Realtime Compute for Apache Flink provides powerful real-time data ingestion capabilities. Features such as automatic full and incremental switchover, automatic metadata discovery, automatic schema evolution synchronization, and whole-database synchronization simplify the real-time ingestion pipeline. This makes real-time data synchronization more efficient and user-friendly. This topic shows you how to quickly build a data ingestion job that moves data from MySQL to Hologres.
Background information
Assume your MySQL instance contains a database named tpc_ds, with 24 business tables that have different schemas. It also contains three databases named user_db1, user_db2, and user_db3. Because of sharding, each of these databases contains three tables with identical schemas. Together, they contain nine tables named user01 through user09. The following figure shows the databases and tables in MySQL, as viewed in the Alibaba Cloud DMS console.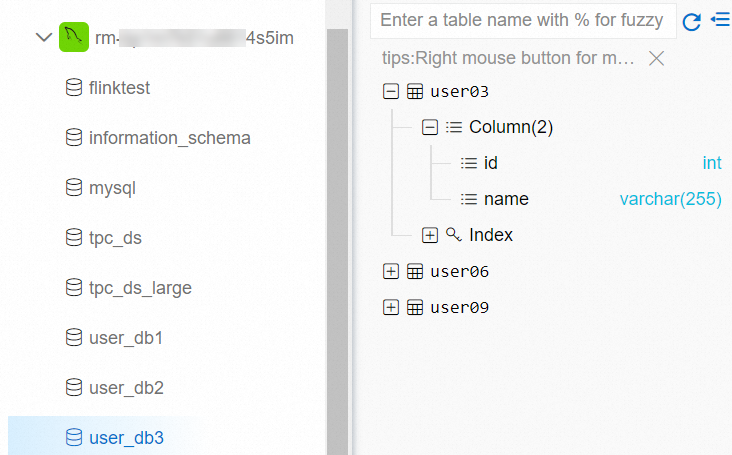
To build a data ingestion job that synchronizes all these tables and their data to Hologres and merges the sharded user tables into a single Hologres table, follow these steps:
This topic uses the Flink CDC Data Ingestion Job Development (Public Preview) feature to perform whole-database synchronization and merge sharded tables into one target table. This feature also supports one-click full and incremental synchronization and real-time schema evolution synchronization.
Prerequisites
-
If you access the service using a Resource Access Management (RAM) user or RAM role, confirm that you have the required permissions for the Flink console. For more information, see Permission Management.
-
Create a Flink workspace. For more information, see Enable Realtime Compute for Apache Flink.
-
Data Sources and Sinks
-
Create an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. For more information, see (Deprecated, redirected to “Step 1”) Quickly create an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
-
You have created a Hologres instance. For more information, see Purchase Hologres Instances.
NoteThe ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL and Hologres instances must be in the same region and VPC as your Flink workspace. If they are not, you must configure network connectivity. For more information, see How do I access other services across VPCs? and How do I access the Internet?.
-
-
Prepare test data and configure IP whitelists. For more information, see Prepare MySQL test data and a Hologres database and Configure IP whitelists.
Prepare MySQL test data and a Hologres database
-
Click tpc_ds.sql, user_db1.sql, user_db2.sql, and user_db3.sql to download the test data to your local machine.
-
In the DMS Data Management console, prepare test data for your ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
-
Log on to your ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance using DMS.
For more information, see (Deprecated, redirected to “Step 2”) Log on to ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL using DMS.
-
In the SQLConsole window, you can enter the following commands and click Execute.
Create four databases: tpc_ds, user_db1, user_db2, and user_db3.
CREATE DATABASE tpc_ds; CREATE DATABASE user_db1; CREATE DATABASE user_db2; CREATE DATABASE user_db3; -
On the top shortcut menu bar, click Data Import.
-
On the Batch Data Import tab, you can select the target database, upload the corresponding SQL file, click Submit Application, and then click Execute Change. In the dialog box that appears, you can click Confirm Execution.
Repeat this process for the tpc_ds, user_db1, user_db2, and user_db3 databases to import their respective data files.

-
-
In the Hologres console, create a database named my_user to store the merged user table data.
For more information, see Create a database.
Configure IP whitelists
To allow Flink to access your ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL and Hologres instances, you must add the CIDR block of your Flink workspace to the IP whitelists of both instances.
-
Obtain the VPC CIDR block of your Flink workspace.
-
Log on to the Realtime Compute console.
-
In the Workspace list, find your target workspace. In the Actions column, choose .
-
In the Workspace Details dialog box, view the VPC CIDR block of the virtual switch that Flink uses.
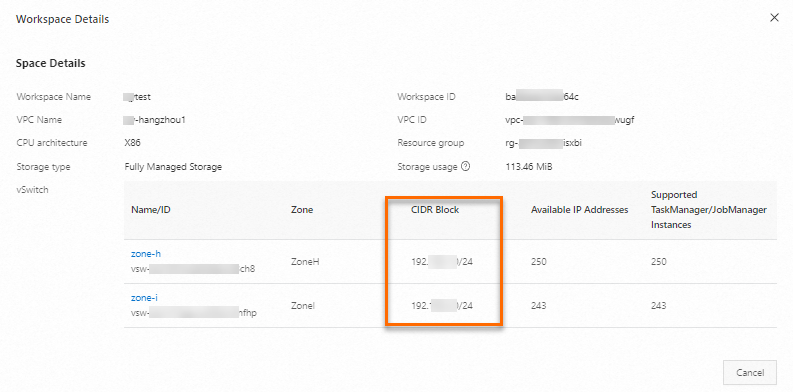
-
-
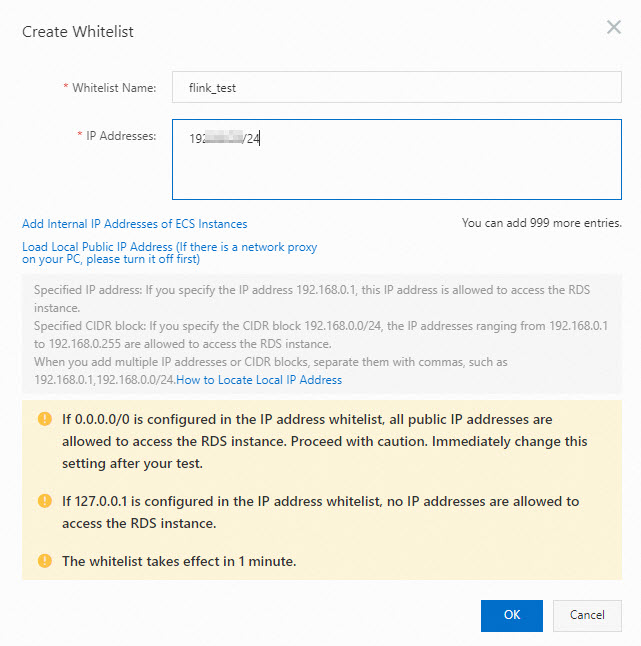
Add the Flink CIDR block to the IP whitelist of your ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
For more information, see Configure IP whitelists.
-
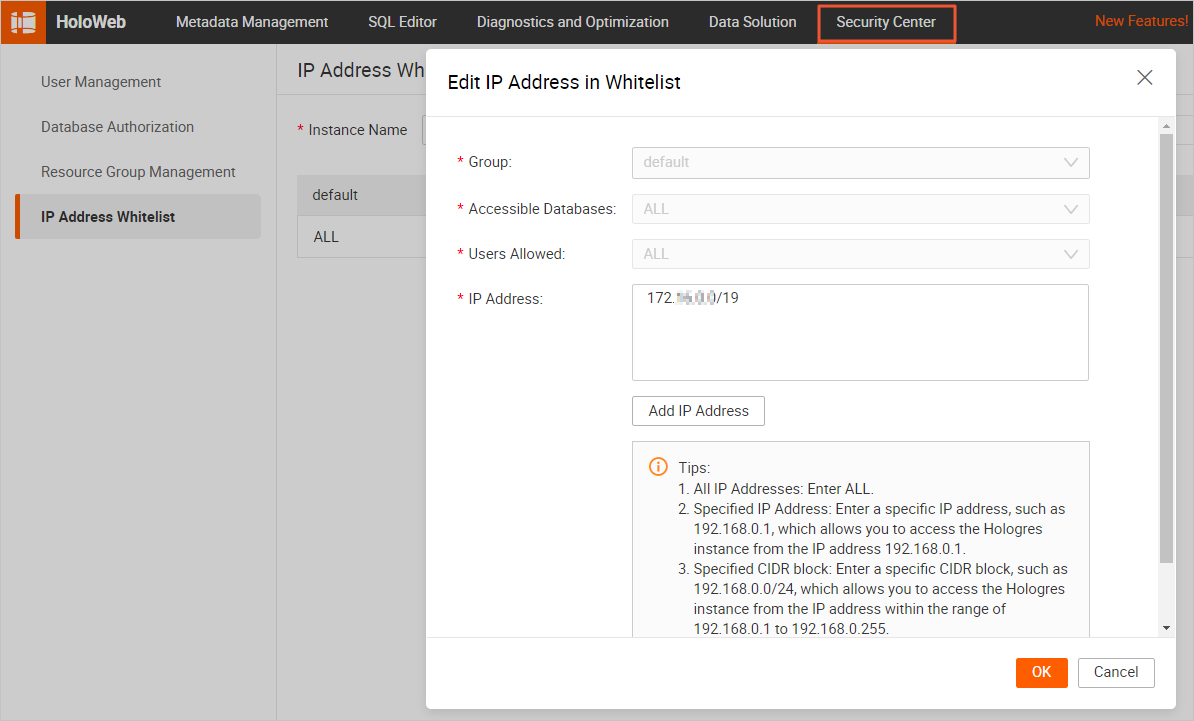
Add the Flink CIDR block to the IP whitelist of your Hologres instance.
When you configure a data connection in HoloWeb, you must set Login Method to Passwordless Login for Current User before you can configure an IP whitelist for the connection. For more information, see IP Whitelist.
Step 1: Develop a data synchronization job
-
Log on to the Flink development console and create a new job.
-
On the page, click New.
-
You can click Blank Data Ingestion Draft.
Flink provides many code templates. Each template includes a use case, sample code, and usage guidance. You can click a template to learn about Flink features and syntax, and to implement your business logic.
-
You can click Next.
-
In the New Data Ingestion Job Draft dialog box, specify the configuration.
Job Parameter
Description
Example
File Name
Name of the job.
NoteThe job name must be unique within the current project.
flink-test
Storage Location
Folder where the job code file is stored.
You can also click the
 icon to the right of an existing folder to create a subfolder.
icon to the right of an existing folder to create a subfolder.Job Draft
Engine Version
Flink engine version used by the job. For details about version numbers, version mappings, and lifecycle milestones, see Engine Version Overview.
vvr-11.1-jdk11-flink-1.20
-
Click OK.
-
-
Copy the following job code into the job editor.
This job synchronizes all tables from the tpc_ds database to Hologres and merges the sharded user tables into a single Hologres table. Sample code:
source: type: mysql name: MySQL Source hostname: localhost port: 3306 username: username password: password tables: tpc_ds.\.*,user_db[0-9]+.user[0-9]+ server-id: 8601-8604 # (Optional) Synchronize table and column comments. include-comments.enabled: true # (Optional) Prioritize unbounded chunk distribution to avoid possible TaskManager OutOfMemory errors. scan.incremental.snapshot.unbounded-chunk-first.enabled: true # (Optional) Enable parsing filters to speed up reading. scan.only.deserialize.captured.tables.changelog.enabled: true sink: type: hologres name: Hologres Sink endpoint: ****.hologres.aliyuncs.com:80 dbname: cdcyaml_test username: ${secret_values.holo-username} password: ${secret_values.holo-password} sink.type-normalize-strategy: BROADEN route: # Merge sharded user tables into the my_user.users table. - source-table: user_db[0-9]+.user[0-9]+ sink-table: my_user.usersNoteAll tables in the MySQL tpc_ds database map directly to identically named tables in the downstream database. No additional mapping is needed in the route section. To sync them to a different database, such as ods_tps_ds, configure the route section as follows:
route: # Merge sharded user tables into the my_user.users table. - source-table: user_db[0-9]+.user[0-9]+ sink-table: my_user.users # Sync all tables from the tpc_ds database to the ods_tps_ds database. - source-table: tpc_ds.\.* sink-table: ods_tps_ds.<> replace-symbol: <>
Step 2: Start the job
-
On the page, click Deploy. In the dialog box that appears, click Confirm.
-
On the page, click Actions next to your target job, and then click Start. For more information, see Start a job.
-
Click Start.
After the job starts, you can monitor its status and runtime information on the Job Operations page.
Step 3: Monitor full data synchronization results
-
Log on to the Hologres Management Console.
-
On the Metadata Management tab, view the 24 tables and their data in the tpc_ds database.
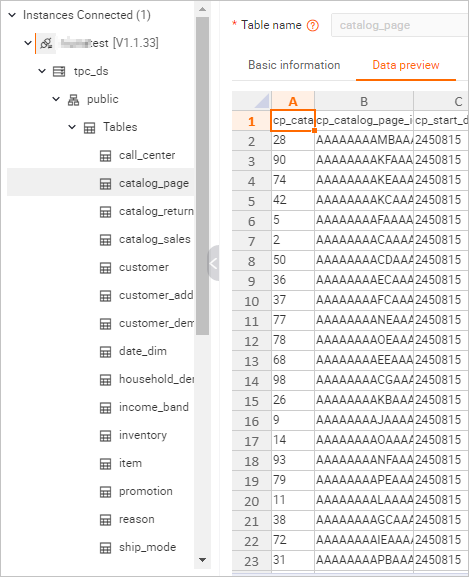
-
On the Metadata Management tab, you can view the schema of the users table in the my_user database.
The synchronized schema and data are shown in the following figures.
-
Schema
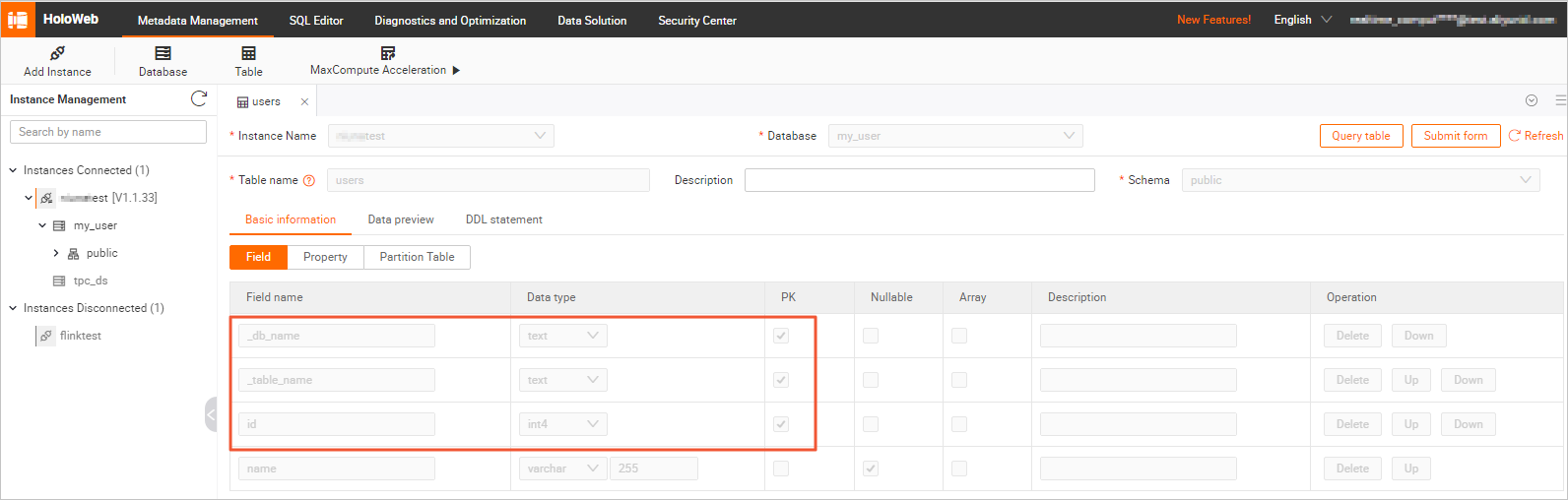
The users table schema includes two extra columns: _db_name and _table_name. These columns record the source database and table names. They also form part of a composite primary key to ensure uniqueness after the sharded tables are merged.
-
Table data
In the upper-right corner of the users table details page, click Query Table, enter the following command, and then click Run.
select * from users order by _db_name,_table_name,id;The query result is shown in the following figure.
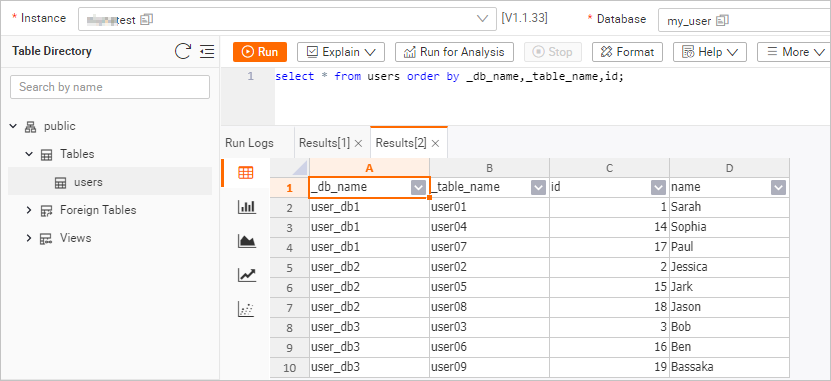
-
Step 4: Monitor incremental synchronization results
After full data synchronization is complete, the job automatically switches to incremental synchronization. No manual intervention is required. You can check the currentEmitEventTimeLag metric on the Monitoring and Alerts tab to determine the current synchronization phase.
-
Log on to the Realtime Compute console.
-
Find your target workspace and click Console in the Actions column.
-
On the page, click the name of your target job.
-
You can click the Monitoring and Alerts tab (or the Data Curve tab).
-
Check the currentEmitEventTimeLag curve to identify the synchronization phase.
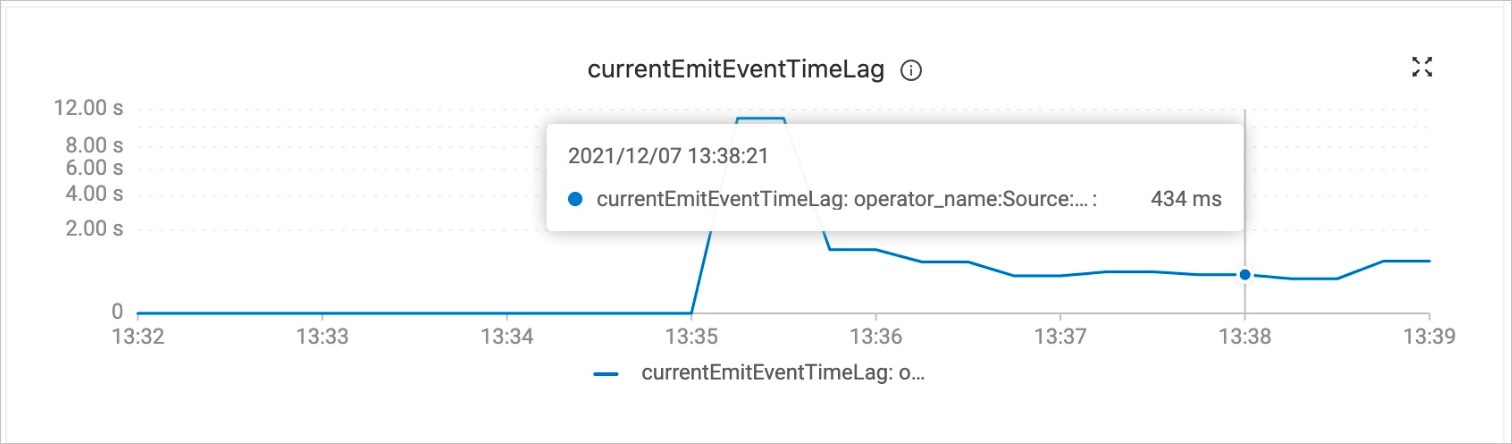
-
A value of 0 indicates that full synchronization is still in progress.
-
A value greater than 0 indicates that incremental synchronization has started.
-
-
Verify real-time synchronization of data and schema changes.
MySQL CDC sources support real-time synchronization of data and schema changes during incremental synchronization. After the job enters the incremental synchronization phase, you can modify the schema and data of a sharded user table in MySQL to verify this capability.
-
Log on to your ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance using DMS.
For more information, see (Deprecated, redirected to “Step 2”) Log on to ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL using DMS.
-
In the user_db2 database, run the following commands to modify the schema of the user02 table and insert and update data.
USE DATABASE `user_db2`; ALTER TABLE `user02` ADD COLUMN `age` INT; -- Add the age column. INSERT INTO `user02` (id, name, age) VALUES (27, 'Tony', 30); -- Insert data with age. UPDATE `user05` SET name='JARK' WHERE id=15; -- Update another table and change the name to uppercase. -
In the Hologres console, check the changes to the users table schema and data.
In the upper-right corner of the details page of the users table, click Query Table, enter the following command, and click Run.
select * from users order by _db_name,_table_name,id;The query result is shown in the following figure.
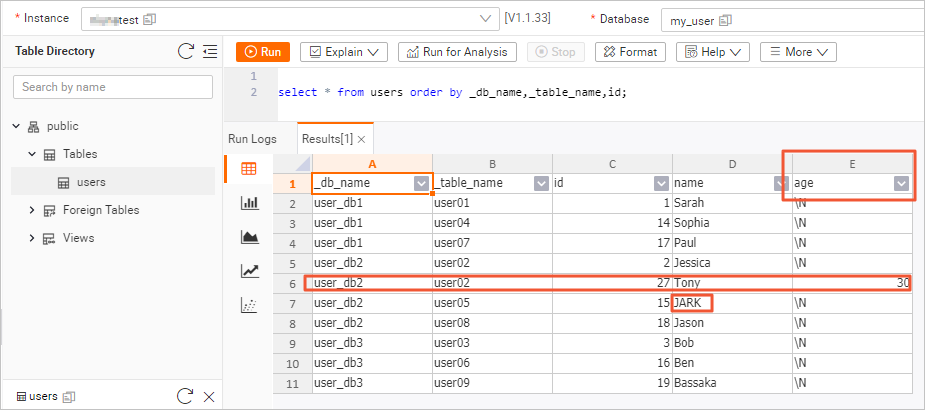 Although the schemas of the sharded tables differ, the schema and data changes made to the user02 table are synchronized in real time to the downstream users table. In Hologres, the users table now includes the new age column, the inserted Tony record, and the updated JARK record.
Although the schemas of the sharded tables differ, the schema and data changes made to the user02 table are synchronized in real time to the downstream users table. In Hologres, the users table now includes the new age column, the inserted Tony record, and the updated JARK record.
-
(Optional) Step 5: Configure job resources
Data volume varies. To optimize job performance, you can adjust the concurrency and TaskManager resources. You can use resource configuration to tune the job concurrency and memory or CU allocation.
-
On the page, click the name of your target job.
-
On the Deployment Details tab, click Resource Configuration, and then click Edit in the upper-right corner.
-
Manually set resource parameters such as TaskManager memory and concurrency.
-
In the upper-right corner of the Resource Configuration section, click Save.
-
Restart the job.
Resource configuration changes take effect only after you restart the job.
References
-
For more information about the syntax of data ingestion modules, see Flink CDC Data Ingestion Job Development Reference.
-
If an exception occurs while you run a data ingestion job, see Common Issues and Solutions for Data Ingestion Jobs.