Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) is a high-performance database service. This topic describes the development and O&M standards for Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) that you can follow to design a more efficient business system and make better use of Tair. The standards are developed by Alibaba Cloud based on years of O&M experience and apply to the following scenarios: business deployment, key design, SDK usage, command usage, and O&M management.
Performance boundaries of Tair
Figure 1. Performance boundaries of Tair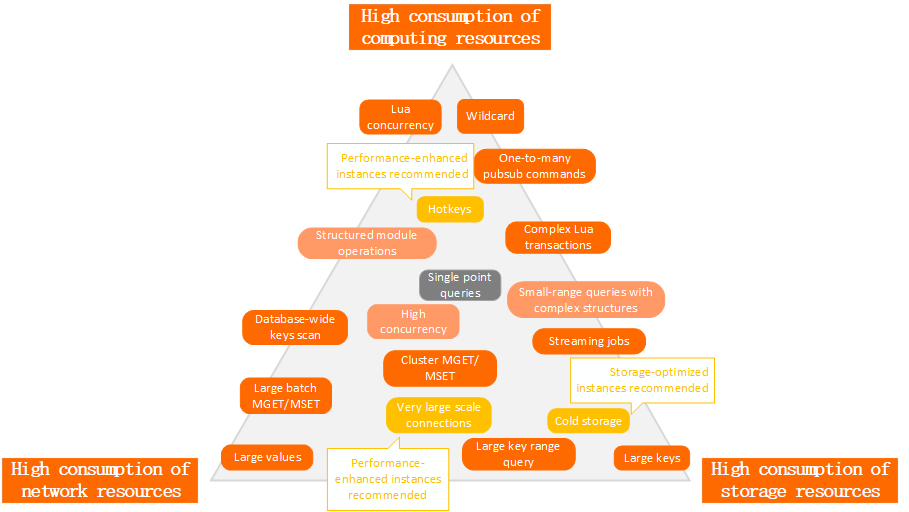
Resource type | Description |
Computing resources | Wildcard characters, concurrent Lua scripts, one-to-many PUBSUB, and hotkeys consume a large amount of computing resources. For cluster instances, these items can also cause skewed requests and underutilization of data shards. |
Storage resources | Streaming jobs and large keys consume a large amount of storage resources. For cluster instances, these items can also cause data skew and underutilization of data shards. |
Network resources | Database-wide scans (by running the KEYS command) and range queries of large keys and values (by running the HGETALL command) consume a large amount of network resources and often cause thread congestion. Important The high-concurrency capability of Tair does not significantly improve access performance as expected but does affect the overall performance of Tair. For example, the storage of large values in Tair does not improve access performance to a large degree. |
For cluster instances, hotkeys, large keys, or large values can also cause skewed storage or skewed requests . In a production environment, it is important to avoid reaching the performance boundaries of Tair.
Business deployment standards
Importance | Standard | Description |
★★★★★ | Determine whether the scenario is high-speed cache or in-memory databases . |
|
★★★★★ | Deploy your business close to Tair instances. For example, you can deploy your business in an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance that resides in the same virtual private cloud (VPC) as your Tair instances. | Tair is a high-performance database service. However, if you deploy your business server far from Tair instances and the business server is connected to the instances over the Internet, the performance of Tair is greatly compromised due to network latency. Note For cross-region deployment, you can use the geo-replication capability of Global Distributed Cache to implement geo-disaster recovery or active geo-redundancy, reduce network latency, and simplify business design. For more information, see Global Distributed Cache. |
★★★★☆ | Create a Tair instance for each service. | Do not use a Tair instance for different services. For example, do not use a Tair instance for both high-speed caching and in-memory database services. Otherwise, the eviction policies, slow queries, and FLUSHDB command execution of one service affect other services. |
★★★★☆ | Configure appropriate eviction policies to evict expired keys. | The default eviction policy for expired keys in Tair is volatile-lru . For more information about eviction policies, see Parameters that can be configured for Redis Open-Source Edition instances. |
★★★☆☆ | Manage stress testing data and duration. | Tair does not delete stress testing data. To prevent impacts on your business, you must manage stress testing data and duration yourself. |
Key design standards
Importance | Standard | Description |
★★★★★ | Configure key values to an appropriate size. We recommend that you keep the size of values stored in keys below 10 KB. | Excessively large values can cause data skew, hotkeys, high bandwidth, or high CPU utilization. You can prevent these issues from the beginning by making sure that key values are of proper size. |
★★★★★ | Configure proper key names that have proper length. |
|
★★★★★ | For complex data structures that support sub-keys, you must avoid including excessive sub-keys in one key. We recommend that you include less than 1,000 sub-keys in a key. Note Common complex data structures include Hash, Set, Zset, Geo, and Stream, and structures specific to Tair (Enterprise Edition), such as exHash, Bloom, and TairGIS. | The time complexity of specific commands such as HGETALL is directly related to the number of sub-keys. If you frequently run commands whose time complexity is O(N) or higher, and the key contains too many sub-keys, issues such as slow queries, data skew, and hotkeys occur. |
★★★★☆ | Use the serialization method to convert values into readable structures. | The bytecode of a programming language may change when the version of the language changes. If you store naked objects (such as Java objects and C# objects) in Tair instances, the software stack may be difficult to upgrade. We recommend that you use the serialization method to convert values into readable structures. |
SDK usage standards
Importance | Standard | Description |
★★★★★ | Use JedisPool or JedisCluster to connect to Tair instances. Note We recommend that you use the TairJedis client to connect to Tair (Enterprise Edition) DRAM-based instances, because the TairJedis client provides encapsulation classes for new data structures. For more information, see Use a client to connect to an instance. | If you use a single connection, the client cannot automatically reconnect to Tair instances after the connection times out. For more information about how to use JedisPool to connect to Tair instances, see Use a client to connect to an instance, JedisPool optimization, and JedisCluster. |
★★★★☆ | Design proper fault tolerance mechanisms for your clients. | Network fluctuations and high usage of resources may cause connection timeouts or slow queries in Tair. To prevent these risks, you must design proper fault tolerance mechanisms for your clients. |
★★★★☆ | Set longer retry intervals for your clients. | If retry intervals are shorter than required (such as shorter than 200 milliseconds), many retries may occur in a short period of time. This can result in a service avalanche. For more information, see Retry mechanisms for Redis clients. |
Command usage standards
Importance | Standard | Description |
★★★★★ | Avoid range queries, such as those executed by running the KEYS * command. Instead, use multiple point queries or run the SCAN command to reduce latency. | Range queries may cause service interruptions, slow queries, or congestion. |
★★★★★ | Use extended data structures to perform complex operations. For more information, see Integration of multiple data modules. Do not use Lua scripts. | Lua scripts consume a large amount of computing and memory resources and do not support multi-threading acceleration. Overly complex or improper Lua scripts may result in the exhaustion of resources. |
★★★★☆ | Use pipelines to reduce the round-trip time (RTT) of data. | If you want to send multiple commands to a server and your client does not depend on each response from the server, you can use a pipeline to send the commands at a time. Take note of the following items when you use pipelines:
|
★★★★☆ | Use Redis commands correctly. | When you use transaction commands, take note of the following limits:
|
★★★★☆ | Do not use Redis commands to perform many message distribution tasks. | The Pub and Sub command group does not support data persistence or acknowledge mechanisms that ensure data reliability. We recommend that you do not use Pub or Sub commands to perform many message distribution tasks. For example, if you use these commands to distribute a message whose size is greater than 1 KB to more than 100 subscriber clients, server resources may be exhausted and subscriber clients may not receive the message. Note To improve performance and balance, Tair is optimized for Pub and Sub commands. In cluster instances, proxy nodes calculate the hash values of commands based on channel names and allocate commands to corresponding data nodes. |
O&M management standards
Importance | Standard | Description |
★★★★★ | Understand the impacts of different instance management operations. | Configuration changes or restarts affect the status of a Tair instance. For example, transient connections may occur on the instance. Before you perform the preceding operations, make sure that you understand the impacts. For more information, see Instance states and impacts. |
★★★★★ | Verify the error handling capabilities or disaster recovery logic of a client. | Tair can monitor the health status of nodes. If the master node in an instance becomes unavailable, Tair automatically triggers a master-replica switchover. The roles of master and replica nodes are switched over to ensure the high availability of the instance. Before a client is generally available, we recommend that you manually trigger a master-replica switchover. This can help you verify the error handling capabilities or disaster recovery logic of the client. For more information, see Manually switch workloads from a master node to a replica node. |
★★★★★ | Disable time-consuming or high-risk commands. | In a production environment, abuse of commands may cause problems. For example, the FLUSHALL command can delete all data. The KEYS command may cause network congestion. To improve the stability and efficiency of services, you can disable specific commands to minimize risks. For more information, see Disable high-risk commands. |
★★★★☆ | Handle pending events at the earliest opportunity. | To enhance user experience and provide improved service performance and stability, Alibaba Cloud occasionally generates pending events to upgrade the hardware and software of specific servers or replace network facilities. For example, a pending event is generated when the minor version of databases needs to be updated. After you receive an event notification from Alibaba Cloud, you can check the impacts of the event and change the scheduled time of the event to meet your business requirements. For more information, see View and manage scheduled events. |
★★★★☆ | Configure alerts for core metrics to better monitor the status of your instances. | Configure alerts for core metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and bandwidth usage to monitor the status of your instances in real time. For more information, see Alert settings. |
★★★★☆ | Use the O&M features provided by Tair to check the status of instances or troubleshoot resource usage exceptions on a regular basis. |
|
★★★☆☆ | Enable the audit log feature and evaluate audit logs. | After you enable the audit log feature, the audit statistics about write operations are recorded. Tair also allows you to query, analyze online, and export audit logs. These features help you monitor the security and performance of your Tair instances. For more information, see Audit Log. Important After you enable the audit log feature, the performance of Tair instances may degrade by 5% to 15%. The actual performance degradation varies based on the number of write operations or audit operations. If your business expects many write operations on Tair instances, we recommend that you enable the audit log feature only when you perform O&M operations, such as troubleshooting. This helps you prevent performance degradation. |