This topic describes how to purchase a PolarDB cluster on the Custom Purchase page in the PolarDB console.
If you have an existing ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, you can upgrade it to a PolarDB for MySQL cluster with a single click. After the upgrade, the PolarDB cluster retains the accounts, databases, IP address whitelists, and necessary parameters from the source RDS instance. For more information, see Upgrade an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance to a PolarDB for MySQL cluster.
If you have an existing PolarDB for MySQL cluster, you can perform a major engine version upgrade by migrating the source PolarDB for MySQL cluster to a new PolarDB for MySQL cluster. The new cluster contains the account information, database information, IP address whitelist, and necessary parameters from the source cluster. For more information, see major engine version upgrade.
Prerequisites
You have registered and logged on to an Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see Register and log on to an Alibaba Cloud account.
Procedure
Go to the PolarDB cluster purchase page.
Set the basic configuration parameters for your cluster. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Billing Method
Subscription: a prepaid model where you select resources of fixed specifications and pay upfront when you create a cluster. The longer the subscription duration, the greater the discount. This method is suitable for businesses with stable and long-term resource needs.
Pay-as-you-go: a postpaid model where you select resources of fixed specifications but do not need to pay upfront when you create a cluster. Billing is based on your actual resource usage. This method is suitable for businesses with flexible or variable resource demands.
Serverless: a postpaid model where you do not need to select resources of fixed specifications or pay upfront when you create a cluster. PolarDB automatically scales resources based on the workload demands. This method is applicable to businesses with fluctuating or unpredictable workloads.
NoteFor a detailed comparison of billing methods, see Billing methods.
Billing method conversion rules: You can switch between Subscription and Pay-as-you-go. However, you cannot convert a Serverless cluster to another billing method.
Region
A region refers to the geographic area where a data center is located, typically defined by the city where the data center resides.
NoteSelecting a region close to your location reduces network latency. You cannot change the region after purchase.
Create your PolarDB cluster in the same region as your ECS instance. Otherwise, they cannot communicate over the internal network (private network) and must use the Internet (public network), which prevents the cluster from delivering optimal performance.
Creation Method
PolarDB supports multiple creation methods. By default, Create Primary Cluster is selected, which creates a new PolarDB cluster. Other options include the following:
Create Secondary Cluster: Creates a secondary cluster for a global database network (GDN). You must first create a GDN before adding a secondary cluster.
Upgrade/Migrate from PolarDB: Suitable for major version upgrades between different kernel versions or different editions. This involves replicating full data from the source PolarDB cluster, followed by incremental synchronization. For more information, see Major version upgrades.
Migrate from RDS: Migrates an RDS instance to a PolarDB cluster. During migration, the system automatically synchronizes the RDS instance’s accounts, databases, IP address whitelists, and necessary parameter configurations. You can also choose to retain the original database endpoint to simplify migration and ensure smooth business transition. For more information, see Upgrade an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance to a PolarDB for MySQL cluster.
NoteThe available list of RDS instances excludes read-only instances and instances that use non-InnoDB engines.
Clone from RDS: Quickly clones a PolarDB cluster that is an exact replica of the selected RDS instance. Incremental data from the RDS instance is not synchronized to the PolarDB cluster. For more information, see Clone an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance to a PolarDB for MySQL cluster.
NoteThe available list of RDS instances excludes read-only instances and instances that use non-InnoDB engines.
Restore from Recycle Bin: Restores a deleted PolarDB cluster using backup sets retained in the cluster recycle bin.
NoteIf the original PolarDB cluster has X-Engine enabled and contains corresponding database tables, set Storage Engine to InnoDB & X-Engine. Otherwise, the new PolarDB cluster cannot access data stored in X-Engine.
Database Engine
Select a MySQL-compatible version.
MySQL 8.0.2: Fully compatible with community MySQL 8.0.18 and earlier versions.
MySQL 8.0.1: Fully compatible with community MySQL 8.0.13 and earlier versions.
MySQL 5.7: Fully compatible with MySQL 5.7.
MySQL 5.6: Fully compatible with MySQL 5.6.
NoteFeatures vary by kernel version. For more information, see Feature comparison for MySQL 5.6, 5.7, and 8.0.
Edition
Select Enterprise Edition or Standard Edition.
NoteFeatures vary by edition. For more information, see Feature comparison between Enterprise Edition and Standard Edition.
Series
Enterprise Edition supports Cluster Edition and Multi-master Cluster (Limitless). This option is unavailable for Standard Edition.
NoteThe two series differ in architecture and applicable scenarios. For more information, see Enterprise Edition series.
Sub-series
Select Dedicated or General-purpose:
Dedicated Specification: Each cluster exclusively uses its allocated compute resources (such as CPU) and does not share them with other clusters on the same server, ensuring stable and reliable performance.
General Specification: Clusters on the same server share idle compute resources (such as CPU) with each other, leveraging resource reuse for better cost efficiency.
For a detailed comparison of the two sub-series, see How to choose between General Specification and Dedicated Specification.
CPU Architecture
Select X86 or ARM.
x86: The x86 architecture powered by Intel processors and high-performance networking capabilities delivers comprehensive performance and stability enhancements. It is ideal for enterprise-level applications that require high business stability and computing power.
ARM: The ARM architecture equipped with Alibaba Cloud's proprietary YiTian 710 processor chips and 25 GE intelligent high-speed network cards provides robust computing power and high-performance networking capabilities. It can address the needs of public service sectors and enterprises, such as Internet companies, that require cost-effective, secure, and stable cloud services.
NoteEnterprise Edition uses X86 only.
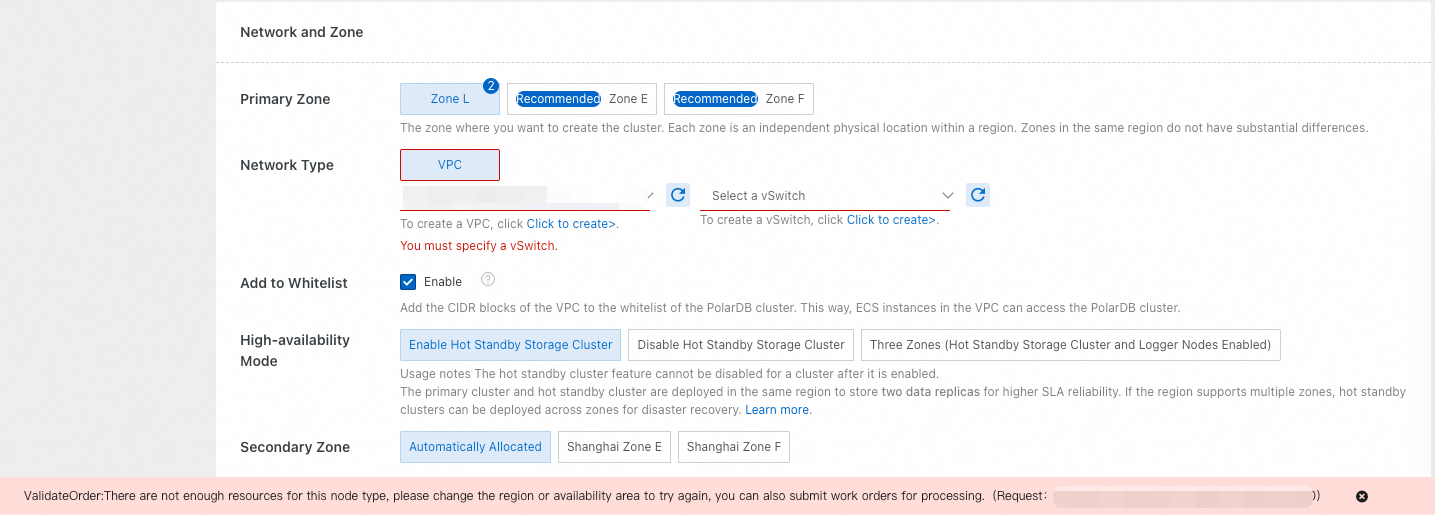
Primary Zone
A zone is a physically isolated area within a region with independent power and network infrastructure. Zones have no functional differences. You can create your PolarDB cluster and ECS instance in the same zone or different zones.
Network Type
Fixed as VPC.
Select the same virtual private cloud (VPC) as your ECS instance. Otherwise, they cannot communicate over the internal network (private network) and must use the Internet (public network), which prevents the cluster from delivering optimal performance.
If you have created a VPC that meets your network requirements, select it directly. For example, if your ECS instance resides in a VPC that fits your planning, select that VPC.
If you have not created a suitable VPC, use the default VPC and vSwitch.
NoteIf the default VPC and vSwitch do not meet your requirements, you can create a VPC and vSwitch.
Add to Whitelist
We recommend that you Enable this option to add the CIDR blocks of the selected VPC to the whitelists of the PolarDB cluster. This allows ECS instances in the same VPC to directly access the PolarDB cluster, eliminating the need to manually add whitelist entries after cluster creation.
High-availability Mode
PolarDB provides multiple high availability modes. After you enable the hot standby storage cluster feature for a PolarDB cluster, a hot standby storage cluster is created in the secondary zone of the region in which the PolarDB cluster resides or in a different data center in the same zone. The hot standby storage cluster has independent storage resources. Whether the hot standby storage cluster has independent compute resources varies based on the high availability mode. When the PolarDB cluster in the primary zone fails, the hot standby storage cluster immediately takes over and handles read and write operations and storage tasks.
NoteFor more information about the hot standby storage cluster and related solutions, see High availability modes (hot standby clusters).
Rules for changing high availability modes:
You cannot directly change the high availability mode of a cluster from Double Zones (Hot Standby Storage Cluster Enabled) or Double Zones (Hot Standby Storage and Compute Clusters Enabled) to Single Zone (Hot Standby Storage Cluster Disabled).
For such change of the high availability mode, we recommend that you purchase a new cluster and select the Single Zone (Hot Standby Storage Cluster Disabled) high availability mode for the cluster. Then, migrate the existing cluster to the new cluster by using Data Transmission Service (DTS). For information about how to migrate an existing cluster to a new cluster, see Migrate data between PolarDB for MySQL clusters.
You can select the Three Zones high availability mode only when you purchase a new cluster. You cannot change the high availability mode of a cluster from Three Zones to other high availability modes and vice versa.
You can manually change the high availability mode of a cluster from Single Zone (Hot Standby Storage Cluster Disabled) to a different high availability mode. For more information, see High availability modes (hot standby clusters).
Set resource scaling range for Serverless clusters
You can set the resource scaling range for a Serverless cluster only when the Billing Method is Serverless:
Minimum Read-only Nodes: the minimum number of read-only nodes that can be added. Valid values: 0 to 15.
Maximum Read-only Nodes: the maximum number of read-only nodes that can be added. Valid values: 0 to 15.
NoteThe number of read-only nodes automatically increases or decreases within the specified range based on the actual workloads. For more information, see Scaling.
To ensure high availability of serverless clusters, we recommend that you set Minimum Read-only Nodes to 1.
Minimum PCUs per Node: the minimum number of PCUs per node in the cluster. Valid values: 0.25 PCU to 31 PCUs.
Maximum PCUs per Node: the maximum number of PCUs per node in the cluster. Valid values: 1 PCU to 32 PCUs.
NotePCUs are the unit for second-level billing and resource scaling for the serverless feature. One PCU is approximately equal to 1 core and 2 GB of memory The PCUs of a node is dynamically adjusted within the specified range based on the workloads. The minimum granularity for scaling is 0.5 PCUs.
Example: If you set the Minimum PCUs per Node parameter to 2 PCUs and the Maximum PCUs per Node parameter to 16 PCUs, the default specifications of a node in the serverless cluster are 2 PCUs (2 CPU cores and 4 GB memory). When the business load increases, the system automatically increases the number of PCUs of the primary node or read-only nodes. However, the maximum number of PCUs can only be increased to 16 PCUs (16 CPU cores and 32 GB memory) based on the settings.
Current Specification
Specifications differ in CPU, memory, maximum storage capacity, and IOPS. Select based on your business needs.
NoteAvailable compute node specifications vary by edition. For details, see Compute node specifications for Enterprise Edition and Compute node specifications for Standard Edition.
Enable Serverless
You can enable the serverless feature for a cluster with defined specifications when you create a PolarDB cluster.
After enabling, the cluster gains dynamic elastic scaling capabilities in addition to the fixed compute node specifications you selected. However, this incurs scale-up fees.
NoteBy default, a Serverless cluster has a maximum of 8 PCUs per node, a minimum of 0 PCUs per node, a maximum of 1 read-only node, and a minimum of 0 read-only nodes. You can adjust these parameters anytime on the cluster details page.
Number of Nodes
By default, the cluster has two nodes (one read/write and one read-only). Configure based on your business needs.
NoteOnly Multi-master Cluster (Limitless) Edition in Enterprise Edition supports multiple read/write nodes. Other series support only one read/write node.
The single-node series is discontinued, but you can purchase a single-node PolarDB cluster by setting the number of read-only nodes to 0.
If you set the number of read-only nodes to 1 or more during purchase, you cannot reduce it to 0 afterward. To change an existing cluster to zero read-only nodes, purchase a new cluster and migrate data using a tool like DTS or the major version upgrade feature.
Description:
Read/write node: Also called the primary node, it handles write operations and some read operations. It works with read-only nodes using an active-active failover mechanism to provide high availability.
Read-only node: Handles read operations to offload the primary node, offering high availability and scalability. You can dynamically adjust the number after cluster creation.
Read-only column store node: A functional node for In-Memory Column Index (IMCI). IMCI uses columnar storage to accelerate analytical queries (OLAP), enabling PolarDB for MySQL clusters to handle real-time transaction processing and analytics together. After you add a read-only IMCI node, configure automatic request distribution among row store and column store nodes, and add columnstore indexes to business tables, OLAP queries automatically route to read-only row store or column store nodes instead of the primary node.
Database Proxy Specification
Choose between Standard Enterprise Edition and Dedicated Enterprise Edition. The type depends on your cluster’s sub-series: General Specification uses Standard Enterprise Edition, and Dedicated Specification uses Dedicated Enterprise Edition.
You can configure the database proxy specification separately, with options from 4C to 16C (4 vCPUs to 16 vCPUs). We recommend selecting automatic matching.
NoteThis option is available only for Standard Edition clusters.
Storage Type
PolarDB supports ESSD, PSL4, or PSL5 storage types. ESSD is available only for Standard Edition clusters.
ESSDs are ultra-high performance disks developed by Alibaba Cloud. ESSDs use a next-generation distributed block storage architecture and support 25 Gigabit Ethernet networks and Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA). Each ESSD has low one-way latency and can deliver up to 1 million random read/write IOPS. ESSDs are divided into the following categories:
PL0 ESSD: Basic performance level.
PL1 ESSD: Delivers 5× higher IOPS and ~2× higher throughput than PL0.
PL2 ESSD: Delivers ~2× higher IOPS and throughput than PL1.
PL3 ESSD: Delivers up to 10× higher IOPS and 5× higher throughput than PL2, ideal for scenarios requiring extreme concurrent I/O performance and stable low read/write latency.
ESSD AutoPL disk: Decouples IOPS from capacity, allowing flexible configuration and on-demand adjustments to reduce total cost of ownership (TCO).
ImportantFor ESSD performance details, see ESSD.
When a disk's storage space is full, the disk is locked and becomes read-only.
To avoid service disruption, you can enable automatic ESSD storage expansion.
PSL4 and PSL5 are storage types designed by PolarDB for different scenarios. Differences are as follows:
Storage class
Features
Scenarios
PSL5 (PolarStore Level 5)
A storage class supported in earlier versions of PolarDB. It is the default storage class for PolarDB clusters purchased before June 7, 2022. It provides better performance, reliability, and availability.
Business scenarios that require high performance and reliability, where the database is a core system. Such scenarios include finance, e-commerce, government services, and medium-to-large Internet businesses.
PSL4 (PolarStore Level 4)
PolarDB launched this new storage class that uses Alibaba's proprietary smart-SSD technology. This technology compresses and decompresses data at the physical SSD disk layer. This lowers the storage price per unit of data while keeping the performance impact under control.
Application scenarios that require cost reduction and high cost-effectiveness.
NoteStorage class conversion rules:
Some product series support storage class upgrades, which means that PSL4 storage can be upgraded to PSL5 storage.
Downgrading the storage class is not supported. You cannot downgrade PSL5 storage to PSL4 storage.
To switch from PSL5 storage to PSL4 storage, you can purchase a new cluster and migrate the data from the original cluster to the new cluster using a migration tool such as DTS or the major version upgrade feature.
Storage Engine
Two engine types are supported: InnoDB and InnoDB & High-compression Engine.
NoteInnoDB & X-Engine: A hybrid engine combining InnoDB and X-Engine. After selection, you can set the X-Engine ratio. For details, see X-Engine.
Storage Billing Method
Storage supports two billing methods: Billing By Capacity (Pay-As-You-Go) and Billing By Space (Subscription).
Pay-as-you-go (billed by capacity): No capacity selection needed during purchase. Storage scales automatically as data grows, and you pay only for actual used space.
Subscription (billed by space): Prepay for cluster storage space during purchase.
NoteAvailable only when Billing Method is Subscription.
Storage Capacity
Configure the pre-purchased storage size.
NoteRequired only when:
Storage type is ESSD.
Billing Method is Subscription, and Storage Billing Method is Subscription (billed by space).
(Optional) Configure advanced options.
Parameter
Description
Cluster Name
Set a name for the cluster based on your business needs. If you do not specify a name, the system generates one. You can modify the name at any time after the cluster is created. The name must meet the following requirements:
The name cannot start with
http://orhttps://.The name must be 2 to 256 characters in length.
Resource Group
Select a resource group from your created resource groups.
NoteA resource group is a container that you can use to manage resources under your Alibaba Cloud account. Each resource can belong to only one resource group. For more information, see Resource grouping and authorization.
Parameter Template
Set the parameter template for the cluster. You can select a system-provided template or a custom template.
NoteThe drop-down list displays all custom and system default parameter templates in the current region.
Time Zone
Set the time zone for the cluster. The default value is UTC+08:00.
Table Name Case Sensitivity
Specify whether table names are case-sensitive. The default setting is case-insensitive.
NoteIf your on-premises database is case-sensitive, we recommend that you select Case-sensitive to ensure data consistency and simplify migration.
This setting cannot be changed after the cluster is created. Select a setting with caution.
Deleting (releasing) a cluster
Set the retention policy for backups after the cluster is deleted (released).
Retain last backup (automatic backup before release) (Default): The last backup is retained in the cluster recycle bin. You are charged for the retained backup.
Retain all backups: All backups are retained in the cluster recycle bin. You are charged for the retained backups.
Delete all backups (cannot be restored): All data and backups are permanently deleted and cannot be recovered. No fees are incurred.
Enable TDE
You can enable transparent data encryption (TDE) when you create the cluster. You do not need to configure TDE after the cluster is created.
NoteAfter you enable TDE, you cannot disable it.
TDE depends on KMS. After you enable TDE, you must configure a service-linked role and authorize PolarDB to access KMS.
After you enable TDE, PolarDB transparently encrypts the data files of the cluster. This process does not affect applications. TDE has a 5% to 10% performance impact.
On the right side of the page, confirm the purchase quantity and cluster configuration, and then complete the purchase.
Parameter
Description
Quantity
Select the number of clusters to purchase.
NoteYou can create up to 50 clusters at a time. This is useful for scenarios such as launching game servers in bulk.
The total number of clusters that can be purchased for an Alibaba Cloud account is 50.
Duration
Select the cluster subscription duration.
NoteThis parameter is available only when the Billing Method is Subscription. It is not available for pay-as-you-go clusters.
Auto-renewal
Specify whether to enable auto-renewal. To prevent service interruptions caused by a missed renewal, we recommend that you enable this feature.
NoteThis parameter is available only when the Billing Method is Subscription. It is not available for pay-as-you-go clusters.
In addition to configuring the cluster during the purchase process, you can also configure it later in Expenses and Costs.
After you configure the parameters, review the cluster configuration, payment amount, and service agreement. If the information is correct, click Buy Now.
After you complete the purchase, wait 10 to 15 minutes for the system to create the cluster. Then, you can view the new cluster in the cluster list of the PolarDB console.
NoteIf the status of the cluster nodes is Creating, the cluster is being created and is unavailable. The cluster is ready to use only when its status changes to Running.
Ensure you select the correct region in the top-left corner of the console. Otherwise, you cannot find your cluster.
What to do next
FAQ
Related API operations
In addition to creating clusters in the console, you can use API operations. The following table lists the relevant API operations.
API | Description |
Creates a PolarDB cluster. | |
You can view the cluster list. | |
Queries the detailed attributes of a specified PolarDB cluster. | |
Queries the auto-renewal settings of a subscription PolarDB cluster. | |
Modifies the auto-renewal settings for a subscription PolarDB cluster. |