By Yu Cheng
Traditional load balancing algorithms are primarily designed for general web services or microservices architectures, aiming to enhance overall system efficiency by minimizing response time, maximizing throughput, or maintaining server load balancing. Common load balancing algorithms include round-robin, random, least connections, and consistent hashing. However, when it comes to LLM services, these traditional methods often expose several key flaws:
1. Ignoring task complexity differences: The complexity differences in LLM inference requests can be significant. For instance, a long text generation task might require several times the computational resources of a short text classification task. Traditional load balancers cannot perceive these differences, often leading to overload on some nodes while others remain idle, resulting in resource waste and response delays.
2. Lack of awareness of GPU resource levels: In LLM inference services, computational bottlenecks are often concentrated on GPUs. Traditional load balancers often fail to perceive this fine-grained resource consumption situation, leading to some GPU nodes rejecting requests or responding slowly due to insufficient memory, while others are idle.
3. Lack of KV Cache reuse capabilities: In concurrent request processing, if multiple requests share similar prefixes, their KV Caches may have overlapping parts. By sharing or compressing these, memory usage can be reduced and generation speed increased. Traditional load balancing strategies do not consider the semantic similarities between requests or the reusability of KV Caches, making it difficult to allocate requests with potential reuse value to the same GPU instance, thus missing optimization opportunities.
In response to the characteristics of LLM services, the Higress AI gateway provides load balancing algorithms geared toward LLM services in a plug-in form, including global least connections load balancing, prefix matching load balancing, and GPU-aware load balancing. This can enhance system throughput, reduce response delays, and achieve fairer and more efficient task scheduling without increasing hardware costs.
Taking prefix matching load balancing as an example, the stress testing tool used is NVIDIA GenAI-Perf, with an average input of 200 tokens per round, an average output of 800 tokens, and a concurrency of 20. Each session contains 5 rounds of dialogue, totaling 60 sessions. The performance metrics before and after comparison are as follows:
| Metric | No Load Balancing | Prefix Matching Load Balancing |
|---|---|---|
| TTFT | 240ms | 120ms |
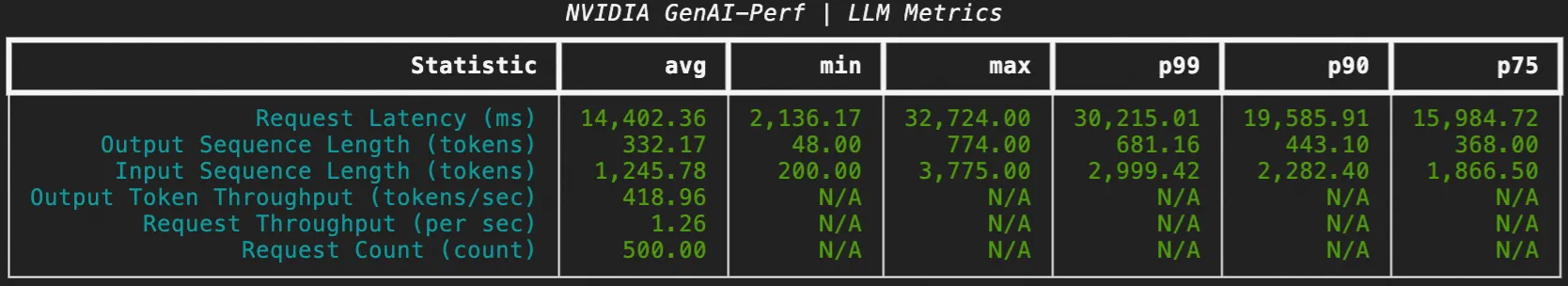
| Average RT | 14934.85ms | 14402.36ms |
| P99 RT | 35345.65ms | 30215.01ms |
| Token Throughput | 367.48 (token/s) | 418.96 (token/s) |
| Prefix Cache Hit Rate | 40%+ | 80%+ |
Currently, there are many excellent open-source projects, such as Envoy AI Gateway and AIBrix, that implement load balancing geared towards LLM using the Envoy External Processing mechanism with an external load balancer, deployed in the form of a sidecar or k8s service.
The Higress AI gateway provides core load balancing capabilities for LLM services in the form of a wasm plugin and has the following features:
Next, this article will introduce the three load balancing algorithms provided by the Higress AI gateway: global least connections load balancing, prefix matching load balancing, and GPU-aware load balancing.
In a distributed environment, gateway instances often have multiple nodes, and traditional load balancing strategies involve local load balancing for each node, lacking a global perspective. In the Higress AI gateway, we leverage Redis to implement a global least connections load balancing algorithm based on the number of requests being processed on each LLM Pod.
The approximate process for selecting Pods is as follows:
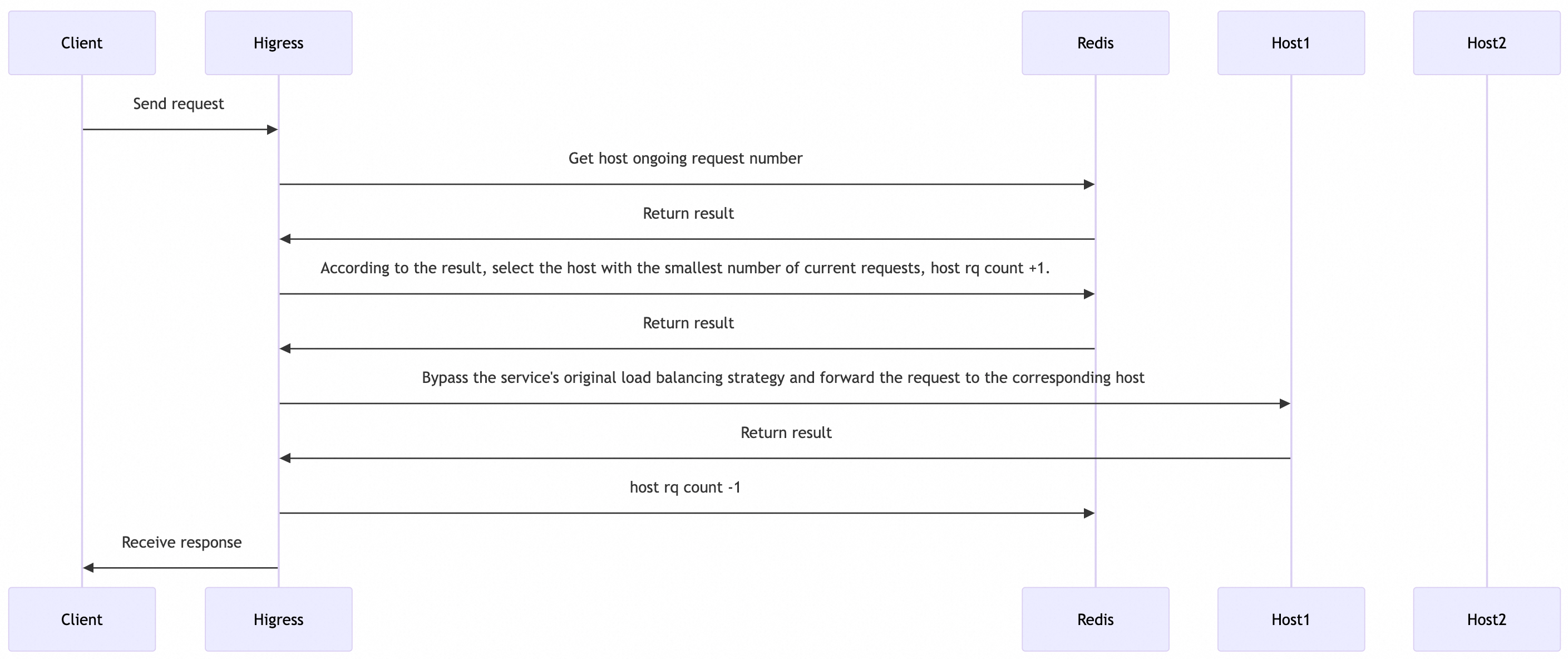
In global least connections load balancing, we focus on processing during request anomalies (e.g., backend service inaccessible, client disconnection, server disconnection, etc.) By making unified changes to counts in the HttpStreamDone phase, we ensure that requests interrupted due to anomalies also have their counts updated, avoiding abnormal counting due to request anomalies.
In multi-turn dialogue scenarios, a session can involve multiple LLM calls, each carrying the same contextual information. If we can perceive this contextual information and route multiple requests belonging to the same session to the same LLM Pod, we can fully utilize the KV Cache of the LLM Pod, significantly improving performance metrics such as RT and token throughput.
In the Higress AI gateway, we leverage Redis to implement a global prefix matching load balancing algorithm that can fully adapt to distributed environments. When a request reaches the gateway, it performs prefix matching based on the current prefix tree information. If matched successfully, it routes to the corresponding LLM Pod; if no prefix matches, it selects the LLM Pod currently processing the least requests based on the global least connections load balancing method.
The approximate process for selecting Pods is as follows:
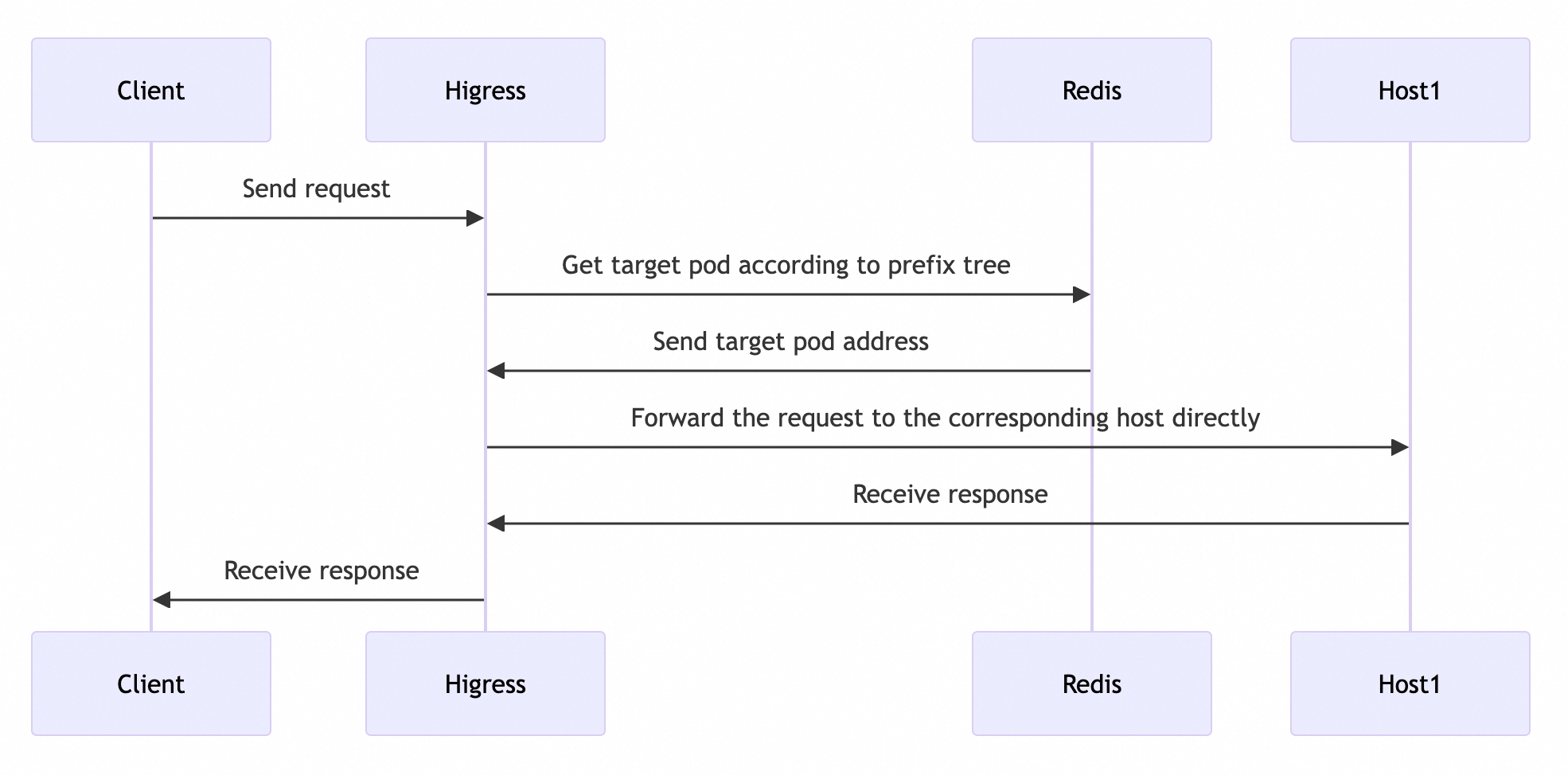
Next, we will briefly introduce how to construct a prefix tree in Redis.
First, the messages of the LLM request are divided into different blocks based on user boundaries, and a 16-character hexadecimal string is obtained through hashing, as shown in the figure below. The messages are divided into two blocks, and the SHA-1 value for each block is calculated:

Assuming a request is divided into n blocks, the process for prefix matching is as follows:
1. Query in Redis whether sha-1(block 1) exists
2. Query in Redis whether sha-1(block 1) XOR sha-1(block 2) exists
3. Query in Redis whether sha-1(block 1) XOR sha-1(block 2) XOR ... XOR sha-1(block n) exists
Through the above process, multiple requests belonging to the same session can be routed to the same pod, thus improving KV Cache reuse.
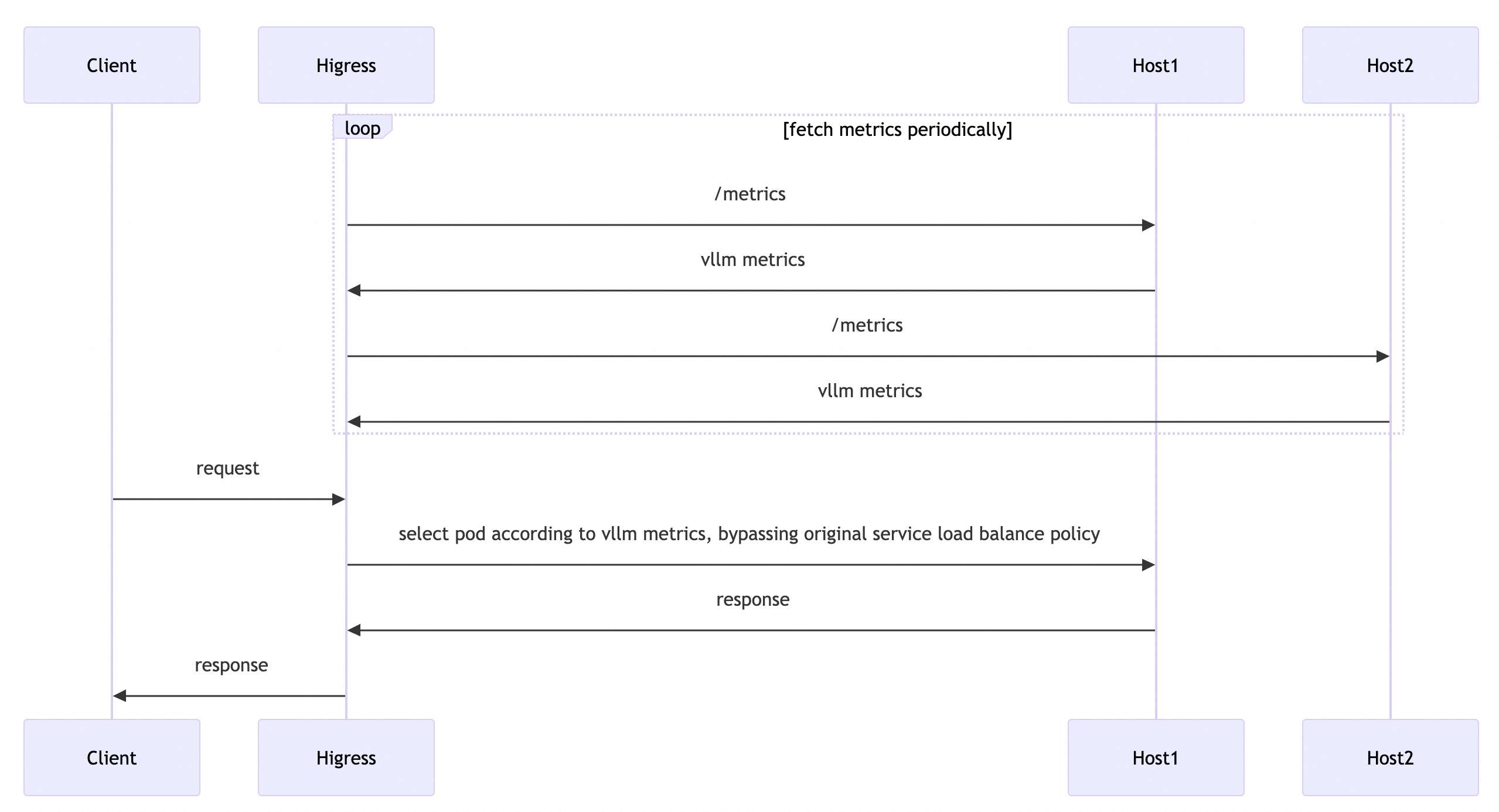
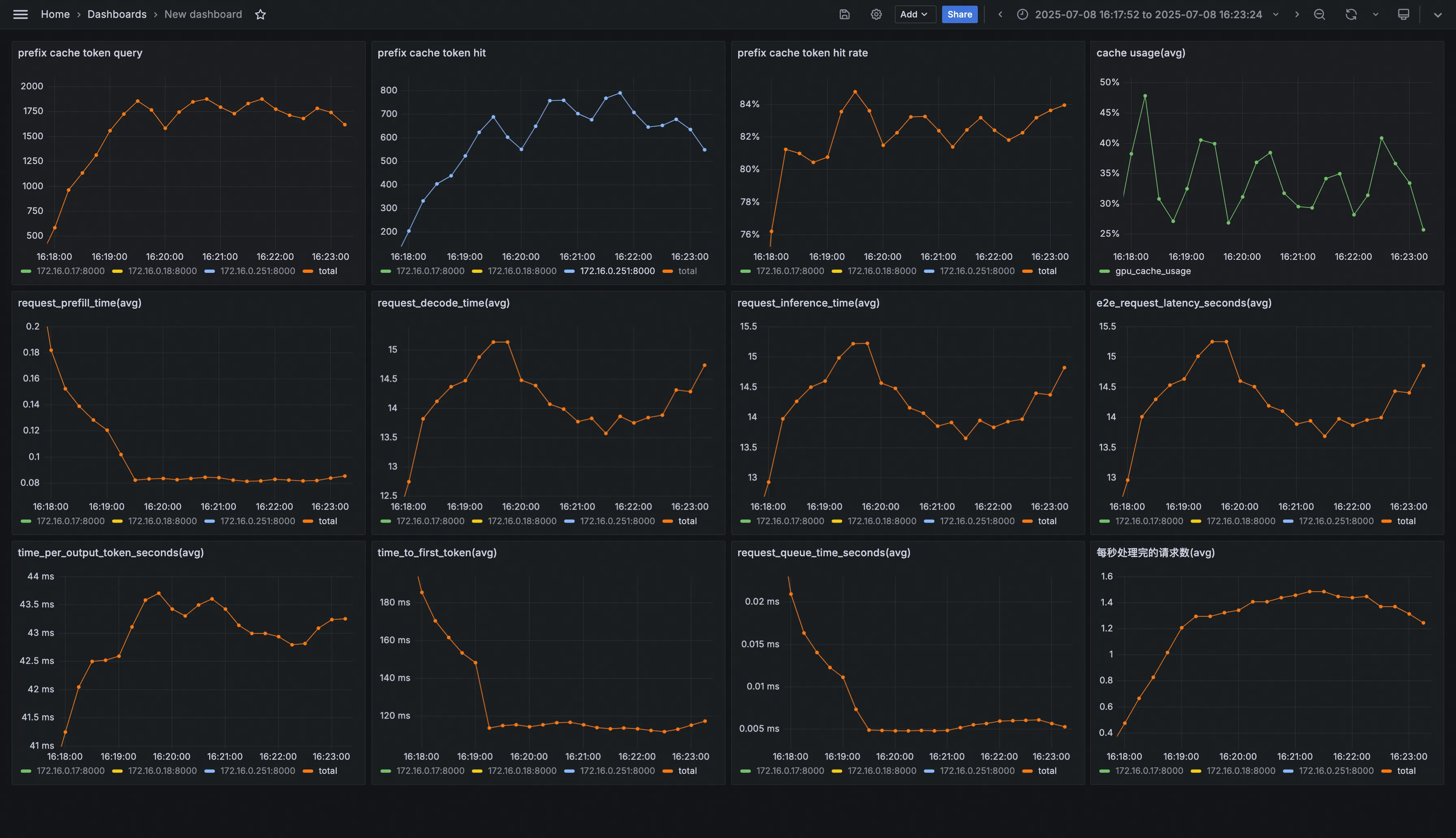
Some LLM server frameworks (such as vllm, sglang, etc.) expose certain monitoring metrics that can reflect GPU load information in real time. Based on these monitoring metrics, a GPU-aware load balancing algorithm can be implemented to make traffic allocation more suitable for LLM services.
Some open-source projects have already implemented GPU-aware load balancing algorithms based on the envoy ext-proc mechanism, but the ext-proc mechanism requires the use of an external process, making deployment and maintenance more complex. The Higress AI gateway implements a mechanism to periodically pull metrics in the background (currently supporting vllm) and provides GPU-aware load balancing capabilities in the form of hot-plug plugins. Moreover, this capability is not limited to k8s environments; any service source supported by the Higress AI gateway can use this capability.
The approximate process for selecting Pods is as follows:
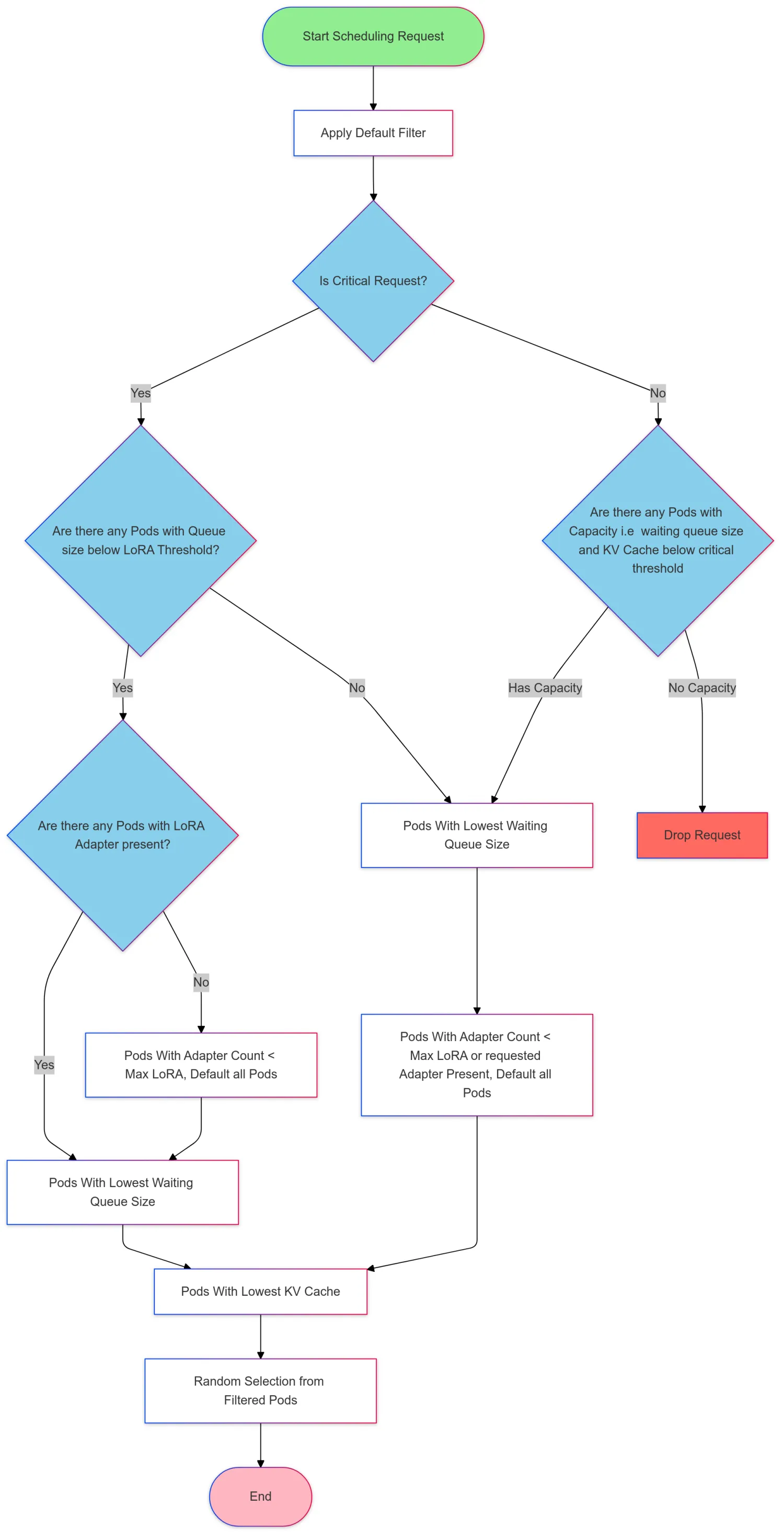
Currently, the metrics-based load balancing strategy follows the gateway-api-inference-extension pod selection algorithm, based on LoRA Adapter affinity, queue length, and KV Cache utilization for load balancing. The selection process is illustrated in the following figure:
Taking prefix matching load balancing as an example:
1. Prepare Redis resources: Log in to the Alibaba Cloud Redis console, create a Redis instance, and set the connection password. For detailed operations, please refer to the Redis quick start overview.
2. Prepare LLM services: Deploy the llama3 model based on the vllm framework in the form of ECS, with a total of 3 nodes.
3. Configure services in the gateway: Import Redis service and LLM service into the gateway instance, where Redis is a DNS type service, and llama3 is a fixed address type service.
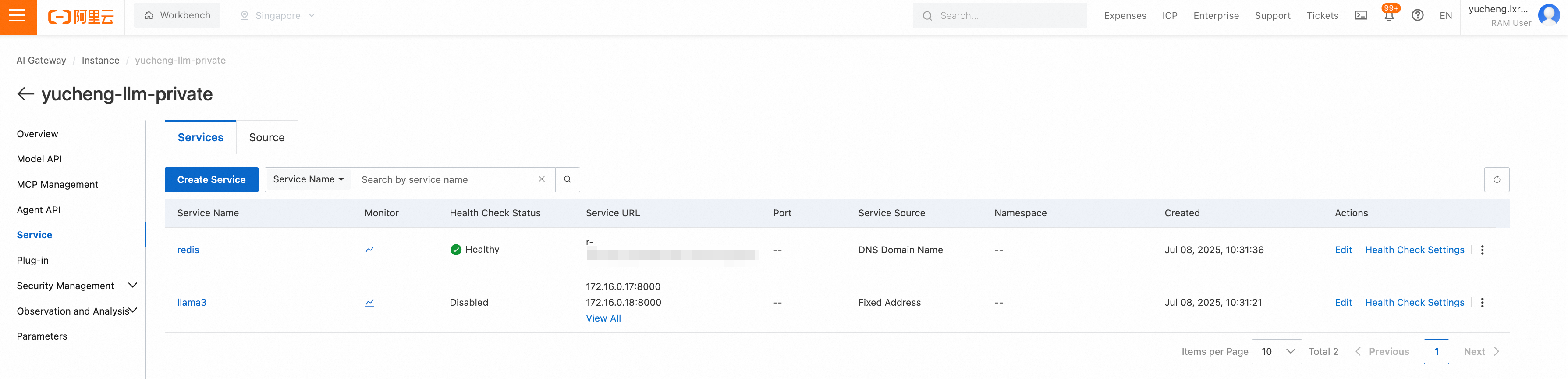
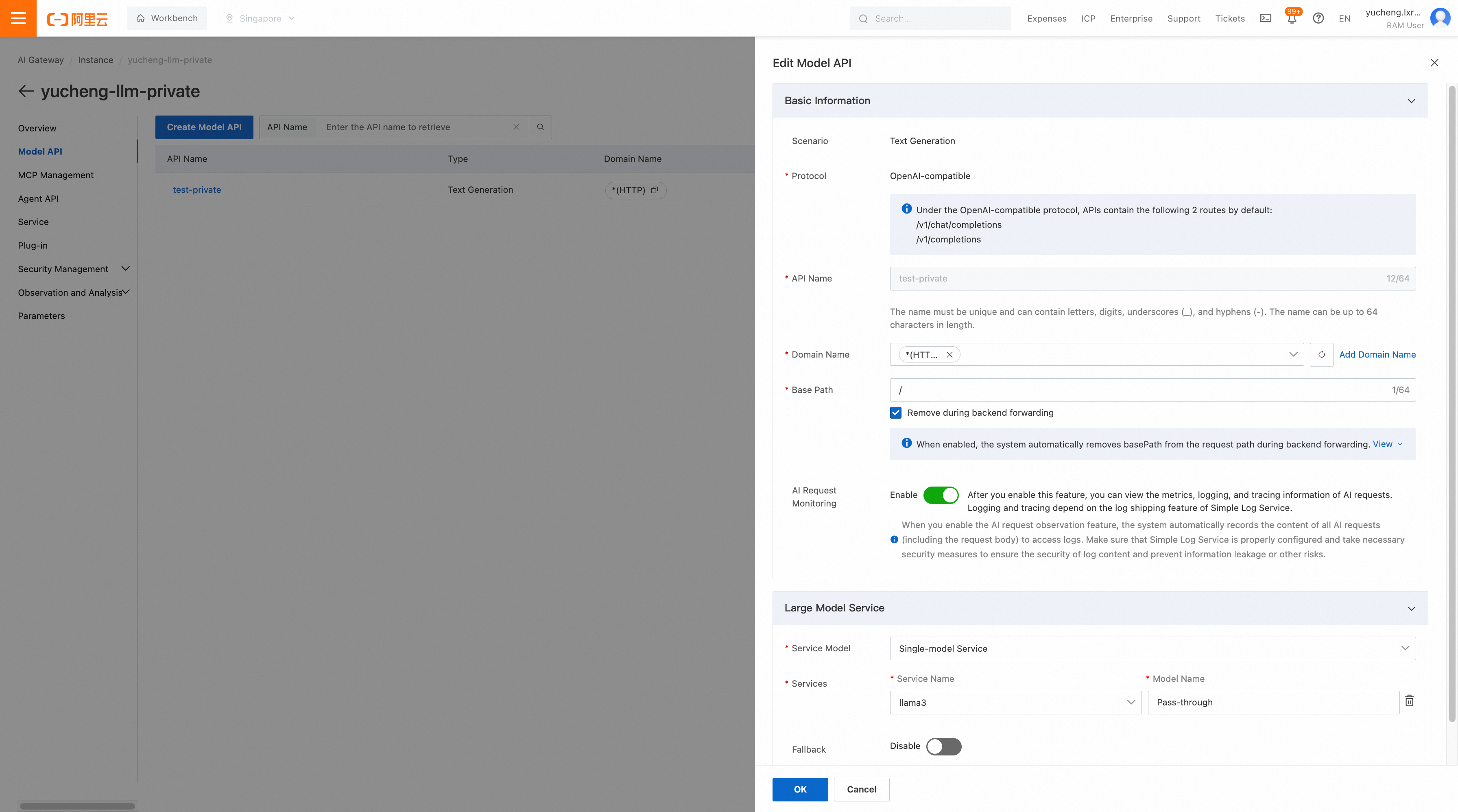
4. Configure API in the gateway: Create an LLM API in the gateway, with the backend service pointing to llama3.
5. Configure plugins in the gateway: Find the ai-load-balancer plugin in the plugin market for installation, then configure the load balancing strategy for the LLM API that was just created under the LLM API granularity.
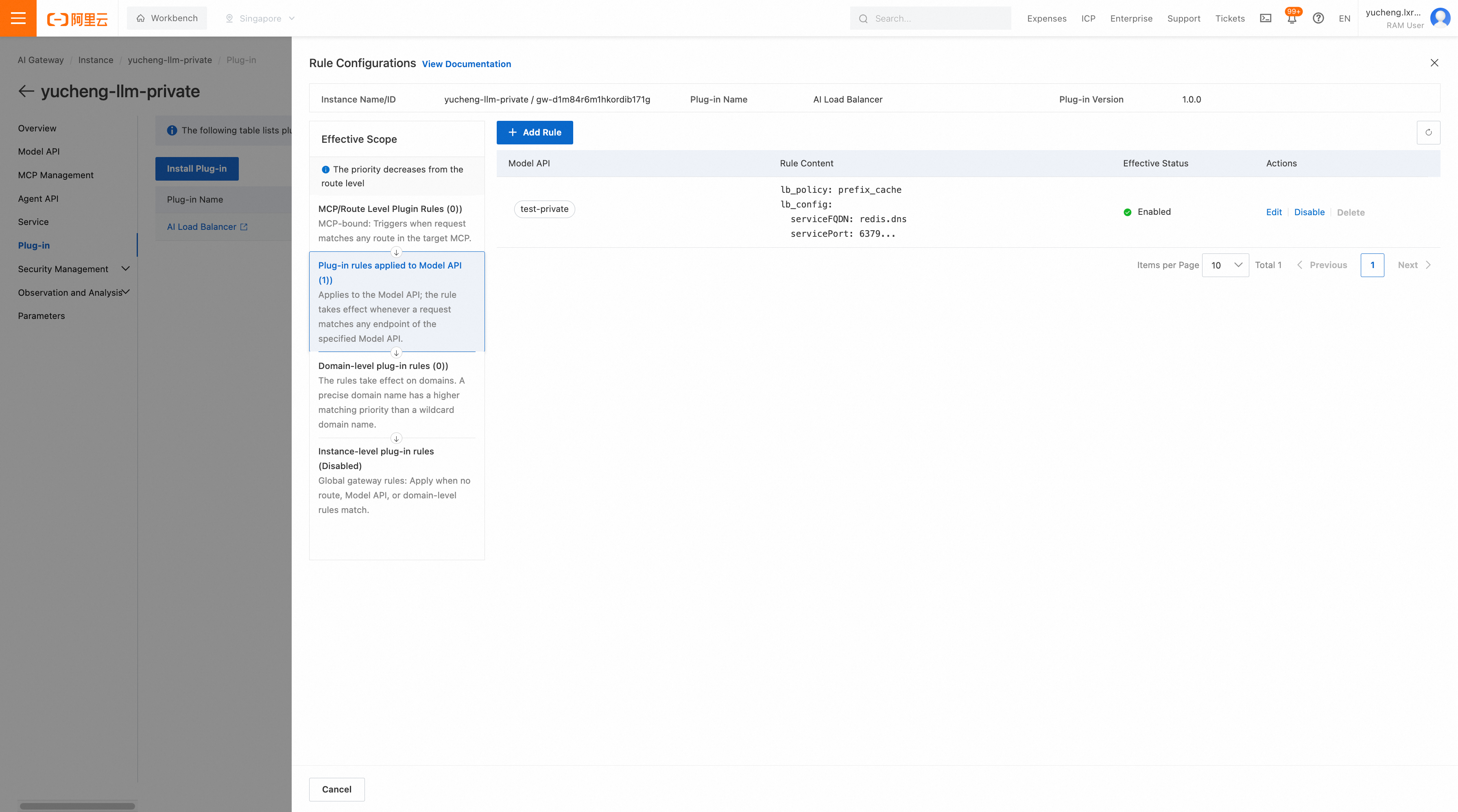
An example of plugin configuration is as follows:
lb_policy: prefix_cache
lb_config:
serviceFQDN: redis.dns
servicePort: 6379
username: default
password: xxxxxxxxxxxx
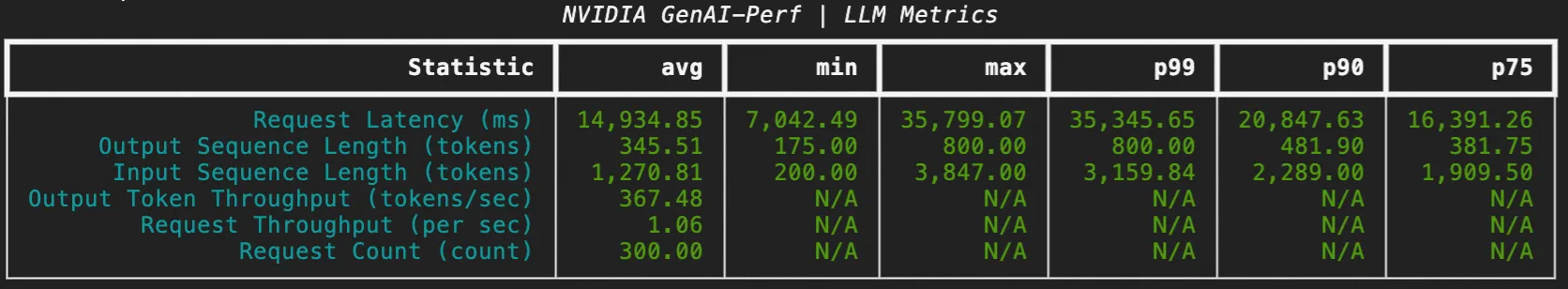
redisKeyTTL: 60GenAI-Perf statistics are as follows:
vllm monitoring is as follows:
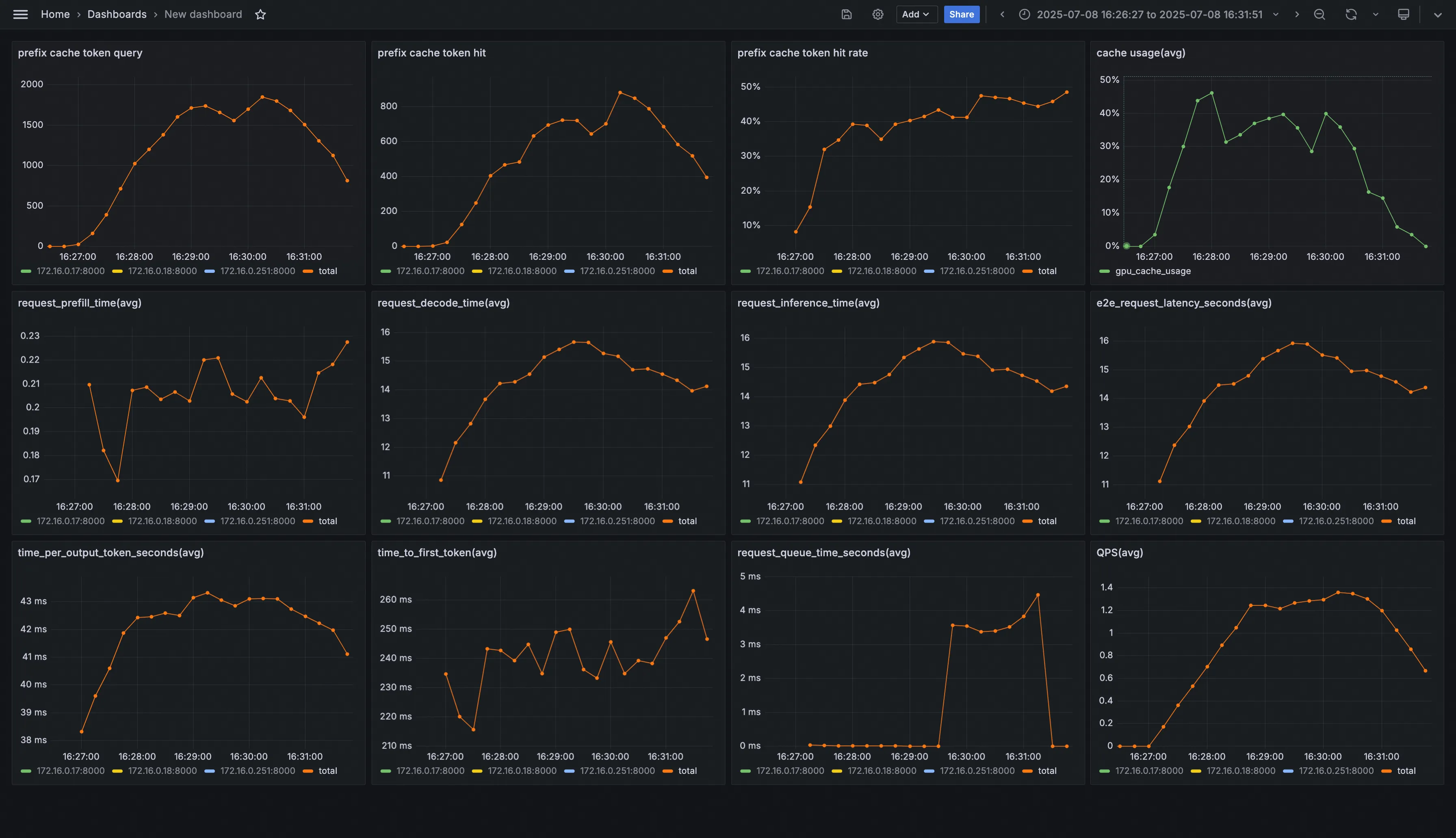
GenAI-Perf statistics are as follows:
vllm monitoring is as follows:
If you want to learn more about Alibaba Cloud API Gateway (Higress), please click: https://higress.ai/en/

634 posts | 55 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native Community - September 9, 2025
ApsaraDB - December 29, 2025
Alibaba Container Service - July 10, 2025
Alibaba Container Service - July 25, 2025
Alibaba Container Service - July 10, 2025
Kidd Ip - September 30, 2025

634 posts | 55 followers
Follow Microservices Engine (MSE)
Microservices Engine (MSE)
MSE provides a fully managed registration and configuration center, and gateway and microservices governance capabilities.
Learn More AI Acceleration Solution
AI Acceleration Solution
Accelerate AI-driven business and AI model training and inference with Alibaba Cloud GPU technology
Learn More Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline SDKs for visual production, such as image segmentation, video segmentation, and character recognition, based on deep learning technologies developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Top-performance foundation models from Alibaba Cloud
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Native Community