A common issue that affects the service performance of Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) is connection timeouts caused by slow requests. The slow query log feature of Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) allows you to find the IP addresses of the clients that send these requests and troubleshoot issues based on the details of slow query logs.
Overview
Slow query logs record requests that take longer than a specified threshold to execute. Slow query logs can be generated for both data nodes and proxy nodes.
The methods provided in this topic to query slow query logs are not supported for Redis Open-Source Edition 2.8 instances. You can choose in the console to view slow query logs of such instances. Slow query logs of Redis Open-Source Edition 2.8 instances do not include information such as client IP addresses.
Slow query logs of data nodes
The command execution duration collected in slow query logs that are generated on a data node includes only the amount of time required to actually run a command on the data node. The amount of time required for the data node to communicate with a proxy node or client and the execution latency of the command in the single-threaded queue are not included.
Slow query logs of data nodes are retained for 72 hours. The number of slow query logs that can be stored is unlimited.
In most cases, few slow query logs are generated on data nodes due to high instance performance.
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
slowlog-log-slower-than | The threshold of the command execution duration for slow query logs of data nodes. If a command runs for a period of time that exceeds this threshold, the command is recorded in a slow query log. Default value: 20000. Unit: microseconds. 20000 microseconds is equal to 20 milliseconds. Note In most cases, the actual latency is higher than the specified value of this parameter because this value does not include the amount of time required to transmit and process data among clients, proxy nodes, and data nodes. |
slowlog-max-len | The maximum number of slow query log entries that can be stored. Default value: 1024. |
For more information, see Configure instance parameters.
Slow query logs of proxy nodes
The command execution duration collected in slow query logs of proxy nodes starts from the time when a proxy node sends a request to a data node and ends at the time when the proxy node receives the response from the data node. This includes the command execution duration on the data node, the duration of data transmission over the network, and the queuing latency of the command.
Slow query logs of proxy nodes are retained for 72 hours. The number of slow query logs that can be stored is unlimited.
In most cases, the latency value recorded in a slow query log of proxy nodes is closer to the actual latency of the application. Therefore, we recommend that you check this type of slow query log when you troubleshoot timeout issues.
Standard instances do not involve slow query logs of proxy nodes.
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
rt_threshold_ms | The threshold of the command execution duration for slow query logs of proxy nodes. Default value: 500. Unit: milliseconds. We recommend that you set the threshold to a value close to the client timeout period, which is anywhere from 200 milliseconds to 500 milliseconds. |
For more information, see Configure instance parameters.
Methods used to query slow query logs
Slow query log type | Method |
Slow query logs of data nodes |
|
Slow query logs of proxy nodes | Log on to the console or call an API operation: |
Procedure
In most cases, service timeouts are caused by slow requests. We recommend that you perform the following steps to troubleshoot timeout issues:
If a service timeout issue occurs, first check the slow query logs generated on proxy nodes. For more information, see Query slow query logs.
NoteFor standard instances, go to Step 3 and analyze slow query logs from data nodes.
If no slow query logs exist on proxy nodes, you can check the network between the client and the instance.
Find the command recorded by the earliest slow query log of proxy nodes.
NoteIf slow requests accumulate on data nodes, these requests are recorded in slow query logs of proxy nodes.
In this example, the earliest recorded slow query log is generated by the KEYS command. The IP address on the right of the log entry is the IP address of the client that sends the command.
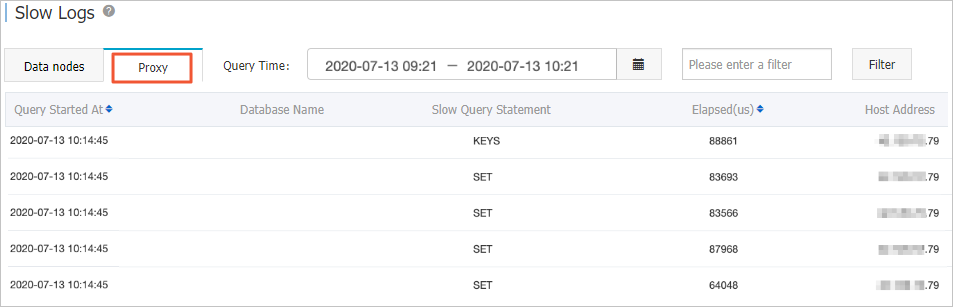
Check the slow query logs of data nodes to identify the slow query logs of proxy nodes that cause the timeout issue.
NoteTypically, the commands that generate slow query logs first on proxy nodes will also generate slow query logs on data nodes. The slow query logs of data nodes are generally fewer than those of proxy nodes due to differences in how execution time is defined and the threshold for what is considered a slow query log on the two types of nodes.
In this example, after you view slow query logs of proxy nodes, you can find that the slow query log generated by the KEYS command also exists on data nodes. No other slow query logs that are displayed on the Proxy tab exist on the Data nodes tab. This shows that the KEYS command causes the timeout issue.
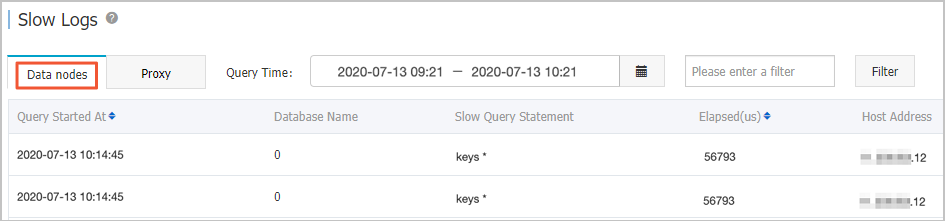
In slow query logs of proxy nodes, you can search for the client IP address for optimization based on the command found in Step 2.