In September 2025, the open-source PolarDB-X project officially released version 2.4.2. This release focuses on enhancing its integration with the surrounding ecosystem, including a new client driver (PolarDB-X Connector) and the newly open-sourced polardbx-proxy component. It also introduces optimizations for database operations and stability, with proven practices for scenarios involving hundred-billion-row tables, and includes fixes for multiple issues related to online DDL changes, database scaling, and data TTL. For details, please refer to the ChangeLog[1].
PolarDB for Xscale (PolarDB-X) is a cloud-native database product developed by Alibaba Cloud that integrates both centralized and distributed architectures. It employs a shared-nothing architecture based on the separation of storage and compute, supporting capabilities like horizontal scaling, distributed transactions, and mixed workloads. It is characterized by financial-grade high availability, high throughput, large storage capacity, low latency, easy scalability, and high compatibility with the MySQL system and its ecosystem. For more information on its features and capabilities, please see the related product documentation[2].
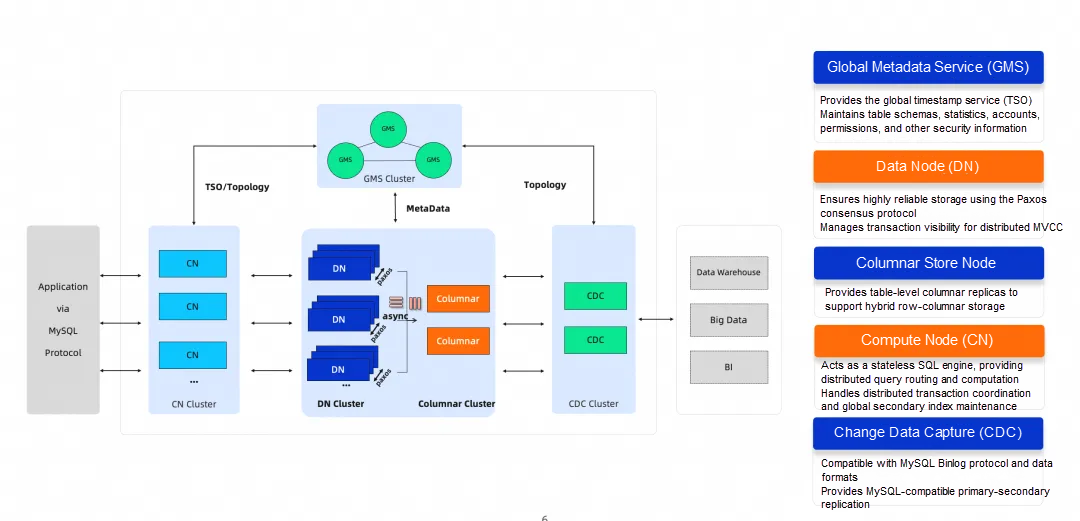
PolarDB-X Architecture
PolarDB is available in various product forms: public cloud, private cloud, DBStack, and a lightweight edition (software-only deployment). These different product offerings share the same kernel version, which allows them to fully leverage the management and rapid iteration advantages of the public cloud product, ensuring business compatibility for customers whether on-cloud or on-premises and reducing database management costs.
In October 2021, Alibaba Cloud announced the open-sourcing of its cloud-native distributed database, PolarDB-X, under a full-kernel open-source model. The open-sourced content includes the compute engine, storage engine, log engine, columnar engine, and more. For details on its open-source journey, visit the PolarDB Open Source Community[3].
polardbx-proxy is a high-performance proxy for PolarDB-X Standard Edition, developed in Java. It provides features such as automatic primary node detection, seamless high availability (HA) failover, read-write splitting, and instance-level connection pooling. It can be deployed in front of PolarDB-X Standard Edition to offer a simpler and more convenient user experience. (Open-source address [4])
Supported features:
• Read-write splitting & load balancing based on active requests
• Consistent reads from replicas
• Transaction-level connection pool
• Support for fast HA detection & idempotent connection retry
• Support for Prepared Statement performance enhancement & passthrough
You can pull and run polardbx-proxy with a single command using a Docker image.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/polardb/polardbx-proxy/refs/heads/main/polardbx-proxy/quick_start.sh
quick_start.sh -e backend_address=127.0.0.1:3306 -e backend_username=appuser -e backend_password=appuser -e memory=4294967296• backend_address: The database address (format: ip:port, can be the leader or a follower address).
• backend_username: The database username.
• backend_password: The database password (a password is required and must use mysql_native_password authentication).
• memory: Memory allocated to the proxy (unit: bytes; please configure correctly to avoid OOM errors. 16 GB is recommended, with a minimum of 4 GB).
With minimal configuration, you can connect directly to the default port, 3307.
mysql -Ac -h127.1 -P3307 -uappuser -pappuserThe overall experience is nearly identical to connecting directly to PolarDB-X Standard Edition. It seamlessly adapts to the database's usernames, schemas, etc. Note that polardbx-proxy only supports connecting to a single PolarDB-X instance (with multiple replicas) and does not support connecting to different PolarDB-X instances.
Useful management commands:
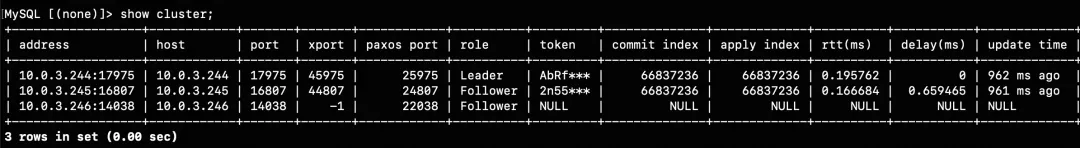
1. show cluster (Query backend PolarDB-X Paxos cluster information)
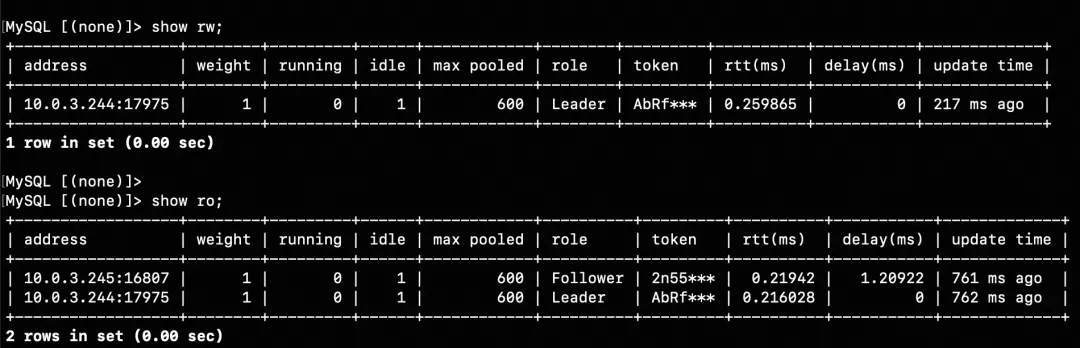
2. show rw / show ro (Query the proxy's connection pool status)
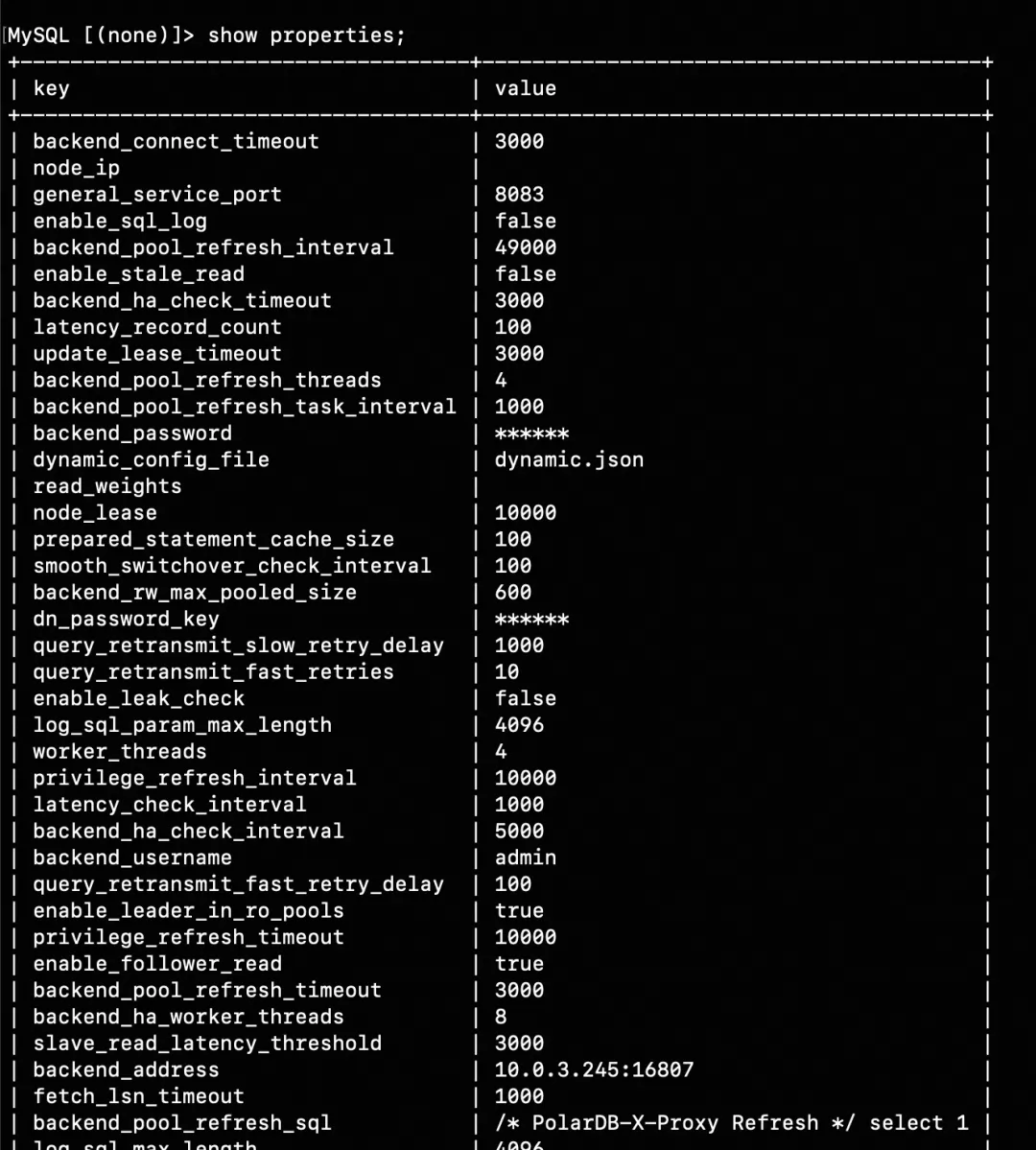
3. show properties (Query the proxy's configuration parameters)
We purchased a set of ECS instances for testing: three instances (32C128G each) to deploy PolarDB-X Standard Edition, and one instance (32C64G) to deploy the proxy. We then benchmarked the proxy's performance, focusing on its SQL forwarding capabilities in the simplest scenario (sysbench's oltp_point_select).
| Test Scenario sysbench oltp_point_select | 1000 concurrent threads |
|---|---|
| Direct connection to PolarDB-X Standard Edition (no proxy) QPS: 1100089.10 | DB CPU: 98% |
| Proxy with out-of-the-box settings (read-write splitting + full SQL audit enabled by default) QPS: 769210.60 | Proxy CPU: 80% |
| Proxy with out-of-the-box settings + read-write splitting enabled + SQL audit disabled QPS: 1094244.83 | Proxy CPU: 90% |
| Proxy with out-of-the-box settings + read-write splitting enabled + delayed reads from replicas + SQL audit disabled QPS: 1284683.56 | Proxy CPU: 98% |
| Proxy with out-of-the-box settings + read-write splitting disabled + SQL audit disabled QPS: 1081086.38 | Proxy CPU: 90% |
Conclusions:
The PolarDB-X Connector provides driver implementations in multiple languages, allowing for easy integration into applications. It offers features like automatic primary node detection, seamless HA failover, read-write splitting, and load balancing. Compared to using polardbx-proxy, this approach reduces the need for deploying additional proxy resources.
Supported features:
• Multi-language support, including JDBC, Go, and C++.
• Direct connection to PolarDB-X 2.0 Standard Edition, with automatic reconnection to the new primary after an HA event and seamless failover.
• Direct connection to PolarDB-X 2.0 Enterprise Edition, with load balancing across multiple nodes.
| Client-side driver | Software Address |
| Java | https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/alibaba/polardbx/polardbx-connector-java |
| GO | https://github.com/polardb/polardbx-connector-go |
| C++ | https://github.com/polardb/polardbx-connector-cpp |
Taking the JDBC driver as an example, refer to the JDBC usage documentation[5].
A simple Maven usage example:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.polardbx</groupId>
<artifactId>polardbx-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>2.2.10</version>
</dependency>JDBC URL Example:
jdbc:polardbx://11.167.60.147:6991/test● Driver Class Name: com.alibaba.polardbx.Driver
● Protocol Header: polardbx
● IP Address and Port Specification:
1. Directly connect to PolarDB-X using the driver
Class.forName("com.alibaba.polardbx.Driver");
try (final Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:polardbx://127.0.0.1:3306/", "root", "*****");
final Statement stmt = conn.createStatement()) {
try (final ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select 1")) {
for (int i = 0; i < rs.getMetaData().getColumnCount(); ++i) {
System.out.print(rs.getMetaData().getColumnName(i + 1) + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
while (rs.next()) {
for (int i = 0; i < rs.getMetaData().getColumnCount(); ++i) {
System.out.print(rs.getObject(i + 1) + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}2. Use the Druid Connection Pool
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.alibaba.polardbx.Driver" />
<!-- Basic properties: URL, user, password -->
<property name="url" value="jdbc:polardbx://ip:port/db?autoReconnect=true&rewriteBatchedStatements=true&socketTimeout=30000&connectTimeout=3000" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
<!-- Configure initial, min, and max sizes -->
<property name="maxActive" value="20" />
<property name="initialSize" value="3" />
<property name="minIdle" value="3" />
<!-- maxWait: Timeout for waiting to get a connection -->
<property name="maxWait" value="60000" />
<!-- timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: Interval for detecting and closing idle connections (in ms) -->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="60000" />
<!-- minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: Minimum idle time for a connection in the pool (in ms)-->
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="300000" />
<!-- SQL query to validate connection availability -->
<property name="validationQuery" value="select 'z' from dual" />
<!-- Whether to enable idle connection checks -->
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="true" />
<!-- Whether to check connection status before borrowing -->
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="false" />
<!-- Whether to check connection status when returning -->
<property name="testOnReturn" value="false" />
<!-- Whether to close connections after a fixed time. Helps balance backend nodes. -->
<property name="phyTimeoutMillis" value="600000" />
<!-- Whether to close connections after a fixed number of SQL executions. Helps balance backend nodes.-->
<property name="phyMaxUseCount" value="10000" />
</bean>Go driver polardbx-connector-go installation:
go get github.com/polardb/polardbx-connector-goUsage Example:
import (
_ "github.com/polardb/polardbx-connector-go"
)
db, err := sql.Open("polardbx", "user:password@tcp(ip:port)/dbname")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
db.SetConnMaxLifetime(time.Minute * 3)
db.SetMaxOpenConns(10)
db.SetMaxIdleConns(10)PolarDB-X, in combination with the polardbx-connector-java driver, provides seamless failover capabilities for the database.
For example, when a DBA performs a planned maintenance operation to take the primary node offline, the database will undergo an expected HA failover. With the seamless failover capability of PolarDB-X and its driver, business SQL queries will not be interrupted or report errors, greatly improving the application's experience with the database.
How Seamless Failover Works:
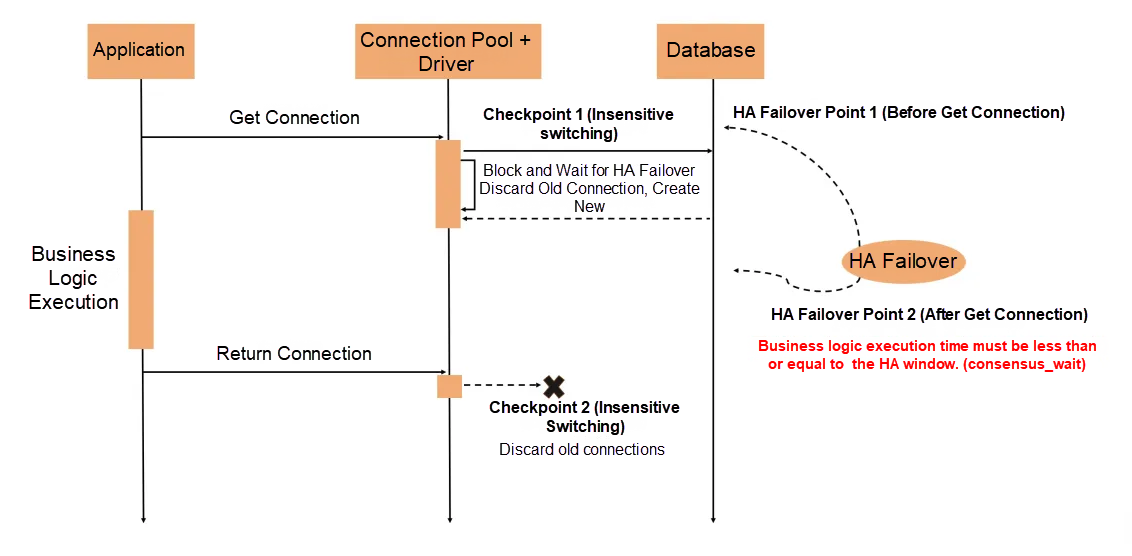
The seamless failover provided by PolarDB-X works by allowing the driver to perceive the state of the three-node PolarDB-X Standard Edition cluster in real-time. Before the HA failover is complete:
• The client driver blocks the allocation of new connections until the failover is finished.
• For connections already held by the application, it ensures requests are completed as quickly as possible and then marks the connections as non-reusable.
Precautions:
• The client driver adds two checkpoints for seamless failover (when getting a connection and when returning one). By perceiving the cluster state in real-time, it dynamically rebuilds connections after an HA event. This only increases the time it takes to acquire a new connection but does not cause errors for requests on existing connections, achieving a seamless experience during planned failovers.
• For applications that have acquired a database Connection, it is recommended to use standard try-with-resources for database operations. As long as the business logic within the try block executes in less time than the HA window configured in PolarDB-X (the consensus_wait_millisecond_before_change_leader threshold, default is 1 second), it will not fail due to a planned failover. However, long-running transactions that hold a connection longer than this threshold will span the failover process and fail afterward because they can no longer write.
• Currently, the seamless failover capability of PolarDB-X is recommended for use with Druid [6] version 1.2.24 or later.
For migrating self-managed MySQL to PolarDB-X, PolarDB-X offers excellent compatibility. A primary user demand is for a standard solution for data migration and reverse replication. In its commercial version, PolarDB-X provides professional data migration and synchronization tools, such as Alibaba's self-developed DTS. For a complete guide, see the official solution documentation: "Solution: Migrating Self-Managed MySQL to PolarDB-X"[7].
PolarDB-X also provides a manual migration solution compatible with the open-source MySQL ecosystem, which is suitable for DBAs familiar with MySQL. Full data synchronization can be done using mysqldump, but the main challenge lies in incremental synchronization and reverse replication.
In v2.4.2, PolarDB-X now supports primary-replica replication compatible with open-source MySQL, enabling incremental synchronization based on MySQL's Binlog replication. In this setup, the primary is a MySQL source database, and the replica is the Leader node of a PolarDB-X DN (Data Node) as the target.
1. On the primary MySQL instance:
#1. On the primary instance, create a user for replication.
create user rep identified with mysql_native_password by '123456';
grant replication slave on *.* to rep;
#2. Display the list of registered replica hosts on the primary.
mysql> show slave hosts;
Empty set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)2. On the PolarDB-X replica (on the Leader node):。
#3.Filter out system databases that do not need to be synchronized, such as old heartbeat tables.
# Add the following parameters to the replica's cnf file and restart for them to take effect.
replicate_ignore_db=aaa:mysql
replicate_ignore_db=aaa:sys
replicate_ignore_db=aaa:__recycle_bin__
replicate_ignore_db=aaa:information_schema
replicate_ignore_db=aaa:performance_schema
#4. On the replica, stop the previously created 'aaa' channel.
stop slave for channel 'aaa';
reset slave all for channel 'aaa';
#5. Configure the replication channel 'aaa'. master_host and master_port are the host and port of the primary.
#master_user is the replication account created earlier.
change master to master_host = '127.0.0.1', master_port = 13050, \
master_user = 'rep', master_password = '123456', \
master_auto_position=1 \
for channel 'aaa';
#6. Verify that Slave_IO_Running and Slave_SQL_Running are both 'No' for this channel.
show slave status for channel 'aaa'\G
#7. On the replica's leader node, start the 'aaa' replication channel.
start slave for channel 'aaa';
#8. Verify that Slave_IO_Running and Slave_SQL_Running are both 'Yes' for this channel.
show slave status for channel 'aaa'\G3. Back on the primary MySQL instance:
#9. Log in to the primary and display the list of registered replica hosts.
mysql> show slave hosts;
+-----------+------+-------+-----------+--------------------------------------+
| Server_id | Host | Port | Master_id | Slave_UUID |
+-----------+------+-------+-----------+--------------------------------------+
| 10 | | 13060 | 2 | 26663b57-91e6-11f0-8700-b8599f3009a8 |
+-----------+------+-------+-----------+--------------------------------------+
1row in set(0.00 sec)1. On the PolarDB-X primary (on the Leader node):
#1. Check the latest binlog file.
mysql> show consensus logs;
+---------------+-----------+-----------------+
| Log_name | File_size | Start_log_index |
+---------------+-----------+-----------------+
| binlog.000001 | 15777 | 1 |
| binlog.000002 | 7611 | 44 |
+---------------+-----------+-----------------+
2rows in set(0.00 sec)
#2. Find the End_log_pos of the last event in the latest binlog file.
mysql> show binlog events in 'binlog.000002';
+---------------+------+--------------------------+-----------+-------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| Log_name | Pos | Event_type | Server_id | End_log_pos | Info |
+---------------+------+--------------------------+-----------+-------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| binlog.000002 | 4 | Format_desc | 10 | 190 | Server ver: 8.0.32-X-Cluster-8.4.20-20241014, Binlog ver: 4 |
| binlog.000002 | 190 | Previous_consensus_index | 10 | 221 | ##PREV_CONSENSUS_INDEX: 44' |
| binlog.000002 | 221 | Previous_gtids | 10 | 332 | 37a1bb4b-91f9-11f0-b12d-b8599f3009a8:1-30,
902b4fe0-92a4-11f0-92ea-b8599f3009a8:1-11 |
.......
| binlog.000002 | 7580 | Xid | 3 | 7611 | COMMIT /* xid=237 */ |
+---------------+------+--------------------------+-----------+-------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
78rows in set(0.00 sec)2. On the MySQL replica:
#3.Filter out system databases that do not need to be synchronized.
# Add the following parameters to the replica's cnf file and restart for them to take effect.
replicate_ignore_db=mysql
replicate_ignore_db=sys
replicate_ignore_db=__recycle_bin__
replicate_ignore_db=information_schema
replicate_ignore_db=performance_schema
#4. On the replica, stop the previously created 'bbb' channel.
stop slave for channel 'bbb';
reset slave all for channel 'bbb';
#5. Configure the replication channel 'bbb'. master_host and master_port are the host and port of the primary.
#master_log_file and master_log_pos are the values obtained from the primary above.
change master to master_host = '127.0.0.1', master_port = 13050, \
master_user = 'rep', master_password = '123456', \
master_log_file='binlog.000002' \
master_log_pos=7611 \
for channel 'bbb';
#6. Verify that Slave_IO_Running and Slave_SQL_Running are both 'No' for this channel.
show slave status for channel 'bbb'\G
#7. On the replica, start the 'bbb' replication channel.
start slave for channel 'bbb';
#8. Verify that Slave_IO_Running and Slave_SQL_Running are both 'Yes' for this channel.
show slave status for channel 'bbb'\G3. Back on the PolarDB-X primary (on the Leader node):
#9. Log in to the primary and display the list of registered replica hosts.
mysql> show slave hosts;
+-----------+------+-------+-----------+--------------------------------------+
| Server_id | Host | Port | Master_id | Slave_UUID |
+-----------+------+-------+-----------+--------------------------------------+
| 1 | | 13010 | 2 | 902b4fe0-92a4-11f0-92ea-b8599f3009a8 |
+-----------+------+-------+-----------+--------------------------------------+
1row in set(0.00 sec)PolarDB-X uses the X-Paxos protocol, replacing the traditional binlog-based primary-replica replication of MySQL. It introduces its own log management mechanism, merging binlog and relay log into a binlog-based format and providing the show consensus log command.
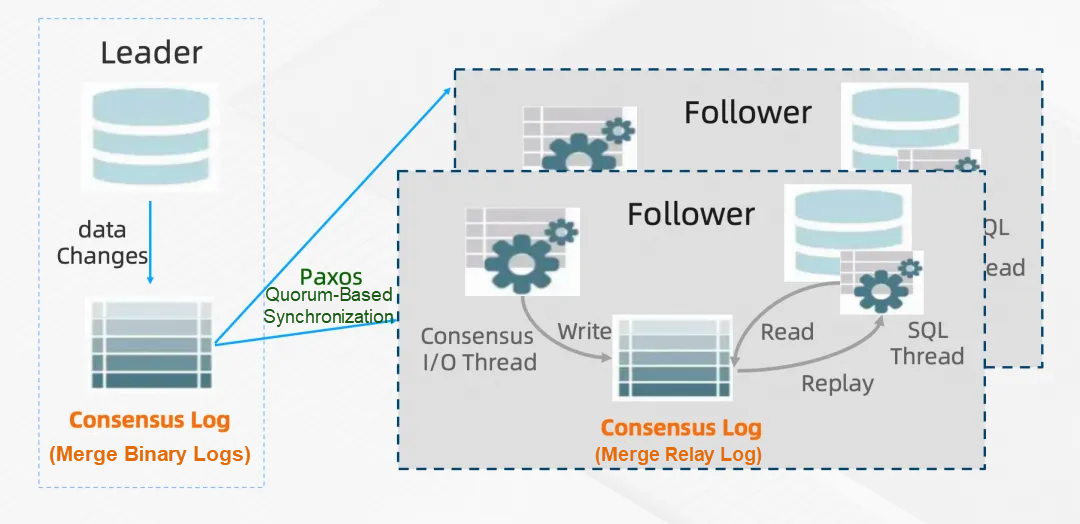
A common issue for open-source users was the management of incremental logs in PolarDB-X. Accustomed to the automatic binlog cleanup mechanism in MySQL, they found it didn't work in early PolarDB-X versions, leading to several instances of full disks.
In PolarDB-X v2.4.2, compatibility with MySQL's expire_logs_days is introduced.
[mysqld]
expire_logs_days = 7PolarDB-X v2.4.2 further expands its open-source ecosystem capabilities by launching the PolarDB-X Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server, designed specifically for interaction between AI Agents and the PolarDB-X database. The PolarDB-X MCP Server provides a standardized set of tools and resources to help developers efficiently build intelligent database applications.
Open-source address: https://github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-polardbx-mcp-server/?utm_content=g_1000407378
Currently, the PolarDB-X MCP Server offers the following tools and resources:
Tools:
• SQL Query Execution: AI agents can run SQL queries directly through the query interface.
• Database Status Monitoring: Real-time access to PolarDB-X cluster status (e.g., QPS, slow SQL count, node load) to assist with dynamic tuning.
• Command Management: Provides the operational commands and syntax specifications supported by PolarDB-X for large models to use.
Resources:
• Schema Information Query: Provides table structure information in JSON format, including column names, data types, and index definitions. For example, polardbx://<database_name>/<table_name> allows an AI Agent to quickly parse complex table structures and generate context-aware query suggestions.
Based on the capabilities provided by the PolarDB-X MCP Server, developers can build powerful AI Agents around PolarDB-X for scenarios such as:
• Intelligent Database Operations: An AI Agent retrieves database status and schema information via the MCP Server to automatically diagnose performance bottlenecks (like uneven data distribution or deadlocks) and generate repair suggestions.
• Data Agent / Chat BI: Connect to a read-only instance of PolarDB-X via the SQL interface to provide data analysis and reporting services.
• Vibe Coding / Low-code Development: AI tools use the MCP Server's schema query interface to automatically parse database structures and generate code snippets that match the actual version. The SQL execution interface allows AI tools to automatically validate the correctness of SQL.
The PolarDB-X MCP Server is now published to the npm package repository and can be installed and deployed with a single npm command:
1. Install with npm:
# Install globally
npm install -g polardbx-mcp
# Or install in current project only
npm install polardbx-mcp2. Use in an MCP client with the following configuration:
{
"mcpServers": {
"polardbx-mcp": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"polardbx-mcp"
],
"env": {
"POLARDB_X_HOST": "your_database_host",
"POLARDB_X_PORT": "your_database_port",
"POLARDB_X_USER": "your_database_user",
"POLARDB_X_PASSWORD": "your_database_password",
"POLARDB_X_DATABASE": "your_database_name"
},
}
}
}PolarDB-X remains committed to independent research, development, and innovation, offering 100% compatibility with native community ecosystems and mainstream database management tools. It supports various disaster recovery architectures, including same-city and remote disaster recovery. For more details, please visit our official website [9].
[1] https://github.com/polardb/polardbx-sql/releases/tag/polardbx-sql-5.4.19-20250822-17558320
[3] https://openpolardb.com/about
[4] https://github.com/polardb/polardbx-proxy
[5] https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/11275225196
[7] https://www.aliyun.com/solution/tech-solution/mysql-migration-polardb-x?utm_content=g_1000407382
[8] https://github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-polardbx-mcp-server/?utm_content=g_1000407378
[9] https://www.aliyun.com/activity/database/polardbx-v2?utm_content=g_1000407377
Alibaba Clouder - September 28, 2020
ApsaraDB - July 23, 2021
ApsaraDB - January 17, 2025
ApsaraDB - January 3, 2024
ApsaraDB - June 19, 2024
ApsaraDB - June 19, 2024
 PolarDB for MySQL
PolarDB for MySQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for MySQL is a cloud-native relational database service 100% compatible with MySQL.
Learn More PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn More PolarDB for Xscale
PolarDB for Xscale
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for Xscale (PolarDB-X) is a cloud-native high-performance distributed database service independently developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More Managed Service for Prometheus
Managed Service for Prometheus
Multi-source metrics are aggregated to monitor the status of your business and services in real time.
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB