By Alibaba Cloud Container Team
Amid the rapid advancement of generative AI, enterprise applications are accelerating their shift from model research to business deployment. Whether for large-scale data processing, training and inference of large-scale models, or deploying autonomous AI agents, these scenarios all demand stable, efficient, and elastically scalable resource scheduling and management capabilities.
With their advantages in environmental consistency, cross-platform deployment, and efficient scheduling, containers are a natural fit for the demands of AI scenarios—including diverse computing power, rapid iteration, and large-scale distribution—making them the de facto foundational technology of the AI era. However, to meet production-scale demands, their product forms and underlying technologies must evolve accordingly.
Against this backdrop, this article delves into four key stages—large-scale data processing, model training, model inference, and AI agent deployment—to explore the core requirements for containers in AI and examine how the technology is evolving at each stage to enable these workloads at scale in business scenarios.
If an AI system is viewed as a product or project with a lifecycle, its process can be divided into four stages: large-scale data processing, model training, model inference, and AI agent deployment. Drawing on Alibaba Cloud's practical experience in the open source community and its use cases across multiple industries, these four stages share a set of foundational technical capabilities, yet also present distinct technical requirements due to their unique roles.
Computing power scheduling and resource utilization optimization: Ensure optimal performance for critical tasks while maximizing global computing power utilization in cross-region, multi-tenant, and heterogeneous hardware environments.
Data access and throughput: Reduce data access latency to ensure the continuous and efficient operation of high-value computing resources, such as GPUs, during model training and inference.
Stability and recoverability: Establish multi-dimensional observability, rapid fault detection, self-healing, and seamless recovery mechanisms for long-running tasks to minimize the business impact of abnormal events.
Security and isolation: Provide runtime environment isolation and risk protection to prevent potentially high-risk operations and resource misuse, especially when running generated code in agent sandboxes, invoking multiple toolchains, or handling high-concurrency requests.
Beyond the common requirements, each of the four stages presents its own specific technical demands.
Data processing: The core tasks involve scheduling and elastic optimization for large-scale data processing, orchestrating complex workflows, and enabling the efficient, collaborative execution of heterogeneous computing resources (CPUs and GPUs).
Model training: Key requirements include maximizing GPU computing power, allocating resources appropriately for training tasks, achieving low-latency distributed communication, and providing high-speed loading channels for massive volumes of training data.
Model inference: Performance goals center on shortening startup times, optimizing long-tail response latency, and improving service responsiveness through timely and effective elasticity policies, all while ensuring high service availability.
AI agent deployment: The infrastructure must ensure security for tool calls and code execution, support large-scale elastic scaling, and provide task state persistence.
As a lightweight virtualization technology, containers deploy and manage applications in a unified, isolated runtime by encapsulating them with their dependencies. Compared to traditional VMs, containers boast faster startup speeds, higher resource utilization, and cross-environment consistency, ensuring applications run stably throughout their entire lifecycle of development, testing, deployment, and O&M.
In the AI field, the advantages of containers—such as environmental consistency, cross-platform deployment, and efficient scheduling—naturally meet the demands of AI scenarios for diverse computing power, rapid iteration, and large-scale distribution. This has made them the de facto native foundation of the AI era. Gartner predicts that by 2028, 95% of new AI deployments will run in containerized environments. However, to meet the high-performance and high-stability demands of AI at a production scale, container technology and product forms must evolve, undergoing deep optimization and capability expansion tailored for AI scenarios.
Based on this analysis, the Alibaba Cloud Container Service team has comprehensively upgraded its products and flagship open source projects, offering a new paradigm for enterprises to build reliable and efficient AI-native infrastructure.
In an AI system, data preparation is the starting point of the value chain, directly determining the quality and efficiency of model training and inference. This stage presents two primary challenges: process complexity and the pressure of large-scale batch processing.
● Complex processes: This involves multi-stage tasks such as cleaning, annotation, segmentation, enhancement (data augmentation), and feature extraction. Dependencies change dynamically, requiring precise version management and guaranteed consistency.
● Large-scale batch processing pressure: To efficiently complete offline processing of data volumes often reaching terabytes or even petabytes within a limited time, the system must schedule massive computing resources across a hybrid architecture of CPU and GPU resources. Even under prolonged high loads, it must still ensure stability, high throughput, and high resource utilization.
To address these challenges, the Alibaba Cloud technical team, based on an in-depth analysis of existing open source solutions, has deeply optimized the community edition of Argo Workflows and innovatively proposed the Ray on Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) hybrid architecture.
Fully managed Argo Workflows addresses the limitations of the community edition, including scheduling bottlenecks, low resource utilization, task queuing, version conflicts, and control plane instability. It supports declarative orchestration, queue management, and dependency control.
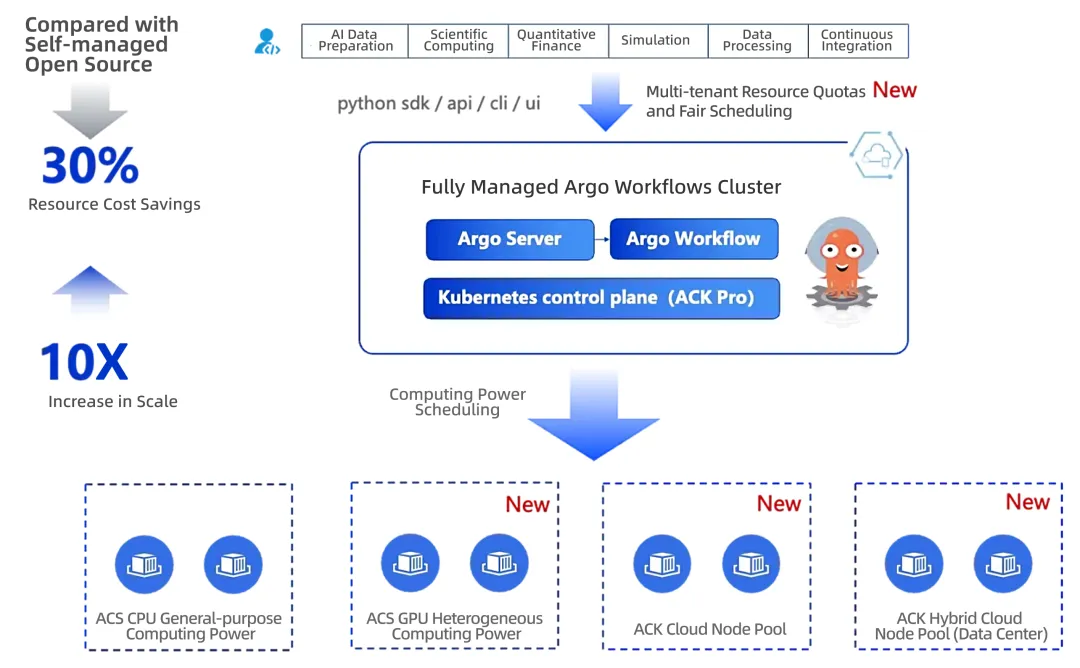
This architecture uses Ray as the high-performance distributed computing kernel to execute data processing tasks. Meanwhile, the ACK scheduler centrally manages a mix of CPU, GPU, and different compute class resources. Combined with mechanisms such as task queuing, batch scheduling, and elastic scaling, it enables fine-grained task scheduling, elastic scaling, and priority-based resource allocation.
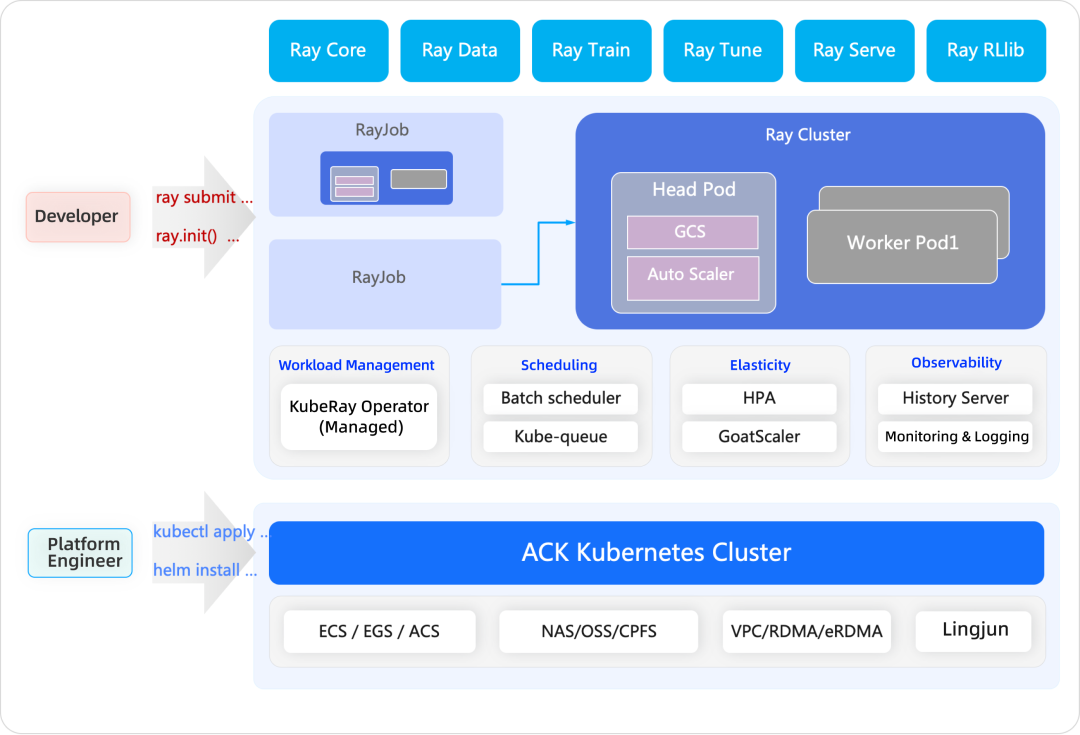
Based on these optimizations and this architecture, Alibaba Cloud's container technology forms a complete closed loop of orchestration and execution capabilities, demonstrating significant advantages in ultra-large-scale deployment, heterogeneous computing, high elasticity, and multi-tenant security:
● A single cluster can stably support tens of thousands of nodes and hundreds of thousands of CPU or GPU cores, meeting the execution demands of tens of thousands of concurrent workflows and hundreds of thousands of tasks.
● It supports efficient elastic scaling of CPU and GPU resources using Alibaba Cloud Container Compute Service (ACS) serverless containers, and reuses subscription nodes in ACK clusters and node pools in hybrid cloud environments, thereby improving overall resource utilization.
● By integrating gang scheduling, capacity scheduling, and elastic resource policies with preemption, it ensures resource guarantees for critical tasks and fairness in multi-tenant scenarios.
● Ray History Server, in conjunction with Alibaba Cloud Application Real-Time Monitoring Service (ARMS), provides end-to-end logging and fault localization, significantly enhancing stability and operational efficiency.
In practice, these container technology upgrades for data processing have delivered remarkable results: data processing throughput has increased approximately tenfold, GPU resource utilization has improved significantly, and O&M costs have been reduced by about 30%, providing a solid data foundation for subsequent model training and inference.
Model training, as the core value-creation step, has evolved from simply stacking computing power to a comprehensive test of underlying infrastructure scheduling and data link optimization. Especially in scenarios involving large language models (LLMs) with tens of billions of parameters, this presents three key challenges:
● Distributed communication bottlenecks: The performance of distributed training is highly dependent on the communication bandwidth between GPUs. Inefficient job scheduling can lead to high-latency communication across vSwitches or zones, significantly extending the training cycle.
● Data loading latency: Directly reading massive training datasets (terabytes to petabytes) from remote storage introduces high latency and redundant access overhead, causing GPUs to idle while waiting for data.
● Low GPU utilization: Tasks such as debugging, small-scale experiments, or specific inference phases often do not require an entire dedicated GPU, leading to the inefficient use of expensive GPU resources.
To address these challenges, Alibaba Cloud has implemented targeted optimizations at the scheduling, data, and resource management layers of its container technology system.
ACK and ACS introduce a multi-level, topology-aware scheduling mechanism. This mechanism incorporates awareness of intra-node topologies—including CPU NUMA, Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe), and scale-up NVLink—as well as inter-node scale-out Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) network topologies. The system preferentially schedules pods that require high-bandwidth communication to the same vSwitch or node and arranges them in an optimal sequence to maximize communication efficiency for collective tasks.
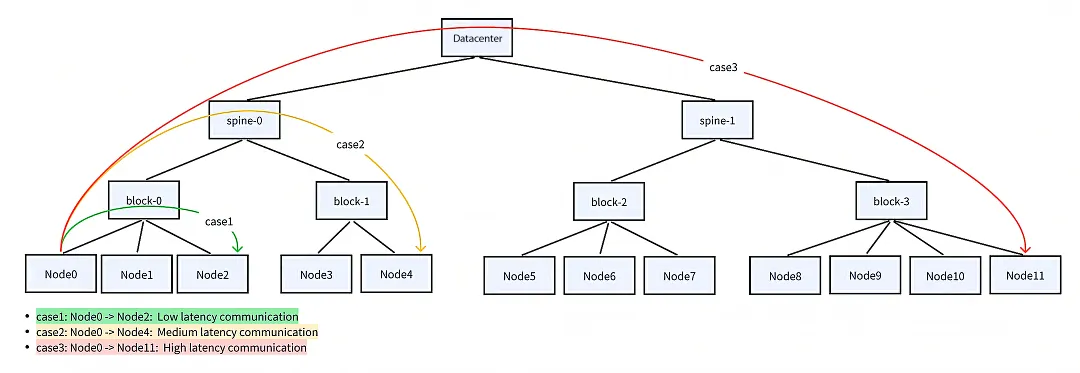
By using Fluid, a Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) open source project, Alibaba Cloud builds a distributed caching system to cache remote datasets to compute nodes on demand. This system supports data prefetching and multi-level caching, delivering read performance close to that of local disks for training tasks while allowing dynamic scaling of data access bandwidth.
GPU sharing and isolation are implemented based on both GPU memory and compute dimensions, splitting a single physical GPU into multiple logical instances for efficient use by multiple tasks. In addition, multi-tenant quotas and a fair scheduling mechanism ensure that critical tasks are prioritized with sufficient resources.
Through optimizations in multi-level topology-aware scheduling, localized data acceleration, and fine-grained GPU sharing, resource-to-task matching in the training stage becomes significantly more efficient:
● Topology-aware scheduling minimizes communication latency to the sub-second level, dramatically improving synchronization efficiency in distributed training and boosting the performance of typical AllReduce operators by 30%.
● Fluid-based distributed caching reduces remote data loading latency by over 90%, leading to higher GPU Model FLOPs Utilization (MFU).
● GPU sharing, which splits a physical GPU into multiple logical instances, improves resource utilization by 3 to 5 times. Combined with multi-tenant quotas and fair scheduling, it ensures that critical tasks run with priority.
Production data shows a significant reduction in the overall time cost of LLM training. The loading speed for a 600 GB training dataset has increased by more than 10 times, and the overall computing power cost has been reduced by over 40%. This marks a breakthrough from merely "runnable" to "optimally run."
While LLMs have matured in capability through extensive training, from a practical deployment standpoint, this maturity does not guarantee smooth operation in an enterprise production environment. Therefore, "how to efficiently deploy inference services" has become a central challenge.
To understand this, let's first examine the internal structure of the inference process. A complete inference request can be divided into two stages: Prefill and Decode.
● The Prefill stage computes the key-value (KV) cache for the input prompt, a process that is compute-intensive.
● The Decode stage must store all previously computed KV pairs, making it GPU memory-intensive.
When both stages run on the same GPU, their resource needs are mutually exclusive. One stage must wait for the other to release either compute or GPU memory resources before it can proceed. This prevents parallel GPU utilization, leading to increased overall response latency and degraded performance.
Furthermore, deploying inference services at a large scale commonly introduces the following challenges:
● Diverse deployment architectures: Various Prefill-Decode separation solutions available in the open source community (such as vLLM, SGLang, Mooncake, and Dynamo) differ in their component structure, deployment methods, and configuration requirements, increasing the complexity of selection and O&M for users.
● Startup and loading latency: Loading ultra-large model images and weight files can take tens of minutes, causing significant cold start delays for inference services and impacting business responsiveness.
● High concurrency and long-tail response latency: During peak access times or in complex context scenarios, response latency can fluctuate significantly, affecting the Service Level Agreement (SLA) of model services.
● GPU reliability: Over long-running periods, issues such as GPU hangs, driver crashes, and memory errors are prone to occur, leading to service interruptions.
To address these issues, Alibaba Cloud has introduced the ACK AI Serving Stack. This suite, built on ACK as a unified foundation, integrates capabilities such as inference framework management, intelligent traffic routing, and distributed cache acceleration to manage the entire lifecycle of LLM inference services.
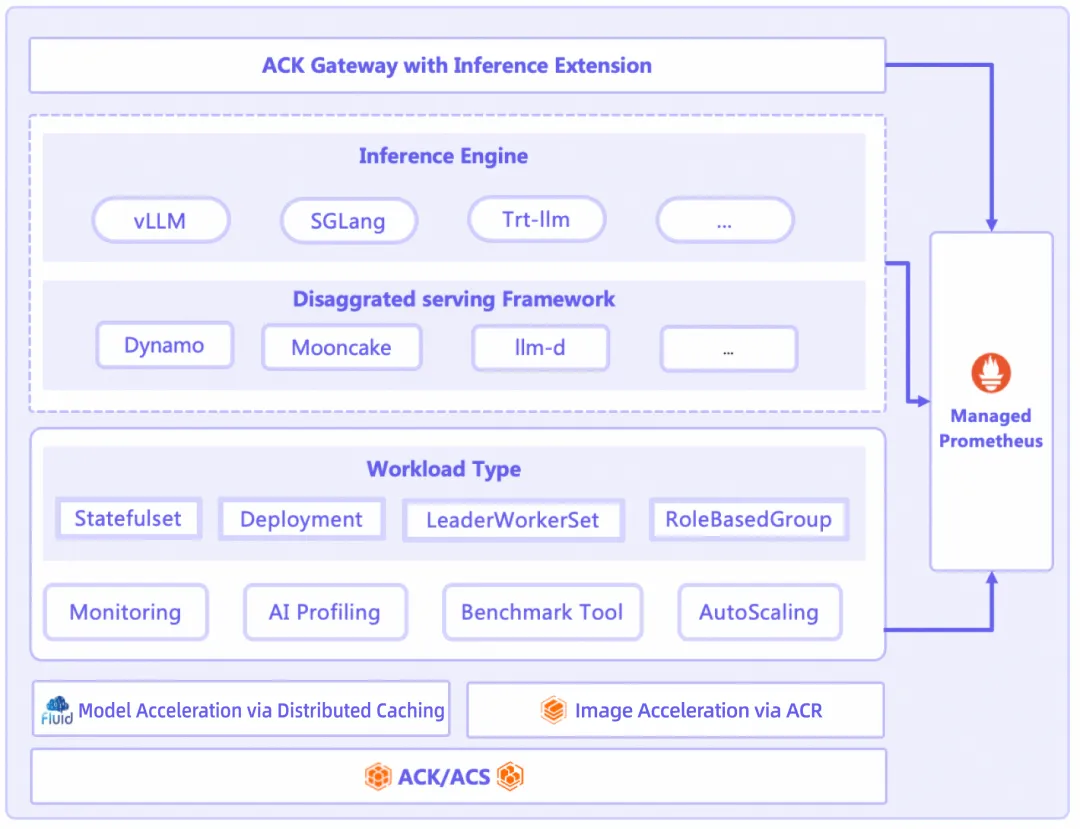
Within the ACK AI Serving Stack's technical architecture, three key components work together to provide its core capabilities.
This component supports one-click deployment of various open source Prefill-Decode separation frameworks, allows flexible and dynamic configuration of the Prefill-to-Decode resource ratio to meet different SLAs, and provides a unified runtime abstraction (InferenceRuntime) across multiple inference engines.
This component provides request scheduling and load balancing capabilities that are deeply optimized for AI inference. Through precise, prefix cache-aware scheduling, it significantly increases the KV cache hit rate, boosts the inference throughput of LLM services, and reduces end-to-end latency, thereby substantially lowering inference costs.
This component is used to build a distributed caching system that preloads remote model files to local nodes, achieving zero redundancy and high-speed startup.
In practical applications, this technology stack has achieved multiple breakthroughs in deployment consistency, response performance, and stability assurance:
● It enables one-click deployment of multiple inference frameworks and full lifecycle management of inference services, simplifying O&M.
● It dynamically adjusts the ratio of Prefill-to-Decode containers to ensure that key metrics such as response time and throughput meet SLA requirements.
● Prefix-aware traffic routing improves TTFT (Time to First Token) in long-tail scenarios by about 73% and increases overall response speed by about 40%.
● Leveraging Fluid's distributed caching and model preheating capabilities, the loading time for a 600 GB model is reduced from 40 minutes to less than 4 minutes (a latency reduction of about 90%).
● GPU failure detection and self-healing mechanisms significantly reduce the mean time to recovery (MTTR).
● Online AI profiling improves the efficiency of identifying GPU application performance bottlenecks by about 50%.
These breakthroughs enable model inference services to achieve efficient startup, stable operation, and continuous optimization in production environments, providing end-users with a faster and more stable AI application delivery experience.
As LLMs continue to advance in their training and inference capabilities, AI applications are evolving from "reactive response" to "proactive execution." A growing number of enterprises are building AI agents with autonomous planning, tool-calling, and multi-step task completion capabilities for use in scenarios such as customer service, data analysis, and automated O&M.
Unlike the batch-oriented training process and some inference scenarios, AI agents are characterized by real-time interaction, multiple tool calls, and multi-step tasks. While these features build on the performance and architectural baselines of inference systems, they also place higher demands on the underlying infrastructure. Systematic optimization is particularly needed in the areas of secure business isolation, elastic scaling for concurrency, and state persistence for long-running tasks.
● More secure and isolated environments: These are needed to prevent attackers from using prompt engineering to induce agents to perform malicious actions, such as accessing sensitive data, launching network attacks, running malicious code, or executing unauthorized operations. It also helps mitigate risks from model hallucinations, such as executing a command to delete the root directory.
● Greater elasticity: Agent applications driven by LLMs may involve a single agent repeatedly calling tools or multiple agents collaborating to call tools, amplifying the need for elasticity.
● Long-running, multi-step, and stateful nature: The state of sandboxes must be preserved in a cost-effective manner.
So, how can a reliable agent runtime environment be built? ACS has been systematically optimized for AI agent scenarios, implementing upgrades for strong security isolation, large-scale elasticity, and state persistence.
ACS creates code, browser, and desktop sandboxes with compute environments that are strongly isolated by default. This is further enhanced by capabilities such as network policy and Fluid, achieving end-to-end security isolation across the runtime environment, storage, and network.
ACS has released a new image cache acceleration feature. Leveraging disk snapshot technology, ACS can load images for thousands of pods in seconds. Combined with sandbox resource pre-scheduling optimized for user workload characteristics, ACS enables large-scale concurrent elasticity of 15,000 sandboxes per minute, allowing users to confidently use elastic cloud resources on demand.
ACS will soon release a sandbox state persistence feature, supporting one-click hibernation and rapid wake-up. During hibernation, the sandbox's CPU and memory resources are released to reduce costs. Upon request, the sandbox can be quickly woken up, with its memory state fully restored to the pre-hibernation environment, achieving an optimal balance between cost and user experience.
Furthermore, the single-core performance of ACS performance-optimized instances is improved by up to 24%. Existing customers can seamlessly enjoy this performance boost without any code changes, further improving the runtime efficiency of various agent workloads.
These capabilities have been validated in practice: Even when facing instantaneous high concurrency, complex task chains, and long-running operations, the platform provides a stable, secure, and efficient execution environment. This offers robust support for the large-scale deployment of next-generation intelligent agent applications.
In summary, the Alibaba Cloud container technology system demonstrates significant leadership in the following areas:
The system efficiently schedules GPU computing power and RDMA network resources, with native support for AI workloads. It supports fine-grained GPU sharing and isolation and includes built-in network topology-aware scheduling to improve cluster resource utilization and operational efficiency. The system also enables unified management and flexible scaling of computing resources across public clouds, hybrid clouds, on-premises data centers, and multi-cloud environments.
Covering the entire process from data processing to model training and inference, the system accelerates access to training and model data through distributed caching and data affinity scheduling. The system also provides comprehensive monitoring and diagnostics, along with fault detection and self-healing within seconds, to ensure stable operation and predictable responses for long-running AI services.
For scenarios involving AI agents with multiple tool calls and high concurrency, the system provides secure sandboxes, state persistence, and the ability for large-scale resource creation within minutes. This effectively mitigates the risks of high-risk command execution and resource misuse.
Alibaba Cloud delivers core feature upgrades in projects such as Argo Workflows (ultra-large-scale task orchestration), Fluid (distributed data acceleration), Koordinator (a scheduler for AI applications and large-scale co-location), and RBG (AI inference workload management). These advancements are contributed back to the open source community, driving the standardization of AI workload management.
This bottom-up, end-to-end technical advantage not only helps enterprises run AI applications reliably in the AI-native era but also provides industry-leading capabilities for continuous performance optimization and cost reduction. It lays a solid foundation for defining the standard architecture of future AI infrastructure.
Today, Alibaba Cloud's container technologies have been deployed at scale across AI scenarios in multiple industries and are serving leading customers.
Alibaba Cloud's container technology has also been highly recognized by authoritative institutions.
In the 2025 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Container Management, Alibaba Cloud was named a Leader, making it the only technology company in the Asia-Pacific region to receive this recognition for three consecutive years. Furthermore, in the 2025 Gartner® Critical Capabilities for Container Management report, Alibaba Cloud ranked third globally in the AI Workload use case.
Additionally, at KubeCon + CloudNativeCon North America in Atlanta, the Cloud Native Computing Foundation® (CNCF®) announced that Alibaba Cloud was one of the first global vendors to achieve its v1.0 certification for AI. This certification signifies that Alibaba Cloud's Kubernetes platform provides a consistent deployment experience and stable cross-environment performance when running mainstream AI frameworks and production-grade AI applications.

Looking ahead, as AI continues to drive digital transformation across industries, it will place ever-increasing demands on infrastructure. Larger model scales, more complex task chains, stricter security isolation, and shorter iteration cycles all mean that the underlying technology must continuously evolve. Alibaba Cloud's container services will continue to optimize performance, stability, security, and cost-effectiveness, providing robust support for the AI-native era. This enables enterprises to navigate the rapidly changing technological landscape with confidence and co-create value.
How ASM Ambient Mode Innovates Kubernetes Egress Traffic Management

228 posts | 33 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native Community - March 6, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - October 23, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - September 9, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - December 11, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Big Data and AI - October 27, 2025
Apache Flink Community - October 15, 2025

228 posts | 33 followers
Follow AI Acceleration Solution
AI Acceleration Solution
Accelerate AI-driven business and AI model training and inference with Alibaba Cloud GPU technology
Learn More Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline SDKs for visual production, such as image segmentation, video segmentation, and character recognition, based on deep learning technologies developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More ACK One
ACK One
Provides a control plane to allow users to manage Kubernetes clusters that run based on different infrastructure resources
Learn More Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Top-performance foundation models from Alibaba Cloud
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Container Service