By Wen Ting, Wu Ming, Mo Ling, Zhi Liu
As the wave of Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) sweeps across the globe, Large Language Models (LLMs) are profoundly reshaping industries and reconstructing application development paradigms. This technology revolution, driven by models and algorithms, brings unprecedented opportunities but also introduces new, rigorous engineering challenges for developers building AI applications: How do we ensure continuity in long-running conversations? How do we schedule limited compute resources fairly and efficiently? How do we prevent cascading blockages in multi-Agent systems or complex workflows?
The core requirement underlying these challenges is the need for a reliable and efficient asynchronous communication mechanism to support the collaborative interaction between applications, data, and models. As an indispensable foundational component of distributed systems, Apache RocketMQ excels in microservices decoupling and data stream processing. In the AI era, adapting to complex, variable business scenarios while meeting higher standards for performance and user experience has become a critical theme in Apache RocketMQ's evolution.
In traditional distributed architectures, message queues are a proven solution for asynchronous decoupling, traffic shaping, and data stream processing. However, the fundamental shifts in interaction modes, resource forms, and application architectures brought by AI applications present significant new challenges for clients using synchronous blocking architectures or asynchronous architectures based on traditional message queues.
• Interaction Mode: From "Request-Response" to "Long-lived Sessions"
Traditional applications typically employ a stateless, rapid "request-response" mode, where a user request (like bookmarking an item, adding to a cart, or placing an order) returns results in milliseconds. In contrast, AI application interactions (such as multi-turn dialogues or multi-modal tasks) are characterized by long durations (single inference taking seconds to minutes), deep dependency on multi-turn context (dozens of history rounds), and high compute consumption. If existing AI applications rely on protocols like HTTP long-lived connections or WebSocket combined with a backend synchronous blocking architecture, accidental issues like network jitter, gateway restarts, or connection timeouts can easily lead to context loss and interrupted inference tasks. This results in irreversible waste of compute power and damage to the user experience.
• Resource Form: From "General Servers" to "Scarce Compute"
AI inference relies on expensive GPU resources. Instantaneous high-concurrency traffic can impact the stability of inference services, leading to wasted compute resources. While traditional message queues can implement traffic peak shaving, they struggle in multi-tenant shared resource pool scenarios. Due to a lack of fine-grained consumer traffic control mechanisms, it is difficult to achieve refined, differentiated resource scheduling, resulting in low resource utilization.
• Application Architecture: From "Service Calls" to "Agent Collaboration"
AI Agents or multi-step workflows are essentially collaborations of long-cycle tasks. If a synchronous call mechanism is used, a blockage at any single node can trigger a cascading failure of the entire task chain. Therefore, an efficient, reliable asynchronous communication hub is needed to connect these independent, long-running agents or task nodes, enabling non-blocking collaboration and ensuring the stable operation of distributed intelligent systems.
Furthermore, traditional message queues face other hurdles, such as strict limits on message size when handling large AI multi-modal payloads (requiring cumbersome workarounds that increase complexity and failure risk) and the high operational costs and risks of resource leaks associated with manual configuration or script-based Topic management.
Since version 5.0, Apache RocketMQ has fully embraced cloud-native architecture, completing a systematic refactoring from client to server. By adopting a disaggregated storage and compute architecture for resource elasticity, a multi-replica storage mechanism for high availability, and a lightweight SDK for client flexibility, it has achieved the core goals of "high elasticity, high availability, and low cost," laying a solid foundation for solving the engineering problems of the AI era.
Facing the new challenges of the AI era, Apache RocketMQ has undertaken a forward-looking strategic upgrade, evolving from traditional message middleware into a message engine purpose-built for the AI era. It has become a critical piece of infrastructure for building next-generation AI applications.
The core of this evolution lies in two "disruptive innovations":
• Lightweight Communication Model: Supports the dynamic creation of millions of Lite-Topics, making it particularly suitable for scenarios like long-lived sessions, AI workflows, and Agent-to-Agent interactions. This significantly enhances system scalability and flexibility, meeting the complex communication needs of AI applications.
• Intelligent Resource Scheduling: Through features like traffic shaping (peak shaving), rate-limited consumption, adaptive load balancing, and priority queues, it enables fine-grained management and smooth, efficient scheduling of scarce compute resources. This ensures efficient resource utilization in high-concurrency and multi-tenant environments.
These innovations allow Apache RocketMQ to break through the limitations of traditional message queues, precisely matching the unique needs of AI applications and providing a stable, efficient messaging backbone for modern AI systems.
AI application interaction is unique: it involves long durations, multiple rounds, and heavy reliance on costly compute. When applications depend on long connections like SSE or WebSocket, a connection interruption (triggered by gateway restarts, timeouts, or network instability) not only causes the loss of the current session context but also invalidates the AI tasks already in progress, wasting valuable compute resources. Therefore, building a robust session management mechanism that guarantees context continuity and integrity during long dialogues—reducing waste from retries while lowering code complexity—is a core technical challenge.
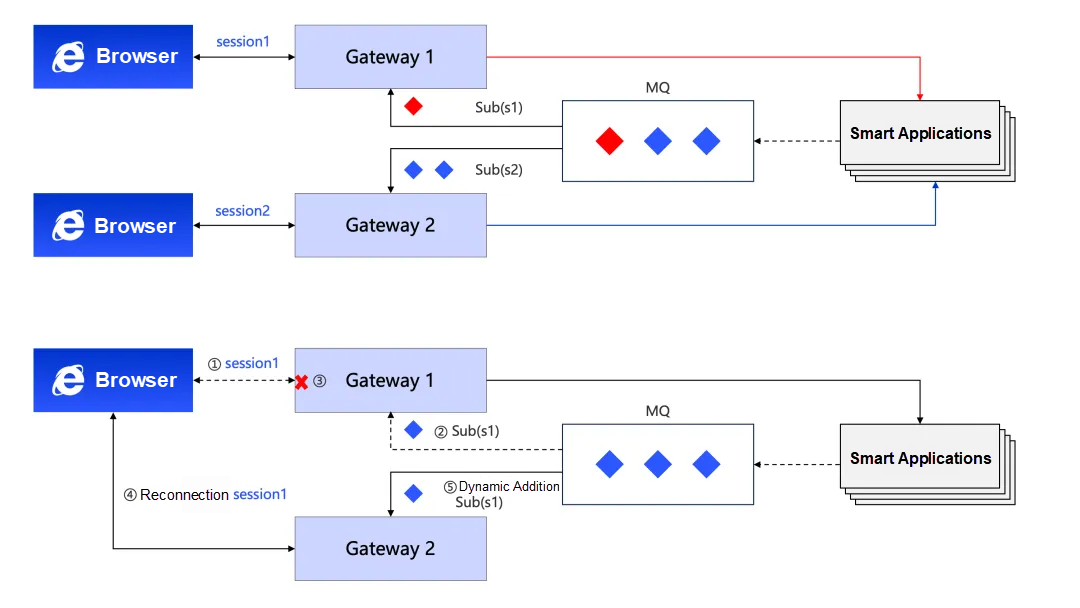
To solve the problem of managing long session states, RocketMQ for AI proposes a revolutionary lightweight solution—"Session as Topic." The system can dynamically create a dedicated lightweight topic (Lite-Topic) for each independent session or question.
When a client establishes a session with an AI service, the system dynamically creates a dedicated queue named with the SessionID (e.g., chatbot/{sessionID} or chatbot/{questionID}). All interaction history and intermediate results of the session are passed sequentially as messages within this topic. Even if the client disconnects, upon reconnection, it simply needs to resume subscribing to the original Lite-Topic chatbot/{sessionID} to seamlessly restore context, achieving breakpoint resumption and continuing to receive response results.
This model effectively resolves the conflict between "stateless backends" and "stateful experiences," completely freeing developers from tedious session state maintenance, reconnection handling, and data consistency validation. It not only drastically simplifies engineering implementation but also fundamentally avoids compute waste caused by task interruption and retries, delivering a smooth, continuous, and stable AI interaction experience for users.
The realization of this innovative mode leverages powerful features designed specifically for AI scenarios:
• Million-level Queue Support: RocketMQ efficiently manages millions of Lite-Topics within a single cluster, providing independent Topics for massive concurrent sessions or tasks without compromising performance.
• Lightweight Resource Management: The creation and destruction of RocketMQ queues are extremely lightweight and automated. The system can automatically create and reclaim Lite-Topics on demand (e.g., when a client disconnects or TTL expires), avoiding resource leaks and manual intervention, thereby significantly reducing operational complexity and costs.
• Large Message Payload Support: RocketMQ can handle message bodies of tens of MBs or larger, fully meeting the transmission needs of massive data payloads common in AIGC scenarios, such as context-heavy Prompts, high-definition images, or long documents.
• Ordered Message Guarantee: In a single session queue, where LLMs typically use a streaming output mode to reduce latency, RocketMQ natively supports ordered messages. This ensures the inference results are streamed to the client in the correct sequence, guaranteeing a coherent conversational experience.
• Comprehensive Observability: RocketMQ fully supports OpenTelemetry standards for Metrics and Tracing. It allows real-time monitoring of key indicators like message traffic and accumulation, as well as querying detailed message trajectories, providing strong support for debugging and optimizing multi-Agent systems.
Alibaba Security Team's "Security Smart Assistant" faced challenges with lost session contexts and resource waste due to task interruptions when handling massive concurrent sessions.
By introducing RocketMQ's Lite-Topic capability to reconstruct the session persistence mechanism, the assistant successfully achieved automated persistence and rapid recovery of session states. This not only enabled fast, precise understanding and response to user security questions in multi-turn dialogues but also significantly simplified engineering complexity and effectively reduced resource waste caused by interruptions, improving both user experience and business efficiency.
Currently, AI Q&A bots across multiple Alibaba Cloud product lines have upgraded using this solution, further verifying the architecture's versatility and effectiveness in diverse AI scenarios.
Large model services generally face two core challenges in resource scheduling:
• Load Mismatch: Front-end requests are highly bursty, while backend compute resources are limited and relatively stable. Direct connection often leads to service overload crashes or wasted resources.
• Indiscriminate Allocation: Once traffic is stabilized, ensuring that high-priority tasks get preferential access to valuable compute resources becomes key to enhancing overall service value.
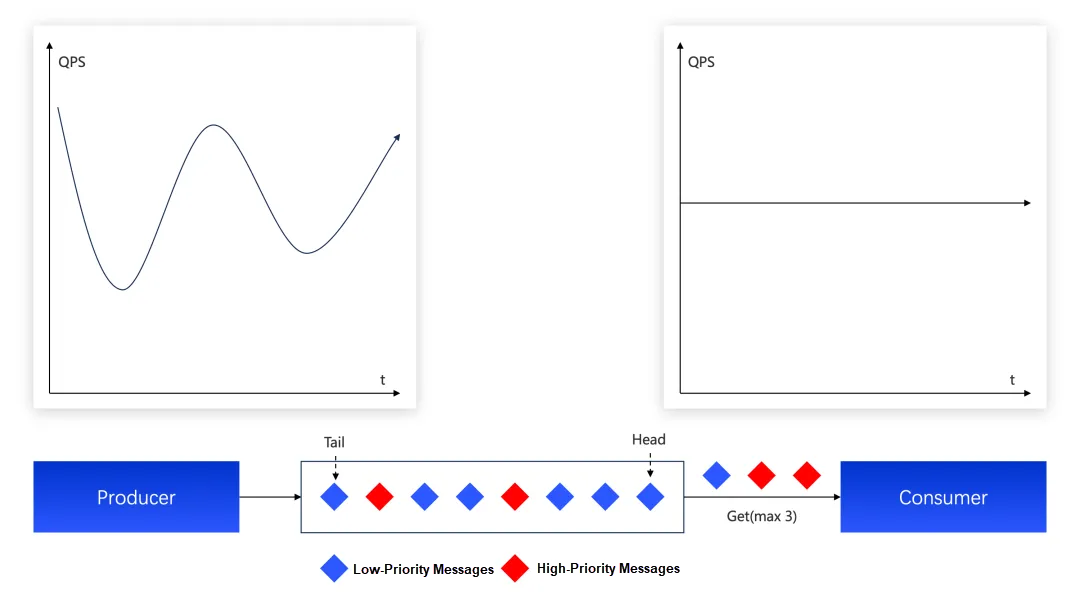
In this context, Apache RocketMQ plays a crucial role. It not only serves as a buffering layer between front-end requests and backend compute services, "shaping" irregular traffic into a smooth, controllable flow, but also provides a "controllable compute scheduling hub" through features like rate-limited consumption and priority queues. This enables fine-grained control over request traffic, drastically improving resource utilization efficiency and service quality.
RocketMQ's core features provide a solid foundation for intelligent compute scheduling:
• Natural Traffic Shaping to Protect Core AI Compute: RocketMQ acts as a natural "traffic reservoir," buffering burst requests. This allows backend AI model services to consume loads adaptively based on their processing capacity (similar to a sliding window), preventing system overload or resource waste.
• Rate-Limited Consumption to Maximize Utilization: RocketMQ supports rate-limited consumption, allowing developers to set consumption quotas for ConsumerGroups. Developers can flexibly define the calls-per-second for AI compute, maximizing throughput without overloading the core system.
• Priority Queues for Intelligent Scheduling: Furthermore, RocketMQ's message priority mechanism offers flexible resource scheduling for complex scenarios:
The gateway system of Alibaba Cloud Model Studio introduced RocketMQ to implement traffic shaping, effectively transforming irregular front-end access pressure into smooth, controllable backend compute scheduling. Simultaneously, utilizing RocketMQ's message priority function, it sets reasonable priorities based on user traffic. This prevents high-volume users from crowding out small-volume users, significantly improving resource utilization and service fairness.
Lingma used RocketMQ to upgrade its codebase RAG architecture from a synchronous process to an asynchronous one, enabling code vectorization and traffic shaping, thus ensuring full-link system stability.
The A2A protocol proposed by Google recommends asynchronous communication to solve the blocking issues caused by long-running AI tasks. Its core mechanism decouples a Request-Reply call into an initial request and an asynchronous notification (pushNotificationConfig). In various Agentic AI platform workflows, nodes must notify downstream nodes of execution results, making asynchronous communication key to supporting this complex collaboration.
Since AI tasks generally run for extended periods, workflow scenarios must address the issue of "cascading blocking caused by synchronous calls." Whether it is external communication between Agents or internal task flow within a workflow, a common challenge exists: How to gracefully handle long-running tasks without blocking the system? The core solution is a unified architectural pattern—transforming long-running, stateful interactions into connections via a stateless, event-driven, reliable asynchronous notification mechanism.
As mentioned, RocketMQ's new Lite-Topic mechanism, with its lightweight, automated dynamic management, efficiently implements the asynchronous Request-Reply pattern. The core process is as follows:
• Dynamic Reply Channel Creation: When Agent A initiates a request to Agent B (e.g., message/send), it does not wait synchronously. Instead, it embeds a unique dynamic reply address in the request, such as a2a-topic/{taskID}. Agent A subscribes to this address, and RocketMQ automatically creates this lightweight Sub-Topic upon the first connection, effectively opening a dedicated asynchronous communication channel for the task.
• Asynchronous Result Delivery: Agent B processes the task at its own pace. Upon completion, it encapsulates the result as a message and publishes it directly to the specified reply address a2a-topic/{taskID}.
• Automatic Resource Reclamation: Once Agent A successfully receives and processes the result, it disconnects from the Lite-Topic. RocketMQ's intelligent resource management detects that the Topic has no consumers and automatically cleans up the resource after a set Time-To-Live (TTL). The entire process is fully automated, requiring no human intervention and eliminating the risk of resource leaks.
The advantage of RocketMQ's Lite-Topic solution lies in its systemic design: mass concurrency with million-level Lite-Topics combined with on-demand creation and zero-overhead automatic disposal. This fundamentally solves scalability and usability issues in large-scale Agent collaboration. Meanwhile, ordered message guarantees ensure logical correctness for streaming or multi-step tasks, and built-in persistence and high availability mechanisms ensure the ultimate consistency and reliability of asynchronous communication. These capabilities collectively build a truly robust, efficient, and scalable asynchronous infrastructure for A2A scenarios.
Alibaba AI Lab built an efficient and reliable Agent orchestration system using RocketMQ for its multi-Agent workflows. Each node in the workflow employs an event-driven architecture for reliable, persistent communication. Leveraging the Lite-Topic mechanism, they also achieved node-level communication between Agents, enabling fine-grained orchestration of task flows.
During multi-Agent collaboration, even if interruptions occur due to Agent restarts or timeouts, the system can continue to advance the interrupted AI tasks through the reliable retry capabilities of the persistent event stream. This effectively avoids resource waste and significantly enhances the user experience.
To realize the innovative models described above, Apache RocketMQ requires the ability to efficiently manage millions of Lite-Topics in a single cluster. However, the original architecture faced two core challenges: at the storage level, the file-based index and metadata management mechanism could not support such a scale; at the dispatch level, when a single consumer subscribed to a massive number of Lite-Topics, the old long-polling mechanism struggled with latency and concurrency performance.
Therefore, managing massive Lite-Topics required overcoming two key technical hurdles:
• Technical solutions for metadata storage and index structure of million-level Lite-Topics;
• Efficient message dispatch and delivery mechanisms for massive Lite-Topic subscription scenarios.
The leap to millions of Lite-Topics meant the previous models for indexing and metadata were obsolete. Maintaining one or more physical file-based index structures for each topic would incur huge system overhead and operational burdens.
To address this, Apache RocketMQ redesigned its metadata management and index storage based on its LMQ storage engine and KV Store capabilities:
• Unified Storage, Multi-Path Dispatch: All messages are stored as a single copy in the underlying CommitLog files, but through a multi-path dispatch mechanism, individual consumption indexes (ConsumerQueues, or CQs) are generated for different Lite-Topics.
• Index Storage Engine Upgrade: The traditional file-based CQ structure was abandoned in favor of the high-performance KV storage engine, RocksDB. By storing queue index information and physical offsets as key-value pairs, RocketMQ leverages RocksDB's high performance in sequential writes to achieve efficient management of millions of queues.
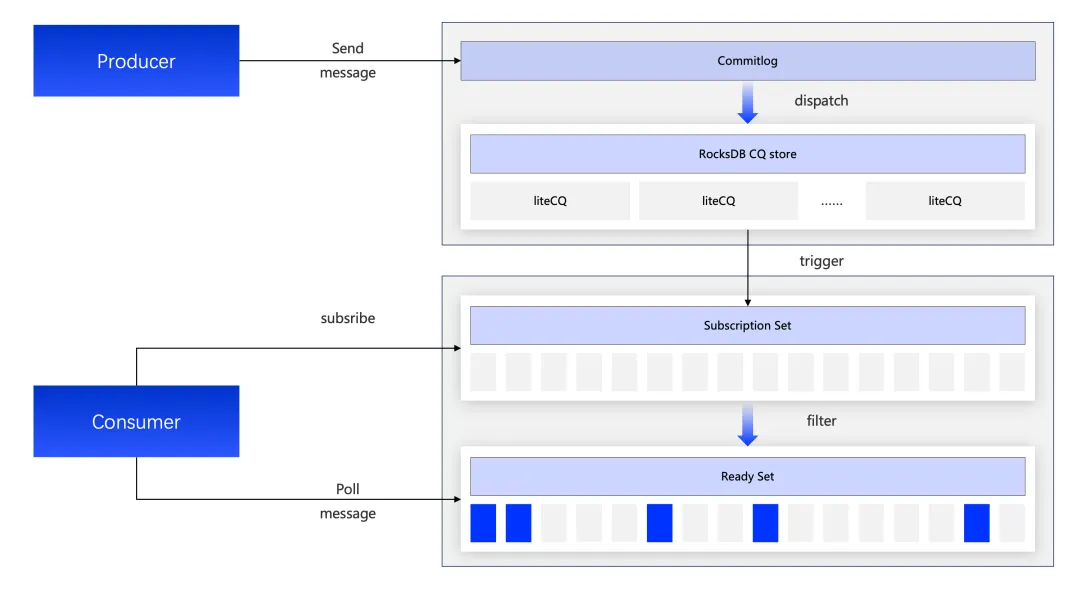
Building on the Lite-Topic storage model, RocketMQ further optimized the message dispatch and delivery mechanism. For scenarios where a single consumer subscribes to tens of thousands of Lite-Topics, a novel Event-Driven Pull mechanism was designed, as shown in Figure 3:
• Subscription Set Management: The Broker manages the "Lite-Topic Set" for consumer subscriptions and supports incremental updates, enabling real-time, active awareness of the match state between messages and subscriptions.
• Event-Driven & Ready Set Maintenance: Whenever a new message is written, the Broker immediately matches it against the maintained Subscription Set and adds the matching message (or its index) to a "Ready Set" maintained for the consumer.
• Efficient Poll Ready Set: The consumer only needs to issue a poll request against the Ready Set to retrieve all matching messages. This allows the Broker to merge and batch messages from different topics and traffic sources, returning them efficiently in a single response. This significantly reduces network interaction frequency and boosts overall performance.
Through innovative upgrades in the storage layer and dispatch mechanism, Apache RocketMQ effectively resolved the key challenges of the Lite-Topic model. At the storage level, replacing traditional file indexes with high-performance RocksDB enabled efficient management of massive metadata. At the dispatch level, the innovative "Event-Driven Pull" model—where the Broker actively maintains subscription and ready sets—transforms the consumer's massive polling into a single, efficient pull of aggregated messages, ensuring low latency and high throughput in massive subscription scenarios.
The evolution of Apache RocketMQ for AI marks its full upgrade from traditional message middleware to a message engine built for the AI era. Through "disruptive innovations" in lightweight communication models and intelligent resource scheduling, Apache RocketMQ has broken the capability boundaries of traditional middleware. It has become a critical infrastructure for building high-availability, scalable AI applications, demonstrating its core value in the AI engineering ecosystem.
The enhanced capabilities of Apache RocketMQ for AI have been validated in large-scale production environments within Alibaba Group and in products like Alibaba Cloud Model Studio and AI Coding Assistant Lingma, fully proving its maturity and reliability in high-concurrency, complex AI scenarios.
Of course, this is just the beginning. AI engineering is still in a stage of rapid development, and as a core infrastructure, Apache RocketMQ still has vast room for optimization and innovation. In the future, the Alibaba Cloud Messaging Team will continue to iterate and upgrade based on user AI scenarios, collaborating with contributors in the Apache RocketMQ open-source community to refine core AI capabilities. We will gradually feed the solutions and features verified by Alibaba Group's AI business back into the open-source community.
We firmly believe that through continuous technical exploration and open collaboration, Apache RocketMQ for AI will drive "AI Native Message Queues" (AI MQ) to become an industry standard. This will help developers worldwide build next-generation intelligent applications more easily and efficiently, jointly promoting the standardization, popularization, and ecological prosperity of AI engineering practices.

650 posts | 55 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native - June 6, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - February 1, 2023
Alibaba Clouder - June 30, 2020
Alibaba Developer - December 17, 2018
Alibaba Cloud Native - April 6, 2022
JJ Lim - January 11, 2022

650 posts | 55 followers
Follow ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ
ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ
ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ is a distributed message queue service that supports reliable message-based asynchronous communication among microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications.
Learn More AliwareMQ for IoT
AliwareMQ for IoT
A message service designed for IoT and mobile Internet (MI).
Learn More Message Queue for RabbitMQ
Message Queue for RabbitMQ
A distributed, fully managed, and professional messaging service that features high throughput, low latency, and high scalability.
Learn More Message Queue for Apache Kafka
Message Queue for Apache Kafka
A fully-managed Apache Kafka service to help you quickly build data pipelines for your big data analytics.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Native Community