The database and table restoration feature restores only specified databases or tables to the original cluster. For example, in a gaming business, you might need to restore data for only one or a few players. In this case, you can use the database and table restoration feature. You can restore from a backup set or to a point in time. This topic describes how to restore specified databases or tables to a point in time.
Introduction
PolarDB provides a database and table restoration feature that creates new databases and tables in the original cluster. This feature does not overwrite, delete, or write data to existing databases and tables. During the restoration process, you can specify new names for the databases or tables. For example, you can restore backup data from db1 to a new database named db2.
The restoration process does not affect normal access to the original cluster. However, it may consume computing resources and increase the CPU utilization and input/output operations per second (IOPS) of the cluster.
Scenarios
Cluster editions
The database and table restoration feature supports PolarDB Enterprise Edition and Standard Edition, but requires specific cluster revision versions. The following table lists the minimum revision versions required for different scenarios.
Basic Features: The minimum revision version required to support database and table restoration.
GDN primary cluster/New restoration process: The minimum revision version required to use the feature on a global database network (GDN) primary cluster or to benefit from the speed optimization of the new restoration process.
NoteThe new restoration flow for the database and table restoration feature is an enhancement that optimizes the speed of restoring data to the original cluster. For more information about the mechanism and speed, see Overall Flow and Estimated Time.
Edition Series | MySQL Version | Architecture | Basic Features (Minimum Revision Version) | GDN Primary Cluster/New Restoration Process (Minimum Revision Version) |
Enterprise Edition (Cluster Edition) | 5.6 | X86 |
|
|
5.7 | X86 |
|
| |
8.0.1 | X86 |
|
| |
8.0.2 | X86 |
|
| |
Standard Edition | 5.6 | X86 |
|
|
5.7 | X86 |
|
| |
8.0.1 | X86 |
|
| |
Yitian (ARM) |
|
| ||
8.0.2 | X86 |
|
|
You can view the kernel version of your cluster in the Configuration Information section on the Basic Information page of your PolarDB for MySQL cluster.
Other limitations
The database and table restoration feature has the following limitations:
Clusters:
The feature is not supported for Multi-master Cluster (Limitless) Edition clusters or secondary clusters in a global database network (GDN).
Database and table restoration is not supported for clusters with more than 50,000 tables in either of the following cases:
The storage type is enterprise SSD (ESSD).
The cluster has no read-only (RO) nodes.
Table schemas and indexes:
Tables that contain a global secondary index (GSI) are not supported.
Restoring a columnstore index (IMCI) is not supported.
Storage engines: Only tables that use the InnoDB storage engine can be restored.
Data status: Tables that are archived as cold data cannot be restored.
If your current cluster does not support the database and table restoration feature, you can use full restoration to restore data to a new cluster, and then migrate the data to the source cluster.
Usage notes
Point-in-time recovery for databases and tables is supported only for level-1 backups. It is not supported for level-2 backups.
Only the tables that you specify are restored. Make sure that you select all tables that you want to restore.
NoteIf you cannot determine which tables to restore, we recommend that you perform a full restoration of your cluster to a new cluster. You can then migrate the required data back to the original cluster. For more information, see Method 1 for full restoration: Restore data from a backup set and Method 2 for full restoration: Restore data to an earlier point in time.
The database and table restoration task fails in the following scenarios:
A database or table with the specified name already exists in the original cluster.
Between the time the backup set was created and the specified point in time for restoration, the table to be restored was deleted, or a database or table with the same name as the destination already exists in the cluster.
If you choose to restore specific tables from a database, you can restore up to 100 tables at a time. If you choose to restore an entire database, all tables in that database are restored.
NoteRestoring many tables at once can take a long time. We recommend that you do not restore too many tables in a single operation.
To restore many tables, we recommend that you perform a full restoration to a new cluster. For more information, see Method 1 for full restoration: Restore data from a backup set and Method 2 for full restoration: Restore data to an earlier point in time.
You can use the database and table restoration feature even if a cluster contains more than 50,000 tables, including system tables.
NoteThis feature is currently in canary release. To use this feature, you can contact us to be added to the whitelist.
To query the number of tables, including system tables, in a cluster, execute the following SQL statement:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM information_schema.tables;To query the number of system tables in a cluster, execute the following SQL statement:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema IN ('sys', 'performance_schema', 'mysql', 'information_schema', '__recycle_bin__');
The database and table restoration feature does not restore triggers. If an original table has a trigger, the trigger is not restored.
The database and table restoration feature does not restore foreign keys. If an original table has a foreign key, the foreign key is not restored.
Procedure
Log on to the PolarDB console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters. Select the region where the cluster is located, and then click the cluster ID to go to the cluster details page.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Click Restore Databases/Tables.
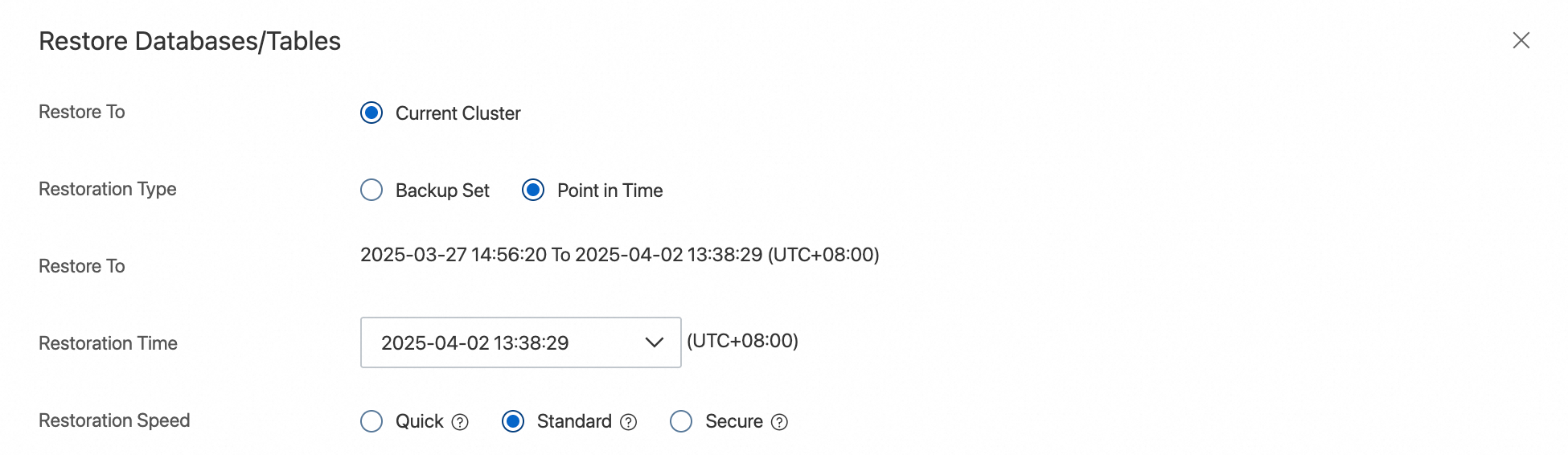
In the dialog box that appears, set Restoration Type to Point in Time and select a point in time for Restoration Time.
 Note
NoteThe point in time you select for Restoration Time must be within the Restore To. To use the Point in Time restoration feature, the full backup set closest to the specified point in time must contain the tables to be restored. The restorable time range depends on the Log Retention Period (Days) period, which is 7 days by default.
The database and table restoration feature provides three configurations based on IOPS consumption: Quick, Regular, and Secure. You can select a configuration based on your actual requirements. For the estimated restoration duration of each configuration, see Database and table restoration speed test data reference.
Quick: Consumes many IOPS (about 60%). Select this option during off-peak hours.
Regular (Recommended): Consumes a moderate number of IOPS (about 30%).
Secure: Consumes a small number of IOPS (about 15%). This may significantly slow down the restoration.
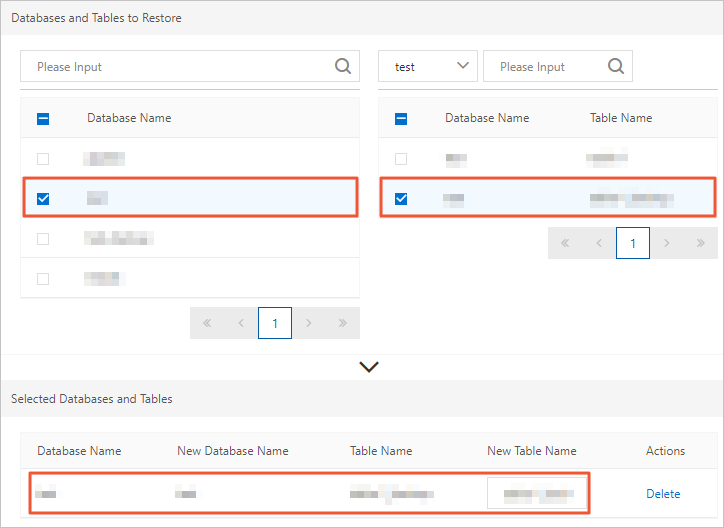
In the Databases and Tables to Restore section, select the source database on the left and the source tables on the right.
 Note
NoteIf you do not specify new names, the system automatically creates names by adding the
_backupsuffix to the original names. For example, if the original table is namedtest, the new table is namedtest_backup.If you select a database but do not select any tables, all tables in the database are restored by default.
After you confirm the selected databases and tables, click OK.
Related API operations
API operation | Description |
Queries the metadata of the database or table that you want to restore. | |
Restores the databases or tables of a PolarDB cluster. |