This topic describes how to synchronize an entire MySQL database to Kafka. This method helps reduce the load that multiple tasks place on the MySQL database.
Background information
MySQL Change Data Capture (CDC) tables retrieve data from MySQL and synchronize table modifications in real time. They are often used for complex computing. For example, you can use a MySQL CDC table as a dimension table and join it with other data tables. A single MySQL table can be a dependency for multiple jobs. When these jobs process data from the same table, the MySQL database establishes multiple connections. This creates a heavy load on the MySQL server and network.
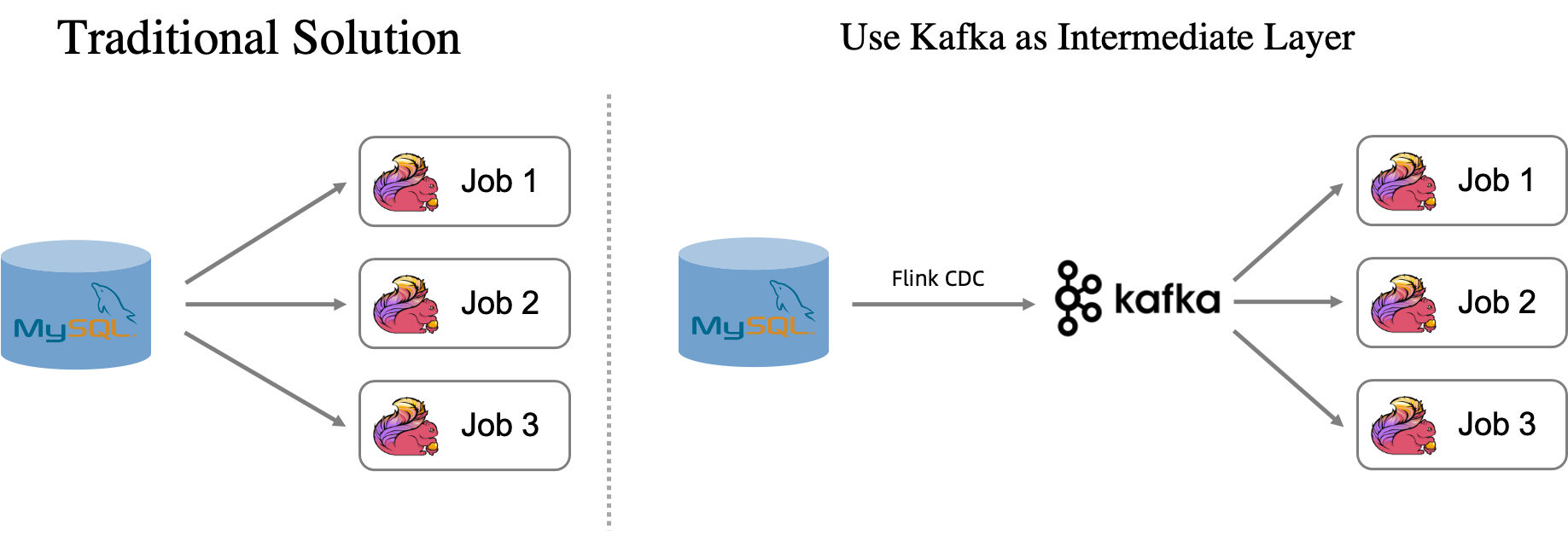
Solution architecture
To reduce the load on the upstream MySQL database, Realtime Compute for Apache Flink lets you synchronize an entire MySQL database to Kafka. This solution uses Kafka as an intermediate layer. A Flink CDC data ingestion job synchronizes the data to Kafka.
A single job synchronizes data from the upstream MySQL database to Kafka in real time. Each MySQL table is written to a corresponding Kafka topic in upsert mode. Downstream jobs then use an Upsert Kafka connector to read data from the topics instead of directly accessing the MySQL tables. This method significantly reduces the load on the MySQL database.
Limits
The MySQL tables to be synchronized must have primary keys.
You can use a self-managed Kafka cluster, an EMR Kafka cluster, or ApsaraMQ for Kafka. When you use ApsaraMQ for Kafka, you must use the default endpoint.
The Kafka cluster must have more storage space than the source tables. Otherwise, data loss can occur due to insufficient space. The topics created for database synchronization are compacted. In a compacted topic, only the latest message for each key is retained, and the data never expires. This means the topic stores an amount of data that is roughly equal to the size of the source table.
Use case
Consider a real-time analysis of order reviews. You have three tables: `user`, `order`, and `feedback`. The following figure shows the data in these tables.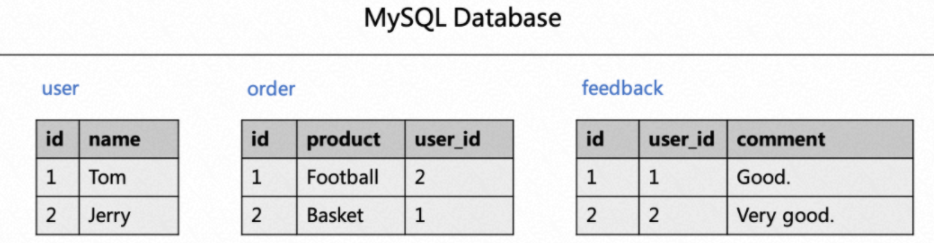
To display order details and user reviews, you must join the `user` table to retrieve the username from the `name` field. The following SQL statements show how this is done.
-- Join the order information with the user table to show the username and product name for each order.
SELECT order.id as order_id, product, user.name as user_name
FROM order LEFT JOIN user
ON order.user_id = user.id;
-- Join the reviews with the user table to show the content of each review and the corresponding username.
SELECT feedback.id as feedback_id, comment, user.name as user_name
FROM feedback LEFT JOIN user
ON feedback.user_id = user.id;In the two SQL tasks, the `user` table is used by both jobs. At runtime, both jobs read the full and incremental data from MySQL. Reading the full data requires a MySQL connection, and reading incremental data requires a binary logging (Binlog) client. As the number of jobs grows, the required MySQL connections and Binlog client resources also increase. This creates a heavy load on the upstream database. To reduce this load, you can use a Flink CDC data ingestion job to synchronize the upstream MySQL data to Kafka in real time. The data is then available for multiple downstream jobs to consume.
Prerequisites
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink is activated. For more information, see Activate Realtime Compute for Apache Flink.
ApsaraMQ for Kafka is activated. For more information, see Deploy an ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance.
ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL is activated. For more information, see Create an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink, ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, and ApsaraMQ for Kafka must be in the same VPC. If they are in different VPCs, you must enable cross-VPC network communication or access them over the Internet. For more information, see How do I access other services across VPCs? and How do I access the Internet?.
If you use an identity such as a Resource Access Management (RAM) user or a RAM role, ensure that the identity has the required permissions to access the resources.
Preparations
Create an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance and prepare the data source
Create a database. For more information, see Create a database.
Create a database named
order_dwfor the destination instance.Prepare the MySQL CDC data source.
On the instance product page, click Log on to Database at the top.
In the DMS logon page that appears, enter the username and password for the database account that you created, and then click Logon.
After you log on, double-click the
order_dwdatabase on the left to switch to it.In the SQL Console, write the DDL statements to create the three business tables and the statements to insert data.
CREATE TABLE `user` ( id bigint not null primary key, name varchar(50) not null ); CREATE TABLE `order` ( id bigint not null primary key, product varchar(50) not null, user_id bigint not null ); CREATE TABLE `feedback` ( id bigint not null primary key, user_id bigint not null, comment varchar(50) not null ); -- Prepare data INSERT INTO `user` VALUES(1, 'Tom'),(2, 'Jerry'); INSERT INTO `order` VALUES (1, 'Football', 2), (2, 'Basket', 1); INSERT INTO `feedback` VALUES (1, 1, 'Good.'), (2, 2, 'Very good');
Click Execute, and then click Execute Directly.
Procedure
Create and start a Flink CDC data ingestion task to synchronize data from the upstream MySQL database to Kafka in real time. This makes the data available for multiple downstream jobs. The job automatically creates topics. You can define the topic names using the `route` module. The number of partitions and replicas for the topics uses the default settings of the Kafka cluster, and the `cleanup.policy` is set to `compact`.
Default topic names
A full database sync task creates Kafka topics using a default naming format that combines the MySQL database name and the table name, joined by a period. For example, a job can create topics such as order_dw.user, order_dw.order, and order_dw.feedback.
On the page, create a new Flink CDC data ingestion job, and copy the following code into the YAML editor.
source: type: mysql name: MySQL Source hostname: #{hostname} port: 3306 username: #{usernmae} password: #{password} tables: order_dw.\.* server-id: 28601-28604 # (Optional) Synchronize data from newly created tables during the incremental phase. scan.binlog.newly-added-table.enabled: true # (Optional) Synchronize table and field comments. include-comments.enabled: true # (Optional) Prioritize unbounded chunks to prevent potential TaskManager OutOfMemory issues. scan.incremental.snapshot.unbounded-chunk-first.enabled: true # (Optional) Enable parsing filters to speed up reads. scan.only.deserialize.captured.tables.changelog.enabled: true sink: type: upsert-kafka name: upsert-kafka Sink properties.bootstrap.servers: xxxx.alikafka.aliyuncs.com:9092 # The following parameters are required for ApsaraMQ for Kafka aliyun.kafka.accessKeyId: #{ak} aliyun.kafka.accessKeySecret: #{sk} aliyun.kafka.instanceId: #{instanceId} aliyun.kafka.endpoint: #{endpoint} aliyun.kafka.regionId: #{regionId}In the upper-right corner, click Deploy to deploy the job.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . In the Actions column of the target job, click Start. Select Stateless Start, and then click Start.
Specify topic names
You can use the `route` module in a database synchronization task to specify the topic name for each table. The following job creates three topics: `user1`, `order2`, and `feedback3`.
On the page, create a new Flink CDC data ingestion job, and copy the following code into the YAML editor.
source: type: mysql name: MySQL Source hostname: #{hostname} port: 3306 username: #{usernmae} password: #{password} tables: order_dw.\.* server-id: 28601-28604 # (Optional) Synchronize data from newly created tables during the incremental phase. scan.binlog.newly-added-table.enabled: true # (Optional) Synchronize table and field comments. include-comments.enabled: true # (Optional) Prioritize unbounded chunks to prevent potential TaskManager OutOfMemory issues. scan.incremental.snapshot.unbounded-chunk-first.enabled: true # (Optional) Enable parsing filters to speed up reads. scan.only.deserialize.captured.tables.changelog.enabled: true route: - source-table: order_dw.user sink-table: user1 - source-table: order_dw.order sink-table: order2 - source-table: order_dw.feedback sink-table: feedback3 sink: type: upsert-kafka name: upsert-kafka Sink properties.bootstrap.servers: xxxx.alikafka.aliyuncs.com:9092 # The following parameters are required for ApsaraMQ for Kafka aliyun.kafka.accessKeyId: #{ak} aliyun.kafka.accessKeySecret: #{sk} aliyun.kafka.instanceId: #{instanceId} aliyun.kafka.endpoint: #{endpoint} aliyun.kafka.regionId: #{regionId}In the upper-right corner, click Deploy to deploy the job.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . In the Actions column of the target job, click Start. Select Stateless Start, and then click Start.
Set topic names in batches
You can use the `route` module in a database synchronization task to specify a pattern for the generated topic names in batches. The following job creates three topics: `topic_user`, `topic_order`, and `topic_feedback`.
On the page, create a new Flink CDC data ingestion job, and copy the following code into the YAML editor.
source: type: mysql name: MySQL Source hostname: #{hostname} port: 3306 username: #{usernmae} password: #{password} tables: order_dw.\.* server-id: 28601-28604 # (Optional) Synchronize data from newly created tables during the incremental phase. scan.binlog.newly-added-table.enabled: true # (Optional) Synchronize table and field comments. include-comments.enabled: true # (Optional) Prioritize unbounded chunks to prevent potential TaskManager OutOfMemory issues. scan.incremental.snapshot.unbounded-chunk-first.enabled: true # (Optional) Enable parsing filters to speed up reads. scan.only.deserialize.captured.tables.changelog.enabled: true route: - source-table: order_dw.\.* sink-table: topic_<> replace-symbol: <> sink: type: upsert-kafka name: upsert-kafka Sink properties.bootstrap.servers: xxxx.alikafka.aliyuncs.com:9092 # The following parameters are required for ApsaraMQ for Kafka aliyun.kafka.accessKeyId: #{ak} aliyun.kafka.accessKeySecret: #{sk} aliyun.kafka.instanceId: #{instanceId} aliyun.kafka.endpoint: #{endpoint} aliyun.kafka.regionId: #{regionId}In the upper-right corner, click Deploy to deploy the job.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . In the Actions column of the target job, click Start. Select Stateless Start, and then click Start.
Consume Kafka data in real time.
Data from the upstream MySQL database is written to Kafka in JSON format. A single Kafka topic can be consumed by multiple downstream jobs, which read from the topic to retrieve the latest table data. You can consume data from the synchronized tables in the following two ways:
Consume data directly through a catalog
Read data from the Kafka topic as a source table.
On the page, create a new SQL stream job and copy the following code to the SQL editor.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE print_user_proudct( order_id BIGINT, product STRING, user_name STRING ) WITH ( 'connector'='print', 'logger'='true' ); CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE print_user_feedback( feedback_id BIGINT, `comment` STRING, user_name STRING ) WITH ( 'connector'='print', 'logger'='true' ); BEGIN STATEMENT SET; -- Required when writing to multiple sinks. -- Join the order information with the user table in the Kafka JSON catalog to show the username and product name for each order. INSERT INTO print_user_proudct SELECT `order`.key_id as order_id, value_product as product, `user`.value_name as user_name FROM `kafka-catalog`.`kafka`.`order`/*+OPTIONS('properties.group.id'='<yourGroupName>', 'scan.startup.mode'='earliest-offset')*/ as `order` -- Specify the group and startup mode LEFT JOIN `kafka-catalog`.`kafka`.`user`/*+OPTIONS('properties.group.id'='<yourGroupName>', 'scan.startup.mode'='earliest-offset')*/ as `user` -- Specify the group and startup mode ON `order`.value_user_id = `user`.key_id; -- Join the reviews with the user table to show the content of each review and the corresponding username. INSERT INTO print_user_feedback SELECT feedback.key_id as feedback_id, value_comment as `comment`, `user`.value_name as user_name FROM `kafka-catalog`.`kafka`.feedback/*+OPTIONS('properties.group.id'='<yourGroupName>', 'scan.startup.mode'='earliest-offset')*/ as feedback -- Specify the group and startup mode LEFT JOIN `kafka-catalog`.`kafka`.`user`/*+OPTIONS('properties.group.id'='<yourGroupName>', 'scan.startup.mode'='earliest-offset')*/ as `user` -- Specify the group and startup mode ON feedback.value_user_id = `user`.key_id; END; -- Required when writing to multiple sinks.This example uses the Print connector to print the results directly. You can also output the results to a sink table of a connector for further analysis and computation. For more information about the syntax for writing to multiple sinks, see INSERT INTO statement.
NoteIf a MySQL table schema is changed during data synchronization, the schema parsed by the Kafka JSON catalog may become out of sync with the actual table schema. For example, if fields are deleted from the MySQL table but still appear in the parsed schema from the catalog, the values for these fields may be null.
The schema read from the Catalog consists of fields from the consumed data. If a field is deleted but messages containing it have not expired, the schema may include fields that no longer exist. The value of such fields is null. This situation does not require any special handling.
In the upper-right corner, click Deploy to deploy the job.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . In the Actions column of the target job, click Start. Select Stateless Start, and then click Start.
Consume data by creating a temporary table
Define a custom schema and read data from a temporary table.
On the page, you can create a new SQL stream job and copy the following code to the SQL editor.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE user_source ( key_id BIGINT, value_name STRING ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'kafka', 'topic' = 'user', 'properties.bootstrap.servers' = '<yourKafkaBrokers>', 'scan.startup.mode' = 'earliest-offset', 'key.format' = 'json', 'value.format' = 'json', 'key.fields' = 'key_id', 'key.fields-prefix' = 'key_', 'value.fields-prefix' = 'value_', 'value.fields-include' = 'EXCEPT_KEY', 'value.json.infer-schema.flatten-nested-columns.enable' = 'false', 'value.json.infer-schema.primitive-as-string' = 'false' ); CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE order_source ( key_id BIGINT, value_product STRING, value_user_id BIGINT ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'kafka', 'topic' = 'order', 'properties.bootstrap.servers' = '<yourKafkaBrokers>', 'scan.startup.mode' = 'earliest-offset', 'key.format' = 'json', 'value.format' = 'json', 'key.fields' = 'key_id', 'key.fields-prefix' = 'key_', 'value.fields-prefix' = 'value_', 'value.fields-include' = 'EXCEPT_KEY', 'value.json.infer-schema.flatten-nested-columns.enable' = 'false', 'value.json.infer-schema.primitive-as-string' = 'false' ); CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE feedback_source ( key_id BIGINT, value_user_id BIGINT, value_comment STRING ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'kafka', 'topic' = 'feedback', 'properties.bootstrap.servers' = '<yourKafkaBrokers>', 'scan.startup.mode' = 'earliest-offset', 'key.format' = 'json', 'value.format' = 'json', 'key.fields' = 'key_id', 'key.fields-prefix' = 'key_', 'value.fields-prefix' = 'value_', 'value.fields-include' = 'EXCEPT_KEY', 'value.json.infer-schema.flatten-nested-columns.enable' = 'false', 'value.json.infer-schema.primitive-as-string' = 'false' ); CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE print_user_proudct( order_id BIGINT, product STRING, user_name STRING ) WITH ( 'connector'='print', 'logger'='true' ); CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE print_user_feedback( feedback_id BIGINT, `comment` STRING, user_name STRING ) WITH ( 'connector'='print', 'logger'='true' ); BEGIN STATEMENT SET; -- Required when writing to multiple sinks. -- Join the order information with the user table in the Kafka JSON catalog to show the username and product name for each order. INSERT INTO print_user_proudct SELECT order_source.key_id as order_id, value_product as product, user_source.value_name as user_name FROM order_source LEFT JOIN user_source ON order_source.value_user_id = user_source.key_id; -- Join the reviews with the user table to show the content of each review and the corresponding username. INSERT INTO print_user_feedback SELECT feedback_source.key_id as feedback_id, value_comment as `comment`, user_source.value_name as user_name FROM feedback_source LEFT JOIN user_source ON feedback_source.value_user_id = user_source.key_id; END; -- Required when writing to multiple sinks.This example uses the Print connector to print the results directly. You can also output the results to a sink table of a connector for further analysis and computation. For more information about the syntax for writing to multiple sinks, see INSERT INTO statement.
The following table describes the parameters for configuring the temporary table.
Parameter
Description
Notes
connector
The connector type.
The value must be `kafka`.
topic
The name of the corresponding topic.
This must be the same as the description in the Kafka JSON catalog.
properties.bootstrap.servers
The Kafka broker addresses.
The format is
host:port,host:port,host:port. Use commas (,) to separate addresses.scan.startup.mode
The start offset for reading data from Kafka.
Valid values:
earliest-offset: Read from the earliest partition in Kafka.
latest-offset: Read from the latest offset in Kafka.
group-offsets (default): Read from the committed offset of the specified properties.group.id.
timestamp: Read from the timestamp specified by scan.startup.timestamp-millis.
specific-offsets: Read from the offset specified by scan.startup.specific-offsets.
Note
This parameter takes effect only when the job starts without a state. If the job restarts from a checkpoint or recovers its state, it prioritizes using the progress saved in the state to resume reading.
key.format
The format used by the Flink Kafka connector to serialize or deserialize the Kafka message key.
The value must be `json`.
key.fields
The fields in the source or sink table that correspond to the Kafka message key.
Use semicolons (;) to separate multiple field names. For example,
field1;field2.key.fields-prefix
A custom prefix for all Kafka message keys to avoid name conflicts with fields in the message value or metadata.
This must be the same as the value of the key.fields-prefix parameter in the Kafka JSON catalog.
value.format
The format used by the Flink Kafka connector to serialize or deserialize the Kafka message value.
The value must be `json`.
value.fields-prefix
A custom prefix for all Kafka message values to avoid name conflicts with fields in the message key or metadata.
This must be the same as the value of the value.fields-prefix parameter in the Kafka JSON catalog.
value.fields-include
Specifies the policy for handling the message key field in the message body.
A fixed value of EXCEPT_KEY indicates that the message body does not contain the message key field.
value.json.infer-schema.flatten-nested-columns.enable
Specifies whether to recursively expand nested columns in the JSON of the Kafka message value.
Corresponds to the value of the infer-schema.flatten-nested-columns.enable parameter in the catalog.
value.json.infer-schema.primitive-as-string
Specifies whether to infer all primitive data types as the String type in the Kafka message value.
Corresponds to the value of the infer-schema.primitive-as-string parameter in the catalog.
In the upper-right corner, click Deploy to deploy the job.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . In the Actions column of the target job, click Start. Select Stateless Start, and then click Start.
View the job results.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose , and then click the target job.
On the Job Logs tab, click the task under Path, ID on the Running Task Managers tab.
Click Logs and search the page for log information related to
PrintSinkOutputWriter.