After you add a service to an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance, traffic that is destined for the service is redirected to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance to ensure the stability and reliability of the origin server. This prevents service unavailability when volumetric DDoS attacks occur. This topic describes the best practices for adding a service to an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance and configuring mitigation policies in various scenarios.
Scenarios
Scenario | Configuration process |
Configuration in normal scenarios | |
Configuration in emergency scenarios in which the service is under attack | Read Precautions in emergency scenarios and then add the service based on the configuration process for normal scenarios. |
Step 1: Analyze the service
Before you add a service to an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance, we recommend that you analyze the service status and data.
Item | Description | Suggestion |
Website and service information | ||
Daily peak traffic of the website or application, including the bandwidth in Mbit/s and queries per second (QPS) | Determine the point in time at which risks may occur. | This information is required to configure the clean bandwidth and QPS of the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance. |
Information about major user groups such as the geographical locations of users | Determine the source of attacks. | This information is required to configure the location blacklist. For more information, see Configure the location blacklist (domain names) feature. |
Whether your service is deployed in the C/S architecture | If the C/S architecture is used, determine whether app clients, Windows clients, Linux clients, clients used for callbacks, and clients of other environments are deployed. | None. |
Whether the origin server is deployed in a region outside the Chinese mainland | Determine whether the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance is suitable for your network architecture. | If the origin server is deployed outside the Chinese mainland, we recommend that you use Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland). For more information, see What is Anti-DDoS Proxy? |
Operating system of the origin server, such as Linux or Windows, and web service middleware, such as Apache, NGINX, or IIS | Determine whether access control policies are configured for the origin server. The policies may block traffic from the back-to-origin IP addresses of Anti-DDoS Proxy. | If access control policies are configured, you must allow the back-to-origin IP addresses to access the origin server. For more information, see Allow back-to-origin IP addresses to access the origin server. |
Whether the service needs to support IPv6 | None. | If the service needs to support IPv6, we recommend that you use Anti-DDoS Origin. For more information, see What is Anti-DDoS Origin? |
Protocol that is used by the service | None. | This information is required to select a protocol when you add a website to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance. |
Service ports | None. | Determine whether the service ports of the origin server are supported by Anti-DDoS Proxy. For more information, see Specify custom ports. |
Whether the HTTP request header contains custom fields and whether the origin server provides a verification mechanism | Determine whether Anti-DDoS Proxy affects custom fields and causes verification failures on the origin server. | None. |
Whether the origin server has a mechanism to obtain and verify the originating IP address of the client | After you add the service to Anti-DDoS Proxy, the originating source IP addresses of requests are changed. Determine whether to adjust the mechanism that is used by the origin server to obtain the originating IP address to prevent service interruptions. | For more information, see Obtain the originating IP addresses of requests. |
Whether the service uses TLS 1.0 or a weak cipher suite | Determine whether the cipher suite of your service is supported. | After the service is added, you must configure TLS policies. For more information, see Configure a custom TLS security policy. |
(HTTPS services) Whether the origin server uses mutual authentication | None. | Anti-DDoS Proxy does not support mutual authentication. You must change the authentication method. |
(HTTPS services) Whether the clients support SNI | None. | After you add a domain name of an HTTPS website to Anti-DDoS Proxy, both the clients and servers need to be configured to support SNI. |
(HTTPS services) Whether session persistence is enabled | The default connection timeout period for HTTP and HTTPS is 120 seconds. | If the service requires persistent sessions in scenarios such as file uploading and user logon, we recommend that you use cookies to implement session persistence at Layer 7. |
Whether the service requires transmission of empty data packets | For example, the server sends empty packets to prevent session interruption. After you add the service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance, the service may be affected. | None. |
Service interaction process | Determine the service interaction process and processing logic based on which mitigation policies are configured. | None. |
Number of active users | Determine the severity of emergent attack events and take low-risk countermeasures. | None. |
Service and attack information | ||
The type and characteristics of the service (for example, whether the service is a gaming, website, or app service) | Analyze attack characteristics. Then, take countermeasures. | None. |
The volume of inbound service traffic | Determine whether malicious traffic exists. For example, the average volume of daily access traffic is 100 Mbit/s. If the traffic volume exceeds 100 Mbit/s, an attack may have occurred. | None. |
The volume of outbound service traffic | Determine whether attacks occur and whether to increase the clean bandwidth. | None. |
The volume and connections of inbound traffic by user or by IP address | Determine whether rate limiting policies can be configured for individual IP addresses. | For more information, see Configure frequency control. |
Users | For example, users may access your service from household LANs, Internet cafes, and proxy servers. | This information is required to determine whether concurrent requests are sent from a single egress IP address and prevent Anti-DDoS Proxy from blocking service traffic. |
Whether your service suffered volumetric attacks and the types of the attacks | Configure DDoS mitigation policies based on the types of historical attacks. | None. |
Peak volume of attacks that the service experienced | Select the specifications of the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance based on the peak attack traffic. | For more information, see Purchase an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance. |
Whether the service suffered HTTP flood attacks | Analyze the characteristics of historical attacks and configure preventive policies. | None. |
Peak QPS of HTTP flood attacks that the service experienced | Analyze the characteristics of historical attacks and configure preventive policies. | None. |
Whether the service supports API operations | None. | If API operations are supported, we recommend that you do not use the frequency control feature of Anti-DDoS Proxy. You can analyze the characteristics of API access and configure HTTP flood mitigation policies based on the characteristics. This prevents normal API requests from being blocked. |
Whether a stress test is performed on the service | Evaluate the request processing performance of the origin server and determine whether service exceptions are caused by attacks. | None. |
Step 2: Make preparations
We recommend that you add a service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance in a test environment. After you verify that the service runs as expected, add the service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance in the production environment.
Before you add a service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance, make the preparations that are described in the following table.
Service type | Preparation |
Website service |
|
Non-website service |
|
Step 3: Add the service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance and configure mitigation policies
Add the service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance.
NoteIf the service is under attack before you add it to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance, we recommend that you change the IP address of the origin server. Before you change the IP address, check whether the code of the client or app contains the IP address. If the code of the client or app contains the IP address, update the code before you change the IP address to avoid negative impacts on normal service access. For more information, see Change the public IP address of an ECS origin server.
Add the service based on the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance and your service scenario:
Configure protection for the origin server.
To prevent attackers from bypassing Anti-DDoS Proxy to attack the origin server, configure protection for the origin server. For more information, see Configure protection for an origin server.
Configure mitigation policies.
Website service provided by using domain names
HTTP flood protection
The service runs as expected: Two or three days after you add the service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance, analyze service application logs, including information about URLs and the average QPS of individual source IP addresses. Then, configure frequency control rules based on the analysis to protect the service from attacks.
The service is under an HTTP flood attack: Go to the Security Overview page in the Anti-DDoS Proxy console to obtain information about your domain name, such as the most requested URLs and IP addresses, source IP addresses, and user agents. Then, configure frequency control rules based on the obtained information and observe the protection effect. For more information, see Security Overview and Create a custom frequency control rule.
ImportantThe Emergency mode of Frequency Control may block traffic of specific service types. We recommend that you do not specify Emergency as the mode of Frequency Control. If your service is an app or web API service, do not use the Emergency mode.
If you use the Normal mode of Frequency Control but service traffic is still blocked, add the service IP addresses to a whitelist.
Intelligent protection for a website service
The Strict mode of intelligent protection may block service traffic. After you add the domain name of your website to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance, your service is protected against Layer 4 DDoS attacks. We recommend that you use the Normal mode instead of the Strict mode. For more information, see Use the intelligent protection feature.
Log analysis
We recommend that you enable the log analysis feature. For more information, see Use the log analysis feature. If the service encounters Layer 7 DDoS attacks, you can use the log analysis feature to analyze attack characteristics and configure mitigation policies.
NoteIf you enable the log analysis feature, you are charged additional fees.
Non-website service provided by using ports
In most cases, you can add a non-website service to an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance and use the default protection settings. After the service runs for two or three days, you can adjust the mode of Layer 4 intelligent protection based on the service characteristics to optimize protection against Layer 4 HTTP flood attacks. For more information, see Configure the intelligent protection feature for Layer-4 services.
NoteIf the service provides frequently called APIs or is visited from a single IP address, such as an egress IP address of an enterprise network or a server IP address, do not use the Strict level for Intelligent Protection. If you want to use the Strict level, contact Alibaba Cloud technical support to analyze the service before you select this level to avoid service interruptions.
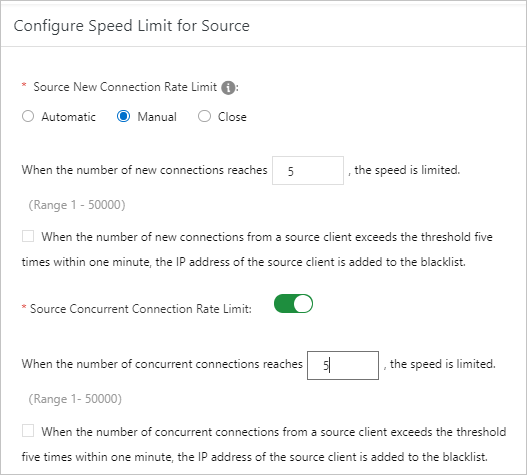
If attack traffic is transparently transmitted to the origin server, you can enable Speed Limit for Source and Speed Limit for Destination. For more information, see Create an anti-DDoS protection policy. We recommend that you initially set Source New Connection Rate Limit and Source Concurrent Connection Rate Limit to 5. If service traffic is blocked, you can increase the limit values.
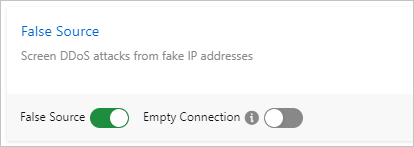
If the origin server of your service sends empty data packets, you must disable Empty Connection to avoid negative impacts on the service. For more information, see Create an anti-DDoS protection policy.
Test the service.
After you complete the configuration, test the accuracy of the configurations.
NoteYou can modify the hosts file on an on-premises computer to perform the test.
Table 1. Check items of configurations No.
Check item
Website service provided by using a domain name (required)
1
Check whether the added domain name is correct.
2
Check whether ICP filing is complete for the domain name.
3
Check whether the configured protocol is correct.
4
Check whether the configured port is correct.
5
Check whether the IP address of the origin server is correct. Make sure that you do not enter the IP address of the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance or another service.
6
Check whether the uploaded certificate is correct.
7
Check whether the certificate is valid. For example, the encryption algorithm may be invalid or you uploaded the certificate of another domain name.
8
Check whether the certificate chain is complete.
9
Make sure that you know the billing method of burstable protection in Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland).
10
Check whether WebSocket and WebSockets are enabled.
11
Check whether the Emergency or Strict mode of Frequency Control is enabled.
Non-website service provided by using a port (required)
1
Check whether the service port can be accessed.
2
Check whether the UDP or TCP protocol is correctly configured.
3
Check whether the IP address of the origin server is correct. Make sure that you do not enter the IP address of the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance or another service.
4
Make sure that you know the billing method of burstable protection in Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland).
5
Check whether the Strict level of intelligent protection is selected.
Table 2. Check items of service availability No.
Check item
1 (required)
Test whether the service can be accessed as expected.
2 (required)
Test whether the session persistence feature for user logons works as expected.
3 (required)
(For website services that are provided by using domain names) Check the number of 4XX and 5XX status codes in the returned responses and make sure that the back-to-origin IP addresses are not blocked.
4 (required)
(For website services that are provided by using domain names) If your service is an app service, test whether HTTPS links are normal. Check whether SNI is configured as expected.
5 (recommended)
Check whether the origin server is configured to obtain the originating source IP addresses of requests.
6 (recommended)
(For website services that are provided by using domain names) Check whether mitigation policies are configured for the origin server. This prevents attackers from bypassing Anti-DDoS Proxy to attack the origin server.
7 (required)
Test whether the TCP service port is accessible.
Switch service traffic to Anti-DDoS Proxy.
After you verify all check items, we recommend that you separately change the DNS records to gradually switch service traffic to Anti-DDoS Proxy. This prevents potential service exceptions. If an exception occurs after the service traffic is redirected to Anti-DDoS Proxy, you must restore the DNS records.
NoteChanges to DNS records take effect in approximately 10 minutes.
After you switch service traffic, verify the check items of service availability again to make sure that the service runs as expected.
Configure monitoring and alerts.
Use CloudMonitor to monitor availability and returned HTTP status codes (5XX and 4XX) for the domain names, forwarding ports, and origin server ports that are protected by Anti-DDoS Proxy. This way, you can identify service exceptions at the earliest opportunity. For more information, see Configure an alert rule for Anti-DDoS Proxy.
Perform routine O&M.
Use burstable protection of Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland) and advanced mitigation sessions of Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) of the Insurance mitigation plan.
The first time you purchase an Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland) instance, you can obtain three Anti-DDoS plans free of charge. Each Anti-DDoS plan provides one mitigation session and can be used to offset the fee that is charged for up to 300 Gbit/s of protection bandwidth. For more information, see Anti-DDoS plans. We recommend that you bind the plans to the Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland) instance and set the burstable protection bandwidth to 300 Gbit/s. If DDoS attacks whose traffic volume does not exceed 300 Gbit/s occur within a calendar day, a plan can be used to offset burstable protection fees for the day.
NoteIf you do not want to use burstable protection after the mitigation sessions of the plans are exhausted or the plans expire, change the burstable protection bandwidth to the basic protection bandwidth.
If you want to enable burstable protection of Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland), we recommend that you view the billing methods to determine the costs. For more information, see Billing of Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland).
If you purchase an Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) instance of the Insurance mitigation plan, you can obtain two advanced mitigation sessions each month free of charge. Select an edition and mitigation plan based on your business requirements.
Determine attack types.
If HTTP flood attacks and DDoS attacks occur, you can view attack information on the Security Overview page in the Anti-DDoS Proxy console to determine the types of specific attacks. For more information, see Security Overview.
DDoS attack: On the Instances tab, the protection reports show attack traffic fluctuations, and traffic scrubbing is triggered. However, the protection reports on the Domain Names tab do not show fluctuations
HTTP flood attack: On the Instances tab, the protection reports show attack traffic fluctuations, and traffic scrubbing is triggered. On the Domain Names tab, the protection reports also show fluctuations.
For more information, see How do I identify the types of attacks against an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance?
Handle service access latency and packet loss.
If the origin server is deployed outside the Chinese mainland and the users of your service are from the Chinese mainland, the users may experience high latency and packet loss due to unstable links of cross-carrier network access. In this case, we recommend that you purchase an Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) instance of the Chinese Mainland Acceleration (CMA) mitigation plan.
Delete a domain name or a port forwarding rule.
If you want to delete a domain name or a port forwarding rule, check whether your service traffic is switched to Anti-DDoS Proxy.
If your service traffic is not switched, delete the domain name or port forwarding rule in the Anti-DDoS Proxy console.
If your service traffic is switched, go to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console to modify the DNS records to switch the traffic back to the origin server. Then, delete the domain name or port forwarding rule.
NoteBefore you delete the domain name or port forwarding rule, make sure that the DNS records or service traffic of the domain name is switched back to the origin server.
After you delete the domain name or port forwarding rule, Anti-DDoS Proxy no longer protects your service.
Precautions in emergency scenarios
If a service is under attack, add the service to your Anti-DDoS Proxy instance based on the following scenarios:
The service is under a DDoS attack.
In most cases, you can add the service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance and use the default protection settings.
If traffic of a Layer 4 HTTP flood attack is transparently transmitted to the origin server, you can enable Speed Limit for Source and Speed Limit for Destination. For more information, see Create an anti-DDoS protection policy.
Blackhole filtering is triggered for the IP address of the origin server.
You can use an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) or Server Load Balancer (SLB) instance as the origin server. If you have not added the attacked service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance but blackhole filtering is triggered, you must change the public IP address of the origin server. For more information, see Change the public IP address of an ECS origin server. After you change the IP address, add the service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance at the earliest opportunity to prevent the new IP address from being exposed.
If you do not want to change the IP address of the origin server or the new IP address is already exposed, we recommend that you deploy an SLB instance as the origin server to connect the ECS instance and add the public IP address of the SLB instance to Anti-DDoS Proxy.
NoteIf the service is under attack but the origin server is not deployed on Alibaba Cloud, you can add the service to Anti-DDoS Proxy for emergency response. In this case, make sure that the domain name of the service has ICP filing completed and contact Alibaba Cloud technical support to provide the required assistance. Then, add the service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance.
The service is under HTTP flood attacks or crawler attacks.
If the service is under an HTTP flood or crawler attack, add the service to the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance. Then, analyze HTTP access logs to identify attack characteristics and configure mitigation policies. For example, you can check whether request fields, such as the source IP address, URL, Referer, User-Agent, Params, and Header, are correct.