By Yi Zhan
AgentScope is an open-source framework launched by Alibaba that is developer-centric and focuses on intelligent agent development. It is a strategic product at the Agent layer following ModelScope (Magic Community) . Its core goal is to solve the challenges faced by intelligent agents in construction, operation, and management, providing a production-grade solution that covers the full lifecycle of "development, deployment, and optimization," making the development of intelligent agent applications simpler, more stable, and more effective.
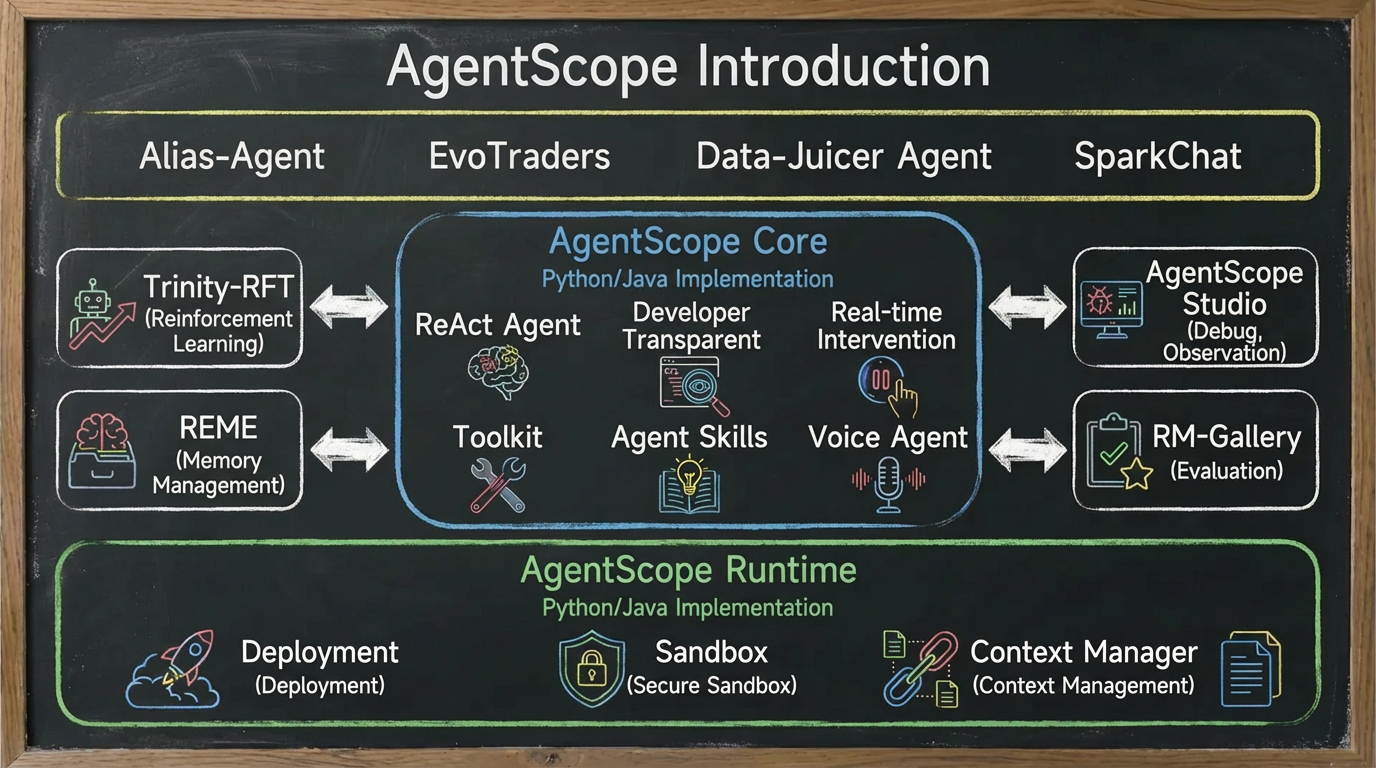
Recently, AgentScope has welcomed a major update for the December version, which is a significant infrastructure upgrade aimed at production-grade intelligent agent applications, allowing agents to transition from "lab prototypes" to "business implementation." This update revolves around three core themes: ready-to-use intelligent agents that instantly empower various real-world scenarios; infrastructure enhancements that comprehensively upgrade the underlying capabilities that make agents "smarter"; runtime × multi-language × front-end, delivering production-ready agents in a three-in-one manner.
For a long time, the Java language has dominated development in the fields of finance, government affairs, and e-commerce. The developer community has also strongly called for a Java version of AgentScope, and now it has significantly released the 1.0 version of Java, embracing the mainstream technology stack for enterprise development.
Today, we are pleased to announce that the AgentScope Java 1.0 version is officially released, providing enterprise-grade capabilities for building Agentic applications for Java developers.
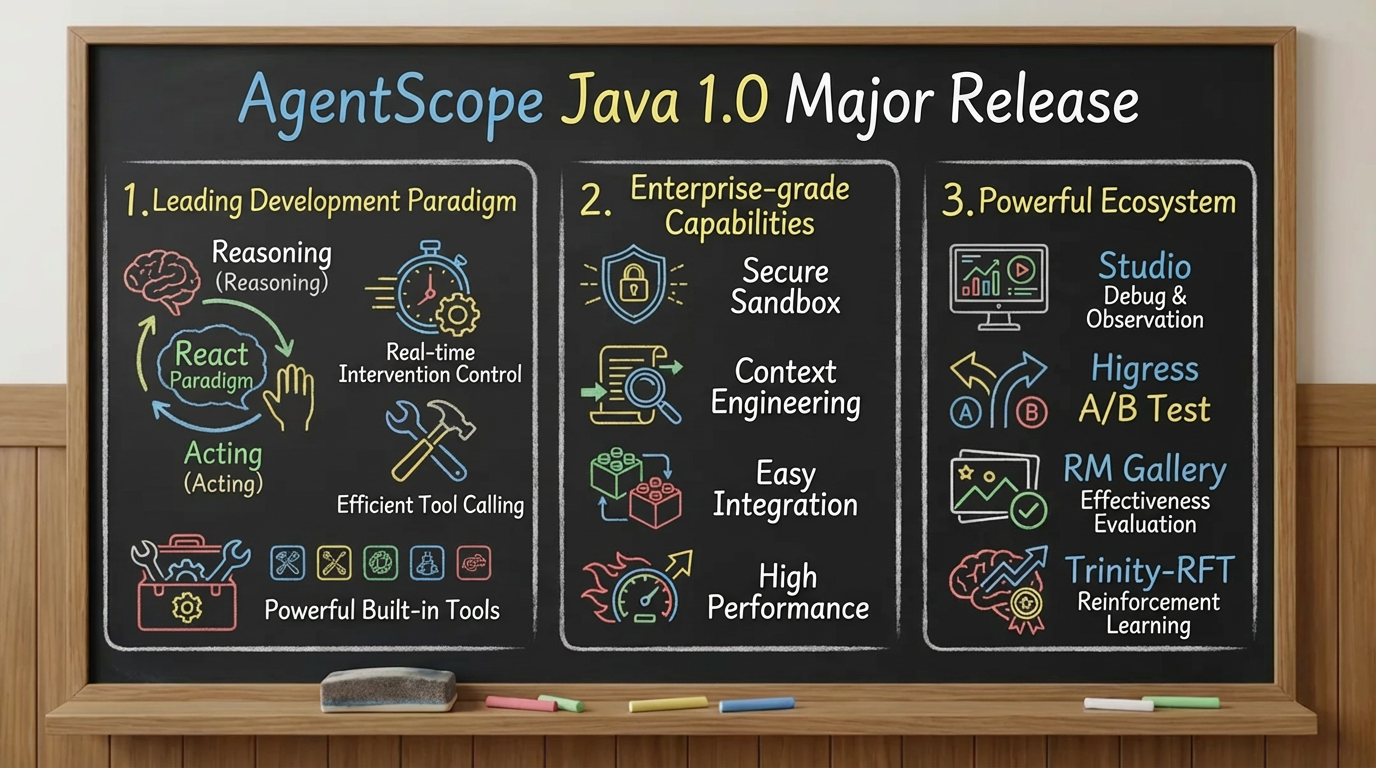
Firstly, in terms of development paradigm, AgentScope adopts the leading ReAct (Reasoning-Action) model, supporting efficient tool invocation and allowing developers to intervene in the agent execution process in real time, achieving a perfect balance between autonomy and controllability.
Secondly, it provides ready-to-use enterprise-grade capabilities. The framework offers a secure sandbox to guarantee the safety of code execution, optimizing model interaction effects through fine-tuned contextual engineering. As a Java framework, it is easy to integrate into existing enterprise technology stacks and boasts a high-performance architecture, ensuring stability and reliability in production environments.
Finally, it possesses a complete ecosystem for development and optimization. It offers a complete toolchain from visual debugging in development mode, A/B testing, to evaluation and reinforcement learning, forming a closed loop for agent development, deployment, and optimization, helping to continuously improve agent effectiveness.
When building complex AI agent applications, developers generally face numerous challenges: rigid workflows that are difficult to adapt to changing tasks, real-time intervention in running agents, chaos in management due to a plethora of tools, unstable model output formats, etc. Systematically solving these pain points is key to enhancing development efficiency and application stability. AgentScope adopts the leading ReAct paradigm, granting LLM autonomous planning capabilities and providing real-time intervention controls and an efficient tool invocation system. Additionally, it integrates powerful tools such as task planning and structured outputs, supporting efficient development of production-grade applications.
1. The leading ReAct paradigm empowers agents with autonomous planning capabilities.
2. Real-time intervention control allows for full control over agent operation. Traditional agents become uninterruptible once started, but AgentScope uses an asynchronous architecture to implement a powerful real-time intervention mechanism.
3. Efficient tool invocation: With the explosion in the number of callable tools, agents face issues of complex tool management, low execution efficiency, and tense context. AgentScope has built a reliable and efficient tool management system.
4. Powerful built-in tools: AgentScope includes many powerful ready-to-use tools that accelerate the development of production-grade applications.
AgentScope provides a secure tool sandbox and contextual engineering capabilities, addressing the core pain points of safety and effectiveness, ensuring that the agent's output meets production standards. Leveraging Java's robust ecosystem in enterprise application development, it offers flexible integration and embedding solutions through standard A2A and MCP protocols, allowing agents to be embedded as independent services in existing systems or to serve as intelligent hubs for connecting and orchestrating other services. Developers need not focus on underlying integration details but can quickly construct production-grade agent applications by concentrating on business logic. Lastly, relying on the capabilities provided by AgentScope Runtime, it supports one-click deployment of agents to Alibaba Cloud Hundred Refinement and function computing platforms, offering commercial-level productization assurance for your agent applications.
1. Secure sandbox:
2. Contextual engineering:
3. Easy Integration
4. High Performance
The AI-native application architecture is profoundly reshaping software engineering paradigms, replacing the determinism of traditional software with the non-determinism of agents, where the final effect is jointly determined by models, data, and context. This evolution transforms traditional "code testing" into complex "effect evaluation." Since any minor change can lead to drastic fluctuations in effect, A/B testing has transitioned from an optimization option to a core release process for ensuring version quality. Therefore, the focus of software engineering must shift from code-centric to data-centric, with success hinging on building an efficient data flywheel.
In the face of this challenge, AgentScope provides a series of ecological tools such as Studio, RM Gallery, and Trinity-RFT, combined with the Higress AI gateway and observable systems, enabling you to quickly practice the AI-native application data flywheel.
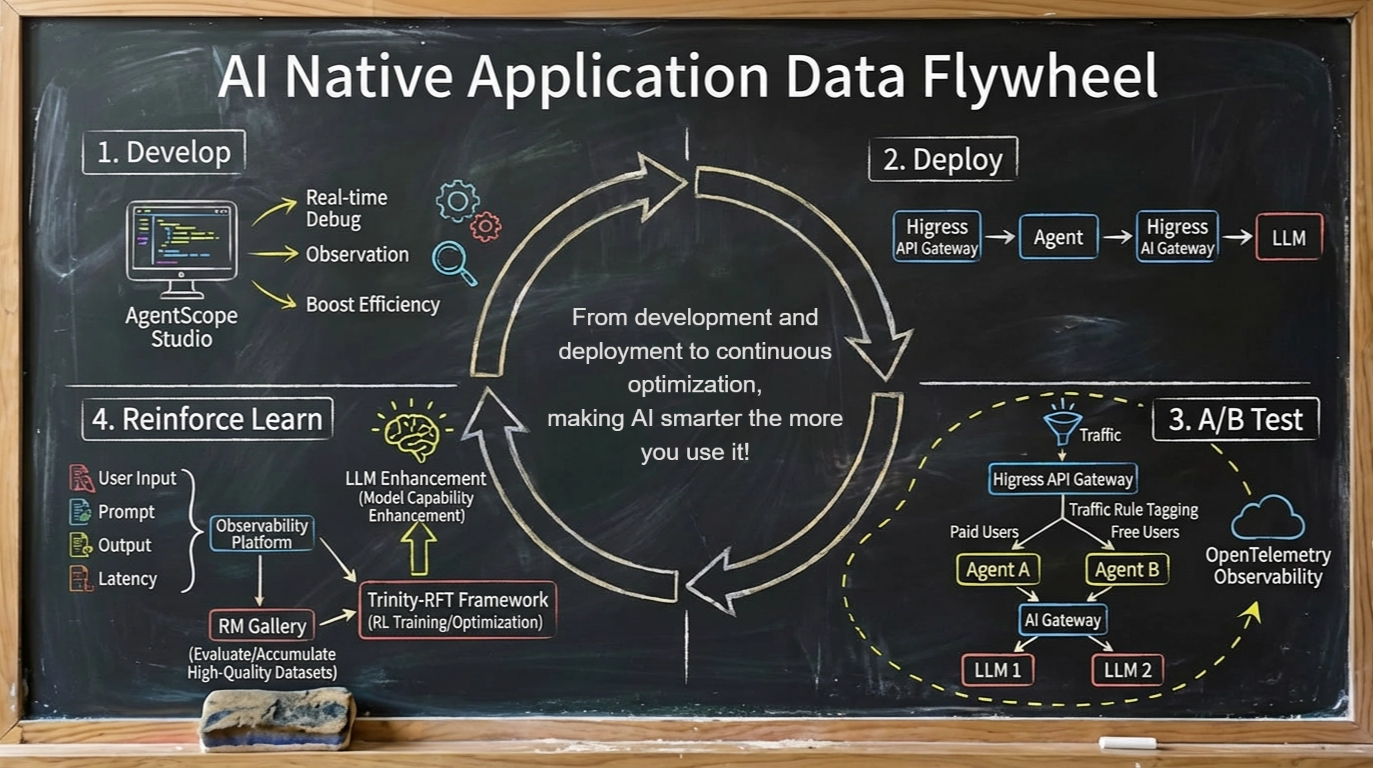
During the agent development phase, we use the AgentScope Studio visualization platform for real-time debugging and observation of agents, significantly enhancing development efficiency. It integrates deeply with OpenTelemetry and LoongSuite, achieving end-to-end full-link tracking.
In the deployment architecture, Higress serves as a unified traffic entry gateway, responsible for routing external requests to the corresponding agents. Agents communicate with LLM through Higress's built-in AI gateway capabilities. With Higress's powerful plugin system, we can flexibly label traffic to achieve precise routing control over agents and LLMs.
During the post-release A/B testing phase, Higress gateway can allocate traffic to different experimental groups based on request content (such as user geographic location, business line, and payment status). For example, paying users could be directed to version A of the agent, while free users are directed to version B for effect comparison. Additionally, the grouping labels of traffic, with observability, will pass through the entire call chain. Thus, the AI gateway can route requests to the corresponding LLM versions based on these labels. This mechanism allows us to perform coordinated A/B testing of agents and LLMs without modifying business code.
Throughout this process, all data generated across the full link—from user input, agent prompts, to model output, latency, and costs—will be reported to the observable system. Based on the RM Gallery's reward function, agent performance across experimental groups will be evaluated and high-quality datasets will be filtered out. Subsequently, our training framework, Trinity-RFT, will use these datasets and reward models to continuously iterate and enhance the model's ability to solve business problems.
Ultimately, this forms a self-optimizing loop driven by data. The system continuously collects real online data, analyzes and evaluates effects, and transforms that into high-quality training data, thereby continuously strengthening model capabilities and building a solid technical competitive barrier.
We welcome you to join our open-source community to build an agent system for the future together!
Apache RocketMQ for AI: A Strategic Upgrade Ushering in the Era of AI MQ

664 posts | 55 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native Community - November 21, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - January 21, 2026
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - October 11, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - January 22, 2026
Alibaba Cloud Community - December 17, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - June 13, 2025

664 posts | 55 followers
Follow AI Acceleration Solution
AI Acceleration Solution
Accelerate AI-driven business and AI model training and inference with Alibaba Cloud GPU technology
Learn More Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline SDKs for visual production, such as image segmentation, video segmentation, and character recognition, based on deep learning technologies developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Top-performance foundation models from Alibaba Cloud
Learn More Network Intelligence Service
Network Intelligence Service
Self-service network O&M service that features network status visualization and intelligent diagnostics capabilities
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Native Community