By Hang Yin (Luying)
ACK Gateway with Inference Extension is designed for LLM inference scenarios, supporting both Layer 4/7 traffic routing and intelligent load balancing capabilities based on model server load. In addition, InferencePool and InferenceModel custom resources (CRDs) help flexibly define traffic distribution policies for inference services, including model canary release and LLM traffic mirroring.
This article introduces the practical process of optimizing the inference service performance based on ACK Gateway with Inference Extension in the large model inference service scenarios deployed across multiple nodes.
vLLM is a high-performance inference system designed for large language models (LLMs). Its goal is to efficiently utilize GPU and multi-node cluster resources while ensuring high throughput and low latency. Given the massive parameter size characteristic of LLMs, it is often difficult for a single GPU or even a single node to accommodate all the parameters at once. This necessitates the underlying architecture to do a lot of work on parallel computing and memory optimization. To this end, vLLM uses a variety of parallelization technologies, including tensor parallel and pipeline parallel, combined with deployment across multiple nodes to achieve efficient large model inference.
Tensor parallel mainly partitions matrix operations in a single layer and distributes computing tasks to multiple GPUs. Its core principles and technical background are as follows:
The fully connected layers and other weight matrices in large neural networks can far exceed the memory capacity of a single GPU. Tensor parallel is used to divide these matrices into several sub-tensors according to a certain method (such as by row, column, or block). Each GPU is only responsible for part of the storage and computing, which can effectively reduce the memory pressure of a single GPU.
In the forward and backward propagation processes, each GPU calculates operations such as multiplication and activation of local submatrices. Finally, each GPU needs to summarize and reduce the results of each part through communication operations (such as All-Reduce or All-Gather) to ensure the final output consistency. This requires an efficient cross-device communication and synchronization strategy to prevent communication bottlenecks that can degrade overall inference latency.
To further improve efficiency, vLLM usually combines task scheduling, pipeline filling (overlapping communication and computation), and other technologies in tensor parallel to optimize load balancing across GPUs, reduce communication latency, and realize efficient parallel computing.
Pipeline parallel focuses on decomposing the entire model into multiple consecutive stages, each running on a separate GPU (or even on a different machine), thus enabling parallel overlap among different stages. Its background and key points include:
For deep models, the network can be hierarchically divided into multiple "stages". Each stage contains several successive layers deployed on separate devices. When an input sample or micro-batch is executed in the first stage, subsequent samples can follow into the previous stage, realizing pipeline processing that maximizes device utilization.
The input is split by micro-batch processing, allowing different micro-batches to be executed concurrently on different stages. This both avoids long idling of stages and optimally overlaps the computing and communication overhead. A sophisticated scheduling mechanism is required to address potential pipeline bubbles or imbalances.
Due to the front-to-back dependency between stages, information such as intermediate activation values and gradients must be passed between stages. This requires a low-latency communication mechanism. Additionally, the scheduling system must ensure timely data input in every device to minimize the latency caused by waiting for data transmission.
Large models in a single node often cannot meet storage and computing requirements due to the large number of parameters. Therefore, they need to be deployed across multi-node clusters. vLLM typically combines tensor parallel with pipeline parallel when deploying across multiple nodes.
In this article, we will deploy the QwQ-32B model across multiple nodes. QwQ-32B is the latest high-efficiency large language model released by Alibaba Cloud. With 3.2 billion parameters, its performance rivals that of DeepSeek-R1 671B. The model performs well on core metrics such as mathematics and code generation, delivering superior inference capabilities with lower resource consumption.
1. Download the model.
GIT_LFS_SKIP_SMUDGE=1 git clone https://www.modelscope.cn/Qwen/QwQ-32B.git
cd QwQ-32B
git lfs pull2. Upload the model to OSS.
ossutil mkdir oss://<Your-Bucket-Name>/QwQ-32B
ossutil cp -r ./QwQ-32B oss://<Your-Bucket-Name>/QwQ-32B3. Configure the PV and PVC for the target cluster.
For more information, see Mount a statically provisioned OSS volume. The following table describes the parameters of a PV.
| Parameter or setting | Description |
|---|---|
| PV Type | OSS |
| Volume Name | llm-model |
| Access Certificate | Specify the AccessKey ID and the AccessKey secret used to access the OSS bucket. |
| Bucket ID | Select the bucket that you created. |
| OSS Path | Select the path of the model, such as /models/QwQ-32B. |
The following table describes the parameters of a PVC.
| Parameter or setting | Description |
|---|---|
| PVC Type | OSS |
| Volume Name | llm-model |
| Allocation Mode | Select Existing Volumes. |
| Existing Volumes | Click Existing Volumes and select the PV that you created. |
Click Existing Volumes and select the PV that you created.
The following command is based on the vLLM framework for deploying the QwQ-32B model inference service across multiple nodes:
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
data:
hostfile-0: |-
qwq-dist-v1.qwq-dist-v1-0.default
qwq-dist-v1.qwq-dist-v1-0-0.default
master.rayInit: |-
#!/bin/bash
ray_port=6379
ray_init_timeout=300
ray_cluster_size=$WORLD_SIZE
master_command=$1
ray start --head --port=$ray_port
for (( i=0; i < $ray_init_timeout; i+=5 )); do
active_nodes=`python3 -c 'import ray; ray.init(); print(sum(node["Alive"] for node in ray.nodes()))'`
if [ $active_nodes -eq $ray_cluster_size ]; then
echo "All ray workers are active and the ray cluster is initialized successfully."
$master_command
exit 0
fi
echo "Wait for all ray workers to be active. $active_nodes/$ray_cluster_size is active"
sleep 5s;
done
echo "Waiting for all ray workers to be active timed out."
exit 1
worker.rayInit: |-
#!/bin/bash
ray_port=6379
ray_init_timeout=300
ray_address=$MASTER_ADDR
worker_command=$1
for (( i=0; i < $ray_init_timeout; i+=5 )); do
ray start --address=$ray_address:$ray_port
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Worker: Ray runtime started with head address $ray_address:$ray_port"
$worker_command
exit 0
fi
echo "Waiting until the ray worker is active..."
sleep 5s;
done
echo "Ray worker starts timeout, head address: $ray_address:$ray_port"
exit 1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
app: distributed-serving
chart: distributed-serving-0.1.0
createdBy: DistributedServing
heritage: Helm
release: qwq-dist-v1
name: qwq-dist-v1-cm
---
apiVersion: leaderworkerset.x-k8s.io/v1
kind: LeaderWorkerSet
metadata:
labels:
app: distributed-serving
release: qwq-dist-v1
serviceName: qwq-dist
servingName: qwq-dist
servingType: distributed-serving
servingVersion: v1
name: qwq-dist-v1-distributed-serving
spec:
leaderWorkerTemplate:
leaderTemplate:
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.io/path: /metrics
prometheus.io/port: "8000"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
labels:
app: distributed-serving
release: qwq-dist-v1
role: leader
serviceName: qwq-dist
servingName: qwq-dist
servingType: distributed-serving
servingVersion: v1
spec:
containers:
- command:
- sh
- -c
- /vllm-workspace/ray_init.sh leader --ray_cluster_size=$(LWS_GROUP_SIZE);
vllm serve /mnt/models/QwQ-32B --port 8000 --trust-remote-code --served-model-name
qwq --max-model-len 16384 --gpu-memory-utilization 0.95 --tensor-parallel-size
2 --pipeline-parallel-size 2 --enforce-eager
env:
- name: MASTER_ADDR
value: $(LWS_LEADER_ADDRESS)
- name: WORLD_SIZE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.annotations['leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/size']
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_INDEX
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.labels['leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/worker-index']
- name: GROUP_INDEX
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.labels['leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/group-index']
- name: GPU_COUNT
value: "2"
- name: HOSTFILE
value: /etc/hostfile
- name: ROLE
value: master
image: kube-ai-registry.cn-shanghai.cr.aliyuncs.com/kube-ai/vllm:v0.7.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: distributed-serving-leader
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
name: restful
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 30
tcpSocket:
port: 8000
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: "2"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /dev/shm
name: dshm
- mountPath: /mnt/models
name: llm-models
- mountPath: /etc/hostfile
name: qwq-dist-v1-cm
subPathExpr: hostfile-$(GROUP_INDEX)
volumes:
- configMap:
items:
- key: hostfile-0
mode: 438
path: hostfile-0
name: qwq-dist-v1-cm
name: qwq-dist-v1-cm
- emptyDir:
medium: Memory
sizeLimit: 30Gi
name: dshm
- name: llm-model
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: llm-model
restartPolicy: RecreateGroupOnPodRestart
size: 2
workerTemplate:
metadata:
labels:
app: distributed-serving
release: qwq-dist-v1
role: worker
serviceName: qwq-dist
servingName: qwq-dist
servingType: distributed-serving
servingVersion: v1
spec:
containers:
- command:
- sh
- -c
- /vllm-workspace/ray_init.sh worker --ray_address=$(LWS_LEADER_ADDRESS)
env:
- name: MASTER_ADDR
value: $(LWS_LEADER_ADDRESS)
- name: WORLD_SIZE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.annotations['leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/size']
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_INDEX
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.labels['leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/worker-index']
- name: GROUP_INDEX
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.labels['leaderworkerset.sigs.k8s.io/group-index']
- name: GPU_COUNT
value: "2"
- name: HOSTFILE
value: /etc/hostfile
- name: ROLE
value: worker
image: kube-ai-registry.cn-shanghai.cr.aliyuncs.com/kube-ai/vllm:v0.7.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: distributed-serving-worker
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: "2"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /dev/shm
name: dshm
- mountPath: /mnt/models
name: llm-models
- mountPath: /etc/hostfile
name: qwq-dist-v1-cm
subPathExpr: hostfile-$(GROUP_INDEX)
volumes:
- configMap:
items:
- key: hostfile-0
mode: 438
path: hostfile-0
name: qwq-dist-v1-cm
name: qwq-dist-v1-cm
- emptyDir:
medium: Memory
sizeLimit: 30Gi
name: dshm
- name: llm-model
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: llm-model
networkConfig:
subdomainPolicy: Shared
replicas: 3
startupPolicy: LeaderCreated
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: distributed-serving
release: qwq-dist-v1
servingName: qwq-dist
servingType: distributed-serving
servingVersion: v1
spec:
ports:
- name: http-serving
port: 8000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8000
selector:
app: distributed-serving
release: qwq-dist-v1
role: leader
type: ClusterIP
EOFThe sample YAML uses LeaderWorkderSet to deploy the QwQ-32B model across multiple nodes. Each group contains a leader pod and a worker pod, each of which is equipped with 2 GPUs to form a RAY cluster.
When vLLM starts, pipeline parallel is enabled between two pods by setting pipeline-parallel-size to 2, and tensor parallel is enabled using two GPUs within a single pod by setting tensor-parallel-size to 2.
Intelligent Routing to Optimize Model Services Deployed across Multiple Nodes
ACK Gateway with AI Extension is a component designed for LLM inference scenarios. It supports traffic routing at Layer 4/7 and provides intelligent load balancing capabilities based on model server load. In addition, InferencePool and InferenceModel custom resources (CRDs) help flexibly define traffic distribution policies for inference services, including model canary release.
ACK Gateway with Inference Extension provides intelligent load balancing capabilities based on model server load. In a deployment environment across multiple nodes combining tensor parallel and pipeline parallel, it can intelligently monitor system load through leader model server metrics, enabling fine-grained routing accordingly to ensure balanced workload distribution across different distributed workload groups.
1. Enable the ACK Gateway with AI Extension component in the Components section of the ACK cluster and select the Enable Gateway API inference extension option when enabled.
2. Create a gateway instance: Use kubectl to connect to the ACK cluster and run the following command to create a gateway with ports 8080 and 8081. Port 8080 deploys a standard HTTP routing to the backend inference service, while port 8081 extends the routing to the backend inference service based on the inference service.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: GatewayClass
metadata:
name: inference-gateway
spec:
controllerName: gateway.envoyproxy.io/gatewayclass-controller
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: inference-gateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: inference-gateway
listeners:
- name: http
protocol: HTTP
port: 8080
- name: llm-gw
protocol: HTTP
port: 8081
---
apiVersion: gateway.envoyproxy.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClientTrafficPolicy
metadata:
name: client-buffer-limit
spec:
connection:
bufferLimit: 20Mi
targetRefs:
- group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: Gateway
name: inference-gateway
---
apiVersion: gateway.envoyproxy.io/v1alpha1
kind: BackendTrafficPolicy
metadata:
name: backend-timeout
spec:
timeout:
http:
requestTimeout: 24h
targetRef:
group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: Gateway
name: inference-gateway
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: reasoning-backend
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: inference-gateway
sectionName: http
rules:
- backendRefs:
- group: ""
kind: Service
name: qwq-dist-v1
port: 8000
weight: 1
matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
EOFUse the InferencePool and InferenceModel resources to enable AI inference extension capabilities. In the CRD provided by the inference extension: InferencePool uses a label selector to declare a set of LLM inference service workloads running in the cluster, while InferenceModel specifies traffic distribution policies for specific models in the InferencePool.
1. Create an InferencePool.
InferencePool uses a label selector to declare a set of LLM inference service workloads:
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: InferencePool
metadata:
annotations:
inference.networking.x-k8s.io/attach-to: |
name: inference-gateway
port: 8081
name: reasoning-pool
spec:
extensionRef:
failureMode: FailClose
group: ""
kind: Service
name: inference-gateway-ext-proc
selector:
app: distributed-serving
release: qwq-dist-v1
role: leader
targetPortNumber: 8000
EOF2. Create an InferenceModel.
InferenceModel defines traffic distribution policies for models and supports canary release. The following example demonstrates a basic use case: all requests for the model named qwq are forwarded to the QwQ-32B model.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: InferenceModel
metadata:
name: reasoning-model
spec:
criticality: Critical
modelName: qwq
poolRef:
group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io
kind: InferencePool
name: reasoning-pool
targetModels:
- name: qwq
weight: 100
EOFSemantic description:
• The targetModels field defines the target models and their weight ratios. For example, the above configuration indicates that 100% of requests will be routed to the QwQ-32B model.
• The criticality field marks the importance of the model, which affects the priority of traffic scheduling.
Run the following command to check whether intelligent routing takes effect:
GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl get gateway/inference-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
curl -X POST ${GATEWAY_IP}/v1/chat/completions \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"model": "qwq",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Who are you?"
}
]
}' -v1. Collect metrics related to the inference service by using the default service discovery mechanism of the Prometheus instance. For more information, see Default service discovery.
2. Monitor the LLM inference service deployed based on vLLM through the Grafana dashboard: Import the vLLM Grafana JSON model to Grafana to create an observable dashboard for the LLM inference service. For more information about the imported JSON model, visit the vLLM official website. For specific import operations, see Grafana dashboard export and import
3. Run the following command to create a stress test tool.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: vllm-benchmark
labels:
app: vllm-benchmark
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: vllm-benchmark
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: vllm-benchmark
spec:
volumes:
- name: llm-model
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: llm-model
containers:
- name: vllm-benchmark
image: kube-ai-registry.cn-shanghai.cr.aliyuncs.com/kube-ai/vllm-benchmark:v1
command:
- "sh"
- "-c"
- "sleep inf"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /models/QwQ-32B
name: llm-model
EOF4. Download the stress test dataset.
# Run the following command to log on to the benchmark pod.
PODNAME=$(kubectl get po -o custom-columns=":metadata.name"|grep "vllm-benchmark")
kubectl exec -it $PODNAME -- bash
# Download the stress test dataset.
pip3 install modelscope
modelscope download --dataset gliang1001/ShareGPT_V3_unfiltered_cleaned_split ShareGPT_V3_unfiltered_cleaned_split.json --local_dir /root/5. Use the following command to initiate two stress tests on port 8080 of the gateway (using the default service routing of the gateway) and port 8081 (using the service routing of the inference extension).
• Run stress tests on the default service routing of the gateway.
python3 /root/vllm/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py \
--backend vllm \
--model /models/QwQ-32B \
--served-model-name qwq \
--trust-remote-code \
--dataset-name random \
--dataset-path /root/ShareGPT_V3_unfiltered_cleaned_split.json \
--random-prefix-len 1000 \
--random-input-len 4000 \
--random-output-len 3000 \
--random-range-ratio 0.2 \
--num-prompts 300 \
--max-concurrency 30 \
--host 192.168.14.126 \ # The internal IP address of ACK gateway.
--port 8080 \ # Request port 8080, which is the default route of the gateway.
--endpoint /v1/completions \
--save-result \
2>&1 | tee benchmark_serving.txt
============ Serving Benchmark Result ============
Successful requests: 300
Benchmark duration (s): 2362.70
Total input tokens: 1014085
Total generated tokens: 537817
Request throughput (req/s): 0.13
Output token throughput (tok/s): 227.63
Total Token throughput (tok/s): 656.83
---------------Time to First Token----------------
Mean TTFT (ms): 10909.18
Median TTFT (ms): 2446.06
P99 TTFT (ms): 119308.83
-----Time per Output Token (excl. 1st token)------
Mean TPOT (ms): 114.18
Median TPOT (ms): 113.00
P99 TPOT (ms): 158.03
---------------Inter-token Latency----------------
Mean ITL (ms): 113.69
Median ITL (ms): 103.10
P99 ITL (ms): 109.65
==================================================• Run stress tests on service routing of inference extension.
python3 /root/vllm/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py \
--backend vllm \
--model /models/QwQ-32B \
--served-model-name qwq \
--trust-remote-code \
--dataset-name random \
--dataset-path /root/ShareGPT_V3_unfiltered_cleaned_split.json \
--random-prefix-len 1000 \
--random-input-len 4000 \
--random-output-len 3000 \
--random-range-ratio 0.2 \
--num-prompts 300 \
--max-concurrency 30 \
--host 192.168.14.126 \
--port 8081 \ # Request port 8081. Use the gateway inference extension for routing.
--endpoint /v1/completions \
--save-result \
2>&1 | tee gie_benchmark_serving.txt
============ Serving Benchmark Result ============
Successful requests: 300
Benchmark duration (s): 2325.10
Total input tokens: 1014085
Total generated tokens: 538158
Request throughput (req/s): 0.13
Output token throughput (tok/s): 231.46
Total Token throughput (tok/s): 667.60
---------------Time to First Token----------------
Mean TTFT (ms): 7335.87
Median TTFT (ms): 2413.13
P99 TTFT (ms): 106624.40
-----Time per Output Token (excl. 1st token)------
Mean TPOT (ms): 117.26
Median TPOT (ms): 114.39
P99 TPOT (ms): 198.15
---------------Inter-token Latency----------------
Mean ITL (ms): 115.99
Median ITL (ms): 103.84
P99 ITL (ms): 109.88
==================================================Stress tests are run on the standard gateway (port 8080) and ACK Gateway with AI Extension (port 8081). The key metrics are as follows:
| Metrics | Metrics | ACK Gateway with AI Extension Intelligent Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Average TTFT (ms) | 10909.18 | 7335.87 |
| P99 TTFT (ms) | 119308.83 | 106624.40 |
| Output Throughput (tok/s) | 656.83 | 667.60 |
At the same time, you can make a visual comparison of the observable dashboard of the vLLM server in the corresponding time periods of the two stress tests.
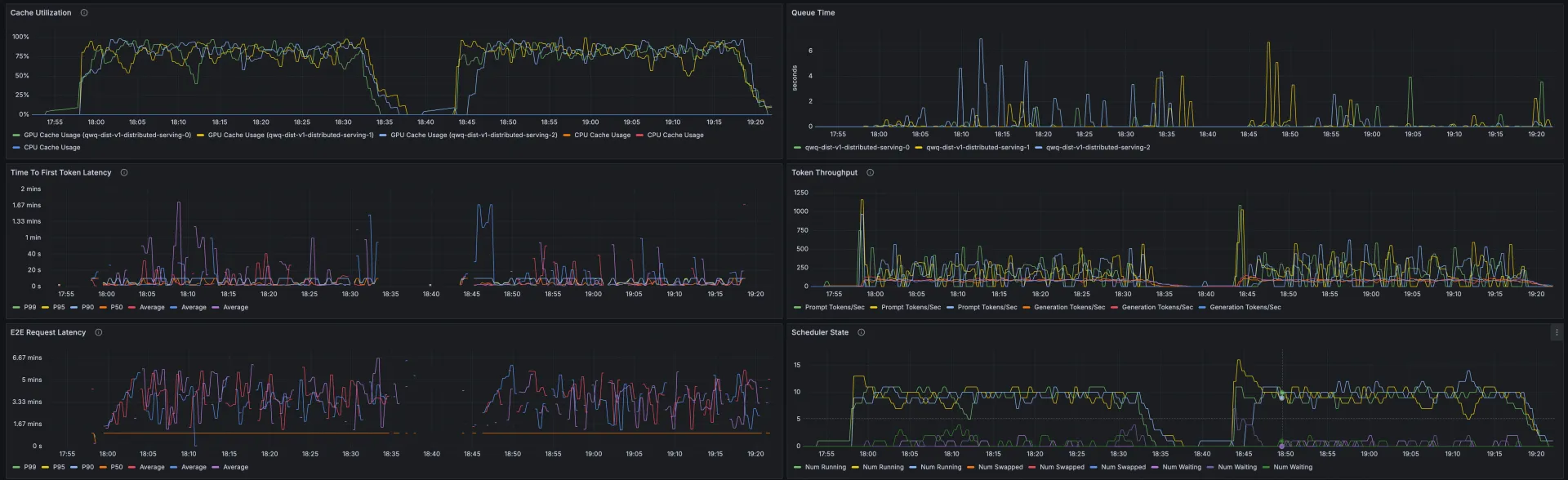
Through stress tests on data and dashboards, you can see that when you use the inference extension based on ACK Gateway to perform routing and load balancing on the inference service, the QwQ-32B inference service has less latency and better throughput, cache utilization, and productivity. Average TTFT is shortened by 32.7% and KV Cache utilization is more uniform across workloads.
Note: The test results are related to many factors, and the above results are for reference only.
ACK Gateway with AI Extension: Intelligent Routing Practice for Kubernetes Large Model Inference
ACK AI Profiling: An Analysis of the Problem from Black Box to Transparency

228 posts | 33 followers
FollowAlibaba Container Service - July 10, 2025
Alibaba Container Service - July 10, 2025
Alibaba Container Service - January 15, 2026
Alibaba Container Service - February 25, 2026
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - September 20, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - February 20, 2025

228 posts | 33 followers
Follow AI Acceleration Solution
AI Acceleration Solution
Accelerate AI-driven business and AI model training and inference with Alibaba Cloud GPU technology
Learn More Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline SDKs for visual production, such as image segmentation, video segmentation, and character recognition, based on deep learning technologies developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More ACK One
ACK One
Provides a control plane to allow users to manage Kubernetes clusters that run based on different infrastructure resources
Learn More Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Top-performance foundation models from Alibaba Cloud
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Container Service