We are excited to announce the release of PolarDB's DynamoDB Compatibility feature (PolarDB-DDB) as part of the latest version of PolarDB for PostgreSQL. This new capability is highly compatible with the Amazon DynamoDB API and includes a comprehensive migration solution. With PolarDB-DDB, you can transition your existing business systems without modifying your code by connecting through native DynamoDB drivers (such as the Python or Go SDK).
PolarDB-DDB boasts enterprise-level capabilities, including instant elastic scaling, massive storage, and high availability, fully meeting the demands for high performance and reliability of modern applications. Furthermore, PolarDB-DDB provides a cost-effective solution that significantly outperforms DynamoDB, thereby empowering businesses to build efficient, stable, and economical data infrastructures perfect for large-scale NoSQL data processing and real-time access applications.
While developers love DynamoDB for its flexible schemaless data model, its costs can escalate quickly with growing data volume and workloads.
PolarDB-DDB is our answer: a solution designed specifically to be compatible with the DynamoDB API. It retains the flexibility of NoSQL data models while offering enhanced data processing capabilities, more comprehensive cloud-native features, and superior cost-effectiveness.
At its core, PolarDB-DDB is powered by a mature PostgreSQL engine, leveraging efficient JSONB storage, flexible indexing, complete ACID transaction capability, and robust SQL analysis. In addition, backed by a vibrant open-source community, PolarDB-DDB is able to continuously provide ongoing feature enhancements, plugin extensions, and security updates, ensuring long-term stable evolution.
1. Convenience and Scalability:
2. Elasticity and Automated Maintenance:
3. Fully Managed Service:
4. Ecosystem Integration and Innovation:
5. High Cost-Effectiveness:
In summary, PolarDB-DDB combines the flexibility of NoSQL and the powerful analytical capabilities of SQL, greatly simplifying data architecture, enabling businesses to benefit from high cost-Effectiveness, ease of maintenance, and sustainable volutive without compromise.
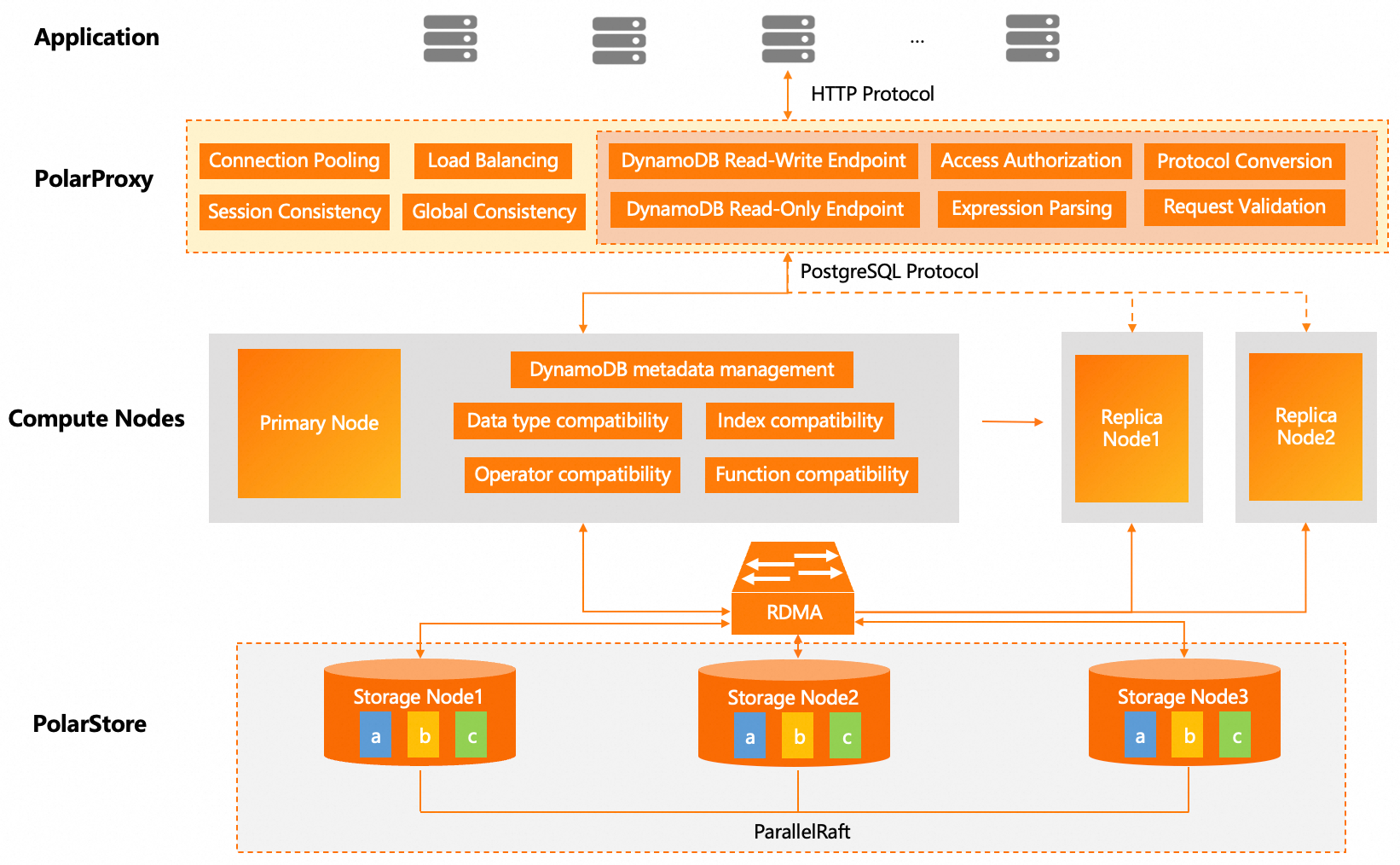
PolarDB-DDB uses a dedicated proxy layer to efficiently convert DynamoDB API requests and translate them to the PostgreSQL protocol. Logic for protocol parsing, authentication, and conversion is centralized at the proxy layer. Communication between the proxy and clients uses the HTTP protocol of DynamoDB, while standard PostgreSQL protocol is used between the proxy and database compute nodes. This bridging and decoupled architecture effectively avoids embedding DynamoDB's specific HTTP interfaces and authentication mechanisms into the PostgreSQL kernel, thus preserving the simplicity and stability of the PostgreSQL architecture. Additionally, this design reuses PolarDB’s connection pool, load balancing, and read-write separation capabilities, mitigating maintenance burdens arising from protocol coupling.
Here's the workflow for a complete DynamoDB request:
This decoupled architecture preserves the stability of the PostgreSQL core while reusing PolarDB’s mature connection pool, load balancing, and read-write separation capabilities, supporting hybrid queries (SQL & NoSQL) that enhance system flexibility.
It’s worth noting that enabling PolarDB-DDB doesn’t introduce extra compute node. PolarDB clusters with PolarDB-DDB feature use a standard primary-replica architecture, scaling from a basic two-node cluster to a cluster comprising one primary node and up to fifteen read-only nodes. The primary node handles all writes and transaction processing, while read-only nodes distribute read loads, significantly boosting concurrency capabilities. In the event of a primary node failure, automatic failover ensures high availability. Through a clear separation of storage and compute, the computing nodes leverage a standard PostgreSQL core, reusing its mature JSONB storage engine and query optimization. The system minimally reconfigures only to adapt string sorting rules, document operators, built-in functions, and datatype semantics to accurately reflect DynamoDB API behavior.
To improve user experience, the system internally manages DynamoDB metadata, concealing the traditional relational database DB/Schema concepts, presenting users with a view consistent with DynamoDB's user-region dimensional table management.
You can use PolarDB-DDB in either of the following ways:
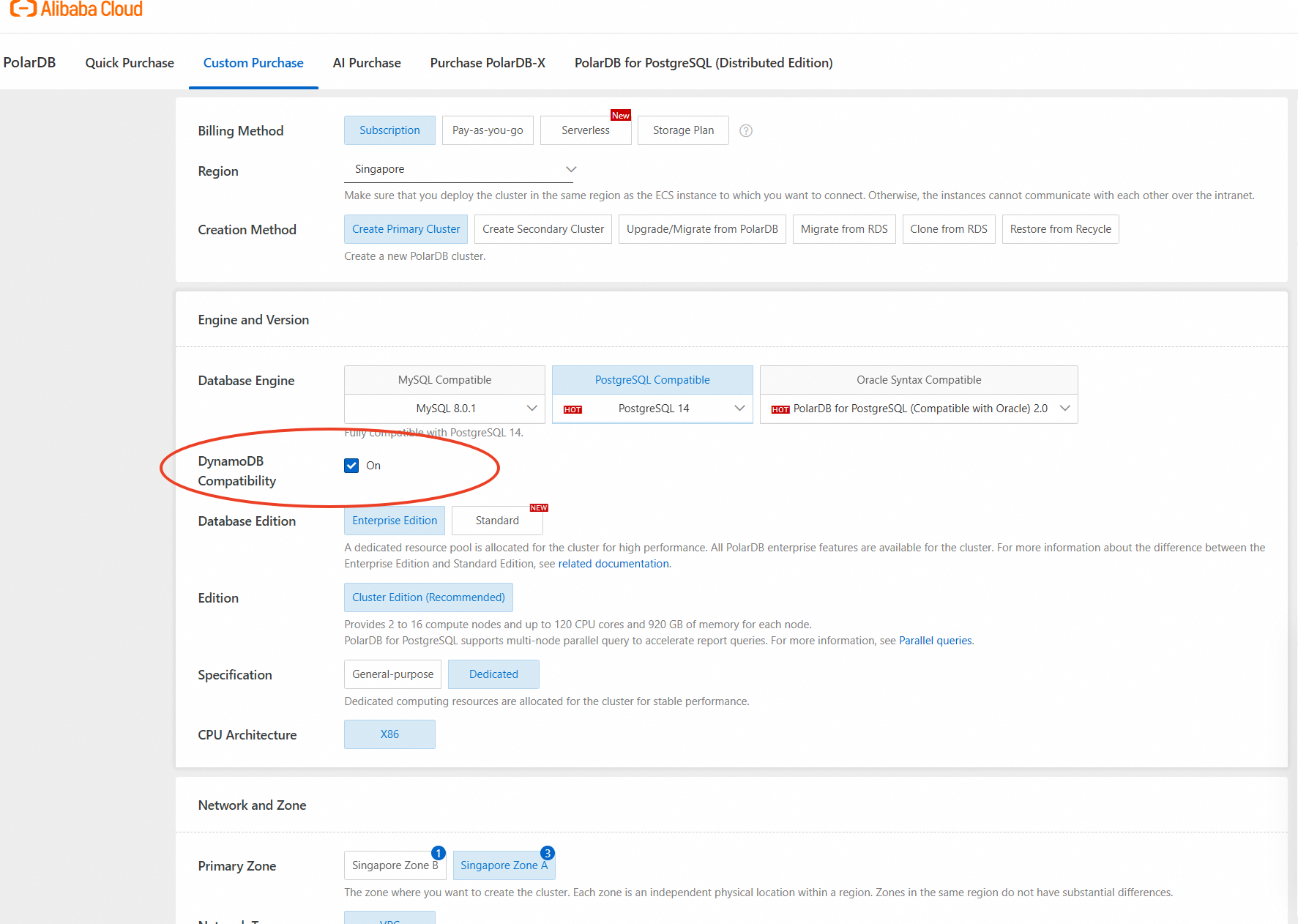
In addition to purchasing new clusters, PolarDB-DDB can also be activated for existing PolarDB for PostgreSQL clusters. Ensure the following database and proxy version requirements are met:
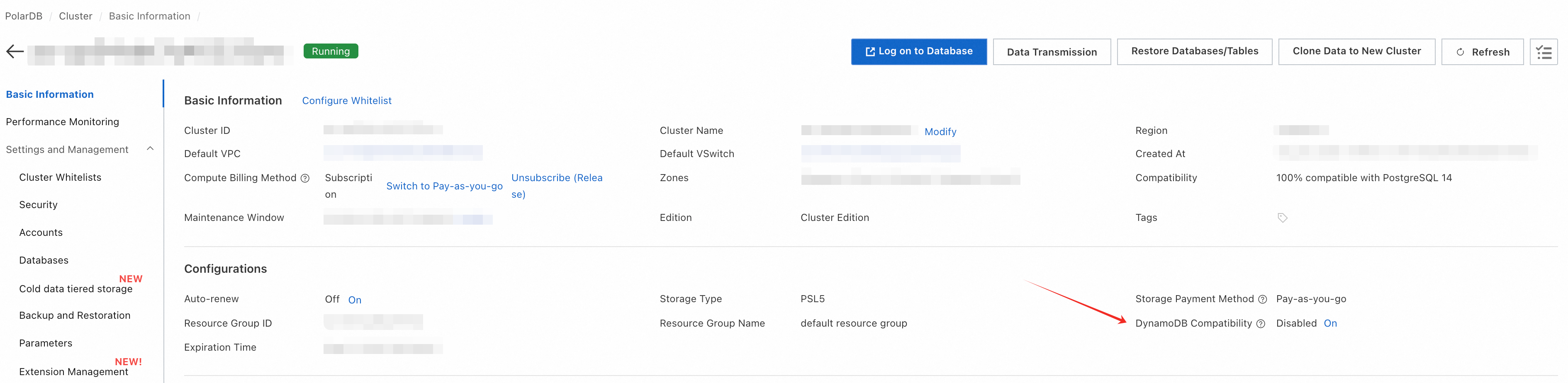
Once DynamoDB Compatibility is enabled, the system will automatically create a DynamoDB endpoint for the cluster. The DynamoDB endpoint is the key to unlocking the full power of PolarDB-DDB.
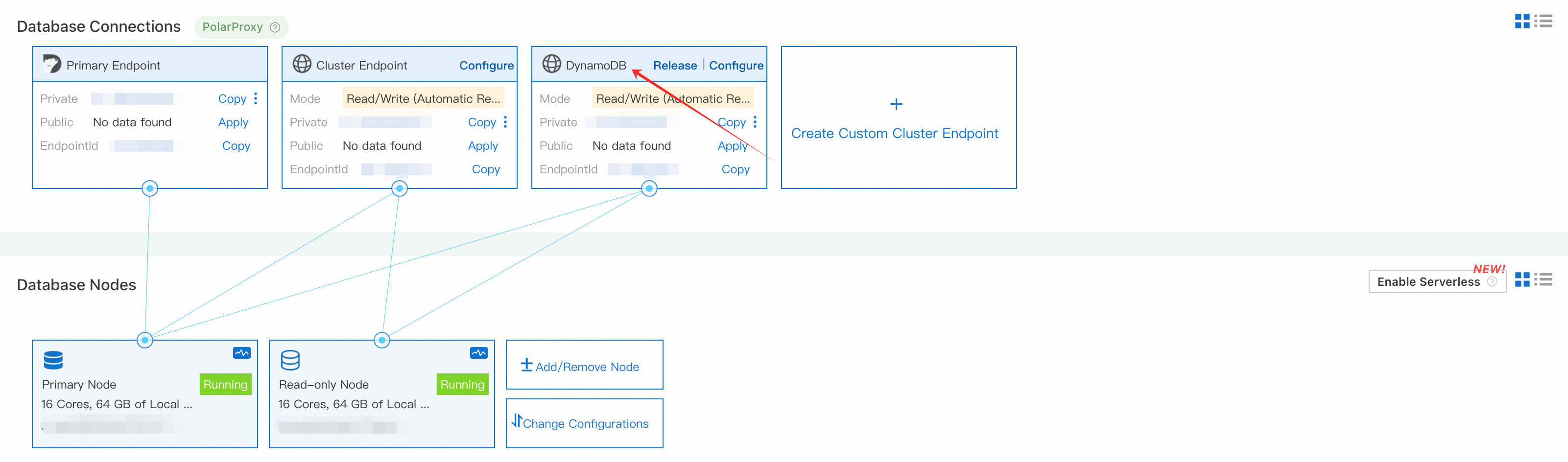
You may also create a customized DynamoDB endpoint pointed to specified node with many other configurations. To do so, click “Create Custom Cluster Endpoint,” and select Endpoint Type as DynamoDB. Here, you have two options on the data consistency settings (defaulting to eventual consistency). You can choose global consistency if stronger data consistency is required. Once global consistency is selected, all read requests under this address will uniformly adopt the global consistency strategy. Please note that global consistency cannot be set in requests via ConsistentRead=True; the consistency type must be configured in advance for the endpoint.
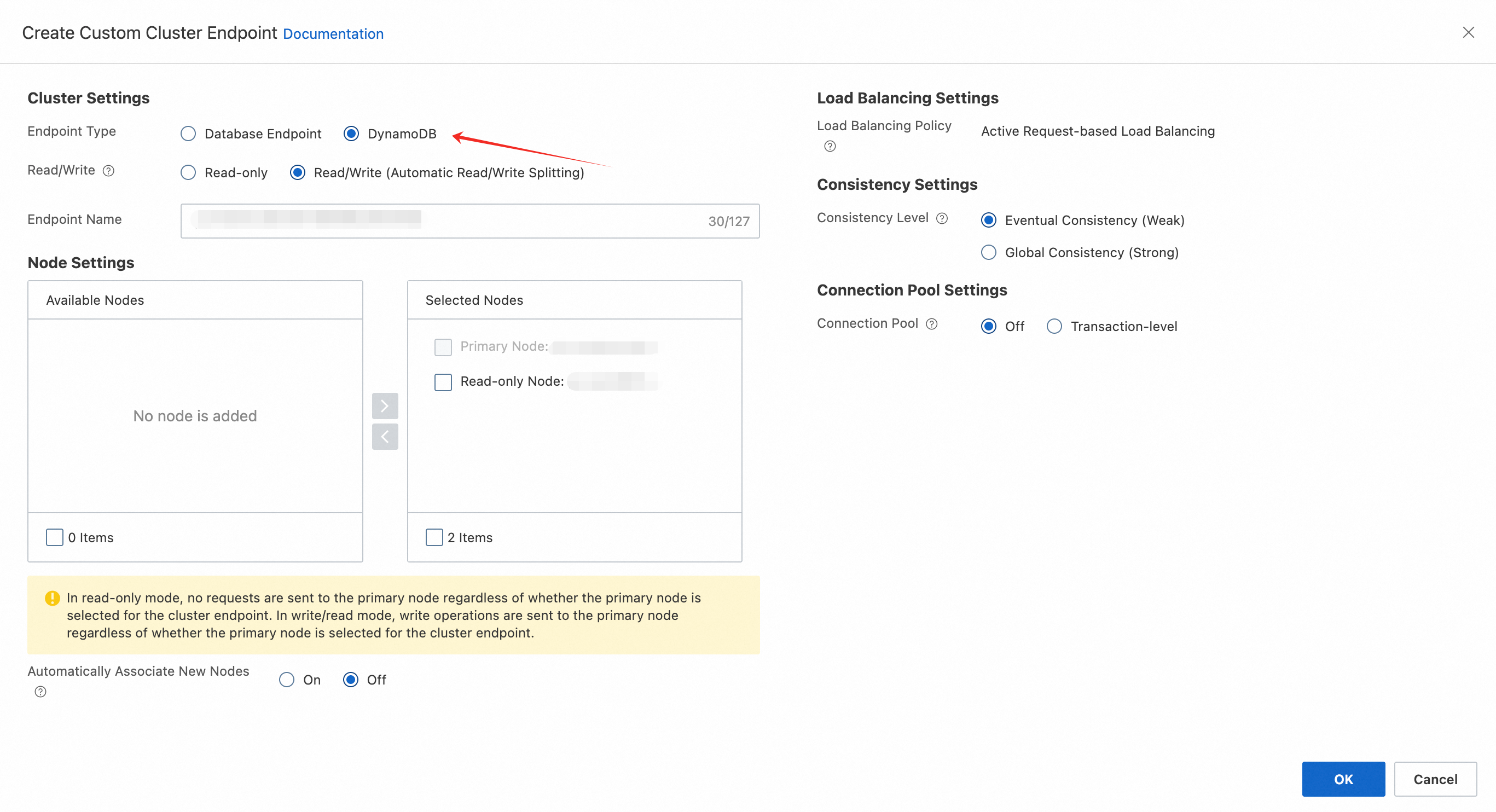
After generating a DynamoDB endpoint, create a dedicated account to access PolarDB-DDB.
Select “Accounts” and click “Create Account.” Choose the Account Type as DynamoDB Account, then customize your own account name and password.
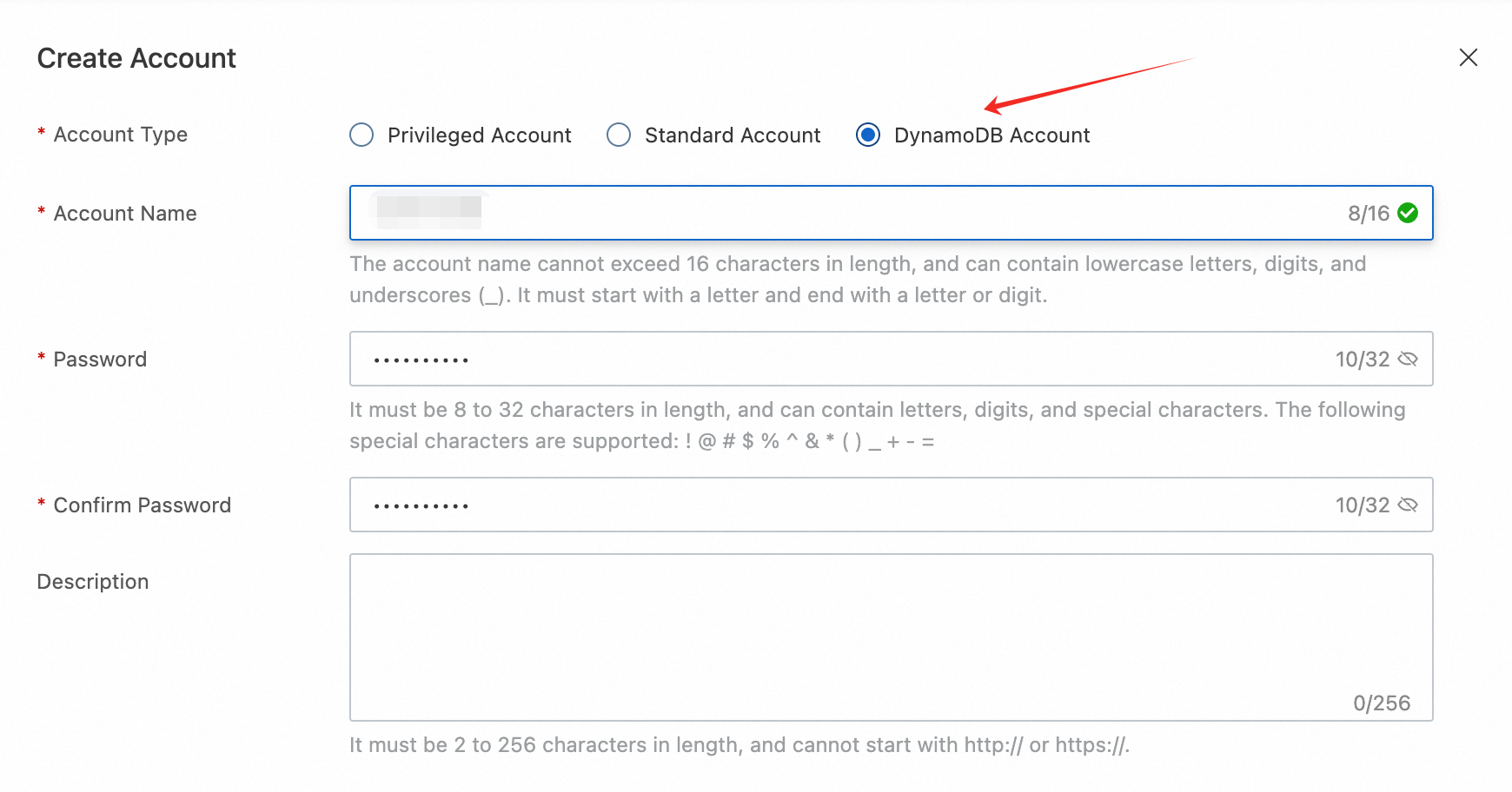
After the account is created, the system will generate your access credentials.

For clients using Alibaba Cloud ECS or other cloud resources, it is recommended to connect to PolarDB-DDB via private endpoint. Ensure your applications are in the same VPC, or that the ECS IP is added to the database whitelist.
For local testing, you can apply for a public endpoint. However, this is recommended only for temporary testing. Be sure to deactivate public access promptly after testing, to reduce security risks.
Here’s an example of Python code using the boto3 SDK to connect to the PolarDB-DDB:
import boto3
from botocore.exceptions import ClientError
import time
# Configure your PolarDB-DDB endpoint (DynamoDB endpoint in step 2), access key (Account Name in step 3), secret access key (Key in step 3), and region
endpoint_url = "http://<your-polardb-ddb-endpoint>"
aws_access_key_id = "<your-access-key-id>"
aws_secret_access_key = "<your-secret-access-key>"
region_name = ""
# Create connection
dynamodb = boto3.resource(
'dynamodb',
aws_access_key_id=aws_access_key_id,
aws_secret_access_key=aws_secret_access_key,
region_name=region_name,
endpoint_url=endpoint_url
)
table_name = 'usertable'
# 1. Create table
def create_table():
try:
table = dynamodb.create_table(
TableName=table_name,
KeySchema=[
{'AttributeName': 'userid', 'KeyType': 'HASH'} # Primary Key
],
AttributeDefinitions=[
{'AttributeName': 'userid', 'AttributeType': 'S'}
],
)
print("Creating table. Waiting for it to be active...")
table.meta.client.get_waiter('table_exists').wait(TableName=table_name)
print("Table created and active!")
return table
except ClientError as e:
if e.response['Error']['Code'] == 'ResourceInUseException':
print("Table already exists.")
return dynamodb.Table(table_name)
else:
print("Error:", e)
raise
# 2. Insert some data
def put_items():
table = dynamodb.Table(table_name)
users = [
{'userid': 'user01', 'name': 'Alice', 'age': 24},
{'userid': 'user02', 'name': 'Bob', 'age': 30},
{'userid': 'user03', 'name': 'Charlie', 'age': 28}
]
for user in users:
table.put_item(Item=user)
print("Inserted items.")
# 3. Query (scan) data
def scan_table():
table = dynamodb.Table(table_name)
response = table.scan()
items = response.get('Items', [])
print(f"Scanned {len(items)} items:")
for item in items:
print(item)
# 4. Delete table
def delete_table():
table = dynamodb.Table(table_name)
table.delete()
print("Deleting table. Waiting for deletion...")
table.meta.client.get_waiter('table_not_exists').wait(TableName=table_name)
print("Table deleted.")
if __name__ == '__main__':
create_table()
put_items()
scan_table()
delete_table()Expected output:
Creating table. Waiting for it to be active...
Table created and active!
Inserted items.
Scanned 3 items:
{'age': Decimal('24'), 'name': 'Alice', 'userid': 'user01'}
{'age': Decimal('30'), 'name': 'Bob', 'userid': 'user02'}
{'age': Decimal('28'), 'name': 'Charlie', 'userid': 'user03'}
Deleting table. Waiting for deletion...
Table deleted.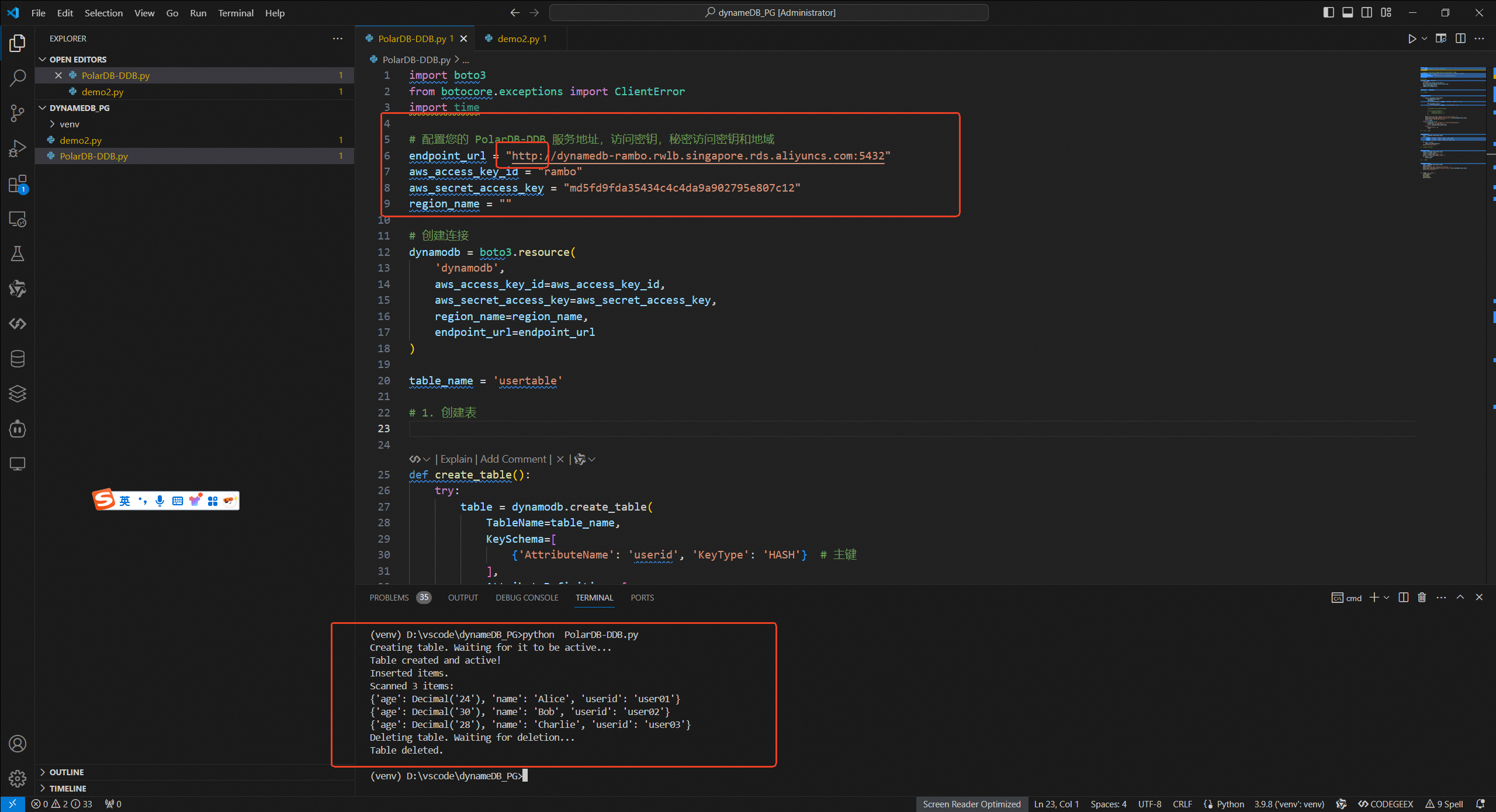
To efficiently evaluate the feasibility of migrating applications built on DynamoDB to PolarDB-DDB, we provide a lightweight and secure scanning tool called polar_ddb_code_digest. This tool analyzes local project code, identifies DynamoDB API calls and parameter usage, and outputs a desensitized interface mapping report to help you evaluate compatibility.
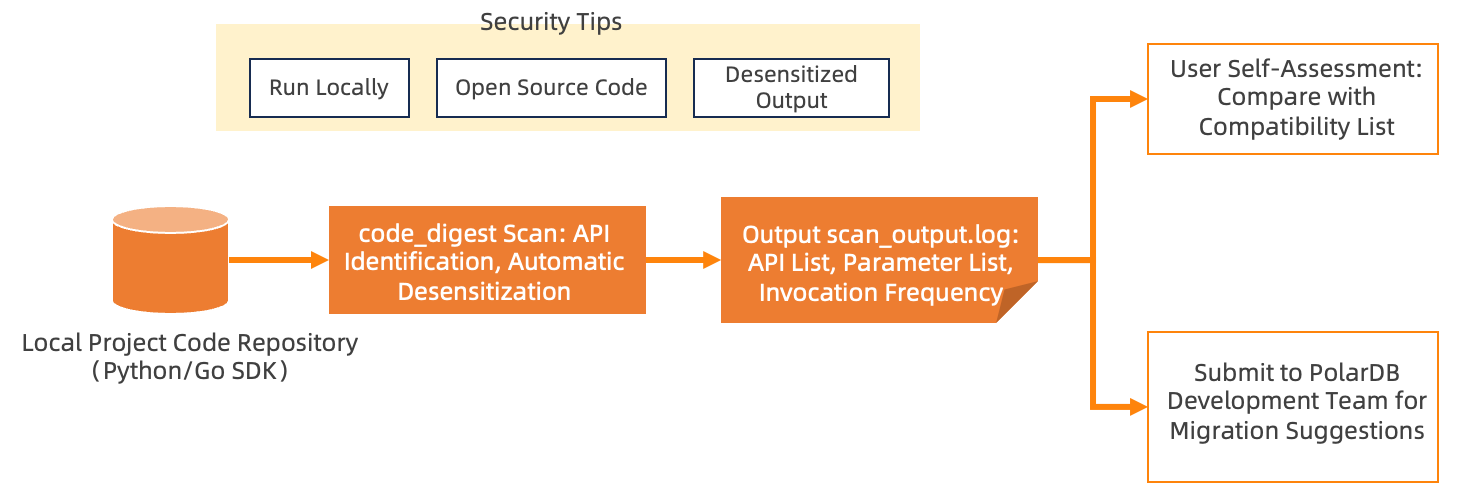
Key features of polar_ddb_code_digest include:
DynamoDB SDK API Call Identification: Based on the AWS official interface specifications, the tool uses syntactic analysis to recognize DynamoDB SDK API calls and extract:
After generating the sanitized report, users can evaluate compatibility against the "PolarDB-DDB Command Support List" or submit the sanitized report to the Alibaba Cloud technical support team for professional migration advice once internal compliance approval is complete.
Currently, the tool supports the Go SDK v2 and the Python Boto3 driver. For detailed command usage or inquiries regarding other SDKs (such as Java, Node.js, etc.), contact us for free technical support.
Upon confirming command compatibility, you only need to adjust the connection code. Below, we detail how to adapt based on two common user habits, with key changes only in AK/SK and region settings.
If the original code is as follows:
aws_access_key_id = "<your-access-key-id>"
aws_secret_access_key = "<your-secret-access-key>"
region_name = "cn-north-1"
# Create connection
dynamodb = boto3.resource(
'dynamodb',
aws_access_key_id=aws_access_key_id,
aws_secret_access_key=aws_secret_access_key,
region_name=region_name
)Modify it to:
# Add the PolarDB-DDB Connection String (the DynamoDB endpoint in step 2)
endpoint_url = "http://<your-polardb-ddb-endpoint>"
aws_access_key_id = "<user-name>"
aws_secret_access_key = "<md5-secret-key>"
# Set region to ""
region_name = ""
# Create connection
dynamodb = boto3.resource(
'dynamodb',
aws_access_key_id=aws_access_key_id,
aws_secret_access_key=aws_secret_access_key,
region_name=region_name,
endpoint_url=endpoint_url
)Modify the access key and secret access key in the ~/.aws/credentials file:
[default]
aws_access_key_id = <user_name>
aws_secret_access_key = <md5-secret-key>Change the region to empty in the ~/.aws/config file:
[default]
region =This section helps you gain a deeper understanding of the adaptation logic and principles.
To connect your existing application, you only need to update a few key parameters. This table shows the direct mapping between DynamoDB's credentials and PolarDB-DDB's connection parameters.
| DynamoDB | PolarDB-DDB | How to configure |
|---|---|---|
| Access Key ID | PolarDB-DDB AccountName | Use the account name you created in the PolarDB console. |
| Secret Access Key | System-Generated Key | Use the key provided in the console (an MD5 hash of your password). |
| Region | Endpoint URL | Set the region_name parameter to an empty string ("") and add the endpoint_url parameter with your PolarDB-DDB connection string. |
Access Key and Secret Access Key
In AWS, the Access Key and Secret Access Key are identity credentials used for programmatic access via SDKs, scripts, or tools:
To ensure compatibility with DynamoDB client drivers, PolarDB-DDB uses the following mapping:
Region and Endpoint
When creating tables in the DynamoDB console, you must specify the region where the data resides, and connections also require the corresponding region configuration. On Alibaba Cloud, this concept corresponds to the region selected when purchasing an cluster. For example, to migrate a DynamoDB data located in the cn-north-1 region, you can create a PolarDB-DDB cluster in Alibaba Cloud’s China (Beijing) region.
Since the region and endpoint for a PolarDB-DDB cluster are determined during cluster creation, clients do not need to locate services by region. Instead, they connect directly by explicitly configuring the endpoint.
PolarDB-DDB features a database migration tool built on nimo-shake, designed to facilitate seamless migration from AWS DynamoDB. The data migration tool leverages certain DynamoDB commands and streaming capabilities, such as Scan (for full table traversal) and Streams (for change data capture).
The tool primarily uses query and insert commands for full synchronization, capturing data changes for incremental synchronization. Below is a preliminary overview of the migration process:
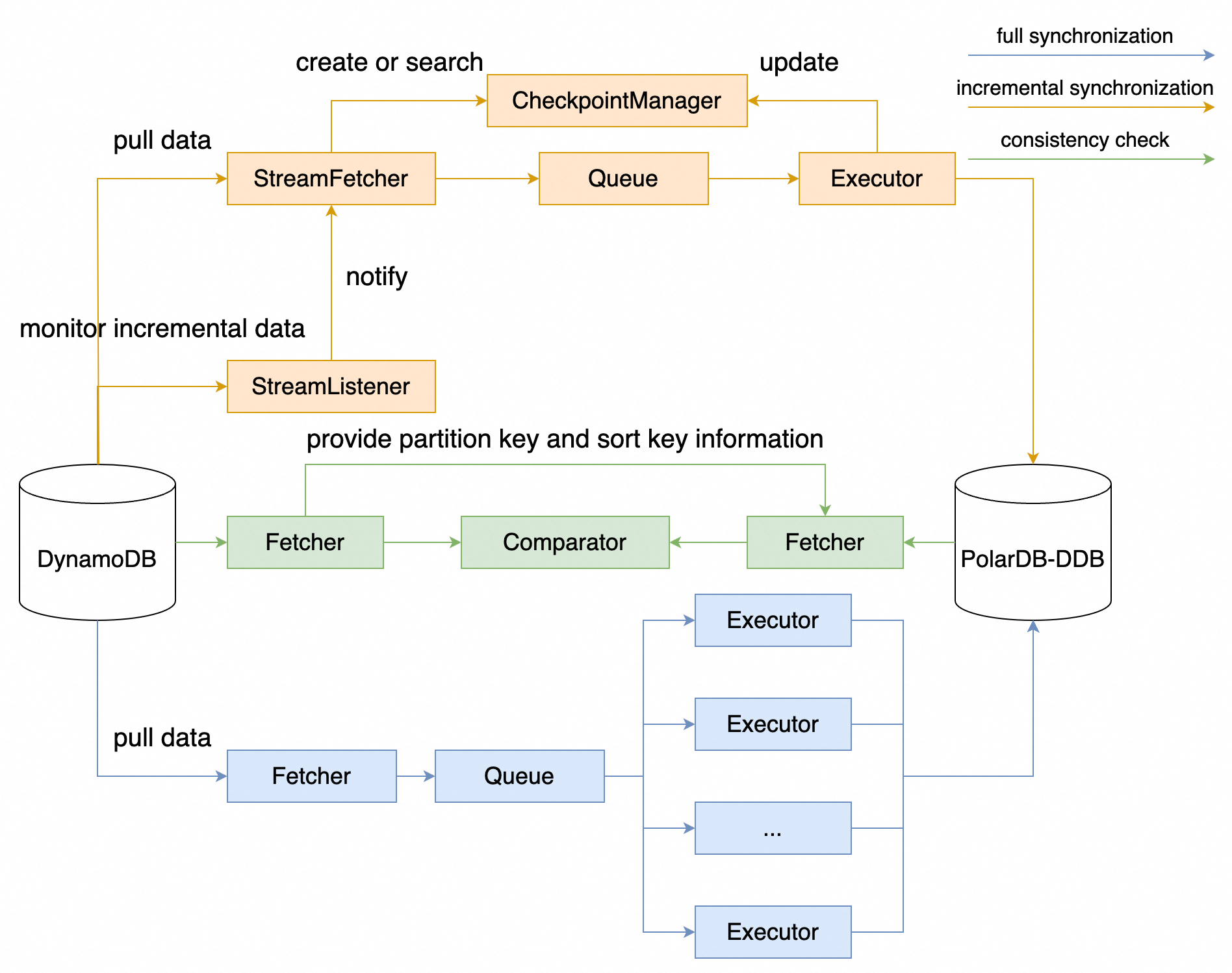
The process is broken down into four key phases.
The Migration tool, nimo-shake, handles the initial full data copy.
ListTables to fetch all table names from DynamoDB, filter the tables that need to be migrated (configurable), and then create tables in PolarDB-DDB using CreateTable.Scan, placing it into a queue, from which the Executor retrieves the data and uses BatchWriteItem to batch write to PolarDB-DDB.Once full synchronization completes, incremental synchronization will start automatically. The StreamListener monitors for changes occurring after the migration point via DynamoDB Streams, notifying the StreamFetcher to fetch incremental data and synchronizing it to PolarDB-DDB through the Executor. Incremental synchronization will record checkpoint information to support resuming from pauses.
Validate consistency via bulk retrieval of DynamoDB data through Scan, matching the partition key and sort key to query corresponding records in PolarDB-DDB with GetItem, thus verifying consistency and generating a difference report.
(Optional) Reverse Synchronization
Prior to fully switching over to the PolarDB-DDB cluster, you can capture incremental data changes from PolarDB-DDB through logical replication and convert these increments into JSON for writing back to DynamoDB using a Python script.
Performing a full data migration will consume resources on both the source and target databases and may increase server load. If your database workload is high or your server specifications are low, this could add significant pressure. We advise thorough evaluations before executing data migration, ideally performing it during low-traffic periods or after appropriate resource scaling.
For detailed configuration options and usage instructions, contact us at https://www.alibabacloud.com/contact-sales
ApsaraDB - September 27, 2025
ApsaraDB - January 3, 2024
ApsaraDB - December 1, 2023
Alibaba Cloud_Academy - September 21, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Community - December 8, 2023
5544031433091282 - April 6, 2025
 PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn More PolarDB for Xscale
PolarDB for Xscale
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for Xscale (PolarDB-X) is a cloud-native high-performance distributed database service independently developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More PolarDB for MySQL
PolarDB for MySQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for MySQL is a cloud-native relational database service 100% compatible with MySQL.
Learn More AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
An online MPP warehousing service based on the Greenplum Database open source program
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB