You can execute the CREATE TABLE AS (CTAS) statement to synchronize data and table schema changes from upstream to downstream systems in real time. This enhances the efficiency of creating a table in the destination system and synchronizing table schema changes. This topic describes how to use the CTAS statement, and examples across various scenarios.
We recommend that you create a job using YAML for data ingestion. You can convert existing SQL drafts containing CTAS or CDAS statements to YAML drafts:
Introduction: You can develop a job by using YAML to synchronize data from the source to the destination.
Advantages: Key capabilities of CTAS and CDAS statements are supported, including synchronization of databases, tables, table schemas, and custom computed columns. Additionally, real-time schema evolution, synchronization of raw binary log data, the WHERE clause, and column pruning are also supported.
For more information, see Data ingestion with Flink CDC.
Features
Data synchronization
Feature | Description |
Synchronize a table | Synchronizes full data and incremental data from a source table to a sink table in real time. (Example: Synchronize a table) |
Consolidate and synchronize table shards | Uses regular expressions to match database and table shards names. Then, you can consolidate these table shards and synchronize the data to a sink table. (Example: Merge and synchronize table shards) Note Carets (^) cannot be used to match the beginning of the name of a table. |
Synchronize custom computed columns | Adds computed columns for converting and processing specific columns. You can use system functions or user-defined functions (UDFs) for computed columns and specify the position of the computed column that you want to add. Newly added computed column will be used as physical columns in the sink table, and the results are synchronized to the sink table in real time. (Example: Synchronize custom computed columns) |
Execute multiple CTAS statements |
|
Schema evolution
During data synchronization, the CTAS statement supports replicating schema changes, including table creation and schema modification, from the source table to the sink table.
Supported schema changes
Schema change
Description
Add a nullable column
Automatically adds the related column to the end of the sink table's schema, with data synchronized data to the added column. The new column is set as a nullable column by default, and the data in this column before the change is automatically set to NULL.
Add a non-null column
Automatically adds the corresponding column to the end of the sink table's schema and synchronizes data.
Delete a nullable column
Automatically fills null values in the nullable column of the sink table instead of deleting the column from the table.
Rename a column
The operation of renaming a column involves adding a column and deleting a column. After a column is renamed in the source table, the column that uses the new name is added to the end of the sink table and the column that uses the original name is filled with null values.
NoteFor example, if the name of the
col_acolumn in the source table is changed tocol_b, thecol_bcolumn is added to the end of the sink table and thecol_acolumn is automatically filled with null values.Modify a column's data type
For downstream systems supporting column type modifications: Currently, Paimon is the only downstream system that supports type changes. The CTAS statement supports modifying a regular column's type, such as from INT to BIGINT.
Compatibility depends on system-specific rules (refer to connector documentation).
For downstream systems that do not support column type modifications: Currently, only Hologres supports using type widening to handle column type changes. Here's the mechanism: At job startup, a Hologres table with wider data types is created, and changes to column types are supported based on the compatibility of the sink. For more information, see Example: Synchronize data in the type normalization mode.
ImportantTo enable Hologres to support type widening, activate type normalization during the initial job launch. For existing jobs, delete the Hologres table and restart without states to apply type normalization settings.
ImportantWhen the CTAS statement is used for synchronization, the system only compares the schema differences and does not identify the specific DDL type. For example,
If a column is dropped and subsquently added again, without any data changes during this period, the system detects no schema changes.
If a column is dropped and subsequently added again, with data changes during this period, the system detects and synchronizes the schema changes.
Unsupported schema changes
Modify constraints, such as primary keys or indexes.
Delete non-nullable columns.
Change from NOT NULL to NULLABLE.
ImportantTo synchronize unsupported schema changes, manually drop the sink table and restart your job to re-synchronize historical data.
Synchronization process
The following flowchart shows the process of synchronizing data from MySQL to Hologres with the CTAS statement.
Flowchart | Description |
 | When executing the CTAS statement, Realtime Compute for Apache Flink does the following:
|
Prerequisites
A catalog of the destination store is created in your workspace. For more information, see Catalogs.
Limits
Limits on syntax
Debugging an SQL draft containing the CTAS statement is not supported.
The CTAS statement cannot be used with the INSERT INTO statement in the same SQL draft.
Data cannot be synchronized to a StarRocks partitioned table.
MiniBatch is not supported.
ImportantEnsure that MiniBatch configurations have been deleted before you create an SQL draft containing a CTAS or CDAS statement. Do the following:
Go to .
Select the Deployment Defaults tab.
In the Other Configuration section, verify MiniBatch configurations are removed.
If errors are reported when you create a deployment from the SQL draft or start the deployment, see How do I fix the "Currently does not support merge StreamExecMiniBatchAssigner type ExecNode in CTAS/CDAS syntax" error?.
Supported upstream and downstream systems
The following table describes the upstream and downstream data stores for which you can use the CTAS statement.
Connector | Source table | Sink table | Notes |
Supported | Not supported |
| |
Supported | Not supported | N/A | |
Supported | Not supported |
| |
Not supported | Supported | N/A | |
Not supported | Supported | Support is limited to StarRocks on Alibaba Cloud EMR. | |
Not supported | Supported | When Hologres serves as the destination system of data synchronization, the system automatically creates connections for each table based on the value of the Note If data types in the source table are not supported by Hologres' fixed plan feature, use the INSERT INTO statement for data synchronization. Do not use the CTAS statement, which delivers lower writing performance because fixed plans cannot be used. | |
Not supported | Supported |
Syntax
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS <sink_table>
(
[ <table_constraint> ]
)
[COMMENT table_comment]
[PARTITIONED BY (partition_column_name1, partition_column_name2, ...)]
WITH (
key1=val1,
key2=val2,
...
)
AS TABLE <source_table> [/*+ OPTIONS(key1=val1, key2=val2, ... ) */]
[ADD COLUMN { <column_component> | (<column_component> [, ...])}];
<sink_table>:
[catalog_name.][db_name.]table_name
<table_constraint>:
[CONSTRAINT constraint_name] PRIMARY KEY (column_name, ...) NOT ENFORCED
<source_table>:
[catalog_name.][db_name.]table_name
<column_component>:
column_name AS computed_column_expression [COMMENT column_comment] [FIRST | AFTER column_name]The CTAS statement uses the basic syntax of the CREATE TABLE statement. The following table describes some of the arguments:
Argument | Description |
| The target table name for data synchronization. Optionally, use the table's fully qualified name by including its catalog and database. |
| The description of the sink table. By default, the description of source_table is used. |
| Specifies the partition columns. Important Data cannot be synchronized to a StarRocks partitioned table. |
| The primary key, which is a unique identifier for each record in the table. |
| The connector options for the sink table. For more information, see the "Connector options in the WITH clause" section in Upsert Kafka connector, Hologres connector, StarRocks, or Paimon connector. Note Both the key and value must be of the STRING type, such as |
| The source table name. Optionally, use a fully qualified name including the table's catalog and database. |
| The connector options for source table. For more information, see "Connector options in the WITH clause" in MySQL connector and Kafka connector. Note Both the key and value must be of the STRING type, such as 'server-id' = '65500'. |
| Adds computed columns to the sink table or renames source columns. Important Pure column mappings (e.g., |
| The description of the new columns. |
| The description of the computed column expression. |
| Specifies that the new column is used as the first field in the sink table. By default, the new column is added at the end of the sink table. |
| Specifies that the new column is added after a specific field. |
The
IF NOT EXISTSkeyword is required. It prompts the system to check the sink table's existence in the destination store. If it is absent, the system will create a sink table. If it is present, table creation is skipped.The created sink table shares the source table's schema, including the primary key and physical field names and types, but excludes computed columns, metadata fields, and watermark configurations.
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink performs data type mappings from the source table to the sink table during data synchronization. For more information about data type mappings, see the specific connector document.
Examples
Synchronize a table
Description: Synchronize the web_sales table from MySQL to Hologres.
Prerequisites:
A Hologres catalog named
holois created.A MySQL catalog named
mysqlis created.
Sample code:
The CTAS statement is often used together with source and destination catalogs to support full and incremental data synchronization. The source catalog automatically parses source table schema and properties without explicit DDL.
USE CATALOG holo;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS web_sales -- Synchronize data to the web_sales table in the default database.
WITH ('jdbcWriteBatchSize' = '1024') -- Optionally configure the connector options for the sink table.
AS TABLE mysql.tpcds.web_sales
/*+ OPTIONS('server-id'='8001-8004') */; -- Optionally configure additional options for the MySQL CDC source table.Consolidate and synchronize table and database shards
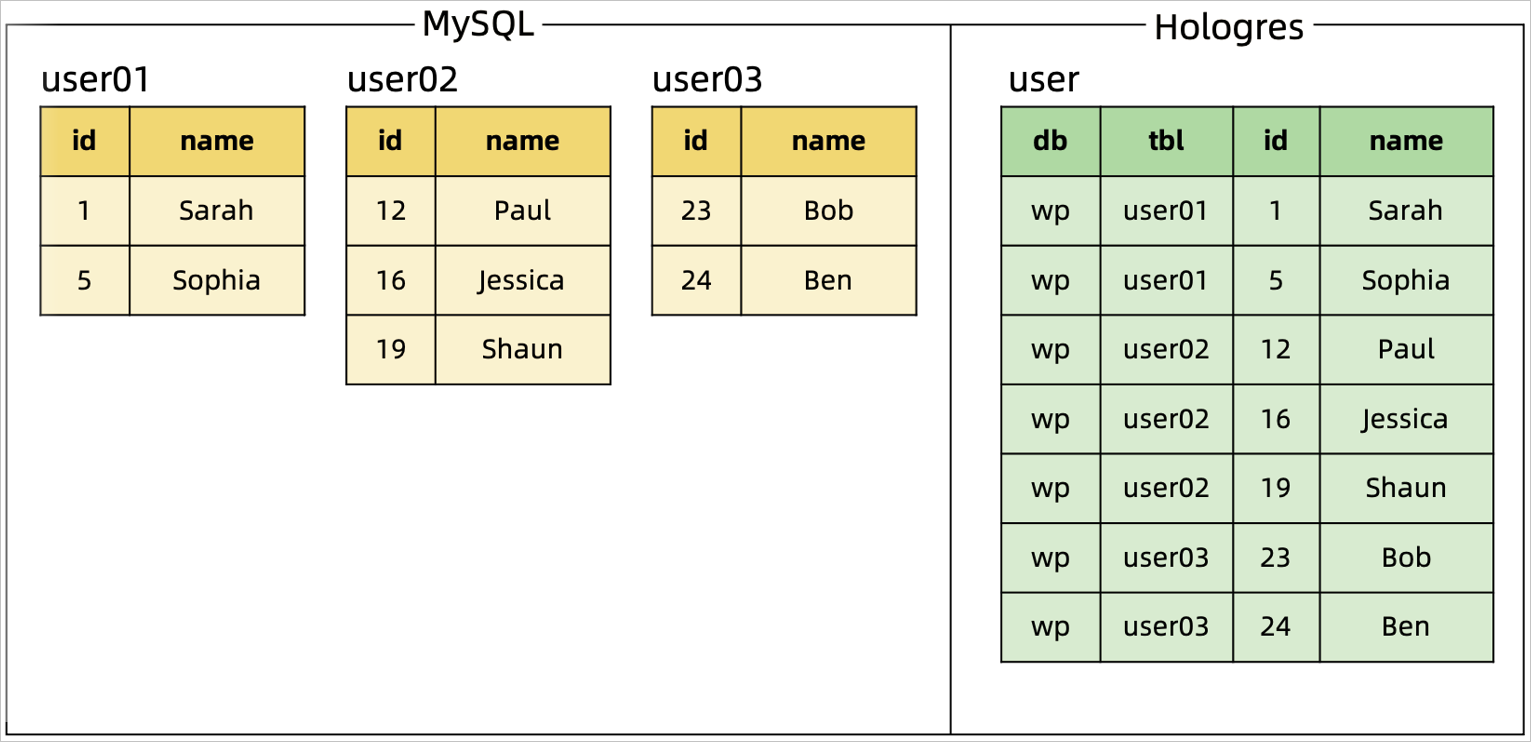
Description: Consolidate sharded MySQL tables and databases before synchronizing data to a Hologres table.
Method: Use the MySQL catalog and regular expressions to match the database and tables that you want to synchronize.
The database and table names are written to the sink table as the values of two additional fields. The sink table's primary key consists of the database name, table name, and original primary key to ensure that the primary key is unique, .
Code and results:
Sample code | Results |
Consolidate and synchronize table shards: |
|
Change source table's schema: Add a new column named |
|
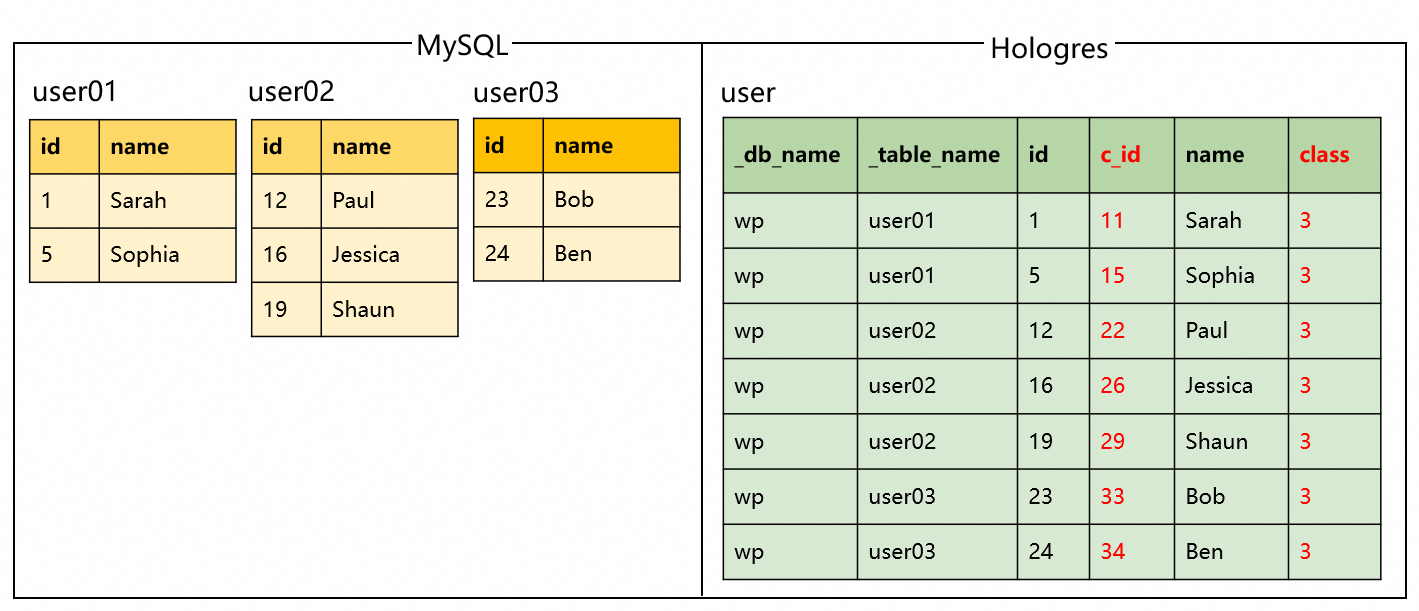
Synchronize custom computed columns
Description: During the synchronization of consolidated table and database shards from MySQL to Hologres, add custom computed columns.
Code and results:
Sample code | Results |
|
|
Execute multiple CTAS statements in a single job
Description: Synchronize the web_sales and user table shards from MySQL to Hologres in a single job.
Method: Use STATEMENT SET to execute multiple CTAS statements as a group. This approach reuses the source vertex to read data from multiple tables, reducing the number of server IDs, database connections, and overall read load.
To reuse the source and optimize performance, ensure the connector options for each source table are identical.
For information about the configuration of server IDs, see Set a different server ID for each client.
Sample code:
USE CATALOG holo;
BEGIN STATEMENT SET;
-- Synchronize data from the web_sales table.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS web_sales
AS TABLE mysql.tpcds.web_sales
/*+ OPTIONS('server-id'='8001-8004') */;
-- Synchronize data from the user table shards.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user
AS TABLE mysql.`wp.*`.`user[0-9]+`
/*+ OPTIONS('server-id'='8001-8004') */;
END;Synchronize data from a source to multiple sinks by using multiple CTAS statements
No computed columns are added to the sink table
USE CATALOG `holo`; BEGIN STATEMENT SET; -- Synchronize data from the user MySQL table to the user table in database1 of Hologres. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `database1`.`user` AS TABLE `mysql`.`tpcds`.`user` /*+ OPTIONS('server-id'='8001-8004') */; -- Synchronize data from the user table of the MySQL database to the user table in database2 of Hologres. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `database2`.`user` AS TABLE `mysql`.`tpcds`.`user` /*+ OPTIONS('server-id'='8001-8004') */; END;Computed columns are added to the sink table
-- Create a temporary table named user_with_changed_id based on the source table user. Define the computed_id column based on the source table's id column. CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE `user_with_changed_id` ( `computed_id` AS `id` + 1000 ) LIKE `mysql`.`tpcds`.`user`; -- Create a temporary table named user_with_changed_age based on the source table user. Define the computed_age column based on the source table's age column. CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE `user_with_changed_age` ( `computed_age` AS `age` + 1 ) LIKE `mysql`.`tpcds`.`user`; BEGIN STATEMENT SET; -- Synchronize data from the user table of the MySQL database to the user_with_changed_id table of Hologres. The user_with_changed_id table contains the IDs that are obtained from the calculation based on the id column of the source table. The obtained IDs are in the computed_id column. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `holo`.`tpcds`.`user_with_changed_id` AS TABLE `user_with_changed_id` /*+ OPTIONS('server-id'='8001-8004') */; -- Synchronize data from the user table of the MySQL database to the user_with_changed_age table of Hologres. The user_with_changed_age table contains the age values that are obtained from the calculation based on the age column of the source table. The obtained age values are in the computed_age column. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `holo`.`tpcds`.`user_with_changed_age` AS TABLE `user_with_changed_age` /*+ OPTIONS('server-id'='8001-8004') */; END;
Synchronize new tables by using multiple CTAS statements
Scenario description: After a job that uses multiple CTAS statements for synchronization is started, add a CTAS statement to replicate new tables.
Method: Enable new table detection for the job, add a CTAS statement to the job's SQL code, and restart from a savepoint. After the new table is captured, data will be replicated.
Limits:
New table detection is supported for VVR 8.0.1 or later.
When data is synchronized from a CDC source table, only jobs started in the initial mode can detect new tables.
The configuration of the source table that is added by using the new CTAS statement must be the same as the configuration of the original source tables. This way, the source vertex can be reused.
Job configuration parameters before and after adding a CTAS statement must be the same. For example, the startup mode should be the same.
Procedure:
On the Deployments page, find the target deployment and click Cancel in the Actions column.
In the dialog, expand the More Strategies section, select Stop With Savepoint, and click OK.
In the job's SQL draft, enable new table detection and add a CTAS statement.
Add the following statement to enable new table detection.
SET 'table.cdas.scan.newly-added-table.enabled' = 'true';Add a CTAS statement. The complete code of the job looks like this:
-- Enable new table detection SET 'table.cdas.scan.newly-added-table.enabled' = 'true'; USE CATALOG holo; BEGIN STATEMENT SET; -- Synchronize data from the web_sales table. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS web_sales AS TABLE mysql.tpcds.web_sales /*+ OPTIONS('server-id'='8001-8004') */; -- Synchronize data from the user table shards. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user AS TABLE mysql.`wp.*`.`user[0-9]+` /*+ OPTIONS('server-id'='8001-8004') */; -- Synchronize data from the product table. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS product AS TABLE mysql.tpcds.product /*+ OPTIONS('server-id'='8001-8004') */; END;Click Deploy.
Recover the job from the savepoint.
On the Deployments page, click the name of your deployment.
On the deployment details page, click the State tab. Then, click the History subtab.
In the Savepoints list, find the savepoint created when the job was canceled.
Choose in the Actions column. For more information, see Start a job deployment.
Synchronize to a partitioned table in Hologres
Scenario description: Replicate data from MySQL to a Hologres partitioned table.
Usage notes: If a primary key is defined for the Hologres table, partition columns must be included in the primary key.
Sample code:
Create a MySQL table:
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
product_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
city VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL
order_date DATE,
purchaser INTEGER,
PRIMARY KEY(order_id, product_id)
);Depending on whether the partition columns are part of the primary key, choose a proper method:
If the source primary key contains partition columns:
Use the CTAS statement directly.
Hologres will automatically verify whether partition columns are included in the primary key.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `holo`.`tpcds`.`orders` PARTITIONED BY (product_id) AS TABLE `mysql`.`tpcds`.`orders`;
If the source primary key excludes partition columns:
Declare the sink table's primary key in the CTAS statement and include the partition columns in primary key definition.
In this case, not re-defining the primary key or including the partition column in it will cause the job to fail.
-- Declare the order_id, product_id, and city fields as the primary key of the Hologres partitioned table. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `holo`.`tpcds`.`orders`( CONSTRAINT `PK_order_id_city` PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`,`product_id`,`city`) NOT ENFORCED ) PARTITIONED BY (city) AS TABLE `mysql`.`tpcds`.`orders`;
Widen data types during replication
Scenario description: During data synchronization, change the precision of a column, such as from VARCHAR(10) to VARCHAR(20), or change a column's data type, like from SMALLINT to INT.
Method:
New jobs: Enable type normalization mode at first launch.
Existing jobs: Drop the Hologres sink table, and restart without states to apply type normalization.
Type normalization rules:
If the new and original data types are normalized into the same data type, the data type can be successfully changed and the job will run normally. Otherwise, an exception will be reported. Details are as follows:
TINYINT, SMALLINT, INT, and BIGINT are converted into BIGINT.
CHAR, VARCHAR, and STRING are converted into STRING.
FLOAT and DOUBLE are converted into DOUBLE.
Other data types are converted based on the data type mappings between Hologres and Flink fields. For more information, see Data type mappings.
Sample code:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `holo`.`tpcds`.`orders`
WITH (
'connector' = 'hologres',
'enableTypeNormalization' = 'true' -- Enable the type normalization mode.
) AS TABLE `mysql`.`tpcds`.`orders`;Synchronize data from MongoDB to Hologres
Limits:
Support is limited to VVR 8.0.6 or later and MongoDB version 6.0 or later.
In connector options for the source table, scan.incremental.snapshot.enabled and scan.full-changelog must be set to
true.The preimage and postimage features must be enabled for the MongoDB database. For more information, see Document Preimages.
To synchronize data from multiple MongoDB collections in a single job, ensure the configurations of the following connector options are identical for all tables:
MongoDB database-related options, including
hosts,scheme,username,password, andconnectionOptionsscan.startup.mode
Sample code:
BEGIN STATEMENT SET;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `holo`.`database`.`table1`
AS TABLE `mongodb`.`database`.`collection1`
/*+ OPTIONS('scan.incremental.snapshot.enabled'='true','scan.full-changelog'='true') */;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `holo`.`database`.`table2`
AS TABLE `mongodb`.`database`.`collection2`
/*+ OPTIONS('scan.incremental.snapshot.enabled'='true','scan.full-changelog'='true') */;
END;FAQ
Runtime errors
Job performance
Data synchronization
References
The CTAS statement is often used with catalogs, which offer persistent metadata management for tables and enable cross-job data access: Popular catalogs:
Best practices for using CTAS and CDAS statements:
For information about synchronization of data from all tables in a database, merging and synchronization of data of tables in a sharded database, or synchronization of data from new tables in the source database, see CREATE DATABASE AS (CDAS).
To reduce data read load on the MySQL database during database synchronization, you can synchronize data in a database to Kafka. Refer to Database synchronization from MySQL to Kafka with Flink CDC.
For information about how to use the CTAS and CDAS statements to perform data synchronization, see Ingest data into data warehouses in real time, Build a real-time data warehouse with Flink and Hologres, or Build a streaming data lakehouse with Flink, Paimon, and StarRocks.
Data ingestion via YAML: