By Hang Yin
In current large language model (LLM) inference scenarios, Kubernetes has become an indispensable infrastructure for LLM inference service deployment. However, in terms of LLM traffic management, due to the unique characteristics of LLM inference services and inference traffic, traditional load balancing and route scheduling algorithms often fail to meet the high-performance and high-reliability requirements of such services. Built upon the Gateway API and Inference Extension specifications of the Kubernetes community, Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes introduces ACK Gateway with AI Extension to provide a series of intelligent routing and load balancing capabilities for LLM inference services in production environments.
This article describes how to use the ACK Gateway with AI Extension plug-in to provide production-level load balancing and intelligent routing capabilities for QwQ-32B models deployed in ACK clusters.
In this article, we demonstrate ACK Gateway with AI Extension capabilities based on QwQ-32B model inference services. QwQ-32B is the latest high-efficiency large language model released by Alibaba Cloud. With 3.2 billion parameters, its performance rivals that of DeepSeek-R1 671B. The model performs well on core metrics such as mathematics and code generation, delivering superior inference capabilities with lower resource consumption.
An ACK cluster that contains GPU-accelerated nodes is created. For more information, see Create an ACK cluster with GPU-accelerated nodes.
Prepare at least one ecs.gn7i-c32g1.32xlarge GPU-accelerated node. In this example, a cluster with five ecs.gn7i-c32g1.32xlarge GPU-accelerated nodes is used.
1. Download the model.
GIT_LFS_SKIP_SMUDGE=1 git clone https://www.modelscope.cn/Qwen/QwQ-32B.git
cd QwQ-32B
git lfs pull2. Upload the model to OSS.
ossutil mkdir oss://<Your-Bucket-Name>/QwQ-32B
ossutil cp -r ./QwQ-32B oss://<Your-Bucket-Name>/QwQ-32B3. Configure the PV and PVC for the target cluster.
For more information, see Mount a statically provisioned OSS volume. The following table describes the parameters of a PV.
| Parameter or setting | Description |
|---|---|
| PV Type | OSS |
| Volume Name | llm-model |
| Access Certificate | The AccessKey pair used to access the OSS bucket. The AccessKey pair consists of an AccessKey ID and an AccessKey secret. |
| Bucket ID | Specify the name of the OSS bucket that you created. |
| OSS Path | Select the path of the model, such as /models/Qwen1.5-4B-Chat. |
The following table describes the parameters of a PVC.
| Parameter or setting | Description |
|---|---|
| PVC Type | OSS |
| Volume Name | llm-model |
| Allocation Mode | Select Existing Volumes. |
| Existing Volumes | Click Select PV. In the Select PV dialog box, find the PV that you want to use and click Select in the Actions column. |
Run the following command to deploy the QwQ-32B model inference service that uses the vLLM framework.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: qwq-32b
name: qwq-32b
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 5 # Adjust based on the number of GPU-accelerated nodes.
selector:
matchLabels:
app: qwq-32b
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: qwq-32b
annotations:
prometheus.io/path: /metrics
prometheus.io/port: "8000"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
spec:
volumes:
- name: model
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: llm-model
- name: dshm
emptyDir:
medium: Memory
sizeLimit: 30Gi
containers:
- command:
- sh
- -c
- vllm serve /models/QwQ-32B --port 8000 --trust-remote-code --served-model-name qwq-32b --tensor-parallel=4 --max-model-len 8192 --gpu-memory-utilization 0.95 --enforce-eager
image: registry-cn-hangzhou.ack.aliyuncs.com/dev/vllm:v0.7.2
name: vllm
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
readinessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 8000
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 30
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: "4"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /models/QwQ-32B
name: model
- mountPath: /dev/shm
name: dshm
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: qwq-32b-v1
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 8000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8000
selector:
app: qwq-32b
EOFACK Gateway with AI Extension is a component designed for LLM inference scenarios. It supports traffic routing at Layer 4/7 and provides intelligent load balancing capabilities based on model server load. In addition, InferencePool and InferenceModel custom resources (CRDs) help flexibly define traffic distribution policies for inference services, including model canary release.
1. Enable the ACK Gateway with AI Extension component in the Components section of the ACK cluster and select the Enable Gateway API inference extension option when enabled.
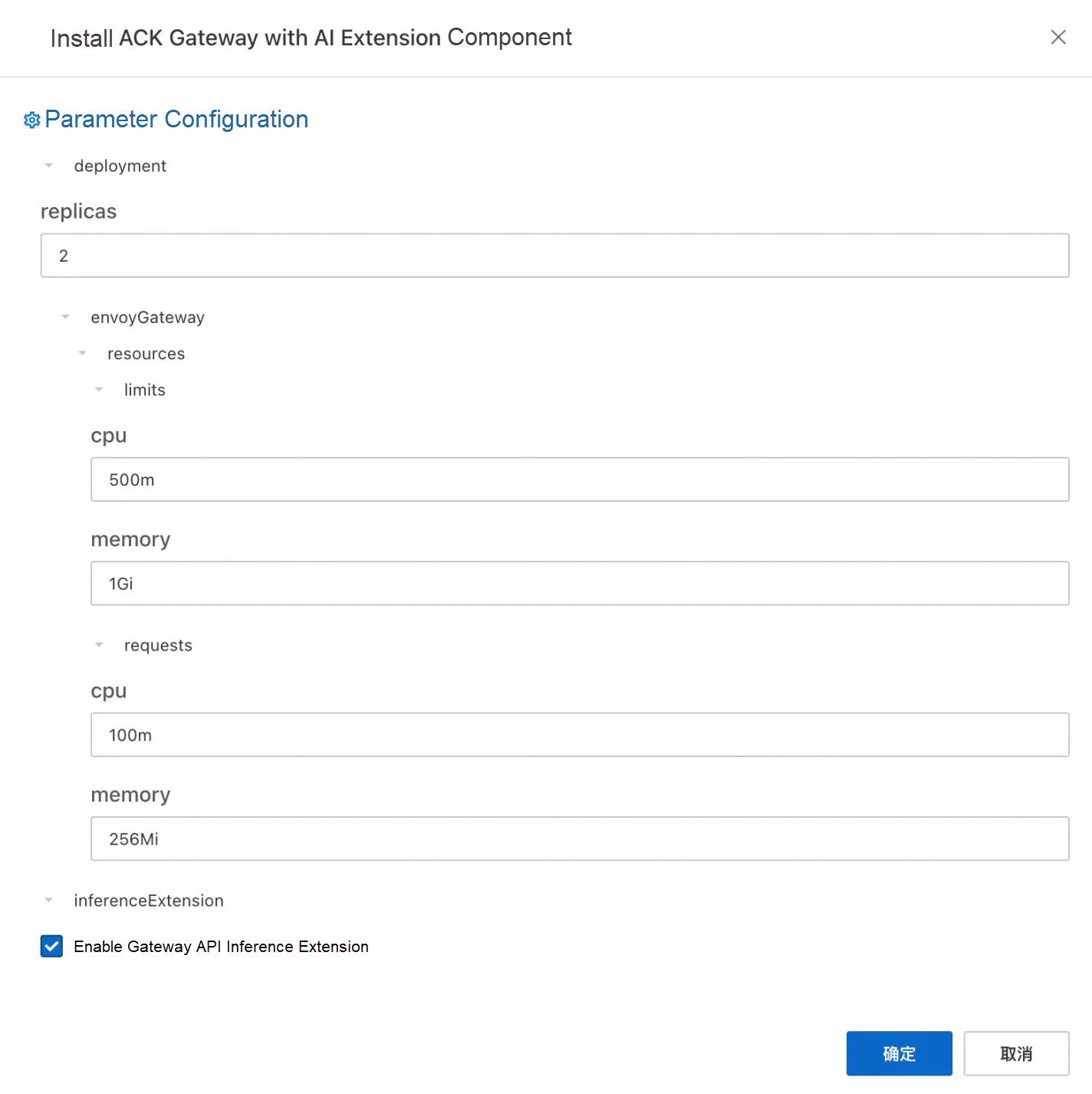
2. Create a gateway instance: Use kubectl to connect to the ACK cluster and run the following command to create a gateway with ports 8080 and 8081. Port 8080 deploys a standard HTTP routing to the backend inference service, while port 8081 extends the routing to the backend inference service based on the inference service.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: GatewayClass
metadata:
name: inference-gateway
spec:
controllerName: gateway.envoyproxy.io/gatewayclass-controller
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: inference-gateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: inference-gateway
listeners:
- name: http
protocol: HTTP
port: 8080
- name: llm-gw
protocol: HTTP
port: 8081
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: backend
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: inference-gateway
sectionName: http
rules:
- backendRefs:
- group: ""
kind: Service
name: vllm-llama2-7b-pool
port: 8000
matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
timeouts:
request: "24h"
backendRequest: "24h"
EOFUse the InferencePool and InferenceModel resources to enable AI inference extension capabilities. In the CRD provided by the inference extension: InferencePool uses a label selector to declare a set of LLM inference service workloads running in the cluster, while InferenceModel specifies traffic distribution policies for specific models in the InferencePool.
1. Create an InferencePool.
InferencePool uses a label selector to declare a set of LLM inference service workloads:
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: InferencePool
metadata:
annotations:
inference.networking.x-k8s.io/attach-to: |
name: inference-gateway
port: 8081
name: reasoning-pool
spec:
targetPortNumber: 8000
selector:
app: qwq-32b
EOF2. Create an InferenceModel.
InferenceModel defines traffic distribution policies for models and supports canary release. The following example demonstrates a basic use case: all requests for the model named qwq are forwarded to the QwQ-32B model.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: InferenceModel
metadata:
name: inferencemodel-sample
spec:
criticality: Critical
modelName: qwq
poolRef:
group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io
kind: InferencePool
name: reasoning-pool
targetModels:
- name: qwq-32b
weight: 100
EOFSemantic description:
The targetModels field defines the target models and their weight ratios. For example, the above configuration indicates that 100% of requests will be routed to the QwQ-32B model.
The criticality field is used to mark the importance of the model, which affects the priority of traffic scheduling.
Run the following command to check whether intelligent routing takes effect:
GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl get gateway/inference-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
curl -X POST ${GATEWAY_IP}/v1/chat/completions \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"model": "qwq",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Who are you?"
}
]
}' -v1. Collect metrics related to the inference service by using the default service discovery mechanism of the Prometheus instance. For more information, see Default service discovery.
2. Monitor the LLM inference service deployed based on vLLM through the Grafana dashboard: Import the vLLM Grafana JSON model to Grafana to create an observable dashboard for the LLM inference service. For more information about the imported JSON model, visit the vLLM official website. For specific import operations, see Grafana dashboard export and import
3. Run the following command to create a stress test tool.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: vllm-benchmark
labels:
app: vllm-benchmark
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: vllm-benchmark
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: vllm-benchmark
spec:
volumes:
- name: llm-model
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: llm-model
containers:
- name: vllm-benchmark
image: kube-ai-registry.cn-shanghai.cr.aliyuncs.com/kube-ai/vllm-benchmark:v1
command:
- "sh"
- "-c"
- "sleep inf"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /models/QwQ-32B
name: llm-model
EOF4. Download the stress test dataset.
# Run the following command to log on to the benchmark pod.
PODNAME=$(kubectl get po -o custom-columns=":metadata.name"|grep "vllm-benchmark")
kubectl exec -it $PODNAME -- bash
# Download the stress test dataset.
pip3 install modelscope
modelscope download --dataset gliang1001/ShareGPT_V3_unfiltered_cleaned_split ShareGPT_V3_unfiltered_cleaned_split.json --local_dir /root/5. Use the following command to initiate two stress tests on port 8080 of the gateway (using the default service routing of the gateway) and port 8081 (using the service routing of the inference extension).
• Run stress tests on the default service routing of the gateway.
python3 /root/vllm/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py \
--backend vllm \
--model /models/QwQ-32B \
--served-model-name qwq-32b \
--trust-remote-code \
--dataset-name random \
--dataset-path /root/ShareGPT_V3_unfiltered_cleaned_split.json \
--random-prefix-len 1000 \
--random-input-len 4000 \
--random-output-len 3000 \
--random-range-ratio 0.2 \
--num-prompts 3000 \
--max-concurrency 60 \
--host 172.16.12.92 \ # The internal IP address of ACK Gateway.
--port 8080 \ # Request port 8080. The gateway routes the inference service by default.
--endpoint /v1/completions \
--save-result \
2>&1 | tee benchmark_serving.txt
============ Serving Benchmark Result ============
Successful requests: 2990
Benchmark duration (s): 5822.60
Total input tokens: 10071917
Total generated tokens: 5334789
Request throughput (req/s): 0.51
Output token throughput (tok/s): 916.22
Total Token throughput (tok/s): 2646.02
---------------Time to First Token----------------
Mean TTFT (ms): 2456.44
Median TTFT (ms): 1366.07
P99 TTFT (ms): 23509.43
-----Time per Output Token (excl. 1st token)------
Mean TPOT (ms): 63.50
Median TPOT (ms): 63.33
P99 TPOT (ms): 75.22
---------------Inter-token Latency----------------
Mean ITL (ms): 63.47
Median ITL (ms): 55.49
P99 ITL (ms): 59.16
==================================================• Run stress tests on service routing of inference extension.
python3 /root/vllm/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py \
--backend vllm \
--model /models/QwQ-32B \
--served-model-name qwq-32b \
--trust-remote-code \
--dataset-name random \
--dataset-path /root/ShareGPT_V3_unfiltered_cleaned_split.json \
--random-prefix-len 1000 \
--random-input-len 4000 \
--random-output-len 3000 \
--random-range-ratio 0.2 \
--num-prompts 3000 \
--max-concurrency 60 \
--host 172.16.12.92 \
--port 8081 \ # Request port 8081. The gateway routes the inference service based on the inference extension.
--endpoint /v1/completions \
--save-result \
2>&1 | tee benchmark_serving_ext.txt
============ Serving Benchmark Result ============
Successful requests: 2990
Benchmark duration (s): 5755.77
Total input tokens: 10071917
Total generated tokens: 5332890
Request throughput (req/s): 0.52
Output token throughput (tok/s): 926.53
Total Token throughput (tok/s): 2676.41
---------------Time to First Token----------------
Mean TTFT (ms): 1796.93
Median TTFT (ms): 1470.97
P99 TTFT (ms): 8857.07
-----Time per Output Token (excl. 1st token)------
Mean TPOT (ms): 63.10
Median TPOT (ms): 63.03
P99 TPOT (ms): 70.68
---------------Inter-token Latency----------------
Mean ITL (ms): 63.06
Median ITL (ms): 55.37
P99 ITL (ms): 59.17
==================================================Stress tests are run on the standard gateway (port 8080) and ACK Gateway with AI Extension (port 8081). The key metrics are as follows:
| Metrics | Standard Gateway Routing | ACK Gateway with AI Extension Intelligent Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Average TTFT (ms) | 2456.44 | 1796.93 |
| P99 TTFT (ms) | 23509.43 | 8857.07 |
| Output Throughput (tok/s) | 916.22 | 926.53 |
At the same time, you can make a visual comparison of the observable dashboard of the vLLM server in the corresponding time periods of the two stress tests.
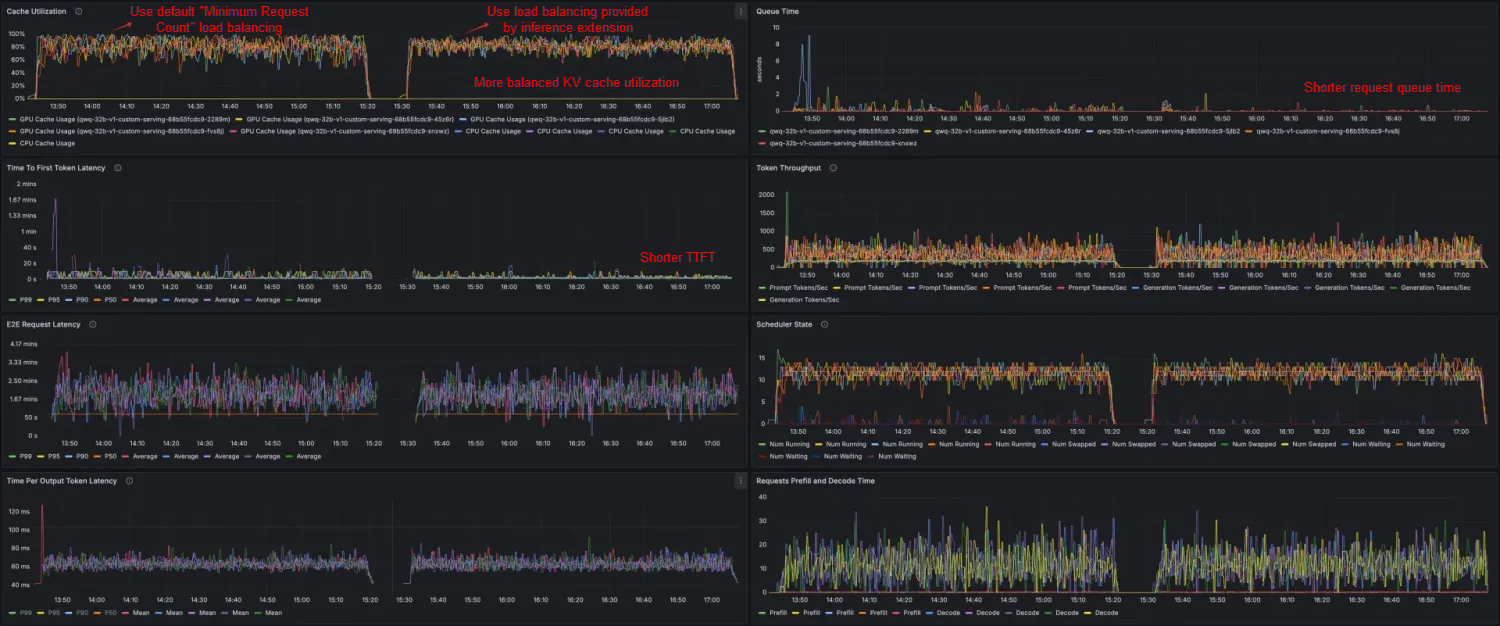
Through stress tests on data and dashboards, you can see that when you use the inference extension based on ACK Gateway to perform routing and load balancing on the inference service, the QwQ-32B inference service has less latency and better throughput, cache utilization, and productivity. The request and token throughput are slightly improved, the average TTFT is shortened by 26.8%, the P99 TTFT is reduced by 62.32%, and the KV Cache utilization is more evenly distributed across different workloads.
Compared with traditional gateways, ACK Gateway with AI Extension significantly improves the latency, throughput, and cache utilization of inference services, providing a better solution for LLM inference scenarios. It also provides scenario-specific capabilities for LLM inference services such as model canary release and traffic mirroring. If you are interested in ACK Gateway with AI Extension, see the official documentation for further exploration!
Note: The test results are related to many factors, and the above results are for reference only.
ACK Gateway with AI Extension: Model Canary Release Practice for Large Model Inference

222 posts | 33 followers
FollowAlibaba Container Service - July 25, 2025
Alibaba Container Service - July 10, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - October 20, 2025
Alibaba Container Service - November 15, 2024
Alibaba Container Service - September 14, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - September 20, 2023

222 posts | 33 followers
Follow Best Practices
Best Practices
Follow our step-by-step best practices guides to build your own business case.
Learn More AI Acceleration Solution
AI Acceleration Solution
Accelerate AI-driven business and AI model training and inference with Alibaba Cloud GPU technology
Learn More Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline SDKs for visual production, such as image segmentation, video segmentation, and character recognition, based on deep learning technologies developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Top-performance foundation models from Alibaba Cloud
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Container Service