This topic describes how to quickly get started with a PolarDB for MySQL cluster. It covers key operations, including creating a cluster, configuring a whitelist, creating a database account, and connecting to a cluster.
Tutorial
If you have questions about the following steps, click the corresponding step for the instructions.
1. Create a cluster
Go to the Quick Purchase page of PolarDB to quickly create a PolarDB for MySQL cluster with minimal configurations. The following table describes the parameters. Retain the default values for the parameters not included in the table. For more information about how to create a cluster, see Purchase an Enterprise Edition cluster or Purchase a Standard Edition cluster.
Parameter | Description |
Billing Method | The billing method of the PolarDB cluster. For more information, see Billing methods.
|
Region | The region of the PolarDB cluster. Note Make sure that you deploy the PolarDB cluster in the same region as the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance on which your applications run. Otherwise, the cluster and instance cannot communicate with each other over the internal network. |
Database Engine | The database engine of the PolarDB cluster.
Note You can select only the MySQL 8.0 database engine for a quick purchase. If you want to select another MySQL version for the cluster, click the Custom Purchase tab in the upper-left corner of the page of the buy page. |
Database Edition | The cluster edition. Valid values:
Note
|
Network Type | The virtual private cloud (VPC) and the vSwitch to which the PolarDB cluster belongs. Note
|
Deployment Mode (optional) | The number of nodes in the PolarDB cluster and the corresponding high-availability (HA) mode. For more information, see High-availability mode (hot standby storage cluster).
Note If you set the Billing Method parameter to Subscription or Pay-as-you-go, you must configure this parameter. |
Node Type | The compute node specifications of the PolarDB cluster. Select the specifications that meet your business requirements. To select other specifications, click the Custom Purchase tab in the upper-left corner of the buy page. |
Storage Capacity (optional) | The storage capacity of the PolarDB cluster. Note If you set the Billing Method parameter to Subscription or Pay-as-you-go and the Database Edition parameter to Standard Edition, you must configure this parameter. |
2. Configure a whitelist
Log on to the PolarDB console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters. In the upper-left corner, select the region of the cluster for which you want to configure a whitelist. In the Clusters list, click the ID of the cluster to go to the Basic Information page. Choose Settings and Management > Cluster Whitelists to add an IP address whitelist or a security group. For more information, see Configure whitelists for a cluster and Configure a security group.

If you want to access the PolarDB cluster from an ECS instance in the same VPC as the cluster, you can add the CIDR block of the VPC to the default group.
If you want to access the PolarDB cluster from an ECS instance in a different VPC from the cluster, add the public IP address of the ECS instance to a new IP address whitelist or add the security group to which the ECS instance belongs to the cluster whitelist.
If you want to access the PolarDB cluster from your on-premises network environment, add the public IP address of your on-premises network to a new IP address whitelist.
Use one of the following methods to obtain the public IP address of your on-premises network environment:
Linux: Open the terminal, enter the
curl ifconfig.mecommand, and then press the Enter key.Windows: Open Command Prompt, enter the
curl ip.mecommand, and then press the Enter key.macOS: Open the terminal, enter the
curl ifconfig.mecommand, and then press the Enter key.
If you use a proxy for your local network environment, the IP address you obtained by using the preceding method may not be the actual public IP address. In this case, add the
0.0.0.0/0CIDR block to a whitelist of the PolarDB cluster. After you connect to the cluster, run theSHOW PROCESSLIST;command to obtain the public IP address and add it to the whitelist of the cluster. Then, delete the0.0.0.0/0CIDR block from the whitelist.
Adding
0.0.0.0/0to an IP whitelist allows all sources to access the cluster. Do not add 0.0.0.0/0 to a whitelist unless necessary.
3. Create a database account
Log on to the PolarDB console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters. In the upper-left corner, select the region of the cluster for which you want to create a database account. In the Clusters list, click the ID of the cluster to go to the Basic Information page. Choose Settings and Management > Accounts to create a database account. For more information, see Create and manage a database account.
You can create a privileged account or a standard account. These two types of accounts have different permissions. Create a database account based on your business requirements. For more information, see Account permissions.
4. Obtain the endpoints of the cluster
Log on to the PolarDB console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters. In the upper-left corner, select the region of the cluster. In the Clusters list, click the ID of the cluster to go to the Basic Information page. In the Database Connections section, you can find the endpoints of the cluster. For more information, see Manage the endpoints of a cluster.
We recommend that you use the cluster endpoint. The default port number is 3306.
Use the Private or Public endpoint based on your access environment.
If you want to access the PolarDB cluster from an ECS instance in the same VPC as the cluster, use the Private endpoint.
If you want to access the PolarDB cluster from your on-premises environment, use the Public endpoint. To apply for a public endpoint, click Apply.
If you use a public endpoint to connect to a PolarDB cluster, the cluster cannot achieve optimal performance.
You cannot use a Private endpoint to connect to a PolarDB cluster from virtual hosts and lightweight servers.
5. Connect to the cluster
You can select a connection method based on your business requirements. See the following examples of connecting to a cluster:
Use DMS to connect to a cluster
DMS is a visualized data management service provided by Alibaba Cloud. DMS provides various management services such as data management, schema management, access control, security audit, business intelligence (BI) charts, data trends, data tracking, performance optimization, and server management. You can manage your PolarDB clusters in DMS without the need to use other tools.
Log on to the PolarDB console. Click Clusters in the left-side navigation pane. Select a region in the upper-left corner and click the ID of the cluster in the list to go to the Basic Information page. In the upper-right corner of the page, click Log on to Database.

In the dialog box that appears, enter the Database Account and Database Password that you created for the PolarDB for MySQL cluster, and click Login.

After you log on to the PolarDB for MySQL cluster, click Instances Connected in the left-side navigation pane to view and manage the PolarDB for MySQL cluster.

Use a client to connect to a cluster
You can use a MySQL client to connect to a PolarDB cluster. MySQL Workbench 8.0.29 is used in this example. The operations by using other types of clients are similar.
Install MySQL Workbench. For more information, visit the MySQL Workbench download page.
Start MySQL Workbench and choose Database > Connect to Database.
Enter the connection information and click OK.
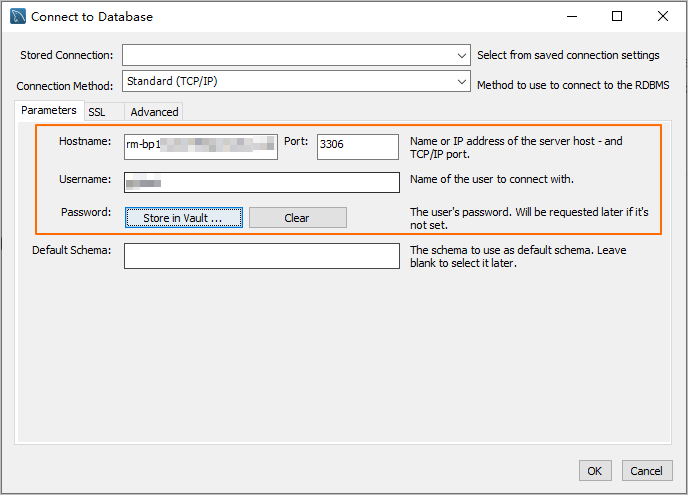
Parameter
Description
Example
Hostname
The database endpoint. For more information, see Database connection.
pc-2***.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com
Port
The port number that corresponds to the database endpoint.
NoteThe default port number is 3306.
3306
Username
The database account. For more information, see Create a database account.
polardb_mysql_user
Password
The password of the database account.
Pass***233
Use the CLI to connect to a cluster
If MySQL client is installed on your server, you can run commands in the CLI to connect to a PolarDB for MySQL cluster.
Syntax:
mysql -h <Endpoint> -P <Port> -u <Account> -p <Password>Example:
mysql -h pc-2***.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com -P3306 -upolardb_mysql_user -pPass***233Parameter | Description | Example |
-h | The database endpoint. For more information, see Database connection. | pc-2***.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com |
-P | The port number that corresponds to the database endpoint. Note
| 3306 |
-u | The database account. For more information, see Create a database account. | polardb_mysql_user |
-p | The password of the database account. Note This parameter is required.
| Pass***233 |
Use an application to connect to a cluster
Connecting to a PolarDB for MySQL cluster is similar to connecting to regular MySQL databases. You only need to replace the endpoint, port, account, and password of the database. The following examples show how to use applications to access a PolarDB database in some development languages:
Java
In this example, a Maven project is used to connect to the PolarDB for MySQL cluster by using the MySQL JDBC driver.
First, add the dependency of the MySQL JDBC driver to the pom.xml file. Sample code:
<dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.27</version> </dependency>Connect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>,<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>, and<YOUR_TABLE_COLUMN_NAME>with the information of your database.import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.Statement; public class DatabaseConnection { public DatabaseConnection() { } public static void main(String[] args) { // The endpoint, port, and database name of the PolarDB cluster to be connected. String url = "jdbc:mysql://<HOST>:3306/<DATABASE>?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC"; // The database account. String user = "<USER>"; // The password of the database account. String password = "<PASSWORD>"; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); // The name of the data table to be queried. ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM `<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>`"); while(rs.next()) { // The column name of the data table to be queried. System.out.println(rs.getString("<YOUR_TABLE_COLUMN_NAME>")); } rs.close(); stmt.close(); conn.close(); } catch (Exception var7) { var7.printStackTrace(); } } }
Python
In this example, Python3 is used to connect to the PolarDB for MySQL cluster by using the PyMySQL library.
First, install the PyMySQL library. You can run the following command to install it:
pip3 install PyMySQLConnect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>, and<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>with the information of your database.import pymysql # The database connection parameters. host = '<HOST>' # The endpoint of the PolarDB cluster. port = 3306 # The default port 3306 user = '<USER>' # The database account. password = '<PASSWORD>' # The password of the database account. database = '<DATABASE>' # The name of the database to be connected. try: # Establish a database connection. connection = pymysql.connect( host=host, port=port, user=user, passwd=password, db=database ) # Obtain the cursor. with connection.cursor() as cursor: # Execute an SQL query. sql = "SELECT * FROM '<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>'" # The name of the table to be queried. cursor.execute(sql) # Obtain the query result. results = cursor.fetchall() for row in results: print(row) finally: # Close the database connection. if 'connection' in locals() and connection.open: connection.close()
Go
In this example, go1.23.0 is used to connect to the PolarDB for MySQL cluster by using the database/sql package and go-sql-driver/mysql driver.
First, install the
go-sql-driver/mysqldriver. You can run the following command to install the driver:go get -u github.com/go-sql-driver/mysqlConnect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>, and<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>with the information of your database.package main import ( "database/sql" "fmt" "log" _ "github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql" ) func main() { // Database connection parameters. dbHost := "<HOST>" // The endpoint of the PolarDB cluster. dbPort := "3306" // The default port 3306. dbUser := "<USER>" // The database account. dbPass := "<PASSWORD>" // The password of the database account. dbName := "<DATABASE>" // The name of the database to be connected. // Build DSN (Data Source Name) dsn := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s@tcp(%s:%s)/%s?charset=utf8mb4&parseTime=True&loc=Local", dbUser, dbPass, dbHost, dbPort, dbName) // Create a database connection. db, err := sql.Open("mysql", dsn) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to connect to database: %v", err) } defer db.Close() // Test the connection. err = db.Ping() if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to ping database: %v", err) } // Create a cursor. var result string err = db.QueryRow("SELECT VERSION()").Scan(&result) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to execute query: %v", err) } // Print the database version. fmt.Printf("Connected to database, version: %s\n", result) // Execute an SQL query. rows, err := db.Query("SELECT * FROM '<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>'") // The name of the data table that is queried. if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to execute query: %v", err) } defer rows.Close() // Process the query results. for rows.Next() { var id int var name string if err := rows.Scan(&id, &name); err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to scan row: %v", err) } fmt.Printf("ID: %d, Name: %s\n", id, name) } // Check for errors. if err := rows.Err(); err != nil { log.Fatalf("Error during iteration: %v", err) } }
Cluster management
Node management | Change of cluster specifications | High availability | Backup and restoration |
PolarProxy | Monitoring and optimization | Version management | Binary logging management |
FAQ
Why cannot I connect to a PolarDB cluster from an ECS instance?
Use the following steps to troubleshoot the issue:
Check whether the PolarDB cluster is in the Running state.
Check whether the database endpoint, port, account, and password are correct. For more information, see Obtain the database endpoint and port.
Check the network conditions. You can run
pingortelnetcommands in the ECS instance to test the network connectivity.If you are using a Private endpoint:
Check whether the ECS instance and the PolarDB cluster reside in the same VPC. If not, you cannot use the Private endpoint. You can use one of the following methods to place the ECS instance and PolarDB clusters in the same VPC:
Switch the VPC in which the ECS instance resides.
If the PolarDB cluster uses the default VPC, you can switch the VPC in which the PolarDB cluster resides. For more information, see Change the default VPC and default vSwitch.
Use Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN) to allow communication between VPCs. For more information, see Connect VPCs in the same region.
Check whether the private IP address, CIDR block, or security group of the ECS instance is added to the whitelist of the PolarDB cluster. For more information, see Configure a whitelist.
If you are using a Public endpoint, check whether the public IP address or security group of the ECS instance is added to the whitelist of the PolarDB cluster. For more information, see Configure a whitelist.
Virtual hosts and lightweight servers cannot be used to connect to a PolarDB cluster by using a Private endpoint.
Why cannot I connect to a PolarDB cluster from my on-premises network environment?
Use the following steps to troubleshoot the issue:
Check whether the PolarDB cluster is in the Running state.
Check whether the database endpoint, port, account, and password are correct. For more information, see Obtain the database endpoint and port.
NoteA Public endpoint must be used. If you are using an ECS instance that resides in the same VPC as the PolarDB cluster, a Private endpoint can be used.
Check the network conditions. You can run
pingortelnetcommands in your local environment to test the network connectivity.Check whether the public IP address or CIDR block of your local environment is added to the whitelist of the PolarDB cluster. For more information, see Configure a whitelist.
Use the following methods to obtain the public IP address of your local environment:
Linux: Open the CLI, enter the
curl ifconfig.mecommand, and then press the Enter key.Windows: Open Command Prompt, enter the
curl ip.mecommand, and then press the Enter key.macOS: Start Terminal, enter the
curl ifconfig.mecommand, and then press the Enter key.
If a proxy is used for your local network environment, the IP address obtained by the preceding method may not be your actual public IP address. You can add the
0.0.0.0/0CIDR block to the whitelist of the PolarDB cluster. After you connect to the cluster, run theSHOW PROCESSLIST;command to obtain the public IP address and add it to the whitelist of the cluster. Then, delete the0.0.0.0/0CIDR block from the whitelist.
I cannot connect to the PolarDB cluster. The following error is returned: Access denied for user 'xxx'@'xxx' (using password: YES)
The database account or password is incorrect. Make sure you enter the correct account and password. You can log on to the PolarDB console and choose Settings and Management > Accounts to manage the database account and password.
I cannot connect to the PolarDB cluster. The following error is returned: Unknown MySQL server host 'xxx'
The database endpoint is incorrect. Make sure you enter the correct endpoint. The endpoint format is pc-xxxxxx.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com. You can log on to the PolarDB console and choose Basic Information > Database Connections to manage the endpoints of your database.
I cannot connect to the PolarDB cluster. The following error is returned: Can't connect to MySQL server on 'xxx'or Connection timed out
It is possible that the public IP address or CIDR block of the current environment is not added to the whitelist of the PolarDB cluster, or the public IP address or CIDR block added to the whitelist is incorrect.
Use the following methods to obtain the public IP address of your local environment:
Linux: Open the CLI, enter the
curl ifconfig.mecommand, and then press the Enter key.Windows: Open Command Prompt, enter the
curl ip.mecommand, and then press the Enter key.macOS: Start Terminal, enter the
curl ifconfig.mecommand, and then press the Enter key.
If a proxy is used for your local network environment, the IP address obtained by the preceding method may not be your actual public IP address. You can add the 0.0.0.0/0 CIDR block to the whitelist of the PolarDB cluster. After you connect to the cluster, run the SHOW PROCESSLIST; command to obtain the public IP address and add it to the whitelist of the cluster. Then, delete the 0.0.0.0/0 CIDR block from the whitelist.
