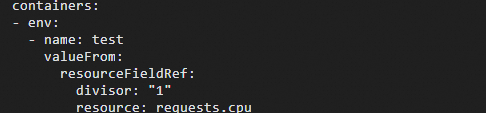
A deployment, also known as a stateless workload, is one of the most common workload types in Kubernetes. A deployment ensures that a specified number of pods run in the cluster in the state that you define. This topic describes how to create a stateless application in a Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster using the console and kubectl.
Before you begin
Before you create a workload, read Workloads to understand the basics of workloads and important considerations. This topic contains the following sections:
Create a deployment: Provides quick-start guides about how to create a deployment using the console and kubectl.
Configuration items: Provides links to the documentation about console configuration items and a sample YAML file for use with kubectl.
The examples in this topic use a public image. To pull a public image, your cluster or nodes must have Internet access:
Enable Internet access for the cluster (Recommended): Create an Internet NAT gateway for the VPC where the cluster resides. This provides Internet access to all resources in the cluster.
Assign a static public IP address to a node: A node with a public IP address can pull public images. However, you must assign a public IP address to every node where you deploy the workload.
Create a deployment
Create a deployment using the console
The following steps describe a simplified workflow for creating a workload. You can follow these steps to quickly deploy and verify the workload. After you are familiar with the basic operations, see Configuration items to customize your workload.
Configure basic information for the application
Log on to the Container Service for Kubernetes console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.On the Clusters page, click the name of the target cluster. In the navigation pane on the left, choose . On the Deployments page, click Create from Image.
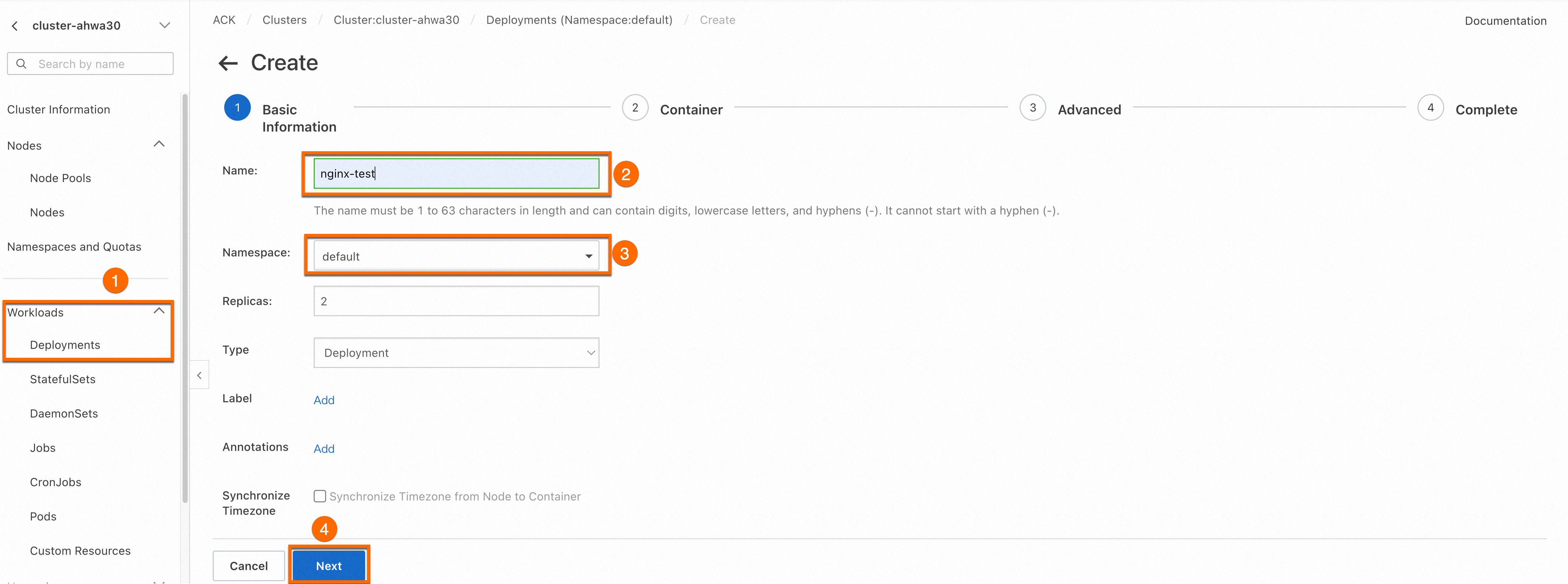
On the Basic Information page, set the basic information for the application, and then click Next to proceed to the Container page.
Configure the container
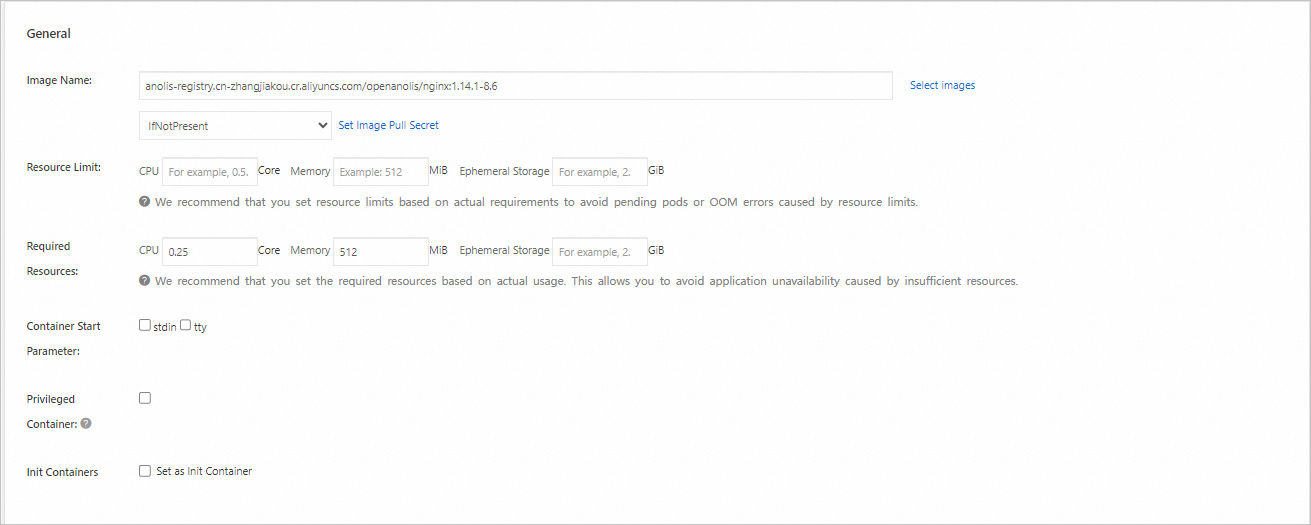
In the Container section, set the Image Name and Port. The other settings are optional. Keep the default values. Then, click Next to go to the Advanced page. The image address is shown below.
ImportantBefore you can pull this image, you must enable Internet access for the cluster. If you kept the default selection for Configure SNAT for VPC when you created the cluster, the cluster already has Internet access. Otherwise, see Enable Internet access for the cluster.
anolis-registry.cn-zhangjiakou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/nginx:1.14.1-8.6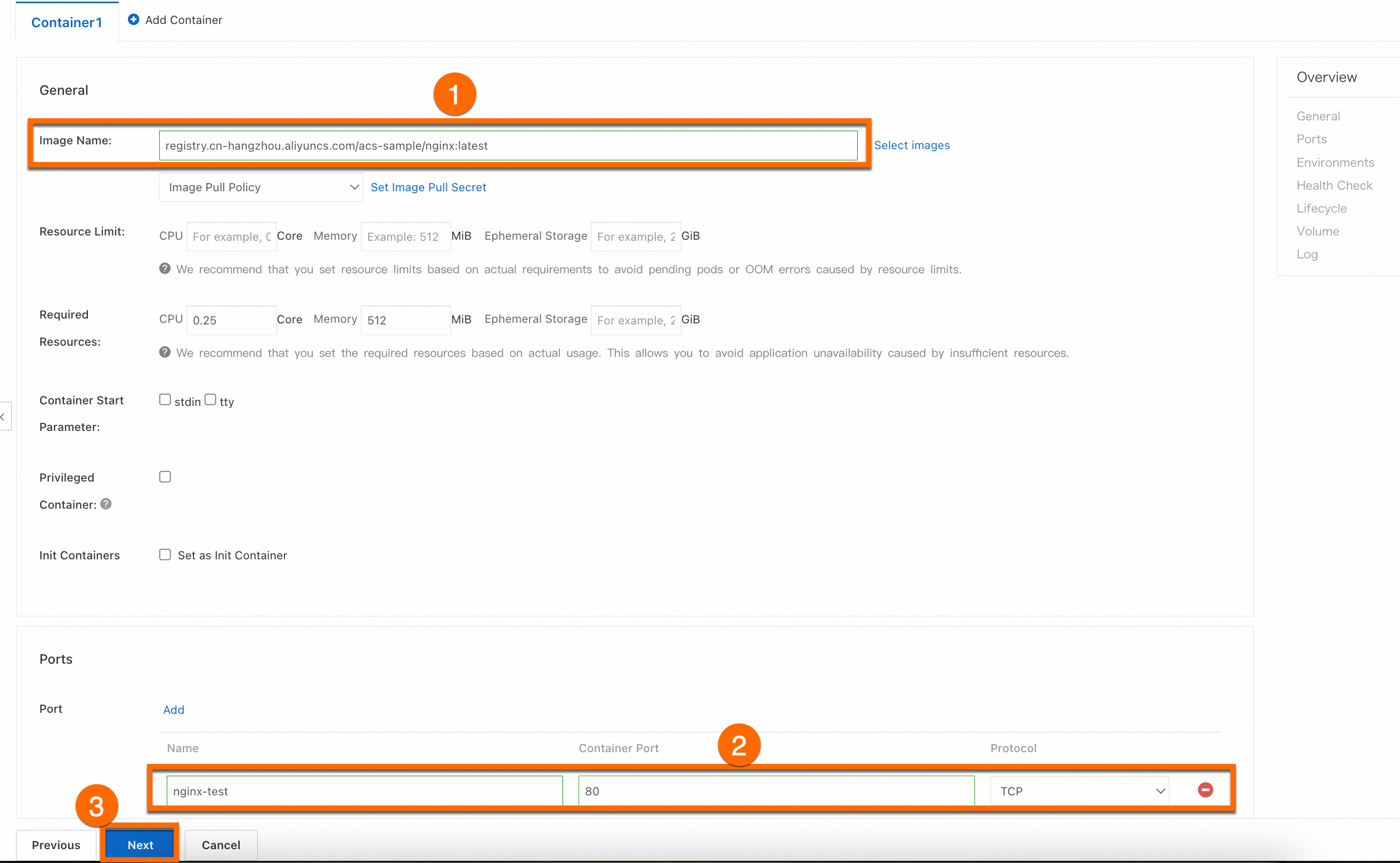
Complete the advanced configuration
On the Advanced page, click Create on the right side of Services to create a SLB type Service. Then, configure Scaling, Scheduling, Labels and Annotations, and click Create at the bottom of the page.
ImportantThis step creates a LoadBalancer service to expose the workload. The SLB instance that is used by this service incurs fees. For more information about billing, see Pay-as-you-go. If you do not plan to use this SLB instance later, release it promptly.
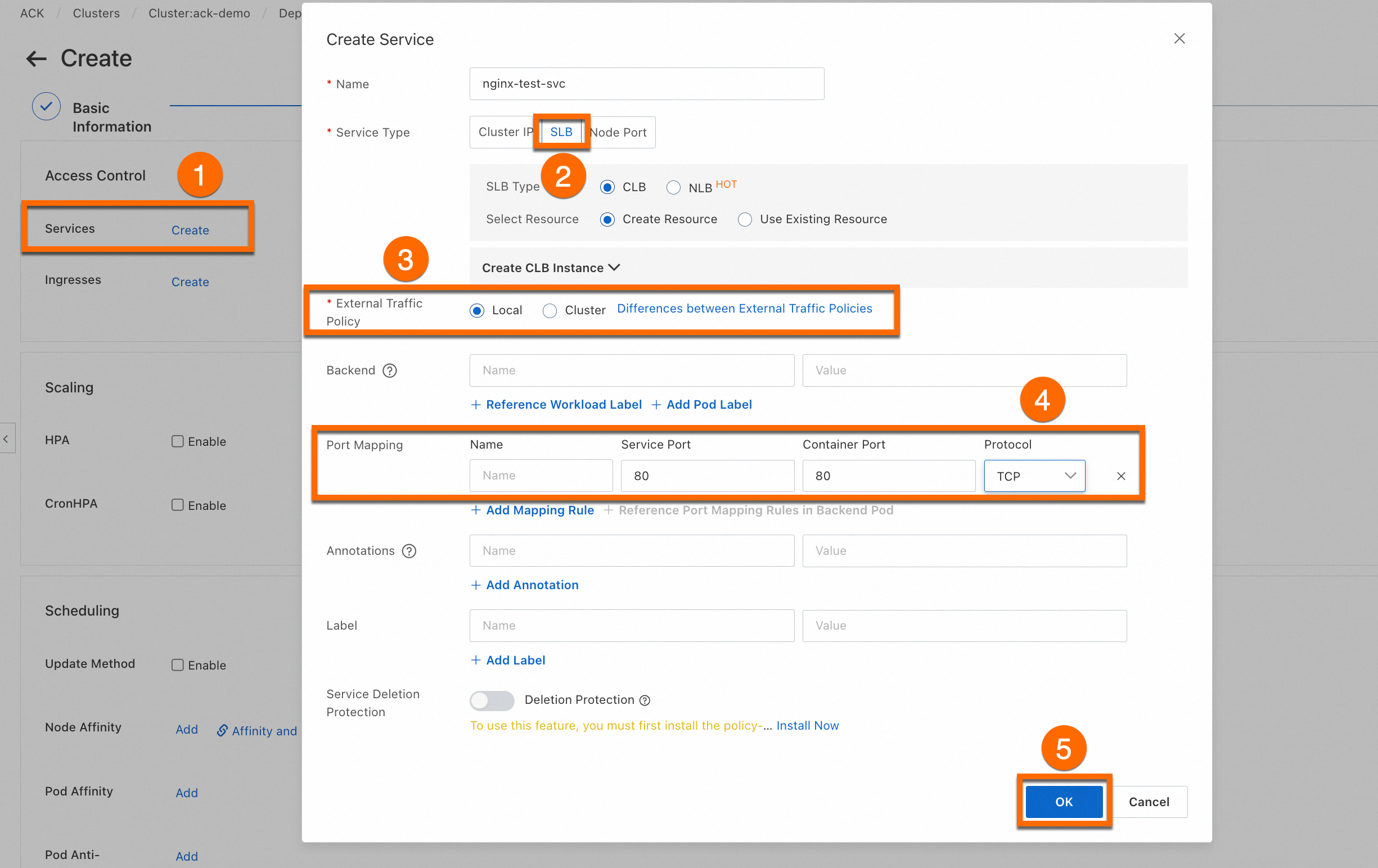
View the application
The Complete page displays the application task. In the Creation Task Submitted panel, click View Details. Click the Access Method tab. Find the newly created service (nginx-test-svc) and click the link in the External Endpoint column to access the service.
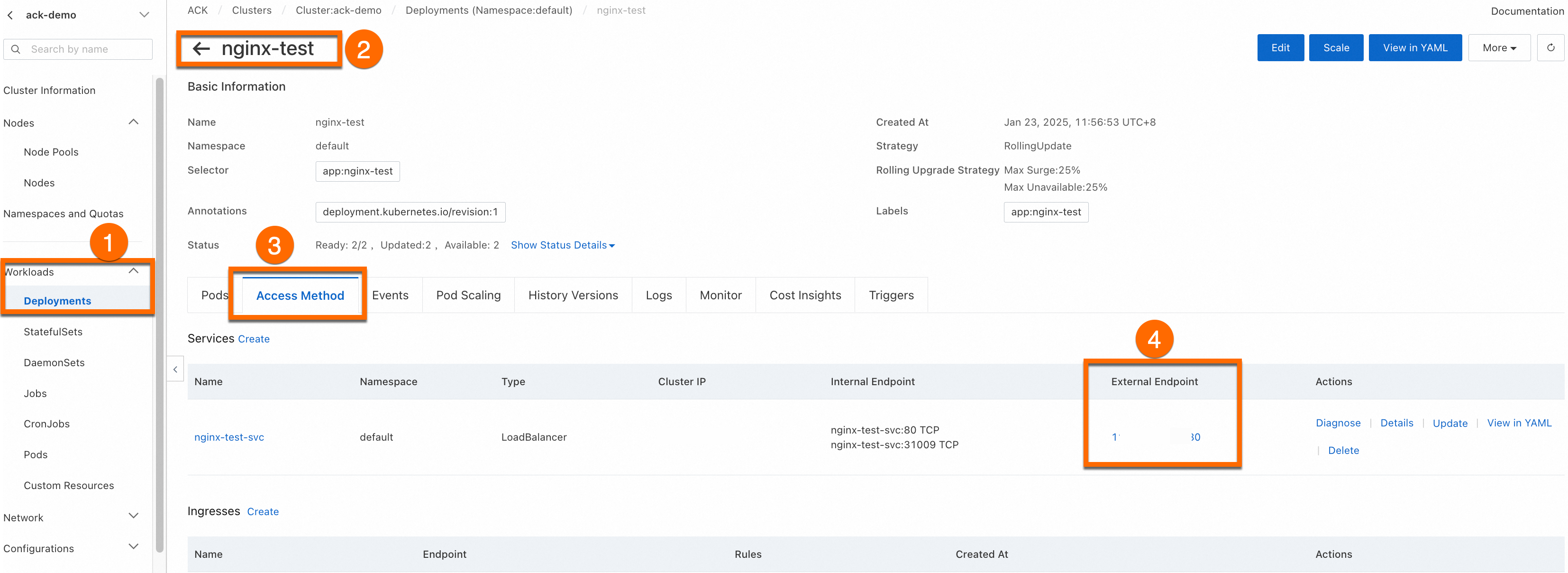
You can View, Edit, and Redeploy the created workload in the console.
Create a deployment using kubectl
Before you create a workload, make sure that you have connected to the cluster using kubectl. For more information, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
Copy the following YAML content and save it to a file named deployment.yaml. The YAML file defines a deployment and a
LoadBalancerservice to expose it.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment # Workload type metadata: name: nginx-test namespace: default # Change the namespace as needed labels: app: nginx spec: replicas: 2 # Specify the number of pods selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: # Pod configuration metadata: labels: # Pod labels app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx # Container name image: anolis-registry.cn-zhangjiakou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/nginx:1.14.1-8.6 # Use a specific version of the Nginx image ports: - containerPort: 80 # Port exposed by the container protocol: TCP # Specify the protocol as TCP or UDP. The default is TCP. --- # service apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx-test-svc namespace: default # Change the namespace as needed labels: app: nginx spec: selector: app: nginx # Match labels to ensure the service points to the correct pods ports: - port: 80 # Port provided by the service within the cluster targetPort: 80 # Points to the port listened to by the application inside the container (containerPort) protocol: TCP # Protocol. The default is TCP. type: LoadBalancer # Service type. The default is ClusterIP for internal access.Run the following command to create the deployment and service:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yamlExpected output:
deployment.apps/nginx-test created service/nginx-test-svc createdRun the following command to view the public IP address of the service:
kubectl get svcExpected output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 172.16.**.*** <none> 443/TCP 4h47m nginx-test-svc LoadBalancer 172.16.**.*** 106.14.**.*** 80:31130/TCP 1h10mIn a browser, enter the public IP address of Nginx (
106.14.**.***) to access the Nginx container of the workload.
Configuration items
Console configuration items
Basic information

Configuration Item | Description |
Name | The name of the workload. The names of the pods belonging to the workload are generated based on this name. |
Namespace | The namespace to which the workload belongs. |
Replicas | The number of pods in the workload. The default is 2. |
Type | The type of the workload. To choose a workload type, see Create a workload. |
Label | The labels of the workload. |
Annotations | The annotations of the workload. |
Synchronize Timezone | Specifies whether the container uses the same time zone as the node where it resides. |
Container
Advanced configuration
Configuration Card | Configuration Item | Description |
Access Control | Services | A service provides a fixed, unified Layer 4 (transport-layer) entry point for a group of pods. It is a required resource for exposing a workload. Services support multiple types, including Cluster IP, Node Port, and SLB. Before configuring a service, see Service management to understand the basics of services. |
Ingresses | An Ingress provides a Layer 7 (application layer) entry point for multiple services in a cluster and forwards requests to different services based on domain name matching. Before using an Ingress, you need to install an Ingress controller. ACK provides several options for different scenarios. See Comparison of Nginx Ingress, ALB Ingress, and MSE Ingress to make a selection. | |
Scaling | HPA | Triggers autoscaling by monitoring the performance metrics of containers. Metrics-based scaling helps you automatically adjust the total resources used by a workload when the business load fluctuates, scaling out to handle high loads and scaling in to save resources during low loads. For more information, see Use Horizontal Pod Autoscaling (HPA). |
CronHPA | Triggers workload scaling at scheduled times. This is suitable for scenarios with periodic changes in business load, such as the cyclical traffic peaks on social media after lunch and dinner. For more information, see Use CronHPA for scheduled horizontal pod autoscaling. | |
Scheduling | Upgrade Method | The mechanism by which a workload replaces old pods with new ones when the pod configuration changes.
|
| Affinity, anti-affinity, and toleration configurations are used for scheduling to ensure pods run on specific nodes. Scheduling operations are complex and require advance planning based on your needs. For detailed operations, see Scheduling. | |
Labels and Annotations | Pod Labels | Adds a label to each pod belonging to this workload. Various resources in the cluster, including workloads and services, match with pods through labels. ACK adds a default label to pods in the format |
Pod Annotations | Adds an annotation to each pod belonging to this workload. Some features in ACK use annotations. You can edit them when using these features. |
Sample workload YAML file
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment # Workload type
metadata:
name: nginx-test
namespace: default # Change the namespace as needed
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 2 # Specify the number of pods
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template: # Pod configuration
metadata:
labels: # Pod labels
app: nginx
annotations: # Pod annotations
description: "This is an application deployment"
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx # Image name
image: nginx:1.7.9 # Use a specific version of the Nginx image
ports:
- name: nginx # name
containerPort: 80 # Port exposed by the container
protocol: TCP # Specify the protocol as TCP or UDP. The default is TCP.
command: ["/bin/sh"] # Container start command
args: [ "-c", "echo $(SPECIAL_LEVEL_KEY) $(SPECIAL_TYPE_KEY) && exec nginx -g 'daemon off;'"] # Output variables, add command to start nginx
stdin: true # Enable standard input
tty: true # Allocate a virtual terminal
env:
- name: SPECIAL_LEVEL_KEY
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: special-config # Name of the configuration item
key: SPECIAL_LEVEL # Key name of the configuration item
securityContext:
privileged: true # true enables privileged mode, false disables it. The default is false.
resources:
limits:
cpu: "500m" # Maximum CPU usage, 500 millicores
memory: "256Mi" # Maximum memory usage, 256 MiB
ephemeral-storage: "1Gi" # Maximum ephemeral storage usage, 1 GiB
requests:
cpu: "200m" # Minimum requested CPU usage, 200 millicores
memory: "128Mi" # Minimum requested memory usage, 128 MiB
ephemeral-storage: "500Mi" # Minimum requested ephemeral storage usage, 500 MiB
livenessProbe: # Liveness probe configuration
httpGet:
path: /
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
readinessProbe: # Readiness probe configuration
httpGet:
path: /
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 10
volumeMounts:
- name: tz-config
mountPath: /etc/localtime
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: tz-config
hostPath:
path: /etc/localtime # Mount the host's /etc/localtime file to the same path in the container using volumeMounts and volumes fields.
---
# service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-test-svc
namespace: default # Change the namespace as needed
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
selector:
app: nginx # Match labels to ensure the service points to the correct pods
ports:
- port: 80 # Port provided by the service within the cluster
targetPort: 80 # Points to the port listened to by the application inside the container (containerPort)
protocol: TCP # Protocol. The default is TCP.
type: ClusterIP # Service type. The default is ClusterIP for internal access.
---
# ingress
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
namespace: default # Change the namespace as needed
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx" # Specify the Ingress controller type
# If using Alibaba Cloud SLB Ingress controller, you can specify the following:
# service.beta.kubernetes.io/alibaba-cloud-loadbalancer-id: "lb-xxxxxxxxxx"
# service.beta.kubernetes.io/alibaba-cloud-loadbalancer-spec: "slb.spec.s1.small"
spec:
rules:
- host: foo.bar.com # Replace with your domain name
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx-service # Backend service name
port:
number: 80 # Backend service port
tls: # Optional, for enabling HTTPS
- hosts:
- foo.bar.com # Replace with your domain name
secretName: tls-secret # TLS certificate Secret nameReferences
For applications that require stable persistent storage, such as databases, you can use a StatefulSet. For more information, see Create a stateful workload (StatefulSet).
If you encounter issues when you create a workload, see Workload FAQ.
If a pod is abnormal, see Troubleshoot pod exceptions.