ACK provides MLPS 2.0 Level 3 compliance based on Alibaba Cloud Linux. You can enable MLPS 2.0 security hardening for a node pool and configure a baseline check policy. ACK automatically configures security hardening items for the cluster and performs a classified protection compliance baseline check to ensure that the operating system meets classified protection requirements.
Classified protection compliance requirements
ACK provides MLPS 2.0 Level 3 compliance for Alibaba Cloud Linux to meet China's classified protection requirements. You can use the following MLPS security hardening configurations to ensure that your ACK clusters comply with the required baselines:
The GB/T 22239-2019 Information Security Technology - Baseline for Classified Protection of Cybersecurity standard specifies the classified protection requirements for operating systems. To meet these requirements, ACK provides the MLPS 2.0 Level 3 edition for Alibaba Cloud Linux. You can enable the MLPS 2.0 security hardening feature to meet the following classified protection compliance requirements.
Identity authentication
Access control
Security audit
Intrusion prevention
Malware prevention
Check rules for Alibaba Cloud Linux MLPS 2.0 Level 3 images
Alibaba Cloud Linux MLPS 2.0 Level 3 images are hardened for classified protection according to the GB/T 22239-2019 Information Security Technology - Baseline for Classified Protection of Cybersecurity standard. The images meet the check items detailed in the following table.
Check item type | Check item name | Check content |
Identity authentication | The identity of logon users must be authenticated and unique. Authentication information must meet complexity requirements and be changed periodically. |
|
Necessary measures must be taken to prevent authentication information from being intercepted during network transmission when a server is managed remotely. |
| |
A logon failure handling feature must be implemented. Measures such as session termination, limits on failed logon attempts, and automatic logout on connection timeout must be configured and enabled. | Check whether a logon failure lockout policy is configured, an idle session timeout is set, and the client is configured to disconnect after a logon timeout. | |
Access control | Assign accounts and permissions to logon users. |
|
Rename or delete default accounts and change their default security tokens. |
| |
The granularity of access control must be at the user or process level for entities and at the file or database table level for objects. | Check whether the permissions of important files, such as access control and user permission configuration files, have user-level granularity. | |
Promptly delete or disable redundant or expired accounts. Avoid using shared accounts. |
| |
Grant administrative users the least privilege required and use permission separation. |
| |
An authorized entity must configure the access control policy, which specifies the rules for entity access to objects. |
| |
Security audit | Audit records must be protected. They must be backed up periodically to prevent unexpected deletion, modification, or overwriting. | Check the `auditd` file size, log splitting configuration, or backup to a log server. If automatic repair fails, you must first fix the check item for enabling the security audit feature. |
Audit records must include the date and time of the event, the user, the event type, the event outcome (success or failure), and other audit-related information. | This item is met if the check item for enabling the security audit feature is met. | |
The security audit feature must be enabled. The audit must cover every user and record important user behaviors and security events. |
| |
Audit processes must be protected from unexpected interruptions. | `auditd` is the daemon process for the `audit` process, and `syslogd` is the daemon process for the `syslog` process. Check whether these system processes are running. | |
Intrusion prevention | Known vulnerabilities must be detected. After thorough testing and evaluation, the vulnerabilities must be patched promptly. | The vulnerability detection and fixing features of Security Center can meet this requirement. If you use other methods, you can provide evidence and ignore this item. |
Follow the principle of minimal installation by installing only necessary components and applications. |
| |
Shut down unnecessary system services, default shares, and vulnerable ports. |
| |
Intrusions on important nodes must be detected, and alerts must be provided for critical intrusion events. | The intrusion detection and alerting features of Security Center can meet this requirement. If you have other detection and alerting methods, you can provide evidence and ignore this item. | |
Restrict management terminals that are managed over the network by setting the connection type or address range. |
| |
Malware protection |
| Check whether Security Center is installed and used. If you have installed other anti-malware software, you can provide evidence and ignore this item. |
Use Alibaba Cloud Linux MLPS 2.0 Level 3
When you create an ACK cluster, you can enable MLPS Security Hardening. ACK automatically configures security hardening items for the cluster to meet the classified protection requirements for operating systems specified in the GB/T 22239-2019 Information Security Technology - Baseline for Classified Protection of Cybersecurity.

To meet the standard requirements of MLPS 2.0 Level 3, ACK creates three regular users by default in the hardened Alibaba Cloud Linux: `ack_admin`, `ack_audit`, and `ack_security`.
To comply with the standard requirements of MLPS 2.0 Level 3, MLPS 2.0 security-hardened Alibaba Cloud Linux prohibits logging on as the root user over SSH. You can use the ECS console to connect to an instance using VNC and create a regular user that can log on over SSH.
Configure a baseline check policy for Alibaba Cloud Linux MLPS 2.0 Level 3 images
Alibaba Cloud provides classified protection compliance baseline check standards and scanners for Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 and Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 MLPS 2.0 Level 3 images. This topic uses Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 as an example and describes how to configure a classified protection compliance baseline check policy to perform classified protection compliance baseline checks on ECS instances.
Prerequisites
You must have purchased a Security Center edition that supports baseline checks. For more information, see Purchase Security Center. Different editions of Security Center provide different levels of support for baseline checks. For more information, see Features.
Procedure
Log on to the Security Center console.
On the page, click Policy Management.
On the Policy Management panel, click the Baseline Check Policy tab to configure a baseline check policy for classified protection compliance as needed.
Set the baseline scan coverage level.
You can select one or more levels: High, Medium, and Low. This configuration applies to all scan policies.
Click Create Standard Policy. On the Baseline Check Policy panel, complete the configuration and click OK. The following list describes only the main configuration items. For more information, see Baseline risk check.
Policy Name: Enter a name for the policy, such as
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 Classified Protection Compliance Check. Select a Detection Cycle and a Check Start Time.Baseline Name: Search for and select
MLPS Level 3 - Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 Compliance Baseline.Scan Method: Select a scan mode for the servers. The options are:
Group: Scans servers by asset group. You can only select all servers in one or more groups.
ECS: Scans servers by ECS instance. You can select some or all servers from different groups.
Effective Server: Select the asset groups to which you want to apply the policy. Newly purchased servers are added to the Default group by default. To apply this policy to new assets, select Default.
After you configure the scan policy, you can also click Edit or Delete in the Actions column of the policy to modify or delete it as required.
NoteA deleted policy cannot be recovered. You cannot delete default policies or modify their baseline check items. You can only modify the start time and the servers to which a default policy applies.
Execute the baseline check policy.
On the page, click the System Baseline Risks tab. On the Baseline Check Policy tab, click the
 icon to expand the policy list. Select the configured classified protection compliance baseline check policy, and then click Check Now in the Check Item Scan section on the right.
icon to expand the policy list. Select the configured classified protection compliance baseline check policy, and then click Check Now in the Check Item Scan section on the right.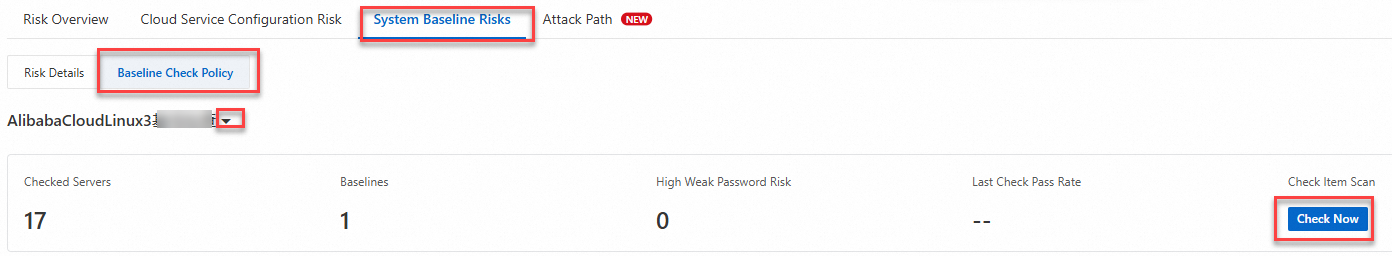
After you execute the scan policy, the Check Now button is unavailable until the scan is complete. After the baseline check is complete, go to the tab to view the check items that failed and their details. Fix the risk items promptly. For more information, see View and handle baseline risk items.