By Yehan
Compute Nest is a service management PaaS platform that Alibaba Cloud provides to ISVs (Independent Software Vendors) and their customers. It aims to solve ISVs' cloud delivery, deployment, and O&M issues and establish channels between ISVs and customers. Considering the actual scenarios faced by ISVs, Compute Nest provides three modes that are private services, fully managed services, and hosted O&M services. The difference between fully managed services and private services is whether it is deployed under an ISV account or a user account.
This article describes how to deploy a Helm chart to an ACK cluster in Compute Nest.
Compute Nest service deployment mainly uses Resource Orchestration Service (ROS) to orchestrate resources. Therefore, the initial implementation method was to use ROS's ClusterHelmApplication directly for deployment. The key part of the corresponding template is as follows:
ClusterHelmApplication:
Type: ALIYUN::CS::ClusterHelmApplication
DependsOn:
- AddonsSleep
Properties:
ChartValues:
Ref: ChartValues
ClusterId:
Fn::If:
- CreateAck
- Fn::GetAtt:
- ManagedKubernetesCluster
- ClusterId
- Ref: ClusterId
ChartUrl:
Ref: ChartUrl
Namespace:
Ref: Namespace
Name:
Ref: NameAfter testing, two issues were discovered with this method:
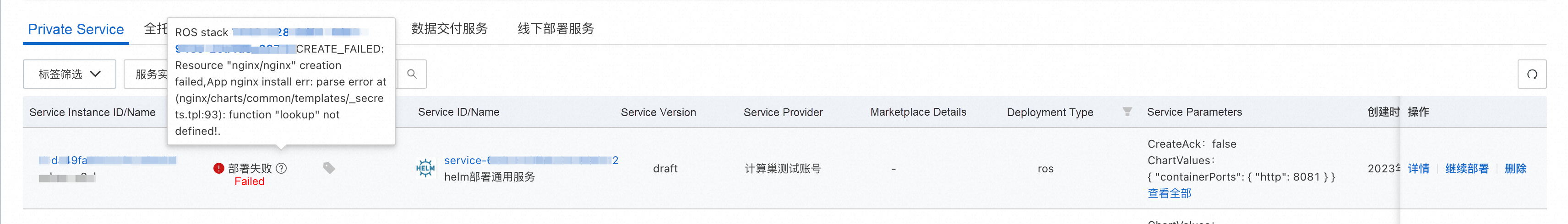
Since ACK's online deployment method is unfeasible, consider directly installing by using Helm commands. You can create a job within the ACK cluster to deploy the Helm chart. The key part of the template is as follows:
Resources:
ClusterUserKubeconfig:
Type: DATASOURCE::CS::ClusterUserKubeconfig
Properties:
ClusterId:
Ref: ClusterId
ClusterApplication:
Type: ALIYUN::CS::ClusterApplication
Properties:
YamlContent:
Fn::Sub:
- |
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: helm-install-job
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: helm-install-job
spec:
containers:
- name: helm-intall
image: alpine/helm:3.12.0
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "--" ]
args: ["cd ~; mkdir ~/.kube; echo '${KubeConfig}' | base64 -d >> ~/.kube/config; chartPackage=$({{ computenest::helmpull::test }}); helm install $chartPackage --generate-name;"]
restartPolicy: Never
- KubeConfig:
Fn::Base64Encode:
Fn::GetAtt:
- ClusterUserKubeconfig
- ConfigWrite the KubeConfig into a config file within the job, and execute the helm pull command. Finally, use the helm install command to install the Helm chart, where the {{ computenest::helmpull::test }} identifier will be replaced with the Helm chart download command.

The issue with this method is that while the job handles the Helm chart deployment, it does not uninstall the Helm chart when the service instance is deleted.
Helm provides the hook functionality to handle Helm chart installation during the post-install-hook phase and uninstallation during the pre-delete-hook phase. This addresses the problem of the job only handling deployment without performing uninstallation.
Similarly, we still use the ROS's ClusterHelmApplication resource type to run the Helm hook template framework, executing Helm chart installation and uninstallation within this framework.
The post-install-hook processing logic is as follows:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: post-install-job-{{ .Release.Name }}
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: {{ .Release.Service | quote }}
app.kubernetes.io/instance: {{ .Release.Name | quote }}
app.kubernetes.io/version: {{ .Chart.AppVersion }}
helm.sh/chart: "{{ .Chart.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Version }}"
annotations:
# This is what defines this resource as a hook. Without this line, the
# job is considered part of the release.
"helm.sh/hook": post-install
"helm.sh/hook-weight": "-5"
"helm.sh/hook-delete-policy": hook-succeeded
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: "{{ .Release.Name }}"
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: {{ .Release.Service | quote }}
app.kubernetes.io/instance: {{ .Release.Name | quote }}
helm.sh/chart: "{{ .Chart.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Version }}"
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: post-install-job
image: "alpine/helm:3.12.0"
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "--" ]
args: ["
set -x;
cd ~;
curl -LO \"https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl\";
install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/bin/kubectl;
mkdir ~/.kube; echo {{ .Values.Kubeconfig }} | base64 -d >> ~/.kube/config;
echo {{ toYaml .Values.ChartValues | b64enc }} | base64 -d > values.yaml;
export HELM_EXPERIMENTAL_OCI=1;
wget {{ .Values.ChartUrl }};
data=$(helm install {{.Values.ReleaseName}} {{ .Values.ChartPackage }} -f values.yaml --namespace {{ .Values.ChartNamespace }} | base64 | tr -d '\n');
if [ -n \"{{ .Values.OutputCmd | b64enc }}\" ];
then
sleep {{ .Values.InstallSeconds }};
echo {{ .Values.OutputCmd | b64enc }} | base64 -d > outputCmd.sh;
data=$(source outputCmd.sh | base64 | tr -d '\n');
fi;
{{ .Values.CurlCli }} -d \"{\\\"Data\\\":\\\"$data\\\",\\\"status\\\":\\\"SUCCESS\\\"}\";
"]The pre-delete-hook processing logic is as follows:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: pre-delete-job-{{ .Release.Name }}
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: {{ .Release.Service | quote }}
app.kubernetes.io/instance: {{ .Release.Name | quote }}
app.kubernetes.io/version: {{ .Chart.AppVersion }}
helm.sh/chart: "{{ .Chart.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Version }}"
annotations:
# This is what defines this resource as a hook. Without this line, the
# job is considered part of the release.
"helm.sh/hook": pre-delete
"helm.sh/hook-weight": "-5"
"helm.sh/hook-delete-policy": hook-succeeded
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: "{{ .Release.Name }}"
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: {{ .Release.Service | quote }}
app.kubernetes.io/instance: {{ .Release.Name | quote }}
helm.sh/chart: "{{ .Chart.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Version }}"
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: pre-delete-job
image: "alpine/helm:3.12.0"
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "--" ]
args: ["
cd ~;
mkdir ~/.kube;
echo {{ .Values.Kubeconfig }} | base64 -d >> ~/.kube/config;
export HELM_EXPERIMENTAL_OCI=1;
helm uninstall {{ .Values.ReleaseName }} --namespace {{ .Values.ChartNamespace }};
"]The key parts of the Compute Nest service template are as follows. Upload the actual chartUrl to be deployed to the Helm hook deployment template by using values:

During the exploration of deploying Helm charts online to ACK clusters in Compute Nest, numerous issues occur. Existing cloud products have inadequate support for API calls and online usage, possibly due to the less frequent use of such methods. Most users tend to execute commands directly. For example, ACR services do not support HTTPS pulls, and the ACK-helm-manager corresponds to an outdated Helm version. Ultimately, alternative paths have to be explored to achieve the desired effect.
Use Flux CD to Deploy a Helm Chart in an ACK Cluster Through Compute Nest
How to Use Istio Service Mesh on ACK Clusters Through Compute Nest

229 posts | 33 followers
FollowAlibaba Container Service - August 18, 2025
Alibaba Clouder - December 17, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - October 29, 2019
Alibaba Container Service - August 18, 2025
Alibaba Container Service - July 16, 2024
H Ohara - May 8, 2024

229 posts | 33 followers
Follow Container Compute Service (ACS)
Container Compute Service (ACS)
A cloud computing service that provides container compute resources that comply with the container specifications of Kubernetes
Learn More Container Service for Kubernetes
Container Service for Kubernetes
Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes is a fully managed cloud container management service that supports native Kubernetes and integrates with other Alibaba Cloud products.
Learn More ACK One
ACK One
Provides a control plane to allow users to manage Kubernetes clusters that run based on different infrastructure resources
Learn More Resource Management
Resource Management
Organize and manage your resources in a hierarchical manner by using resource directories, folders, accounts, and resource groups.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Container Service