By Zongzhi Chen, Manager of Alibaba Cloud RDS Team
One of MySQL's core innovations is its Pluggable Storage Engine Architecture, which enables MySQL to extend its capabilities through various storage engines, supporting diverse business scenarios. MySQL's pluggable architecture is illustrated below:
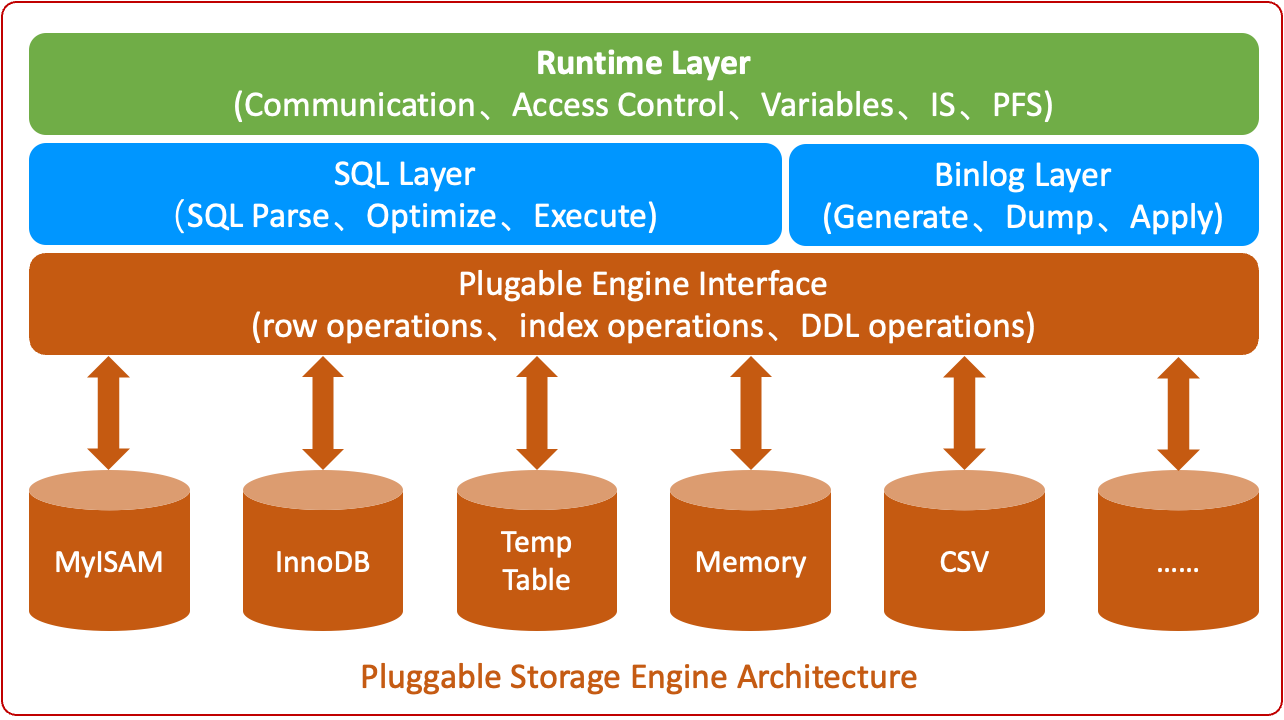
MySQL's pluggable storage engine architecture can be divided into four main parts:
MySQL designs a standardized data access control interface (Plugable Engine Interface) between SQL computation and data storage. The SQL layer performs data updates, queries, and management through this standard interface, enabling storage engines to be "hot-swapped" as independent components.
Currently commonly used storage engines in MySQL include:
The introduction of InnoDB as an engine into MySQL was a very important milestone in MySQL's pluggable engine architecture. In the early days of the internet, MyISAM gained favor in internet businesses due to its simple and efficient access, and together with Linux, Apache, and PHP, it was called the LAMP architecture. With the rise of e-commerce and social internet, MyISAM's shortcomings became increasingly apparent. InnoDB greatly expanded MySQL's capabilities due to its support for transaction ACID, advantages in concurrent access and performance. With InnoDB, MySQL became the most popular open-source OLTP database.
With the widespread use of MySQL, we see more and more analytical queries based on TP data. InnoDB's architecture is naturally designed for OLTP. Although it can deliver excellent performance in TP business scenarios, InnoDB's query efficiency in analytical business scenarios is very low. This greatly limits MySQL's usage scenarios. To this day, MySQL has lacked an analytical query engine. The emergence of DuckDB has shown us a possibility.
DuckDB is an open-source database designed for online analytical processing (OLAP) and data analytics workloads. Due to its lightweight, high-performance, zero-configuration, and easy-to-integrate characteristics, it is rapidly becoming a popular choice in data science, BI tools, and embedded analytics scenarios. DuckDB mainly has the following features:
Based on the above reasons, we believe DuckDB is very suitable to become MySQL's AP storage engine. Therefore, we have integrated DuckDB into AliSQL.
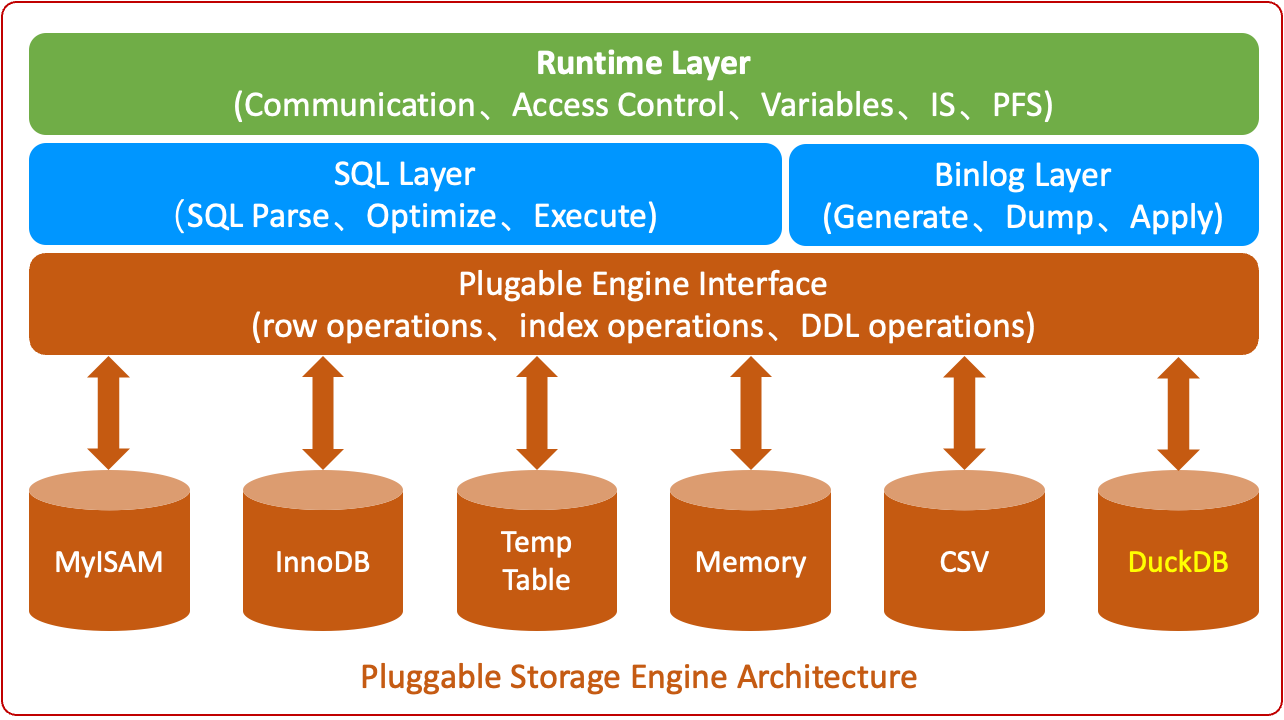
The positioning of the DuckDB engine is to achieve lightweight single-node analytical capabilities. Currently, the RDS MySQL DuckDB read-only instance based on the DuckDB engine has been launched. Welcome to try it. In the future, we will also launch highly available RDS MySQL DuckDB primary instances with master-standby setup. Users can aggregate heterogeneous data to RDS MySQL DuckDB instances through tools like DTS to perform data analysis queries.
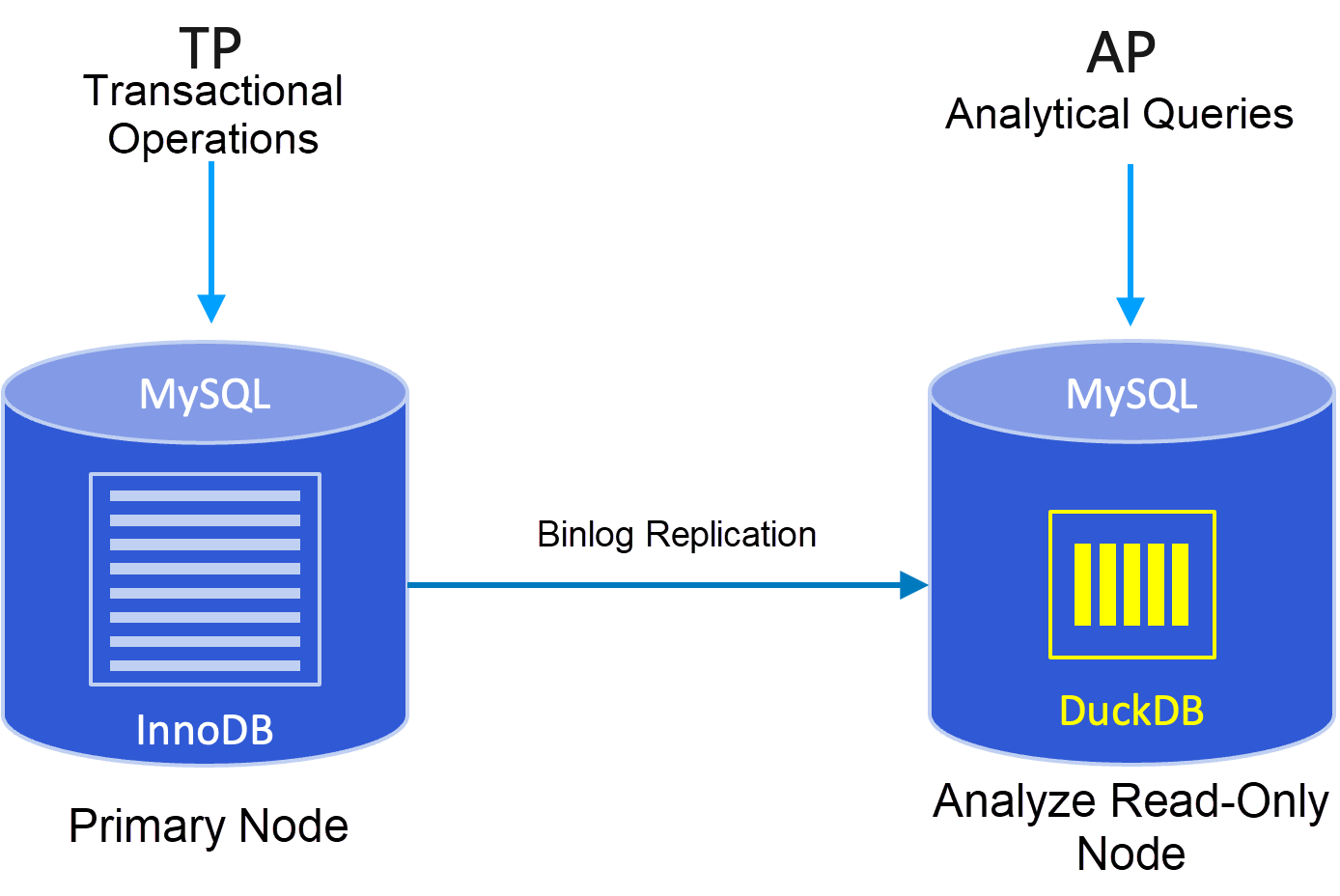
The DuckDB analytical read-only instance adopts a read-write separation architecture. Analytical services and primary instance services are separated without affecting each other. Like ordinary read-only instances, it replicates data from the primary instance through the Binlog replication mechanism. The DuckDB analytical read-only node has the following advantages:
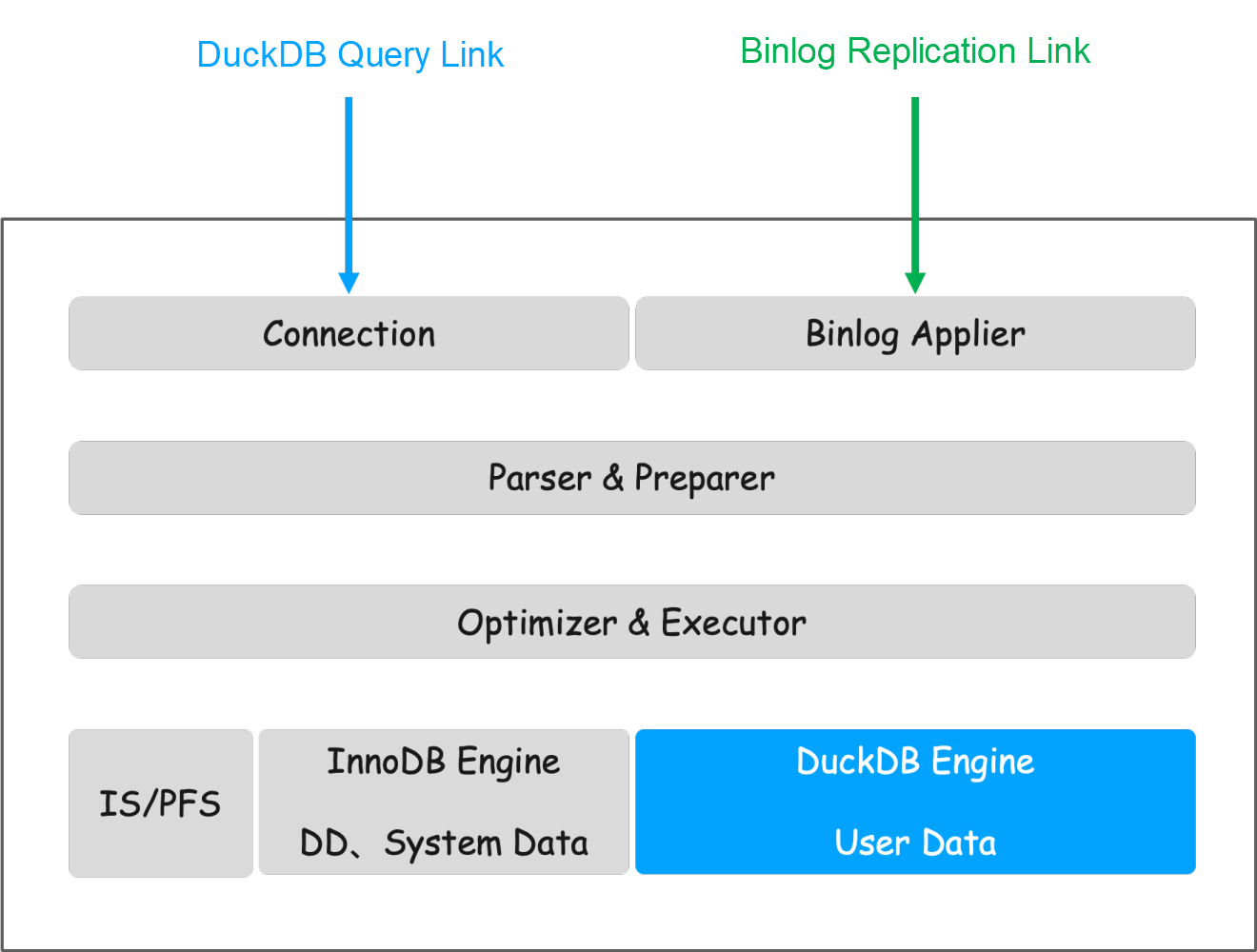
The DuckDB read-only instance can be divided into a query path and a Binlog replication path in usage. The query path accepts user query requests and executes data queries. The Binlog replication path connects to the primary instance for Binlog replication. The technical principles will be introduced separately from these two aspects below.
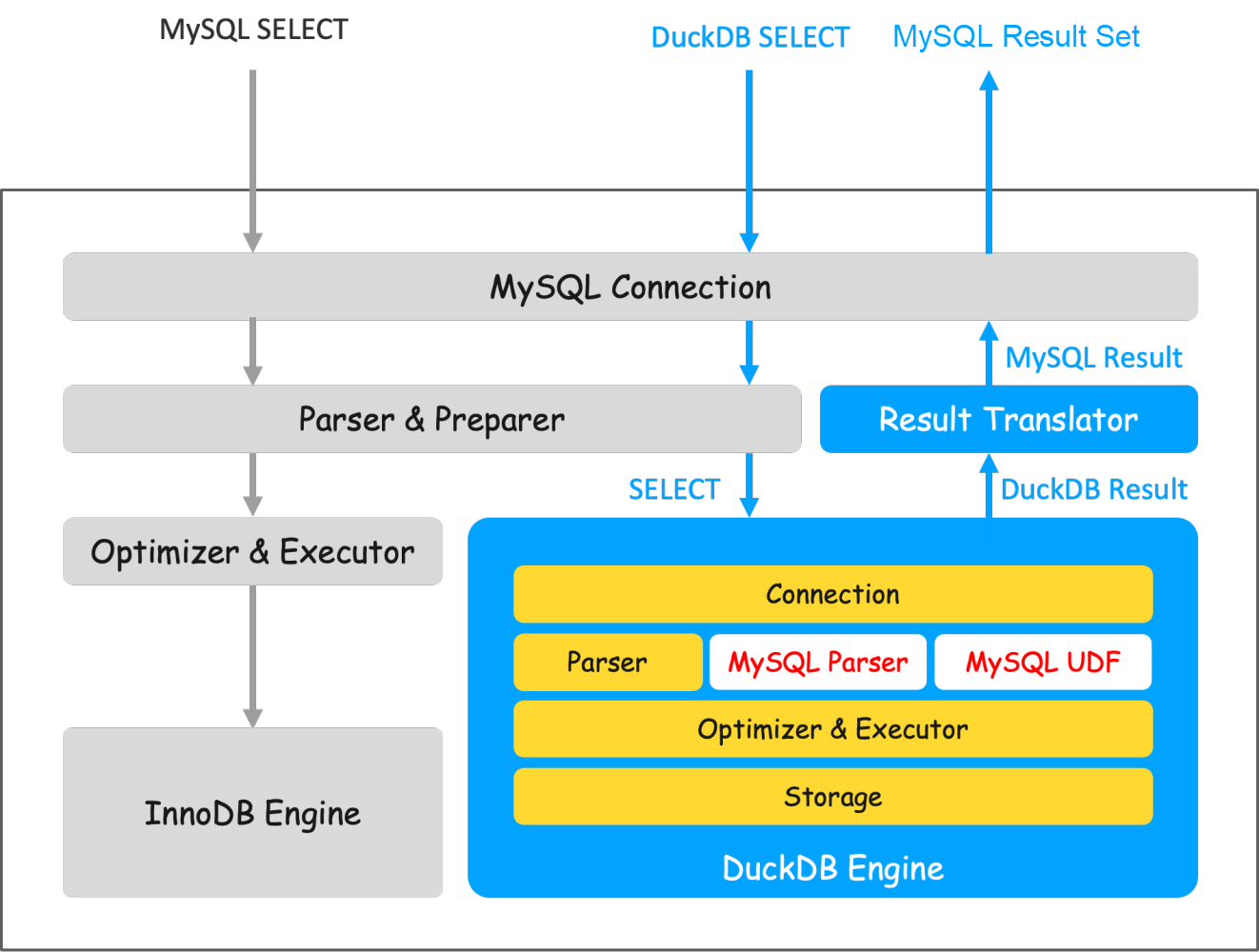
The query execution process is as shown above. InnoDB is only used to store metadata and system information, such as accounts, configurations, etc. All user data is stored in the DuckDB engine.
Users connect to the instance through the MySQL client. After the query arrives, MySQL first performs parsing and necessary processing. Then it sends the SQL to the DuckDB engine for execution. After DuckDB completes execution, it returns the results to the Server layer, which converts the result set into a MySQL result set and returns it to the client.
The most important task of the query path is compatibility work. DuckDB and MySQL data types are basically compatible, but there are significant differences in syntax and function support. To address this, we extended DuckDB's syntax parser to be compatible with MySQL-specific syntax; rewrote a large number of DuckDB functions and added many MySQL functions, allowing common MySQL functions to run accurately. Automated compatibility testing platform with approximately 170,000 SQL tests showed a compatibility rate of 99%. Detailed compatibility information see link
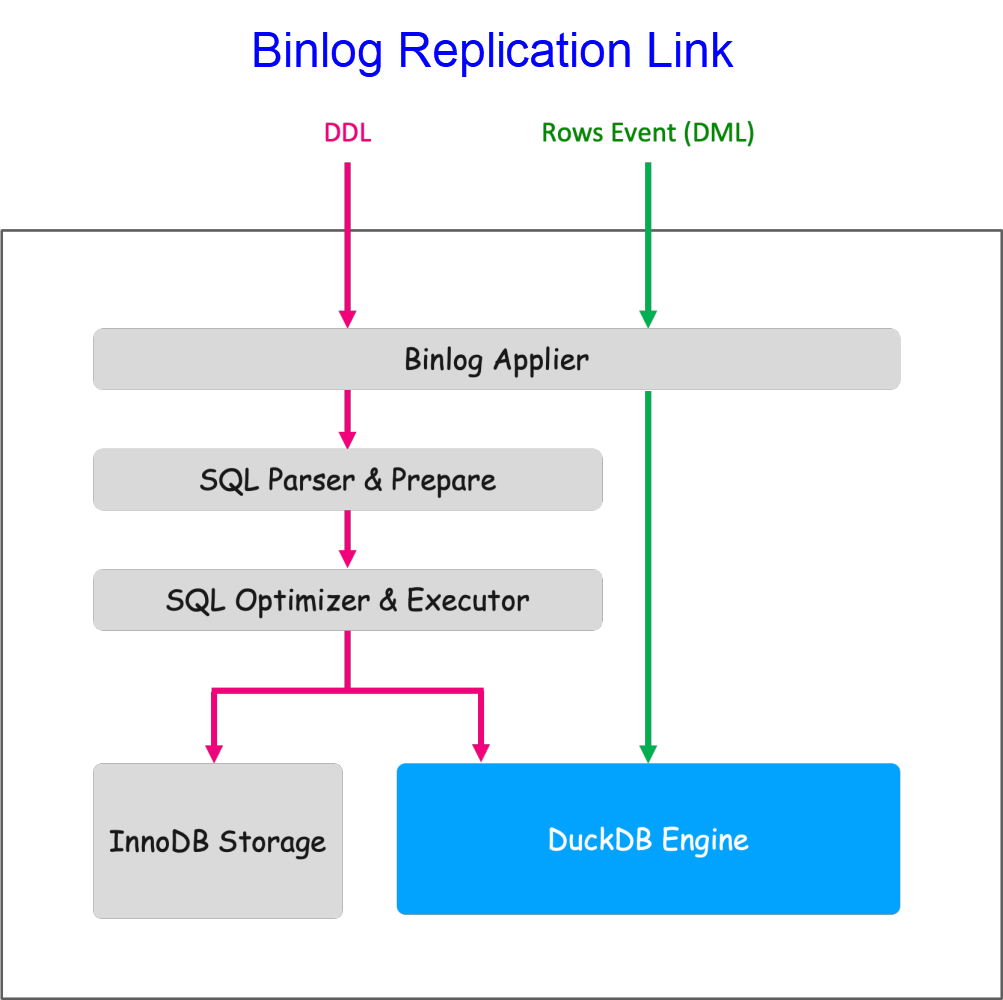
Since DuckDB does not support two-phase commit, it cannot use two-phase commit to ensure consistency between Binlog GTID and data, nor can it ensure consistency between InnoDB metadata and DuckDB during DDL operations. Therefore, we modified the transaction commit process and Binlog replay process to ensure data consistency after instance abnormal crash and restart.
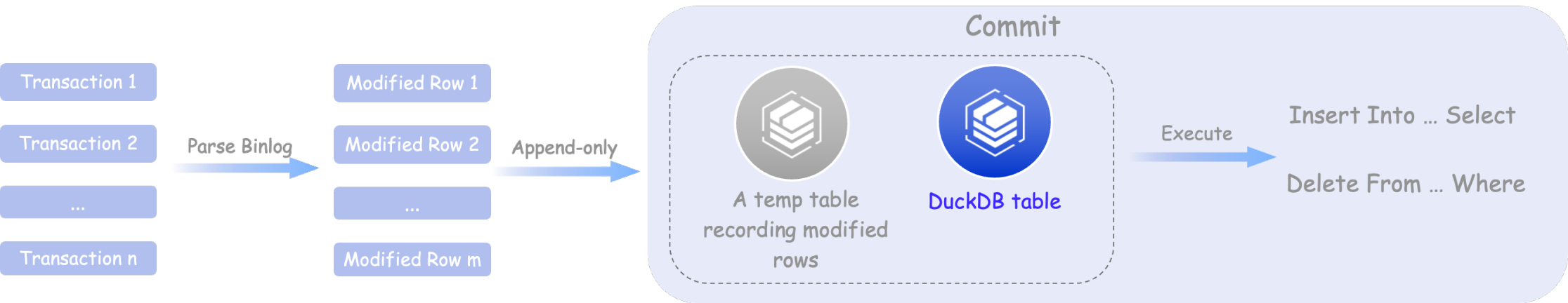
Due to DuckDB's implementation, it favors large transactions. The execution efficiency of frequent small transactions is very low, causing severe replication delays. Therefore, we optimized Binlog replay by adopting a batch approach for transaction replay. After optimization, it can achieve a replay capability of 30 rows/s. In Sysbench stress tests, it achieved no replication delay, with even higher replay performance than InnoDB.
A small number of DDLs in MySQL, such as modifying column order, are not supported by DuckDB. To ensure normal replication, we implemented a Copy DDL mechanism. For DDLs natively supported by DuckDB, they are executed using Inplace/Instant methods. When encountering DDLs not supported by DuckDB, the Copy DDL method is used to create a new table to replace the original table.
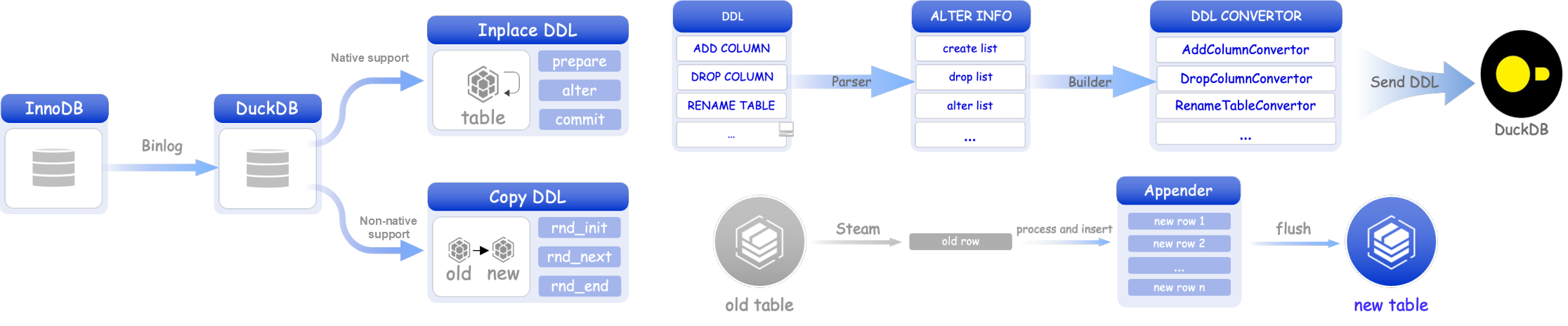
Copy DDL uses multi-threaded parallel execution, reducing execution time by 7 times.
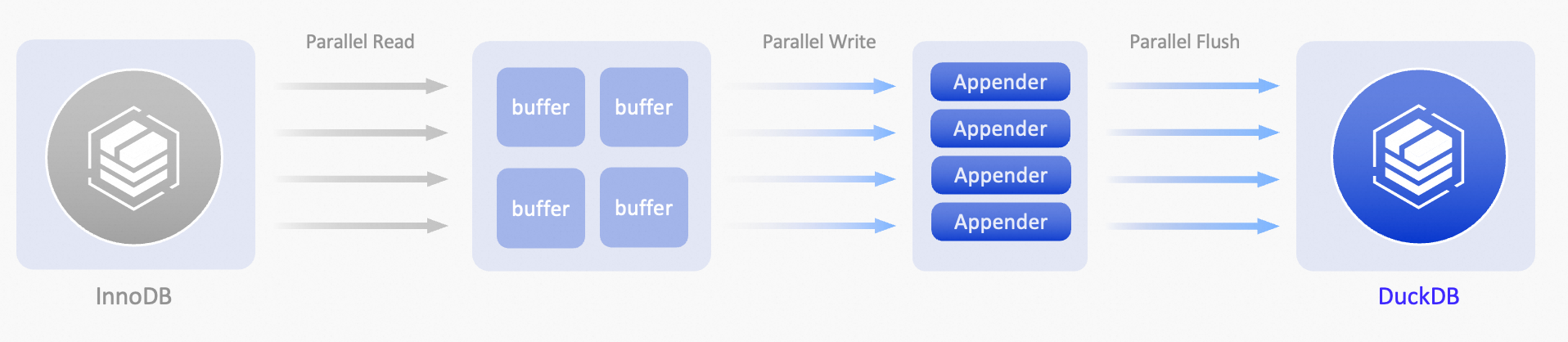
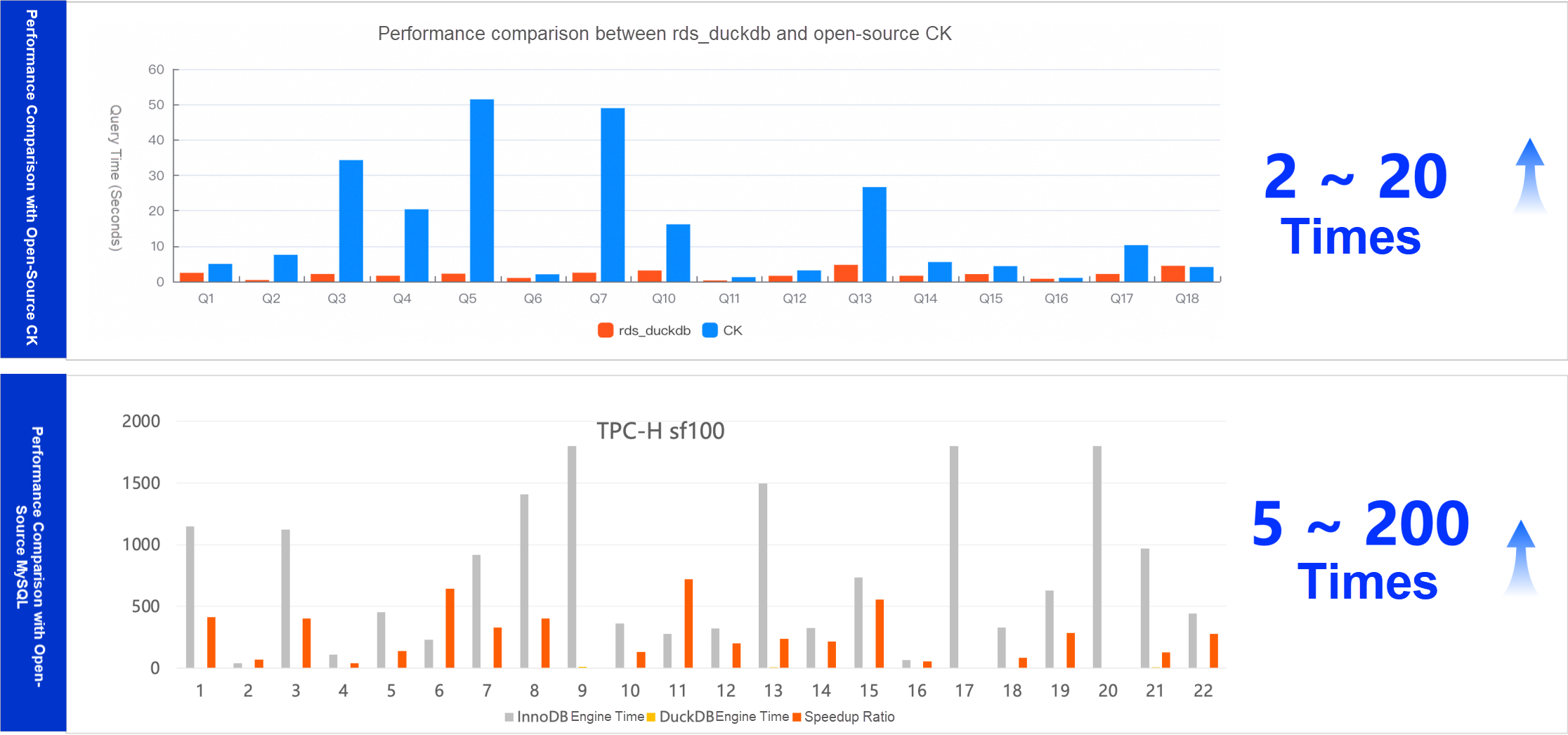
ECS instance 32CPU, 128GB memory, ESSD PL1 cloud disk 500GB
TPC-H SF100
Online purchase of RDS MySQL instances can be directly experienced:
PolarDB-DDB: A High-Performance, Cost-Effective Cloud-Native Alternative to DynamoDB
ApsaraDB - September 27, 2025
ApsaraDB - January 15, 2026
ApsaraDB - November 26, 2025
ApsaraDB - November 24, 2025
ApsaraDB - December 25, 2024
ApsaraDB - November 18, 2025
 ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL
ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL
An on-demand database hosting service for MySQL with automated monitoring, backup and disaster recovery capabilities
Learn More ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL
ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL
An on-demand database hosting service for PostgreSQL with automated monitoring, backup and disaster recovery capabilities
Learn More ApsaraDB for OceanBase
ApsaraDB for OceanBase
A financial-grade distributed relational database that features high stability, high scalability, and high performance.
Learn More ApsaraDB for Cassandra
ApsaraDB for Cassandra
A database engine fully compatible with Apache Cassandra with enterprise-level SLA assurance.
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB