Imagine this: It’s peak season, and your IoT company is processing millions of sensor readings. Suddenly, your analytics dashboard freezes. Critical reports fail. Your database logs show the dreaded "Out of Memory" (OOM) errors - again.
This isn’t just an IT issue; it’s a business disruption. Memory-overloading (MO) queries - like large ETL jobs, complex joins, or ad-hoc scans - can cripple even the most robust data warehouses. The fallout?
● Service outages: Delayed decisions, frustrated users.
● Wasted resources: Queries burn CPU and memory… only to fail.
● Firefighting: Engineers scramble to tweak settings or restart services.
Traditional fixes (manual scaling, static rules) are reactive, inflexible, and can’t handle unpredictable workloads.
AnalyticDB for MySQL’s Intelligent Query Routing automates this chaos. Instead of letting MO queries crash your cluster, it:
AnalyticDB originally offered two methods for handling query routing: Manual Query Routing and Automatic Query Routing. The latter initially used a traditional Ruled-based Query Routing method, which relied on fixed and often rigid rules to determine the routing of queries.
However, with the introduction of Intelligent Query Routing, the system can now leverage advanced AI models to predict a query's risk in real-time, improving decision-making based on historical data and real-time performance metrics.
Here's a comparison highlighting the key differences between Ruled-based Query Routing and Intelligent Query Routing:
| Feature | Ruled-based Query Routing | Intelligent Query Routing |
| Operating Principle | Relies on preset, static rules, such as: - If a query's peak memory usage is over 10 GB. | Based on AI models that predict a query's risk in real time, making dynamic decisions based on historical data. |
| Decision Basis | Fixed, hard-coded rules that struggle to handle complex and evolving query patterns and cluster states. | A multi-dimensional feature vector that combines query plan statistics (e.g., operator cardinalities) and real-time cluster metrics (e.g., memory utilization). |
| Misprediction Correction | Unable to self-correct. Poorly set rules can lead to numerous mispredictions, impacting system performance. |
Features a misprediction correction mechanism. The system maintains an index of past failures and automatically flags new, similar queries as high-risk. |
| Adaptability | Low. Rules require manual adjustment and lack adaptability to new query patterns or changes in the cluster environment. |
High. It can use a global or localized model for different clusters and dynamically adjust policies with self-tuning quota management to adapt to unique cluster characteristics. |
| Scalability | Poor scalability. Manual modification and maintenance of routing rules are required whenever the business or cluster changes. |
Highly scalable. The AI model can automatically learn and adapt to new query patterns, significantly reducing the need for manual intervention. |
The transition from ruled-based to intelligent query routing represents a significant leap in database management efficiency. By replacing static rules with dynamic AI-driven predictions, the system not only improves the accuracy of query routing but also enhances overall system performance and resource utilization.
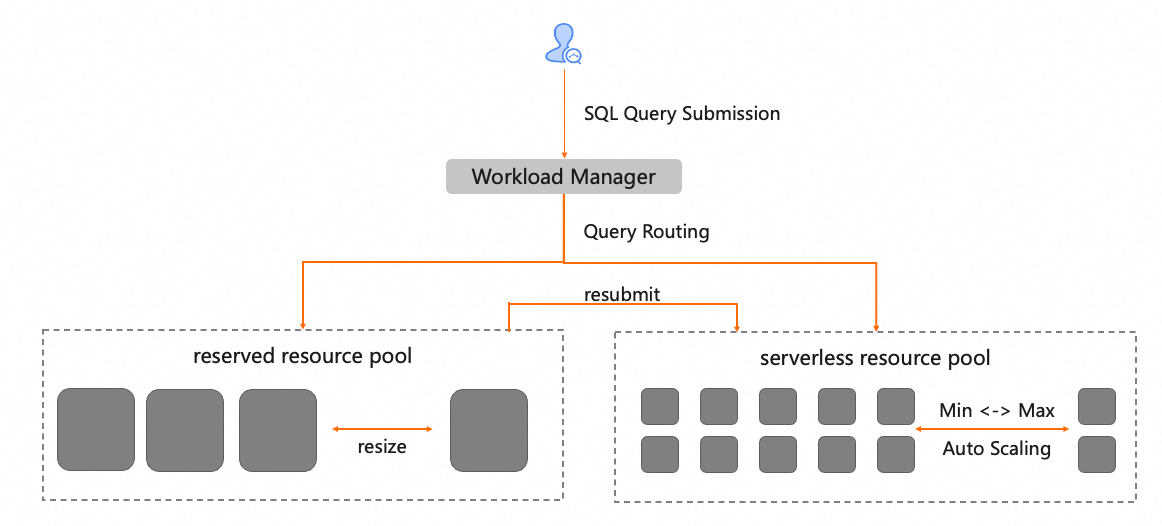
As depicted in the diagram below, intelligent query routing enables users to redirect specific queries from one resource group to another designated resource group. Large queries often result in resource contention, risking system stability. Thus, the query routing feature allows you to direct these demanding queries to a dedicated resource group, preventing interference with other workloads.
1. Smart Detection
2. Hybrid Decision-Making
3. Self-Learning
4. Transparent Routing
The Intelligent Query Routing as a feature of Query Routing function of AnalyticDB for MySQL, it works in the database kernel - between the query optimizer and executor, intercepting queries before execution to predict potential memory overload.
During a peak season, an IoT company's AnalyticDB system might be faced with query timeouts caused by a large query that repeatedly triggered OOM errors, leading to a 20% failure rate for critical queries. This instability disrupted core services. After implementing intelligent query routing, MO queries were rerouted into a lower-impact queue, preventing disruptions and resource waste.
Use Case Highlights:
● Problem: A recurring analytics triggered OOM errors repeatedly, taking down 20% of other queries.
● Fix: The system rerouted it to a dedicated pool.
● Result: Zero timeouts, no wasted retries.
A media company's database encountered regular slowdowns and errors, not due to sudden traffic spikes but due to a mix of long-running, large data scans, and complex JOIN operations—all causing OOM errors. By employing intelligent query routing, the system identified high-risk patterns and rerouted them, eliminating repeated failures and significantly improving overall performance.
Use Case Highlights:
● Problem: Ad-hoc queries with large joins/spikes crashed daily operations.
● Fix: Automatic isolation of recurring OOM culprits.
● Result: Stable performance, no more resource gridlock.
Cost Savings: In general, the Intelligent Query Routing can help enterprises save up to 1 million per year in otherwise wasted compute by avoiding failures and retries caused by MO queries.
Intelligent routing isn’t just about preventing OOMs—it’s about:
● Stability: Protect critical workloads from "noisy neighbors."
● Cost Efficiency: Stop paying for failed queries.
● Less Toil: Engineers spend less time firefighting, more time innovating.
For teams running AnalyticDB, it’s a set-and-forget upgrade. No complex rules. No guesses. Just resource allocation that are smarter.
Ready to try it? Check out the docs.
References: AnalyticDB for MySQL
Practical Operations for Self-built ClickHouse Migration to the Cloud
Intelligent Routing of Memory - Overloading Queries in Serverless Data Warehouses
ApsaraDB - September 25, 2025
Alibaba Clouder - May 20, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - February 8, 2021
ApsaraDB - February 10, 2026
ApsaraDB - October 21, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Indonesia - May 5, 2021
 AnalyticDB for MySQL
AnalyticDB for MySQL
AnalyticDB for MySQL is a real-time data warehousing service that can process petabytes of data with high concurrency and low latency.
Learn More AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
An online MPP warehousing service based on the Greenplum Database open source program
Learn More Database for FinTech Solution
Database for FinTech Solution
Leverage cloud-native database solutions dedicated for FinTech.
Learn More Oracle Database Migration Solution
Oracle Database Migration Solution
Migrate your legacy Oracle databases to Alibaba Cloud to save on long-term costs and take advantage of improved scalability, reliability, robust security, high performance, and cloud-native features.
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB