Data ranking sorts data by size, making it easier for users to compare values. In data analytics, you can view the ranking of measures to help you make informed decisions. This topic describes how to set up data ranking.
Prerequisites
You have created a dashboard. For more information, see Create a Dashboard.
A dataset is selected and chart fields are configured. For more information, see Configure Chart Fields.
Limits
This analysis method is based on the returned result set calculation. The current limit in the public cloud is 10,000. If the total returned data exceeds 10,000, the calculation results may not meet expectations.
The charts that support data ranking are shown below.
Data ranking method
Description
Supported chart types
Overall ranking
Overall ranking refers to the ranking of a data point among all data points.
Line/Area charts: line chart, area chart, stacked area chart, 100% stacked area chart, combination chart.
Column/Bar charts: column chart, stacked bar chart, 100% stacked bar chart, circular column chart, leaderboard, bar chart, stacked bar chart, 100% stacked bar chart, dynamic bar chart, waterfall chart.
Bubble/Scatter charts: bubble chart, scatter chart, facet scatter chart.
Table charts: cross table, detail table, heat map.
Pie/Ring charts: pie chart, rose chart, radar chart, treemap chart.
Geographic charts: color map, bubble map, heat map, flow map, symbol map.
Metric charts: metric card, metric trend chart.
Funnel/Conversion charts: funnel chart, comparison funnel chart.
Other charts: word cloud.
Group ranking
Group ranking refers to the ranking of a data point within its group.
Table charts: cross table.
Configuration Entry
In the Fields panel of the chart, find the measure field that you want to rank, click the  icon on the right, and select Advanced Calculation > Ranking from the dropdown list. Then set the ranking type according to your business scenario.
icon on the right, and select Advanced Calculation > Ranking from the dropdown list. Then set the ranking type according to your business scenario.
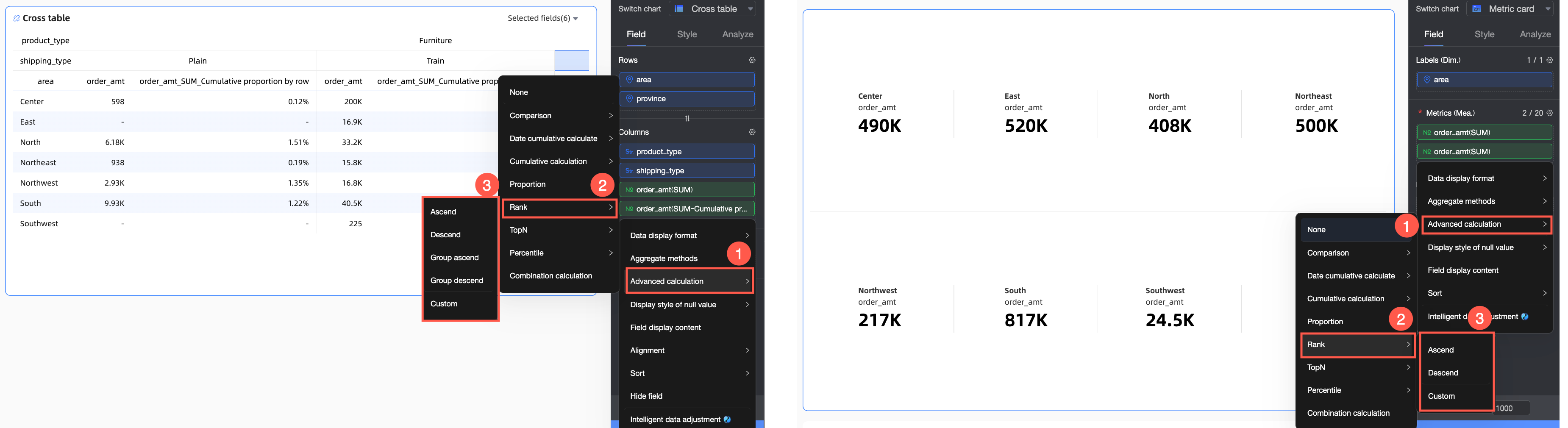
The ranking calculation types and ranking methods available for each chart are described below.
Ranking calculation types
Chart type
Ranking calculation type
Limitations
Calculation logic
Cross table
Ascending
/
Ranks the overall data from smallest to largest based on metric values.
Descending
/
Ranks the overall data from largest to smallest based on metric values.
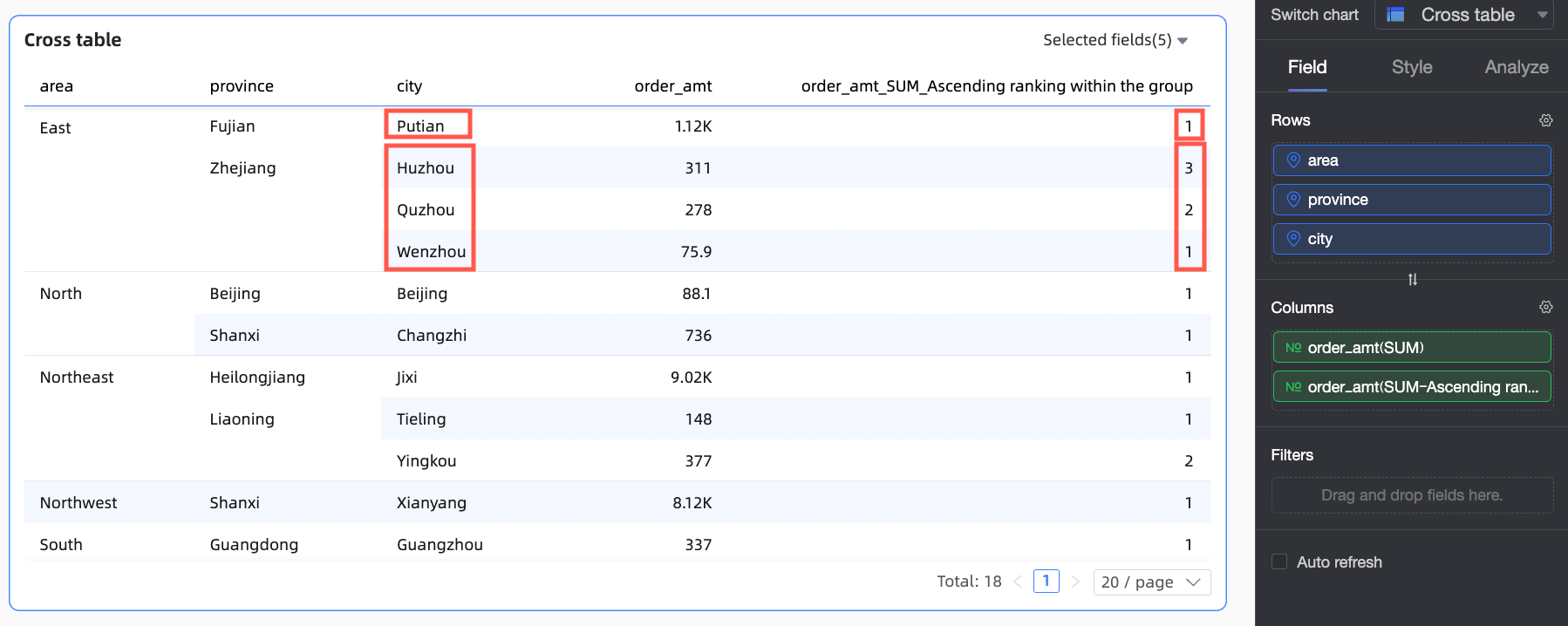
Ascending within group
/
Groups data by the finest granularity and ranks data points from smallest to largest within each group. For example, if there are three dimensions: region, province, and city, cities are grouped by their respective provinces and regions, and then ranked in ascending order.
Descending within group
/
Groups data by the finest granularity and ranks data points from largest to smallest within each group.
Custom
Rank by column
Dimension fields in the Row area
Treats each column as an independent analysis unit and calculates the ranking of a data point within the total number of data points in a column.
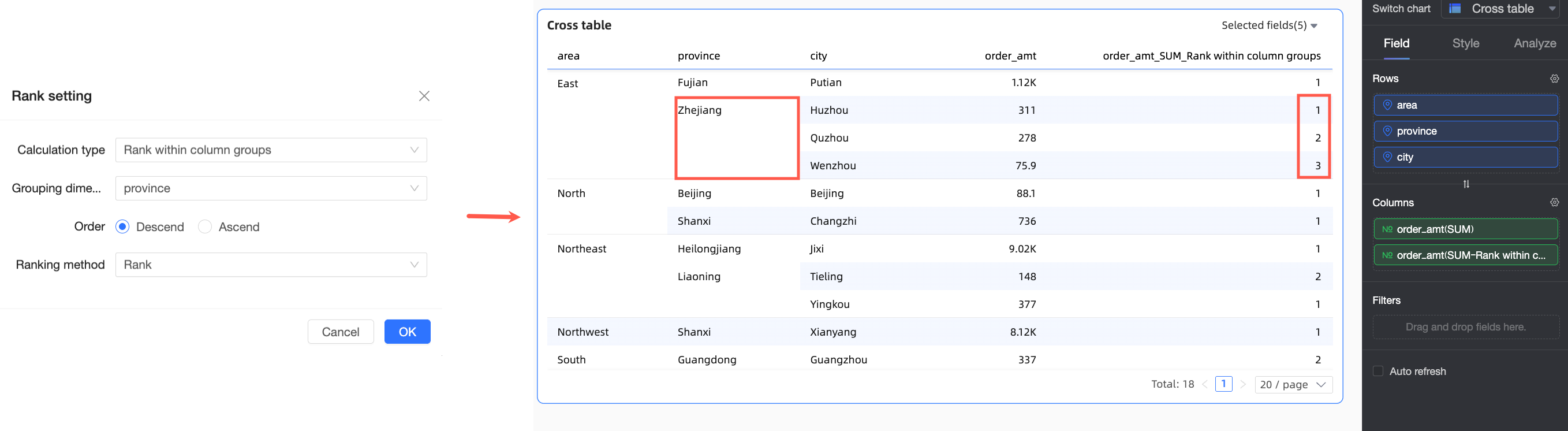
Rank within column group
Two or more dimension fields in the Row area
Calculates the ranking of the current data point within its column group.
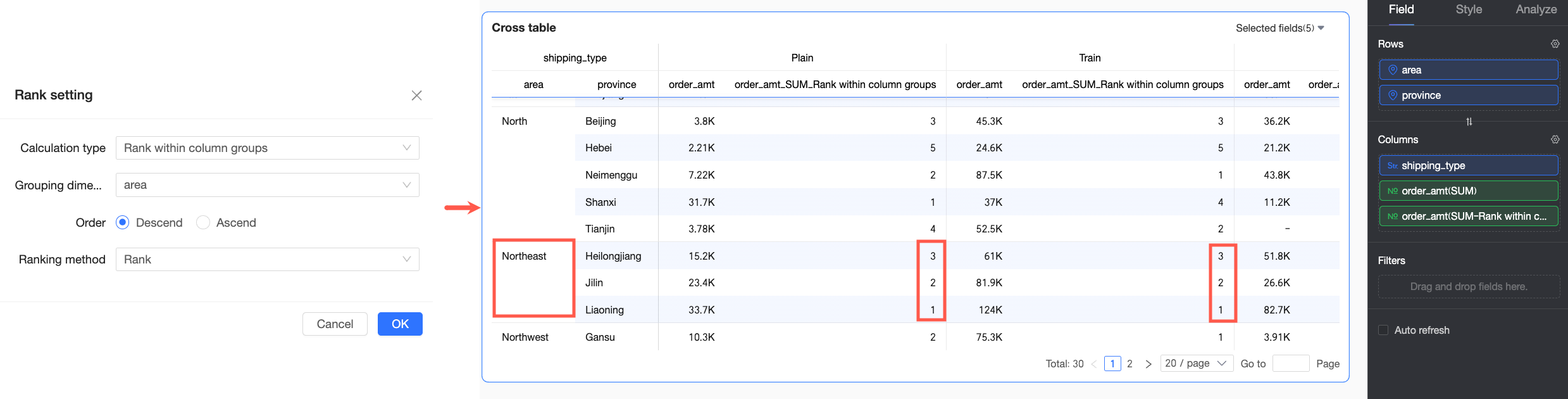
The grouping logic is as follows: starting from the first dimension in the row area up to the selected grouping dimension, all dimensions in between are treated as a whole for grouping. For example, in the following figure, the Region and Province fields are matched for grouping, and ranking is performed at the Province dimension.
Rank by row
Dimension fields in the Column area
Treats each row as an independent analysis unit and calculates the ranking of a data point within the total number of data points in a row.
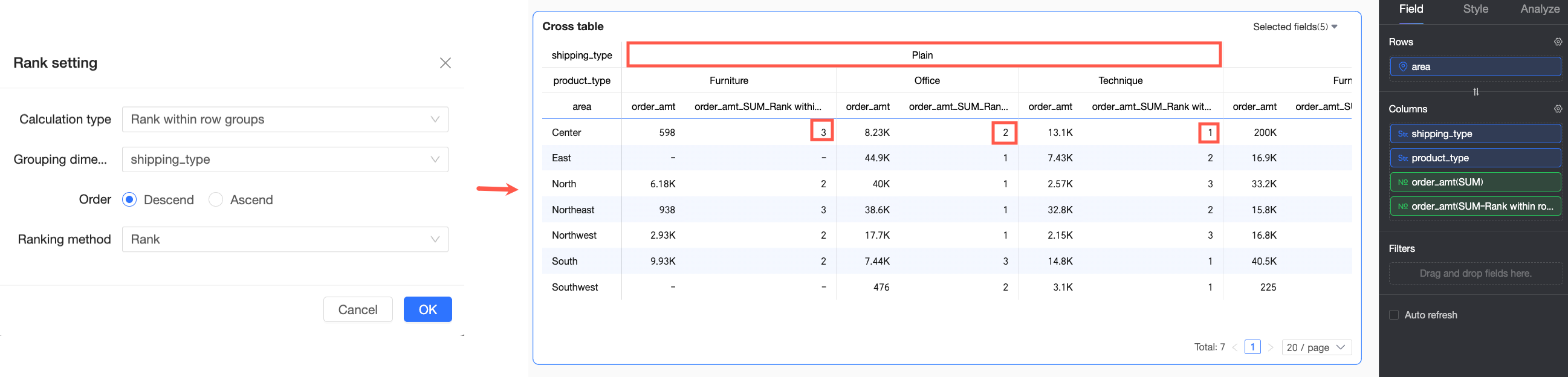
Rank within row group
Two or more dimension fields in the Column area
Calculates the ranking of the current data point within its row group.
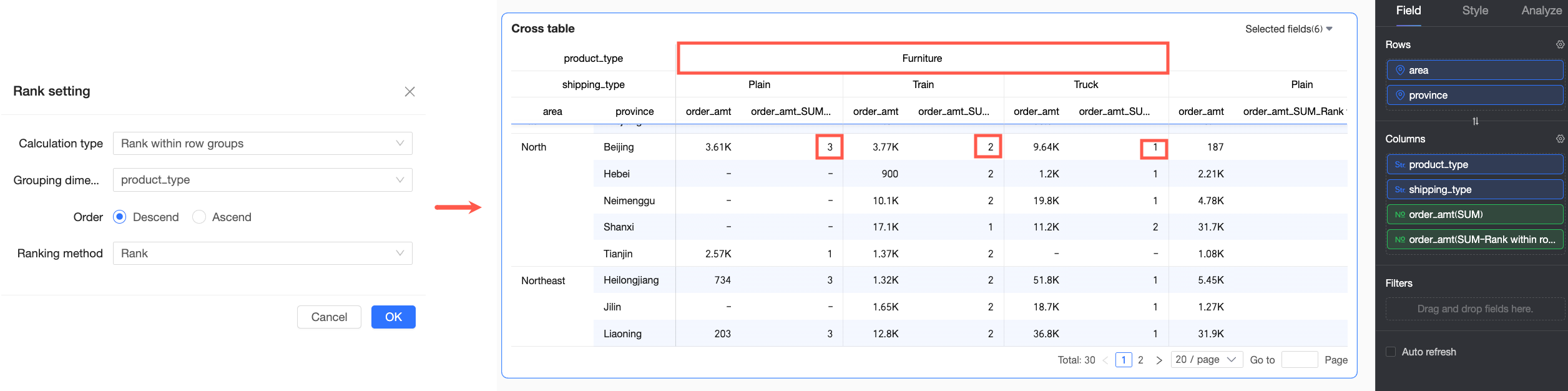
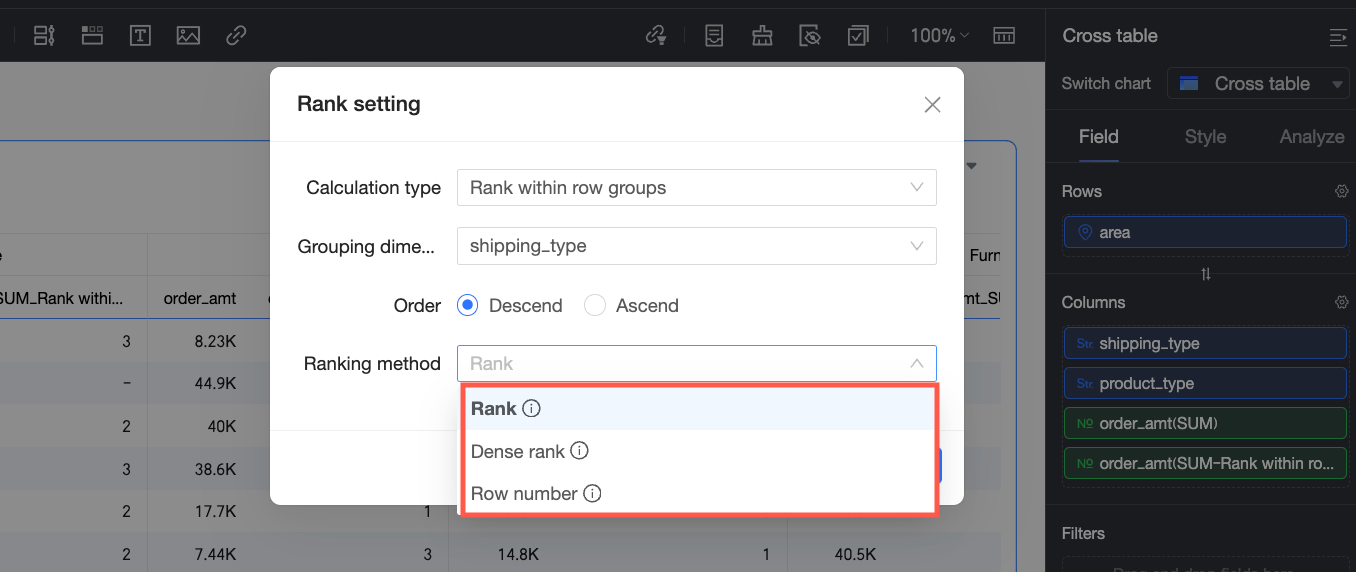
The grouping logic is as follows: starting from the first dimension in the column area up to the selected grouping dimension, all dimensions in between are treated as a whole for grouping. For example, in the following figure, grouping is performed on the Shipping Mode field, and ranking is done within this dimension.
Other charts
Ascending
/
Ranks the overall data from smallest to largest based on metric values.
Descending
/
Ranks the overall data from largest to smallest based on metric values.
Custom
/
Customizes the ranking order and ranking method.
Ranking method: When a chart uses the Custom ranking calculation type, you can configure the Ranking order and Ranking method as needed. The ranking method determines how to handle duplicate values in rankings. You can choose from the following three ranking methods.
Ranking method
Description
Example
Rank
Duplicate values have the same rank and occupy positions.
1, 2, 2, 4
Dense rank
Duplicate values have the same rank but do not occupy positions.
1, 2, 2, 3
Sequential rank
Duplicate values have different ranks.
1, 2, 3, 4
Application example 2: Setting up ranking in other visualization charts
Take the metric card ranking as an example.
Log on to the Quick BI console.
Follow the steps shown in the figure below to enter the dashboard editing page.
In the top menu bar, click Add Chart, find Metric Card, and click or drag it to the dashboard area.
In the Data Panel's Fields tab, configure the metric card data.
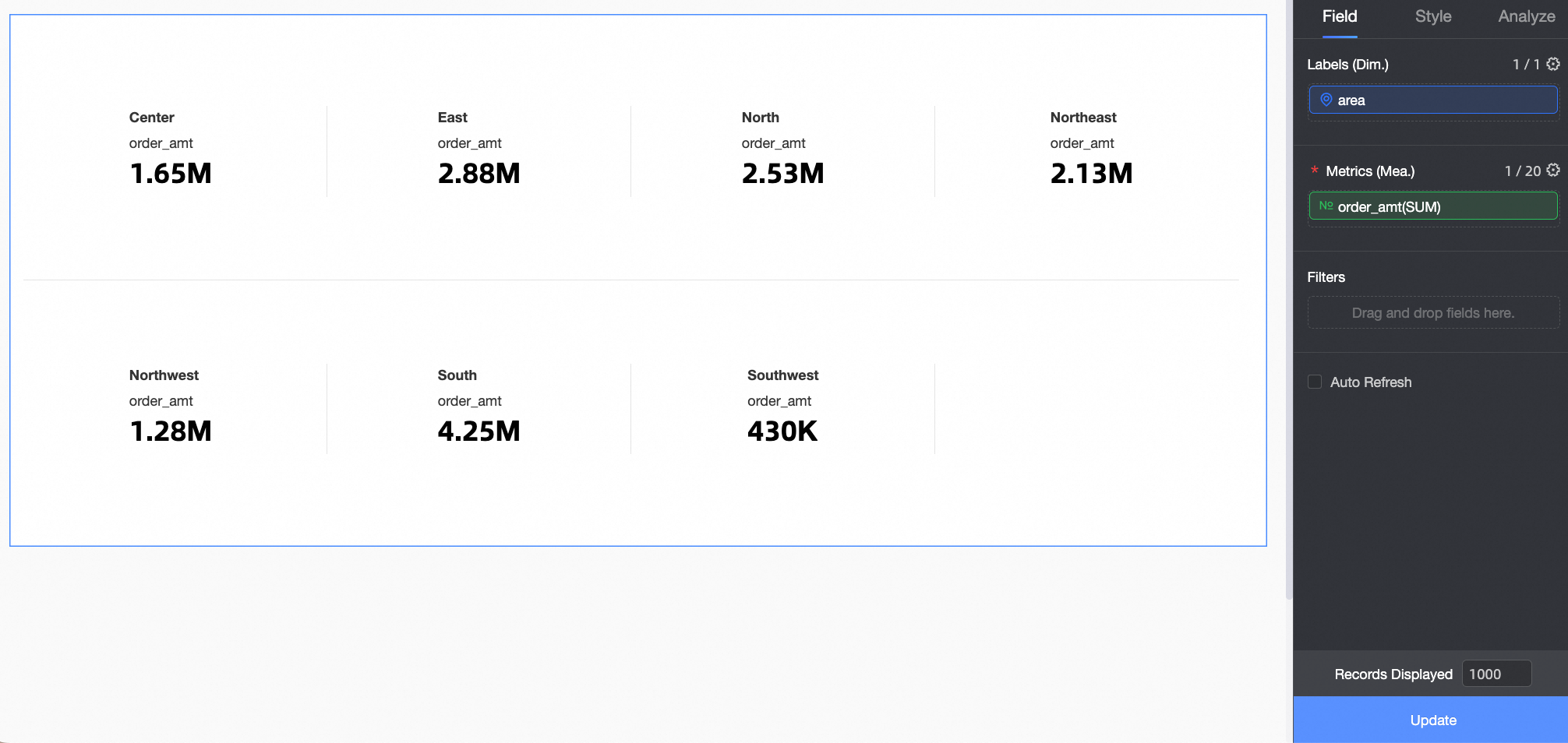
The target dataset is company_sales_record.
Select the required dimension and measure fields, double-click or drag them to the target area.
In the Dimensions list, find Region, double-click or drag it to the Row area.
In the Measures list, find Order Amount, double-click or drag it to the Column area.
Click Update.
The system automatically creates a metric card for you, as shown in the following figure.
Click the
 icon to the right of Order amount, select Advanced Calculation -> Ranking, and follow the steps shown in the figure below to enter the ranking settings.
icon to the right of Order amount, select Advanced Calculation -> Ranking, and follow the steps shown in the figure below to enter the ranking settings.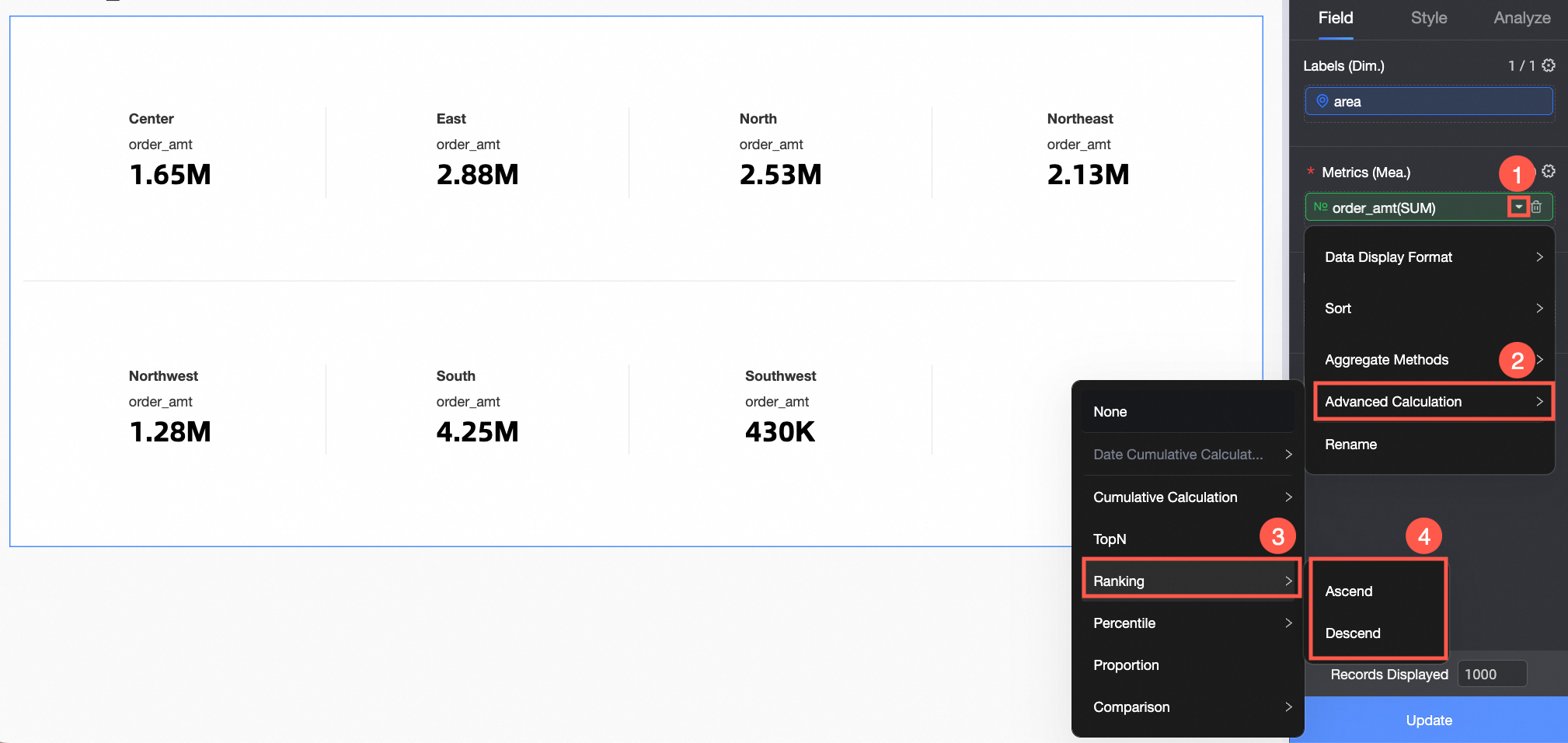
Visualization charts support Ascending and Descending ranking.
Click Update.
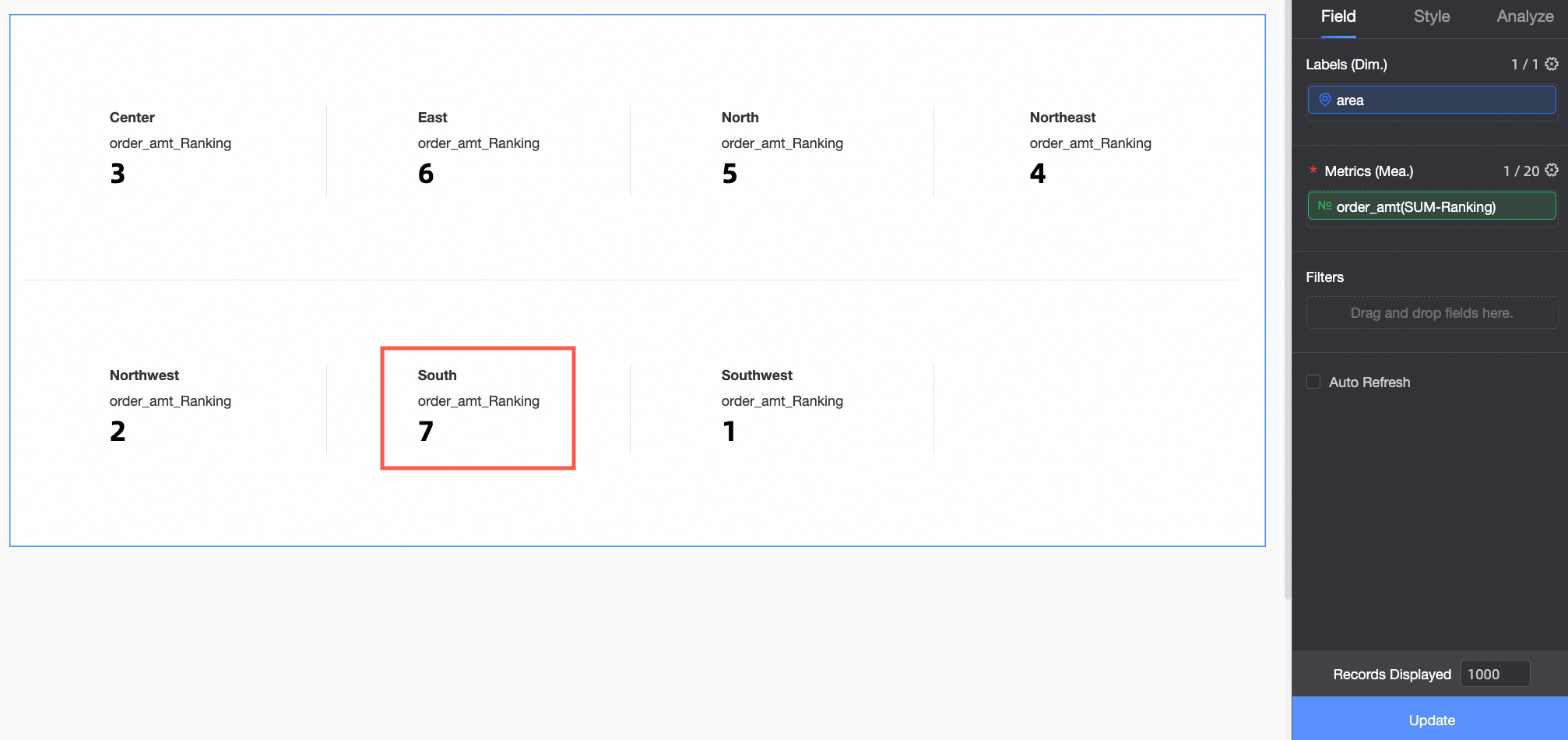
The Order amount ranking in the metric card is shown in the figure below.
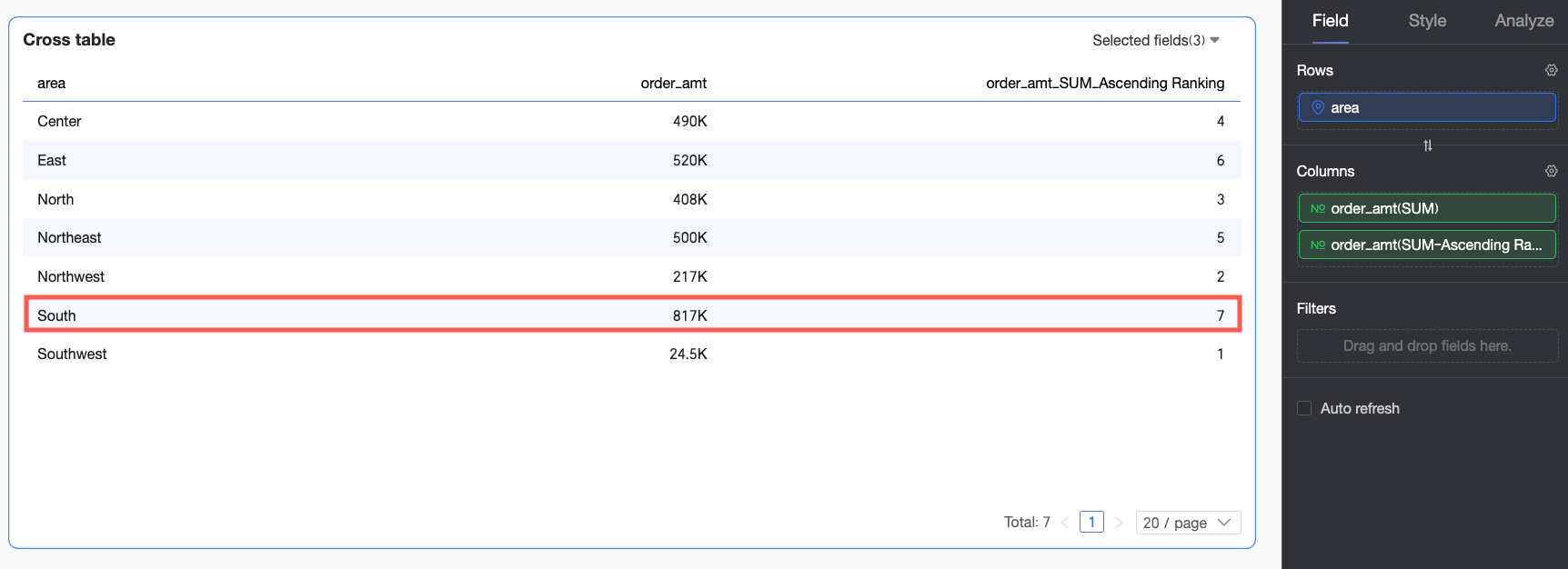
When Ascending ranking is selected for Order amount, the largest Order amount is ranked last. In this example, the South China region has the largest Order amount and is ranked No.7.
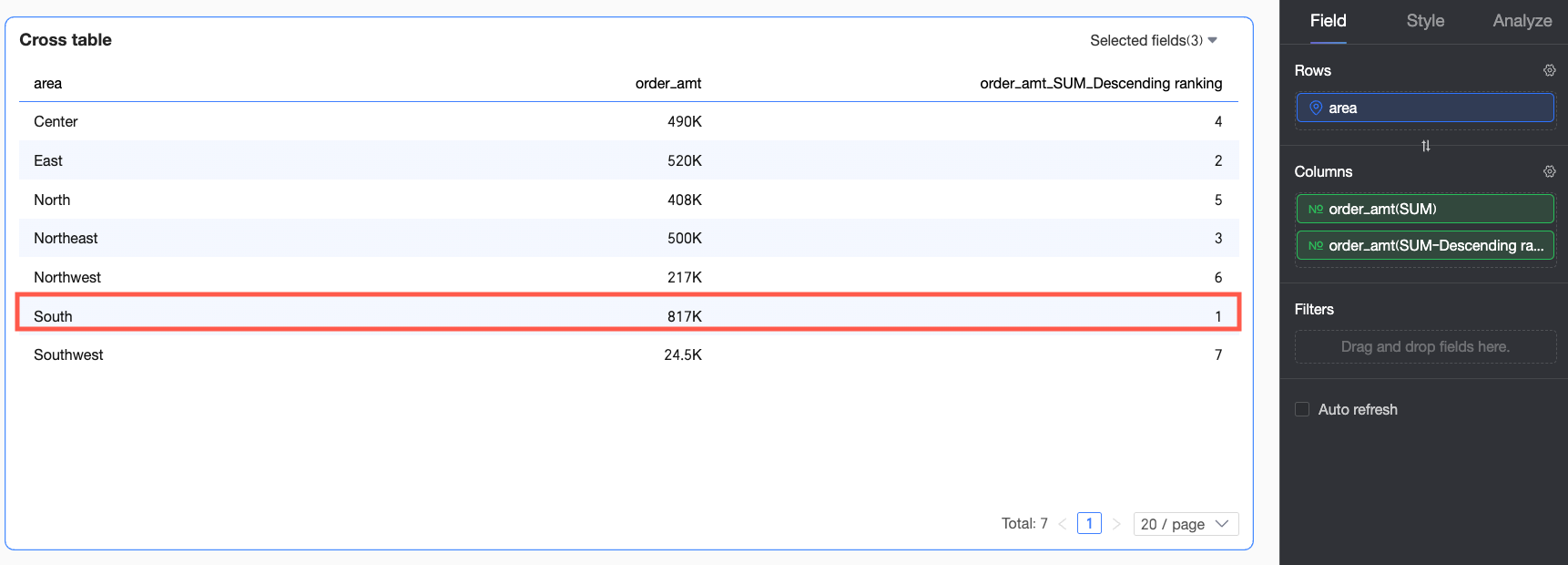
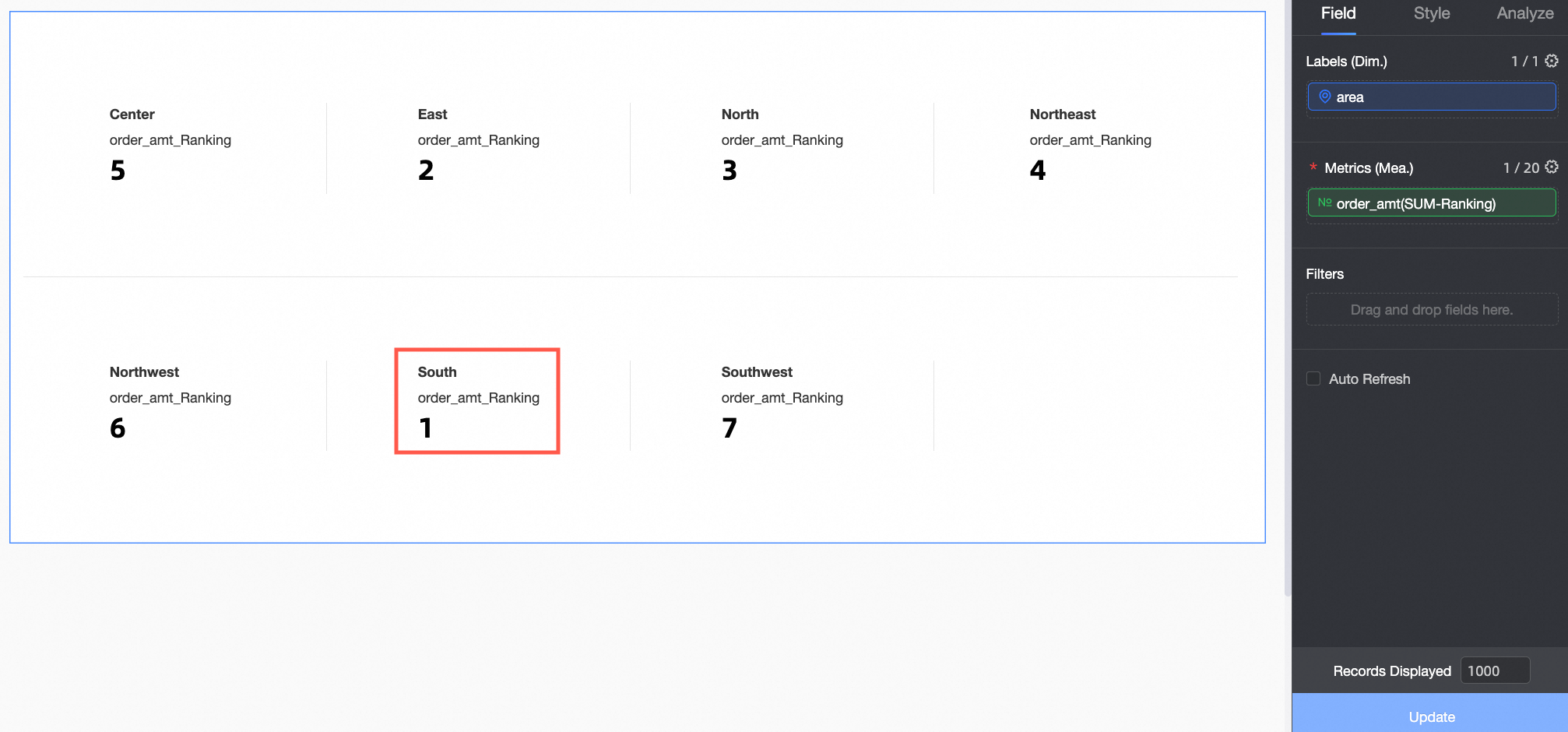
When Descending ranking is selected for Order amount, the largest Order amount is ranked first. In this example, the South China region has the largest Order amount and is ranked No.1.
Application Examples
The following examples help you better understand data ranking calculations.
Example 1: Metric Card
Take the metric card ranking as an example.
Log on to the Quick BI console.
Follow the steps shown in the figure below to enter the dashboard editing page.

In the top menu bar, click Add Chart, find Metric Card, and click or drag it to the dashboard area.
In the Data Panel's Fields tab, configure the metric card data.
Select the required dimension and measure fields, double-click or drag them to the target area.
In the Dimensions list, find Region, double-click or drag it to the Row area.
In the Measures list, find Order amount, double-click or drag it twice to the Column area.
NoteOf the two Order amount fields in the Column area, one displays the raw data and the other is set for cumulative calculation.
When there are two duplicate fields placed on measures, you will see a "Duplicate items exist in measures" prompt. Do not update the data yet. Update after the configuration is complete.
Click the
 icon next to the second Order amount field, select Advanced Calculation > Ranking. You can set different ranking methods for the current chart as needed. Specific examples are shown below.
icon next to the second Order amount field, select Advanced Calculation > Ranking. You can set different ranking methods for the current chart as needed. Specific examples are shown below.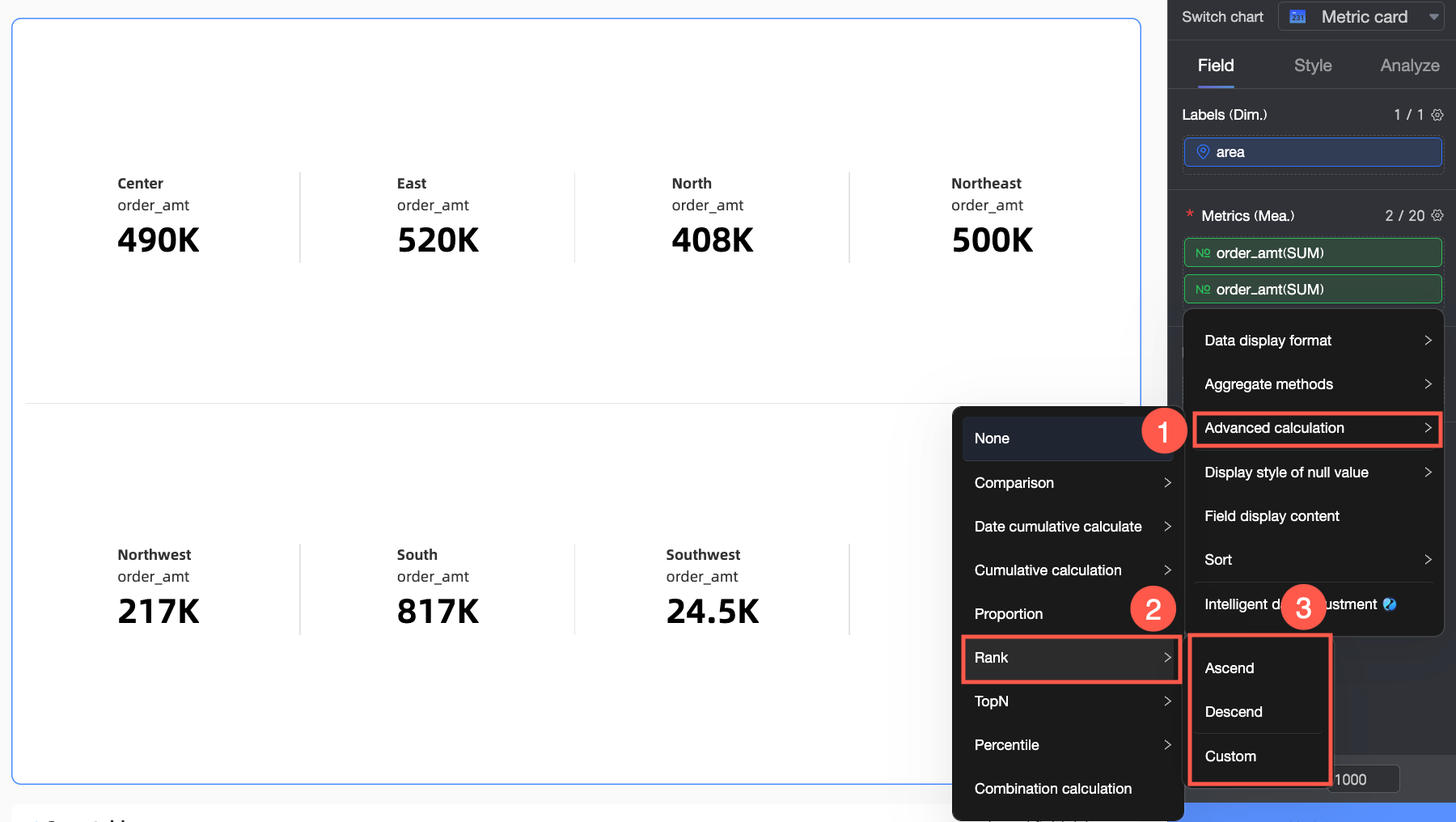
Ranking calculation type
Description
Example effect
Ascending
Overall data is ranked from smallest to largest, so the largest Order amount is ranked last. In this example, the Southwest region has the largest Order amount and is ranked No.7.
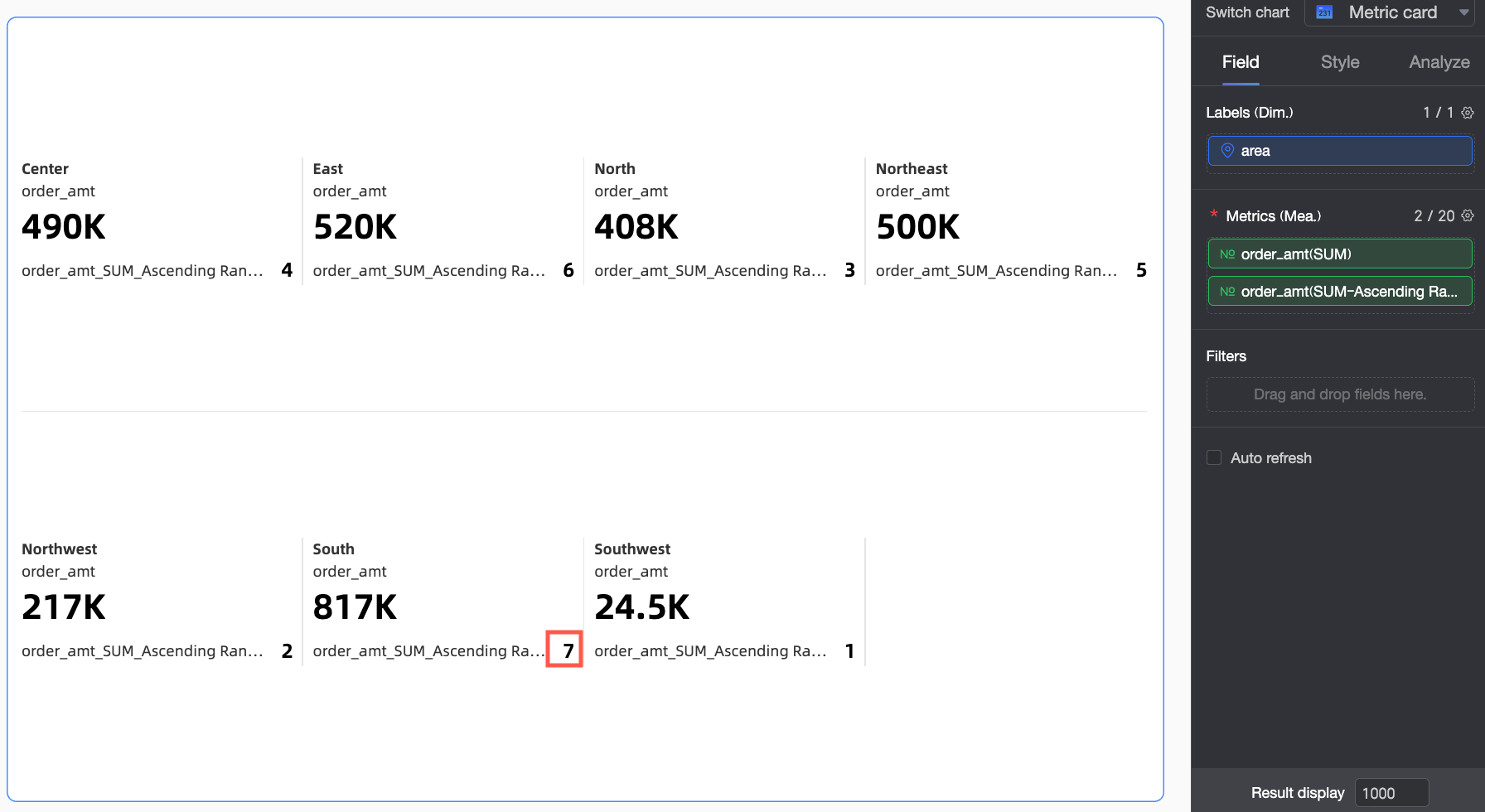
Descending
Overall data is ranked from largest to smallest, so the largest Order amount is ranked first. In this example, the Southwest region has the largest Order amount and is ranked No.1.
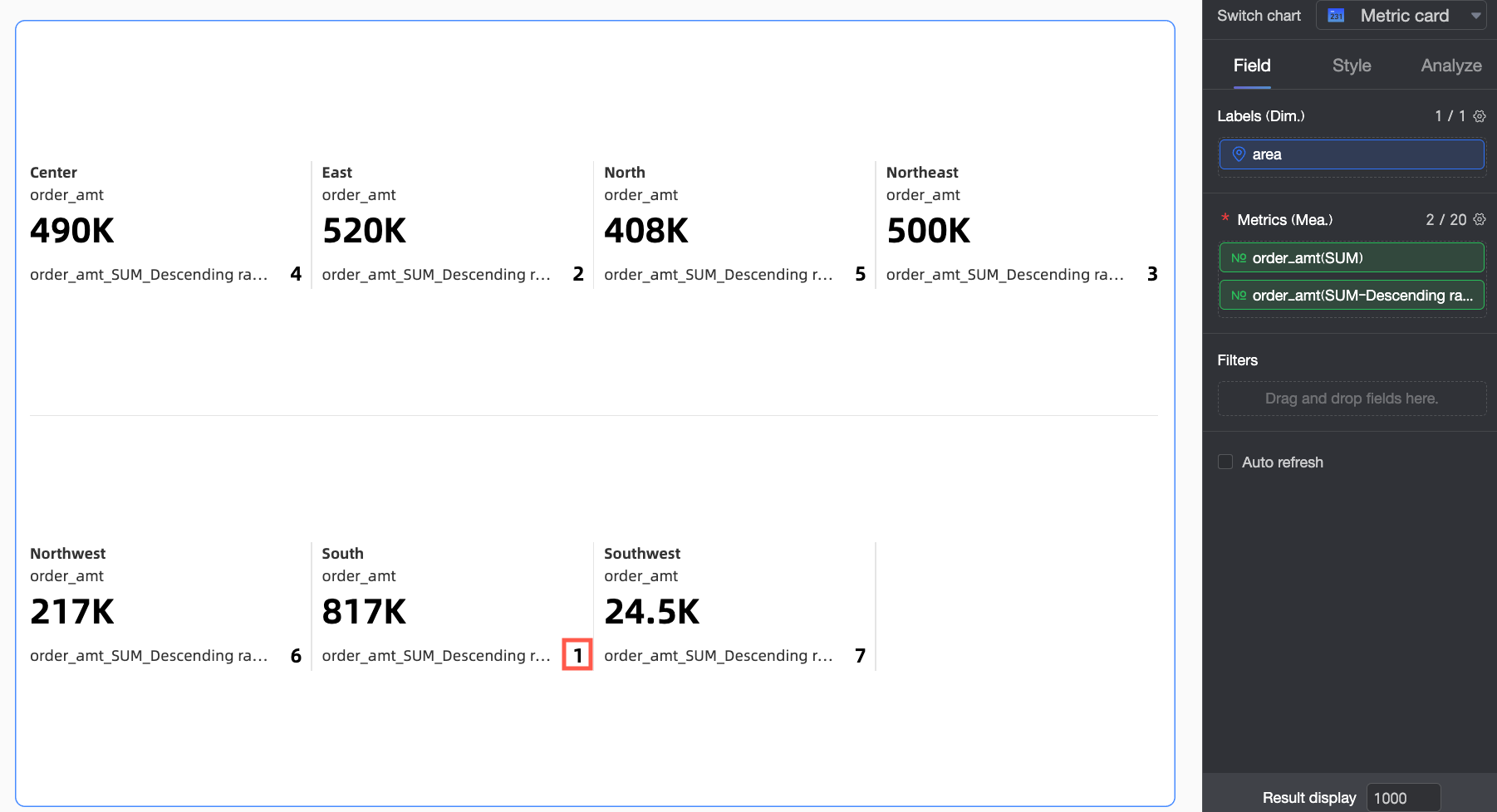
Custom
In this example, Descending order is selected
Rank
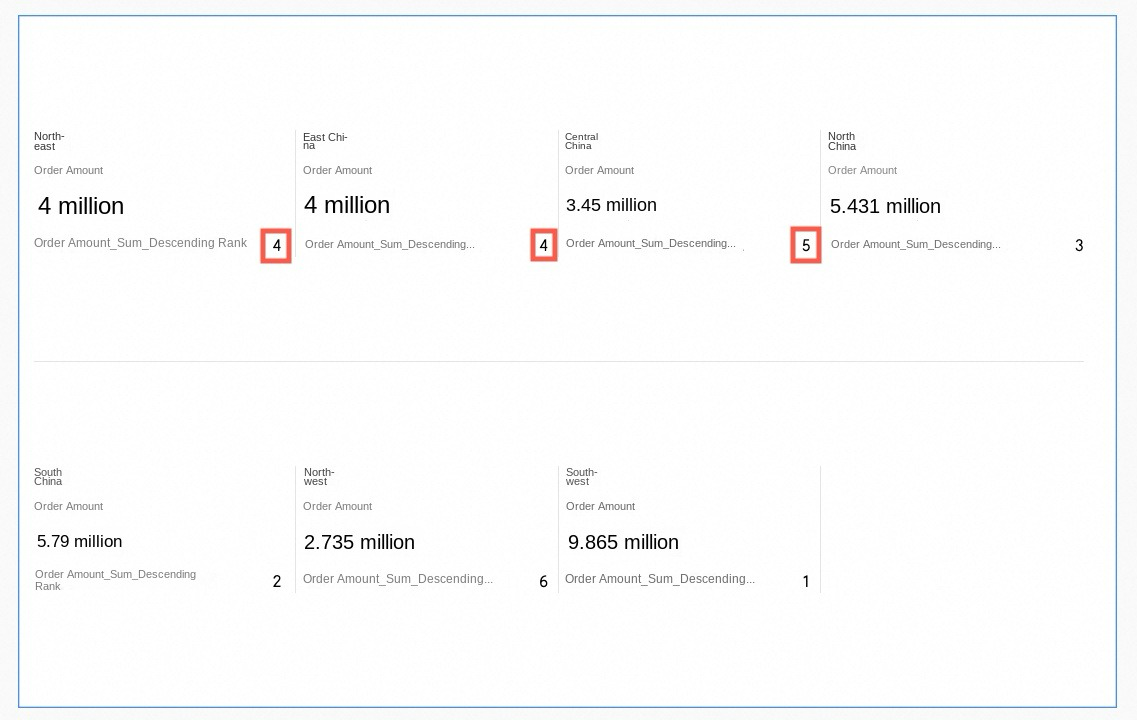
When duplicate values exist, they have the same rank and occupy positions. In this example, Northeast and East China have the same Order amount, both ranked No.4, and they occupy a position, meaning No.5 is skipped.
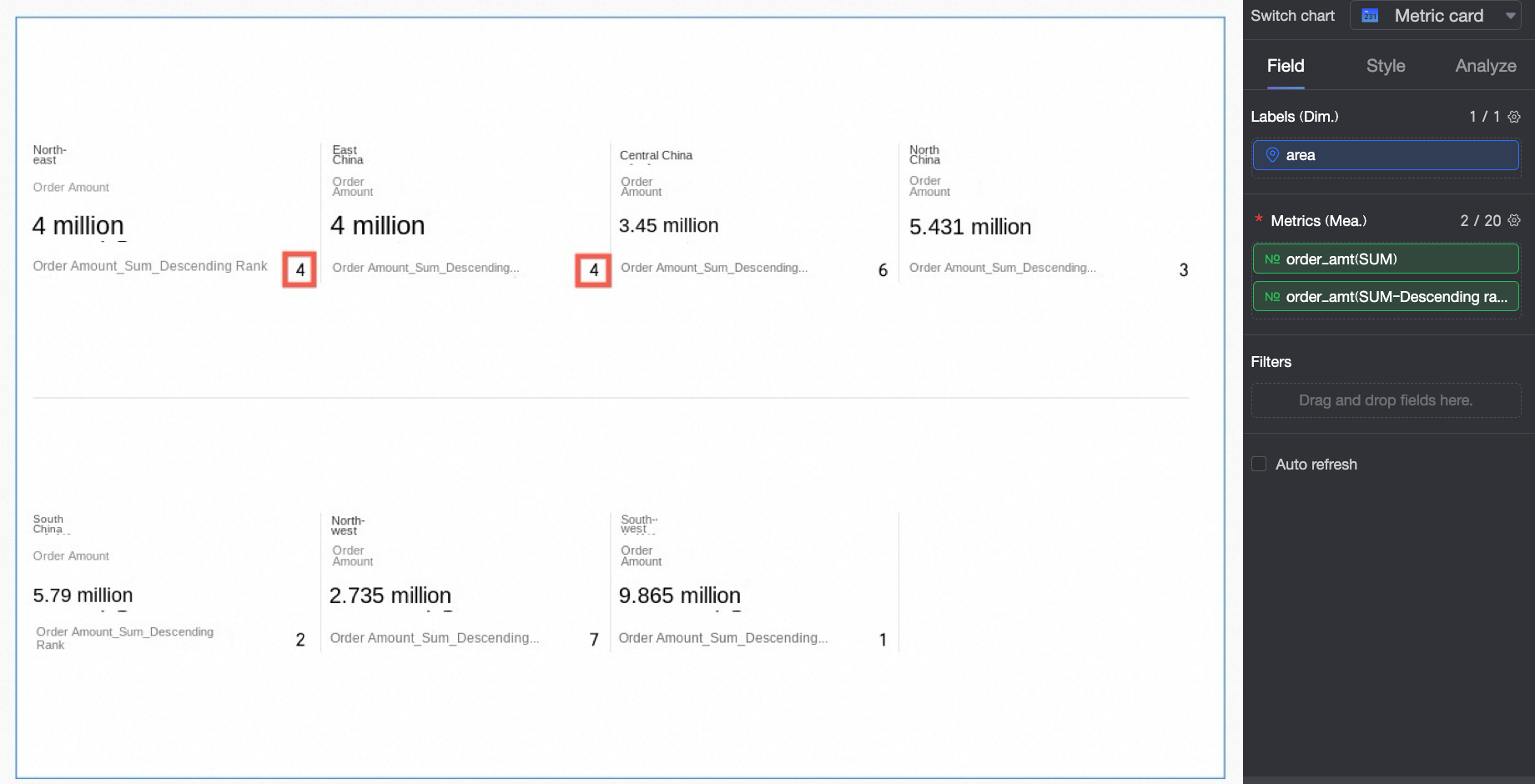
Dense rank
When duplicate values exist, they have the same rank but do not occupy positions. In this example, Northeast and East China have the same Order amount, both ranked No.4, and they do not occupy a position, meaning No.5 still exists.
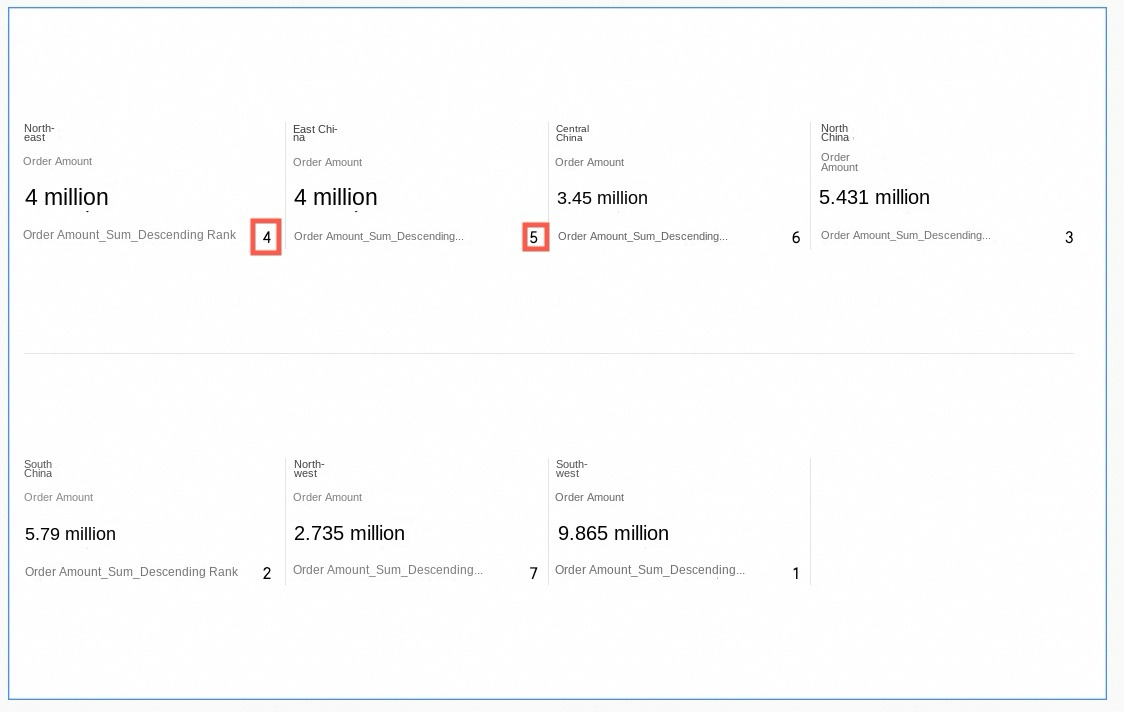
Sequential rank
When duplicate values exist, they have different ranks. In this example, Northeast and East China have the same Order amount, but they have different ranks: Northeast is No.4 and East China is No.5.
Example 2: Cross Table
Cross tables have different ranking calculation methods than other charts. Specific examples are shown below.
Ranking calculation type | Configuration description | Example effect | |
Ascending | Overall data is ranked from smallest to largest, so the largest Order amount is ranked last. In this example, the South China region has the largest Order amount and is ranked No.7. |
| |
Descending | Overall data is ranked from largest to smallest, so the largest Order amount is ranked first. In this example, the South China region has the largest Order amount and is ranked No.1. |
| |
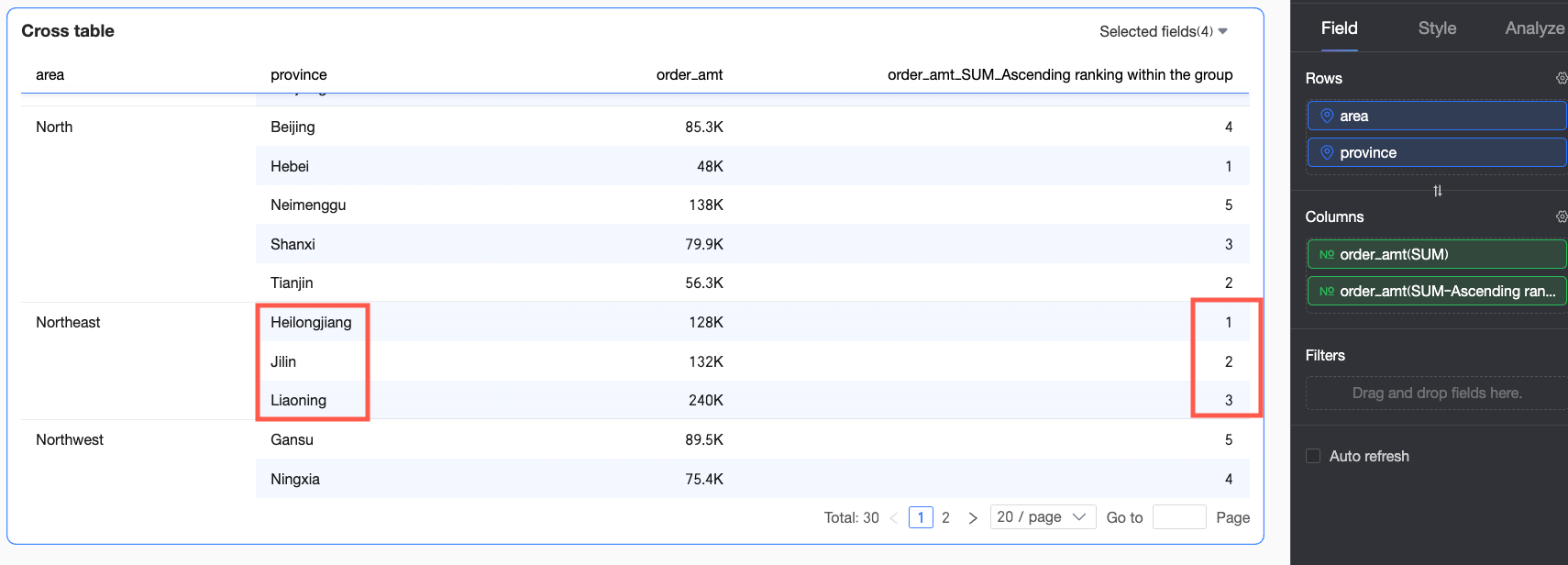
Ascending within group | In this example, provinces are grouped by the region dimension, and Order amounts are ranked from smallest to largest within each region. For example, in the Northeast region, Heilongjiang Province has the smallest Order amount and is ranked No.1. |
| |
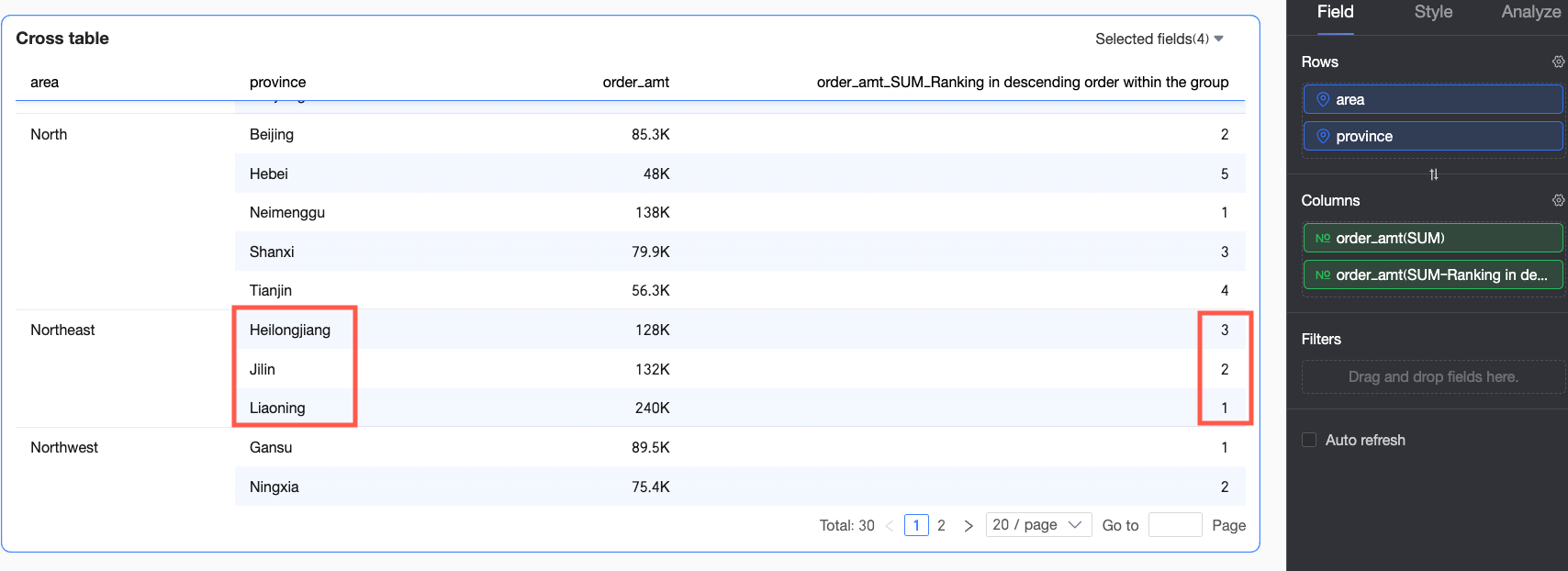
Descending within group | In this example, provinces are grouped by the region dimension, and Order amounts are ranked from largest to smallest within each region. For example, in the Northeast region, Heilongjiang Province has the smallest Order amount and is ranked No.3. |
| |
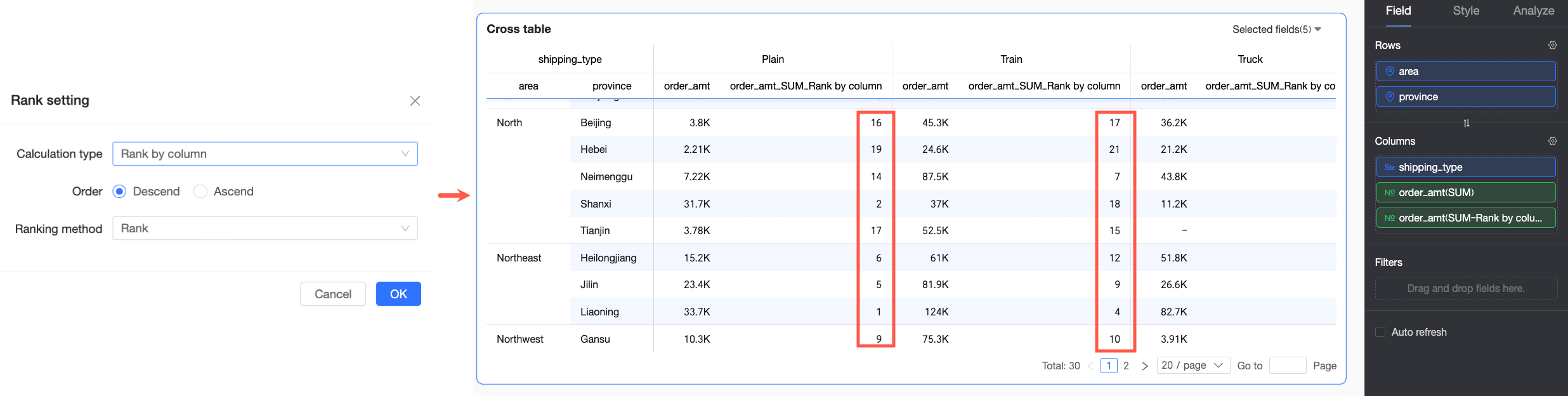
Custom In this example, Descending and Rank are set | Rank by column | In this example, the overall data is ranked in descending order by individual columns. For example, in the Truck shipping mode, South China has the highest Order amount and is ranked No.1. |
|
Rank within column group | In this example, both the first dimension field and the grouping dimension in the Row area are Region, so grouping and descending ranking are based on the Region dimension. For example, in the Northeast region, Heilongjiang Province has the lowest Order amount transported by truck and is ranked No.3. |
| |
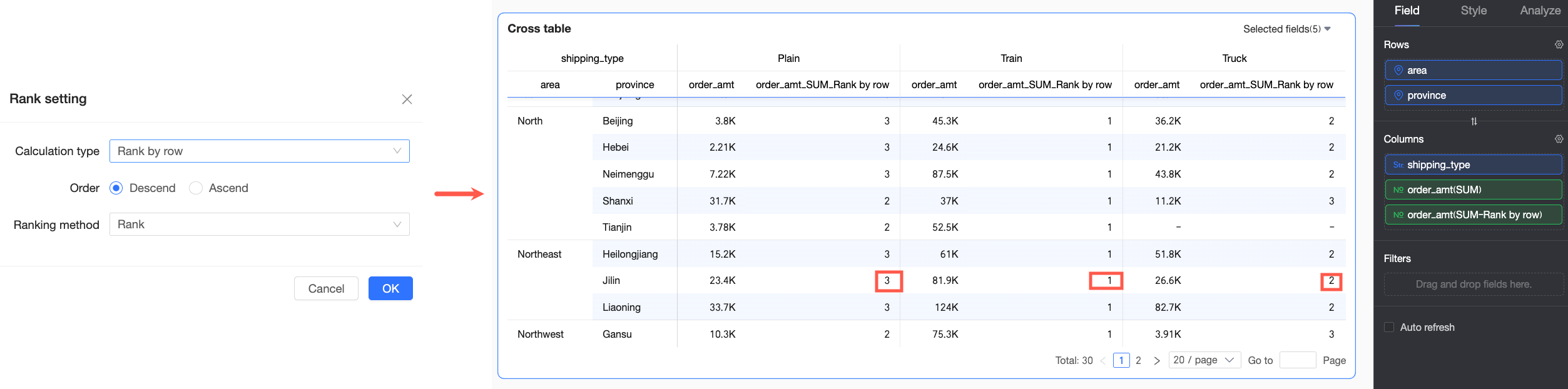
Rank by row | In this example, the overall data is ranked in descending order by individual rows. For example, in Jilin Province, the Train shipping mode has the highest Order amount and is ranked No.1. |
| |
Rank within row group | In this example, both the first dimension field and the grouping dimension in the Column area are Product Type, so grouping and descending ranking are based on the Product Type dimension. For example, for office supplies orders in Jilin Province, the Train shipping mode has the highest Order amount and is ranked No.1. |
| |