This topic answers frequently asked questions (FAQs) and provides solutions for common issues you might encounter when using the Terway or Flannel network plugins. The questions cover topics such as how to select a network plugin, whether third-party network plugins are supported, and how to plan your cluster network.
Index
Terway
What's the difference between Terway's Shared ENI and Exclusive ENI network modes?
How can I tell if my ACK cluster is using Terway in Shared ENI or Exclusive ENI mode?
Does traffic bypass IPVS when using Terway's network acceleration modes (DataPathv2 or IPvlan+eBPF)?
Is it possible to switch the CNI network plugin on an existing ACK cluster?
Why can't my Pods access the Internet after adding a new vSwitch for Terway in my ACK cluster?
What's the difference between the Terway and Flannel network plugins for an ACK Kubernetes cluster?
What determines the maximum number of Pods per node in a Terway cluster?
What is Terway's DataPath V2 mode, and how is it different from the original IPvlan mode?
Why did my Terway component upgrade fail with the error
eip pool is not supported?Why do my Pods sometimes fail to create in a Terway cluster with the error
can't found dev by mac?
Flannel
What's the difference between the Terway and Flannel network plugins for an ACK Kubernetes cluster?
In a Flannel cluster, why can my Pods ping some ECS instances but not others?
Why are newly added nodes in my Flannel cluster getting a NodeNetworkUnavailable taint?
How can I change the Pod CIDR, Service CIDR, or IPs per node for an existing ACK cluster?
kube-proxy
IPv6
How do I troubleshoot common issues in an IPv6 dual-stack cluster?
Other
How do I fix network latency issues immediately after a Pod starts?
What is the correct way to plan the network for an ACK cluster?
How do I identify the network plugin and vSwitches used by my cluster?
How can I increase the Linux connection tracking (conntrack) limit on my nodes?
Is it possible to install a third-party CNI network plugin on an ACK cluster?
Why do I get a no IP addresses available in range set error in my Flannel cluster?
What should I consider when configuring a custom Cluster Domain for my ACK cluster?
What's the difference between Terway's Shared ENI and Exclusive ENI network modes?
Terway offers two primary network modes that determine how Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs) are allocated to Pods.
Shared ENI mode: Multiple Pods on a single node share a set of ENIs. This is the default and most resource-efficient mode. This mode is required for Terway's network acceleration features (DataPathv2 or IPvlan+eBPF).
Exclusive ENI mode: Each Pod is assigned its own dedicated ENI. This provides the best network performance and isolation but consumes a significantly higher number of ENI resources.
In Terway v1.8.0 and later, network acceleration is only available in Shared ENI mode and uses the DataPathv2 implementation, which is an upgrade to the older IPvlan+eBPF mode.
For more information about each mode, see Shared ENI mode and exclusive ENI mode.
How can I tell if my ACK cluster is using Terway in Shared ENI or Exclusive ENI mode?
You can identify the mode by checking the name of the Terway DaemonSet running in the kube-system namespace.
Run the following command to list the Terway DaemonSets:
Identify the mode based on the output:
If the DaemonSet is named
terway-eniip, you are using Shared ENI mode.If the DaemonSet is named
terway-eni, you are using Exclusive ENI mode.
For Terway v1.11.0 and later, Shared ENI mode is the default. You can enable the exclusive ENI mode by configuring the exclusive ENI network mode for a node pool. In earlier versions, the mode was selected at cluster creation.
How do I check if my Terway Shared ENI mode is using DataPathv2 or the legacy IPvlan+eBPF for network acceleration?
Only the shared ENI mode of Terway supports network acceleration (DataPathv2 or IPvlan+eBPF). DataPathv2 is an upgraded version of the IPvlan+eBPF acceleration mode. In Terway v1.8.0 and later, DataPathv2 is the only available acceleration option when you create a cluster and install the Terway plugin.
Check the eniip_virtual_type value in the eni-config ConfigMap in the kube-system namespace.
Retrieve the ConfigMap's data:
In the
datapathv2: Your cluster uses the current DataPathv2 acceleration.ipvlan: Your cluster uses the legacy IPvlan+eBPF acceleration.If the field is absent, network acceleration is disabled.
Network acceleration is only supported in Shared ENI mode. For clusters created with Terway v1.8.0 or later, only DataPathv2 is available as an acceleration option.
Does traffic bypass IPVS when using Terway's network acceleration modes (DataPathv2 or IPvlan+eBPF)?
Yes, for Pod-to-Service traffic within the cluster, Terway's acceleration modes bypass IPVS.
When acceleration (DataPathv2 or IPvlan+eBPF) is enabled, Terway uses eBPF to perform Service-to-backend-Pod address translation directly in the kernel. This avoids the standard kube-proxy IPVS rules and the node's network stack, resulting in lower latency and higher throughput for in-cluster service communication.
For more information about traffic flows, see Network acceleration.
Is it possible to switch the CNI network plugin on an existing ACK cluster?
No, you cannot change the CNI network plugin (e.g., from Flannel to Terway) on an existing ACK cluster.
The network plugin is a fundamental component selected during cluster creation. To switch plugins, you must create a new cluster with the desired CNI plugin and migrate your workloads.
For more information, see Create an ACK managed cluster.
Why can't my Pods access the Internet after adding a new vSwitch for Terway in my ACK cluster?
The new vSwitch likely does not have a route to the Internet. Pods that acquire IPs from this vSwitch will fail to establish outbound public connections.
Solution
Configure a Source NAT (SNAT) rule for the new vSwitch's CIDR block using a NAT Gateway. This allows traffic originating from Pods in that vSwitch to be translated to a public IP address, granting Internet access.
For more information, see Enable Internet access for a cluster.
My nodes are NotReady after upgrading my cluster to Kubernetes 1.16+. How do I fix a Flannel incompatibility?
This issue occurs because you manually updated the Flannel image without updating its CNI configuration to be compatible with newer Kubernetes versions.
Cause
Kubernetes 1.16 and later require the CNI configuration to explicitly specify a cniVersion. Older Flannel configurations lack this field, causing the Kubelet to fail network initialization and mark the node as NotReady.
Solution
Add the cniVersion field to the Flannel ConfigMap.
Steps
Edit the
kube-flannel-cfgConfigMap:kubectl edit cm kube-flannel-cfg -n kube-systemIn the
net-conf.jsondata, add"cniVersion": "0.3.1"to the configuration object."name": "cb0", "cniVersion":"0.3.1", "type": "flannel",Restart the Flannel pods to apply the new configuration:
kubectl delete pod -n kube-system -l app=flannelThe nodes should now correctly initialize their network and transition to the
Readystate.
How do I fix network latency issues immediately after a Pod starts?
Symptom
There is a noticeable delay (a few seconds) before a newly started Pod can communicate on the network.
Cause
This latency is often introduced by the NetworkPolicy enforcement engine in Terway. When a Pod starts, the policy agent needs time to compute and apply the necessary eBPF rules or iptables.
Solution
If you do not use Kubernetes Network Policies, you can disable the feature to eliminate this startup latency.
Edit the Terway
eni-configConfigMap:kubectl edit cm -n kube-system eni-configIn the
data.eni_confsection, add thedisable_network_policy: "true"flag.disable_network_policy: "true"Optional:If you are not using the latest version of Terway, upgrade it in the console.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left navigation pane, click Add-ons.
On the Add-ons page, click the Networking tab, and then click Upgrade for the Terway add-on.
In the dialog box that appears, follow the prompts to complete the configuration and click OK.
Restart the Terway pods to apply the change:
kubectl delete pod -n kube-system -l app=terway-eniip
Why do my Pods get connection errors when trying to access a Service they expose themselves (hairpinning)?
This problem, known as "hairpinning," occurs when a Pod tries to access a Service that routes traffic back to itself. The behavior depends on your network plugin.
Cause
In Flannel clusters, especially older versions, hairpin traffic is often disabled by default, causing connections to fail.
Recommended solution
Use a Headless Service: This is the cleanest and most reliable approach. A Headless Service does not have a
ClusterIPand does not involvekube-proxy. DNS resolves the service name directly to the Pod IPs, allowing the Pod to connect to itself via its own IP address without any network loops.For more information, see Headless Services.
Recreate the cluster and use the Terway network plugin. For more information, see Use the Terway network plugin.
Modify the Flannel configuration, and then recreate the Flannel plugin and the pod.
Alternative solutions
Enable Hairpin Mode in Flannel (Not Recommended): You can manually enable hairpinning, but this configuration might be overwritten by future component upgrades.
Edit the
kube-flannel-cfgConfigMap in thekube-systemnamespace.Add
hairpinMode: trueto thedelegatesection of the CNI configuration.Restart all Flannel pods and then recreate your application pods.
kubectl edit cm kube-flannel-cfg -n kube-systemExample:
cni-conf.json: |
{
"name": "cb0",
"cniVersion":"0.3.1",
"type": "flannel",
"delegate": {
"isDefaultGateway": true,
"hairpinMode": true
}
}kubectl delete pod -n kube-system -l app=flannel Use Terway Plugin: The Terway network plugin handles hairpin traffic correctly by default. If this is a critical requirement, consider creating a new cluster with Terway.
What's the difference between the Terway and Flannel network plugins for an ACK Kubernetes cluster?
Choosing the right network plugin depends on your specific feature and performance requirements.
What it is: A simple and stable CNI plugin from the open-source community that creates a basic overlay network for Pod communication.
Use when: You need a straightforward, reliable network and do not require advanced features like Kubernetes Network Policies.
Limitation: Does not support Kubernetes-native
NetworkPolicyresources for defining traffic rules between Pods.
What it is: An Alibaba Cloud-developed CNI plugin that provides high-performance networking by integrating directly with the underlying VPC. It assigns ENIs and VPC-native IPs to Pods.
Use when: You need advanced networking features, such as:
Kubernetes
NetworkPolicy: For fine-grained, secure traffic control.Pod-level Bandwidth Limiting: To control the throughput of individual Pods.
High Performance: Direct VPC integration often results in lower latency and higher throughput compared to an overlay network.
Recommendation: Terway is generally recommended for most use cases on ACK due to its powerful features and performance benefits.
What is the correct way to plan the network for an ACK cluster?
Proper network planning is crucial to avoid IP exhaustion and network conflicts. Before creating a cluster, you must decide on three key CIDR blocks:
VPC and vSwitch CIDR: This is the address space for your ECS nodes. Ensure it is large enough for your current and future nodes.
Pod CIDR Block: This is the address space for all Pods in the cluster.
It must not overlap with the VPC CIDR or any connected on-premises networks.
Choose a large enough block to accommodate the maximum number of Pods you anticipate. A common mistake is choosing a block that is too small.
Service CIDR Block: This is the address space for virtual IPs assigned to Kubernetes Services (
It must not overlap with the VPC CIDR or the Pod CIDR.
Carefully plan these ranges in advance, as they cannot be changed after the cluster is created.
For more information, see Plan the network for an ACK managed cluster.
Does ACK support hostPort for Pods?
Support for hostPort depends on the CNI network plugin.
Flannel: Supports
hostPort.Terway: Does not support
hostPort.
In general, using hostPort is discouraged in Kubernetes. The recommended ways to expose a service are:
NodePortService: Exposes the service on a static port on every node's IP.LoadBalancerService: Provisions an external cloud load balancer to route traffic to the service.
With Terway, Pods are directly accessible within the VPC via their own IPs, often making hostPort unnecessary for intra-VPC communication.
How do I identify the network plugin and vSwitches used by my cluster?
You can find this information in the ACK console.
To find the network plugin:
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the target cluster and click its name. In the navigation pane on the left, click Cluster Information.
Click the Basic Information tab.
The Network Plug-in field will show either
FlannelorTerway.
To find the Node vSwitch(es):
Go to .
Click Details for a node pool.
The Node vSwitch field shows the vSwitch(es) where the nodes are located.
To find the Pod vSwitch(es) (Terway only):
Go to Add-ons on your cluster's page.
Find the terway-eniip component and click Configuration.
The PodVswitchId field lists the vSwitch(es) used for allocating Pod IPs. (This does not apply to Flannel).
How do I view the cloud resources used by my ACK cluster?
The Basic Information tab on your cluster's details page in the ACK console provides a summary of the core cloud resources associated with your cluster. This includes:
VPC ID
vSwitch IDs
Security Group ID
Worker RAM Role
Kubernetes version and more
What is the correct way to modify the kube-proxy configuration in an ACK cluster?
You can customize kube-proxy behavior, such as its mode (IPVS/iptables) or connection tracking settings, by editing its ConfigMap.
Procedure
Identify the ConfigMap:
For ACK Managed Clusters, you only need to edit
kube-proxy-worker.For ACK Dedicated Clusters, you must edit both
kube-proxy-workerandkube-proxy-master.
Edit the ConfigMap:
Find the appropriate ConfigMap in the
kube-systemnamespace and edit its YAML. The configuration follows the standard KubernetesKubeProxyConfigurationAPI. You can customize the configuration based on this standard. For more information, see kube-proxy Configuration.Apply the Changes:
After saving the ConfigMap, you must restart the
kube-proxypods for the new configuration to take effect. The DaemonSet controller will automatically recreate the pods with the updated configuration.
Restarting kube-proxy does not interrupt existing connections. However, there may be a brief delay in programming new Service rules, so it is best to perform this operation during off-peak hours.
How can I increase the Linux connection tracking (conntrack) limit on my nodes?
If your kernel logs (dmesg) show the error nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet, your node has exhausted its connection tracking table limit.
Solution
Analyze usage: First, identify what is consuming the connections.
Run
conntrack -Sto see statistics andconntrack -Lto list entries.If you see many short-lived TCP connections, consider modifying your application to use long-lived connections.
If you see high DNS traffic, consider enabling
NodeLocal DNSCache. For more information, see Use the NodeLocal DNSCache component.
Increase Limit via kube-proxy: The recommended way is to adjust the
Edit the
kube-proxy-workerConfigMap.Set
conntrack.maxPerCoreto a higher value (e.g.,65536). A value of0means the system's default is used.
# Snippet from kube-proxy config.conf
conntrack:
maxPerCore: 65536Restart the
kube-proxypods to apply the change.
Increase Limit via sysctl (Manual): You can also set the values directly on each node via
/etc/sysctl.conf, but this is less manageable.
In Terway's accelerated modes (DataPath V2, IPvlan), conntrack for container traffic is managed in an eBPF map, not the Linux conntrack table. See the Terway documentation for how to tune its eBPF map sizes.
How do I change the IPVS load balancing algorithm in kube-proxy?
If you are using IPVS mode and observe unbalanced traffic distribution to backend Pods, especially with long-lived connections, you can change the default load balancing algorithm (round-robin) to something more suitable, like least connection (lc).
Steps
Load Kernel Module (if necessary):
On older node images, the desired IPVS scheduler module might not be loaded by default. Log into each worker node and ensure the module is loaded. For the "least connection" algorithm:Replace
lcwith the identifier for your chosen algorithm (e.g.,rr,wrr,sh).Modify kube-proxy ConfigMap:
Edit the
kube-proxy-worker(andkube-proxy-masterfor dedicated clusters) ConfigMap in thekube-systemnamespace. Set theipvs.schedulerfield.Restart kube-proxy Pods:
Delete the
kube-proxypods to force them to restart and pick up the new configuration.Verify: Check the logs of a new
kube-proxypod. It should showUsing ipvs Proxier.and not fall back toiptablesmode.
How do I reduce the UDP session timeout in kube-proxy IPVS mode to fix DNS delays?
When a UDP backend (like a CoreDNS pod) is removed, kube-proxy in IPVS mode can continue to black-hole traffic to it for the duration of the UDP session timeout (default: 300 seconds). This can cause significant DNS resolution delays during CoreDNS rollouts or node restarts.
Solution
Lower the UDP timeout in the kube-proxy configuration.
For Kubernetes v1.18 and later:
Edit the
kube-proxy-worker(andkube-proxy-masterfor dedicated clusters) ConfigMap in thekube-systemnamespace.Add or modify the
ipvs.udpTimeoutfield. A value of10sis a reasonable choice to minimize impact.Restart the
kube-proxypods to apply the change.
For Kubernetes v1.16 and earlier:
These versions do not support the udpTimeout parameter. You must modify the setting directly on each node using ipvsadm. It is recommended to use a tool like OOS (CloudOps Orchestration Service) to run this command in batch across all cluster nodes.
# This command sets the TCP, TCP-FIN, and UDP timeouts respectively.
# The third parameter '10' sets the UDP timeout to 10 seconds.
ipvsadm --set 900 120 10If your applications rely on long-lived UDP sessions, reducing this timeout may cause issues. Proceed with caution.
How do I troubleshoot common issues in an IPv6 dual-stack cluster?
Problem:
kubectl get podshows only an IPv4 address.Solution: A Pod can have multiple IPs. Use JSONPath to view all of them. An IPv6 address should be present in the
podIPslist.
Problem:
kubectl get svcshows only an IPv4CLUSTER-IP.Solution: Ensure the Service's
ipFamilyPolicyis set toPreferDualStackorRequireDualStack. View all cluster IPs with JSONPath:
Problem: I cannot access my Pod via its IPv6 address.
Cause: The application inside the container might not be listening on the IPv6 any-address (
::). For example, some web servers default to listening on0.0.0.0(IPv4 only).Solution:
execinto the Pod and runnetstat -anp. Check the "Local Address" column. Atcp6orudp6entry listening on:::indicates it is correctly listening on IPv6. If not, you must reconfigure your application.
Problem: My Pod is accessible via IPv6 within the cluster, but not from the internet.
Cause: The Pod's IPv6 address does not have public bandwidth configured.
Solution: In the Alibaba Cloud console, enable public bandwidth for the IPv6 address via an IPv6 Gateway.
Problem: Pods cannot access the internet over IPv6.
Solution: To enable outbound IPv6 internet access, you must have an IPv6 Gateway configured for your VPC and ensure the Pods have IPv6 addresses with public bandwidth enabled.
My Pods are stuck in ContainerCreating with "InvalidVSwitchId.IpNotEnough" errors. How do I add more IP addresses?
This error indicates that the vSwitch used by Terway for Pod IPs has run out of available addresses. To resolve this, you need to expand the IP pool by adding a new vSwitch.

Steps
Create a New vSwitch: In the VPC console, create a new vSwitch in the same region and availability zone as the exhausted one. It is recommended to use a large CIDR block (e.g.,
/19or smaller) to provide ample IP addresses.Update Terway Configuration: In the ACK console, go to Add-ons > terway-eniip > Configuration. Add the ID of the newly created vSwitch to the
PodVswitchIdfield.Restart Terway Pods: Apply the configuration by restarting the Terway DaemonSet pods.
Verify: New Pods should now be able to start successfully by acquiring IPs from the new vSwitch.
Why are my Pods getting IPs from an old vSwitch CIDR block even after I updated the Terway configuration?
This happens because existing Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs) on the nodes are still associated with the old vSwitch configuration. Terway only applies the new vSwitch settings when it needs to create a new ENI.
Cause
If a node already has an ENI attached, any new Pods on that node will continue to pull IPs from that existing ENI's pool, ignoring the updated vSwitch settings. This is common when re-using nodes that were part of a different cluster or after manually modifying the Terway configuration without recycling the nodes.
Solution
The most reliable method to enforce the new configuration is to rotate your nodes.
Steps to rotate a node
Drain and remove: Safely drain workloads and remove the node from the cluster.
Detach ENIs: In the ECS console, manually detach any lingering ENIs from the removed instance.
Re-add node: Add the instance back to the cluster. It will now start fresh and create new ENIs based on the current Terway configuration.
I added a new vSwitch to my Terway configuration, but my Pods are still failing to get an IP. Why is this happening?
This issue typically occurs when the nodes have reached their maximum ENI attachment quota for their ECS instance type.
Cause
Even though you've added a new vSwitch to the Terway configuration, Terway cannot create a new ENI to use it because the node's hardware limit for attached ENIs has been reached. Since the existing ENIs are tied to the old, exhausted vSwitches, no new IPs can be allocated.
Solution
The only way to resolve this is to rotate the affected nodes to clear their existing ENI attachments and allow new ones to be created with the updated configuration.
Steps to rotate a node
Drain and remove: Safely drain workloads and remove the node from the cluster.
Detach ENIs: Go to the ECS console and manually detach all ENIs from the instance.
Re-add node: Add the instance back to the cluster. It will now be able to attach a new ENI using the updated vSwitch configuration.
How do I enable in-cluster load balancing for ExternalIP and LoadBalancer Services in an existing Terway IPvlan cluster?
This feature allows Pods within the cluster to access LoadBalancer or ExternalIP services using their external IP, with traffic being routed internally ("hairpinning") instead of leaving the cluster. It is enabled by default in new Terway IPvlan clusters (v1.2.0+) but must be manually enabled on older clusters.
Prerequisites
Terway v1.2.0 or later.
The cluster must be configured in IPvlan mode.
Solution
Enable the feature by editing the eni-config ConfigMap.
Steps
Edit the
eni-configConfigMap in thekube-systemnamespace:In the
data.eni_confsection, add thein_cluster_loadbalance: "true"flag:Restart the Terway pods to apply the change:
To verify, check the logs of a new Terway pod. It should contain the message
enable-in-cluster-loadbalance=true.
How can I assign Pods to a specific vSwitch/CIDR block in a Terway cluster for IP-based allowlisting?
You can force a group of Pods to acquire IPs from a predictable CIDR block, which is useful for allowlisting with external services like databases. This is achieved using Terway's dynamic configuration feature, which overrides the default settings for specific nodes.
Solution
Create a custom Terway ConfigMap:
Create a new ConfigMap in the
kube-systemnamespace (e.g.,eni-config-fixed) that specifies the dedicated vSwitch for your allowlisted Pods.This example uses vsw-2zem796p76viir02c**** and 10.2.1.0/24.
apiVersion: v1 data: eni_conf: | { "vswitches": {"cn-beijing-h":["vsw-2zem796p76viir02c****"]}, "security_group": "sg-bp19k3sj8dk3dcd7****", "security_groups": ["sg-bp1b39sjf3v49c33****","sg-bp1bpdfg35tg****"] } kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: eni-config-fixed namespace: kube-systemConfigure a Node Pool:
Create a new node pool or use an existing one. Apply the following label to its nodes:
terway-config: eni-config-fixed.
It's also a best practice to add a taint (e.g., fixed=true:NoSchedule) to prevent other workloads from being scheduled on these nodes.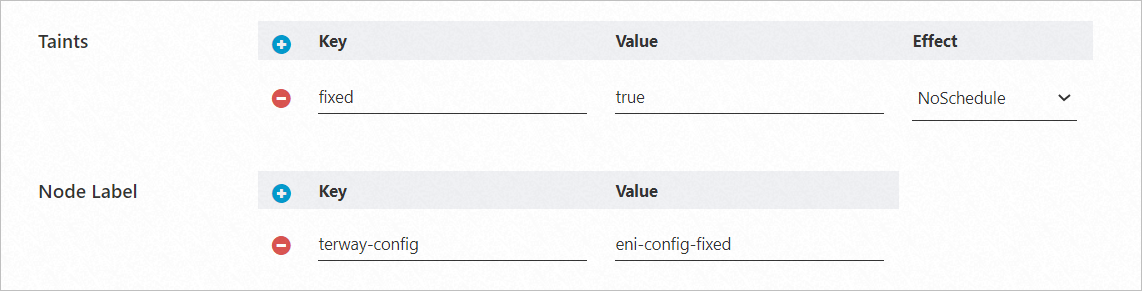
Deploy Pods with Node Selector and Toleration:
Deploy your application with a
nodeSelectorthat matches the label from step 2 and atolerationfor the taint.apiVersion: apps/v1 # For versions earlier than 1.8.0, use apps/v1beta1. kind: Deployment metadata: name: nginx-fixed labels: app: nginx-fixed spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx-fixed template: metadata: labels: app: nginx-fixed spec: tolerations: # Add a toleration. - key: "fixed" operator: "Equal" value: "true" effect: "NoSchedule" nodeSelector: terway-config: eni-config-fixed containers: - name: nginx image: nginx:1.9.0 # Replace with your actual image <image_name:tags>. ports: - containerPort: 80Verification
Pods deployed to this node pool will now get their IPs exclusively from the
vsw-dedicated-for-allowlistvSwitch. You can now safely add this vSwitch's CIDR block to your external service's allowlist.
This method works best with newly created nodes. If you use existing nodes, you must first unbind any pre-existing ENIs from the ECS instances before adding them to the node pool to ensure they pick up the new configuration.
In a Flannel cluster, why can my Pods ping some ECS instances but not others?
Assuming your VPC routes are correctly configured for the Flannel overlay network, this issue is almost always caused by security group rules.
Cause 1: ECS instance is in the same VPC but a different security group.
Solution: Add an inbound rule to the target ECS instance's security group that allows traffic from the source IP range of your cluster's nodes. For a more robust solution, allow traffic from the cluster's Pod CIDR block.
Cause 2: ECS instance is in a different VPC.
Solution: Pods must access the ECS instance via its public IP address. You must add an inbound rule to the ECS instance's security group that allows traffic from your cluster's public egress IP address (e.g., the IP of your NAT Gateway).
Why are newly added nodes in my Flannel cluster getting a NodeNetworkUnavailable taint?
This taint indicates that the node's network is not yet ready for Pods. The cloud-controller-manager (CCM) is responsible for configuring the necessary VPC routes and removing this taint. If it persists, the CCM is failing.
Common causes
VPC route table is full: The VPC route table has reached its quota, and the CCM cannot add a new route for the new node's Pod CIDR block.
Multiple route tables in VPC: Your VPC uses multiple route tables, but the CCM is not configured to manage them. By default, it only interacts with the VPC's main route table.
Solution
Inspect the node's events for error messages from the CCM:
If the route table is full, you must delete unused routes to make space.
If you use multiple route tables, you must configure the CCM to be aware of all relevant route table IDs. Refer to the ACK documentation on Use multiple route tables in a VPC.
Why are my Pods failing to start with the error failed to allocate for range 0: no IP addresses available in range set?
This error means the node has exhausted its assigned subnet of IP addresses for Pods. This is typically caused by an IP address leak, where IPs are not correctly released after Pods are deleted.
Common causes of IP leaks
Old Kubernetes versions (< 1.20): In older versions, rapid Pod restarts or short-lived CronJob Pods could lead to IP leaks due to race conditions.
Old Flannel versions: On versions that store the IP allocation database on disk (
/var/lib/cni/networks/), an unexpected node shutdown could prevent cleanup, causing IPs to remain marked as "allocated".
Long-term solution (recommended)
Upgrade cluster: Upgrade your ACK cluster to Kubernetes 1.20 or a later version.
Upgrade Flannel and configure
tmpfs: Upgrade the Flannel component to a recent version. Then, edit thekube-flannel-cfgConfigMap to configure the IPAM data directory to use a temporary filesystem (/var/run/cni/networks), which is automatically cleared on reboot. This prevents persistent leaks. After configuration, you must restart the nodes.
Temporary workaround (if you cannot upgrade immediately):
Drain the affected node.
Log into the node and manually run a cleanup script. The script should compare the IP allocation files in
/var/lib/cni/networks/cb0/with the list of currently running containers (docker psorcrictl pods) and delete any files corresponding to non-existent containers.Uncordon the node.
This workaround only cleans up existing leaks. The underlying problem will persist until you upgrade.
How can I change the Pod CIDR, Service CIDR, or IPs per node for an existing ACK cluster?
You cannot modify these fundamental network parameters after an ACK cluster has been created.
The Pod CIDR block, Service CIDR block, and the size of the subnet allocated to each node (in Flannel) are defined at cluster creation. Changing them would require a full reconfiguration of the cluster's networking and routing, which is not a supported operation. If you need to change these values, you must create a new cluster with the correct network plan.
When do I need to configure the cloud-controller-manager (CCM) for multiple route tables in a Flannel cluster?
You must configure the CCM to manage multiple route tables in a Flannel cluster in the following scenarios:
Scenario 1: Using custom route tables
If your cluster nodes reside in subnets associated with a custom route table (not the main one), the CCM will fail to add routes for Pod CIDRs unless it is explicitly configured with the ID of that custom route table.
Scenario 2: CCM logs show
multiple route tables founderrorThis error message explicitly states that the CCM has detected more than one route table in the VPC and does not know which one to use for managing Pod network routes.
Scenario 3: Persistent
NodeNetworkUnavailabletaint on new nodesIf new nodes consistently get stuck with this taint, it's a strong indicator that the CCM cannot configure their routes, often due to an unconfigured custom route table.
Is it possible to install a third-party CNI network plugin on an ACK cluster?
No, ACK clusters do not support installing or configuring third-party network plugins.
ACK is deeply integrated with its provided CNI plugins (Terway and Flannel) to manage VPC routing, ENIs, and other cloud resources. Attempting to install another CNI plugin (like Calico or Cilium) manually will conflict with the managed system and likely cause a complete network failure in your cluster.
Why do I get a no IP addresses available in range set error in my Flannel cluster?
This error means a node has no more IP addresses to assign to new Pods from its designated Pod CIDR subnet.
Cause
This is a hard limit. In a Flannel cluster, the total Pod CIDR block is divided into smaller subnets, and one subnet is assigned to each node. Once a node's subnet is full, it cannot create more Pods. This issue arises from inadequate network planning.
Solution
Short-term: Delete unused Pods on the affected node to free up IPs. You can also add a new node to the cluster, which will get its own fresh subnet of IPs.
Long-term: The only permanent fix is to recreate the cluster with a larger Pod CIDR block. Plan your network carefully to allocate enough IP addresses for your expected number of nodes and pods per node.
What determines the maximum number of Pods per node in a Terway cluster?
The maximum number of Pods per node in a Terway cluster is determined by the IP capacity of the underlying ECS instance type.
Terway assigns IPs from ENIs attached to the node. Each ECS instance type has a specific limit on:
The maximum number of ENIs it can attach.
The maximum number of private IP addresses per ENI.
The total number of available IPs (and thus Pods) is calculated as (Number of ENIs) × (IPs per ENI). You can find these limits in the Alibaba Cloud ECS documentation for your specific instance type.
What is Terway's DataPath V2 mode, and how is it different from the original IPvlan mode?
DataPath V2 is the next-generation data plane for Terway's network acceleration feature, serving as an enhancement to the original IPvlan+eBPF mode.
Key points
Default for new clusters: For clusters created with Terway v1.8.0 or later where IPvlan acceleration is enabled, DataPath V2 is used by default.
Backward compatibility: Existing clusters that were already using the legacy IPvlan mode will continue to use it even after upgrading the Terway component. The data plane is not automatically migrated to prevent disruptions.
Benefits: DataPath V2 offers improved compatibility and performance over the original implementation.
What do the different Pod statuses like Pending and ContainerCreating mean in a Terway network context?
By observing a Pod's status, you can understand its network initialization progress within a Terway environment.
Pending: The scheduler has not yet assigned the Pod to a node. This is usually due to resource constraints (CPU, memory) or scheduling rules (taints, affinity). Terway is not yet involved at this stage.ContainerCreating: The Pod has been scheduled to a node, and the Kubelet has instructed the container runtime to create it. For Terway, this is the active phase where the CNI plugin is setting up the Pod's network. This includes attaching an ENI (if necessary) and assigning a private IP address. Delays or failures in this state often point to network resource issues, such as no available IPs in the vSwitch.Running: All containers in the Pod have been created, and Terway has successfully configured its network. The Pod should now be operational and reachable.
You can inspect a Pod's detailed status and events using kubectl describe pod <pod-name>.
Why did my Terway component upgrade fail with the error eip pool is not supported?
This error occurs because the EIP (Elastic IP) pool feature has been deprecated and removed from recent versions of the Terway component.
Solution
Before upgrading Terway, you must migrate your EIP management from Terway to the ack-extend-network-controller component. This controller is now responsible for handling EIP assignments for Pods. Follow the official Alibaba Cloud documentation to migrate your configuration.
Why do my Pods sometimes fail to create in a Terway cluster with the error can't found dev by mac?
This error, failed to do add; error parse config, can't found dev by mac..., means the Terway CNI plugin could not find the network interface (ENI) on the node that corresponds to the expected MAC address.
There are two common causes:
Asynchronous ENI attachment (transient issue):
Explanation: When a new ENI is attached to an ECS instance, there can be a slight delay before the network device is fully initialized in the operating system. If the CNI plugin attempts to configure the network during this brief window, it will fail to find the device.
Solution: This is usually a temporary timing issue. The CNI plugin is designed to retry automatically. In most cases, it will succeed on a subsequent attempt, and the Pod will eventually start. If the Pod becomes
Running, you can safely ignore these transient errors in the logs.
Node driver failure (persistent issue):
Explanation: If the error persists and the Pod never starts, it could indicate a more serious problem. The underlying driver on the node may have failed to initialize the ENI correctly, which can happen if the ECS instance has insufficient high-order memory at the time of attachment.
Solution: Restarting the affected ECS instance will typically resolve this driver-level failure.
What should I consider when configuring a custom Cluster Domain for my ACK cluster?
The Cluster Domain (default: cluster.local) is the DNS suffix for all in-cluster services. If you customize it during cluster creation, you must follow these rules to avoid DNS resolution conflicts.
Cannot be changed: The Cluster Domain can only be set at cluster creation time and cannot be modified later.
Must be unique: The Cluster Domain must not overlap with any external public domains or private DNS zones you use (e.g., in Alibaba Cloud DNS PrivateZone).
Why is this important?
CoreDNS, the cluster's DNS server, is configured to handle all queries for the Cluster Domain internally and will not forward them to upstream DNS servers. This is for security and performance.
If your Cluster Domain is, for example, mycompany.com, and you also have a public website at www.mycompany.com, your Pods will be unable to resolve www.mycompany.com because CoreDNS will assume mycompany.com is an internal-only zone and will not forward the query. This will lead to DNS resolution failures for all external services under that domain.