This topic describes common issues and solutions related to creating, using, and managing clusters.
How do I migrate a self-managed Kubernetes cluster to ACK?
Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) provides a seamless solution for migrating self-managed Kubernetes clusters to ACK clusters. This solution ensures that your business is not affected during the migration. For more information, see Kubernetes Migration Solution Overview.
Are clusters with the Alibaba Cloud Linux operating system compatible with CentOS container images?
Yes, they are. Clusters that run Alibaba Cloud Linux are compatible with CentOS-based container images. For more information, see Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.
If I choose the containerd container runtime when creating a cluster, can I change it to Docker later?
No, you cannot. After a cluster is created, you cannot change its container runtime. However, you can create node pools that use different container runtimes within the same cluster. For more information, see Create and manage node pools.
To migrate the container runtime of a node from Docker to containerd, see Migrate the container runtime of a node from Docker to containerd.
Docker is not supported as a built-in container runtime for clusters that run Kubernetes 1.24 or later. You must use containerd as the node pool runtime for these clusters.
What are the differences between the containerd, Docker, and sandboxed container runtimes?
Container Service for Kubernetes supports three runtimes: containerd, Docker, and Sandboxed-Container. We recommend that you use containerd as the container runtime. You can use Docker as the container runtime in clusters that run Kubernetes 1.22 and earlier. You can use Sandboxed-Container as the container runtime in clusters that run Kubernetes 1.24 and earlier. For a comparison of these runtimes, see Comparison of containerd, Sandboxed-Container, and Docker runtimes. If your cluster uses Docker as the container runtime, you must migrate the container runtime to containerd before you can update the Kubernetes version of your cluster to 1.24 or later. For more information, see Migrate the node container runtime from Docker to containerd.
Is Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) certified for MLPS 2.0 Level 3?
Yes, it is. You can enable classified protection for your cluster and configure baseline check policies. Based on Alibaba Cloud Linux, you can implement MLPS 2.0 Level 3 and configure classified protection compliance baseline checks to meet the following requirements:
Identity authentication
Access control
Security audit
Intrusion prevention
Malicious code prevention
For more information, see ACK MLPS hardening instructions.
Does an ACK cluster support Istio?
Yes, it does. You can use Alibaba Cloud Service Mesh (ASM). ASM is a service mesh product that is fully compatible with community Istio. It provides a fully managed control plane that lets you focus on developing and deploying your business applications. ASM supports multiple operating systems for ACK nodes and various network plug-ins deployed within the cluster. You can add an existing ACK cluster to an ASM instance to use features such as traffic management, fault handling, unified monitoring, and log management. For more information, see Add a cluster to an ASM instance. For information about ASM billing, see ASM Billing.
How do I collect diagnostic information for a Kubernetes cluster?
If a Kubernetes cluster has issues or a node is abnormal, you can use the diagnostic feature provided by ACK to help you locate problems in the cluster. For more information, see Use cluster diagnostics.
If the cluster diagnostic feature does not meet your needs, you can collect diagnostic information from master nodes and abnormal worker nodes. Follow the steps below to collect information from Linux or Windows nodes.
Collect diagnostic information from a Linux node
Worker nodes can run Linux or Windows, but master nodes can only run Linux. The following method applies to both master and worker nodes that run Linux. This example uses a master node.
Log on to a master node of the Kubernetes cluster and run the following command to download the diagnostic script.
curl -o /usr/local/bin/diagnose_k8s.sh http://aliacs-k8s-cn-hangzhou.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/public/diagnose/diagnose_k8s.shNoteThe diagnostic script for Linux nodes can be downloaded only from the China (Hangzhou) region.
Run the following command to grant execute permissions to the diagnostic script.
chmod u+x /usr/local/bin/diagnose_k8s.shRun the following command to change to the specified directory.
cd /usr/local/binRun the following command to run the diagnostic script.
diagnose_k8s.shThe following output is returned. The name of the log file generated by the diagnostic script varies. In this example, the file is named diagnose_1514939155.tar.gz.
...... + echo 'please get diagnose_1514939155.tar.gz for diagnostics' please get diagnose_1514939155.tar.gz for diagnostics + echo 'Please upload diagnose_1514939155.tar.gz' Please upload diagnose_1514939155.tar.gzRun the following command to view the file that stores the cluster diagnostic information.
ls -ltr | grep diagnose_1514939155.tar.gzNoteReplace diagnose_1514939155.tar.gz with the actual name of the log file.
Collect diagnostic information from a Windows node
To collect diagnostic information from a worker node that runs Windows, download and run the diagnostic script.
Windows can be used only for worker nodes.
Log on to the abnormal worker node, and open the command line interface.
Run the following command to enter PowerShell mode.
powershellRun the following command to download and run the diagnostic script.
The diagnostic script for Windows nodes can be downloaded from the region where the cluster resides. Replace
[$Region_ID]in the command with the actual region ID.Invoke-WebRequest -UseBasicParsing -Uri http://aliacs-k8s-[$Region_ID].oss-[$Region_ID].aliyuncs.com/public/pkg/windows/diagnose/diagnose.ps1 | Invoke-ExpressionThe following output indicates that the diagnostic information is collected.
INFO: Compressing diagnosis clues ... INFO: ...done INFO: Please get diagnoses_1514939155.zip for diagnosticsNoteThe diagnoses_1514939155.zip file is saved to the directory where the script is run.
How do I troubleshoot issues in an ACK cluster?
1. Check cluster nodes
Run the following command to view the status of the nodes in the cluster. Confirm that all nodes exist and are in the Ready state.
Run the following command to view detailed information and events for a node.
Replace
[$NODE_NAME]with your node name.kubectl describe node [$NODE_NAME]NoteFor information about the output of kubectl, see Node status.
2. Check cluster components
If you cannot identify the problem after you check the cluster nodes, proceed to check the component logs on the control plane.
Run the following command to view all components in the kube-system namespace.
kubectl get pods -n kube-systemThe expected output is as follows.
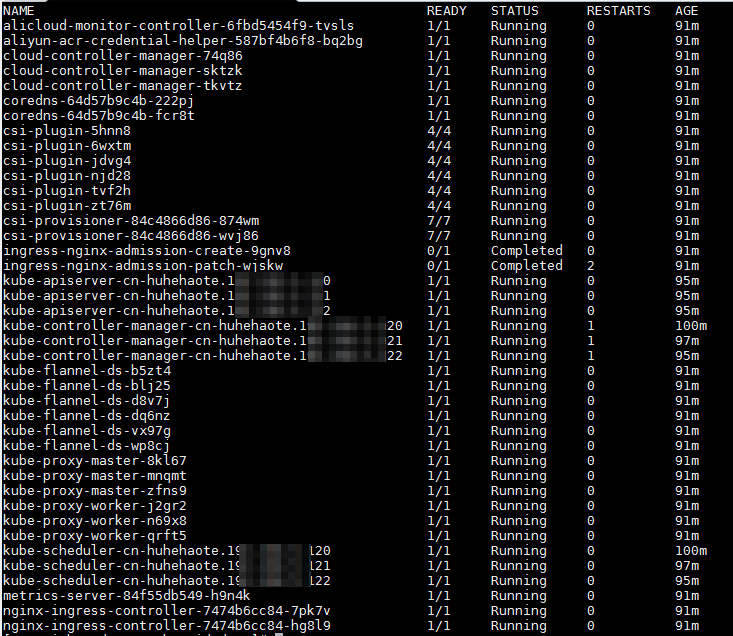 Pods with names that start with `kube-` are system components of the Kubernetes cluster. Pods with names that start with `coredns-` are DNS plug-ins. The expected output indicates that the components are in a normal state. If a component is in an abnormal state, proceed to the next step.
Pods with names that start with `kube-` are system components of the Kubernetes cluster. Pods with names that start with `coredns-` are DNS plug-ins. The expected output indicates that the components are in a normal state. If a component is in an abnormal state, proceed to the next step.Run the following command to view the logs of the abnormal component to locate and resolve the problem.
Replace
[$Component_Name]with the name of the abnormal component.kubectl logs -f [$Component_Name] -n kube-system
3. Check the kubelet component
Run the following command to check the status of the kubelet.
systemctl status kubeletIf the status of the kubelet is not active (running), run the following command to view the kubelet logs to locate and resolve the problem.
journalctl -u kubelet
Common cluster issues
The following table lists some common causes of ACK cluster failures and their solutions.
Troubleshooting Scenarios | Solution |
The API Server component or a master component stops running:
| ACK components have built-in high availability features. Check whether the component itself is abnormal. For example, the API Server of an ACK cluster uses an SLB instance by default. You can troubleshoot the SLB instance to determine the cause of the abnormal status. |
Backend data for the API Server is lost:
| If you have created a snapshot, you can restore data from the snapshot to resolve the problem. If you have not created a snapshot, you can submit a ticket. After the problem is resolved, you can use the following methods to prevent it from recurring:
|
An individual node shuts down, and all pods on that node stop running. | Use workloads, such as deployments, StatefulSets, or DaemonSets, to create pods instead of creating pods directly. This prevents pods from failing to be scheduled to other healthy nodes. |
The kubelet component fails:
|
|
Misconfiguration or other problems. | If you created a snapshot before the problem occurred, you can restore data from the snapshot to resolve it. If you have not created a snapshot, submit a ticket to report the problem. After the problem is resolved, regularly create snapshots for the volumes that are managed by the kubelet. For more information, see Create a snapshot for a single cloud disk persistent volume. |
How do I grant fine-grained permissions when a RAM user operates an ACK cluster?
By default, RAM users and RAM roles do not have permissions to use the OpenAPI of Alibaba Cloud services. You must grant them the AliyunCSFullAccess system permission for Container Service or the required custom permissions to use and manage ACK clusters. For more information, see Grant access permissions to clusters and cloud resources using RAM.
Based on the Kubernetes RBAC mechanism, you must use RBAC to grant permissions to RAM users to manage resources within the cluster, such as creating deployments and services.
For scenarios that require fine-grained control over resource read and write permissions, you can use custom ClusterRoles and Roles to configure more granular RBAC permissions. For more information, see Use custom RBAC to restrict operations on resources in a cluster.
When a RAM user accesses the console, you must also grant the required permissions for the relevant Alibaba Cloud services to use features such as viewing node pool scaling activities and cluster dashboards. For more information, see Container Service console permission dependencies.
When configuring the access control policy for a cluster's API Server SLB instance, which IP address ranges need to be allowed?
The access control list (ACL) rules for the API Server's SLB instance must allow the following IP address ranges.
The CIDR block managed by Container Service for Kubernetes, which is 100.104.0.0/16.
The primary CIDR block and additional CIDR block (if any) of the cluster virtual private cloud (VPC), or the vSwitch CIDR block where the cluster nodes are located.
The egress CIDR block of the client that needs to access the API server connection endpoint on the user side.
In addition to the above CIDR blocks, ACK Edge clusters must allow the egress CIDR blocks of edge nodes.
In addition to the above CIDR blocks, ACK Lingjun clusters must allow the CIDR block of the Lingjun Virtual Private Datacenter (VPD).
For more information, see Configure the access control policy for the API Server.
How is high availability ensured for the control plane of an ACK managed cluster?
The control plane of an ACK managed cluster is hosted by Alibaba Cloud. Alibaba Cloud provides recommended high availability configurations for data plane dimensions, such as nodes, node pools, workloads, and Server Load Balancer, to help you build secure and reliable cluster and application architectures. For more information, see Recommended configurations for high-availability cluster architectures.
Can the API Server domain name of a managed ACK cluster be resolved across VPCs?
No, it cannot. By default, the API Server domain name of an ACK cluster, apiserver.<cluster-id>.<region-id>.cs.aliyuncs.com, is resolved using What is Private DNS?. The DNS record is valid only in the VPC where the cluster is located and cannot be resolved from another VPC.
To resolve the domain name across VPCs, you can follow the instructions in Associate VPCs across accounts to add the Alibaba Cloud account. Then, submit a ticket and provide the VPC information to complete the attachment.
Why does API Server domain name resolution fail for an ACK managed cluster?
ACK registers the API Server domain name of an ACK managed cluster with What is Private DNS?. The API Server domain name may fail to resolve if a node uses a custom DNS server instead of the default Alibaba Cloud DNS servers, 100.100.2.136 and 100.100.2.138.
In this case, set the upstream servers for the API Server domain name (apiserver.<cluster-id>.<region-id>.cs.aliyuncs.com) to 100.100.2.136 and 100.100.2.138.
If the custom DNS server and the ACK managed cluster are in different VPCs, submit a ticket to configure the cross-VPC resolution.
Can the automatically created CLB instance for an ACK managed cluster API Server be reused?
No. The internal network CLB for the API Server acts as the core entry point to the control plane and is dedicated to the API Server. Reusing the instance or modifying its configuration, such as adding listeners or changing backend server groups, can disrupt access to the API Server and compromise the stability of the cluster. Do not modify this CLB instance.
How do I access a master node?
ACK dedicated cluster: For more information, see Connect to the master node of an ACK dedicated cluster using SSH.
ACK managed cluster: The control plane nodes of an ACK managed cluster are fully managed. You cannot log on to the terminals of the control plane nodes. To log on to control plane nodes, consider using an ACK dedicated cluster.
If I accidentally delete a master node from an ACK dedicated cluster, can I still upgrade the cluster?
No, you cannot. After you delete a master node from an ACK dedicated cluster, you cannot add master nodes or upgrade the cluster. You can create an ACK dedicated cluster (Discontinued).
Can I add or remove master nodes from an ACK dedicated cluster? What are the high-risk operations?
No, you cannot. Adding or removing master nodes from an ACK dedicated cluster may cause the cluster to become unusable and unrecoverable.
For the master nodes of an ACK dedicated cluster, improper operations can cause the master nodes or even the entire cluster to become unavailable. High-risk operations include replacing master or etcd certificates, modifying core components, deleting or formatting data in core directories such as /etc/kubernetes on a node, or reinstalling the operating system. For more information, see Cluster-related high-risk operations.
What should I do if the ACK dedicated cluster API Server returns the error "api/v1/namespaces/xxx/resourcequotes": x509: certificate has expired or is not yet valid: current time XXX is after xxx?
Symptoms
When you create a pod in an ACK dedicated cluster, the API Server returns a certificate expiration error, or the logs or events of the kube-controller-manager show a certificate expiration error. The error message is as follows.
"https://localhost:6443/api/v1/namespaces/xxx/resourcequotes": x509: certificate has expired or is not yet valid: current time XXX is after XXX"https://[::1]:6443/api/v1/namespaces/xxx/resourcequotes": x509: certificate has expired or is not yet valid: current time XXX is after XXXCause
In Kubernetes, the API Server has a built-in certificate for its internal LoopbackClient server. In the community version, this certificate has a validity period of one year and cannot be automatically rotated. It is automatically rotated and updated only when the API Server pod restarts. If the Kubernetes version has not been upgraded for more than one year, the internal certificate expires, which causes API requests to fail. For more information, see #86552.
To reduce the risk caused by the short validity period of certificates in ACK clusters that run Kubernetes 1.24 or later, the default validity period of the built-in certificates is extended to 10 years. For more information, see Product Change: Change to the Validity Period of ACK Cluster API Server Internal Certificates.
Solution
Log on to a master node and run the following command to query the expiration time of the LoopbackClient certificate.
In the command, XX.XX.XX.XX is the local IP address of the master node.
curl --resolve apiserver-loopback-client:6443:XX.XX.XX.XX -k -v https://apiserver-loopback-client:6443/healthz 2>&1 |grep expireFor clusters with 1-year certificates that have expired or are about to expire, upgrade the cluster to version 1.24 or later. For more information, see Manually upgrade a cluster. We recommend that you migrate to an ACK Managed Cluster Pro instance. For more information, see Hot migrate an ACK dedicated cluster to an ACK Managed Cluster Pro.
For ACK dedicated clusters that cannot be upgraded in the short term, log on to each master node and manually restart the API Server to generate a new valid certificate.
containerd node
crictl pods |grep kube-apiserver- | awk '{print $1}' | xargs -I '{}' crictl stop {}Docker node
docker ps | grep kube-apiserver- | awk '{print $1}' | xargs -I '{}' docker restart {}