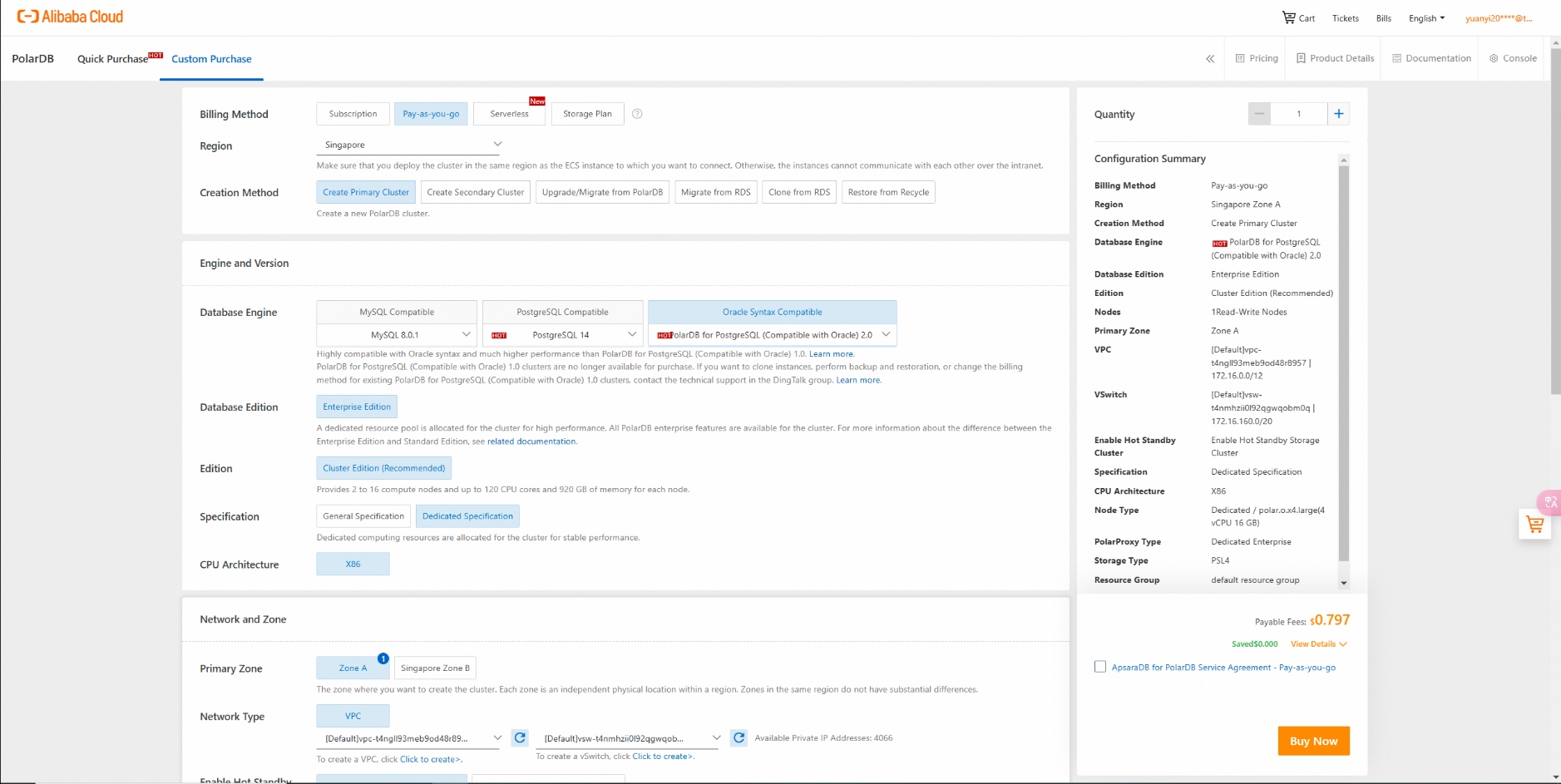
Purchase PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle):
Instance details:
Instance Monitoring page:
Create Account page:
Create Database page:
Check the time zone of the source Oracle database and change it to UTC+8.
Time zone modification command: alter database set time_zone='+8:00';

To check whether the archive mode is enabled for the Oracle database, you can use one of the following methods:
You can query the LOG_MODE column in the V$DATABASE view to see the archive mode status of the database.
SELECT log_mode FROM v$database;This query will return one of the following results:
• NOARCHIVELOG: indicates that the archive mode is not enabled for the database.
• ARCHIVELOG: indicates that the archive mode is enabled for the database.

Run the ARCHIVE LOG LIST command in SQL*Plus to view the archive mode status of the database.
ARCHIVE LOG LIST;Running this command will output status information about archived logs, including the current archive mode.

The query statement. If the value of the SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_ALL column is YES, the full supplemental logging is enabled.
SELECT SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_MIN,
SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_PK,
SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_UI,
SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_FK,
SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_ALL
FROM V$DATABASE;• SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_MIN: whether minimal supplemental logging is enabled.
• SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_PK: whether primary key supplemental logging is enabled.
• SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_UI: whether unique key supplemental logging is enabled.
• SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_FK: whether foreign key supplemental logging is enabled.
• SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_ALL: whether full supplemental logging is enabled.
Run the following statement to enable this feature:
ALTER DATABASE ADD SUPPLEMENTAL LOG DATA (ALL) COLUMNS;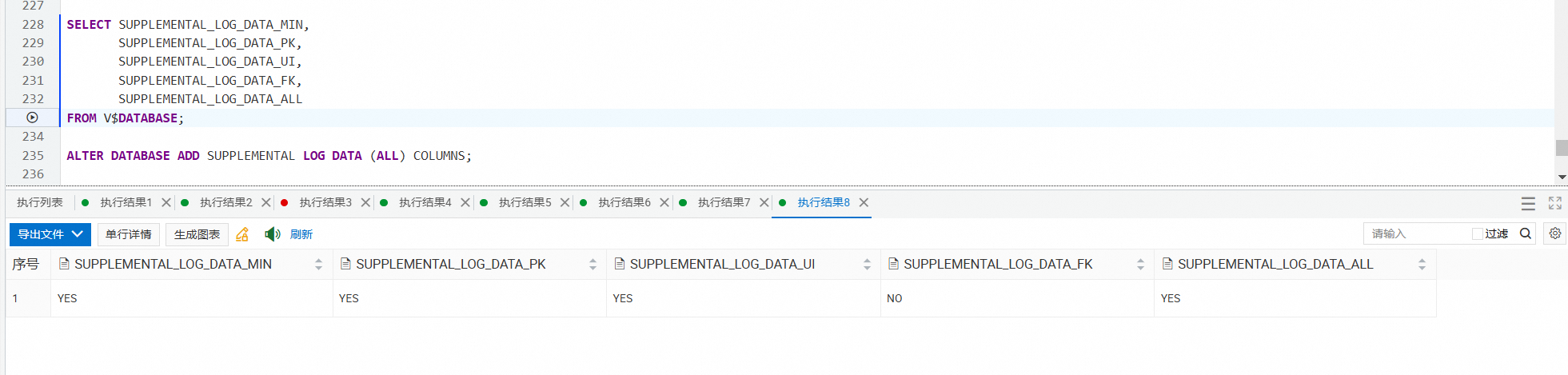
purge recyclebin;
Create test data in the self-managed Oracle database:
Insert data:
Test data generation script
drop table tb_test1;
drop table tb_lob;
drop table tb_part_range;
drop table tb_part_list;
drop table tb_part_hash;
drop table tb_subpart_hash;
drop table tb_part_interval;
drop table tb_range;
drop table tb_list;
drop table tmp_transaction;
drop type TYPE_STR_AGG;
drop table sample_table;
drop procedure INSERT_PROGRAM;
drop function FUN_VISURL;
drop package CMS_PICTURE_VIEW_PARAMS;
drop sequence VAS_AGAINST_MATCHS_SEQ;
drop view CMS_BASE_CONTENT_VIEW;
-- TABLE
create table tb_test1
(
id number(10),
dt date,
time_st timestamp,
chr1 char(20),
str varchar2(20 byte),
str2 varchar2(20 char),
xml xmltype
);
create table tb_lob(
id NUMBER,
f_clob CLOB,
f_blob BLOB,
crt_time DATE,
constraint pk_tab_lob primary key(id)
);
CREATE GLOBAL TEMPORARY TABLE tmp_transaction(
ID NUMBER,
NAME VARCHAR2(20),
CRT_TIME DATE,
CONSTRAINT pk_tmp_transaction PRIMARY KEY(ID)
) ON COMMIT DELETE ROWS;
CREATE TABLE tb_part_range
(
dept_no number,
part_no varchar2(20),
country varchar2(20),
sale_year number,
sale_month number,
sale_day number,
amount number
)
PARTITION BY RANGE(sale_year, sale_month)
(
PARTITION q1_2019 VALUES LESS THAN(2019, 4),
PARTITION q2_2019 VALUES LESS THAN(2019, 7),
PARTITION q3_2019 VALUES LESS THAN(2019, 10),
PARTITION q4_2019 VALUES LESS THAN(2020, 1),
PARTITION pmax VALUES LESS THAN(MAXVALUE,MAXVALUE)
);
CREATE TABLE tb_part_list(
dept_no number,
part_no varchar2(20),
country varchar2(20),
dtime date,
amount number
)
PARTITION BY LIST(country)(
PARTITION europe VALUES('FRANCE', 'ITALY'),
PARTITION asia VALUES('INDIA', 'PAKISTAN'),
PARTITION americas VALUES('US', 'CANADA')
);
CREATE TABLE tb_part_hash(
dept_no number,
part_no varchar2(20),
country varchar2(20),
dtime date,
amount number
)PARTITION BY HASH(part_no)(
PARTITION p1,
PARTITION p2,
PARTITION p3
);
create table tb_part_interval (
id NUMBER,
name VARCHAR2(20),
crt_time date)
partition by range (crt_time) interval (numtoyminterval(1,'month'))
(
partition P202003 values less than (to_date('2020-04-01','YYYY-MM-DD'))
);
create table tb_subpart_hash(
id number,
dt date,
deal_id varchar2(20)
) PARTITION BY RANGE(dt) SUBPARTITION BY HASH(deal_id) SUBPARTITIONS 4(
PARTITION p_1 VALUES LESS THAN(TO_DATE('2020-09-01 00:00:00', 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS')),
PARTITION p_2 VALUES LESS THAN(TO_DATE('2020-10-01 00:00:00', 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS'))
);
CREATE TABLE tb_range(
dept_no number,
part_no varchar2(20),
country varchar2(20),
dtime date,
amount number
)
PARTITION BY RANGE(dtime)
(
PARTITION q1_2012 VALUES LESS THAN(TO_DATE('2012-04-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD')),
PARTITION q2_2012 VALUES LESS THAN(TO_DATE('2012-07-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD')),
PARTITION q3_2012 VALUES LESS THAN(TO_DATE('2012-10-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD')),
PARTITION q4_2012 VALUES LESS THAN(TO_DATE('2013-01-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD'))
);
CREATE TABLE tb_list(
dept_no number,
part_no varchar2(20),
country varchar2(20),
dtime date,
amount number
)
PARTITION BY LIST(country)(
PARTITION europe VALUES('FRANCE', 'ITALY'),
PARTITION asia VALUES('INDIA', 'PAKISTAN'),
PARTITION americas VALUES('US', 'CANADA')
);
INSERT INTO tb_part_list VALUES (40, '9519b', 'US',to_date('2012-04-12','YYYY-MM-DD'), '145000');
INSERT INTO tb_part_list VALUES (10, '4519b', 'FRANCE', to_date('2012-01-17','YYYY-MM-DD'), '45000');
INSERT INTO tb_part_list VALUES (20, '3788a', 'INDIA',to_date('2012-03-01','YYYY-MM-DD'), '75000');
INSERT INTO tb_part_list VALUES (20, '3788a', 'PAKISTAN', to_date('2012-06-04','YYYY-MM-DD'), '37500');
INSERT INTO tb_part_list VALUES (10, '9519b', 'ITALY', to_date('2012-07-07','YYYY-MM-DD'), '15000');
INSERT INTO tb_part_list VALUES (10, '9519a', 'FRANCE',to_date('2012-08-18','YYYY-MM-DD'), '650000');
INSERT INTO tb_part_list VALUES (10, '9519b', 'FRANCE',to_date('2012-08-18','YYYY-MM-DD'), '650000');
INSERT INTO tb_part_list VALUES (20, '3788b', 'INDIA',to_date('2012-09-21','YYYY-MM-DD'), '5090');
INSERT INTO tb_part_list VALUES (20, '4519a', 'INDIA', to_date('2012-10-18','YYYY-MM-DD'), '650000');
INSERT INTO tb_part_list VALUES (20, '4519b', 'INDIA', to_date('2012-12-17','YYYY-MM-DD'), '5090');
-- TYPE
CREATE OR REPLACE TYPE TYPE_STR_AGG AS OBJECT
(
total VARCHAR2(4000),
STATIC FUNCTION odciaggregateinitialize(sctx IN OUT type_str_agg)
RETURN NUMBER,
MEMBER FUNCTION odciaggregateiterate
(
SELF IN OUT type_str_agg,
VALUE IN VARCHAR2
) RETURN NUMBER,
MEMBER FUNCTION odciaggregateterminate
(
SELF IN type_str_agg,
returnvalue OUT VARCHAR2,
flags IN NUMBER
) RETURN NUMBER,
MEMBER FUNCTION odciaggregatemerge
(
SELF IN OUT type_str_agg,
ctx2 IN type_str_agg
) RETURN NUMBER
);
/
-- TYPE BODY
CREATE OR REPLACE TYPE BODY TYPE_STR_AGG IS
STATIC FUNCTION odciaggregateinitialize(sctx IN OUT type_str_agg)
RETURN NUMBER IS
BEGIN
sctx := type_str_agg(NULL);
RETURN odciconst.success;
END;
MEMBER FUNCTION odciaggregateiterate
(
SELF IN OUT type_str_agg,
VALUE IN VARCHAR2
) RETURN NUMBER IS
BEGIN
SELF.total := SELF.total || VALUE;
RETURN odciconst.success;
END;
MEMBER FUNCTION odciaggregateterminate
(
SELF IN type_str_agg,
returnvalue OUT VARCHAR2,
flags IN NUMBER
) RETURN NUMBER IS
BEGIN
returnvalue := SELF.total;
RETURN odciconst.success;
END;
MEMBER FUNCTION odciaggregatemerge
(
SELF IN OUT type_str_agg,
ctx2 IN type_str_agg
) RETURN NUMBER IS
BEGIN
SELF.total := SELF.total || ctx2.total;
RETURN odciconst.success;
END;
END;
/
-- procedure
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE INSERT_PROGRAM
is
id integer := 2212;
i integer := 1;
movie_code integer := 3804;
begin
while i <= 2000
loop
begin
dbms_output.put_line('1111');
end;
end loop;
end;
/
-- function
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION FUN_VISURL(
biz_type VARCHAR2,
biz_code VARCHAR2) RETURN VARCHAR2
AS
vis_url VARCHAR(1024);
v_biz_priviewFlag NUMBER;
v_biz_title VARCHAR(128);
BEGIN
vis_url := '';
IF biz_type = 'tvbar' THEN
IF v_biz_priviewFlag = 1 THEN
vis_url := '/vasroot/frame/php4bestv/portal/' || biz_code || '/1';
END IF;
IF v_biz_priviewFlag = 2 THEN
vis_url := '/vasroot/frame/v2/portal/' || biz_code || '/1';
END IF;
IF v_biz_priviewFlag = 3 THEN
vis_url := '/vasroot/frame/kzone/' || v_biz_title || '/index/index/code/portal/' || biz_code || '/1';
END IF;
END IF;
IF biz_type = 'subject' THEN
vis_url := '/vasroot/frame/v2/subject/' || biz_code || '/1';
END IF;
RETURN vis_url;
EXCEPTION
WHEN NO_DATA_FOUND THEN
dbms_output.put_line('????????????');
RETURN vis_url;
END;
/
-- package
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE CMS_PICTURE_VIEW_PARAMS
IS
FUNCTION get_content_type RETURN VARCHAR2;
FUNCTION set_content_type(
c_type VARCHAR2) RETURN VARCHAR2;
END CMS_PICTURE_VIEW_PARAMS;
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY CMS_PICTURE_VIEW_PARAMS
IS
content_type VARCHAR2(128);
FUNCTION get_content_type RETURN VARCHAR2
IS
BEGIN
RETURN content_type;
END;
FUNCTION set_content_type(
c_type VARCHAR2) RETURN VARCHAR2
IS
BEGIN
content_type := c_type;
RETURN c_type;
END;
END CMS_PICTURE_VIEW_PARAMS;
/
-- comment
COMMENT ON TABLE tb_test1 IS 'Holds a tuple for each file that is being processed whether it is changed or not.';
COMMENT ON COLUMN tb_test1.time_st IS 'content name';
-- sequence
CREATE SEQUENCE VAS_AGAINST_MATCHS_SEQ
MINVALUE 1
MAXVALUE 9223372036854775807
INCREMENT BY 1 START WITH 1
CACHE 20;
-- index
create index tb_part_range_idnx on tb_part_range(dept_no);
-- view
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW CMS_BASE_CONTENT_VIEW(ID, NAME, TYPE, CODE, TAGS, STATUS, CREATE_TIME, LENGTH) AS
select
null as id,
null as name,
null as type,
null as code,
null as tags,
null as status,
null as create_time,
null as length
from
dual;
-- load data
CREATE TABLE sample_table (
id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR2(100),
created_at DATE
);
DECLARE
v_counter NUMBER := 1;
BEGIN
FOR i IN 1..1000 LOOP
INSERT INTO sample_table (id, name, created_at)
VALUES (v_counter, 'Name ' || v_counter, SYSDATE);
v_counter := v_counter + 1;
-- Commit every 1000 records to improve performance.
IF MOD(i, 1000) = 0 THEN
COMMIT;
END IF;
END LOOP;
COMMIT; -- Last commit.
END;
/1. Click Create Task to go to the task configuration page. Configure the source and destination databases. The following figure describes the parameters.
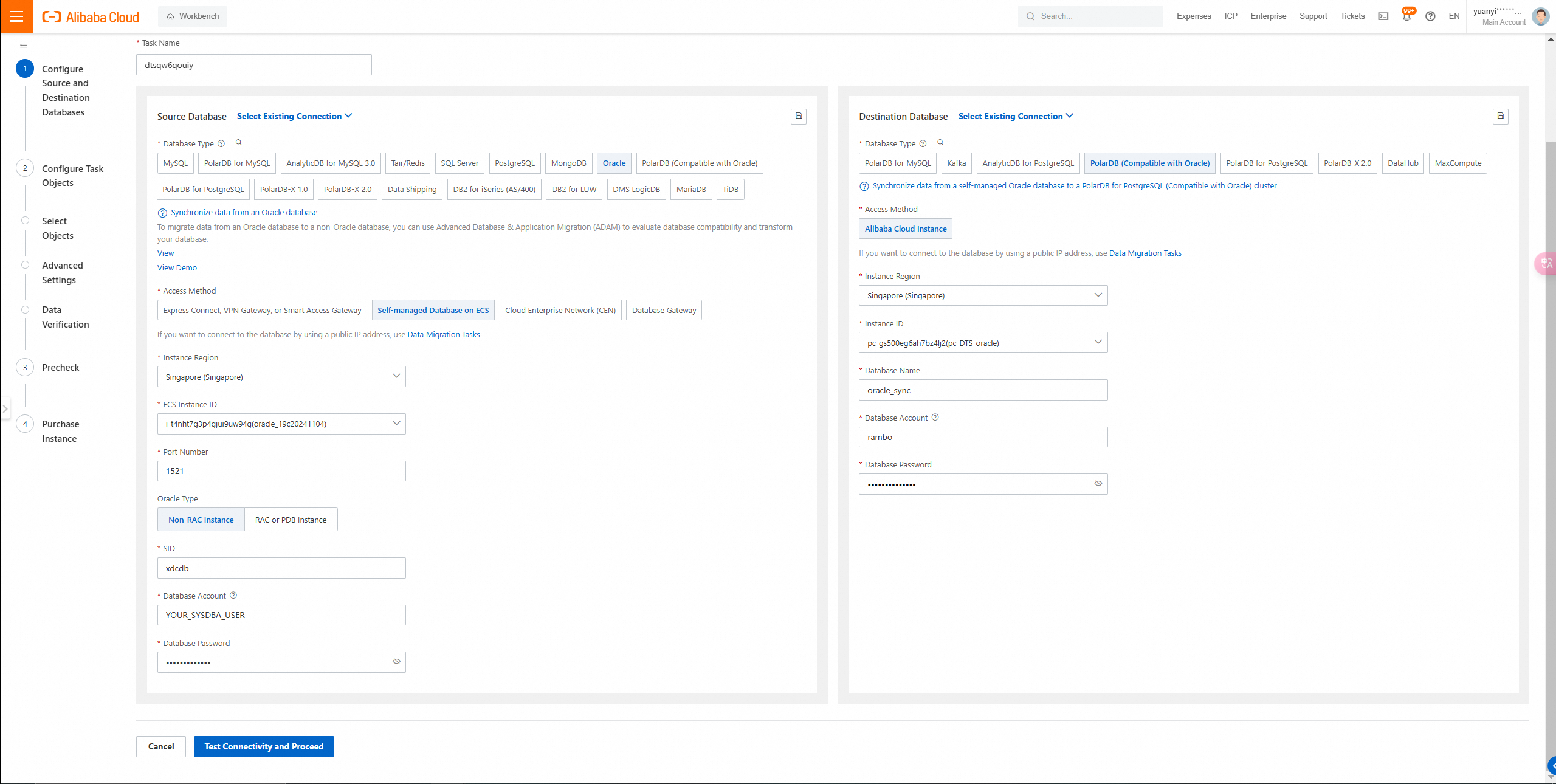
Select the Oracle type:
• If you select Non-RAC Instance, you must specify the SID parameter.
• If you select RAC or PDB Instance, you must specify the Service Name parameter.
In this example, Non-RAC Instance is selected.
SID information query
SELECT INSTANCE_NAME FROM V$INSTANCE;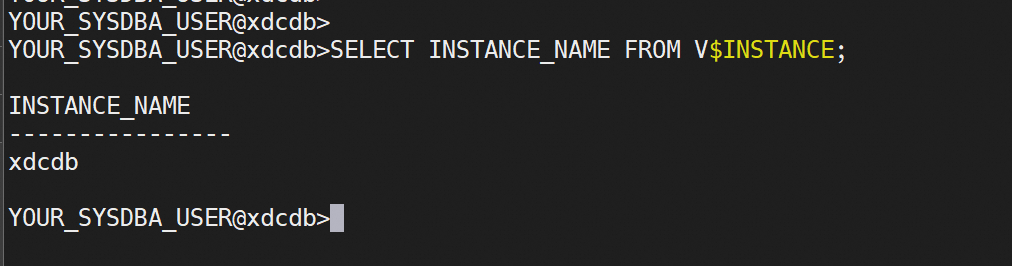
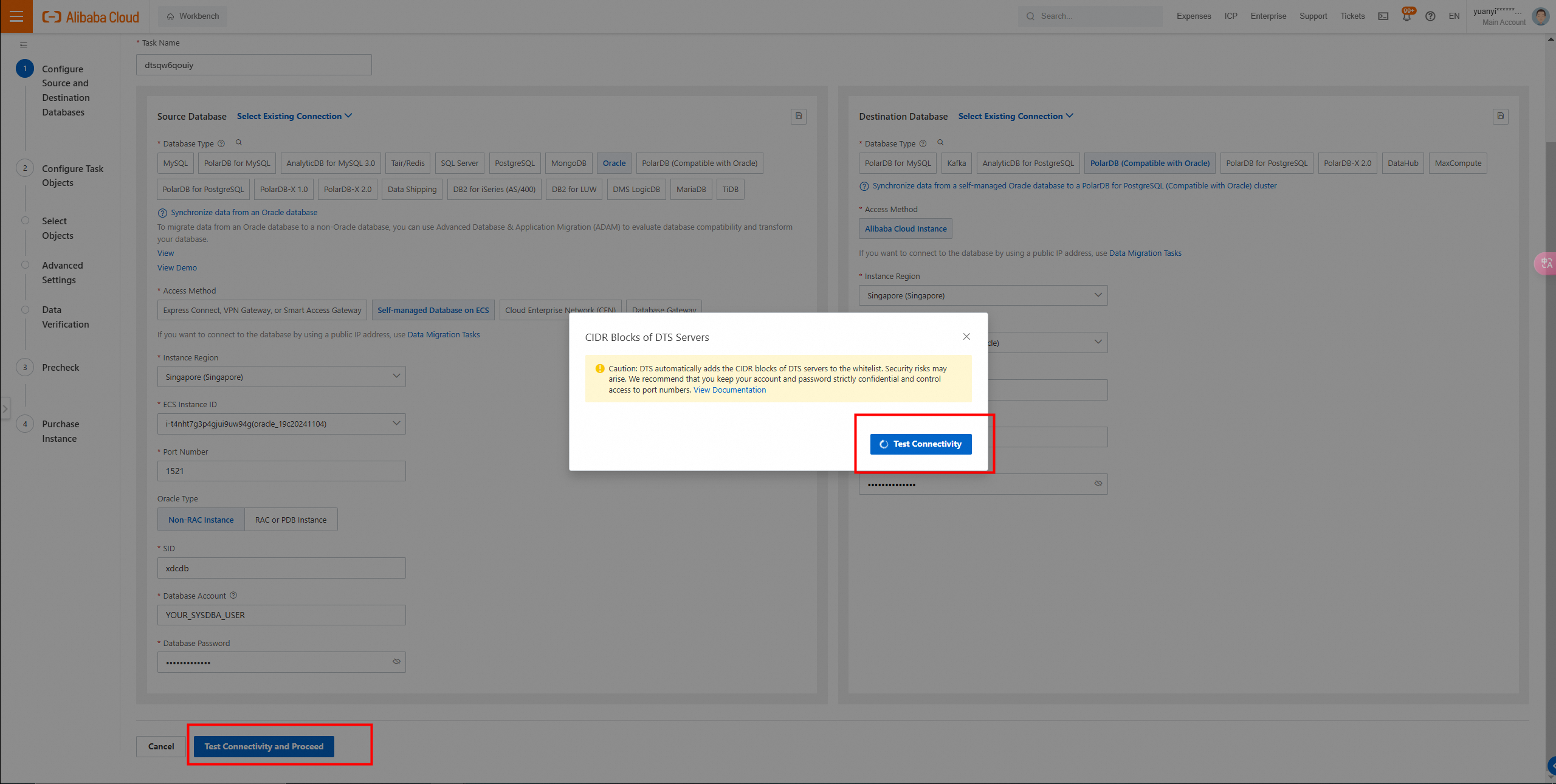
2. In the lower part of the page, click Test Connectivity and Proceed. In the CIDR Blocks of DTS Servers dialog box, click Test Connectivity.
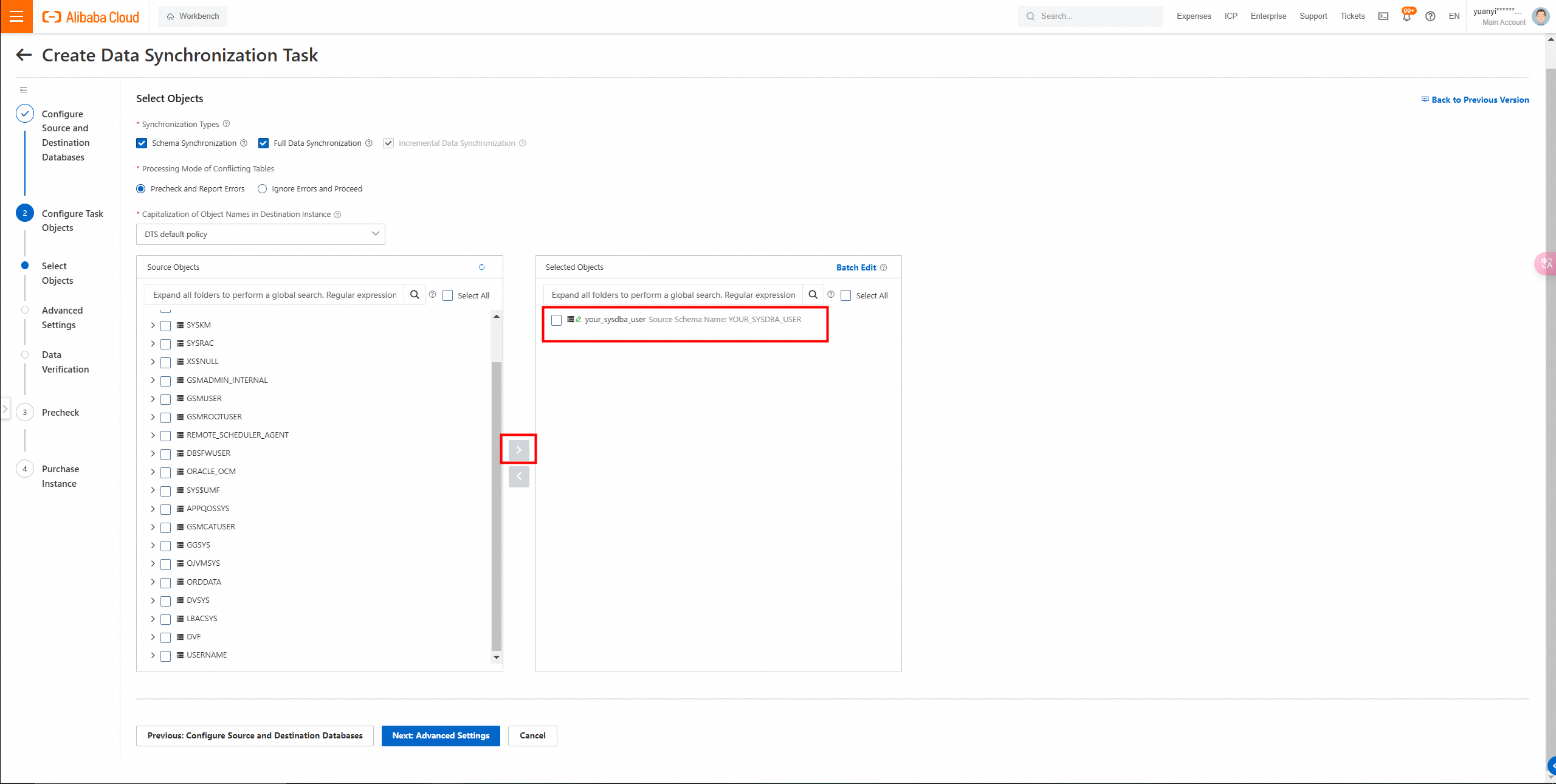
3. Configure the objects from which you want to synchronize data.
Select one or more objects from the Source Objects section. Click the  icon to add the objects to the Selected Objects section.
icon to add the objects to the Selected Objects section.
4. Click Next: Advanced Settings to configure advanced settings.
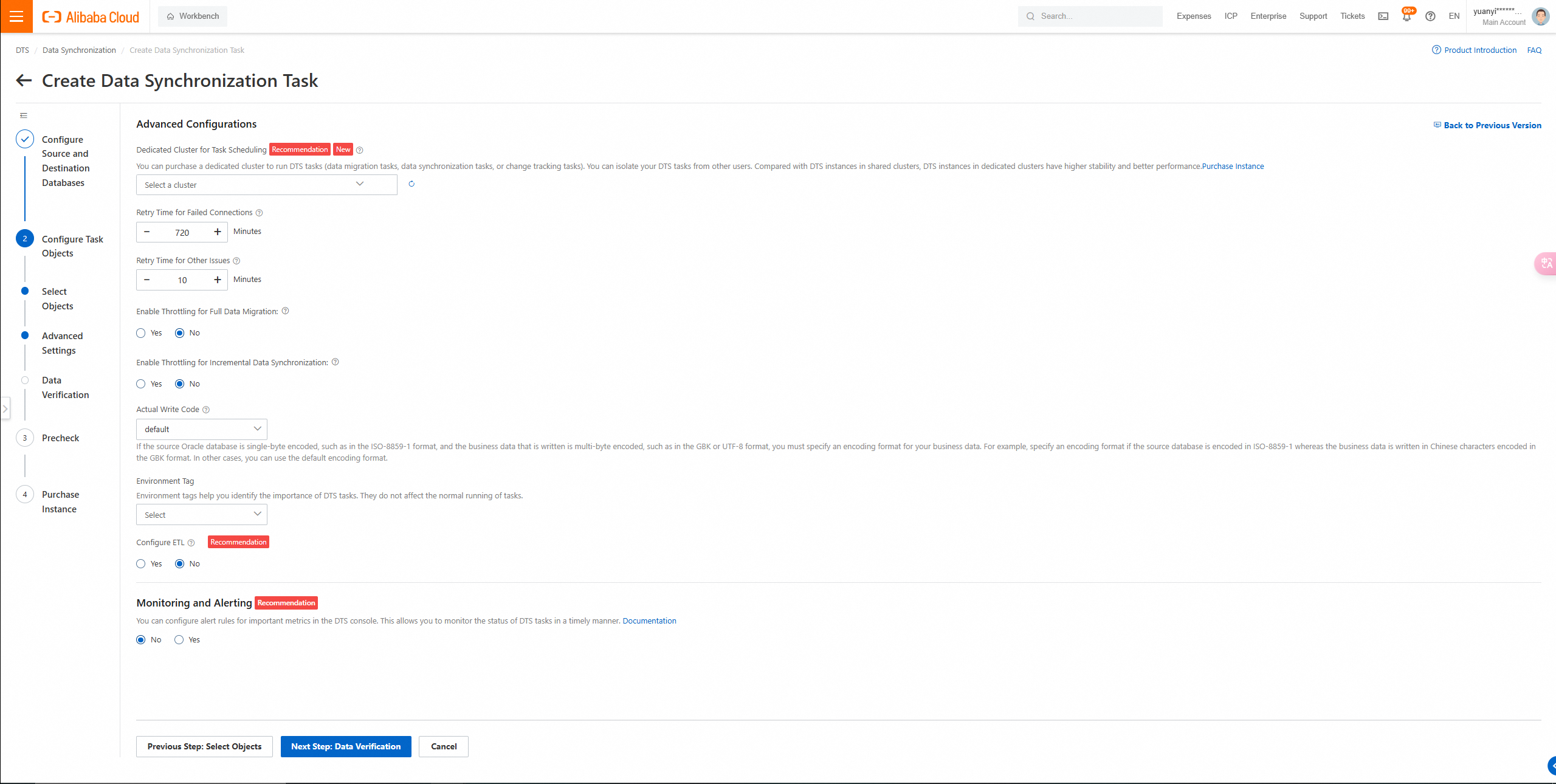
Click Next Step: Data Verification to configure the data verification task.
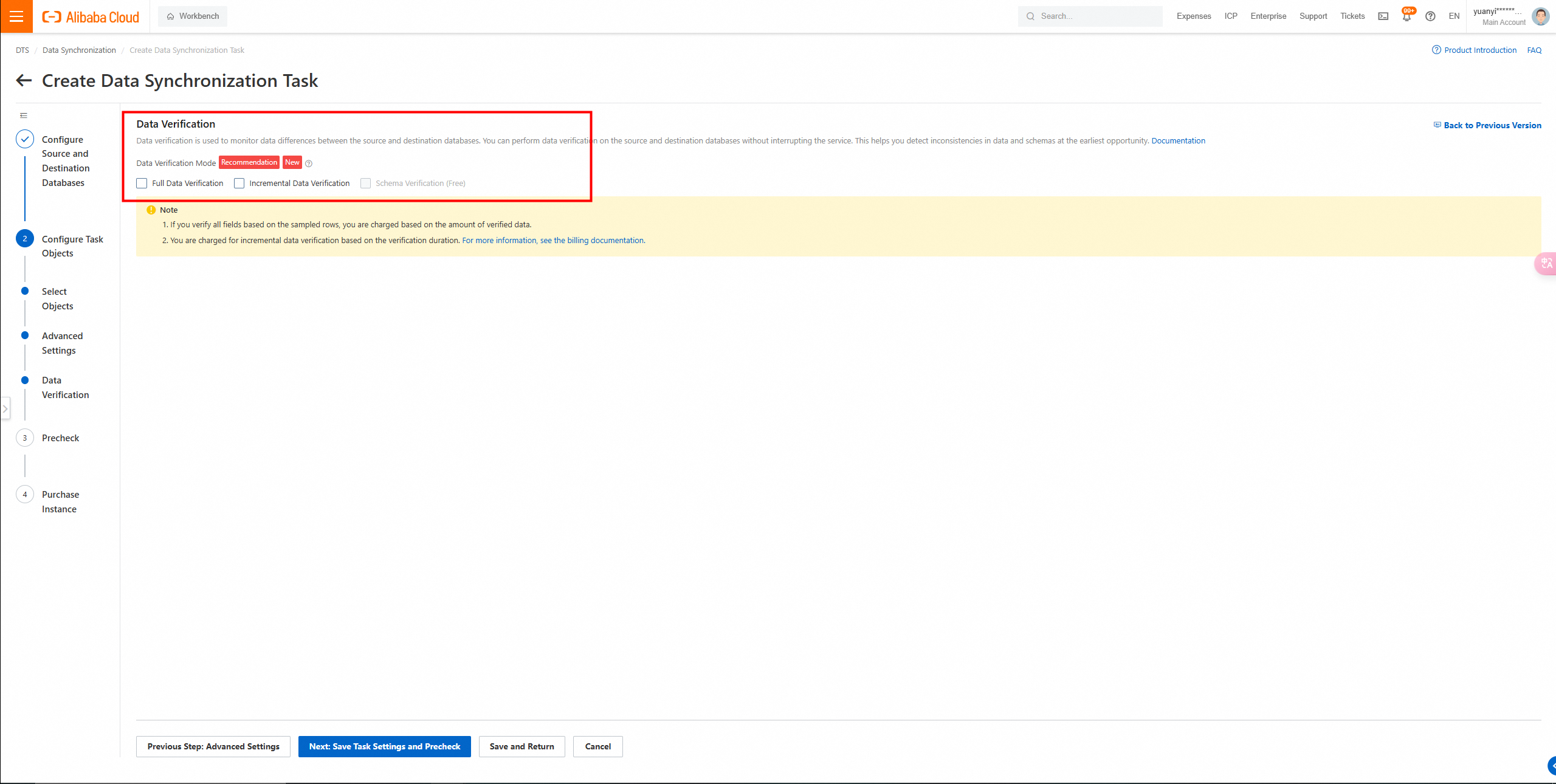
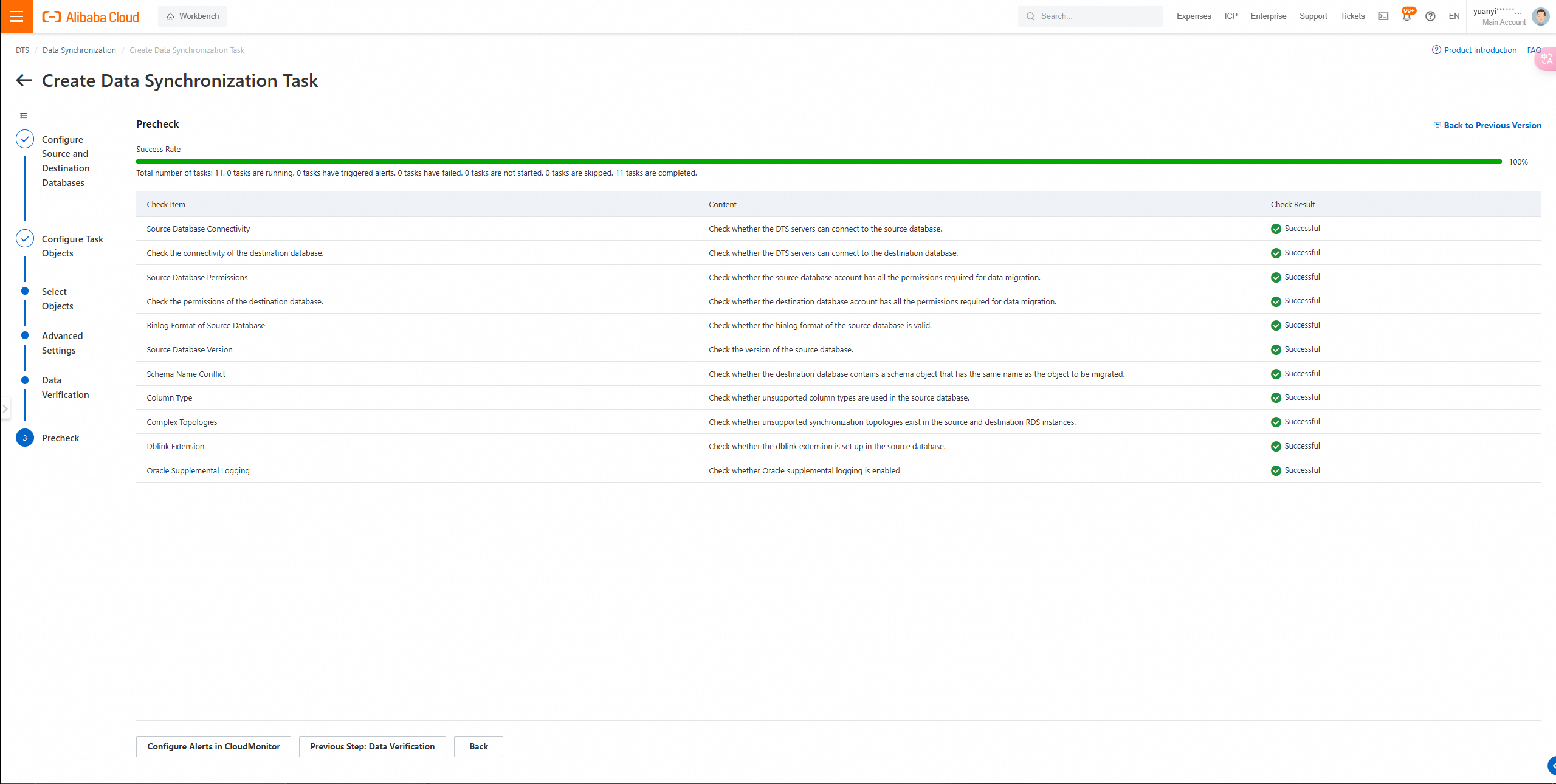
5. Click Next: Save Task Settings and Precheck in the lower part of the page.
Insufficient permissions occurred during the configuration check.
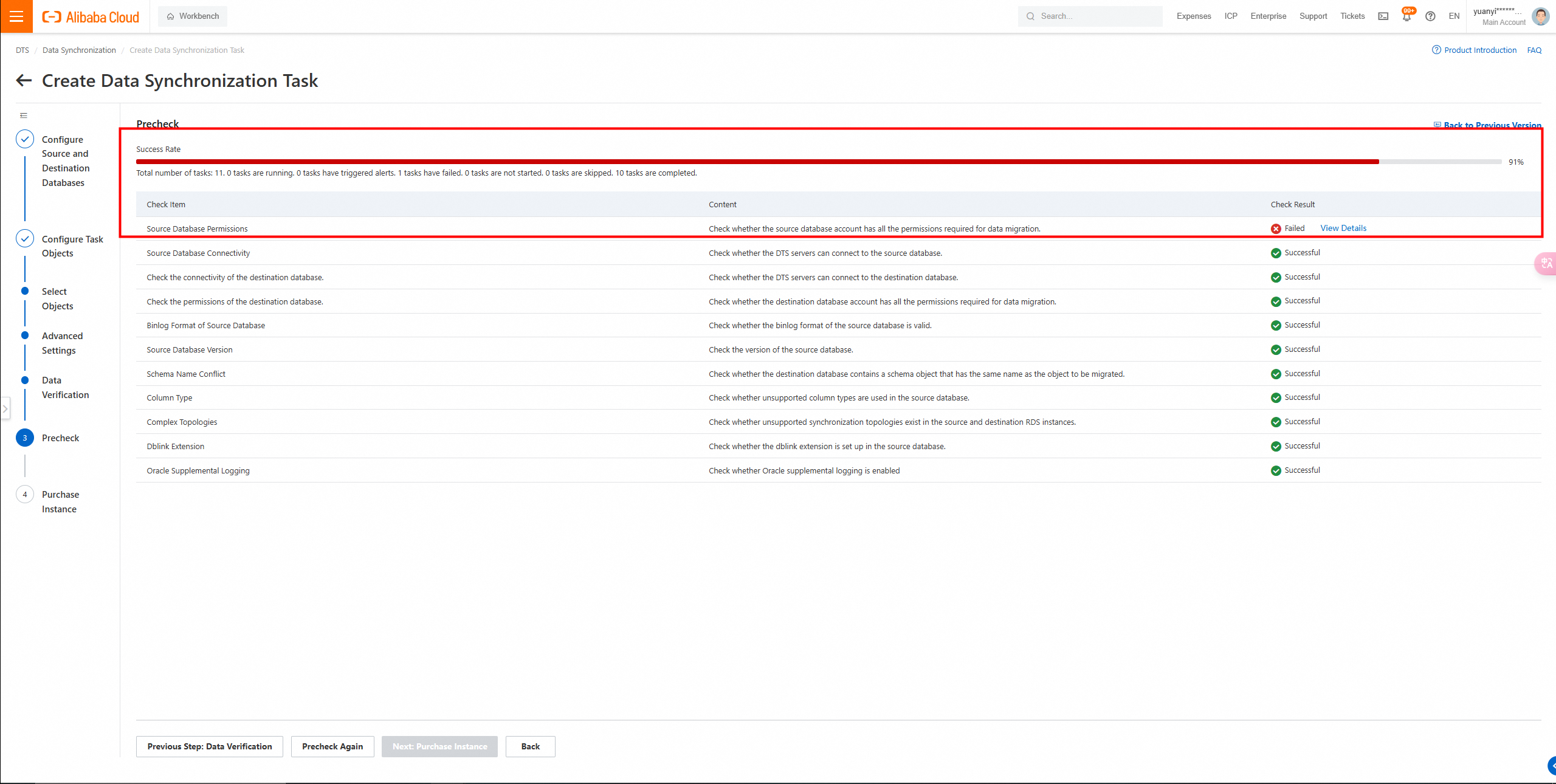
DBS permissions need to be granted.
grant create session to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant connect to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant dba to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant resource to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
-- Fine-grained permissions
grant create session to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant connect to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select_catalog_role to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant logmining to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant execute_catalog_role to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select any table to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select any transaction to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on all_objects to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on all_tab_cols to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on dba_registry to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant execute on sys.dbms_logmnr to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on v_$log to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on v_$logfile to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on v_$standby_log to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
-- If the Oracle database is a standby database in the ADG architecture, you must grant the v_$standby_log permission to the account.
grant select on v_$archived_log to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on v_$parameter to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on v_$database to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on v_$active_instances to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on v_$instance to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on v_$logmnr_contents to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select on sys.USER$ to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant create session to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant connect to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select_catalog_role to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;
grant select any table to YOUR_SYSDBA_USER;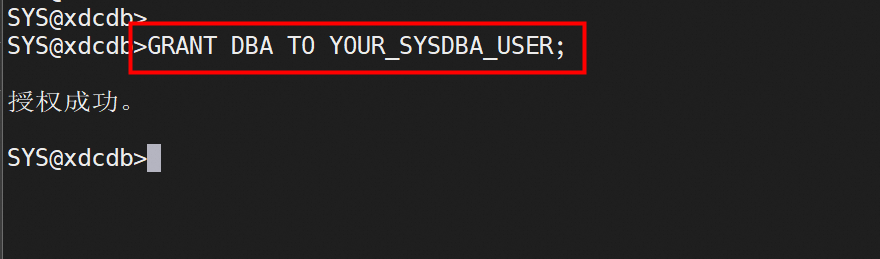
Run a check item again.
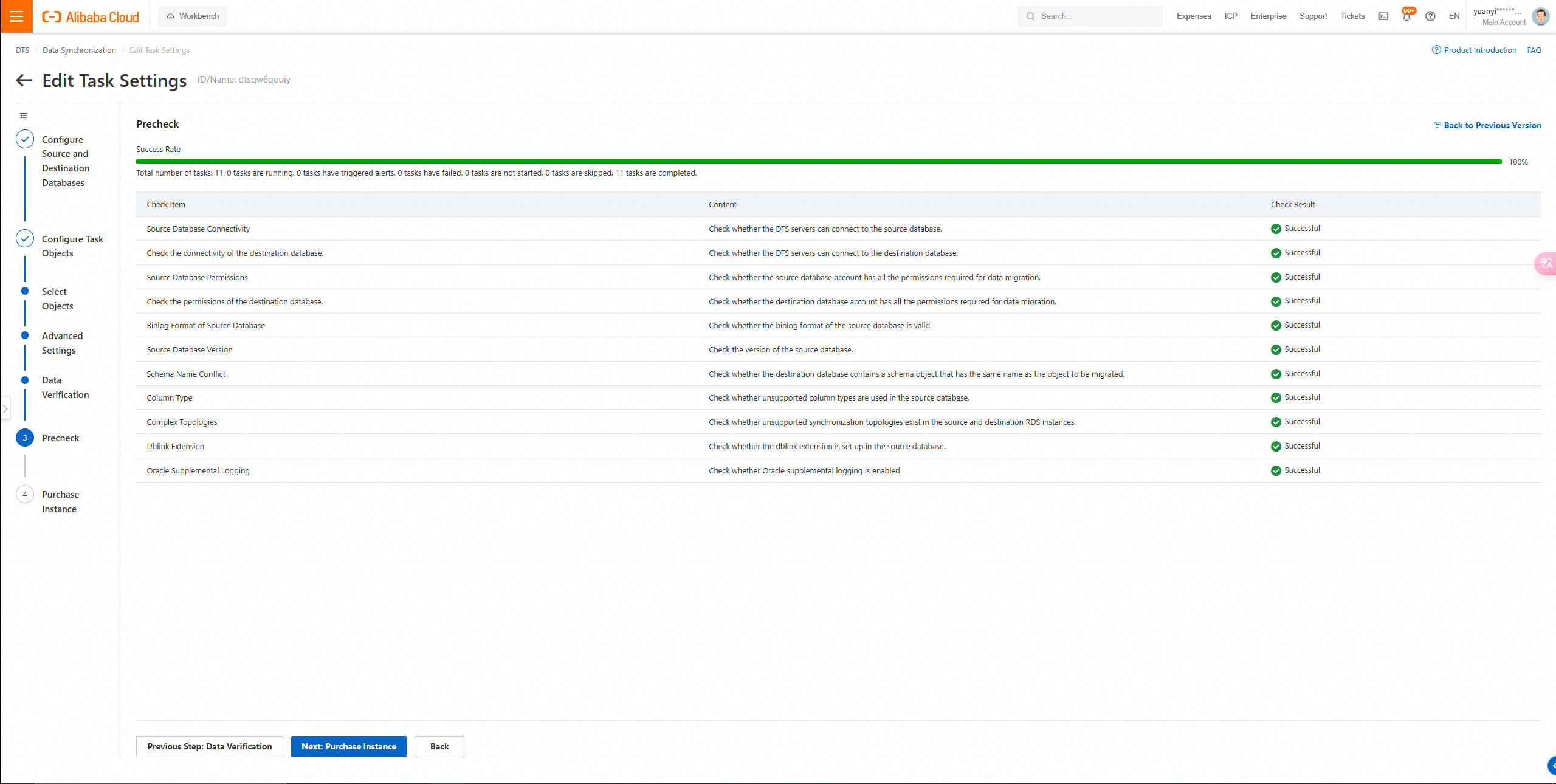
6. Wait until the Success Rate becomes 100%. Then, click Next: Purchase Instance.
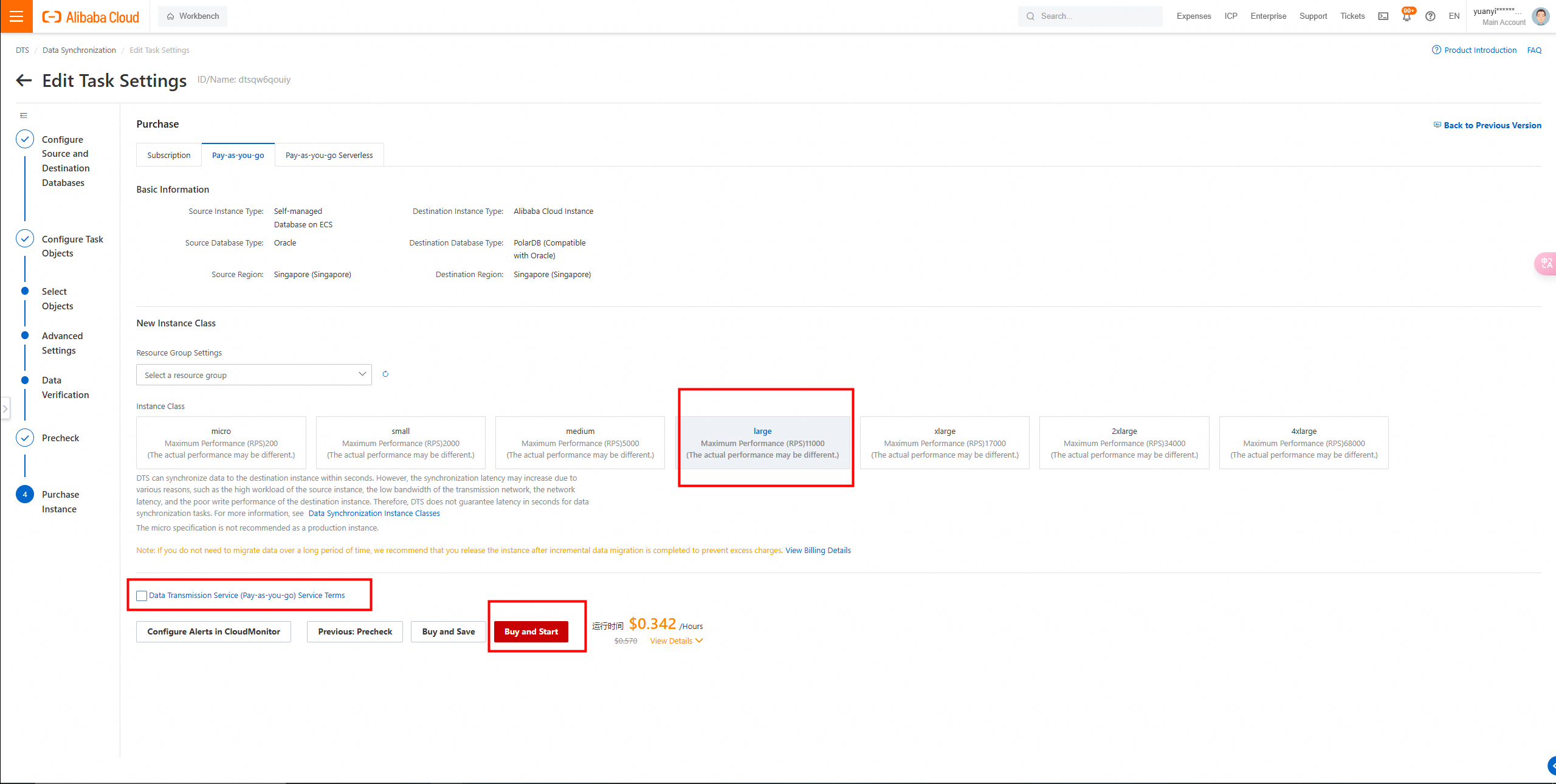
Click Buy and Start. In the message that appears, click OK.
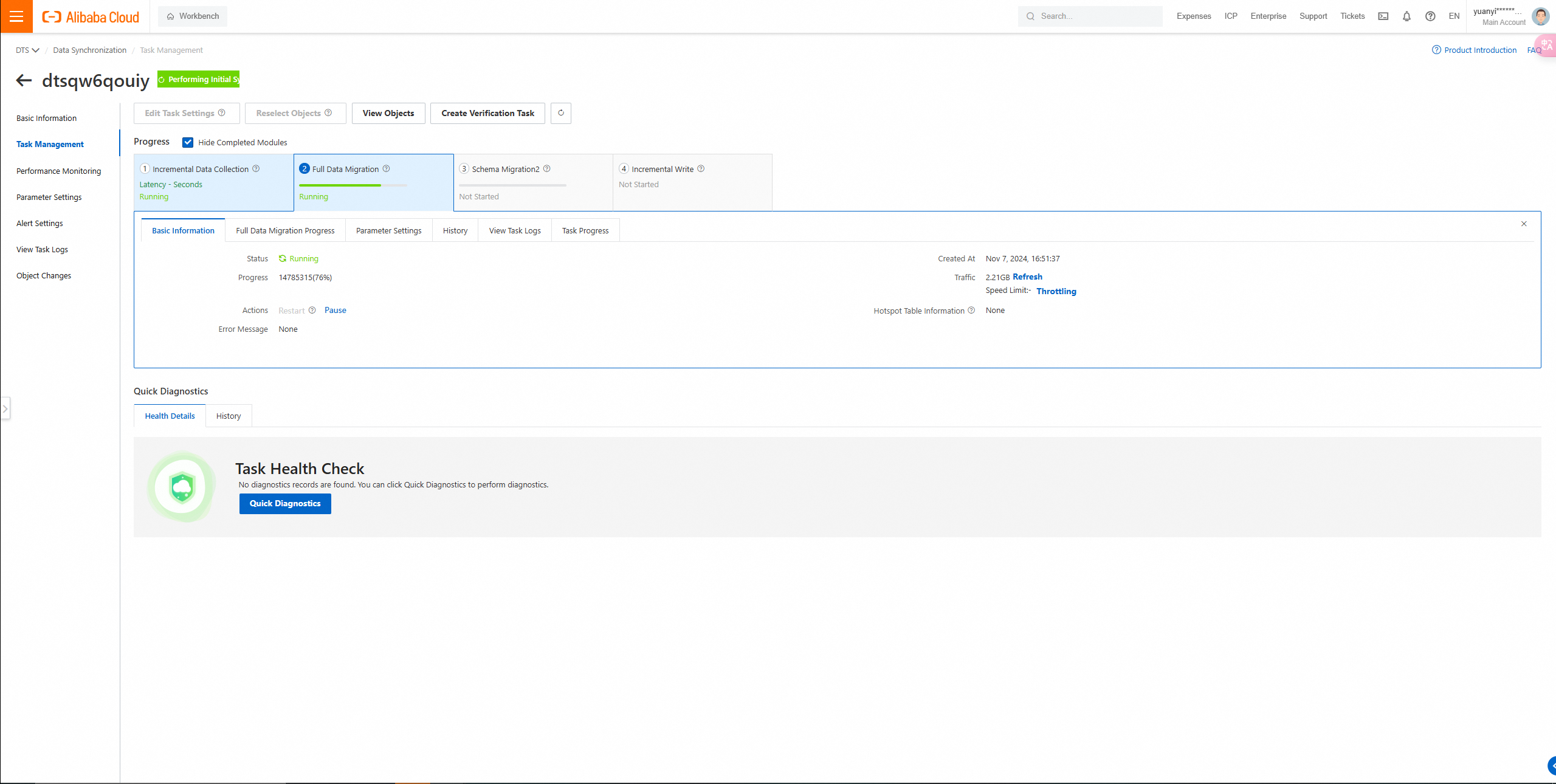
7. View the progress of the data migration task on the Data Migration page.
8. After migration, use DTS to perform full data verification.
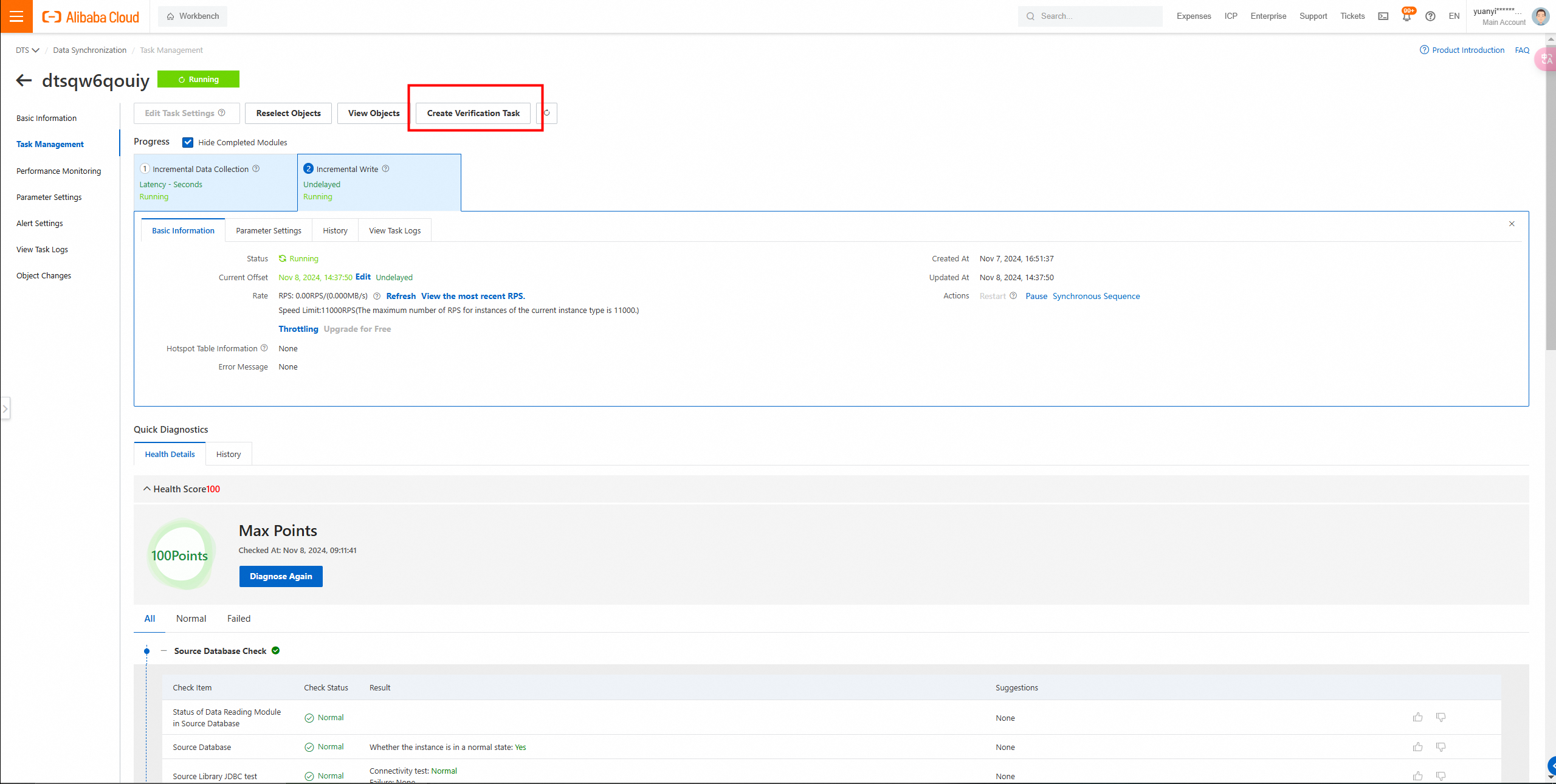
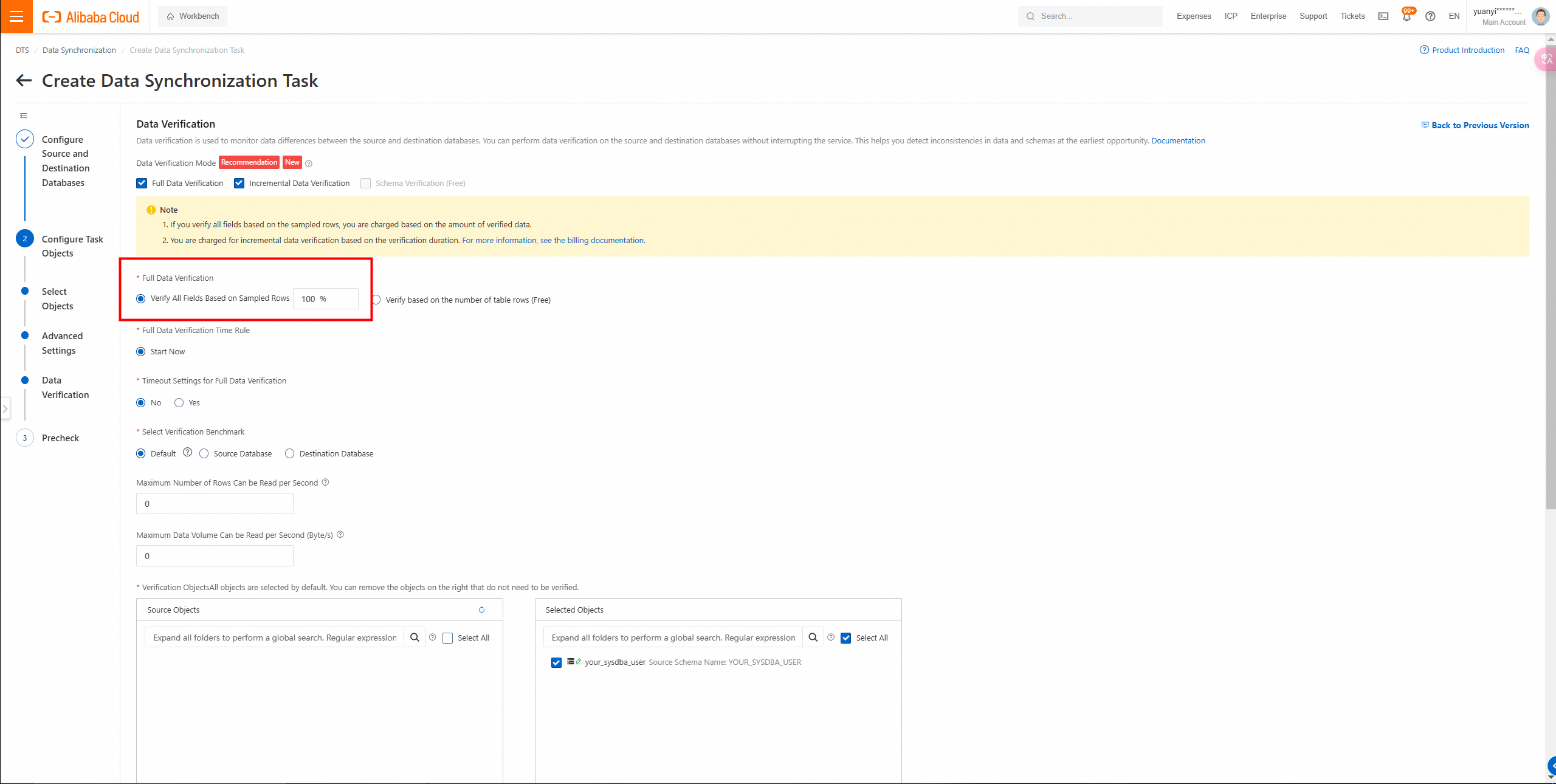
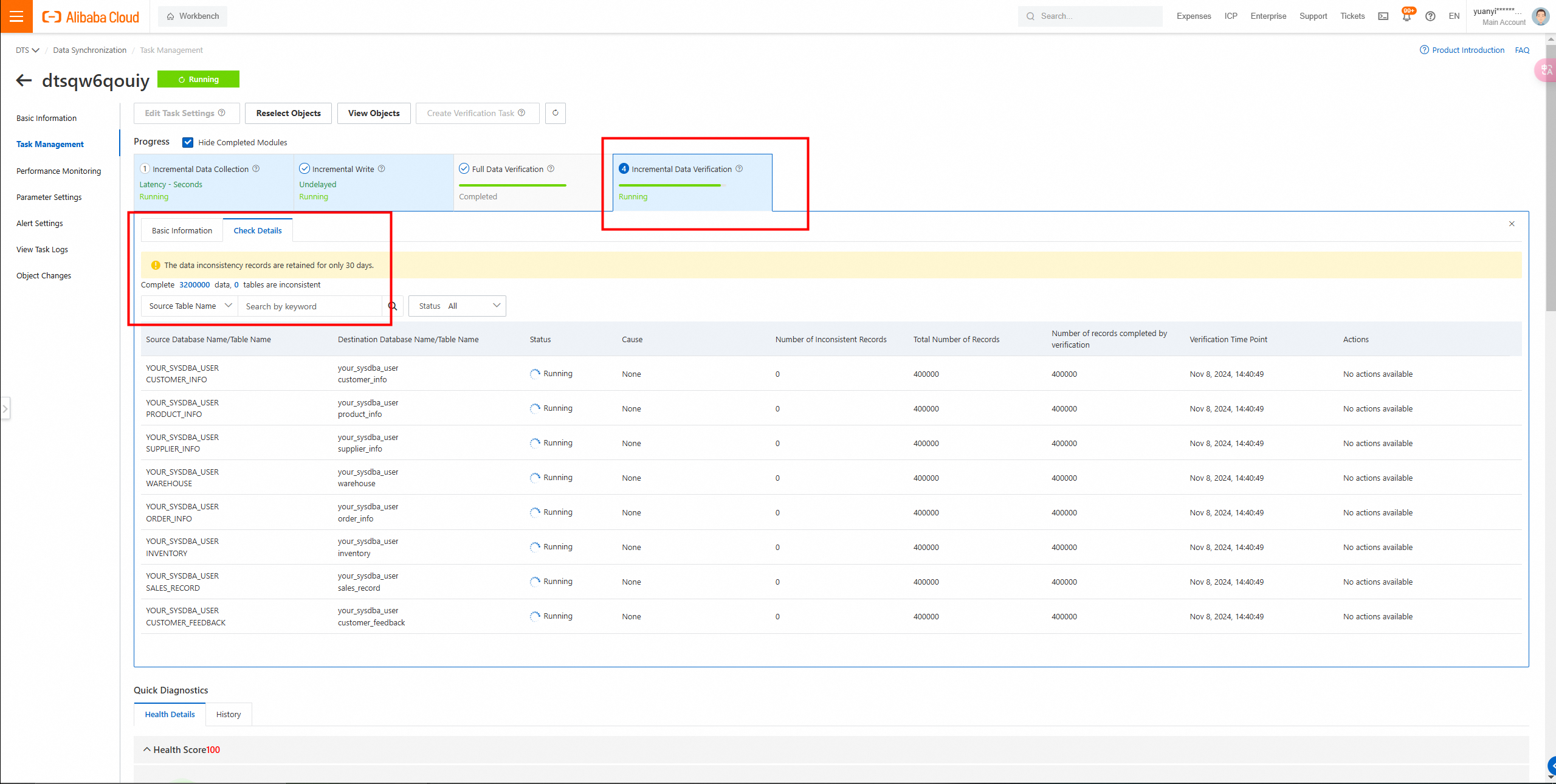
Full data verification: data consistency confirmed.
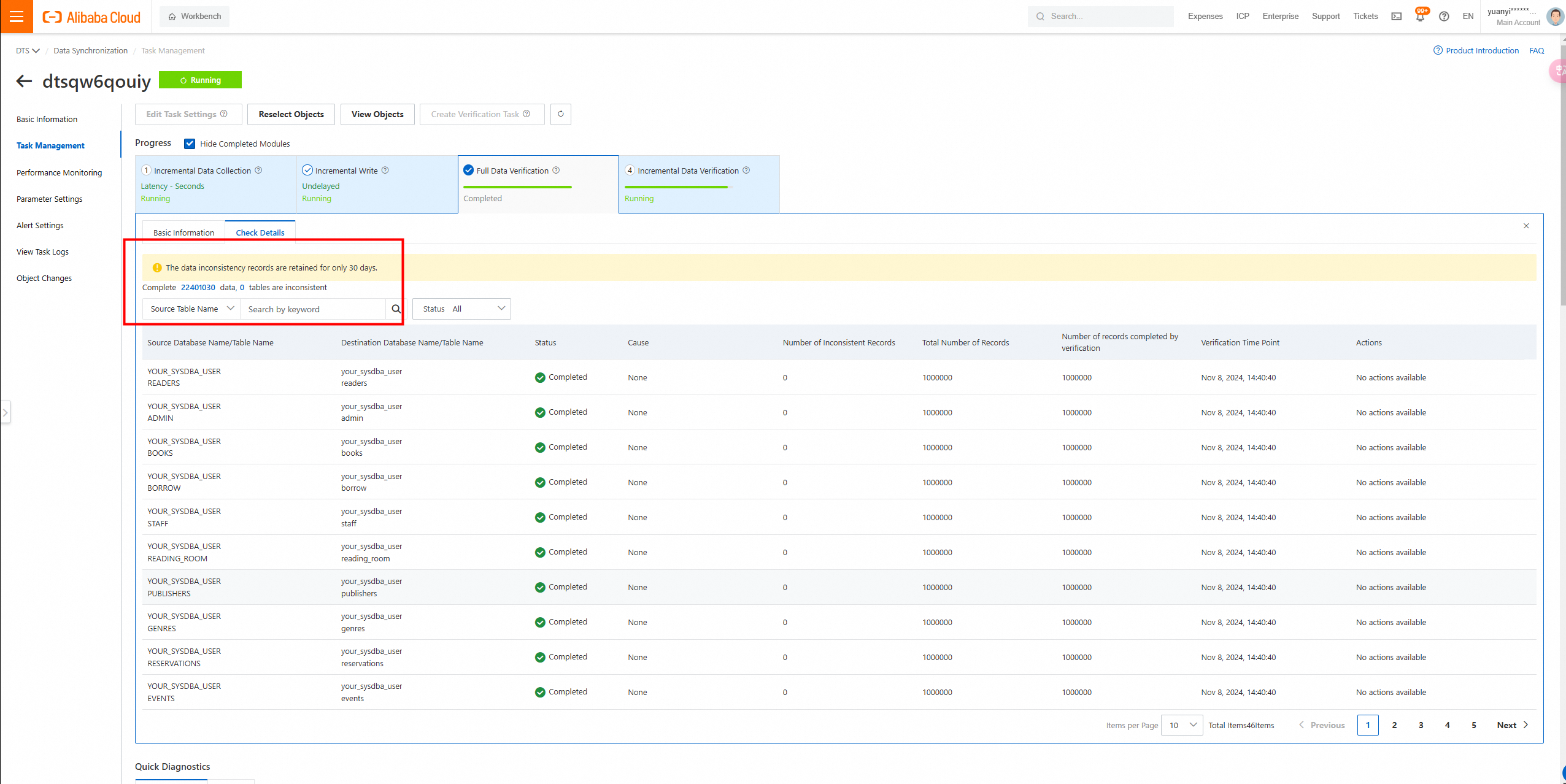
Incremental verification is running synchronously, verifying tasks in real time.
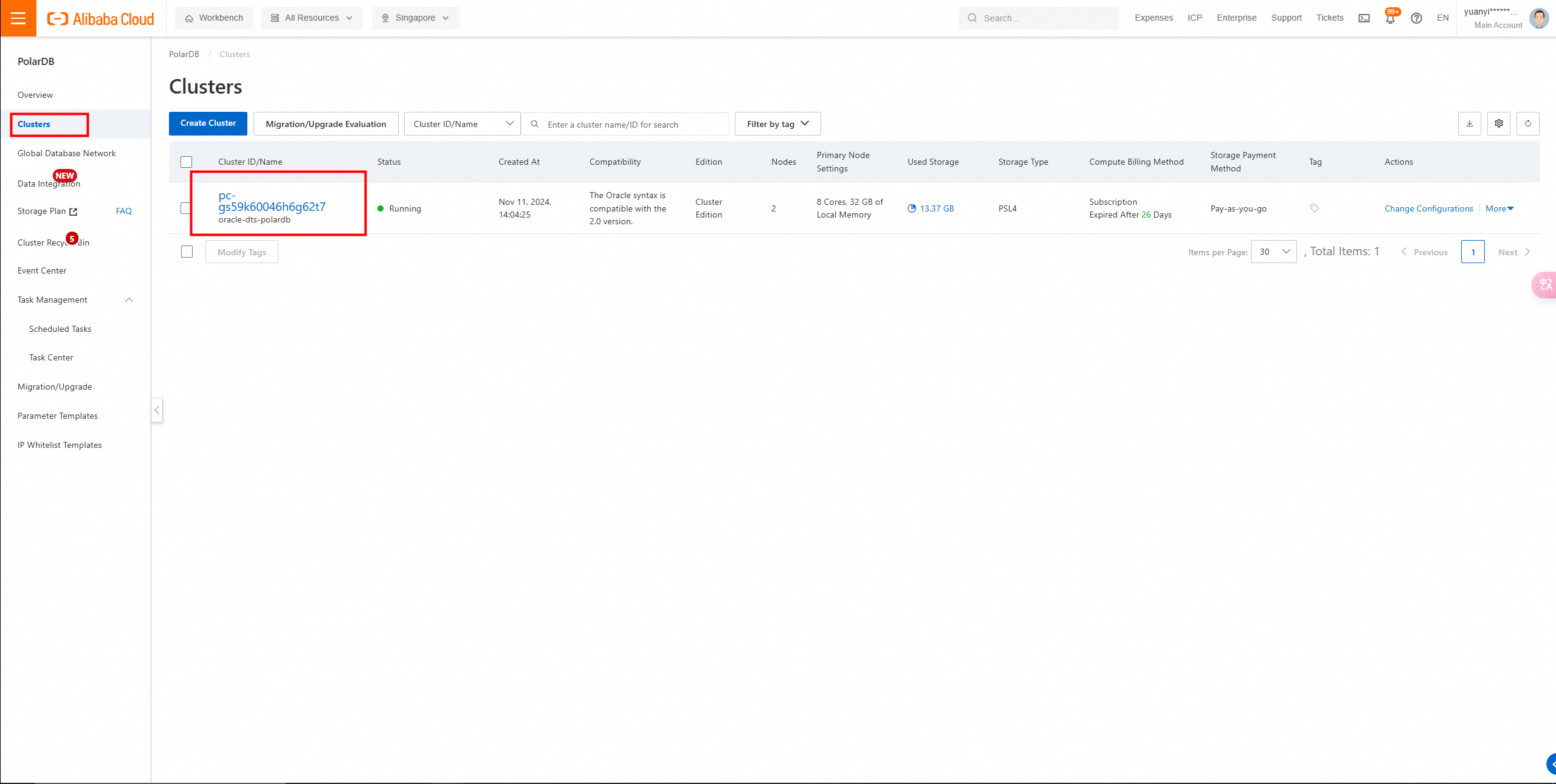
Log on to the PolarDB console to view the created instance.
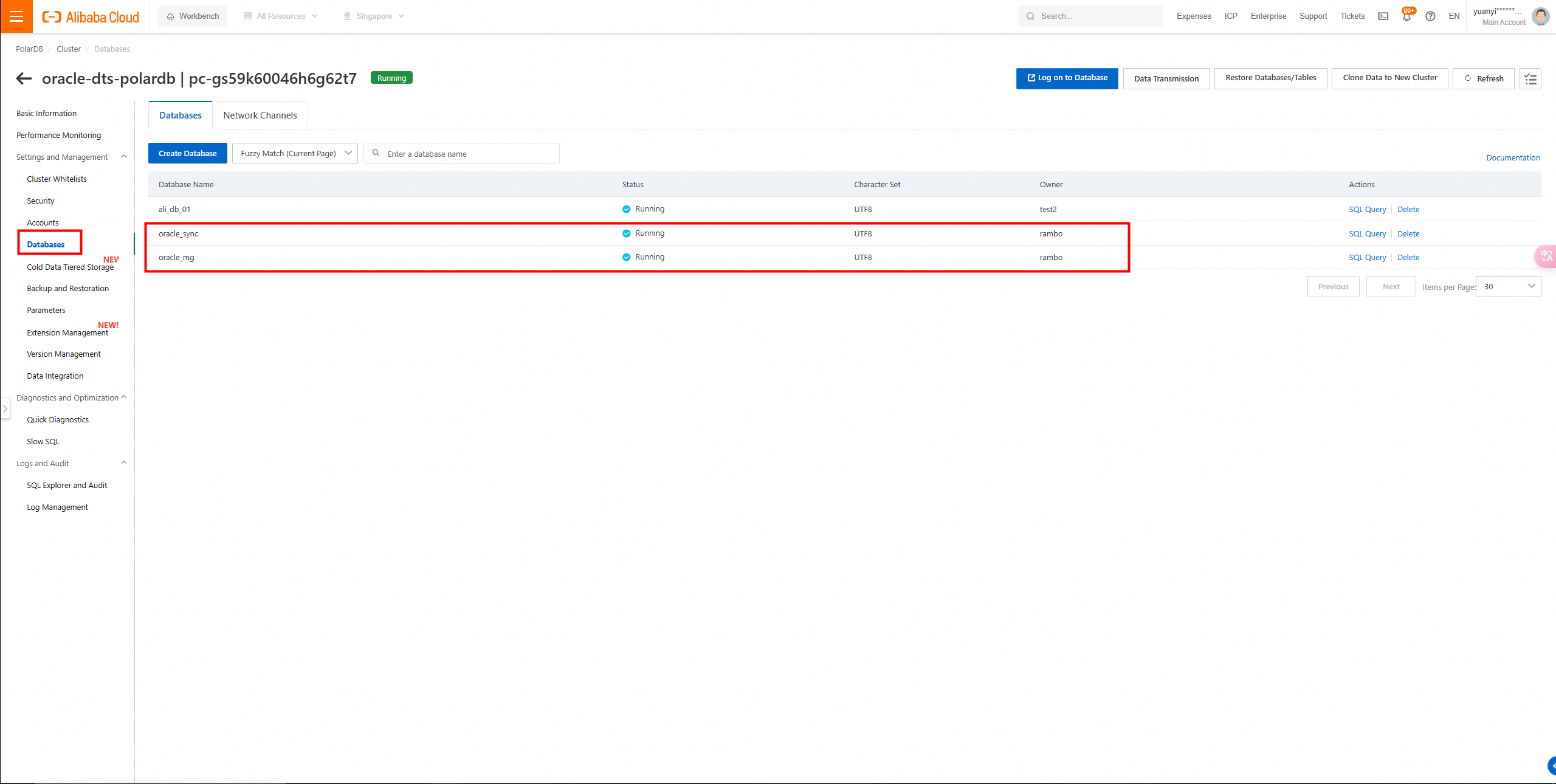
Query the Databases list.
Log on to the DMS console to view the migrated database.
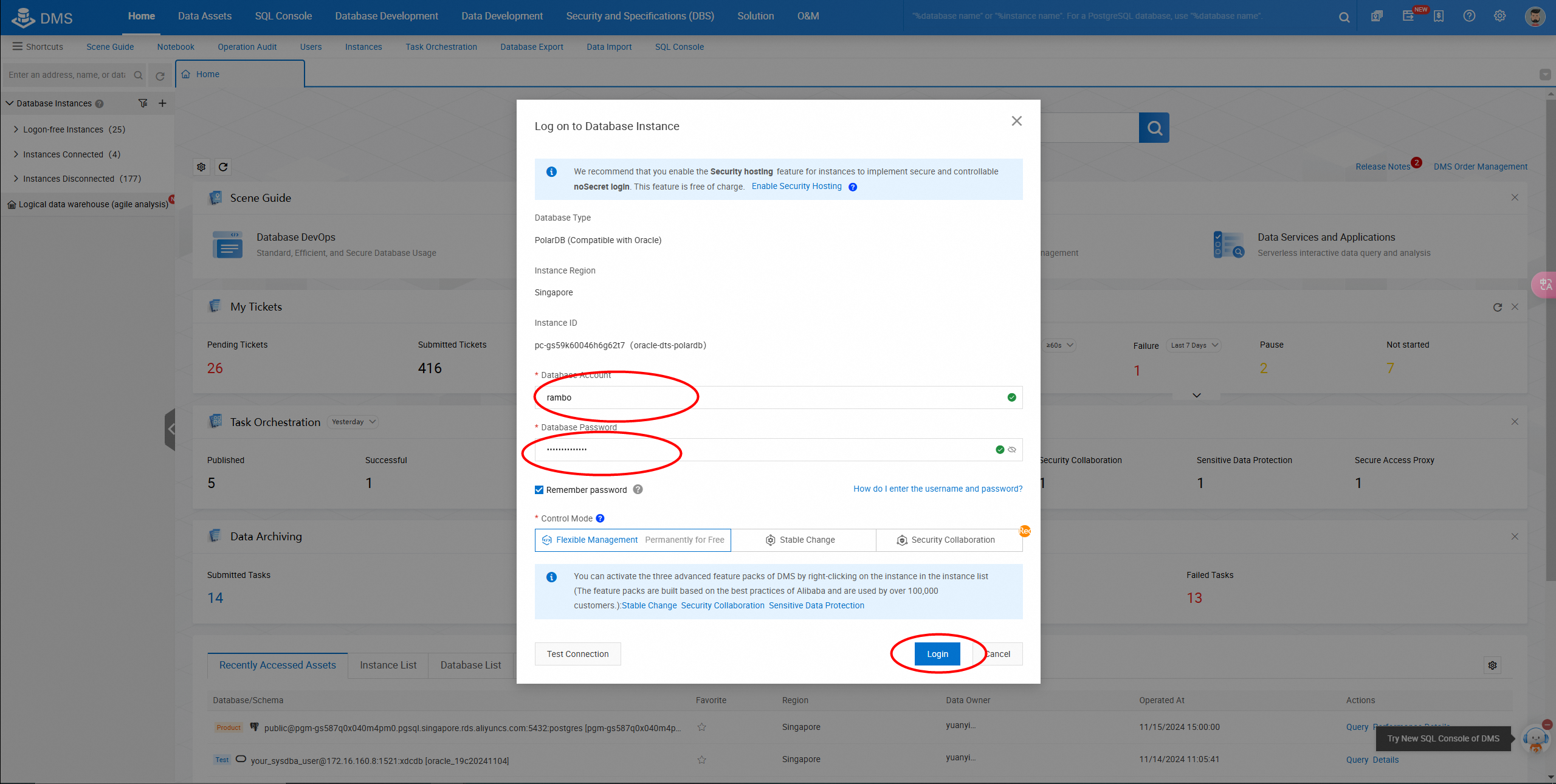
Select the destination database and the corresponding scheme.
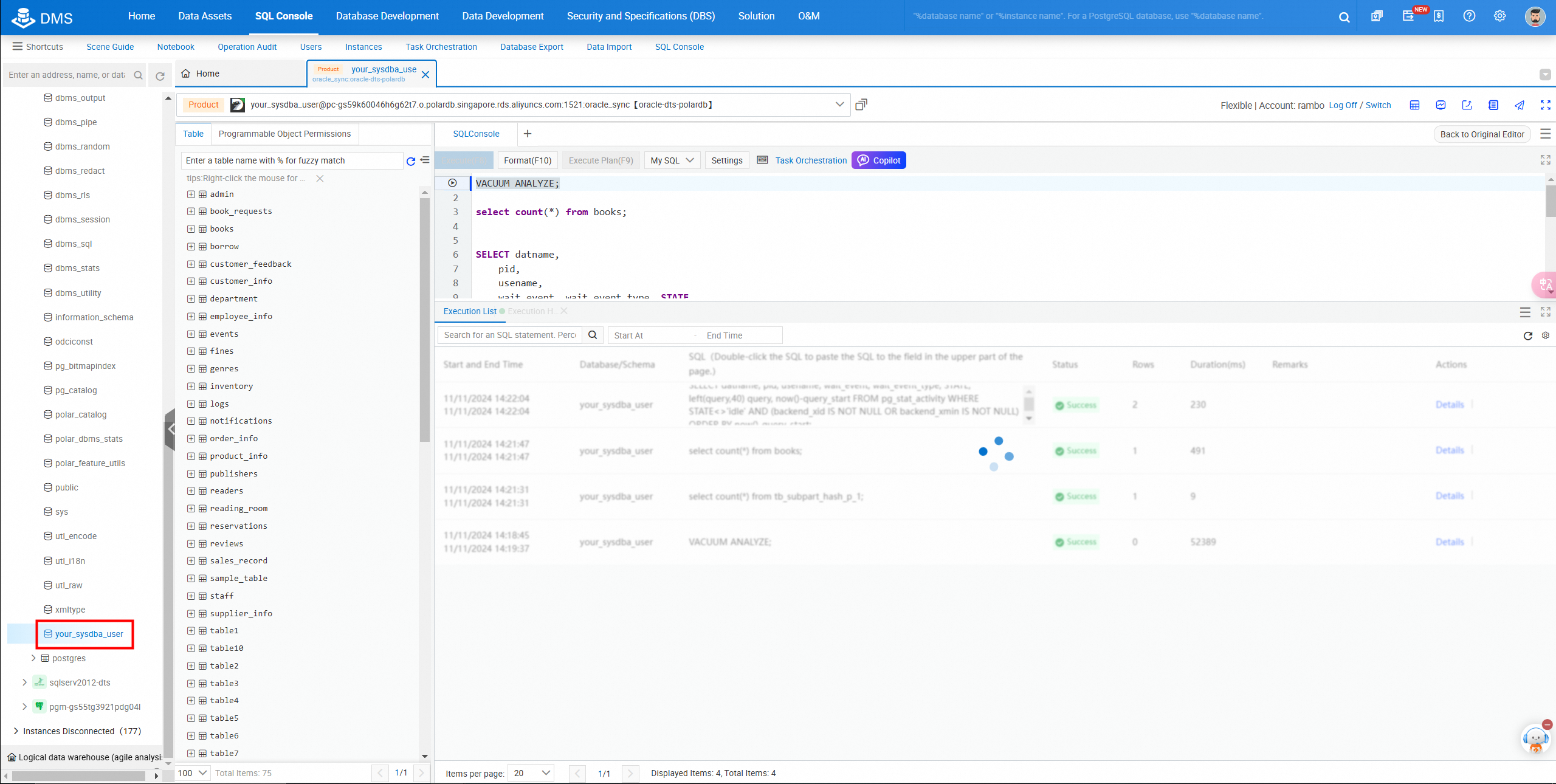
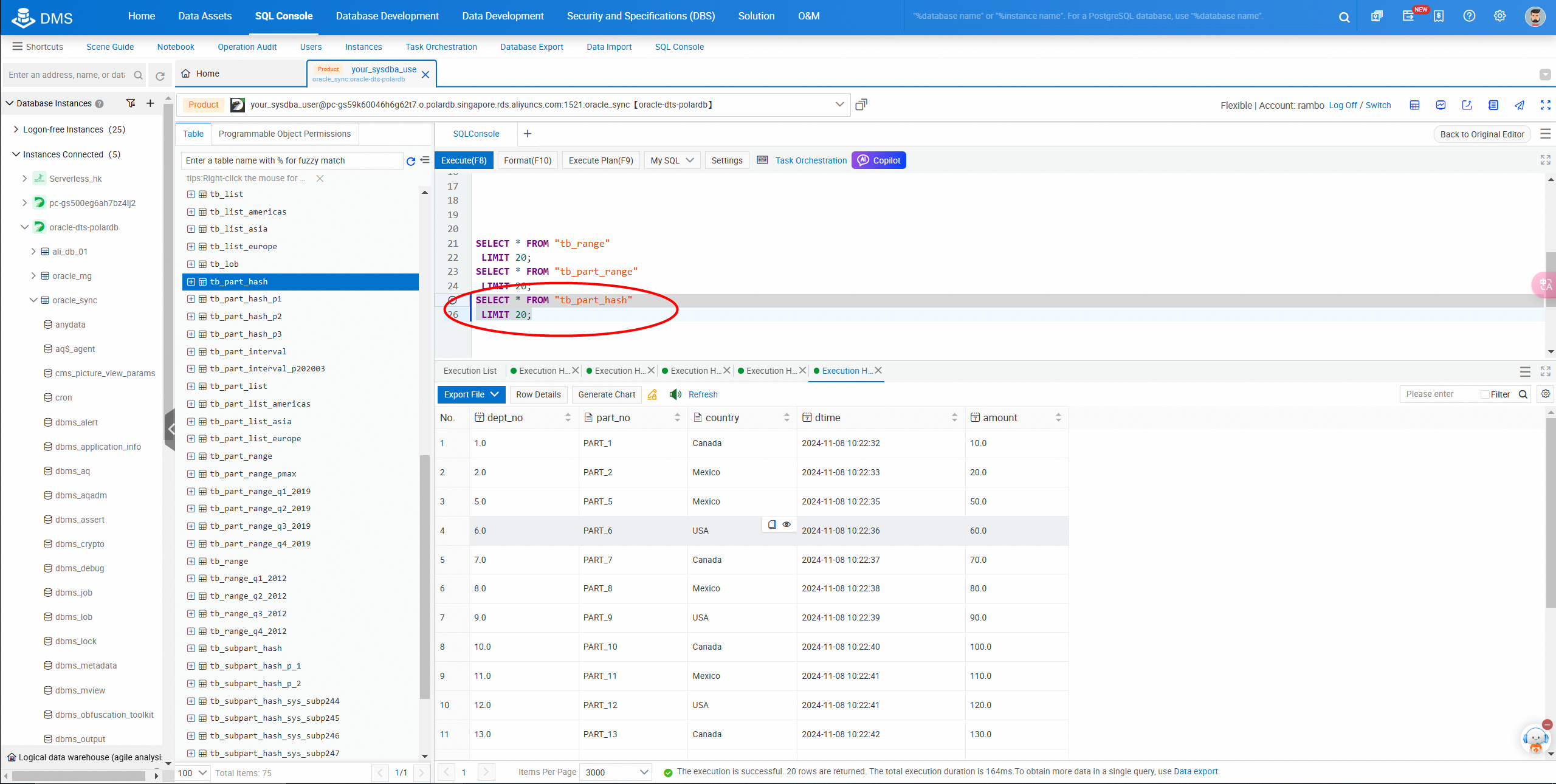
Query table data in the console.
The archived log must be retained for at least three days. Incremental synchronization will fail if the archive mode is not enabled.
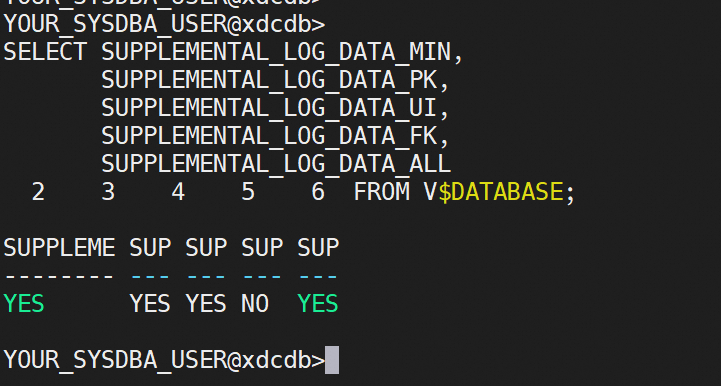
Query statements: SELECT SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_MIN,
SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_PK,
SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_UI,
SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_FK,
SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_ALL
FROM V$DATABASE;
Check whether the authorization is completed.
select * from user_tab_privs;
select granted_role from user_role_privs;Retrieve SID from the V$INSTANCE view:
SELECT INSTANCE_NAME, HOST_NAME
FROM V$INSTANCE;This query returns the name (INSTANCE_NAME) of the current database instance and hostname (HOST_NAME).
Recommended tool: RMAN (Recovery Manager)
1. Start RMAN and connect to the destination database:
rman target /2. View all backups of the database:
RMAN> LIST BACKUP;3. Perform a full database backup:
RMAN> BACKUP DATABASE;4. Back up archived logs of the database:
RMAN> BACKUP ARCHIVELOG ALL;5. Verify the database backup:
RMAN> RESTORE DATABASE VALIDATE;Common operation commands for Oracle databases
Logon to SQLPlus: Log on to SQLPlus as a user with administrator privileges.
sqlplus / as sysdba
-- Check the tablespace usage.
SELECT df.tablespace_name,
(df.totalspace - tu.usedspace) / 1024 / 1024 AS free_space_mb,
tu.usedspace / 1024 / 1024 AS used_space_mb,
df.totalspace / 1024 / 1024 AS total_space_mb
FROM (
SELECT tablespace_name, ROUND(SUM(bytes) / 1024 / 1024) AS totalspace
FROM dba_data_files
GROUP BY tablespace_name
) df,
(
SELECT ROUND(SUM(bytes)/(1024*1024)) AS usedspace, tablespace_name
FROM dba_segments
GROUP BY tablespace_name
) tu
WHERE df.tablespace_name = tu.tablespace_name;
-- Check data file information.
SELECT * FROM DBA_DATA_FILES;
-- Check control file information.
SELECT * FROM V$CONTROLFILE;
-- 7. Check log file information.
SELECT * FROM V$LOG;
--
-- Check current database instance information.
SELECT * FROM V$INSTANCE;
-- Check the tables of the current user.
SELECT * FROM USER_TABLES;
-- Check the tables of all users.
SELECT * FROM ALL_TABLES ;
-- Check all tables in the database.
SELECT * FROM DBA_TABLES where table_name='TABLE1';
-- Check the views of the current user.
SELECT * FROM USER_VIEWS;
-- Check the views of all users.
SELECT * FROM ALL_VIEWS;
-- Check all views in the database.
SELECT * FROM DBA_VIEWS;
-- Check sequences of the current user.
SELECT * FROM USER_SEQUENCES;
SELECT * FROM ALL_SEQUENCES;
-- Check the triggers of the current user.
SELECT * FROM USER_TRIGGERS;
-- Check the stored procedures and functions of the current user.
SELECT * FROM USER_PROCEDURES;
SELECT * FROM ALL_PROCEDURES;
SELECT * FROM DBA_PROCEDURES;
-- 17. Check database parameters.
-- 18. Check database performance statistics.
SELECT * FROM V$SYSSTAT;
-- 19. Check the lock information.
SELECT * FROM V$LOCK;
SELECT * FROM V$SESSION_WAIT;ApsaraDB - June 18, 2021
Alibaba Clouder - February 13, 2021
ApsaraDB - March 3, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - February 7, 2021
ApsaraDB - January 22, 2021
Alibaba Clouder - February 3, 2021
 Oracle Database Migration Solution
Oracle Database Migration Solution
Migrate your legacy Oracle databases to Alibaba Cloud to save on long-term costs and take advantage of improved scalability, reliability, robust security, high performance, and cloud-native features.
Learn More Database Migration Solution
Database Migration Solution
Migrating to fully managed cloud databases brings a host of benefits including scalability, reliability, and cost efficiency.
Learn More ADAM(Advanced Database & Application Migration)
ADAM(Advanced Database & Application Migration)
An easy transformation for heterogeneous database.
Learn More PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB