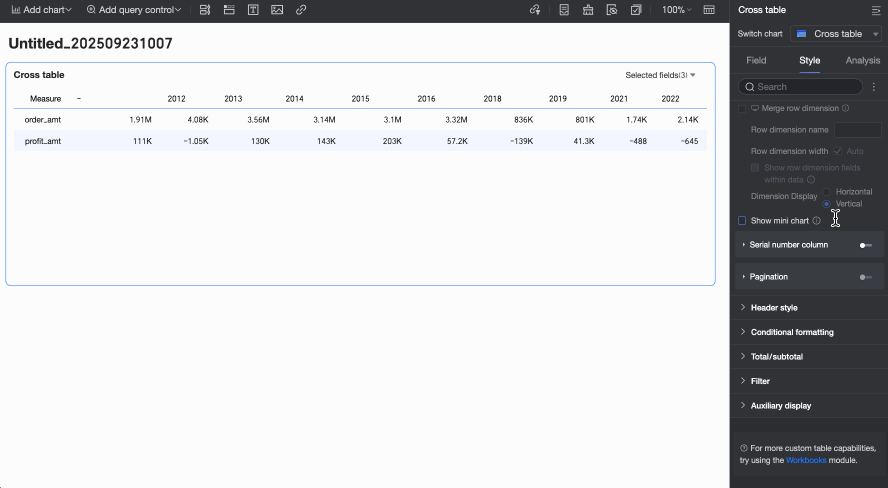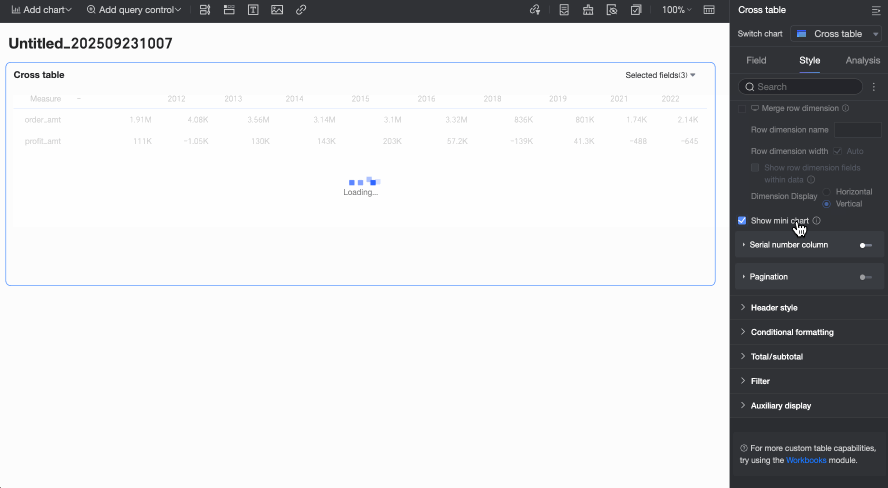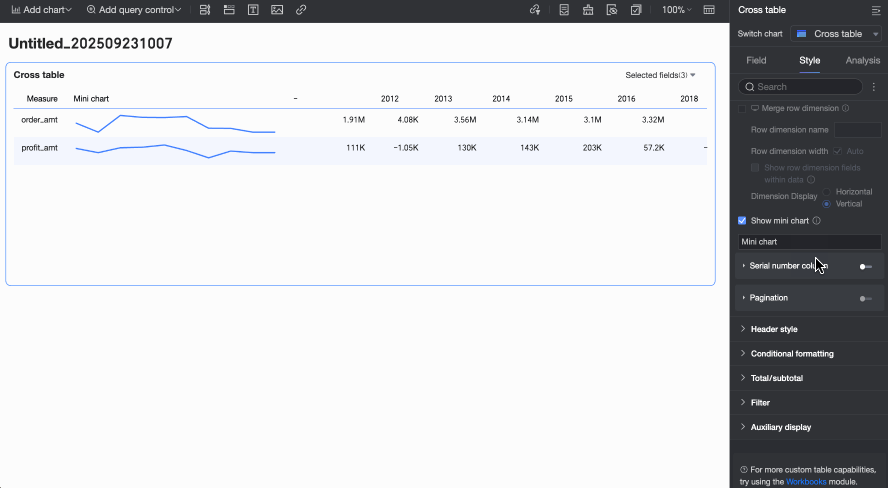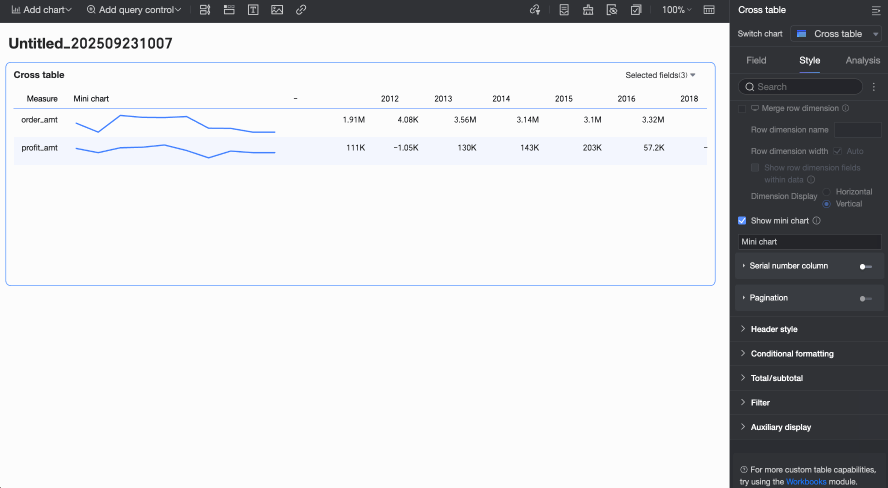
Ordinal number column
If you select this option, the report column header displays ordinal numbers.
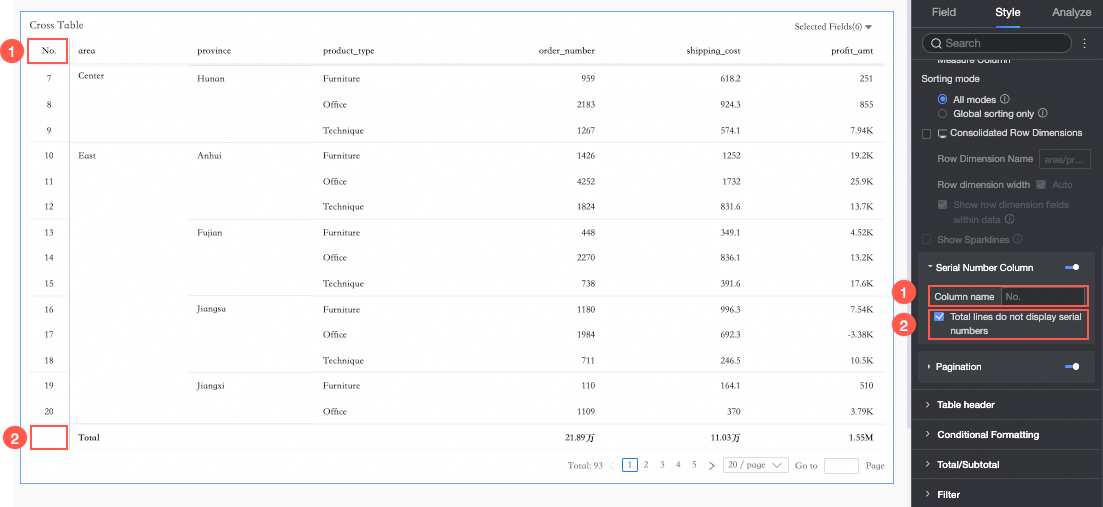
① You can set the name of the ordinal number column.
② You can select Do not display ordinal numbers in total rows.
NoteYou can select Do not display ordinal numbers in total rows only when column totals are enabled for the cross table.
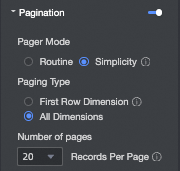
Paginator
Click the paginator icon to open the paginator editing page.
The paginator mode defaults to Regular. When the data volume is large, we recommend that you choose the Simple mode, which does not calculate the total number of data entries.
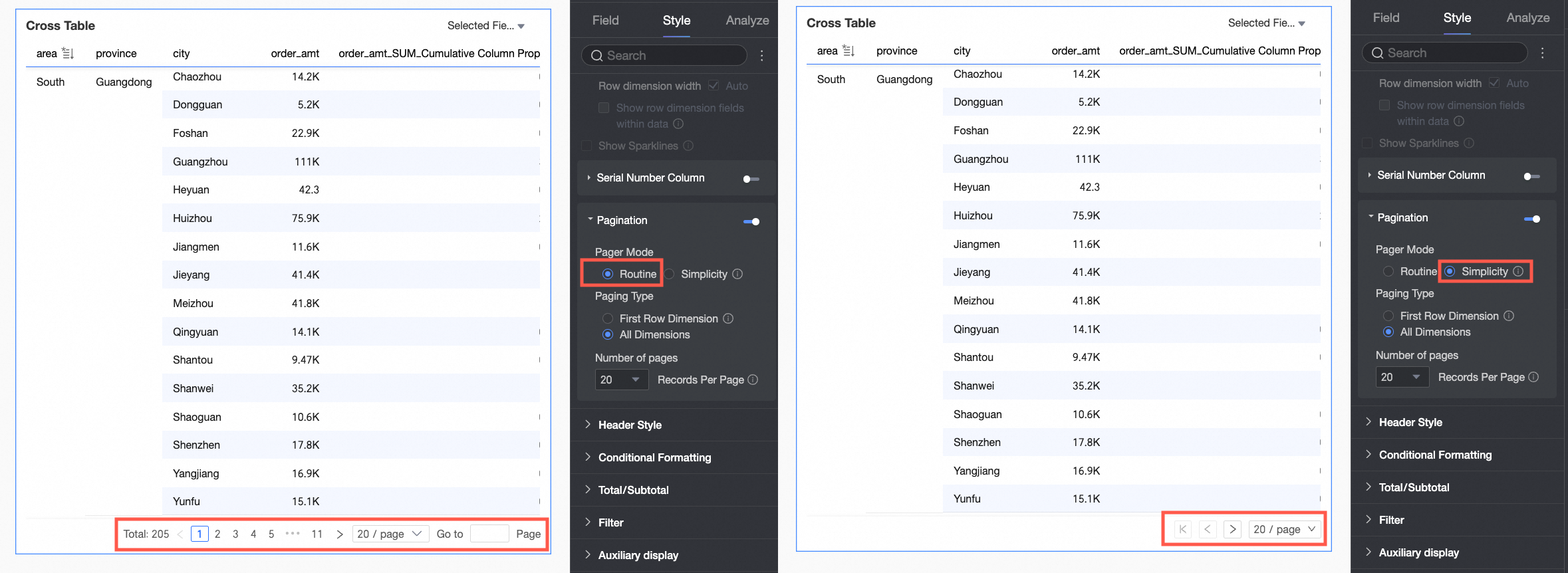
The paging type can be set to First row dimension or All dimensions.
NoteWhen you perform global sorting, first-row dimension paging is automatically disabled.
The supported page sizes are 10, 20, 30, 50, 80, 100, 200, and 500 items per page. The default page size is 20 items per page.
In the Header section, you can set the style of the row and column headers.
Configuration item
Configuration Item Content
Description
Column header
Do not display column header
If checked, the column header content will not be displayed.
Background fill
Set the background fill color for the column header.
Text
Set the text style for the column header.
Set alignment
Set the alignment for the column header. Supports left, center, and right alignment.
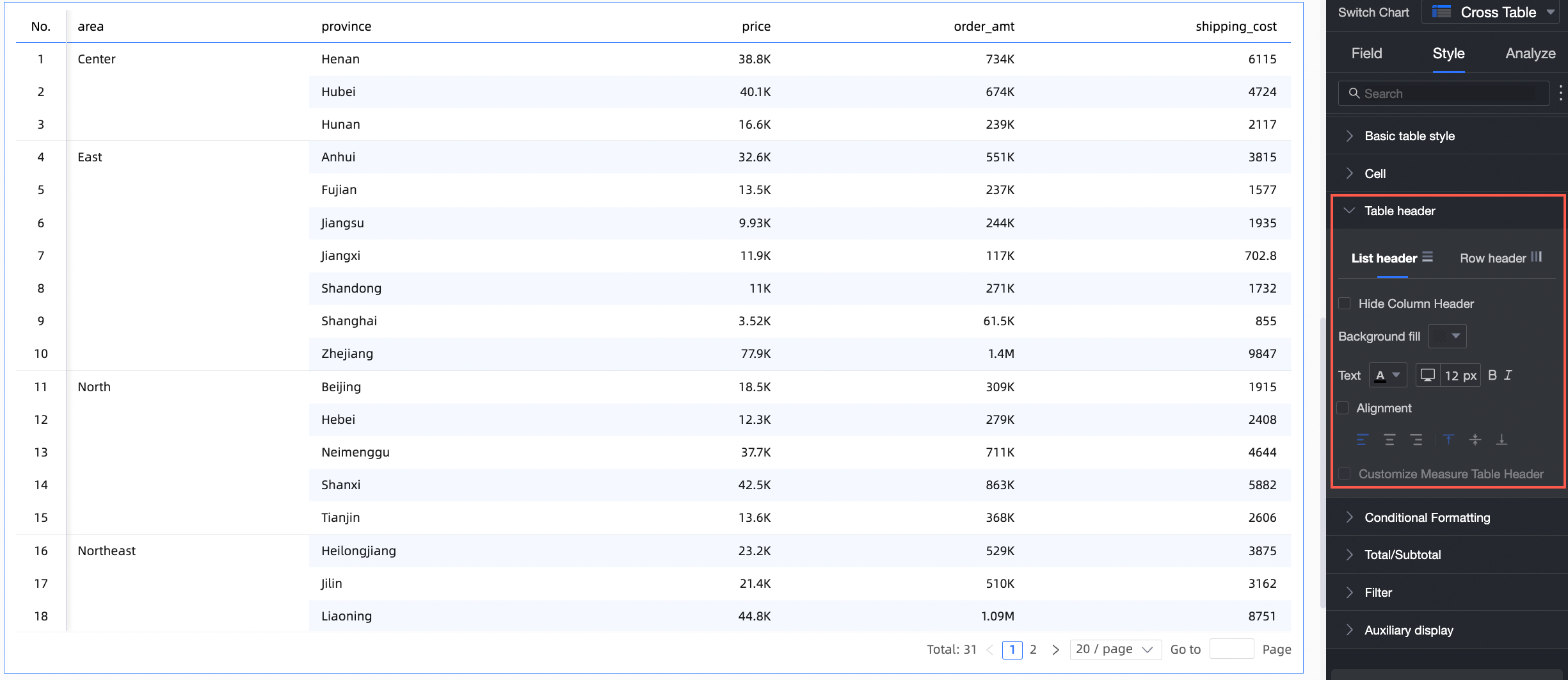
Custom measure header name
When a measure field exists in the row dimension, you can configure a custom measure header name.
Row header
Background fill
Set the background fill color for the row header.
Text
Set the text style for the row header.
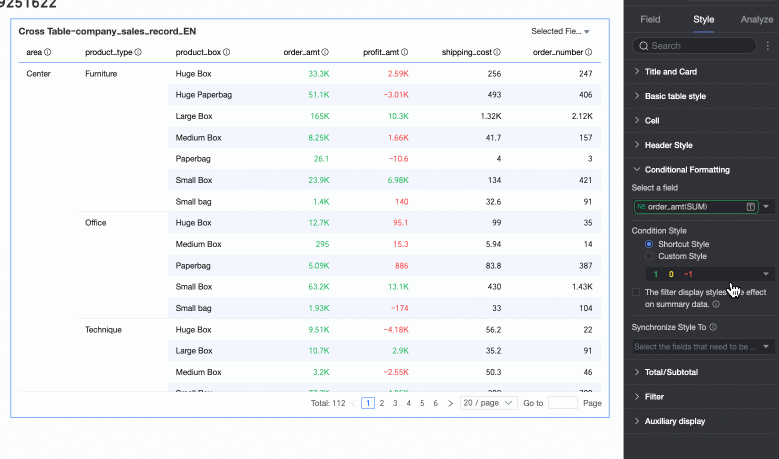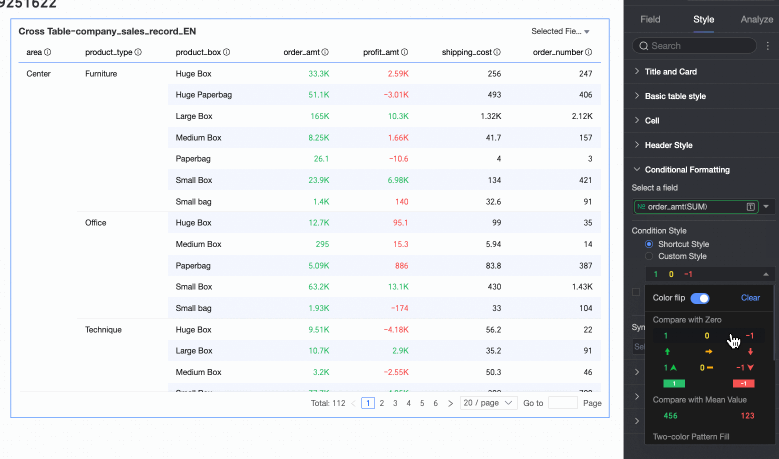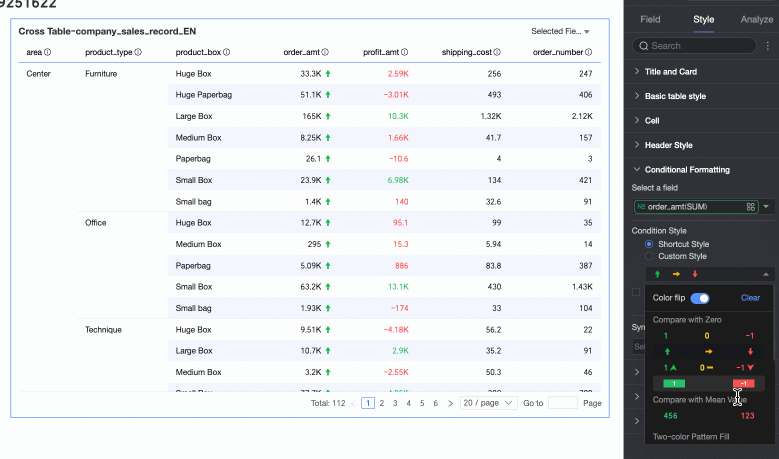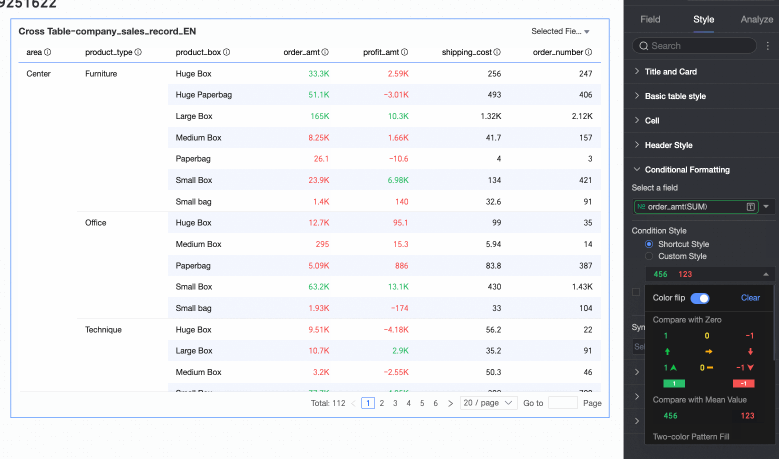
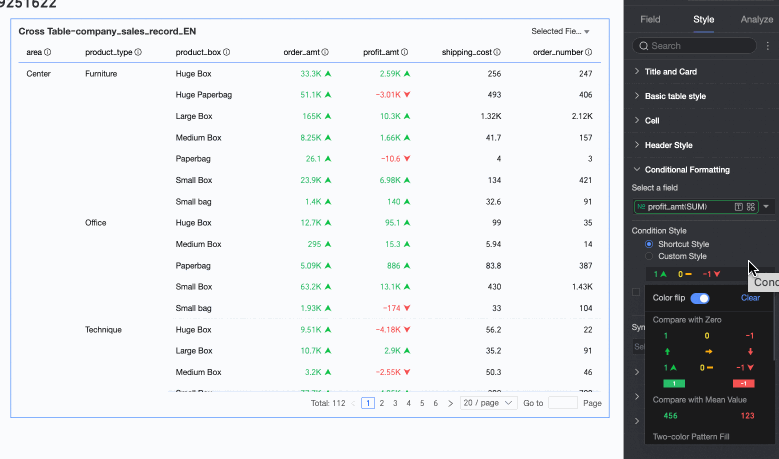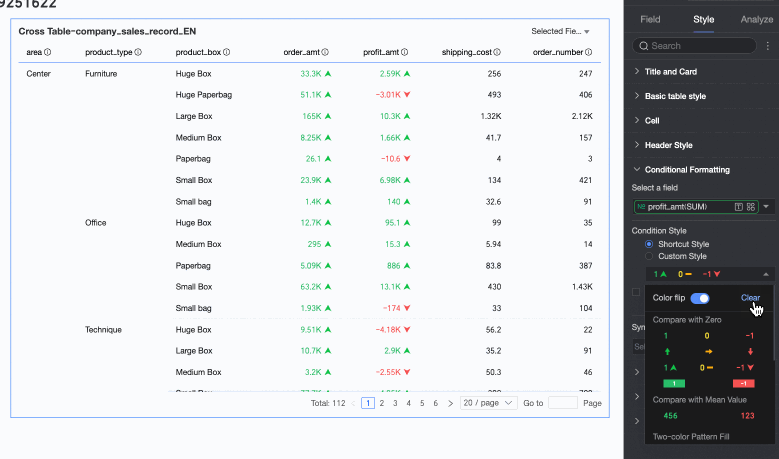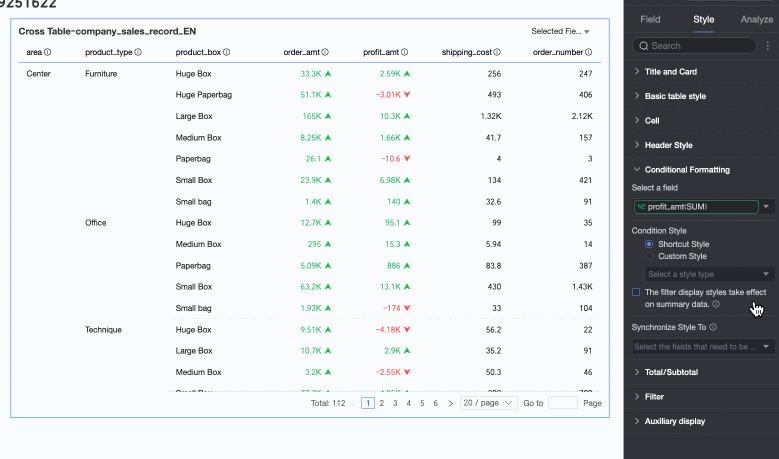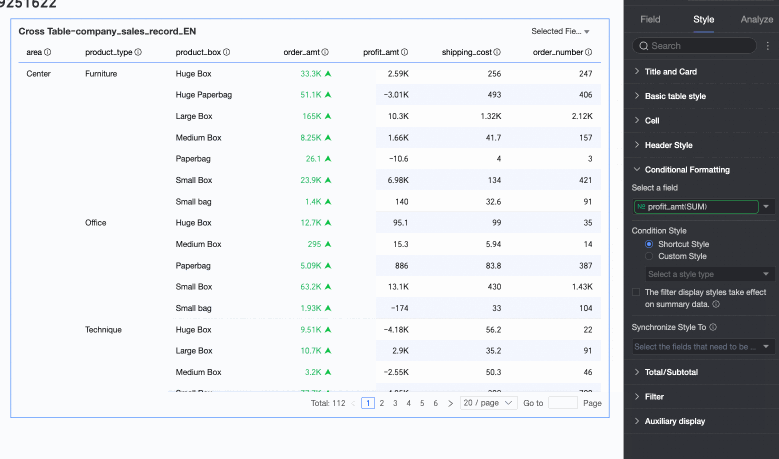
In the Conditional Formatting section, you can set the conditional format for the data.
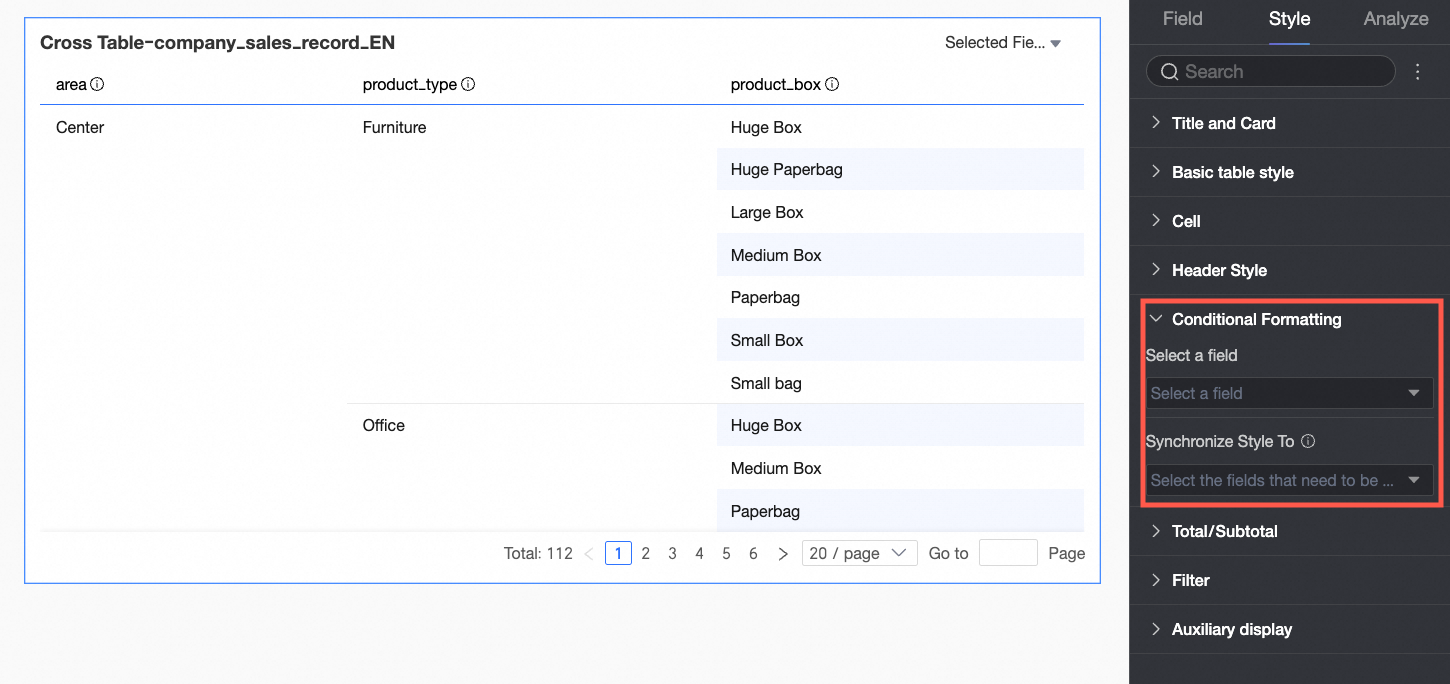
Chart configuration item
Description
Select field
Select the field for which you want to configure conditional formatting. Any field added to the data panel area can be selected.
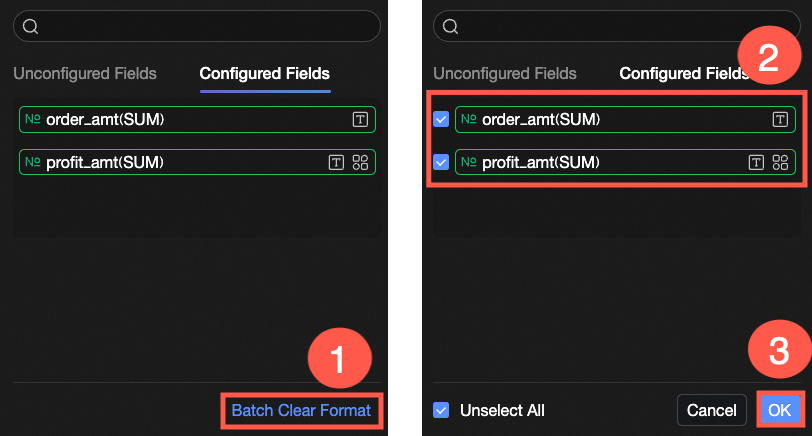
After completing the style configuration, if you no longer need some of the configured conditional formats, you can click Clear formats in batches in the lower right corner of the field panel. In the selection list, choose the conditional formats you want to clear and click OK to finish.
Quick Style
From the system-provided styles, set the marker icon or font display color for the current field. Quick styles can only be configured for measure fields, not for dimension fields.
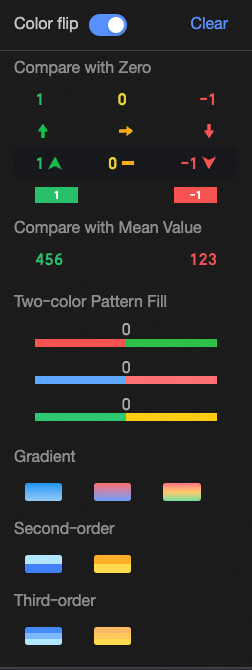
Comparison: You can choose Compare with 0 or Compare with mean.
Two-color fill: You can select the color of the data bars.
 Note
NoteData bar length calculation: When the maximum and minimum values are one positive and one negative, the denominator is the maximum of their absolute values. When the maximum and minimum values are both positive or both negative, the denominator is the difference of their absolute values.
Color scale: You can select Gradient, Two-tier, or Three-tier.
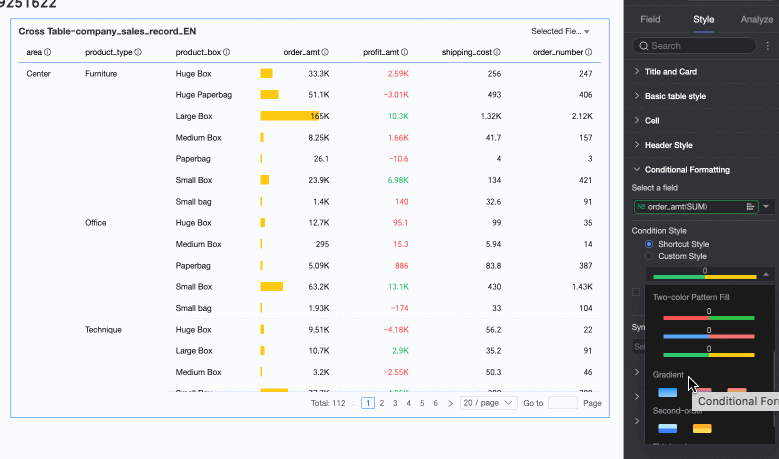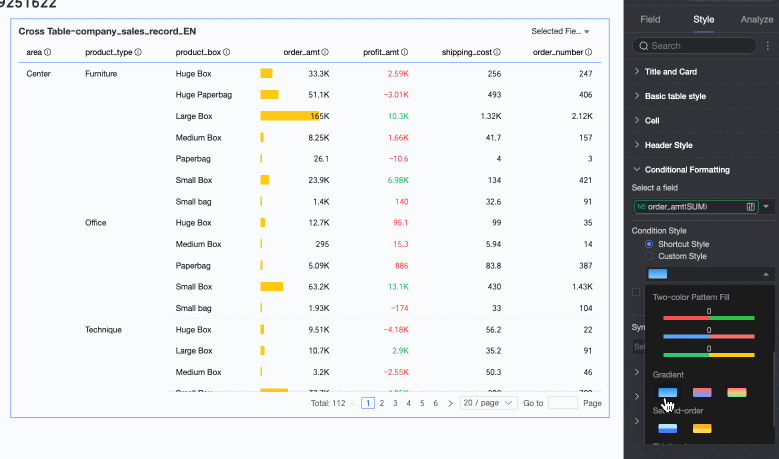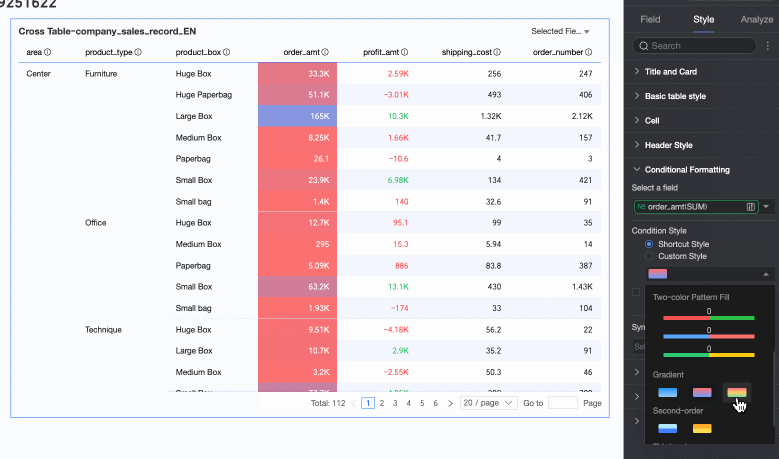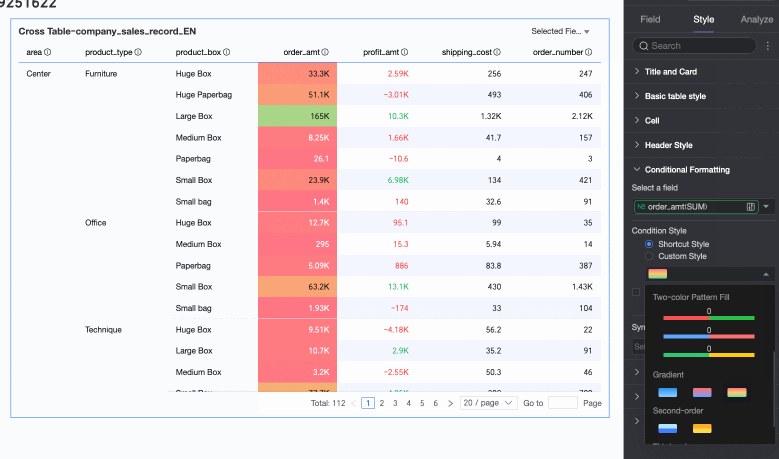
Invert colors
For comparison, for example, less than 0 is red and greater than 0 is green. After inverting, less than 0 becomes green and greater than 0 becomes red.
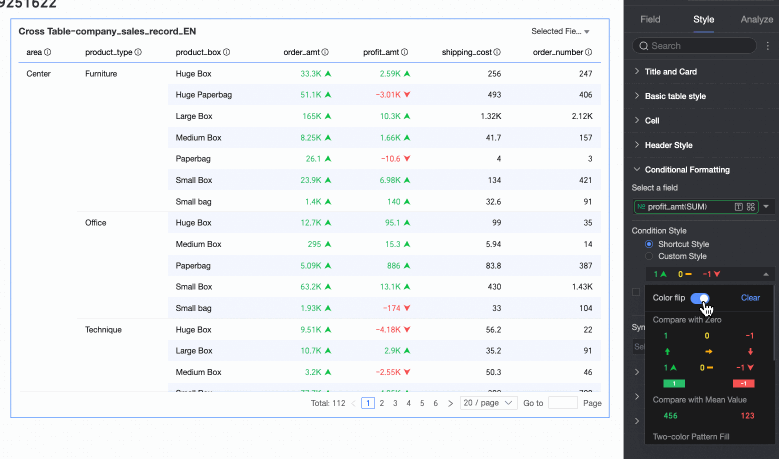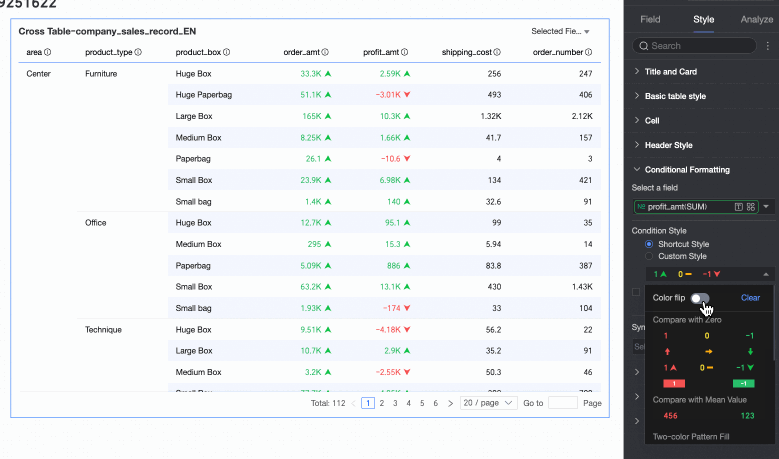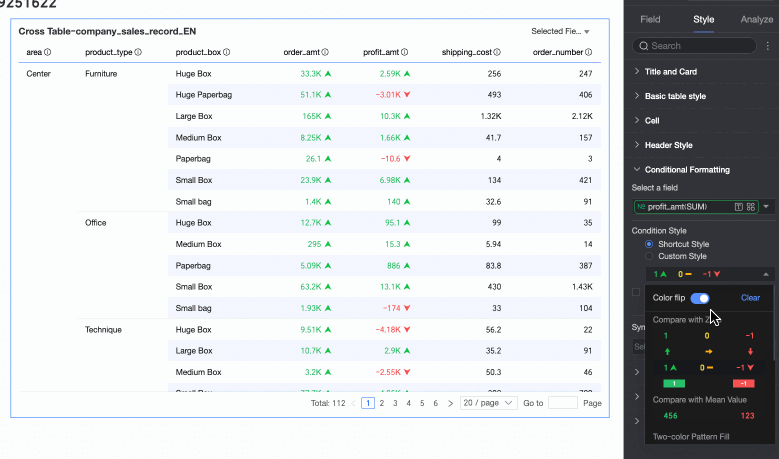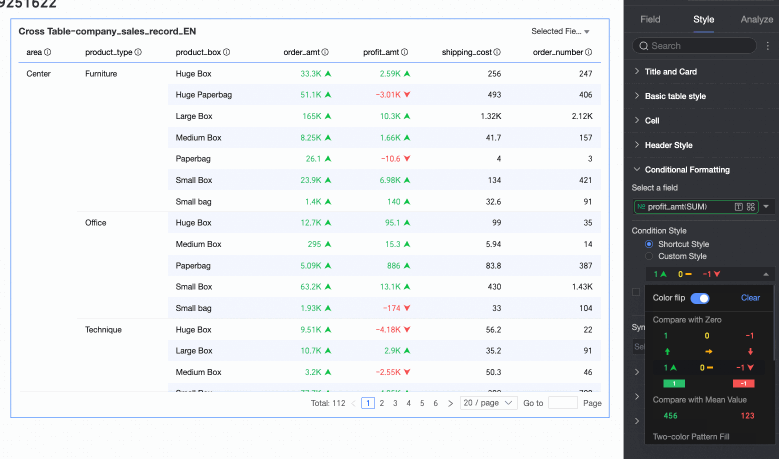
Clear: When a set quick style is no longer needed, click Clear to remove it.
Custom Style
In addition to the quick styles provided by the system, you can configure custom styles as needed. Both measure and dimension fields can have custom styles, but the supported style options differ.
Measure fields: Support configuring Highlight text/background, Icon, Color scale, and Data bar.
Highlight text/background: Configure rules to highlight the field value's text color or background color to visually emphasize key data in the table.
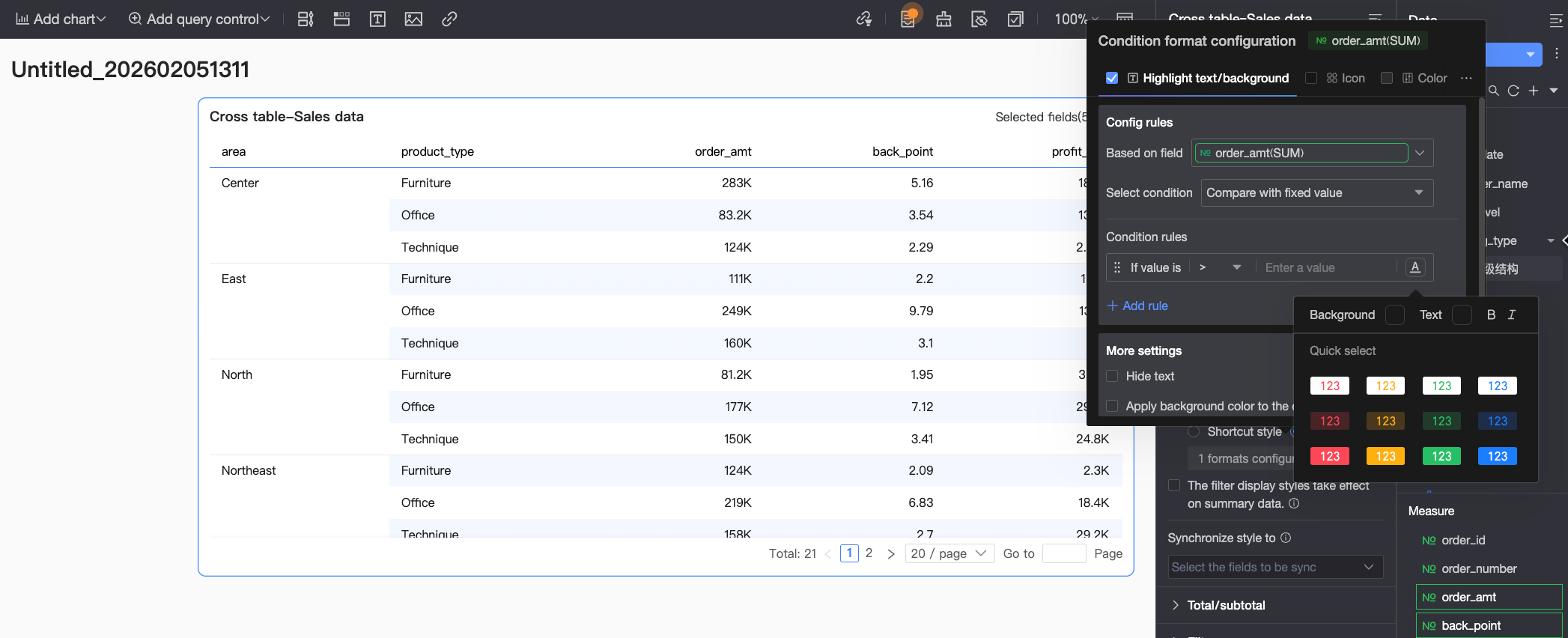 You need to configure the following information.
You need to configure the following information.Based on field: Set which data field the conditional rule applies to. This will default to the field configured in Select field. You can also select other fields in the chart to configure more complex conditional rules based on their values.
Condition selection: Set the comparison baseline for the conditional rule. You can set it to Compare with a fixed value, Divide by percentage range, or Compare with a dynamic field.
Condition rule: Set the specific judgment logic of the conditional rule and the display style for the cell text/background when the rule is met. You can set the text color, whether it is bold or italic, and the background fill color.
Add rule: Click to add a new calculation rule.
More settings: Set whether to hide the text of the current field and whether to apply the background color to the entire row.
Icon: Display a specific marker icon in the corresponding cell based on the numerical comparison result to clearly show the size relationship between the current data and the target data.
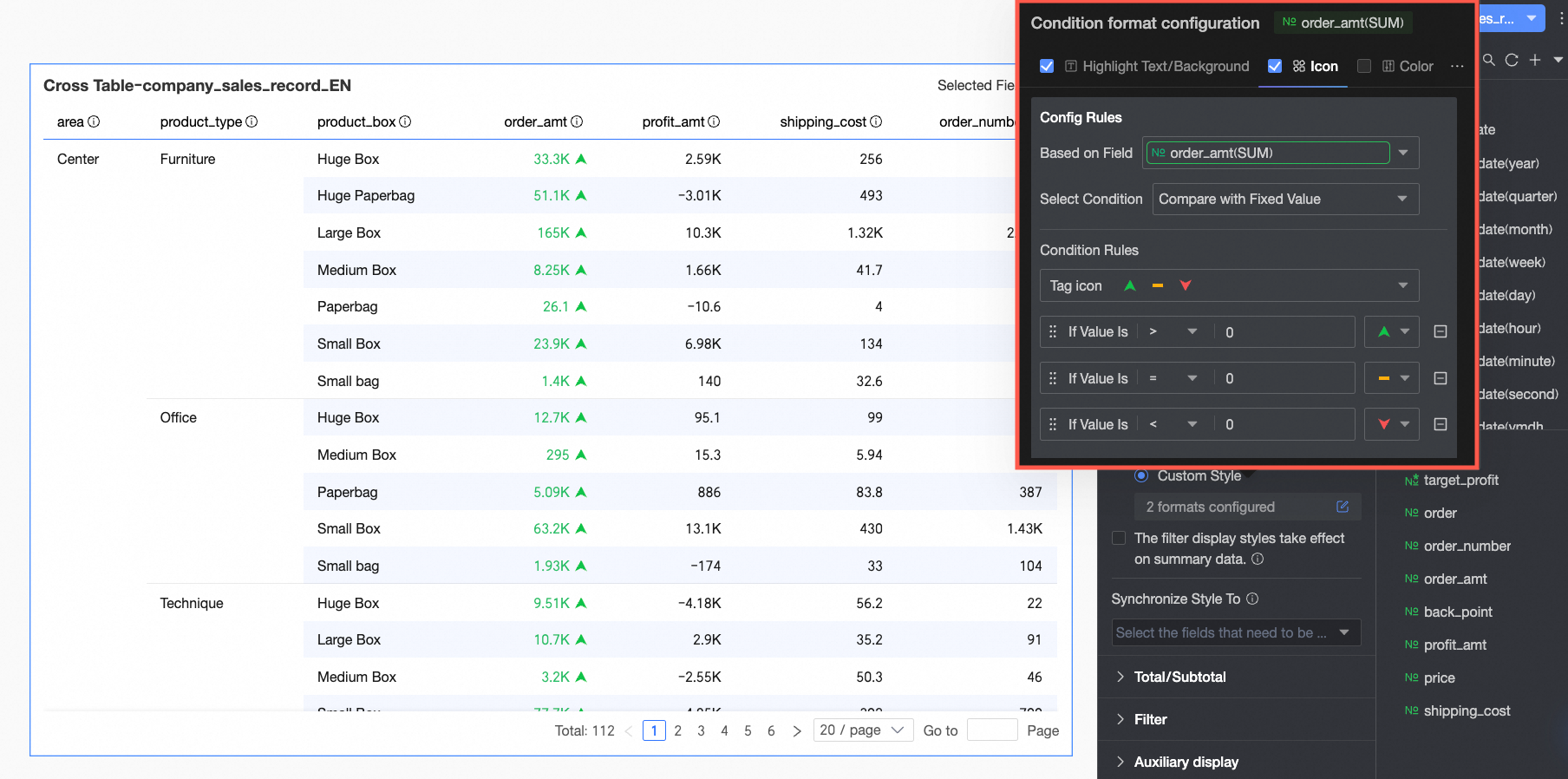 You need to configure the following information.
You need to configure the following information.Based on field: Set which data field the conditional rule applies to. This will default to the field configured in Select field. You can also select other fields in the chart to configure more complex conditional rules based on their values.
Condition selection: Set the comparison baseline for the conditional rule. You can set it to Compare with a fixed value, Divide by percentage range, or Compare with a dynamic field.
Condition rule: Click the Marker icon selection box, choose a suitable icon type from the system-provided sets, and set the specific judgment logic for the data condition corresponding to an icon. You can also select a marker icon for each comparison rule individually.
Add rule: Click to add a new calculation rule.
More settings: Set whether to hide the text of the current field.
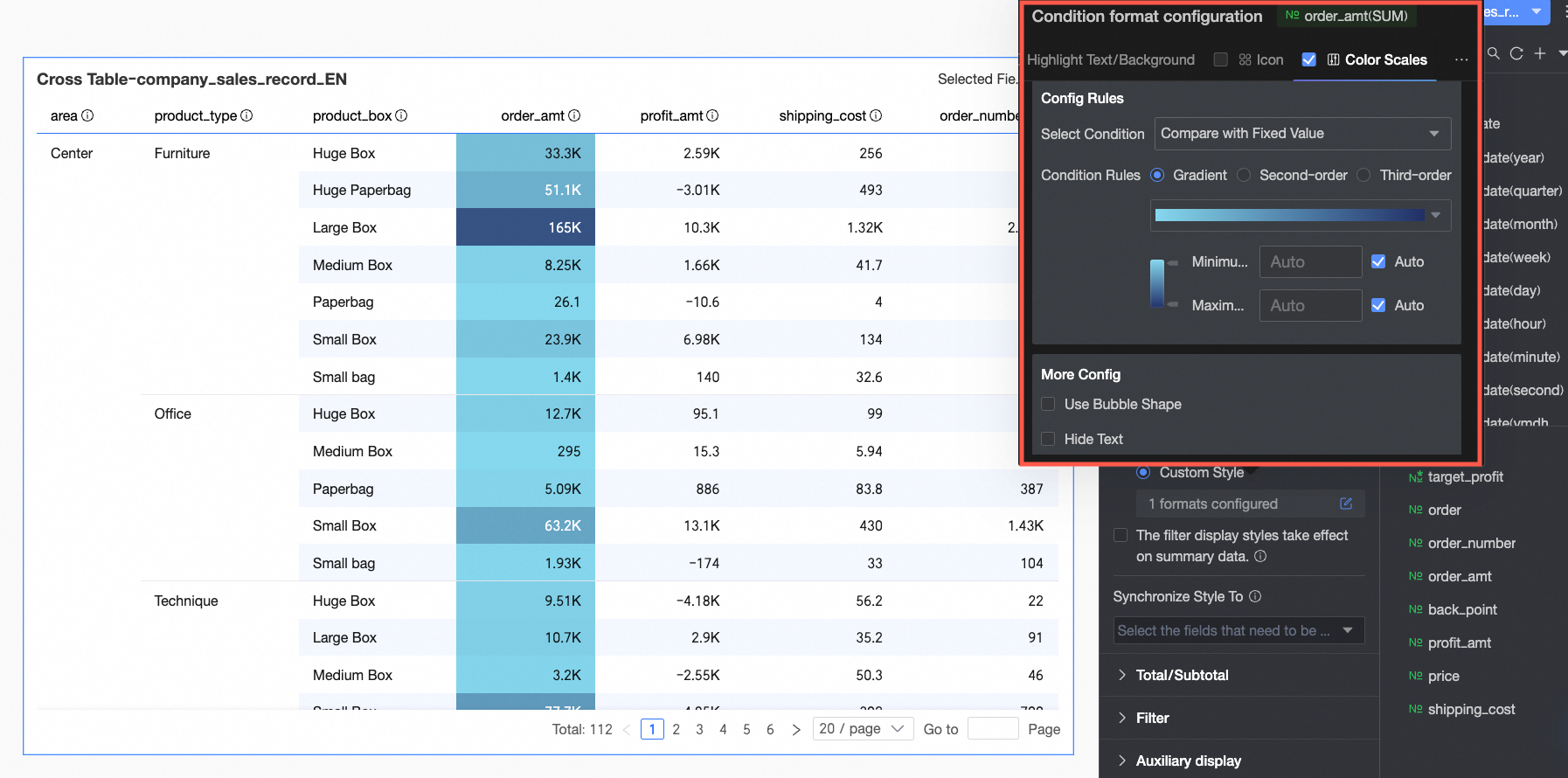
Color scale: Make the cell background show different colors from a specified color scale based on the numerical value, to clearly show the distribution and change trends of the data.
NoteYou can only select and configure a color scale if Highlight text/background, Icon, and Data bar are not selected.
 You need to configure the following information.
You need to configure the following information.Condition selection: Set the comparison baseline for the conditional rule. You can set it to Compare with a fixed value or Divide by percentage range.
Condition rule: Set the color scale style (gradient, one-tier, two-tier) and specify the maximum, minimum, and boundary values for the current style, along with the corresponding colors for each numerical interval.
In More settings: Set the shape of the color scale bar and whether to hide the text of the current field.
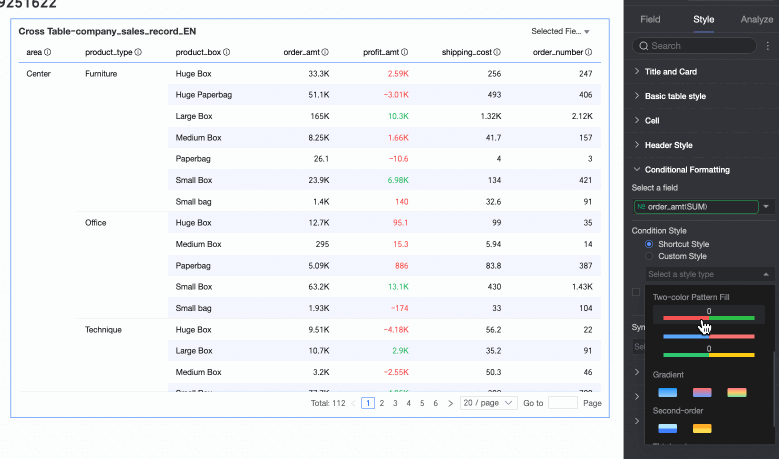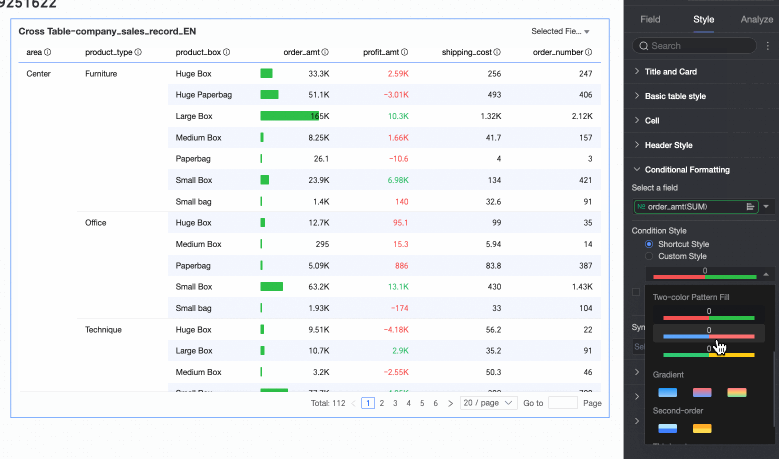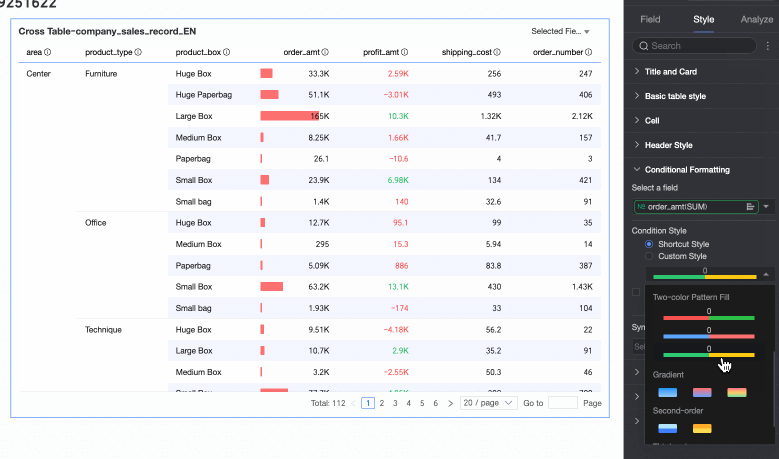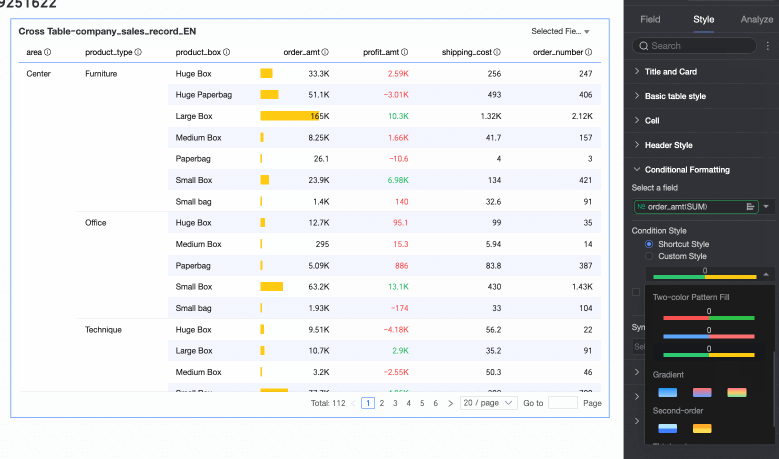
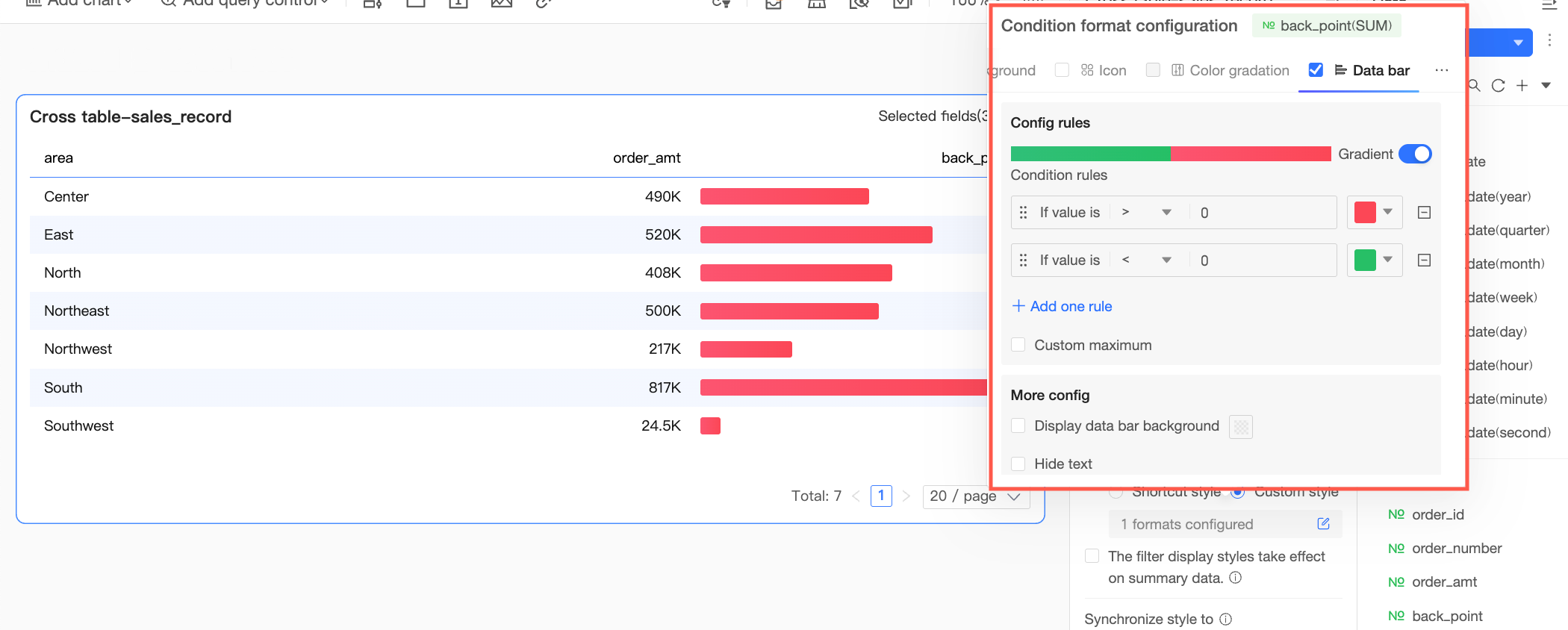
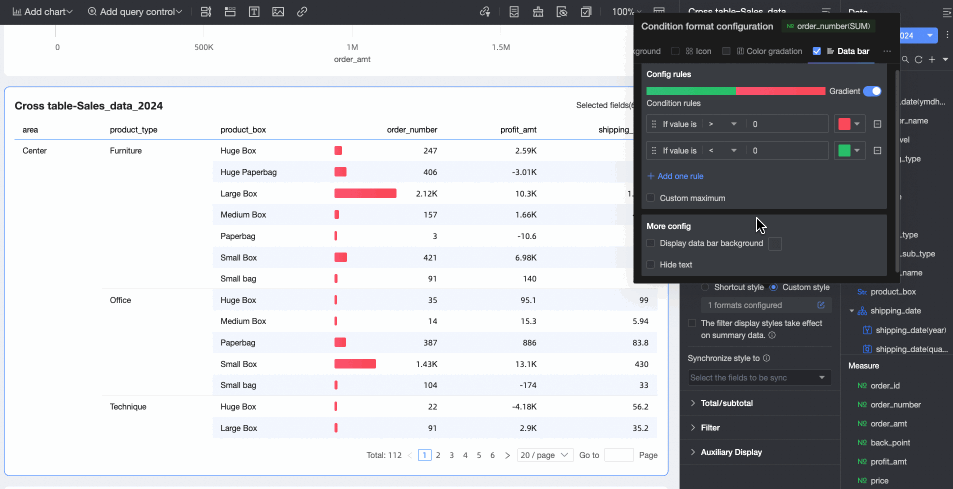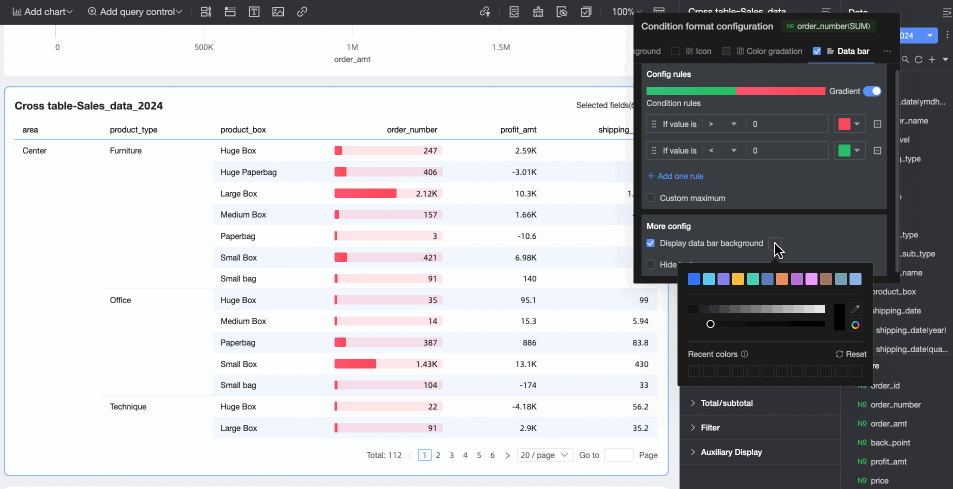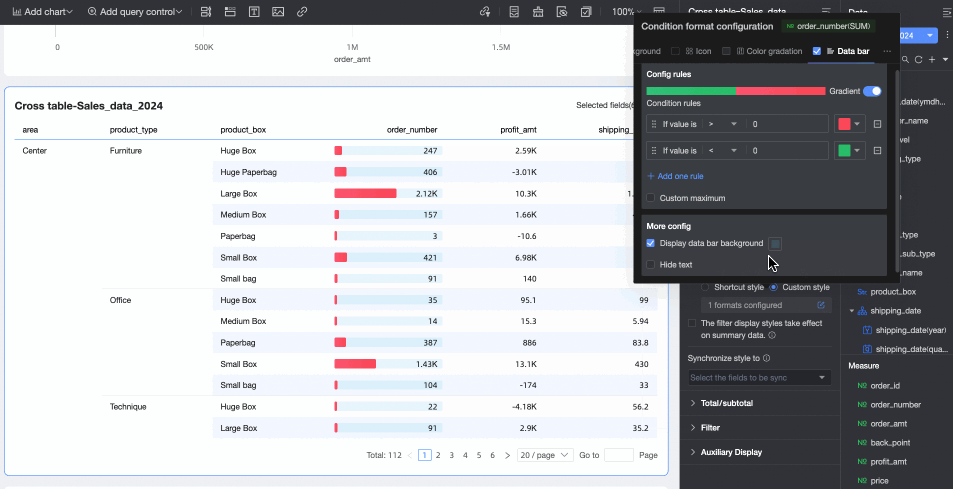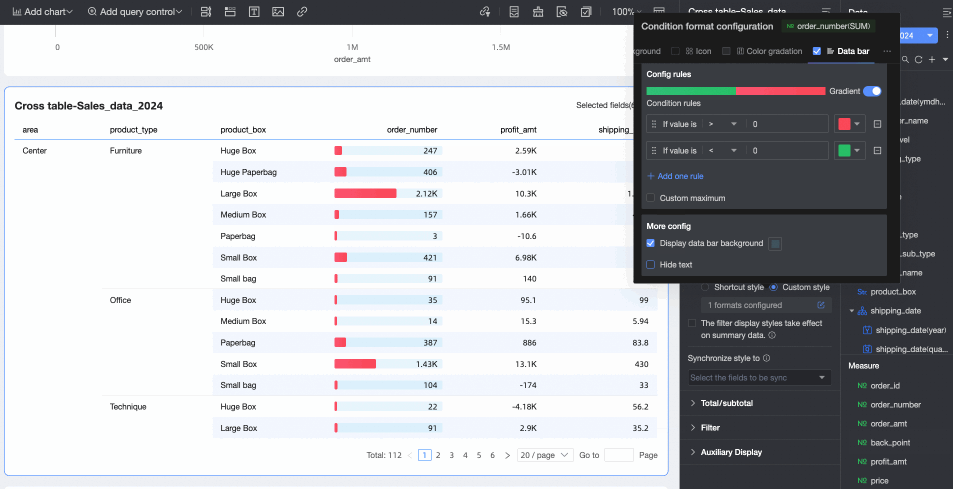
Data bar: Express numerical values in a visual form of length and color, to more intuitively show the relative size or comparison of data.
 You need to configure the following information.
You need to configure the following information.Condition rule: Set the display rule for the data bar of the current measure field. You can specify a corresponding display color for each rule.
Add rule: Click to add a new calculation rule.
Custom max/min: If selected, you can customize the specific values for the maximum and minimum. In automatic mode, the maximum defaults to the highest value in the current field, and the minimum defaults to the lowest value.
More settings: Set whether to show the data bar background and customize its color. Set whether to hide the text of the current field.
Dimension fields: Support configuring Highlight text/background and Icon.
Highlight text/background
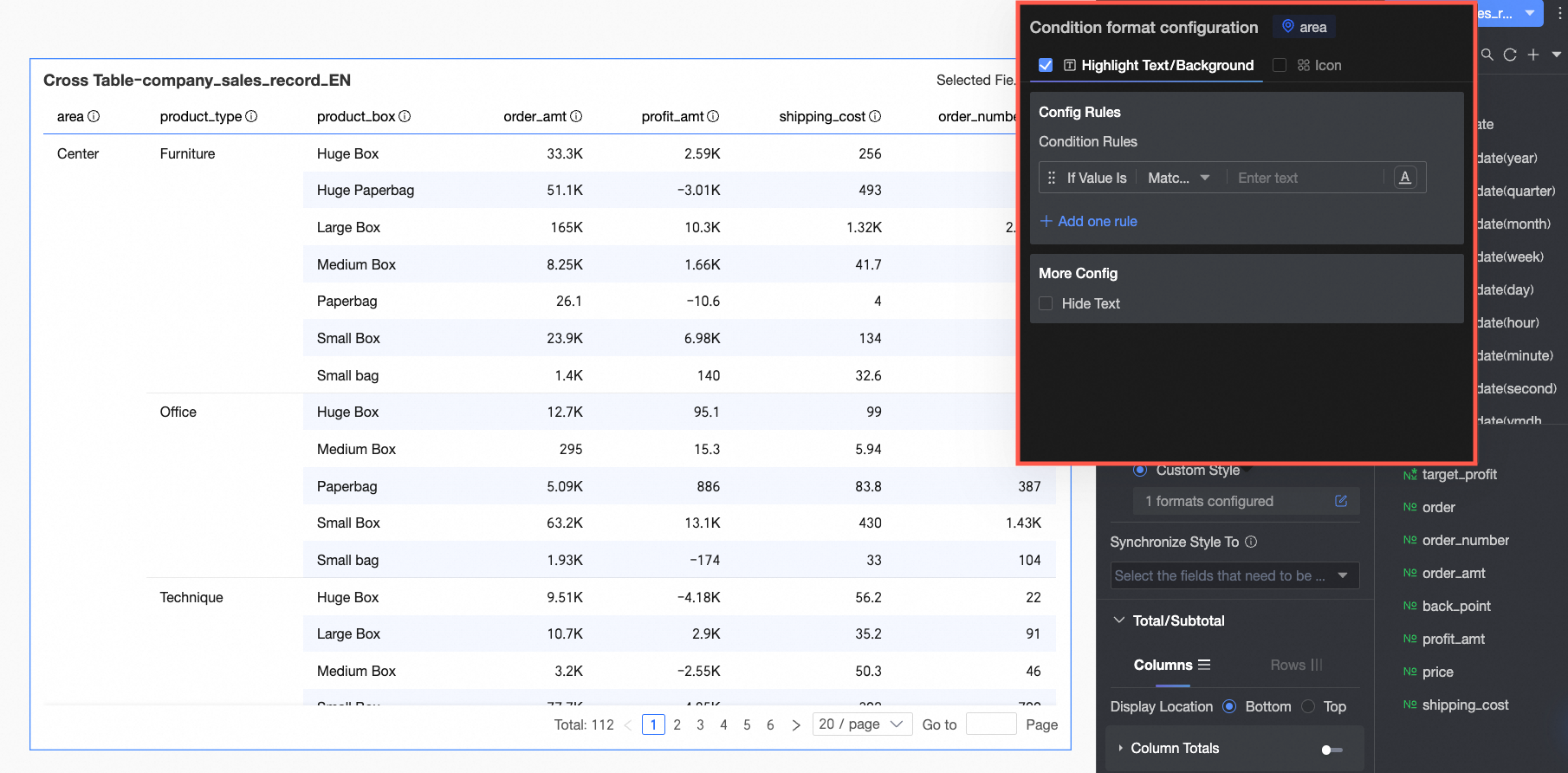
In Rule formulation: Set the conditional rule to highlight the text of the current dimension field. The condition here is a judgment on the dimension value, so only text information can be entered in the condition value input box.
In More settings: Set whether to hide the text of the current field.
Icon
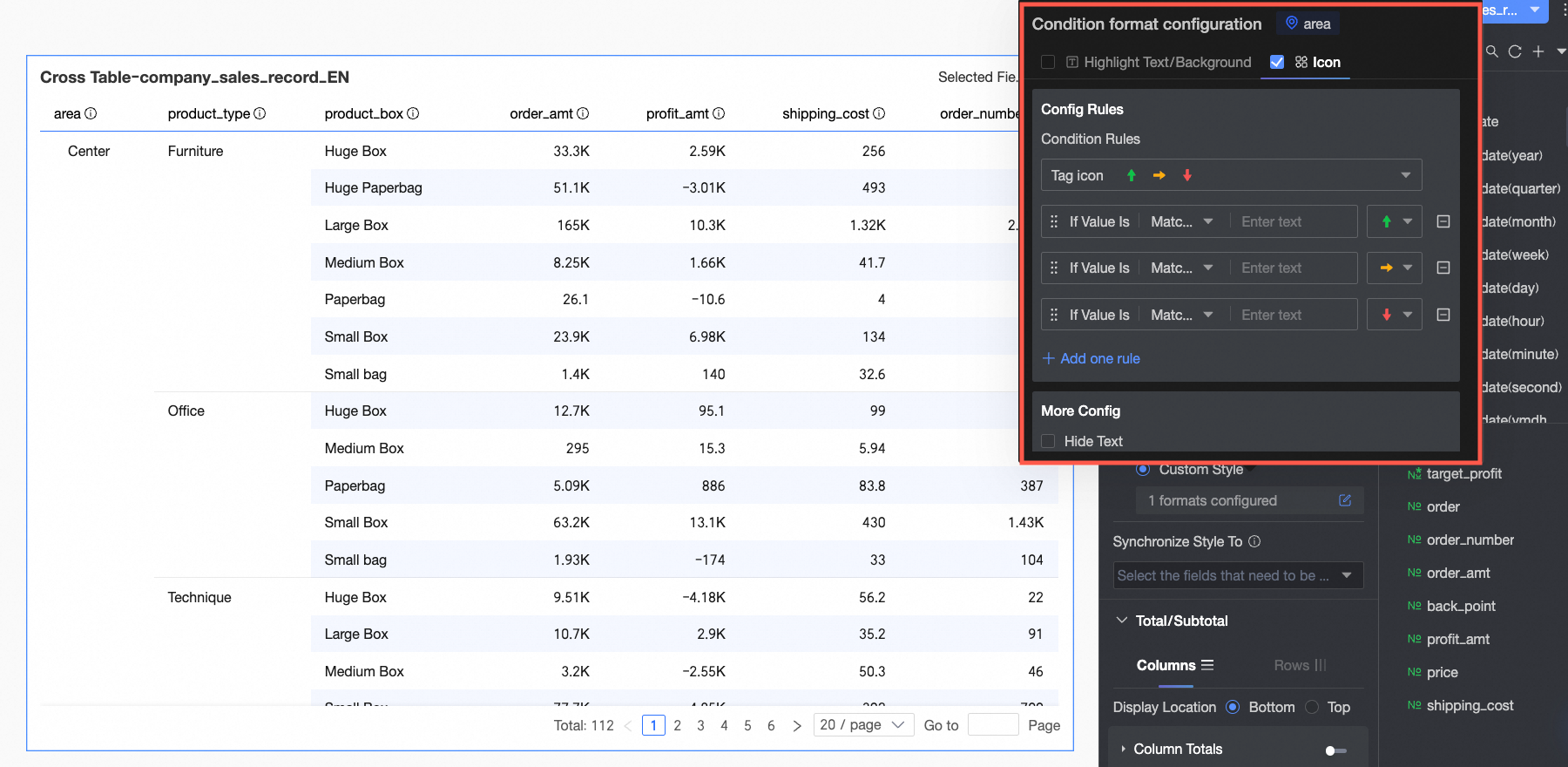
In Rule formulation: Set the icon marking rule for the current dimension field. The condition here is a judgment on the dimension value, so only text information can be entered in the condition value input box.
In More settings: Set whether to hide the text of the current field.
Apply conditional styles to summary data
Choose whether the set conditional styles also apply to summary data. If checked, the calculation of maximum, minimum, and percentage in the conditional rules will include subtotal data but not grand total data.
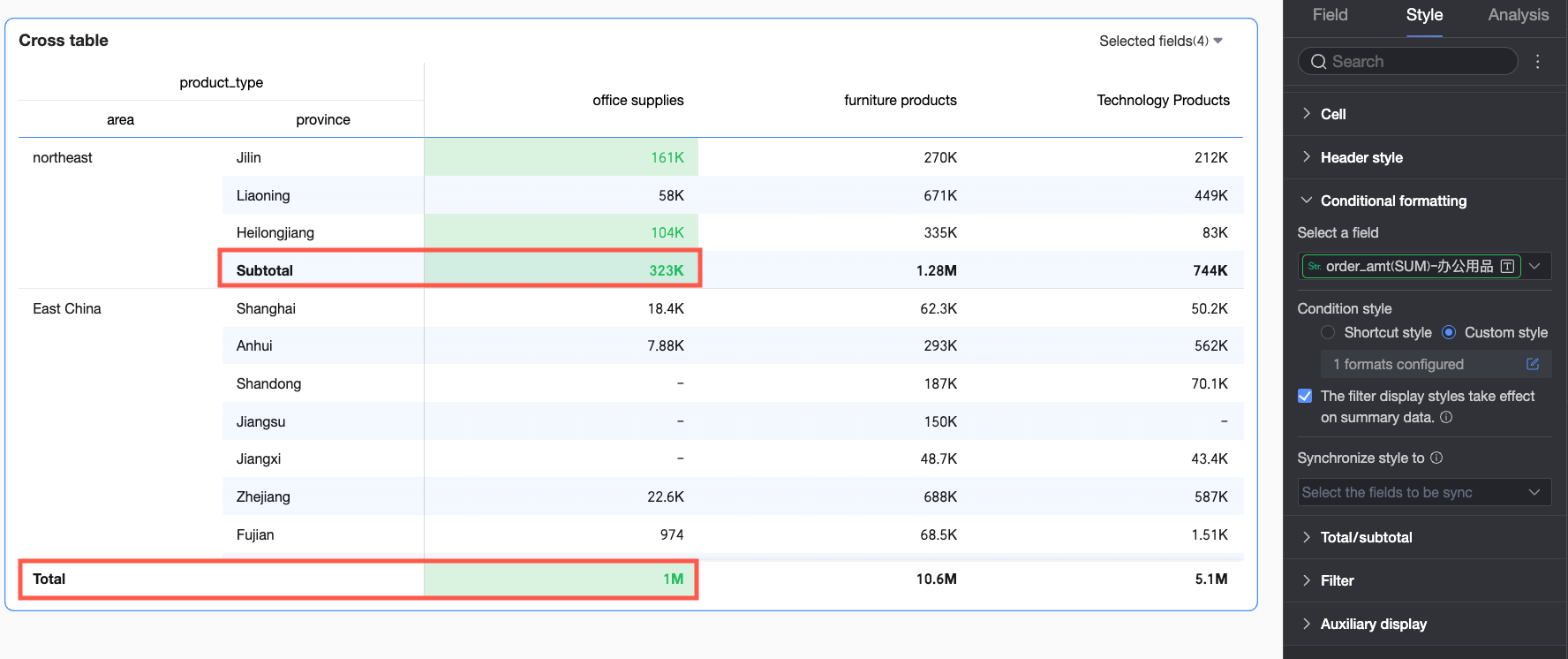
Sync style to
Sync the current conditional format to other fields.
In Totals/Subtotals, set Column Summary and Row Summary for the required dimensions.
Column Summary: Calculates summary data by column. This is unavailable if the cross table has no measures or no row dimensions.
Row Summary: Calculates summary data by row. This is unavailable if the cross table has no measures or no column dimensions.

Configuration item
Description
Column Summary
Display Position
Set the display position for column grand total/subtotal data. You can choose to place it at the bottom or top of the summary data.

Overall Summary (Column Grand Total)
Use the switch
 to enable or disable column grand totals. When enabled, it summarizes all values in a column. You can also configure the following settings.
to enable or disable column grand totals. When enabled, it summarizes all values in a column. You can also configure the following settings.
Total alias: You can set a display name for the grand total data based on its business meaning, for example: Total sales for each region.
Calculation method: Select a uniform grand total aggregation method for all fields. If a field is a calculated field, the selected aggregation method here will not take effect; the original aggregation method will be used.
To set different aggregation methods for each field, select Custom from the dropdown list and configure the aggregation logic for each field in the Custom Calculation module.
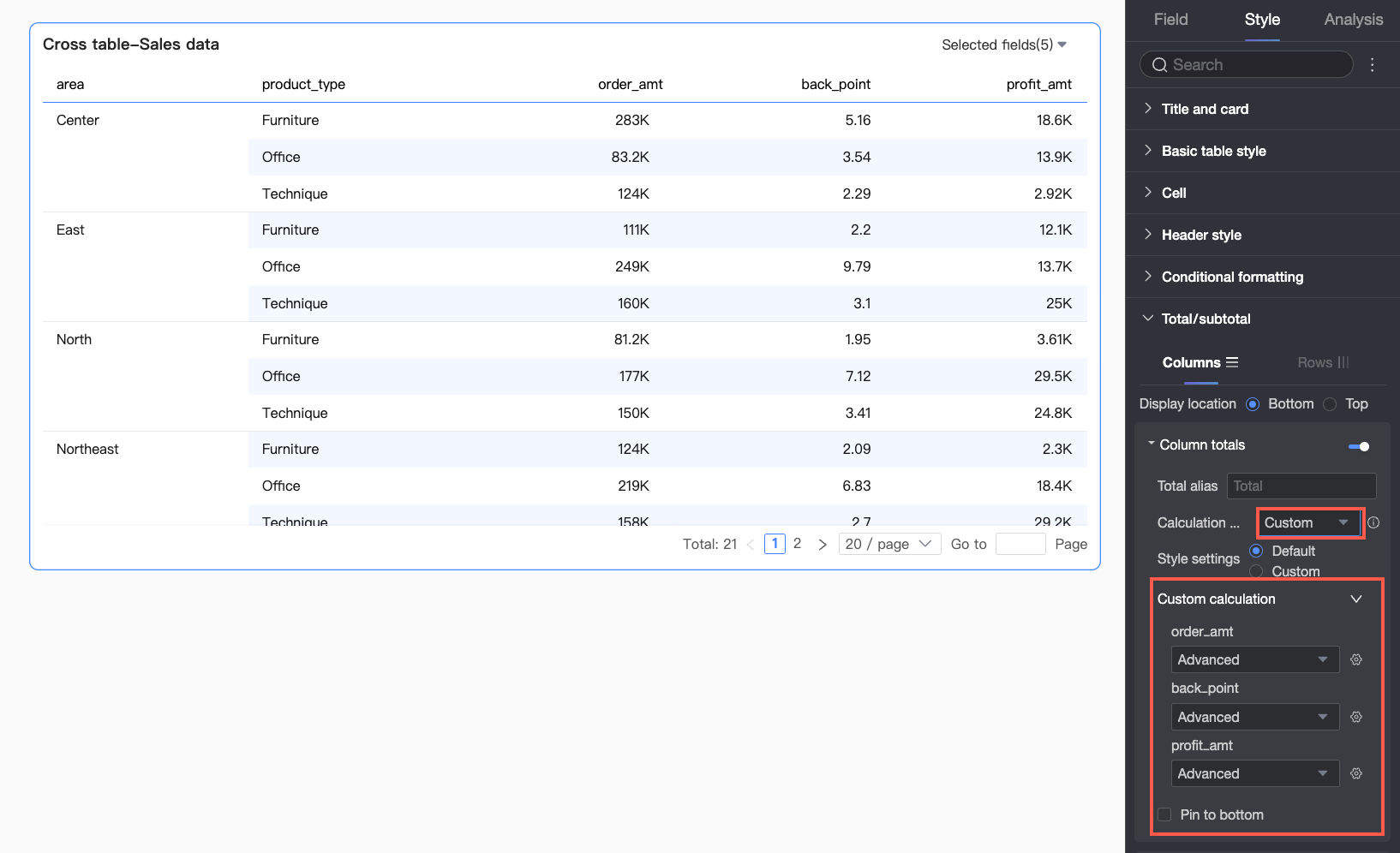
Style configuration: Set the text style for the current grand total data. You can choose to follow the system default or customize the text's font color, background color, weight, etc.
Pin to top: Set whether to pin the column grand total data to the bottom.
NoteWhen column summary is pinned to the bottom or top, you cannot copy the summary data.
Classified Summary (Column Subtotal)
Use the switch
 to enable or disable column subtotals. When enabled, it performs a subtotal operation on each category of data in a column, based on the selected category dimension. You can also configure the following settings.
to enable or disable column subtotals. When enabled, it performs a subtotal operation on each category of data in a column, based on the selected category dimension. You can also configure the following settings.
Subtotal alias: You can set a display name for the subtotal data based on its business meaning, for example: Subtotal of sales in the Northeast region.
Summary dimension: Set the classification dimension for the subtotal, for example, to subtotal the sales for each product type.
Subtotal function: Select a uniform subtotal aggregation method for all fields. If a field is a calculated field, the selected aggregation method here will not take effect; the original aggregation method will be used.
Add subtotal: When you need to observe subtotal data from multiple classification dimensions simultaneously (for example, needing to see subtotals for each product type and sales in each region), you can click Add subtotal to add more subtotal dimensions.
Style configuration: Set the text style for the current subtotal data. You can choose to follow the system default or customize the text's font color, background color, weight, etc.
Row Summary
Display Position
Set the display position for row grand total/subtotal data. You can choose to place it on the left or right side of the summary data.
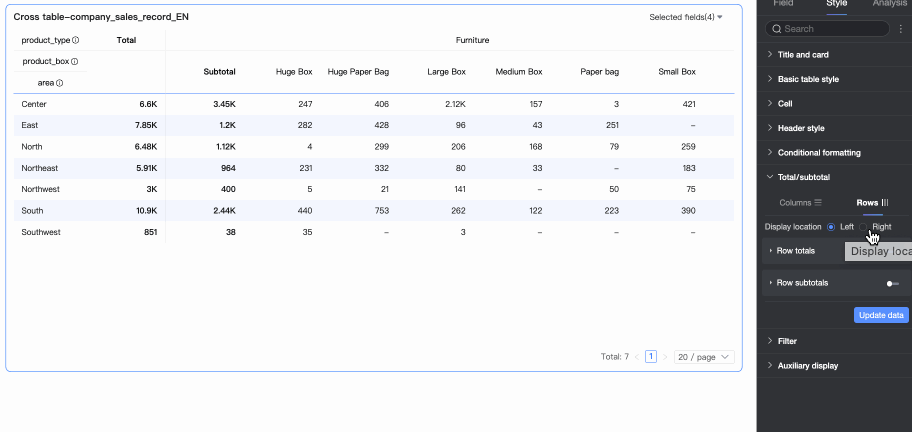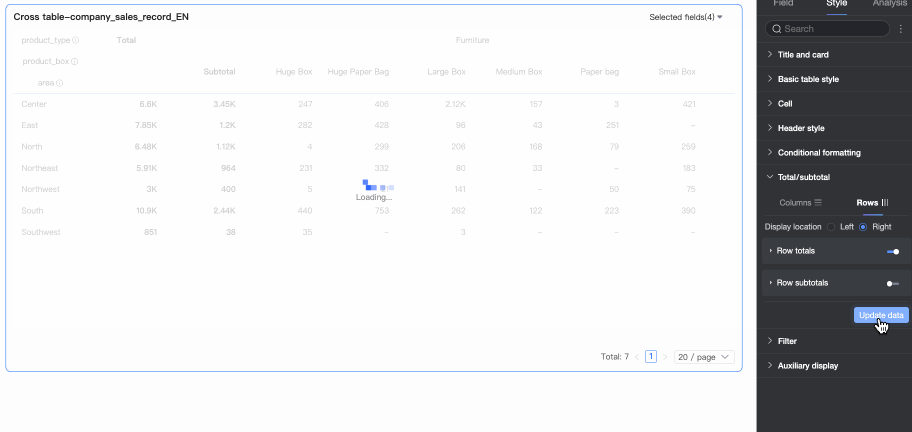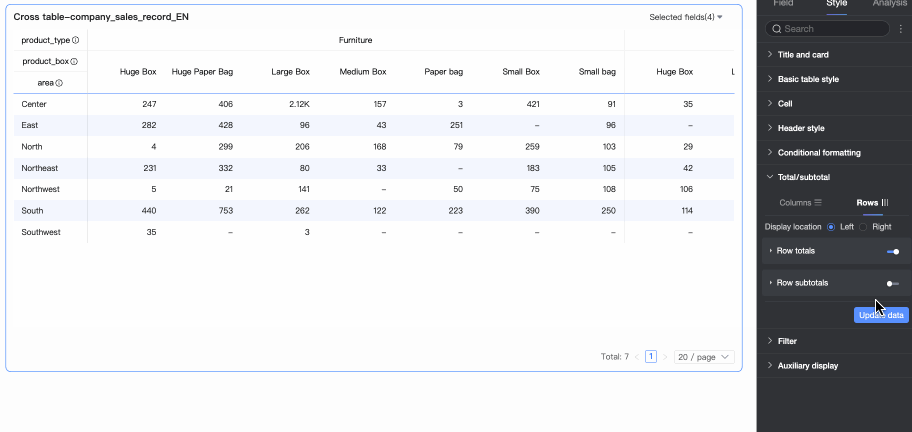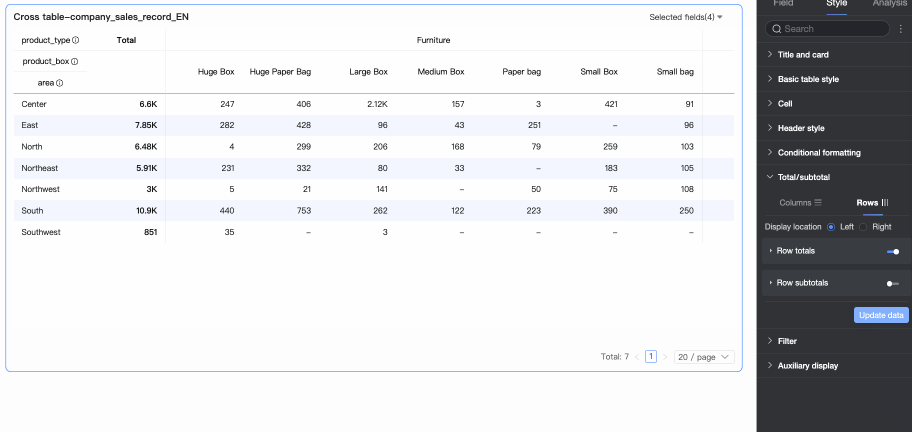
Overall Summary (Row Grand Total)
Use the switch
 to enable or disable row grand totals. When enabled, it performs a grand total operation on all values in a row. You can also configure the following settings.
to enable or disable row grand totals. When enabled, it performs a grand total operation on all values in a row. You can also configure the following settings.
Total alias: You can set a display name for the grand total data based on its business meaning, for example: Total sales for all products.
Calculation method: Select a uniform grand total aggregation method for all fields. If a field is a calculated field, the selected aggregation method here will not take effect; the original aggregation method will be used.
Style configuration: Set the text style for the current grand total data. You can choose to follow the system default or customize the text's font color, background color, weight, etc.
Classified Summary (Row Subtotal)
Use the switch
 to enable or disable row subtotals. When enabled, it performs a subtotal operation on each category of data in a row, based on the selected category dimension. You can also configure the following settings.
to enable or disable row subtotals. When enabled, it performs a subtotal operation on each category of data in a row, based on the selected category dimension. You can also configure the following settings.
Subtotal alias: You can set a display name for the subtotal data based on its business meaning, for example: Subtotal of sales in the Northeast region.
Summary dimension: Set the classification dimension for the subtotal, for example, to subtotal the sales for each product type.
Subtotal function: Select a uniform subtotal aggregation method for all fields. If a field is a calculated field, the selected aggregation method here will not take effect; the original aggregation method will be used.
Add subtotal: When you need to observe subtotal data from multiple classification dimensions simultaneously (for example, needing to see subtotals for each product type and sales in each region), you can click Add subtotal to add more subtotal dimensions.
Style configuration: Set the text style for the current subtotal data. You can choose to follow the system default or customize the text's font color, background color, weight, etc.
NoteFor frequently asked questions about total configuration, see the FAQ section.
In the Filter section
After you enable Enable field content filtering, you can click the Selected Fields dropdown list on the cross table to filter or sort fields in preview mode.
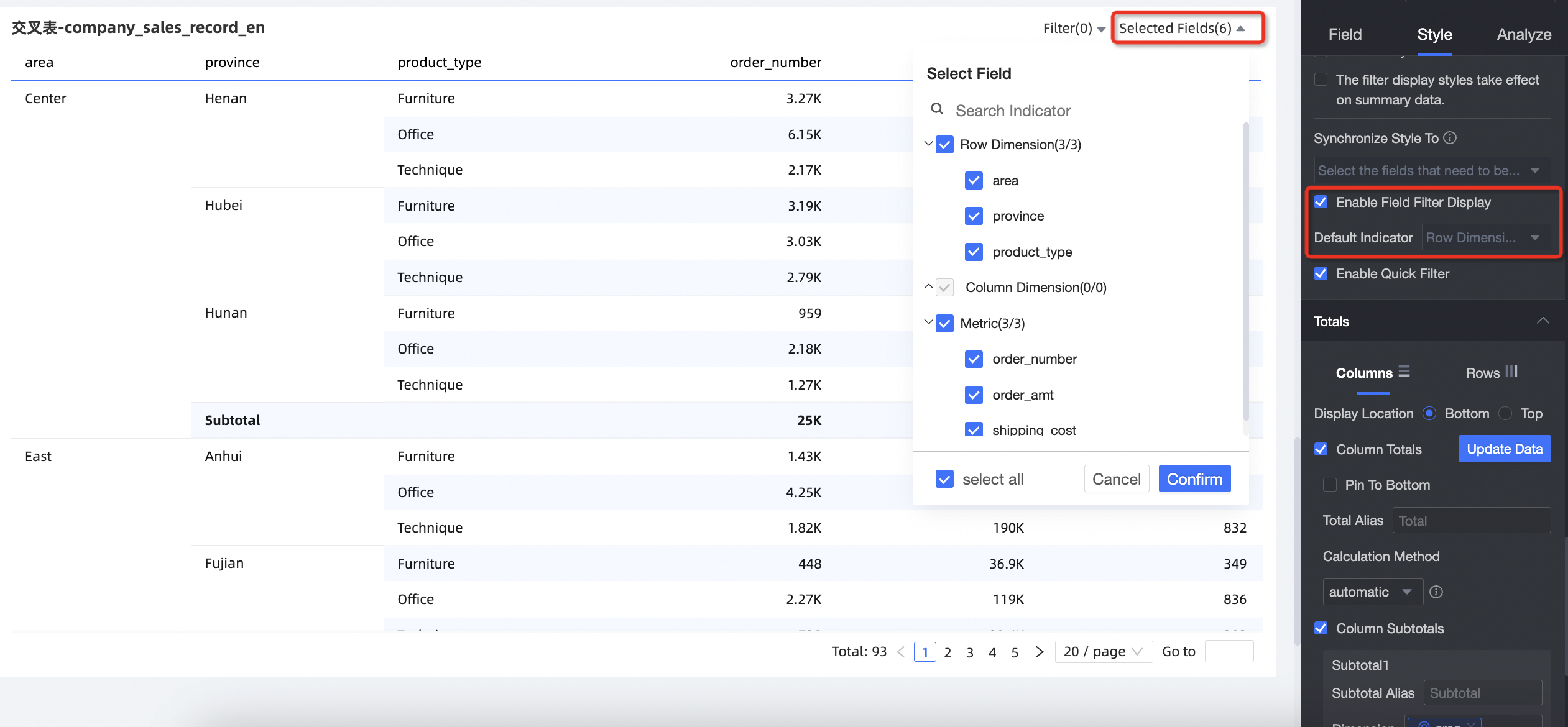
If a Form Entry event is configured and a field bound in the form is deselected, the form entry will not work correctly. For more information, see Field relationship mapping.
You can set default selected dimensions.
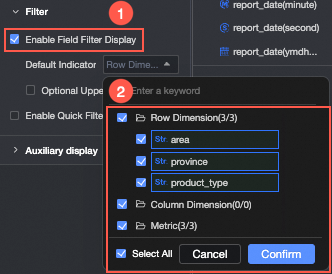
You can set the Maximum selectable dimensions.
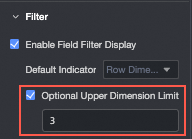
For example, if the maximum number of selectable dimensions is set to 6, you can select a maximum of 6 dimensions to display.
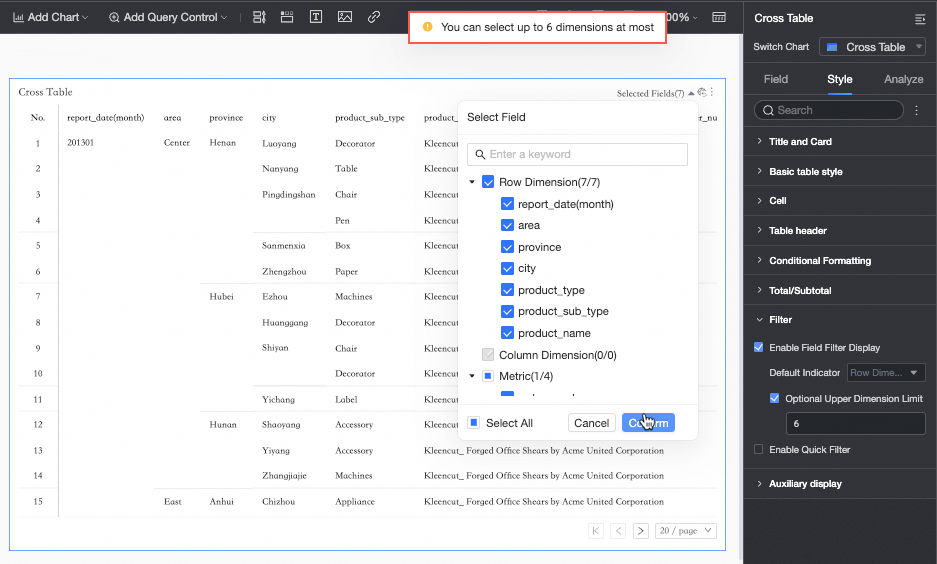
After you select Enable quick filter, you can click the Filter dropdown list on the cross table to filter fields in preview mode.
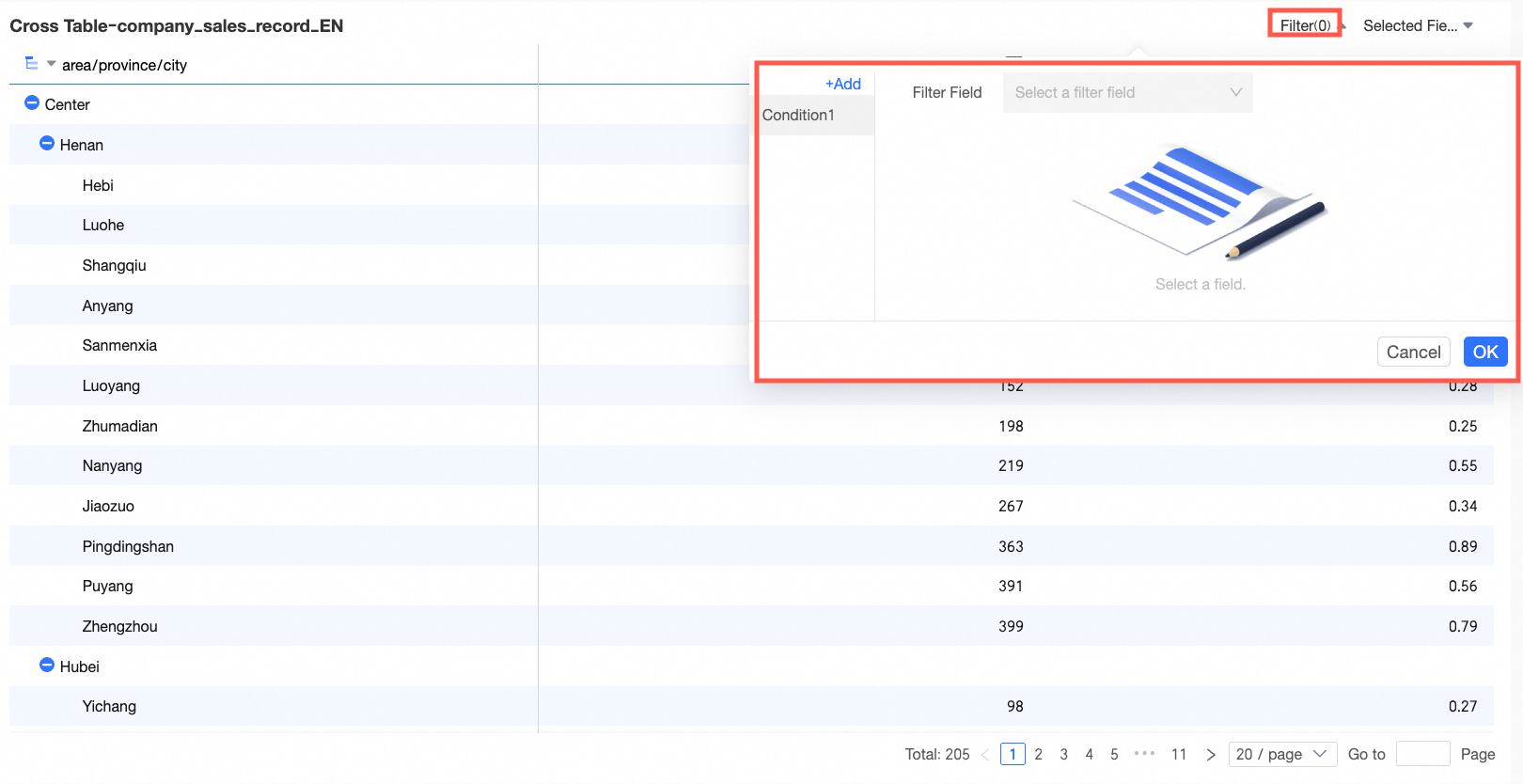
To filter multiple fields simultaneously, you can add multiple conditions in the dialog box that appears.
Scenario example: Analyze the city distribution in the South China region where the shipping cost is
>300and the discount point is>0.5.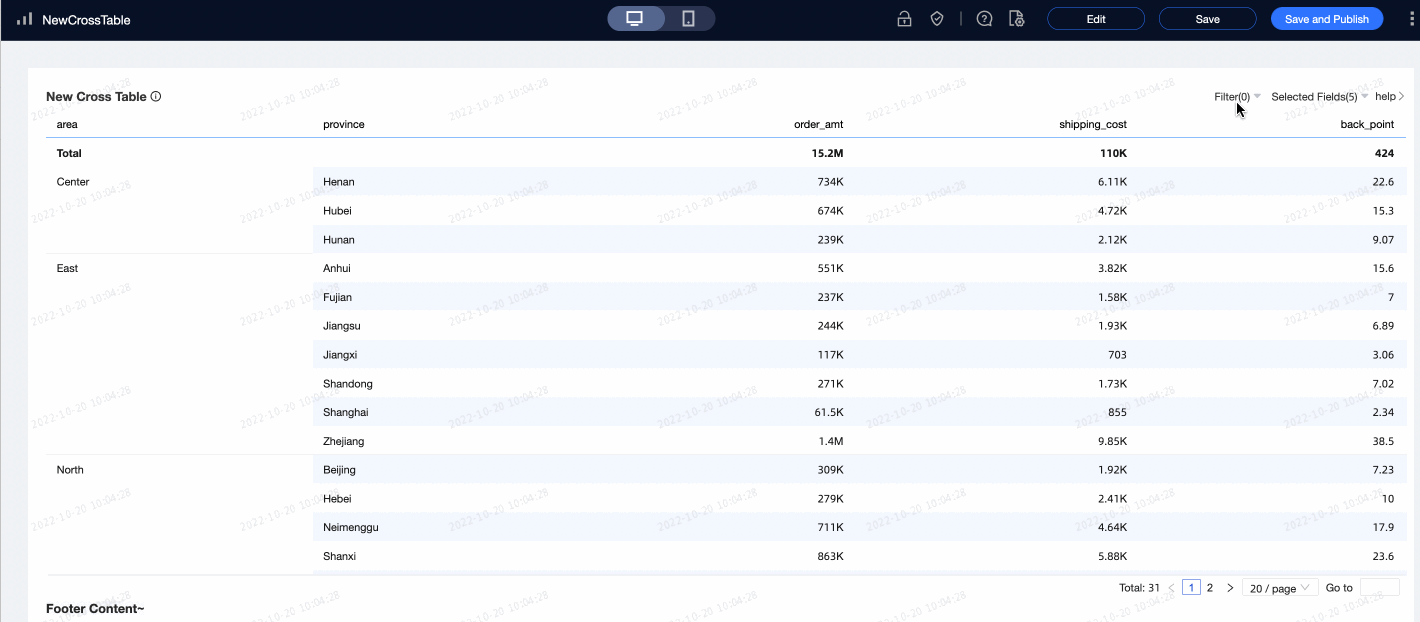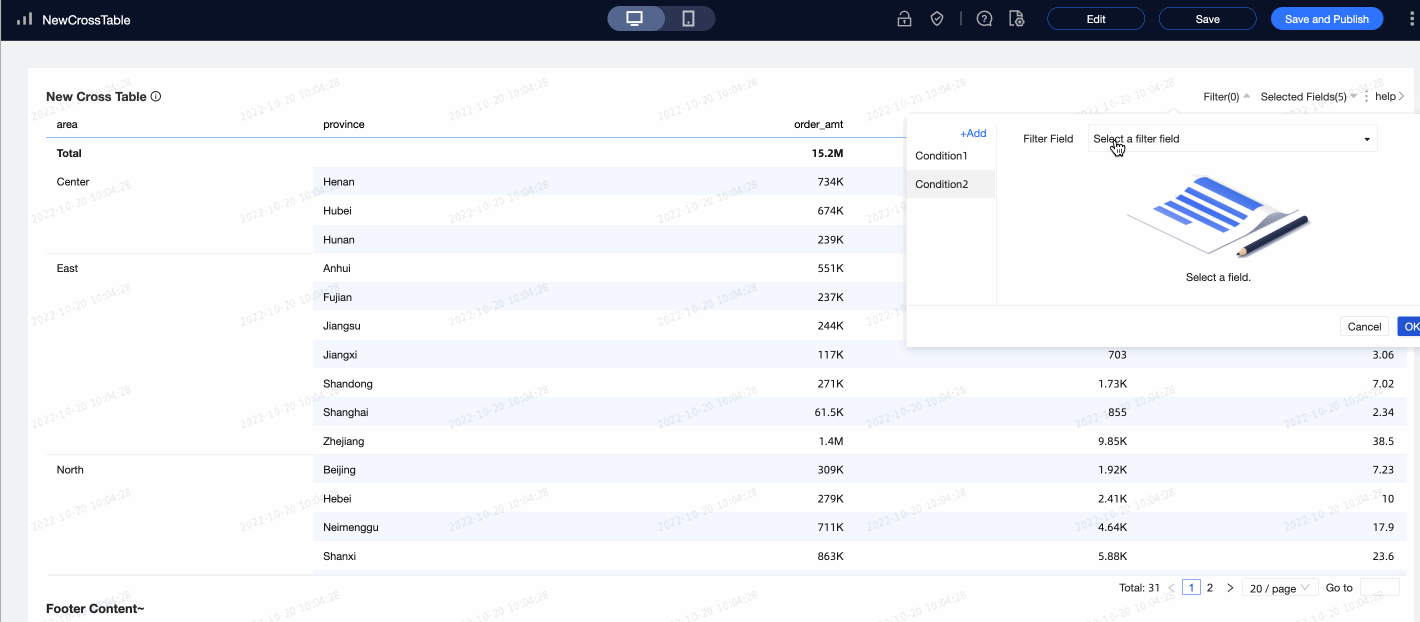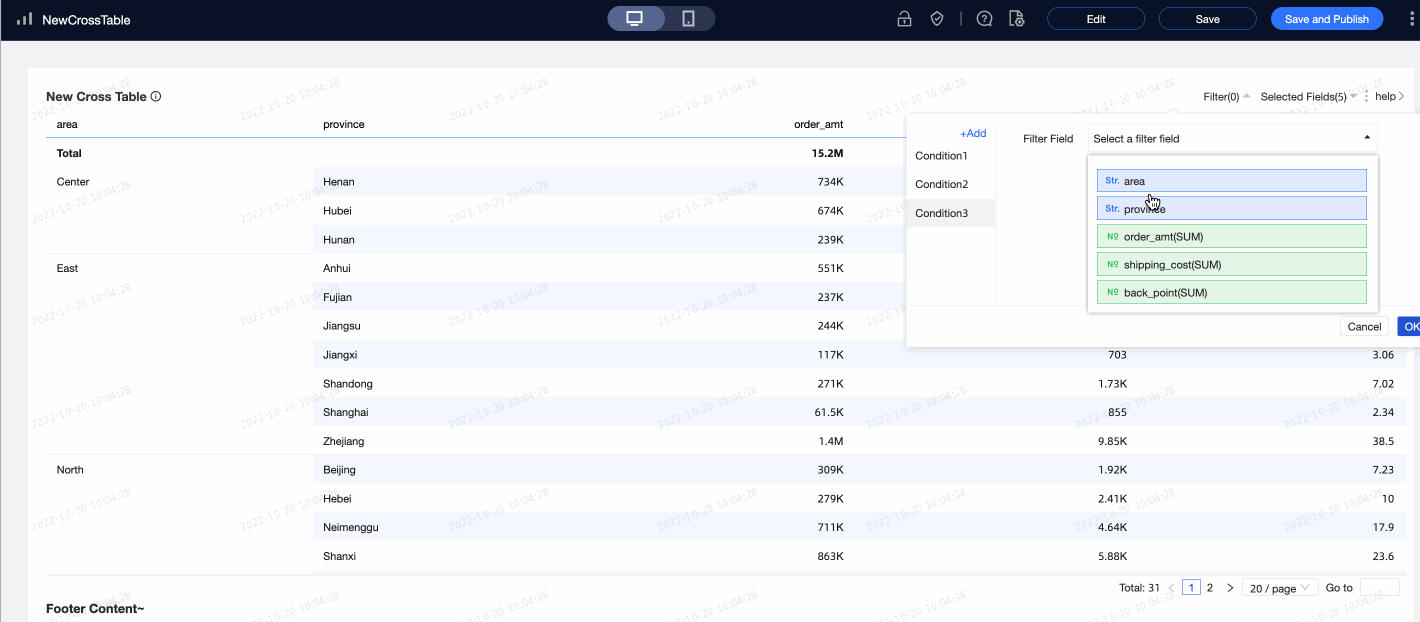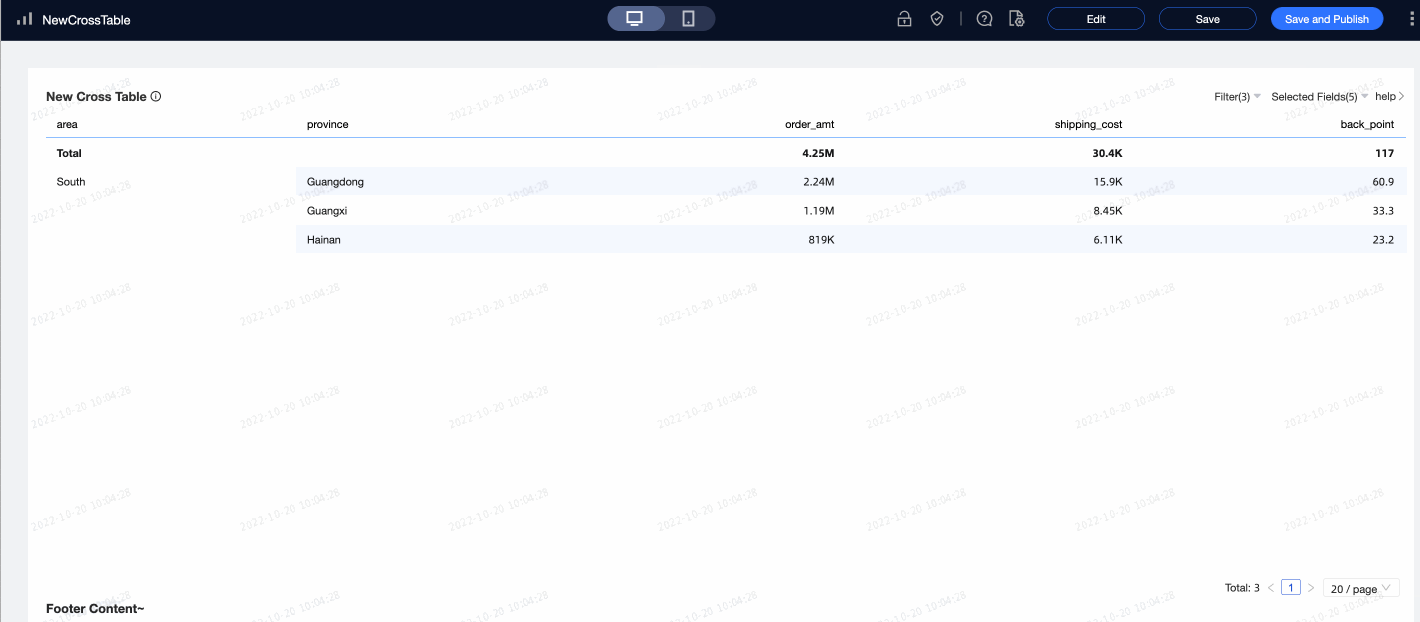 Note
NoteFilter conditions applied in preview mode are not saved by default. If the page is closed and reopened, you must re-apply the filter conditions.
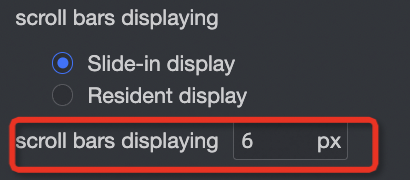
In the Auxiliary Display section, you can set the Scrollbar display mode and Scrollbar thickness.
If you set the display mode to Show on hover, the scrollbar appears only when you move the mouse pointer over the table.
If you need the scrollbar to be always visible, you can select Always show.
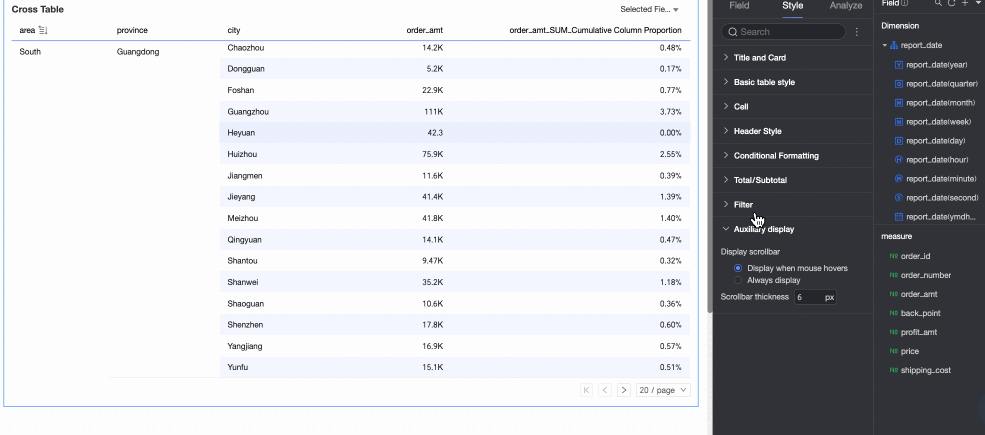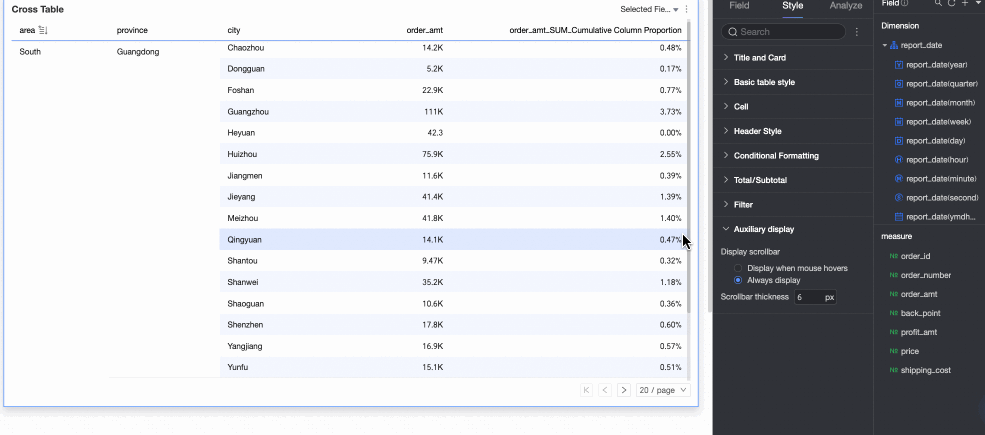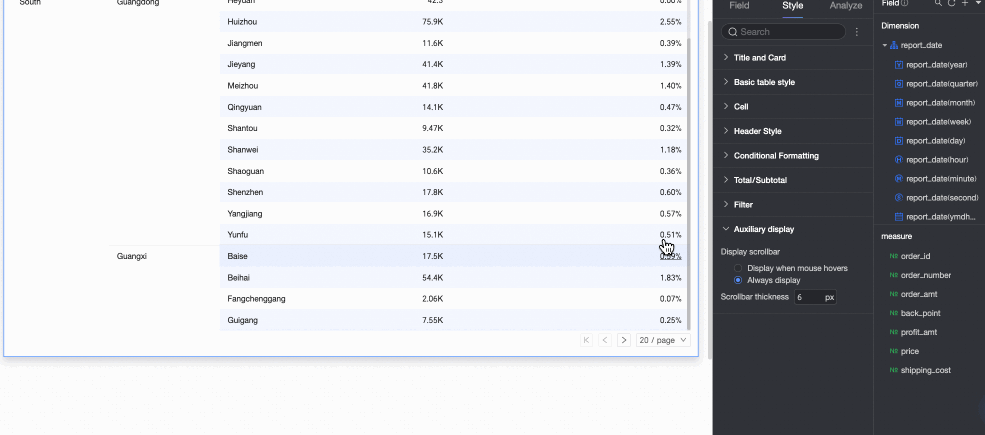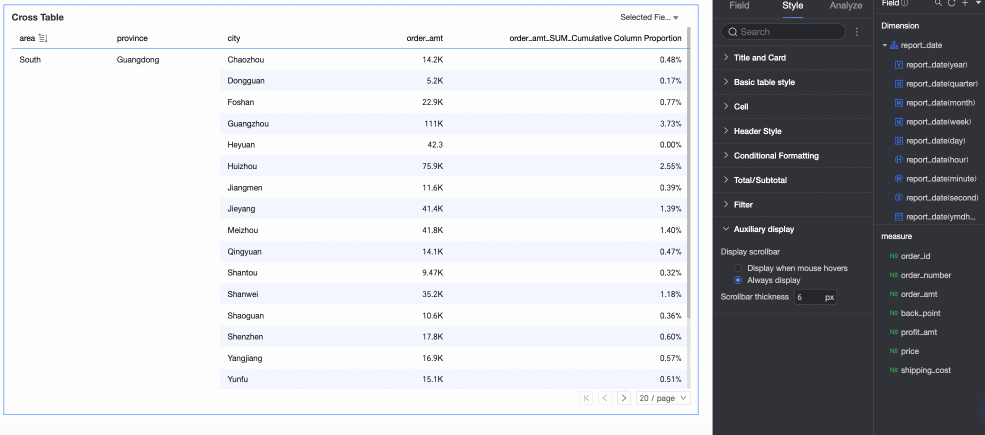
To make the scrollbar more prominent, you can adjust its thickness.
Adjust styles on the Chart
In addition to using the style settings, you can also configure the following options directly on the cross table:
Click a target column on the cross table. A dropdown list with configuration options appears. Configure the cross table as needed.
Adjust the number of items per page on the cross table.
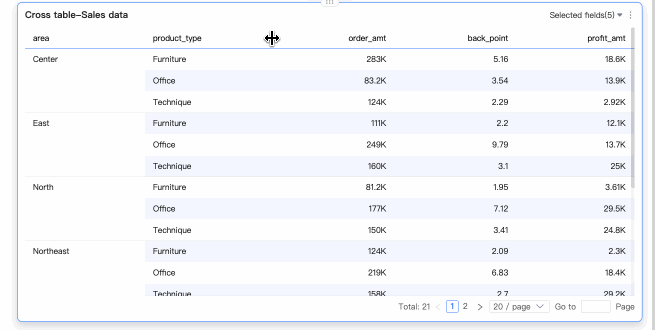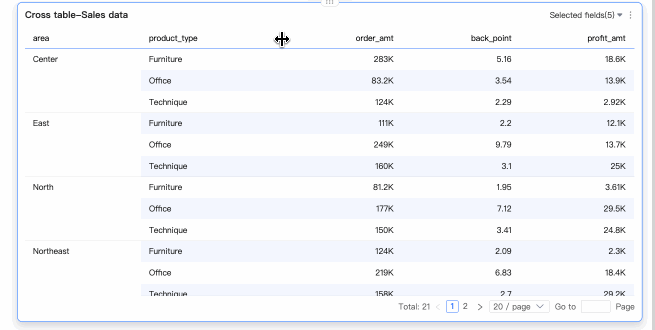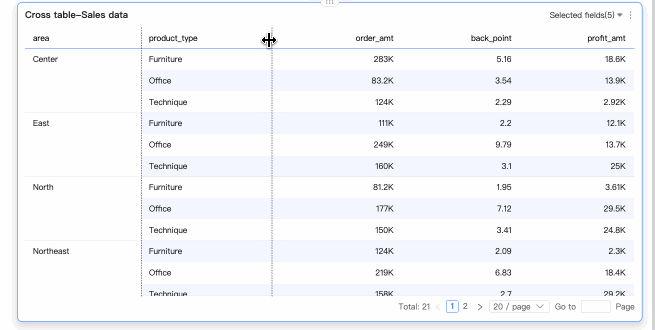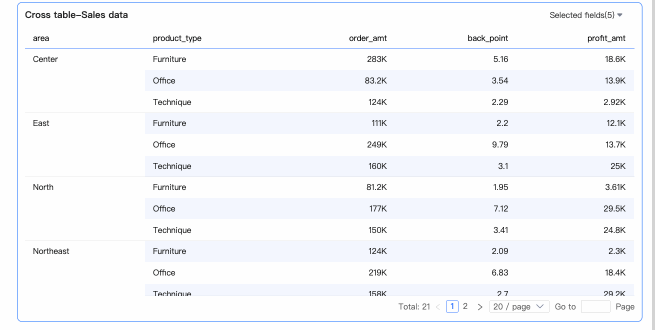
Drag to adjust the column width on the cross table.
Configure chart Analysis
Configuration item | Name | Description |
Data Interaction | Drill-down | When you have configured the drill-down feature for the chart, you can configure the display style of the drill-down level rows. For more information, see Drill-down. |
Linkage | When the data you need to analyze exists in different charts, you can use chart linkage to associate multiple charts for data analysis. For more information, see Linkage. | |
Jump | When the data you need to analyze exists in multiple dashboards, you can use dashboard jumping to associate multiple dashboards for data analysis. Jumping includes two methods: Parameter Jump and External Link. For more information, see Jump. | |
Advanced Settings | Events | After selecting this option, you can perform data entry in the cross table. When column dimensions exist, you can only add row dimensions to configure events. For more information, see Events. |
Enable secondary metric display | Select this option to set the display format for secondary metrics. For more information, see Enable Secondary Metric Display. |
Export Data
You can export data only after you enable the export switch. For more information, see Export controls.
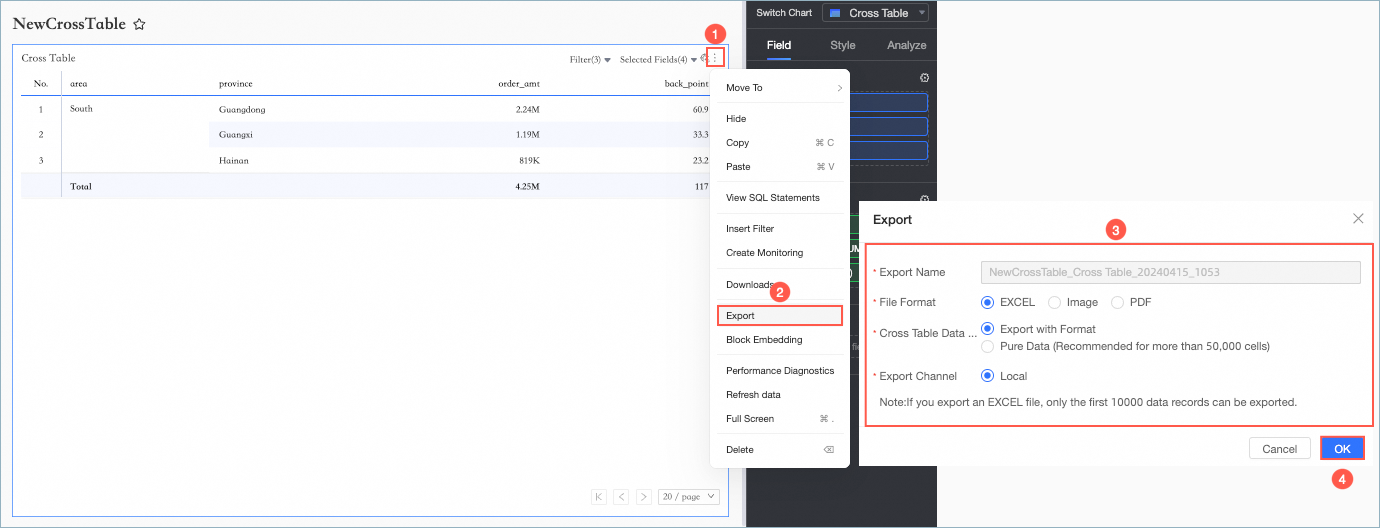
Parameter | Description |
Export Name | You can customize the name of the exported attachment. |
File Format | Supports exporting in Image, PDF, and EXCEL formats. Note When exporting a cross table, if you choose EXCEL as the file format, you can select the cross table data type as Export with format or Pure data.
Organization administrators can configure the data export format. For more information, see Export controls. |
Watermark | You only need to configure this option when the file format is EXCEL. You can choose whether to display a watermark based on your needs. |
Export Channel | Supports exporting to Local or the OSS server. |
Enable Secondary Metric Display
After you configure measures, you can enable and configure secondary measures.
After selecting Enable secondary metric display, you can select any measure from the comparison metric dropdown list.
Comparison date selection: You must select a date field.
NoteIf a date field is in the chart, the secondary measure comparison date can only be the date field with the smallest granularity in the chart.
If no date field is in the chart, the secondary measure comparison date can be any date field in the dataset.
Comparison method: The comparison options displayed depend on the granularity of the date field. A maximum of four comparison fields appear. For example, if the Comparison date is set to day granularity, the Comparison content selection displays compare (day to day), week on week, month on month, and year on year. If the Comparison date is set to month granularity, the Comparison content selection displays month on month and year on year.
Select comparison measure: Select an existing measure on the dimension to configure.
Display content: By default, Difference percentage is selected. You can also select Difference or Original value.
Difference: The data is displayed in the same format as the metric.
When you select Difference, you can also select Calculate percentage point difference for percentage metrics. By default, this is not selected. If you select this option and the measure is in a percentage format, the display content automatically calculates the difference value. For example, 5.2% - 4.1% = 1.1 pt.
Difference percentage: The value is displayed with two decimal places.
Period-over-period comparison (effective only when the query filter is bound to day granularity): If a filter condition is configured, the period-over-period comparison also includes the filter. For example, if the filter condition is set to 2022-01-02, the year-over-year comparison for 2021 also includes the 2021-01-02 filter condition. Day-over-day comparison automatically supports period-over-period comparison, but dynamic period-over-period comparison does not.
When data from the previous period is negative: Select the formula for calculating the difference percentage. The formula you select takes effect only for data items where the previous period's data is less than 0. You can set it to:
(Current period data / Previous period data - 1) * 100% is the default calculation.
(1 - (Current period data / Previous period data)) * 100
Display as -
Synchronize comparison measures: You can sync the configuration of the current measure to other measures.
Display position: The position of the display. The default value is Right of metric. You can also set this parameter to Independent right or Below metric.
Right of metric: A new metric column is added to the right of the current metric. This column is named according to the selected comparison method, such as year-on-year, day-on-day, month-on-month, or week-on-week.
When the measure is in a column, the secondary measures are displayed sequentially to its right.

Independent right: Appears separately to the right of the current metric.
If the metric is in a column, the last column dimension splits to show day-on-day and week-on-week comparisons. As shown in the figure below, the dimension value All splits into All, All (day-on-day), and All (week-on-week). Two metrics appear under each dimension value.

If the measure is in a row, the last row dimension is split to display day-on-day and week-on-week comparisons. This is similar to when the measure is in a column, but the comparison is displayed below instead of to the right.
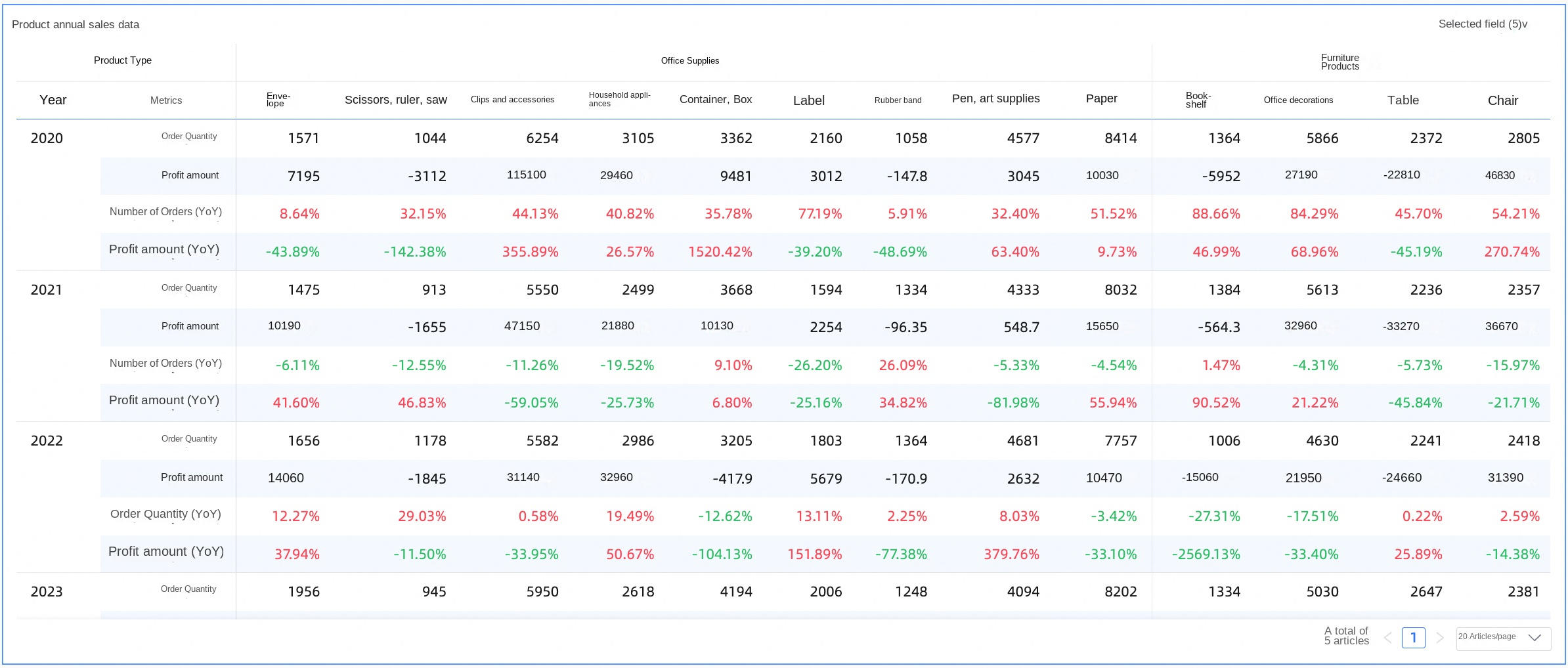
Below metric: Adds multiple rows of comparison metrics below the current metric. The added metrics use the same alignment as the current metric: text is left-aligned and numbers are right-aligned.
It shares a row cell with the current measure. A new row, named after the selected comparison method (such as day-on-day, week-on-week, month-on-month, or year-on-year), is added below the current measure's header name.

Display style: Select the display color for positive and negative numbers in the table. You can choose to follow the Global semantic color settings (the settings in Page Settings > Global Style > Semantic Color), Positive numbers show red, negative numbers show green, or Positive numbers show green, negative numbers show red.
FAQ
1. Totals Configuration FAQ
Notes on total calculation
If the original data is GMV (Sum) and the calculation method for totals and subtotals defaults to Automatic, the calculation logic for both is GMV (Sum). If you switch the total to Custom and select Average as the aggregation method, the calculation logic for the total becomes GMV (Average).
If the user’s original data is id (Distinct Count) and the calculation method for totals and subtotals is set to Automatic, the totals and subtotals are calculated using id (Distinct Count). If the user switches the total calculation to Custom and selects Count as the aggregation method, the total is calculated using id (Count).
What is the calculation logic for ratios?
Define the ratio.
In this example, assume the ratio is defined as (Measure A / Measure B).
You can create a new calculated field in the dataset and set the expression to rate=sum(A)/sum(B).
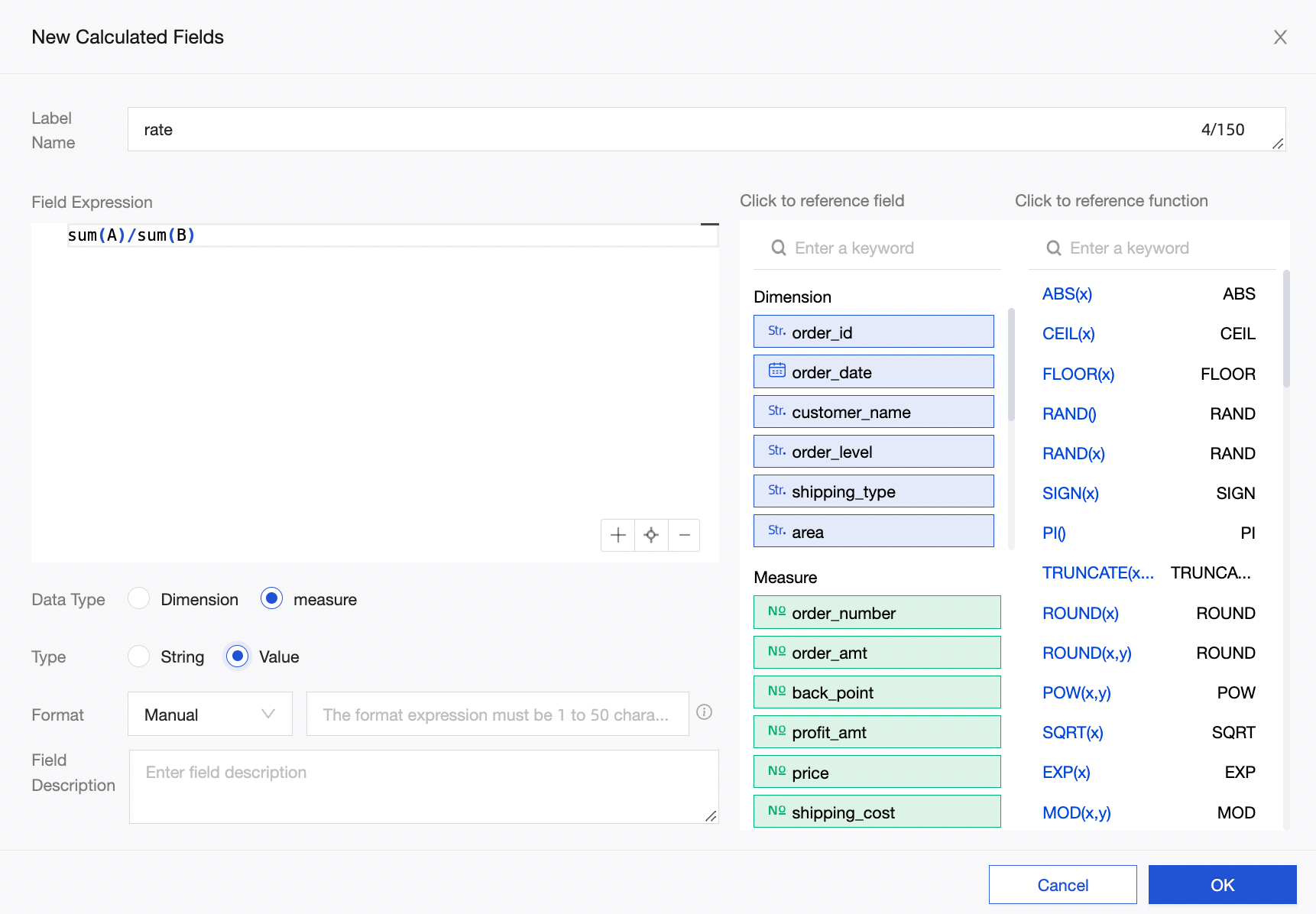
On the dashboard’s data panel, select the rate (Sum) metric and review the totals and subtotals. The calculation logic defaults to automatic rate (Sum), so totals and subtotals use the sum(A)/sum(B) calculation logic.
NoteIf you write the expression in the dataset as rate=A/B and then check totals and subtotals, the automatic calculation logic will use A/B (Sum). This can result in an abnormal situation where the ratio exceeds 100% and the calculation is incorrect.
2. Summary Configuration Notes
For the percentage of the parent column summary to take effect, the following two conditions must be met:
The measure field is placed in Rows, and the dimension field is placed in Columns.
There are 2 or more dimension fields.
3. How do I create a calendar in a cross table?
You can achieve a similar effect by setting a conditional format on the Week number field to hide text, and on the Date field to display different colors for different values.