We recommend that you plan the cluster size, network features, virtual private cloud (VPC)-related configurations (VPCs and vSwitches), and network configurations (container network plug-ins, container CIDR block, and Service CIDR block) in advance to ensure efficient use of network resources and reserve sufficient space for future business expansion. This topic describes how to plan the network architecture of an ACK managed cluster that meet your business requirements in an Alibaba Cloud VPC environment.
Network size planning
Region and zone
Number of VPCs
Number of vSwitches
Cluster scale
Network connection planning
Container network plug-in planning
ACK managed clusters support two types of container network plug-ins: Terway and Flannel. Different plug-ins affect the supported features and network configurations. For example, Terway supports NetworkPolicy, which provides policy-based network control, while Flannel does not. The container CIDR block of Terway is allocated from VPC, while the container CIDR block of Flannel is a specified virtual network segment.
The container network plug-in must be installed when you create a cluster and cannot be changed after the cluster is created. We recommend that you select a network plug-in based on your network requirements.
Feature planning
Item | Terway | Flannel |
NetworkPolicy | You can use network policies in ACK clusters. | Not supported. |
IPv4/IPv6 dual stack | Not supported. Note The Flannel plug-in used in ACK is modified to adapt to the Alibaba Cloud environment and is not synchronized with the open source community. For more information about the release notes of Flannel, see Flannel. | |
Configure static pod IP addresses | You can configure a static IP address, a separate vSwitch, and a separate security group for each pod. | Not supported. |
Bind an EIP to a pod | Not supported. | |
Accesses between multiple clusters | Supported. Pod in different clusters can communicate when the relevant ports are opened in security group rules. | Not supported. |
For more information about the comparison between Terway and Flannel, see Comparison between Terway and Flannel.
CIDR block planning
The control plane of ACK managed clusters uses the 7.0.0.0/8 CIDR block. To prevent network conflicts that may disrupt cluster management access, avoid selecting CIDR ranges overlapping with 7.0.0.0/8.
Terway
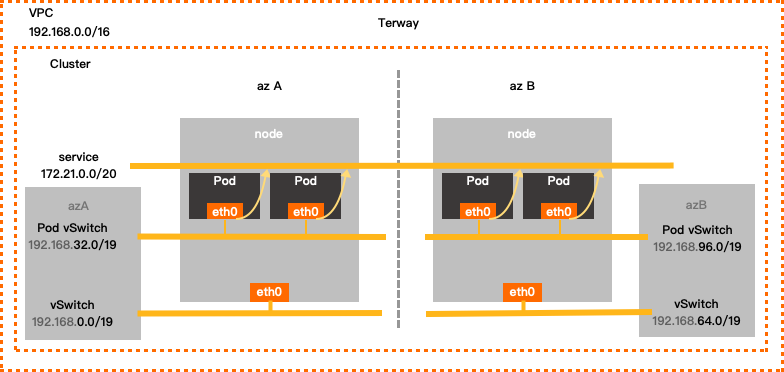
Configuration example
Single-zone configuration of Terway
VPC CIDR Block
vSwitch CIDR Block
Pod vSwitch CIDR block
Service CIDR block
Maximum number of pod IP addresses
192.168.0.0/16
Zone I
192.168.0.0/19
192.168.32.0/19
172.21.0.0/20
8192
Multi-zone deployment of Terway
VPC CIDR Block
vSwitch CIDR Block
Pod vSwitch CIDR block
Service CIDR block
Maximum number of pod IP addresses
192.168.0.0/16
Zone I 192.168.0.0/19
192.168.32.0/19
172.21.0.0/20
8192
Zone J 192.168.64.0/19
192.168.96.0/19
If your cluster uses the Terway network plug-in, you must configure the following parameters:
VPC
You can specify one of the following CIDR blocks or their subsets as the primary IPv4 CIDR block of the VPC: 192.168.0.0/16, 172.16.0.0/12, and 10.0.0.0/8. These CIDR blocks are standard private CIDR blocks as defined by Request for Comments (RFC) documents. The subnet mask must be 8 to 28 bits in length. Example: 192.168.0.0/16.
You may use custom CIDR ranges as the primary IPv4 CIDR block for your VPC, provided they do not overlap with the following reserved network segments or their subnets: 100.64.0.0/10, 224.0.0.0/4, 127.0.0.0/8, 169.254.0.0/16, and 7.0.0.0/8.
In scenarios in which multiple VPCs are used or in hybrid cloud scenarios in which you want to connect data centers to VPCs, we recommend that you use standard RFC CIDR blocks as VPC CIDR blocks with subnet masks no more than 16 bits in length. Make sure that the CIDR blocks of the VPCs and data centers do not overlap.
IPv6 CIDR blocks are assigned by the VPC after you enable IPv6 for the VPC. If you want to enable IPv6 for containers, select Terway for the Network Plug-in parameter.
vSwitch
The vSwitches associated with ECS instances allow nodes to communicate with each other. The CIDR blocks of vSwitches in the VPC must be subsets of the VPC CIDR block. This indicates that the CIDR blocks of vSwitches must be the same as or fall within the VPC CIDR block. When you specify the CIDR block, take note of the following items:
The system allocates IP addresses from the CIDR block of a vSwitch to the ECS instances that are associated with the vSwitch.
You can create multiple vSwitches in a VPC. However, the CIDR blocks of these vSwitches cannot overlap with each other.
The vSwitch and the pod vSwitch must be in the same zone.
Pod vSwitch
The IP addresses of pods are assigned from the CIDR block of pod vSwitches. This allows pods to communicate with each other. Pod is an abstraction in ACK. Each pod has an IP address. The CIDR blocks that you specify when you create pod vSwitches in the VPC must be subsets of the VPC CIDR block. When you specify the CIDR block, take note of the following items:
In a Container Service cluster that has Terway installed, the IP addresses of pods are assigned by pod vSwitches.
The pod vSwitch CIDR block cannot overlap with the Service CIDR block.
The vSwitch and pod vSwitch must be in the same zone.
Service CIDR block
ImportantYou cannot change the Service CIDR block after the creation.
Service is a Kubernetes concept. The Service CIDR block provides IP addresses for ClusterIP type Services. Each Service has an IP address. When you specify the CIDR block, take note of the following items:
The IP address of a Service is effective only within the cluster.
The Service CIDR block cannot overlap with the vSwitch CIDR block.
The Service CIDR block cannot overlap with the pod vSwitch CIDR block.
Service IPv6 CIDR block
If you enable IPv4/IPv6 dual stack, you must specify an IPv6 CIDR block for Services. When you specify the CIDR block, take note of the following items:
You must specify a Unique Local Unicast Address (ULA) space within the address range fc00::/7. The prefix must be 112 bits to 120 bits in length.
We recommend that you specify an IPv6 CIDR block that has the same number of IP addresses as the Service CIDR block.
Flannel
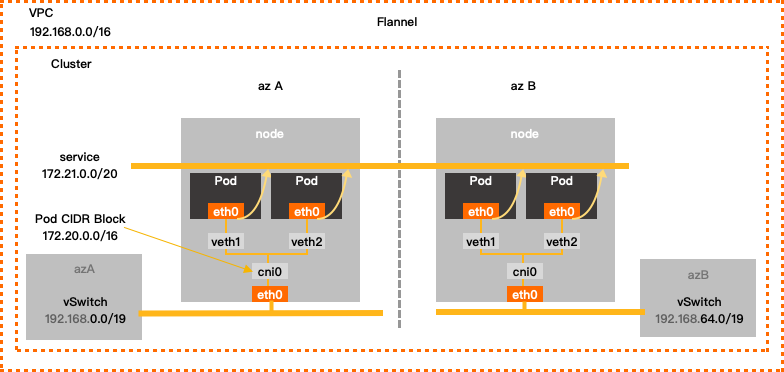
Configuration example
VPC CIDR Block | vSwitch CIDR Block | Container CIDR block | Service CIDR block | Maximum number of pod IP addresses |
192.168.0.0/16 | 192.168.0.0/24 | 172.20.0.0/16 | 172.21.0.0/20 | 65536 |
If your cluster uses the Flannel network plug-in, you must configure the following parameters:
VPC
You can specify one of the following CIDR blocks or their subsets as the primary IPv4 CIDR block of the VPC: 192.168.0.0/16, 172.16.0.0/12, and 10.0.0.0/8. These CIDR blocks are standard private CIDR blocks as defined by Request for Comments (RFC) documents. The subnet mask must be 8 to 28 bits in length. Example: 192.168.0.0/16.
You may use custom CIDR ranges as the primary IPv4 CIDR block for your VPC, provided they do not overlap with the following reserved network segments or their subnets: 100.64.0.0/10, 224.0.0.0/4, 127.0.0.0/8, 169.254.0.0/16, and 7.0.0.0/8.
In scenarios in which multiple VPCs are used or in hybrid cloud scenarios in which you want to connect data centers to VPCs, we recommend that you use standard RFC CIDR blocks as VPC CIDR blocks with subnet masks no more than 16 bits in length. Make sure that the CIDR blocks of the VPCs and data centers do not overlap.
IPv6 CIDR blocks are assigned by the VPC after you enable IPv6 for the VPC. If you want to enable IPv6 for containers, select Terway for the Network Plug-in parameter.
vSwitch
The vSwitches associated with ECS instances allow nodes to communicate with each other. The CIDR blocks of vSwitches in the VPC must be subsets of the VPC CIDR block. This indicates that the CIDR blocks of vSwitches must be the same as or fall within the VPC CIDR block. When you specify the CIDR block, take note of the following items:
The system allocates IP addresses from the CIDR block of a vSwitch to the ECS instances that are associated with the vSwitch.
You can create multiple vSwitches in a VPC. However, the CIDR blocks of these vSwitches cannot overlap with each other.
Container CIDR block
ImportantYou cannot change the container CIDR block after the creation.
The IP addresses of pods are assigned from the container CIDR blocks. This allows pods to communicate with each other. Pod is an abstraction in ACK. Each pod has an IP address. When you specify the CIDR block, take note of the following items:
Enter a CIDR block in the Pod CIDR Block field.
The container CIDR block of pods cannot overlap with the vSwitch CIDR block.
The container CIDR block of pods cannot overlap with the Service CIDR block.
For example, if the VPC CIDR block is 172.16.0.0/12, the container CIDR block cannot be 172.16.0.0/16 or 172.17.0.0/16 because these CIDR blocks are subsets of 172.16.0.0/12.
Service CIDR block
ImportantYou cannot change the Service CIDR block after the creation.
Service is a Kubernetes concept. The Service CIDR block provides IP addresses for ClusterIP type Services. Each Service has an IP address. When you specify the CIDR block, take note of the following items:
The Service CIDR block is effective only within the cluster.
The Service CIDR block cannot overlap with the vSwitch CIDR block.
The Service CIDR block cannot overlap with the container CIDR block.





