Once you have registered your Alibaba Cloud account and completed your account and payment information, you are ready to claim free trials of our products (such as ECS, PolarDB, RDS, and other services). You can claim all the benefits on Alibaba Cloud Free Trial Center.
If you already have existing instances for the lab, please skip this chapter.
1. On Alibaba Cloud Free Trial Center, find ECS and click Try Now >
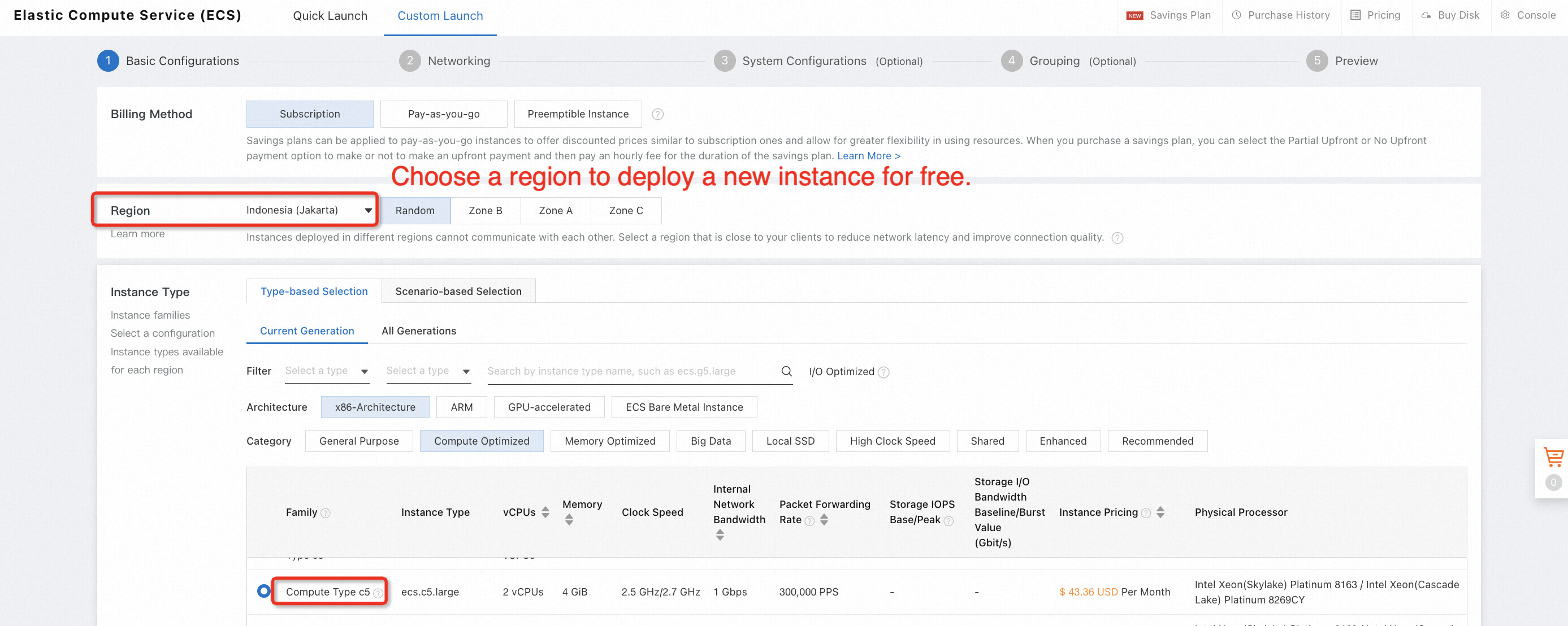
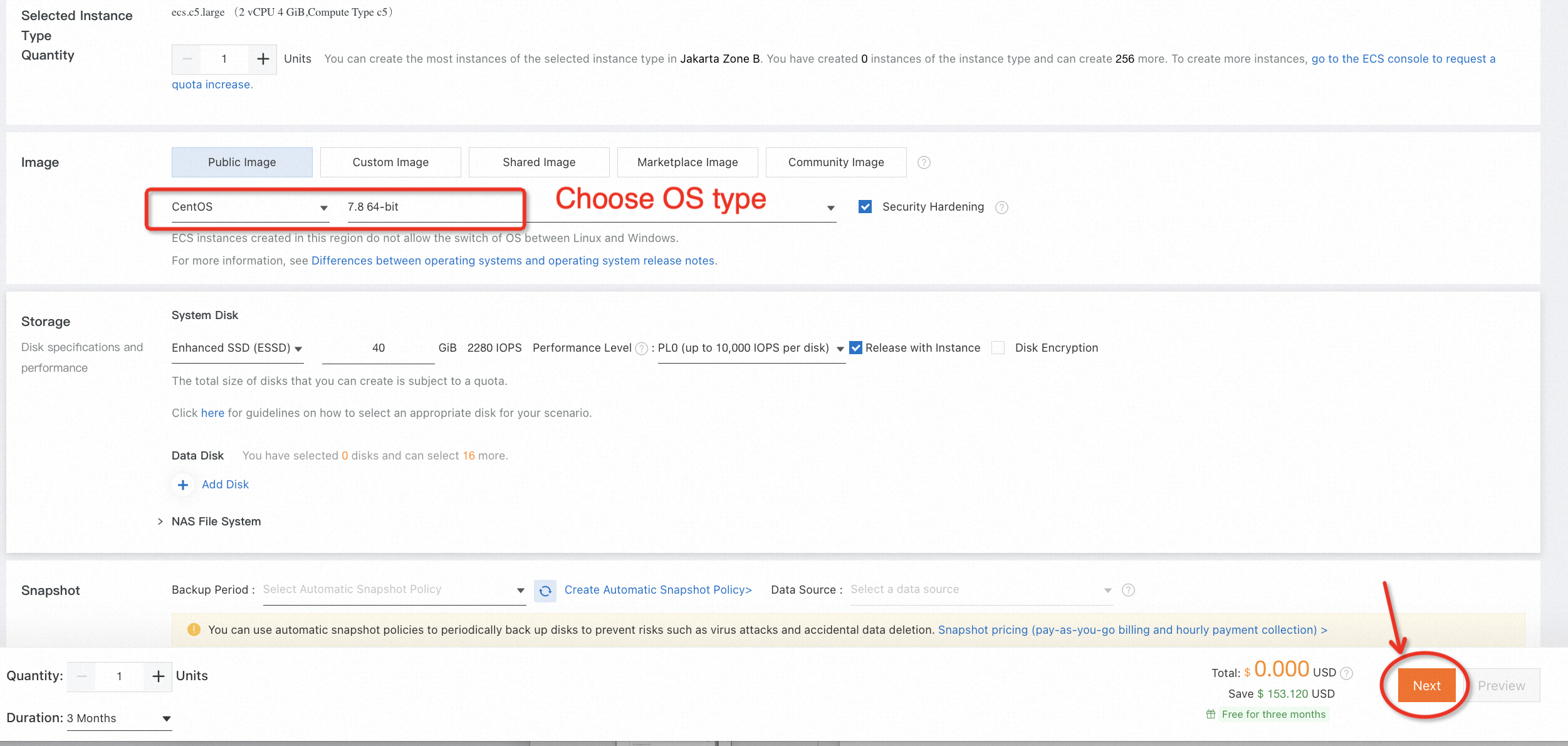
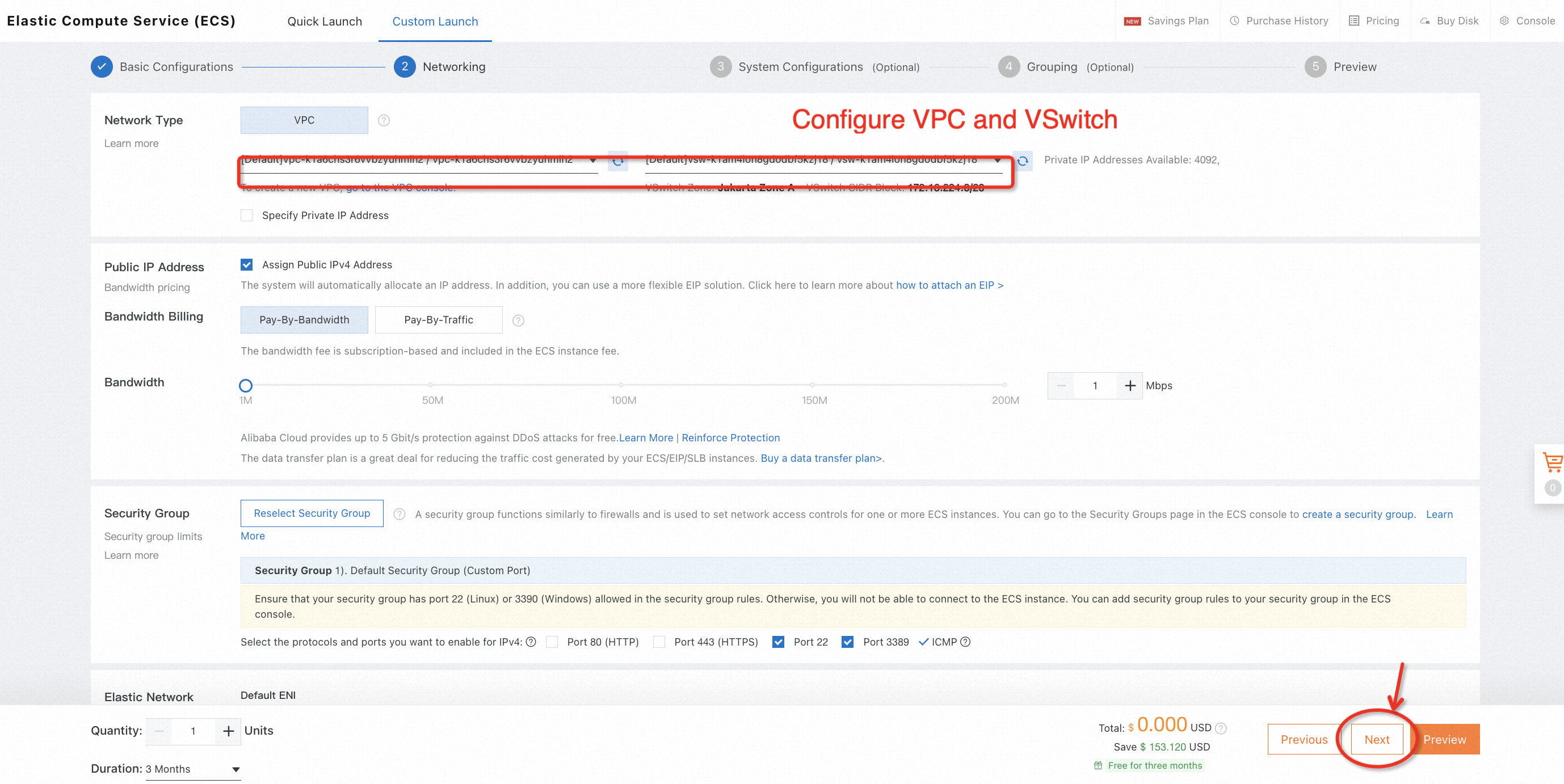
2. Choose a region to deploy the new ECS instance, select the OS type (such as CentOS 7.8 x64), and complete all configurations of the free trial order:
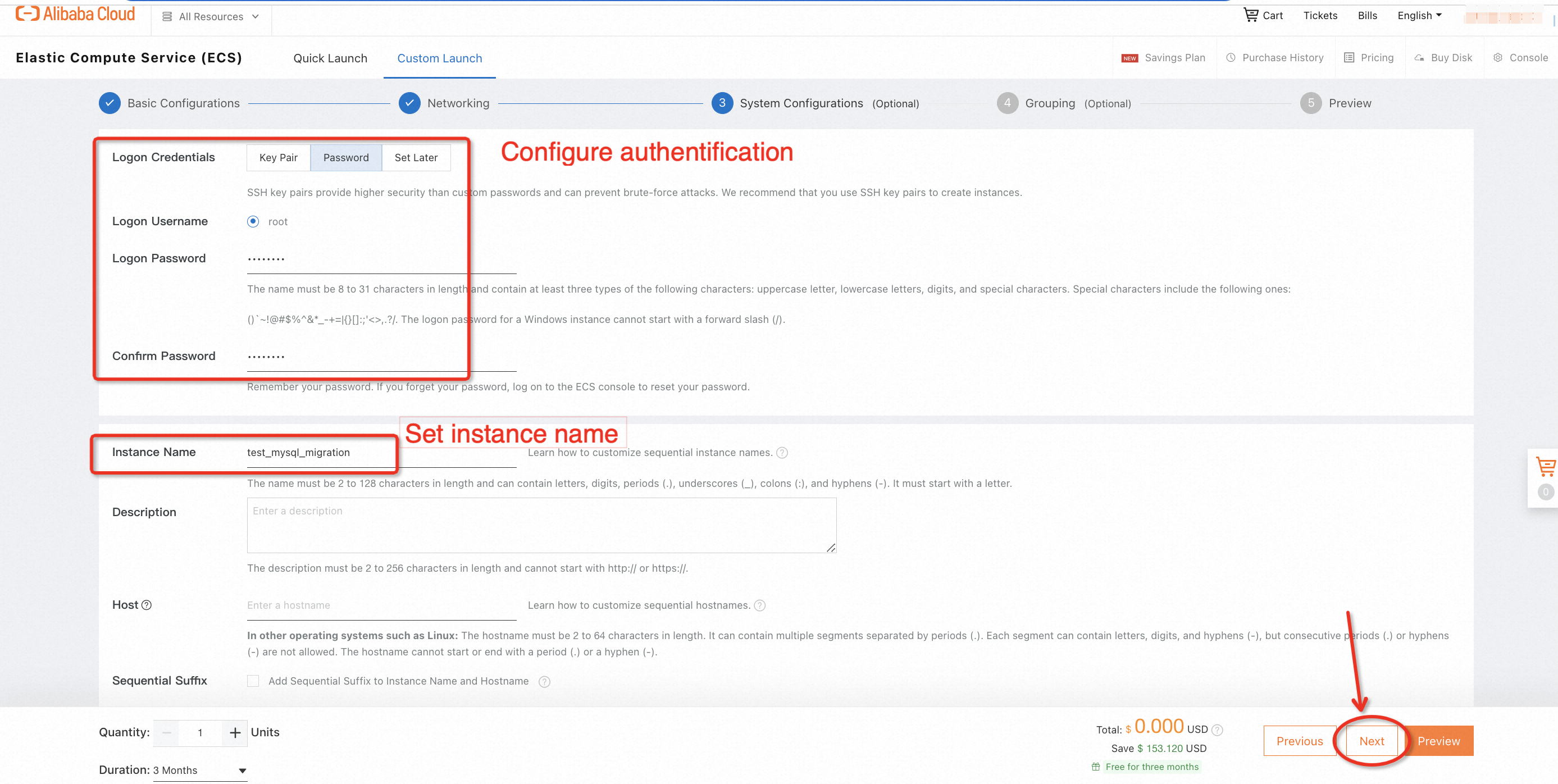
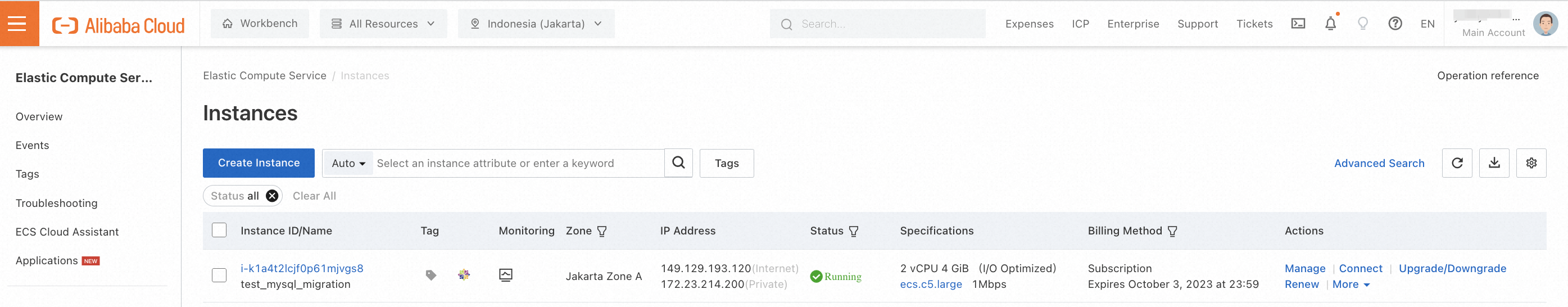
3. Wait for a while and check the status of the instance you just launched. You can also customize the name of the instance when its status becomes Running.
1. On Alibaba Cloud Free Trial Center, find ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL and click Try Now >
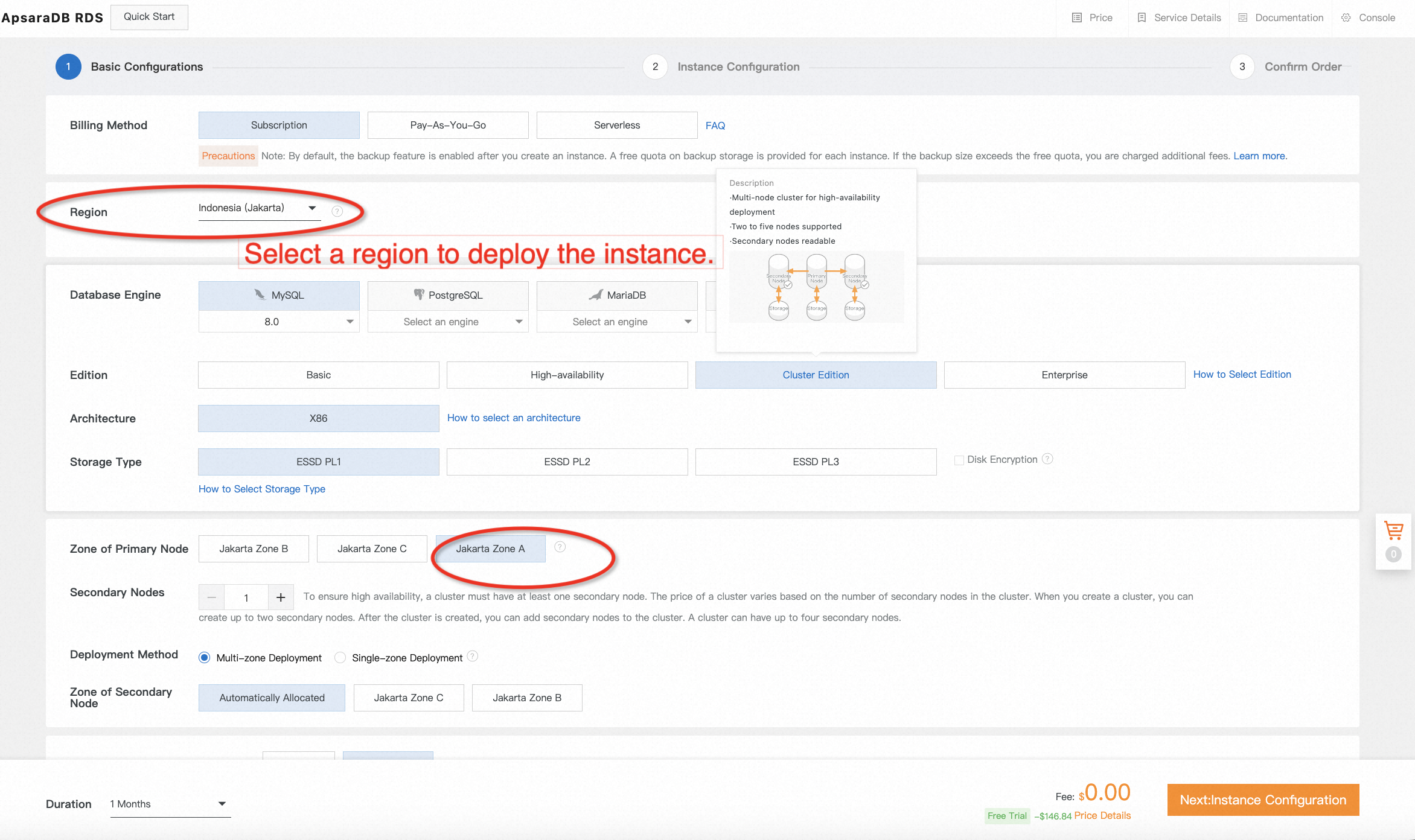
2. Choose a region to deploy your RDS instance and complete all configurations of the free trial order. We recommend selecting the same region, the same Availability Zone (AZ), and the same VPC and VSwitch as your ECS instance to minimize the network latency.
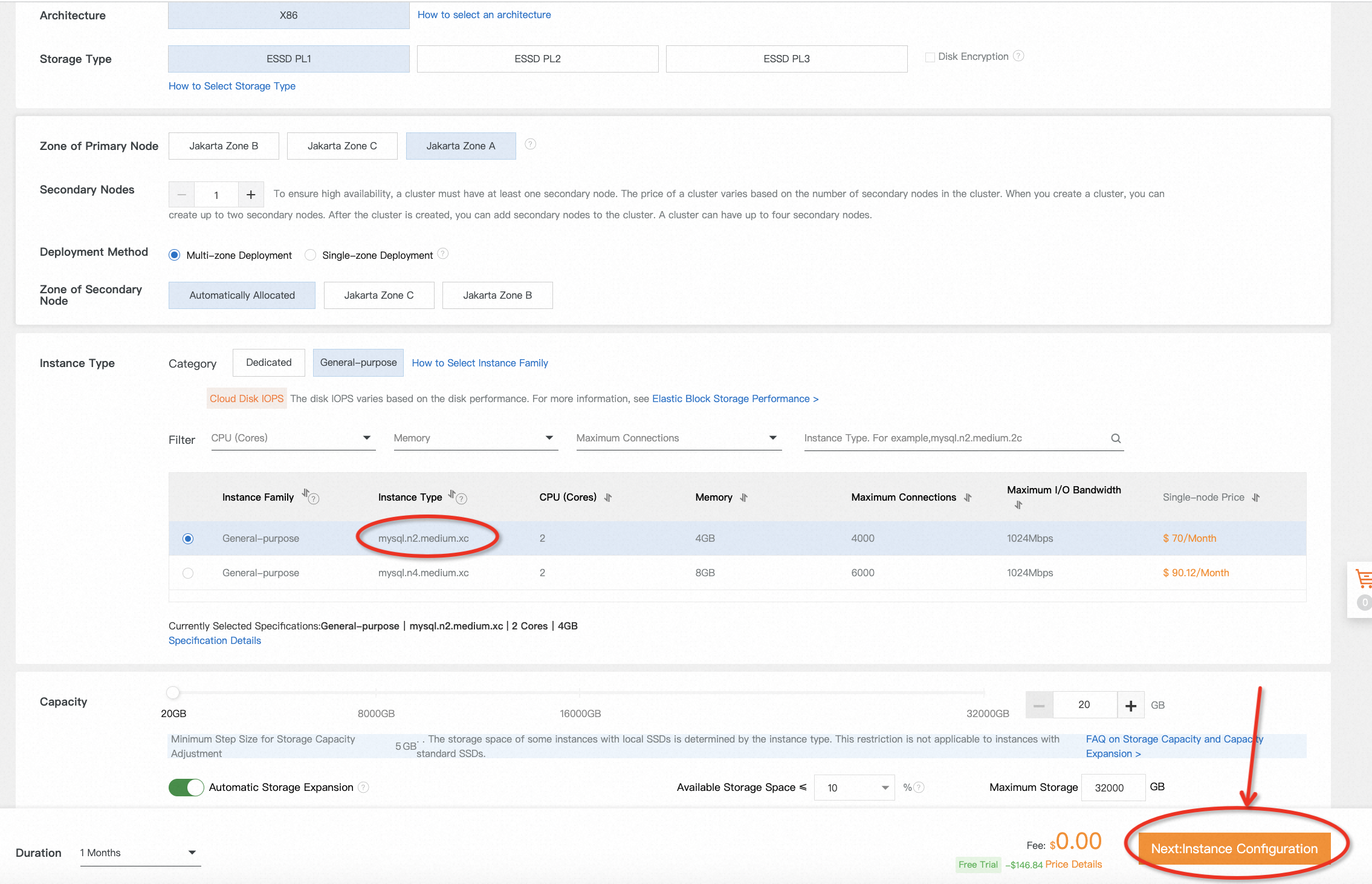
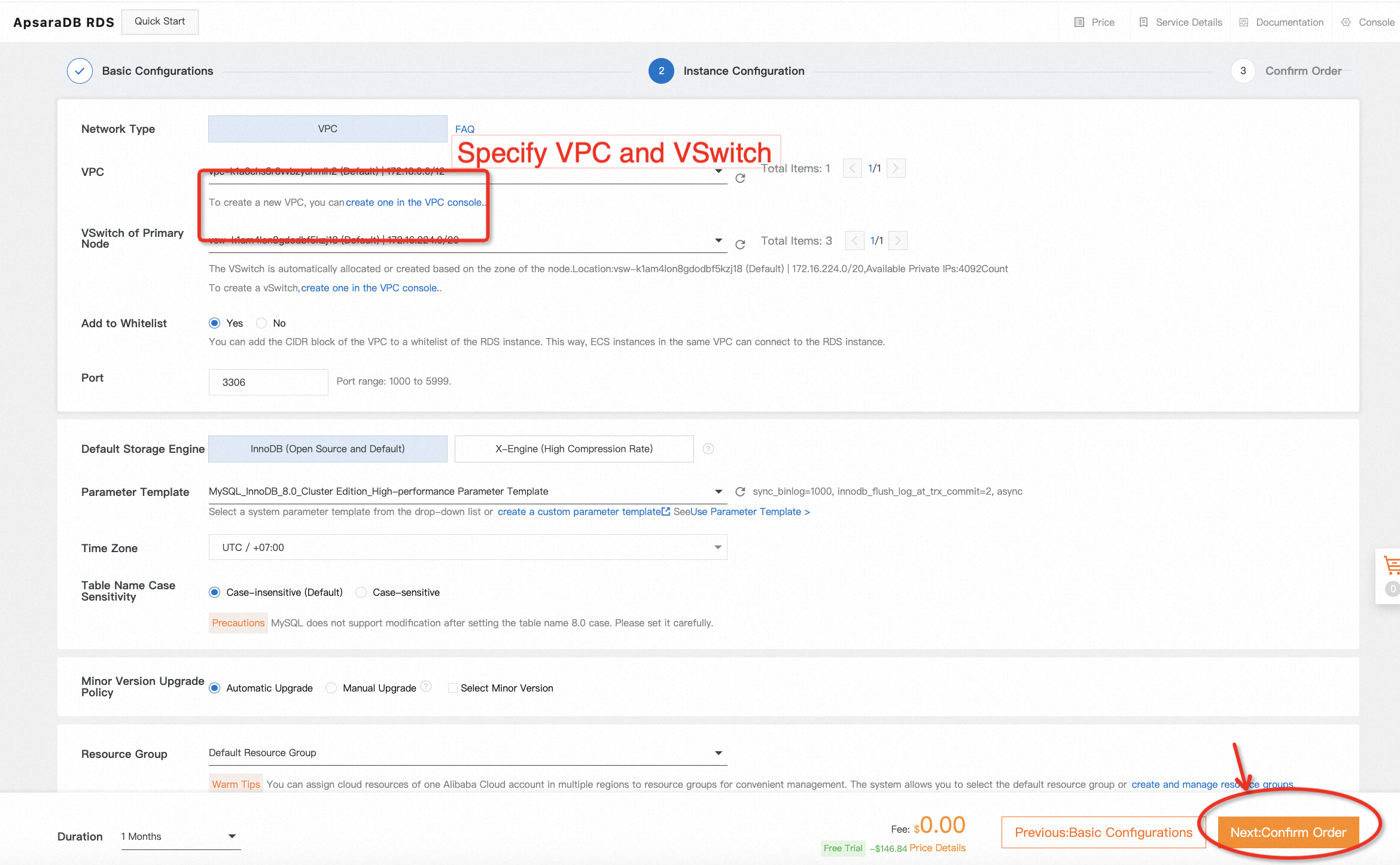
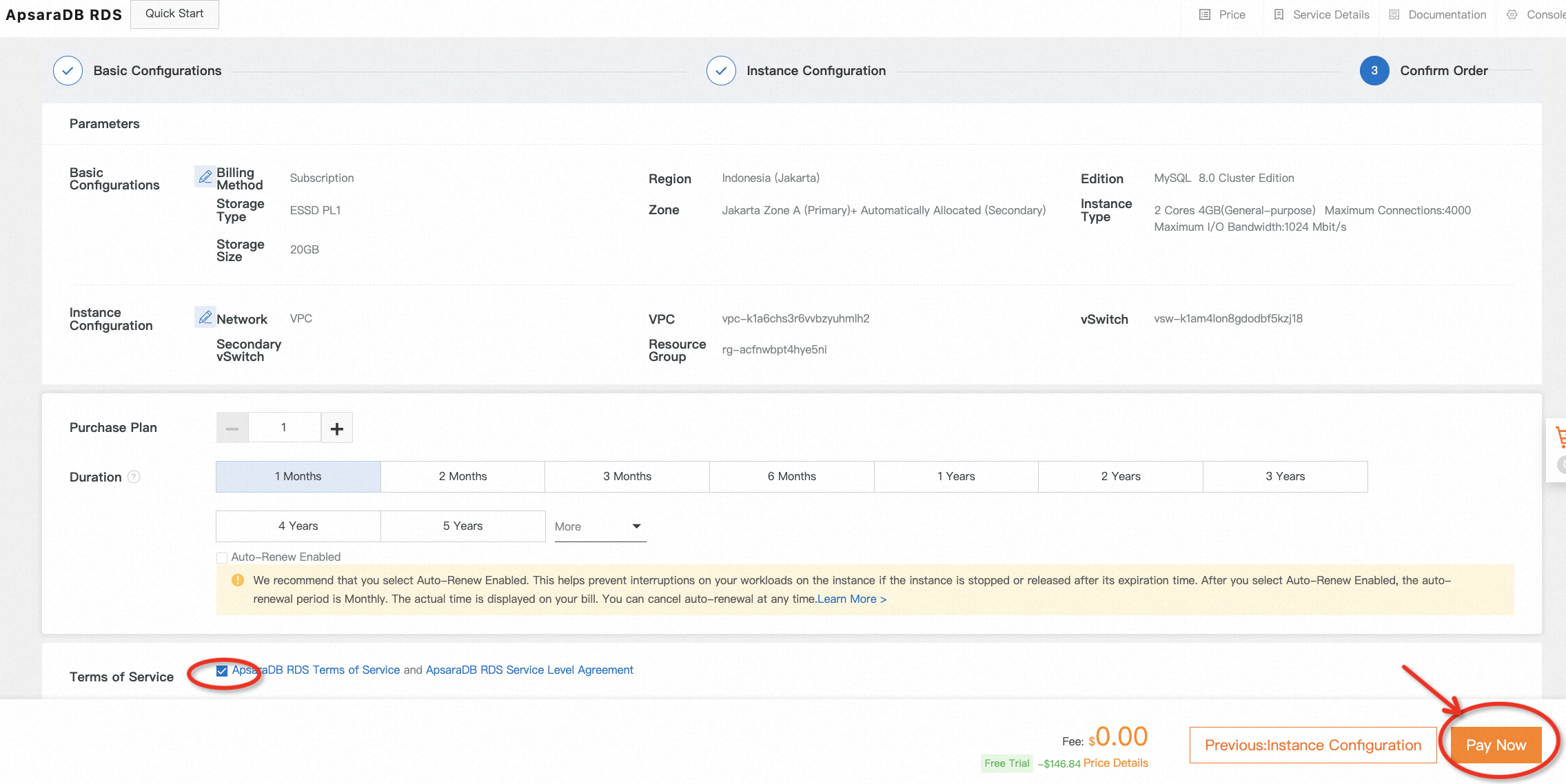
3. The instance will be created after placing a free trial order. It takes several minutes to complete. Come back later to check the status of the instance you just launched. You can also customize the name of the instance when its status becomes Running.
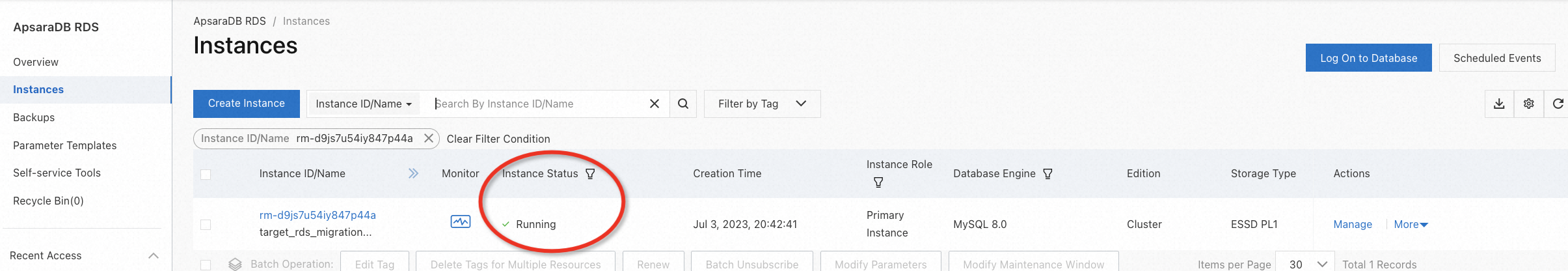
On the right side of the lab page, click the  icon to switch to Web Terminal. Please enter the username and password to log on to the ECS instance.
icon to switch to Web Terminal. Please enter the username and password to log on to the ECS instance.
Run the following command to install MySQL 8.0 and its extension package on ECS. Then, start the service, check the service status, and enable auto start in case of reboot.
Note: This experiment is based on the CentOS 7.8 x64 Operating System. If you are using another operating system, the installation might be different, which is not discussed in this lab.
sudo yum install -y https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-5.noarch.rpm
sudo yum install -y mysql-community-server mysql-community-client
sudo systemctl start mysqld
sudo systemctl enable mysqld
systemctl status mysqld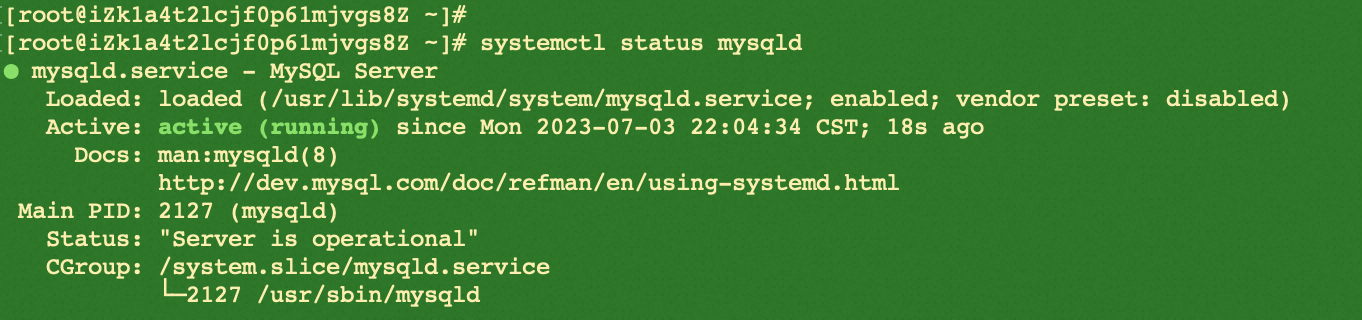
Run the following commands to get the default password which will be used when running secure installation command to init database. You will also be able to set your own password during the process. After then, log in.
grep "password" /var/log/mysqld.log
sudo mysql_secure_installationTo secure your MySQL installation, enter YES for all the questions that follow after resetting MySQL password.

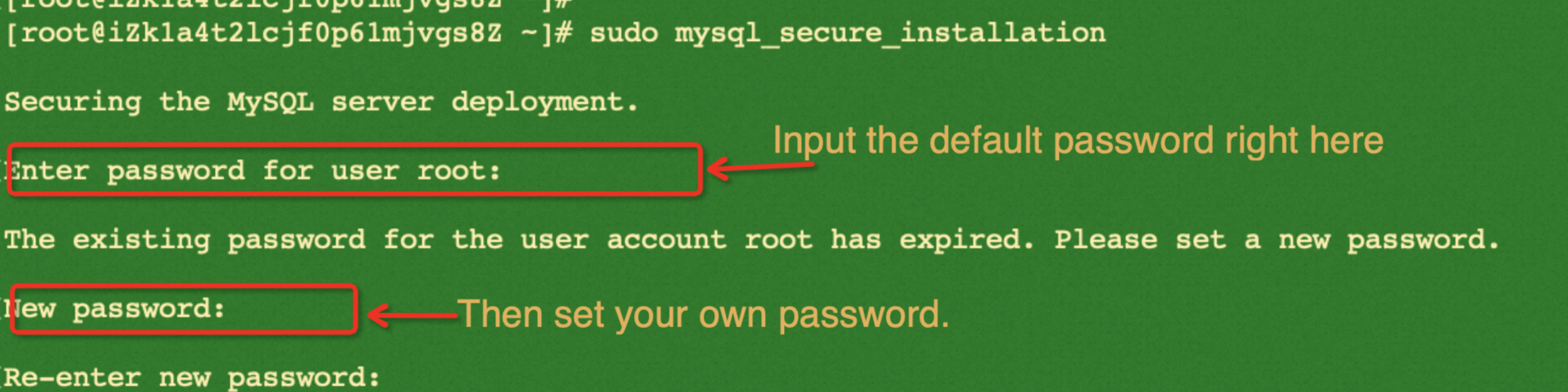
After that, access MySQL database.
sudo mysql -u root -p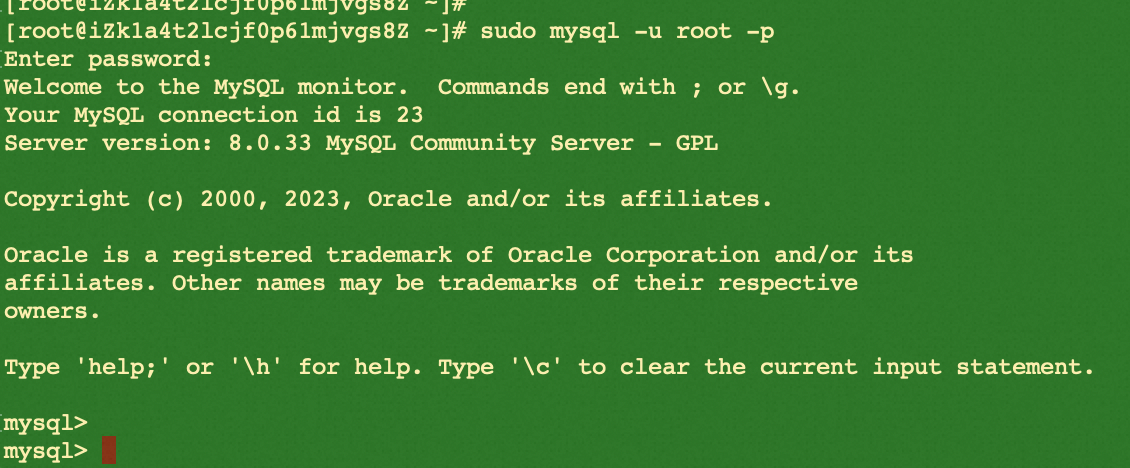
When you see the MySQL version and SQL input prompt as above, you have successfully installed a user-created MySQL and got into the database.
While logged into MySQL, run the following commands to create a database, create a table, and insert the data into MySQL before migration. Then, check the schema of the table and select how much data is generated.
create database testdb;
use testdb;
CREATE TABLE `customer` (
`customer_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`customer_id`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
CREATE TABLE `product` (
`product_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`price` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`product_id`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
INSERT INTO `customer` VALUES ('1', 'Marty1'), ('2', 'Marty2'),('3', 'Marty3'),('4', 'Marty4'),('5', 'Marty5'),('6', 'Marty6'),('7', 'Marty7'),('8', 'Marty8'),('9', 'Marty9'),('10', 'Marty10'),('11', 'Marty11'),('12', 'Marty12'),('13', 'Marty13'),('14', 'Marty14'),('15', 'Marty15'),('16', 'Marty16'),('17', 'Marty17'),('18', 'Marty18'),('19', 'Marty19'),('20', 'Marty20');
INSERT INTO `product` VALUES ('1', 'Bread-1','4'), ('2','Bread-2','7'),('3', 'Bread-3','2'),('4', 'Bread-4','10'),('5', 'Bread-5','5'),('6', 'Bread-6','7'),('7', 'Bread-7','6'),('8', 'Bread-8','3');
show tables;
show columns from customer;
show columns from product;
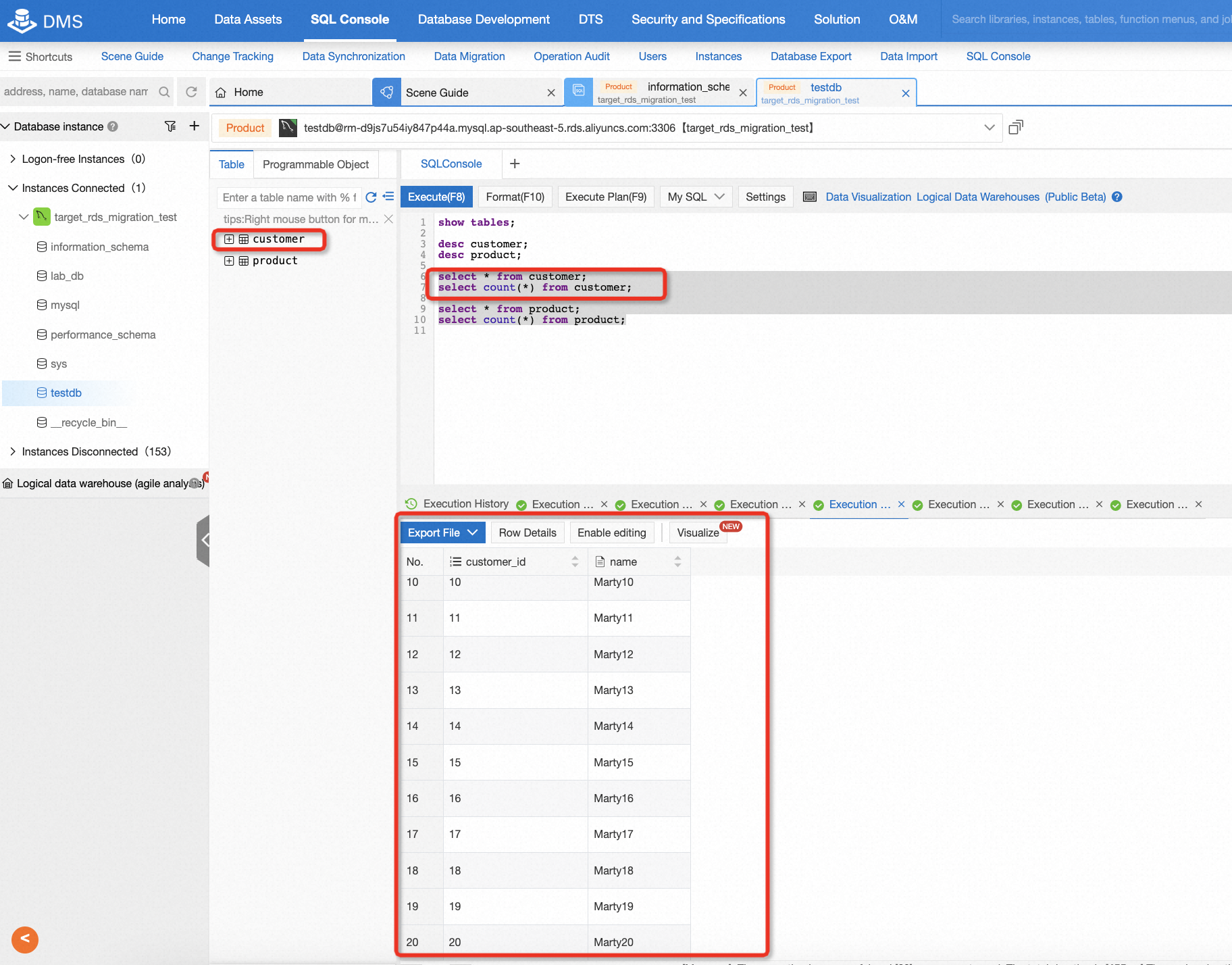
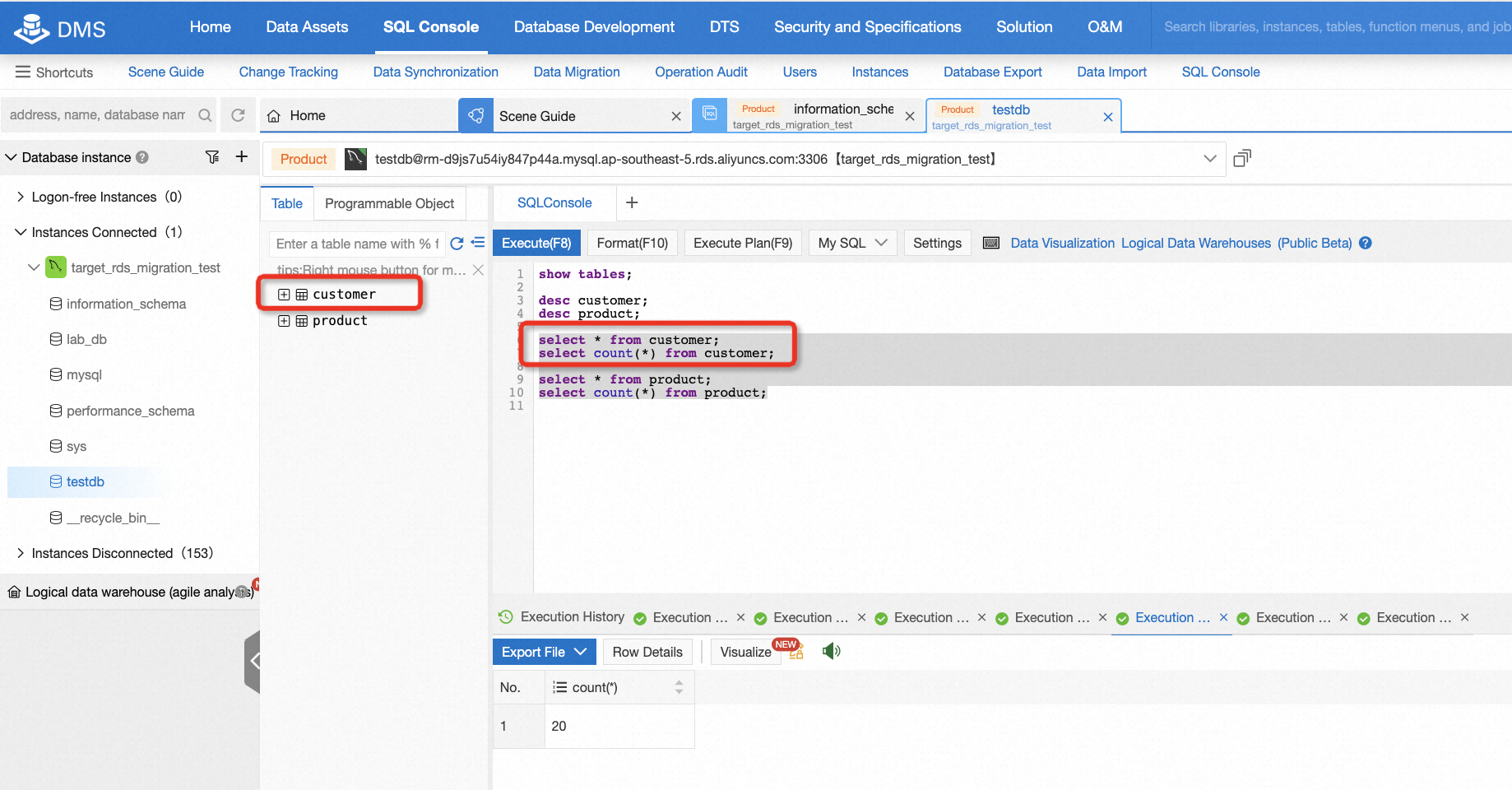
select * from customer;
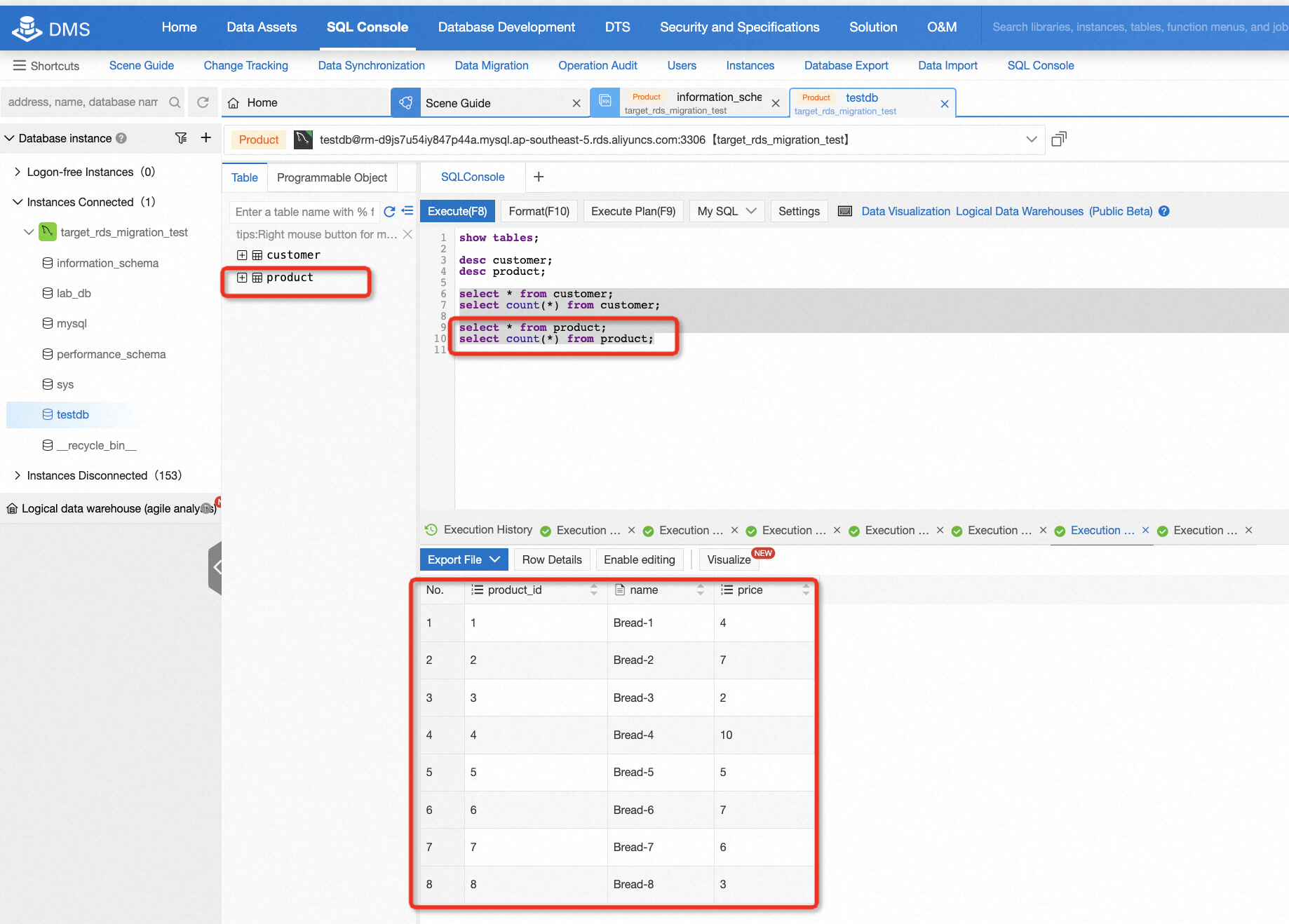
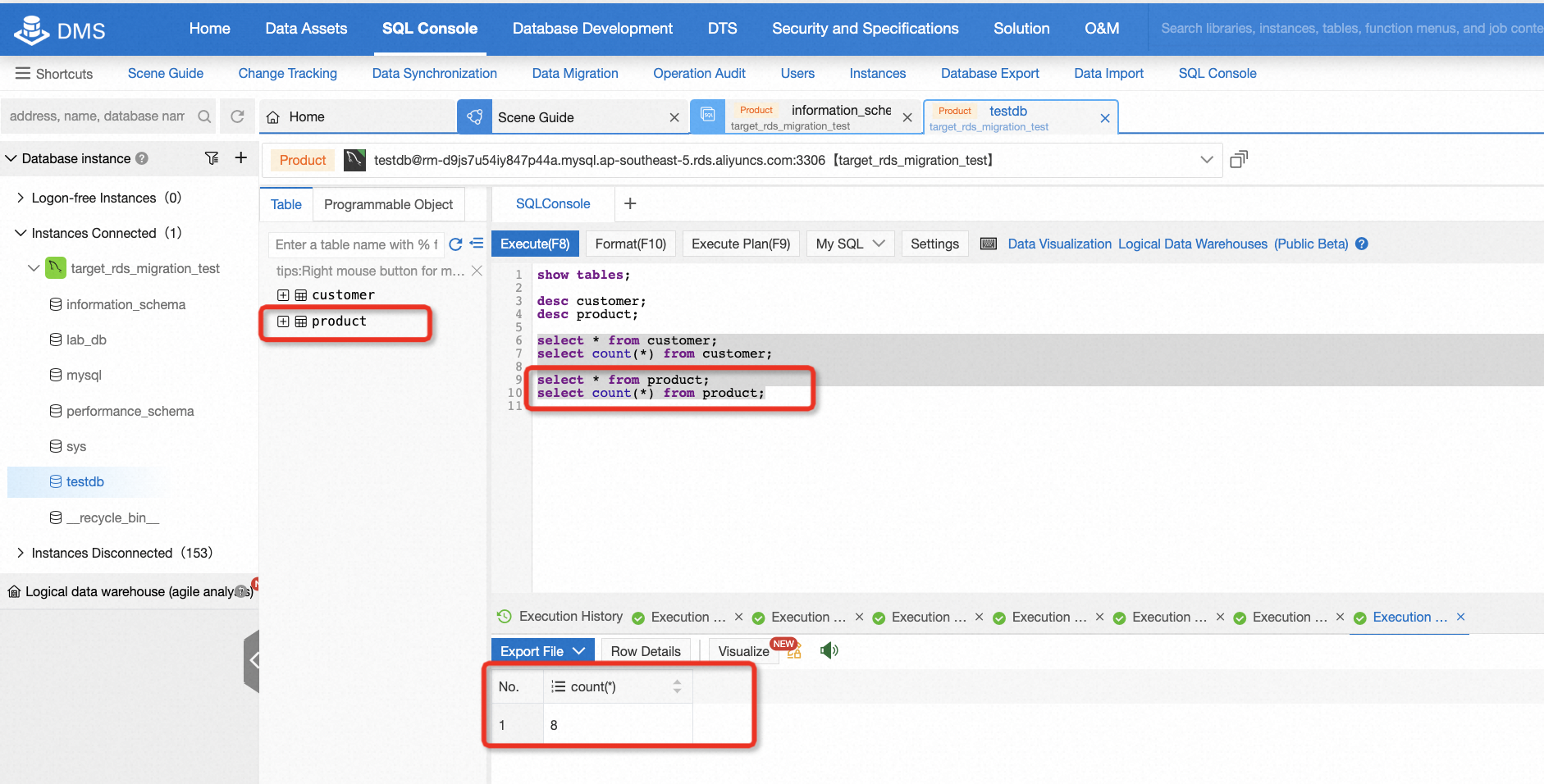
select * from product;
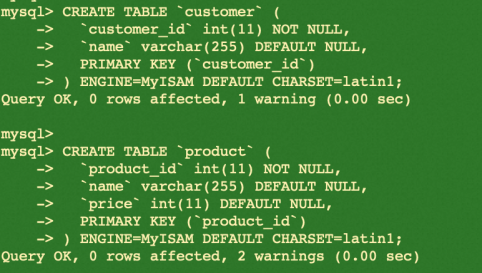

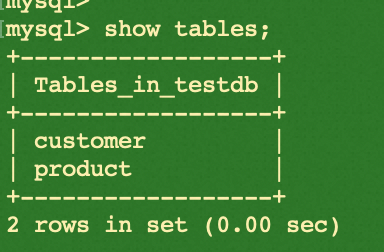
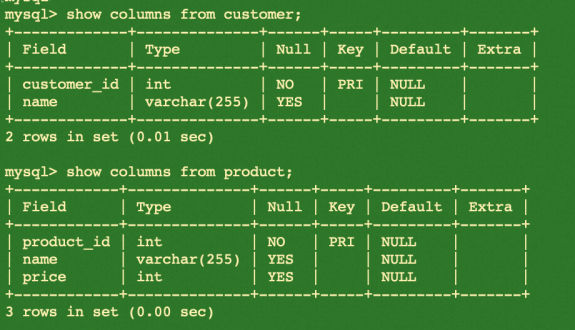
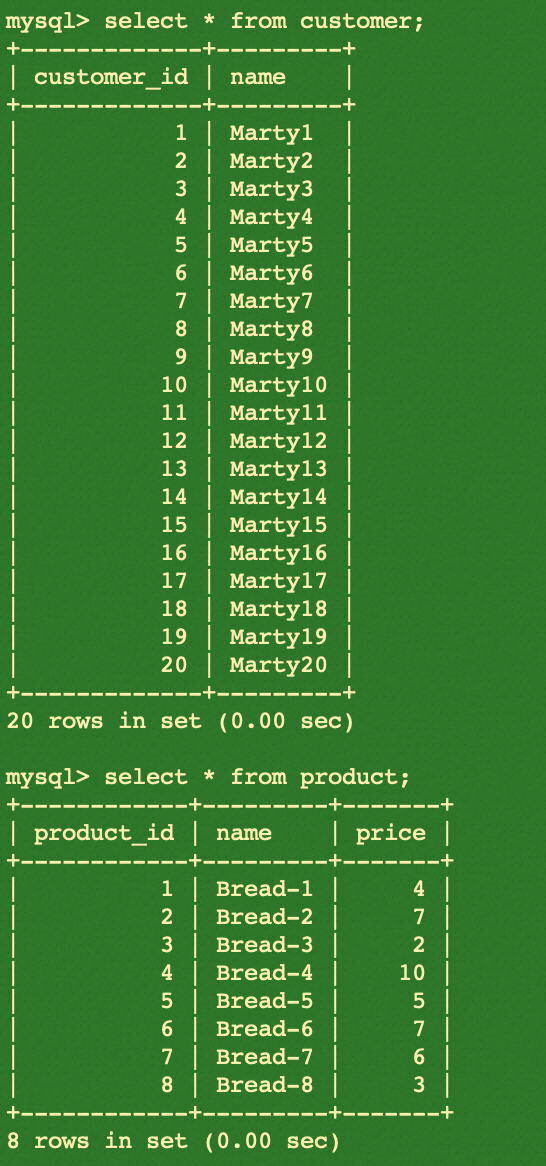
Please find the summary of creations by executing the example code below:
While logged into MySQL, run the following commands to create a new user for migration.
CREATE USER 'dtsmigration'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'Dts123456@';
GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'dtsmigration'@'%';
flush privileges;
exit;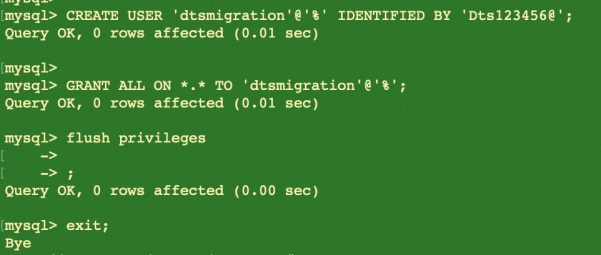
The user dtsmigration will be created as a result.
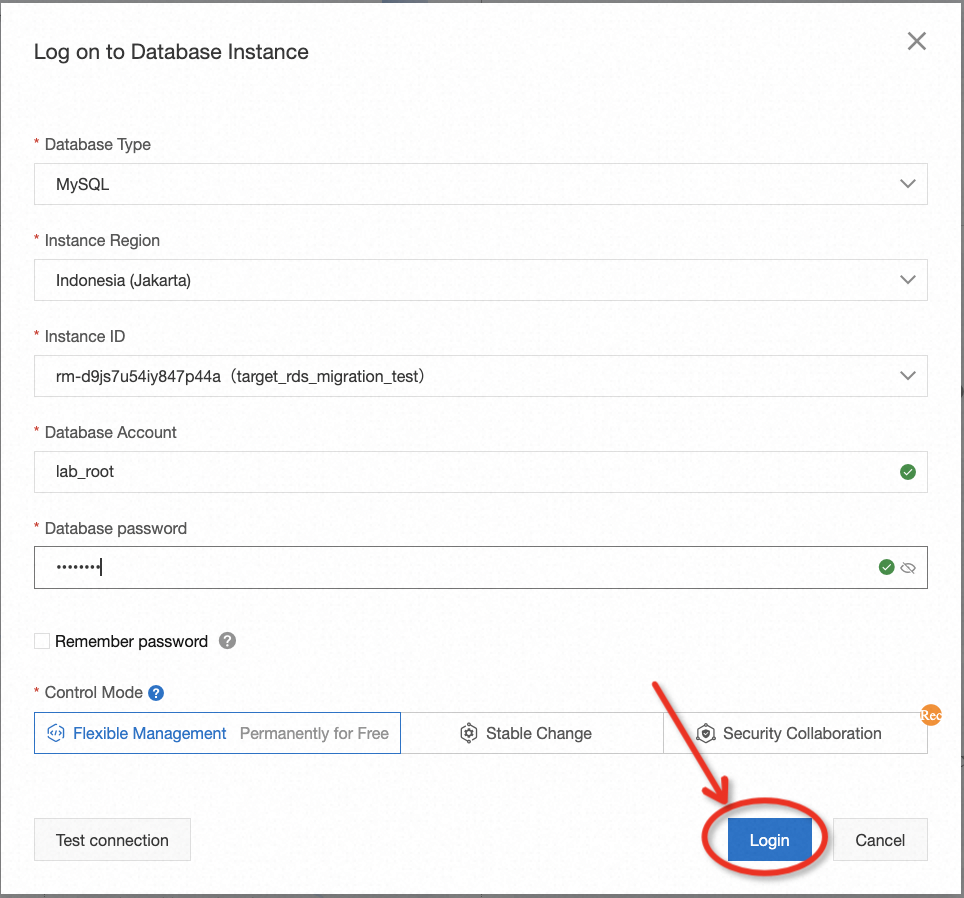
After preparing the data of the source database, go to the RDS console, and switch to the region where the RDS instance is located to create a user on the target database for migration. Please be aware that a privileged account is required. Follow the guide below to ensure you don't miss any important points.
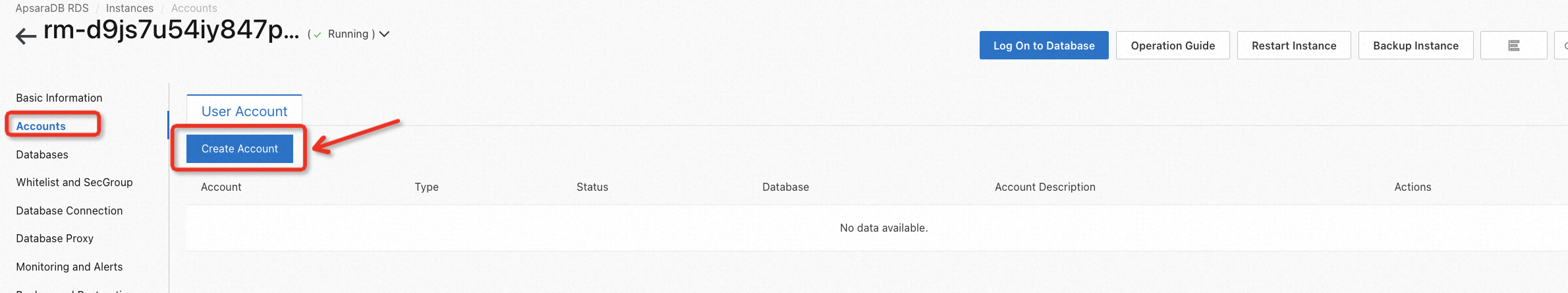
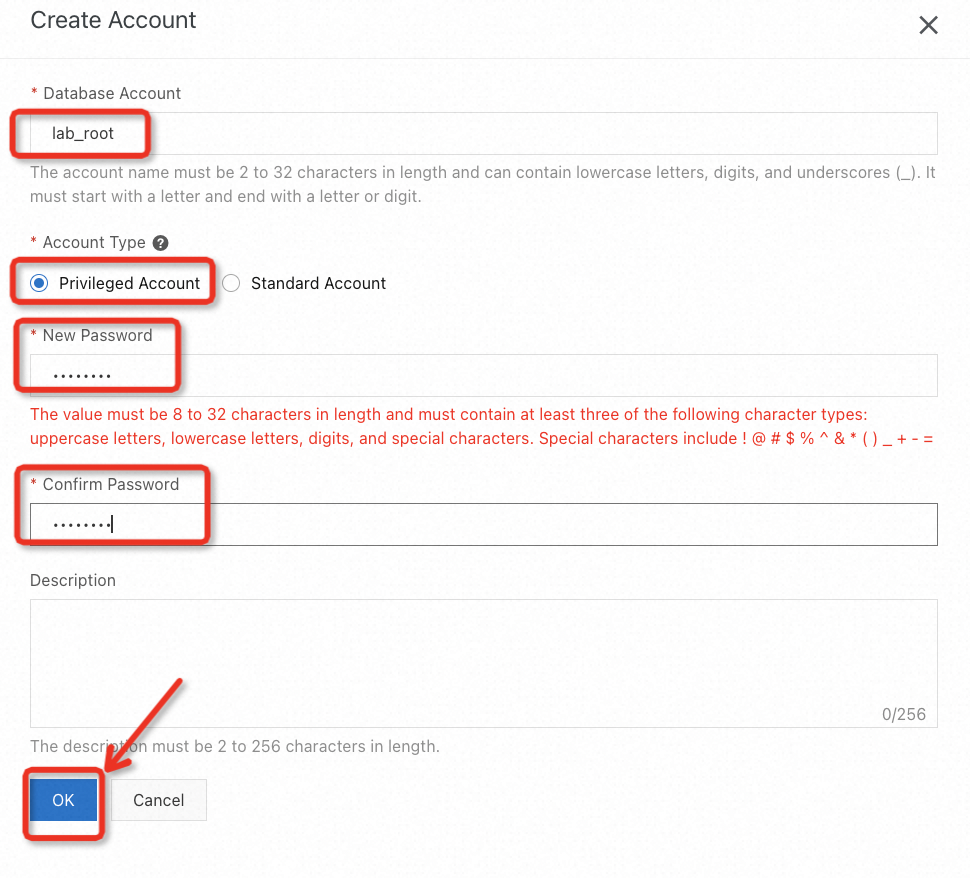
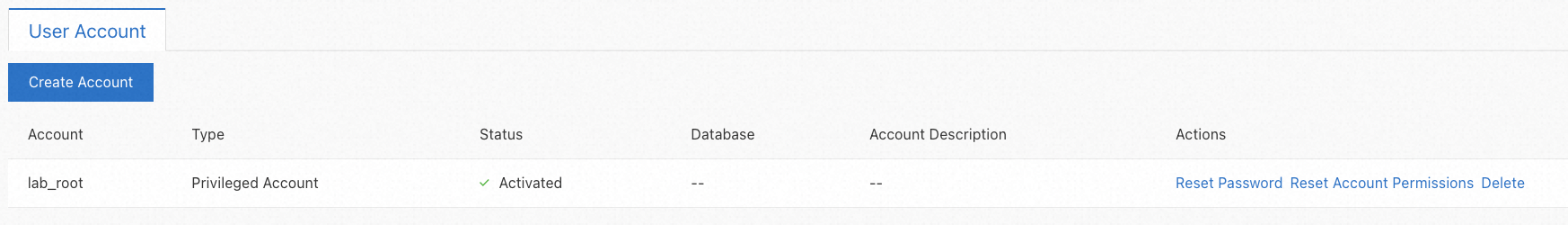
When the status becomes Active, a database user is created successfully.
You are almost there! Let's finish the preparation and move to the next phase. Please do a final environment check to confirm that the network conditions on the source and target side fully meet the requirements.
To access the MySQL database you just created, you need to log in to the ECS instance again. On the right side of the lab page, click the  icon and switch to Web Terminal. Enter your username and password to log in to the ECS instance. If you are still logged in from the previous steps, you can use the same session tab on the web terminal.
icon and switch to Web Terminal. Enter your username and password to log in to the ECS instance. If you are still logged in from the previous steps, you can use the same session tab on the web terminal.

If you exit the MySQL database on your ECS, you can run the following command to log in again.
mysql -u root -pThen, run the following commands to check if the user-created MySQL allows remote access:
SELECT user, host FROM mysql.user;
exit;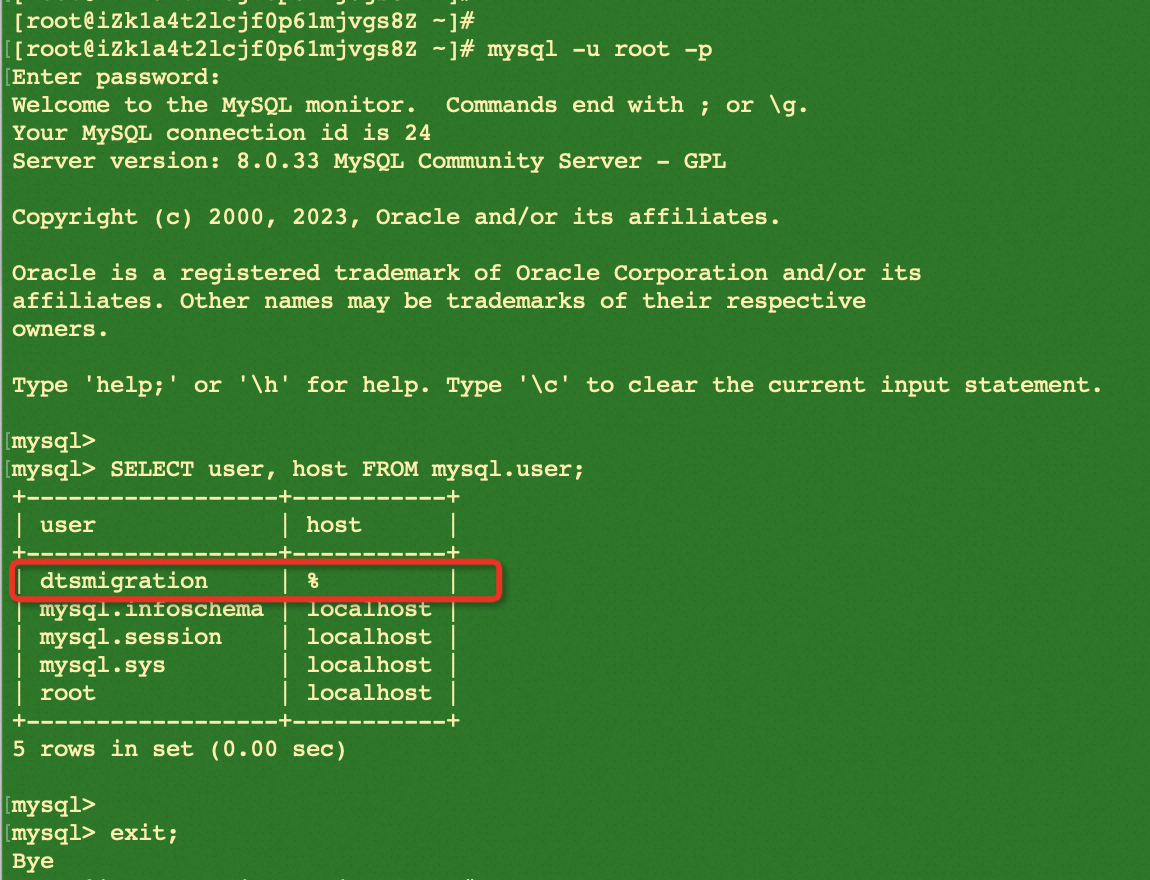
As shown above, the row with % means that the user created for migration is allowed to access the database server from anywhere.
If the host value of the user used for migration is localhost instead, you should make efforts to perform additional configurations not discussed in this lab. Otherwise, you may experience failures during the migration process.
Run the following commands to check the firewall status of the ECS. If it's on, you can temporarily turn it off for the lab but do NOT disable firewall service directly if you are using a production environment. In a production environment, we recommend keeping the firewall on and configuring the relevant inbound and outboard policy according to the actual situation.
systemctl status firewalld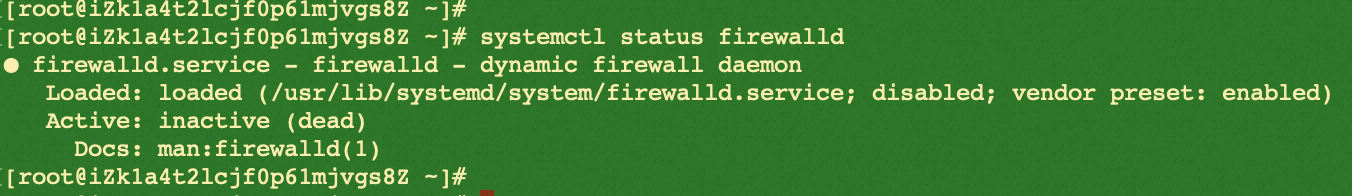
In the lab, as shown above, the firewall is off.
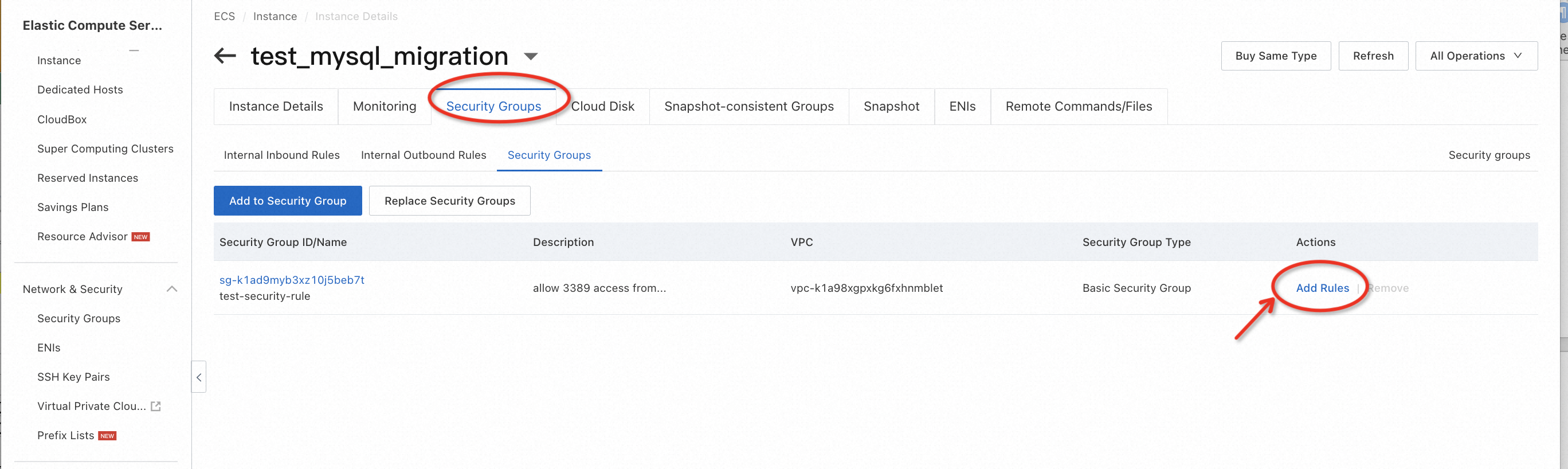
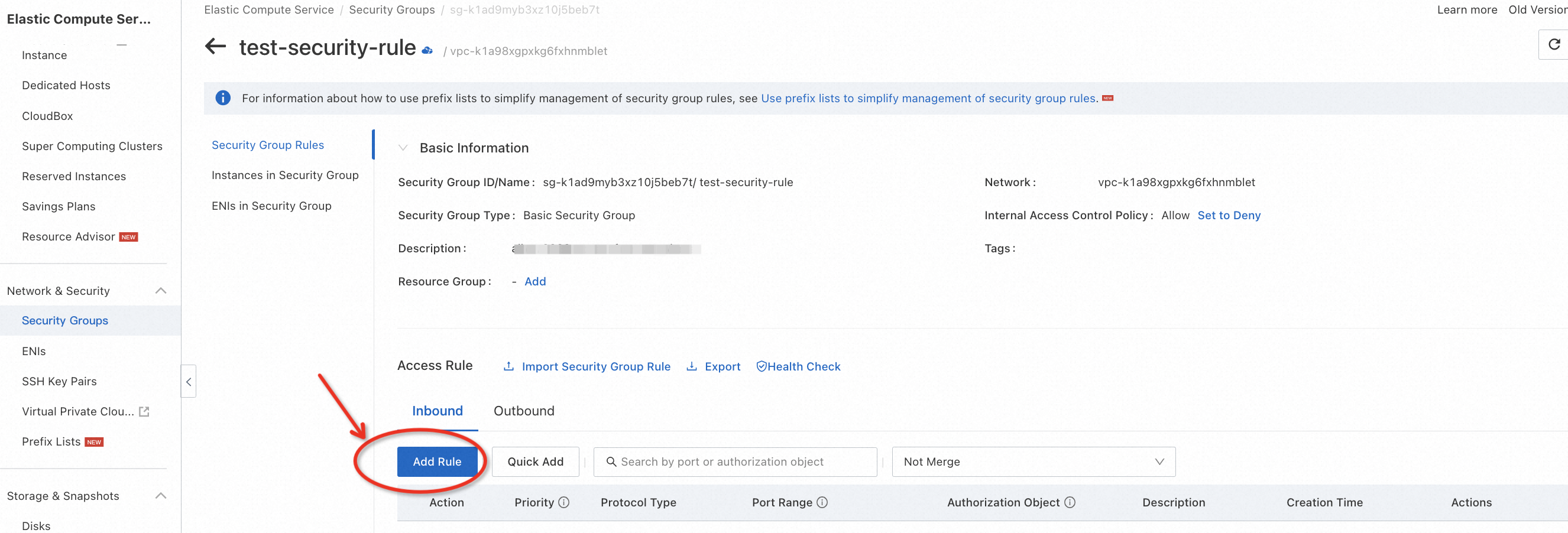
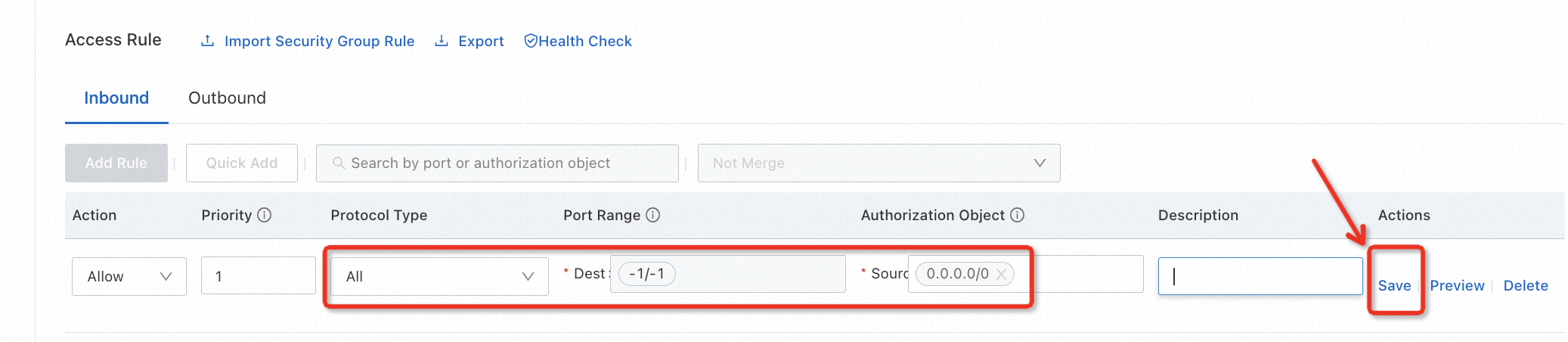
Go to the ECS console, switch to the region where your ECS instance is located, and edit the security rules to allow the target RDS and DTS server to connect to the MySQL service port. Since this is a test environment, for convenience, you can directly refer to the example below to allow all IPs to access all ports on the ECS.
Similar to firewall configurations, you should NOT allow access from anywhere to any port if it's a production environment.
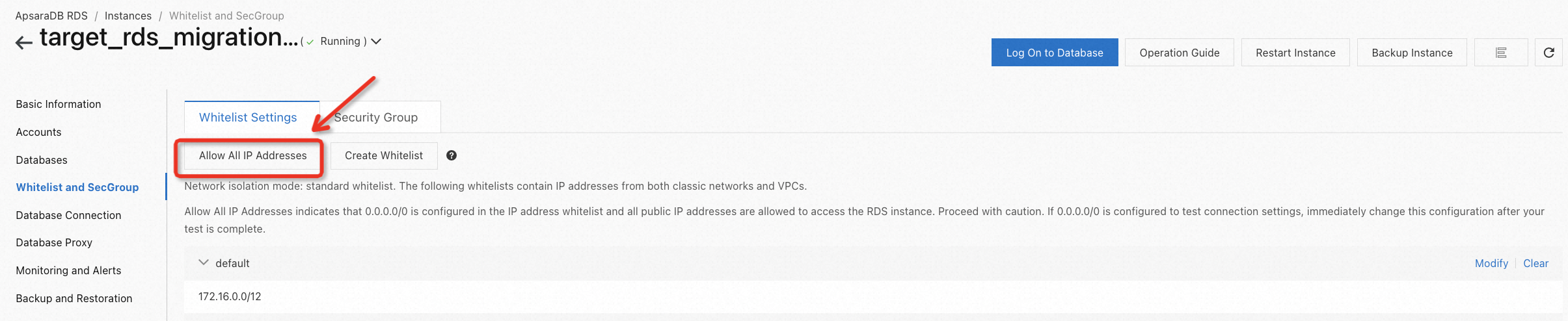
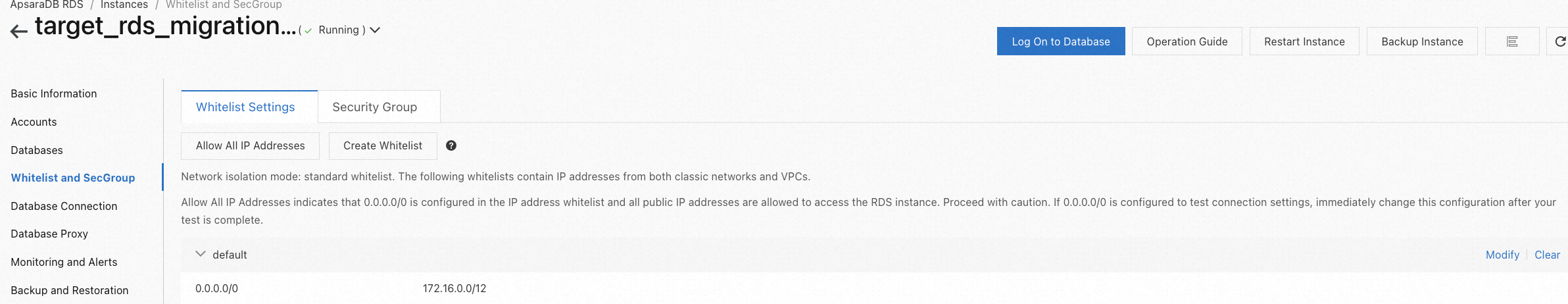
Go to the RDS console and set the whitelist of the instance to determine who can create connections with it. In this lab, for convenience, you can refer to the following example to accept all IPs. However, if you are operating in a production environment, you need to use the configuration 0.0.0.0/0 with caution, as it's not secure.
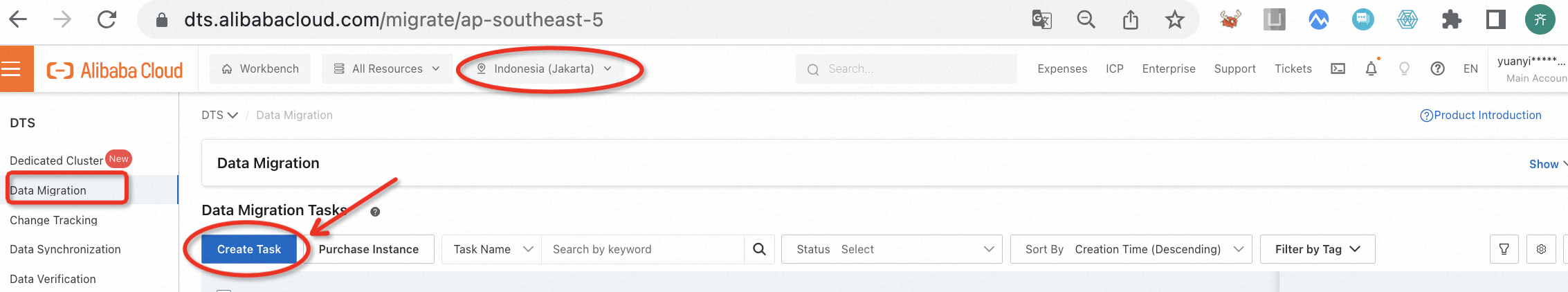
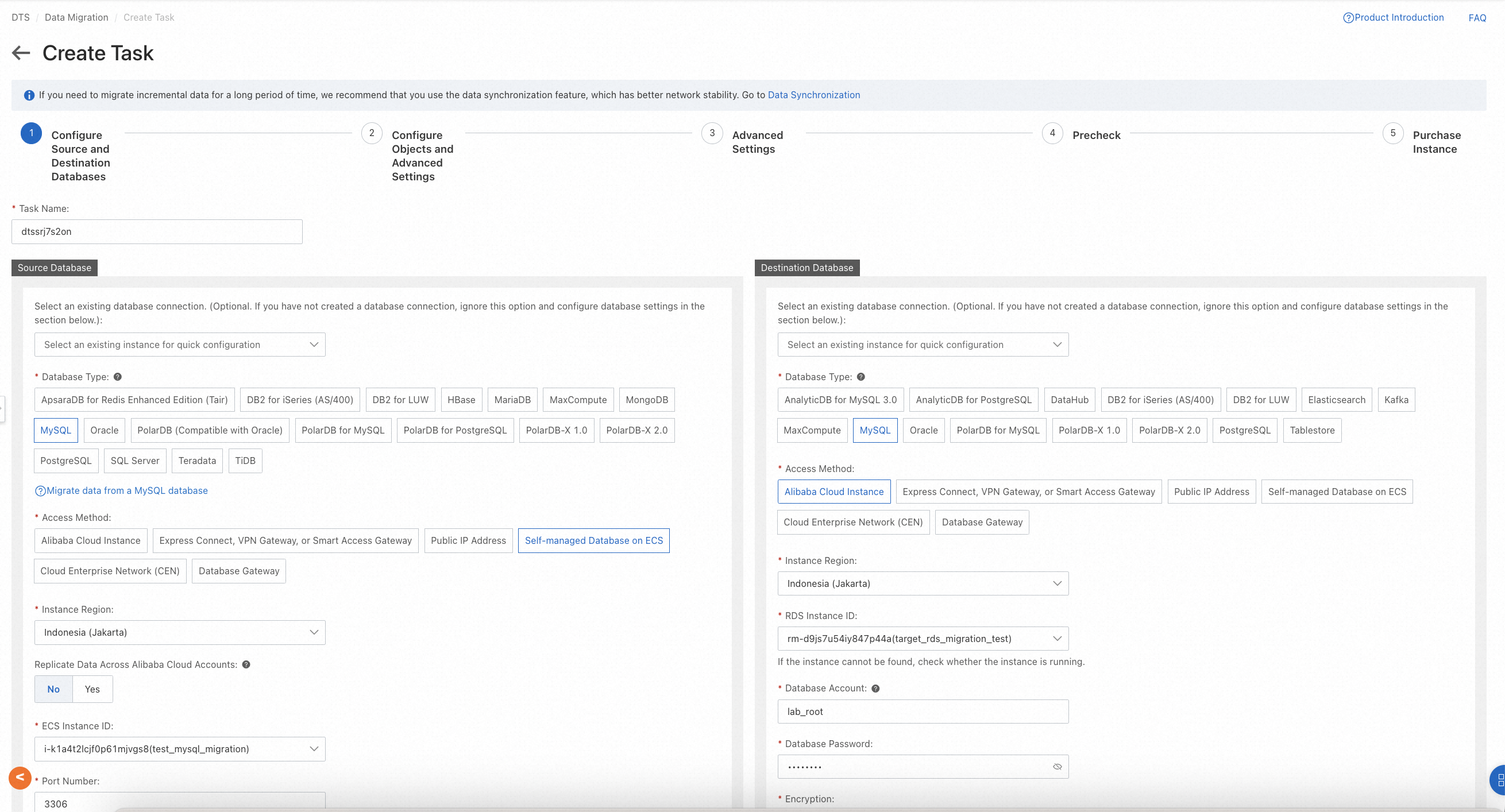
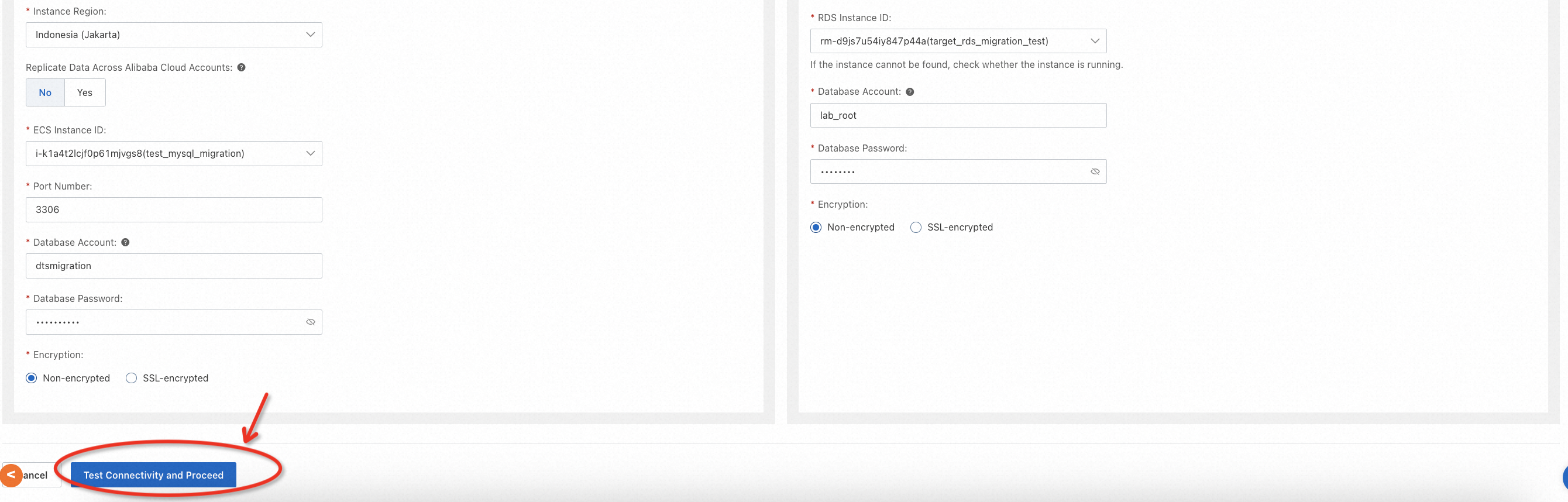
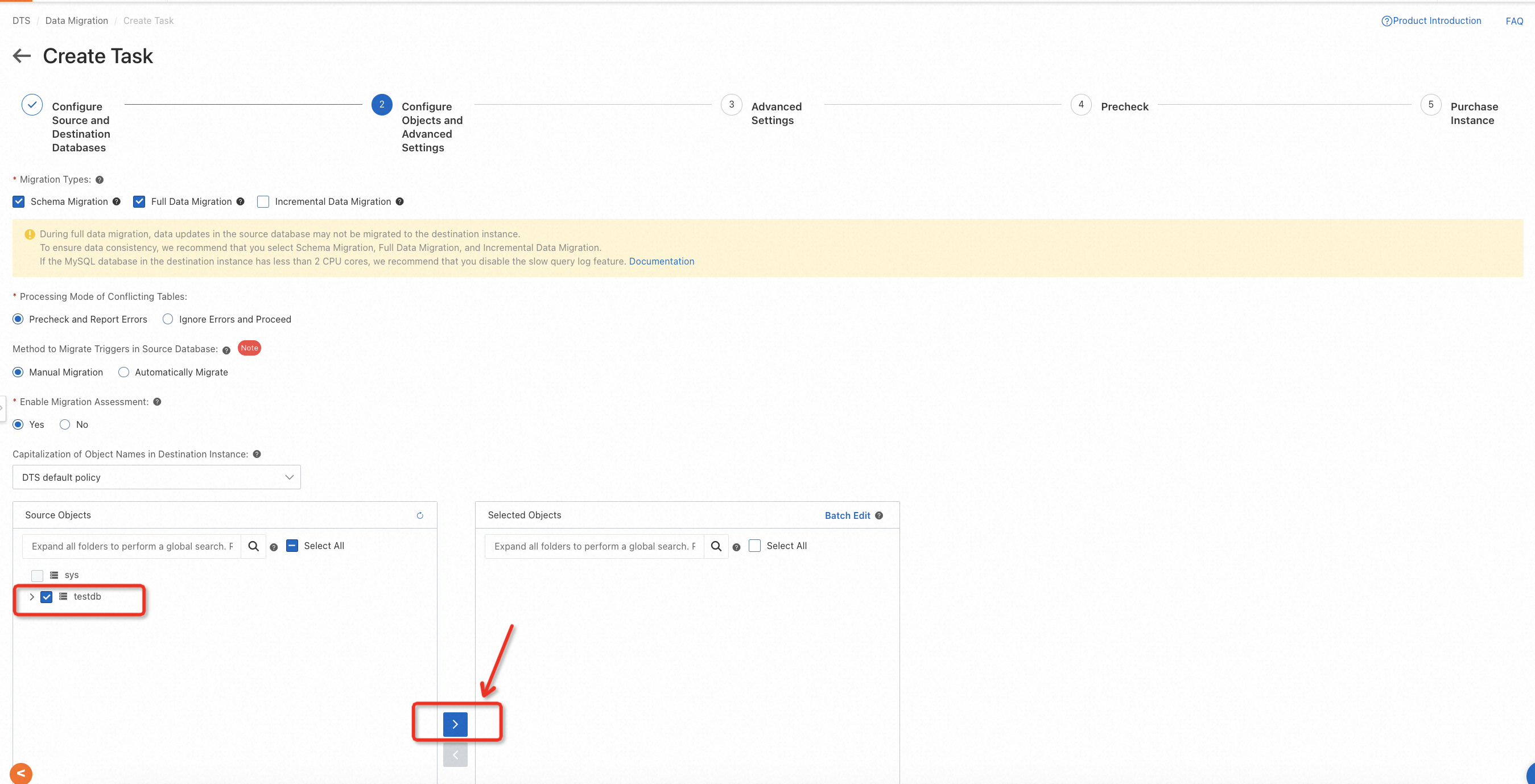
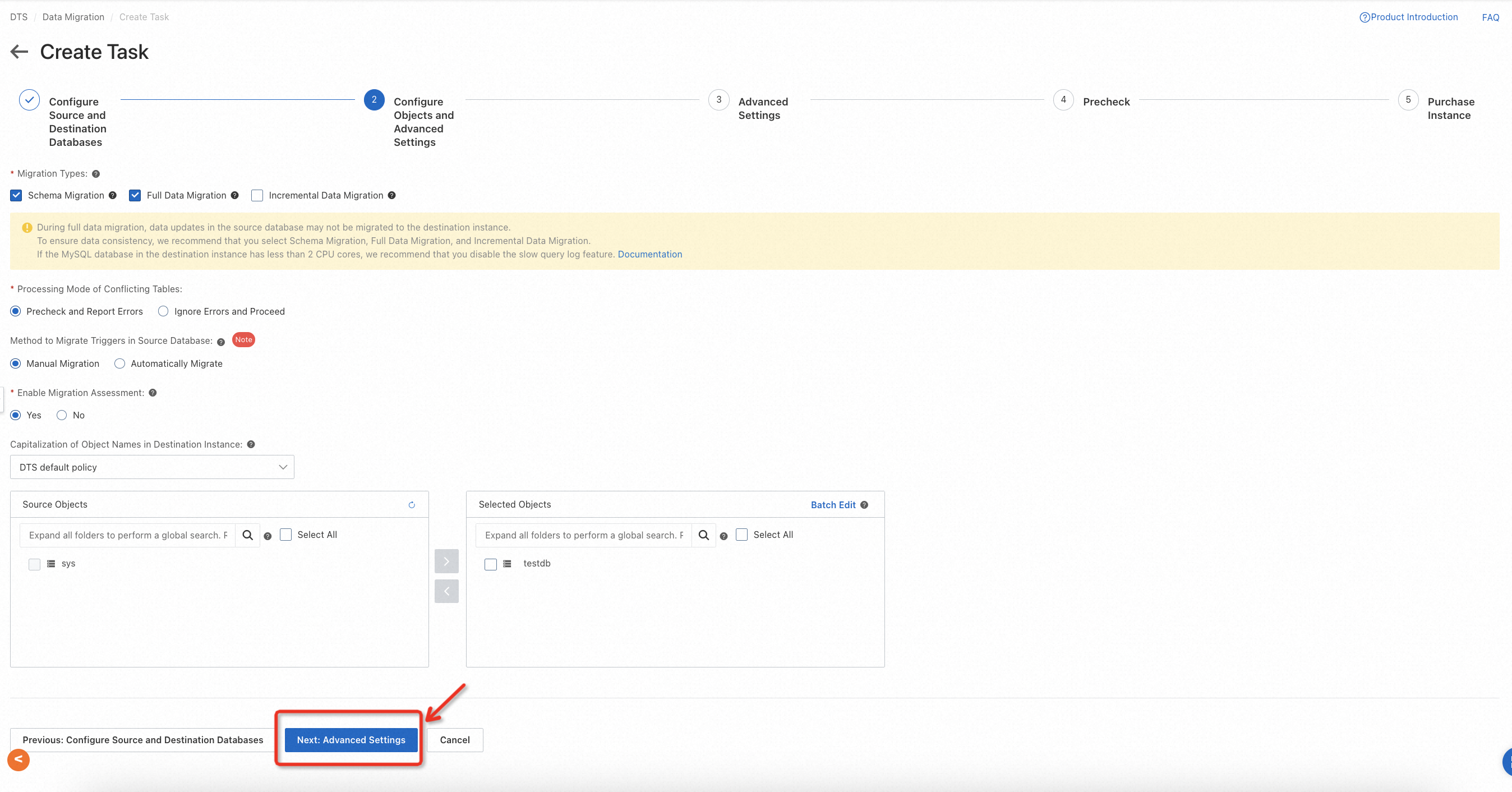
Go to the DTS console, switch to the region where the target database is located, and create a migration task. You will need to configure the information of the source and target databases and specify the migration objects according to the actual environment, as shown in the following example.
Please note that for migration types, only full data migration and schema migration need to be checked during task configuration. Incremental migration may incur extra fees, so please configure it carefully.
In addition, DTS provides the ability to verify data by row or hash. In this lab, this feature is not used, and if you want to try it out, you can explore this feature by configuring the Data Verification Settings.
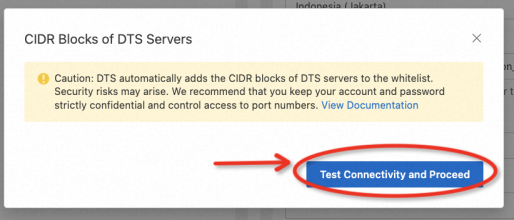
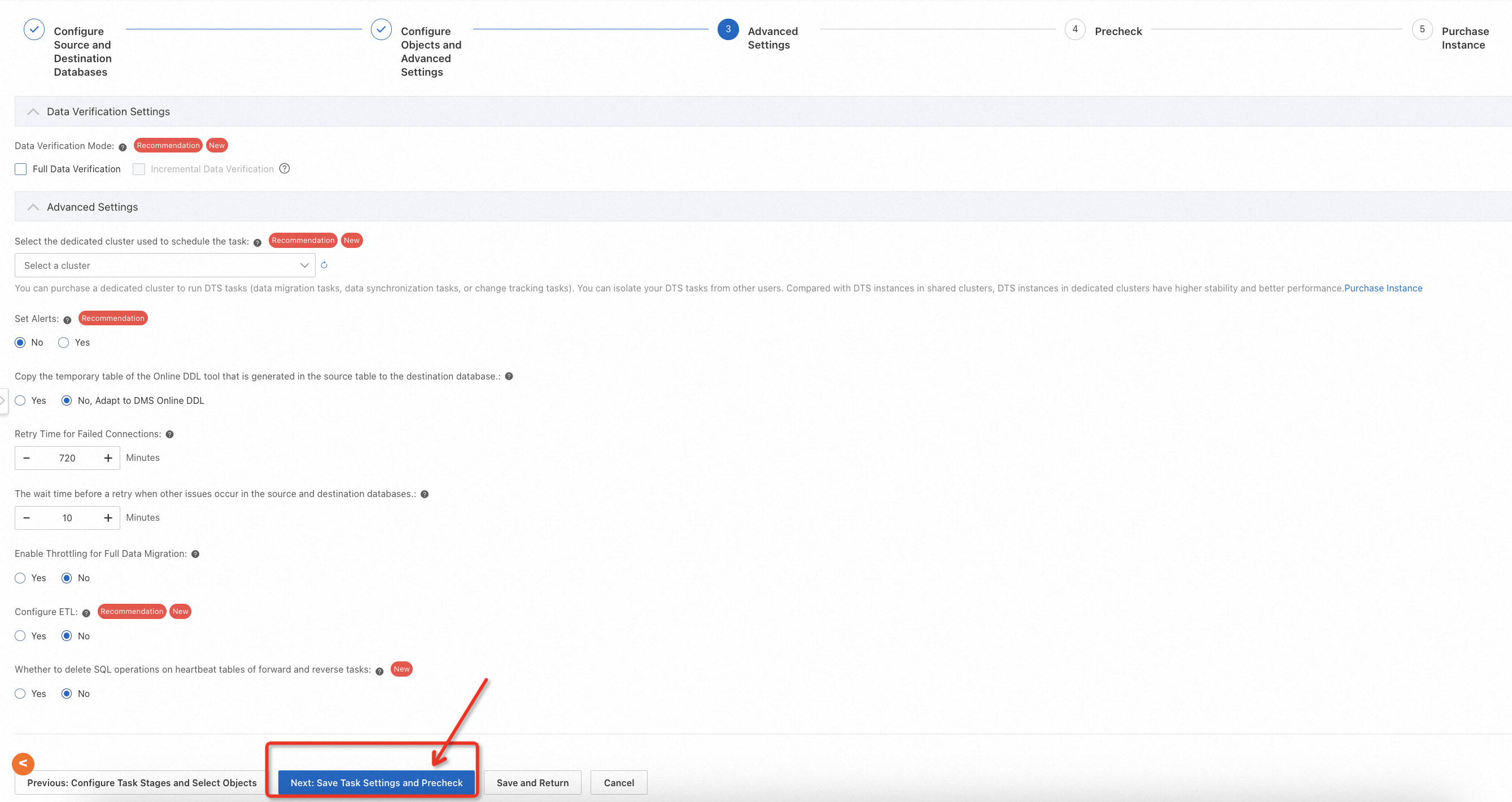
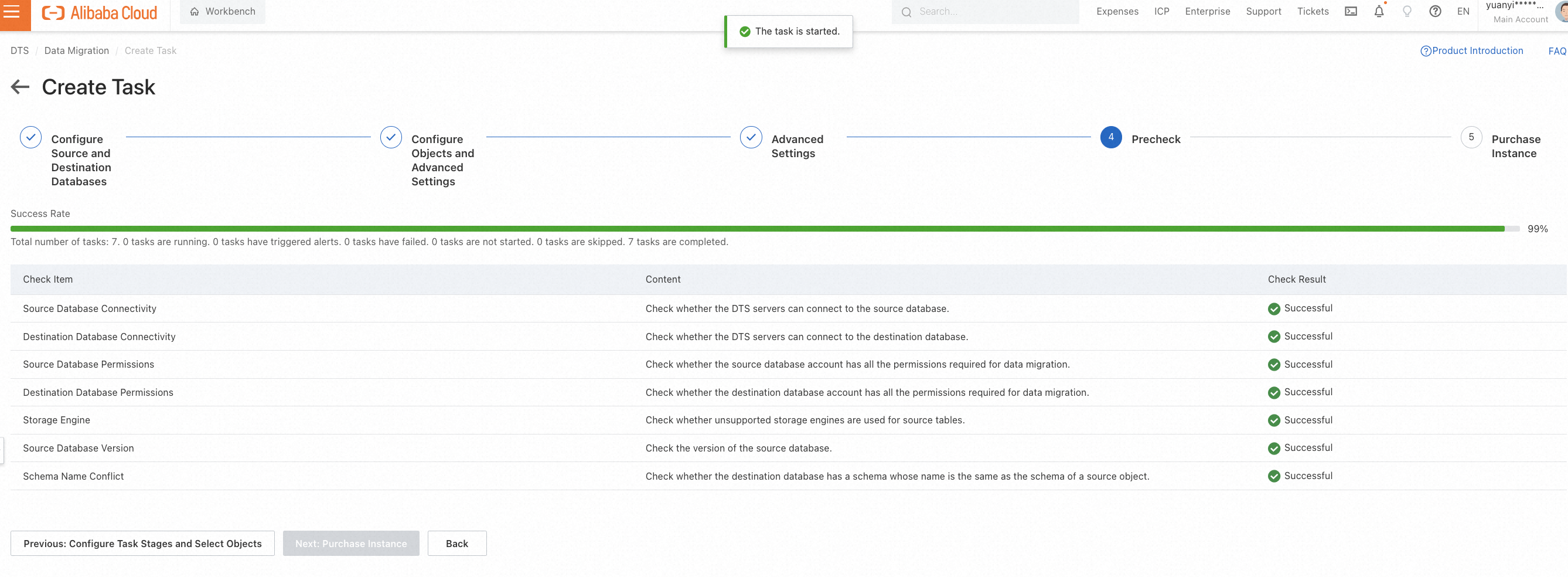
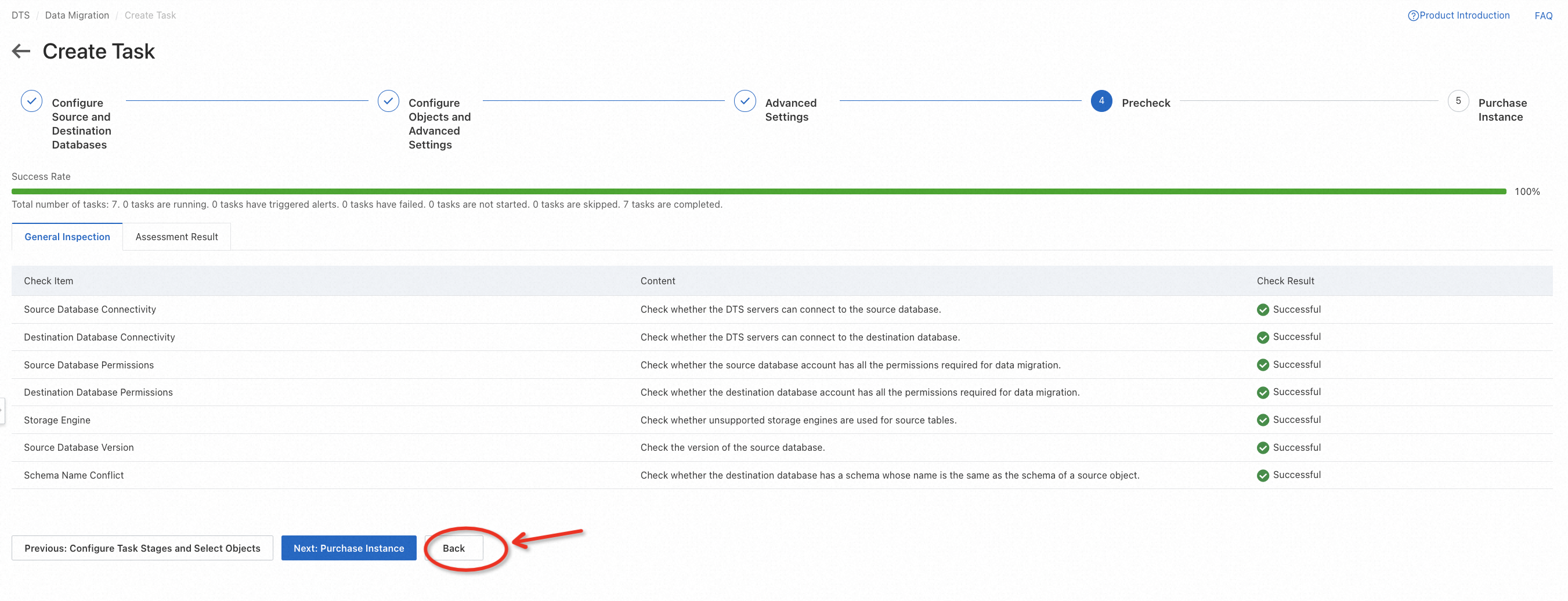
When you finish task configurations, a precheck will be performed automatically.
After precheck, click Start Task on the console. You can witness the following status changes of the task:
Schema Migration -> Full Migration -> Completed
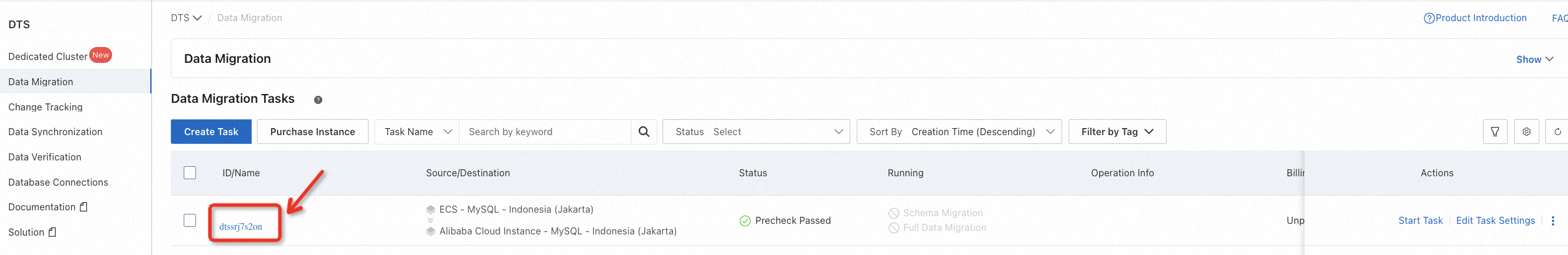
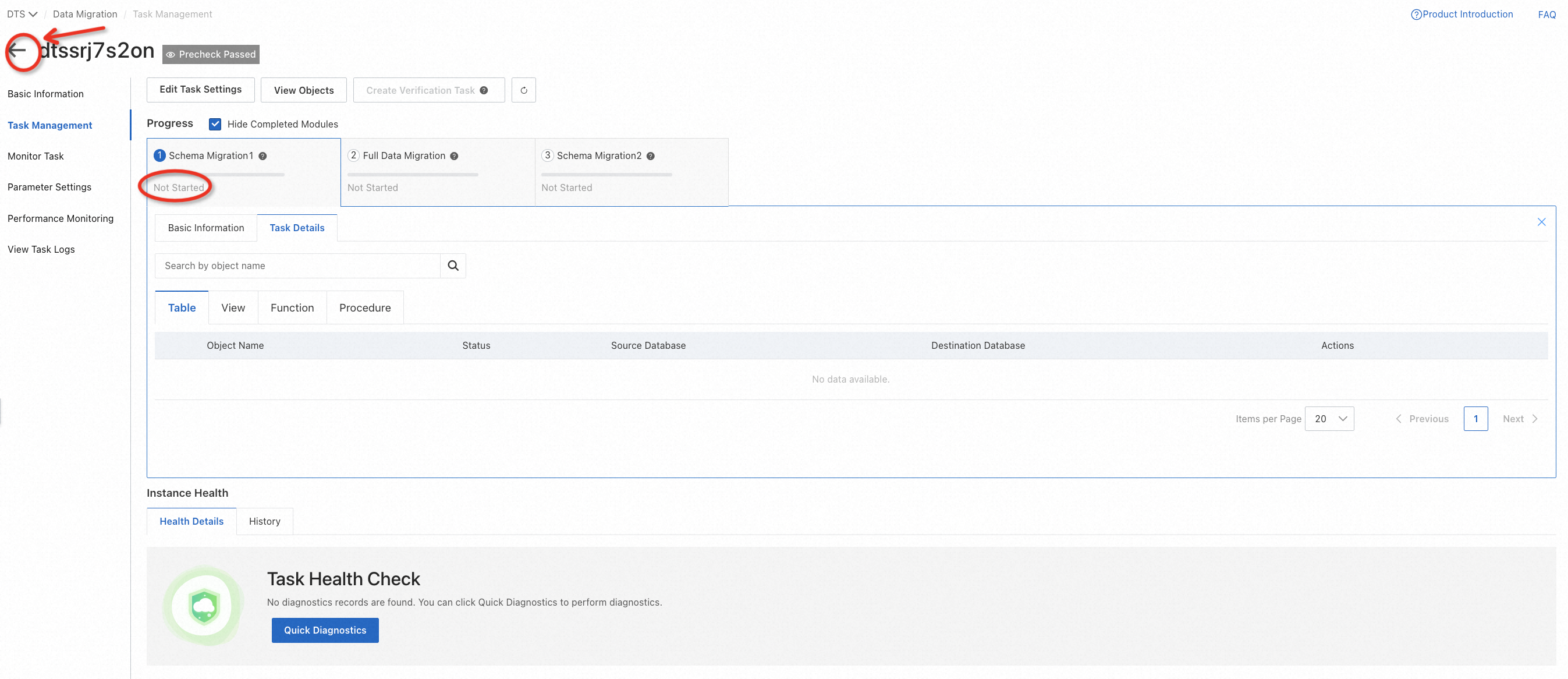
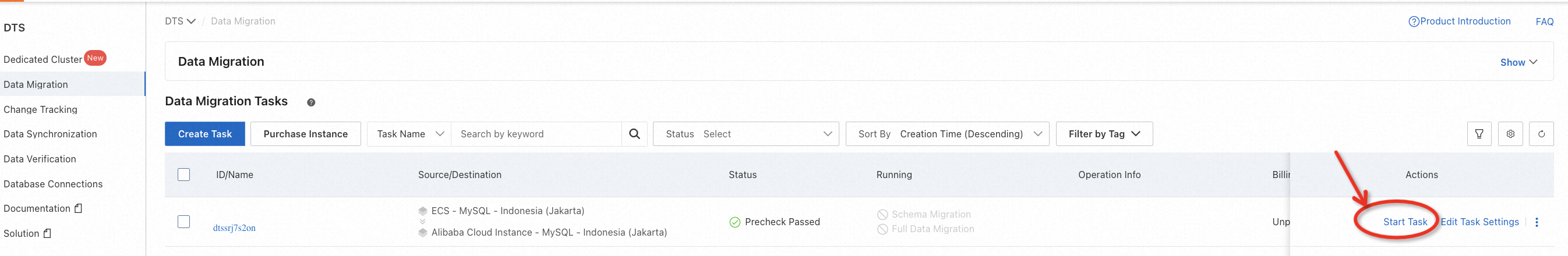

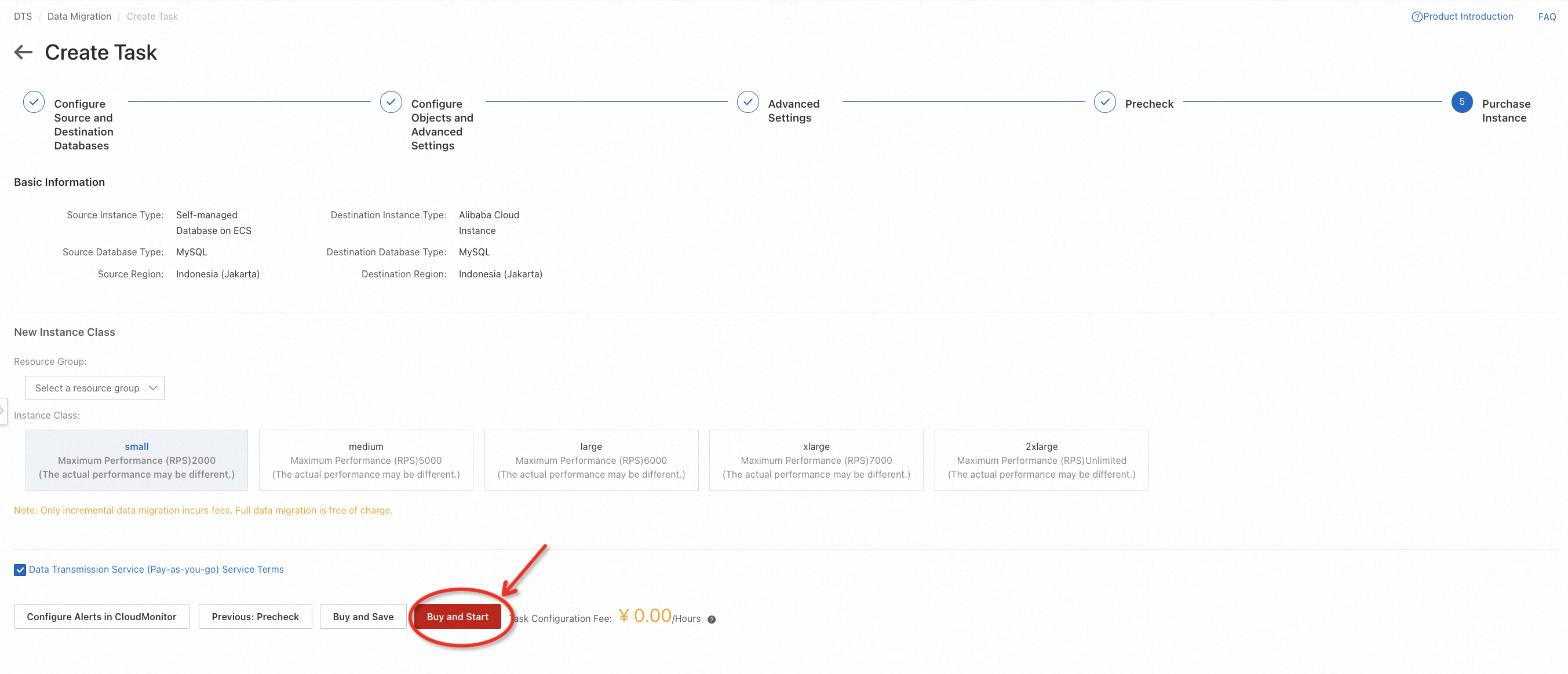

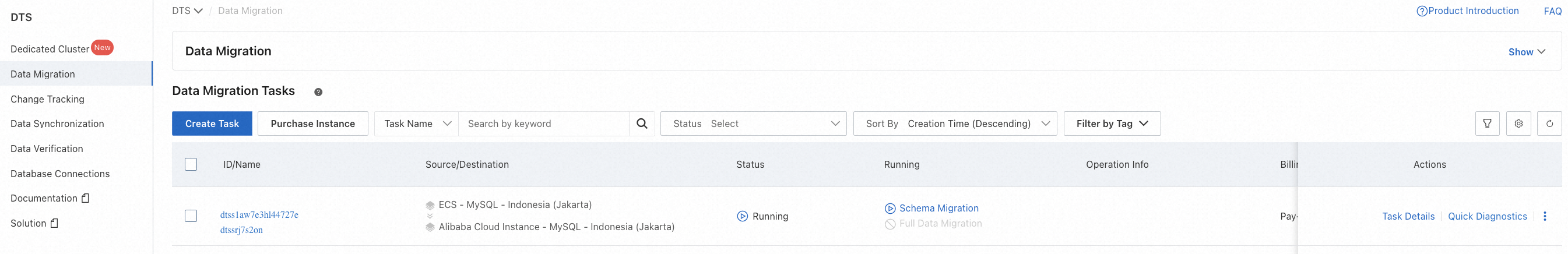


When the task becomes Completed that means the migration is finished.
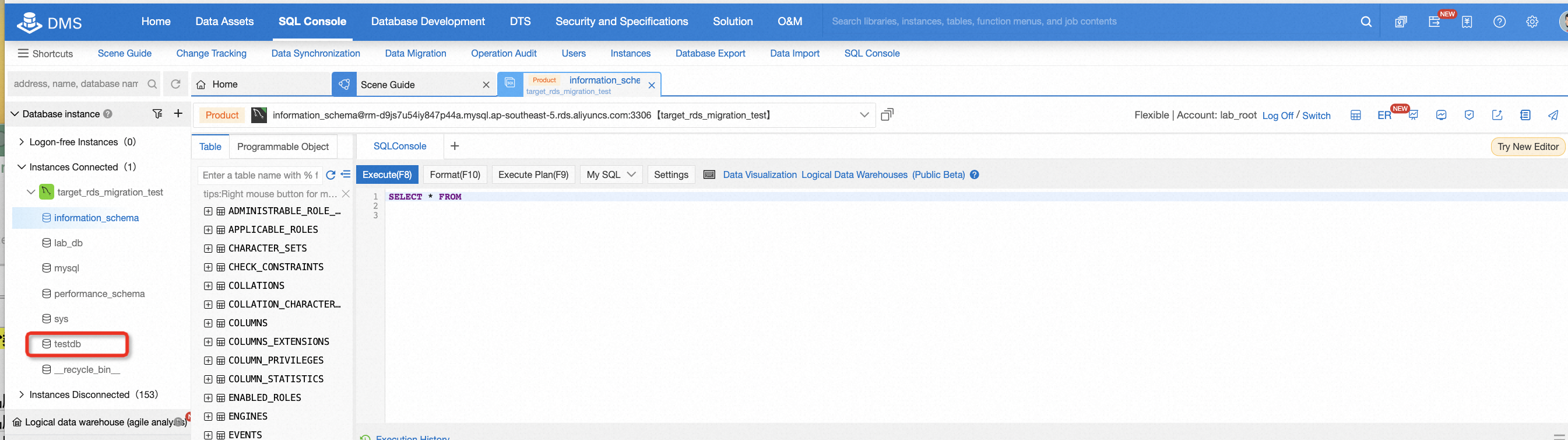
After migration, there is a need to check the data consistency of the source and target database. It's easy to do this if the data is not too much. For example, in this lab, you can log on to the target database and run some basic SQL statements, so that you can easily know the consistency by comparing the count of records or selecting all data from the table.
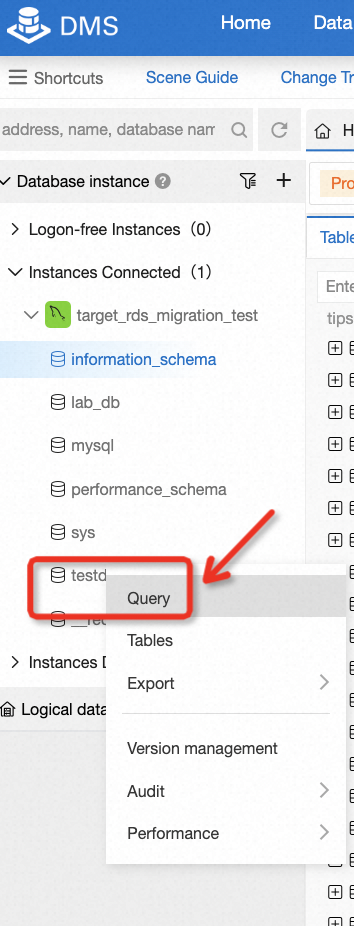
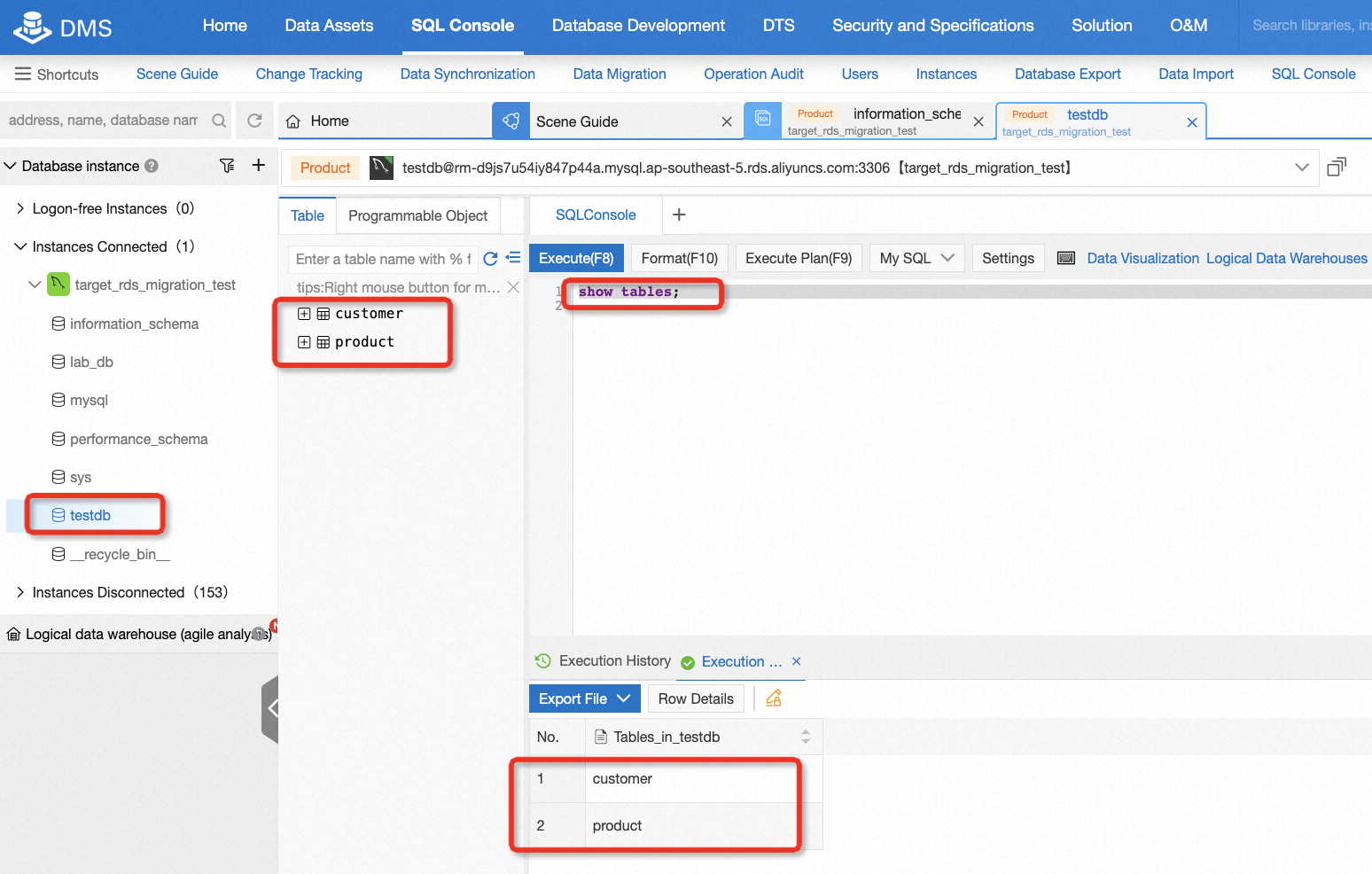
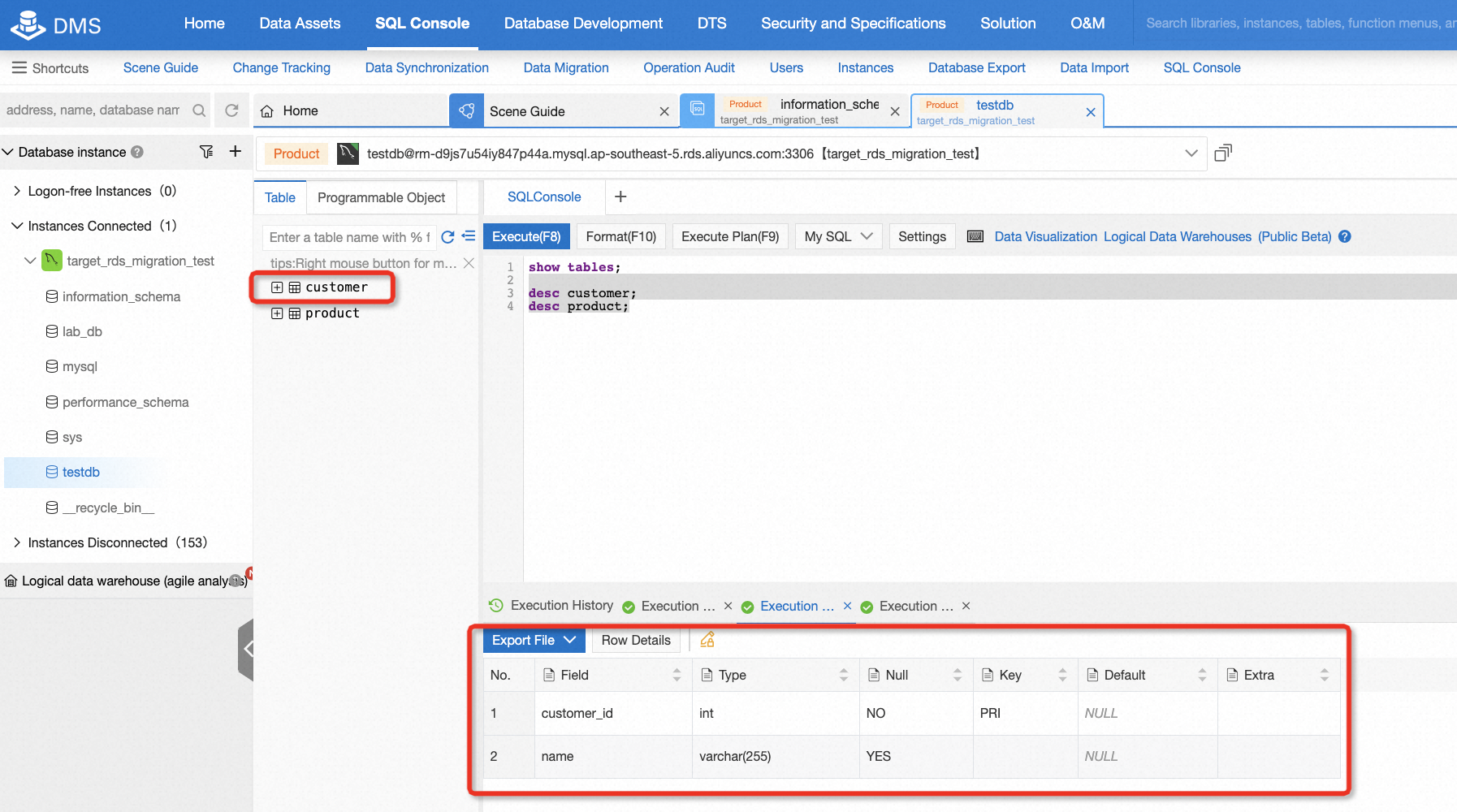
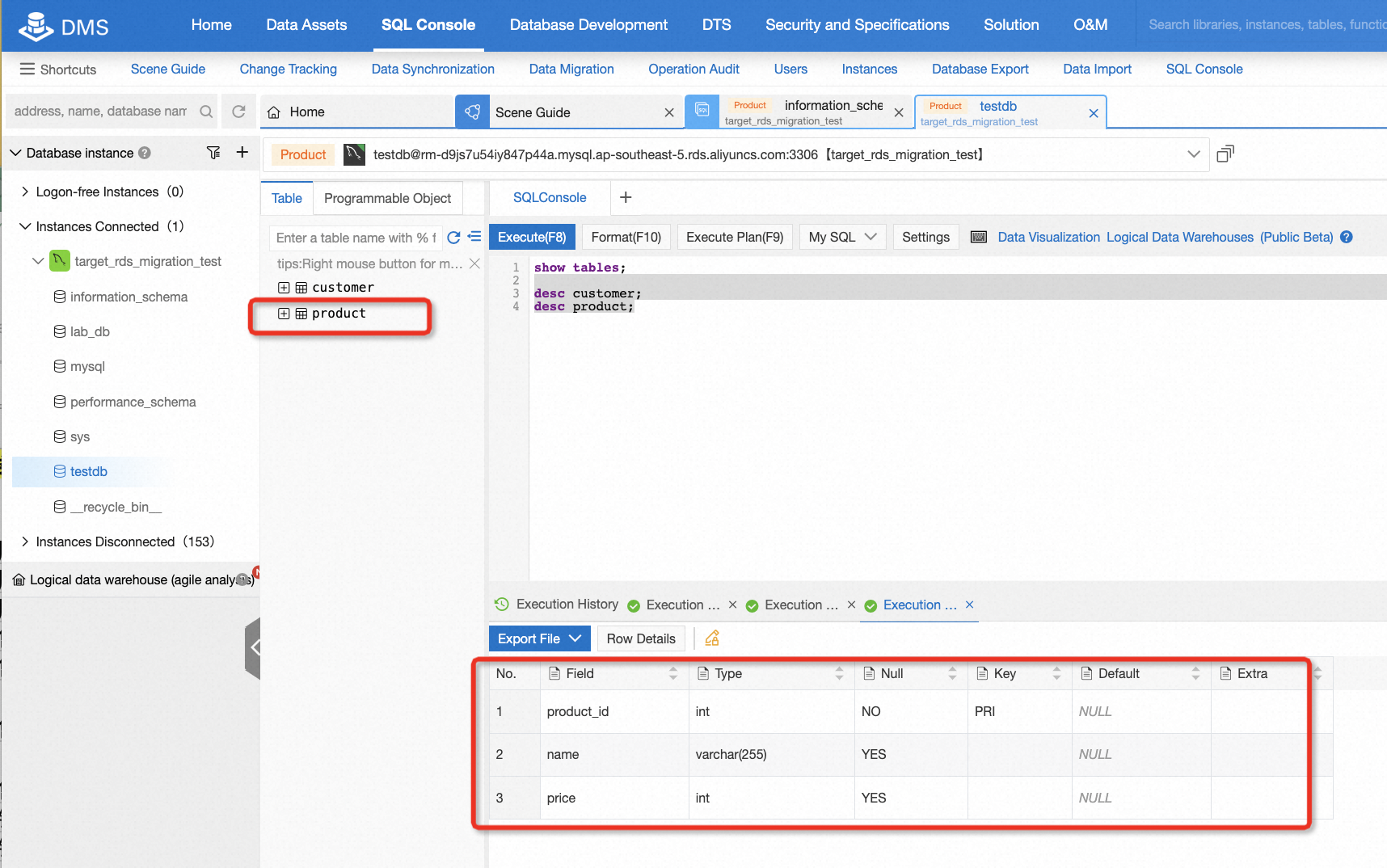
By now, the lab is complete. You can choose to keep the resource for further use or clean it up immediately. For participants exploring through claiming free trials, if you don't plan to continue using the resources and don't want to clean it up, that's okay, you won't be charged for it. However, we strongly suggest releasing instances if you don't intend to continue using it. You can release all resources in two steps:
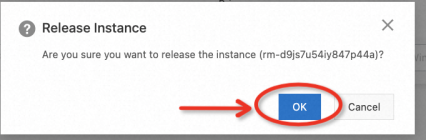
Go to the ECS console, and release the instance step by step according to the example below:
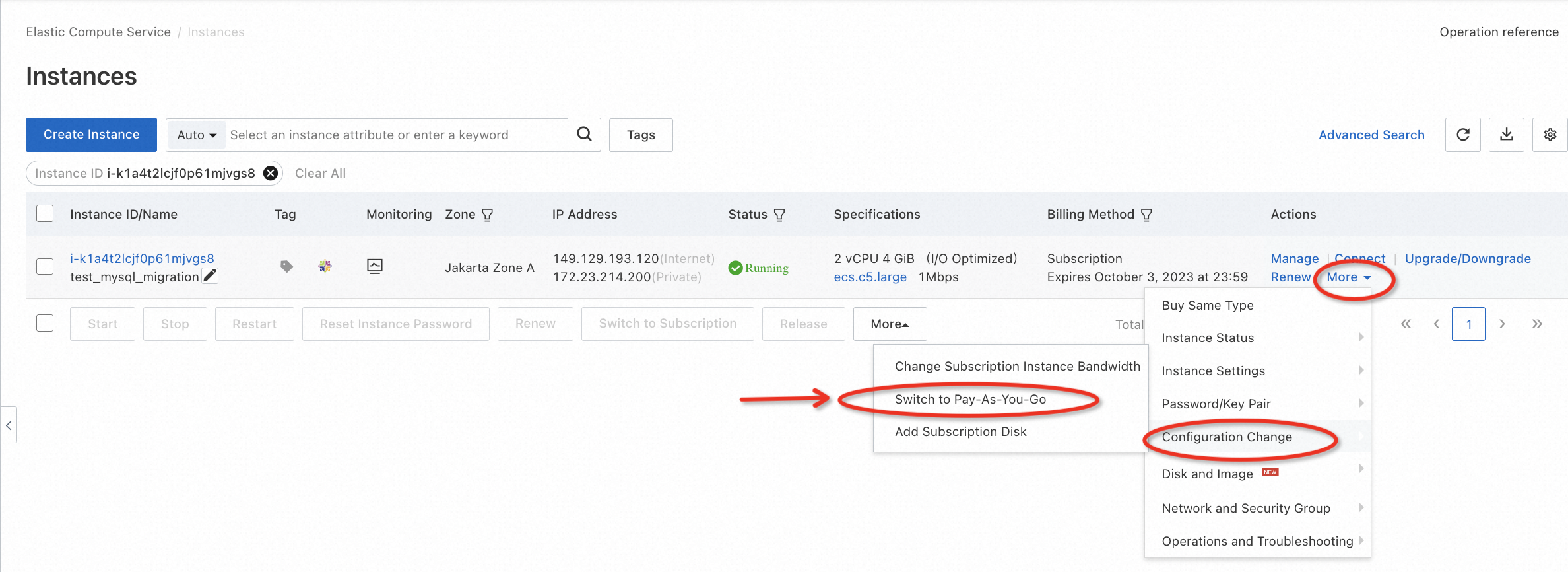
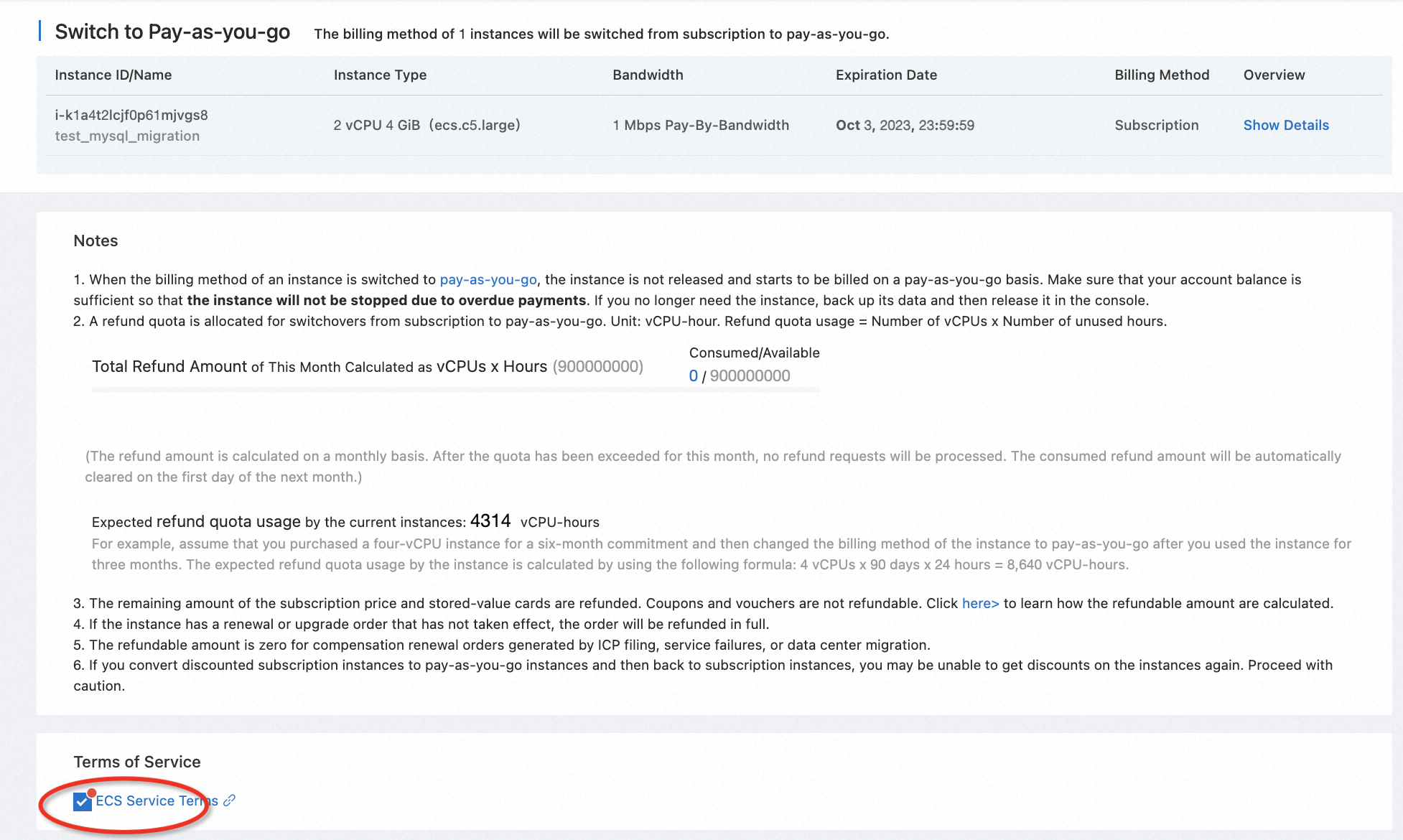
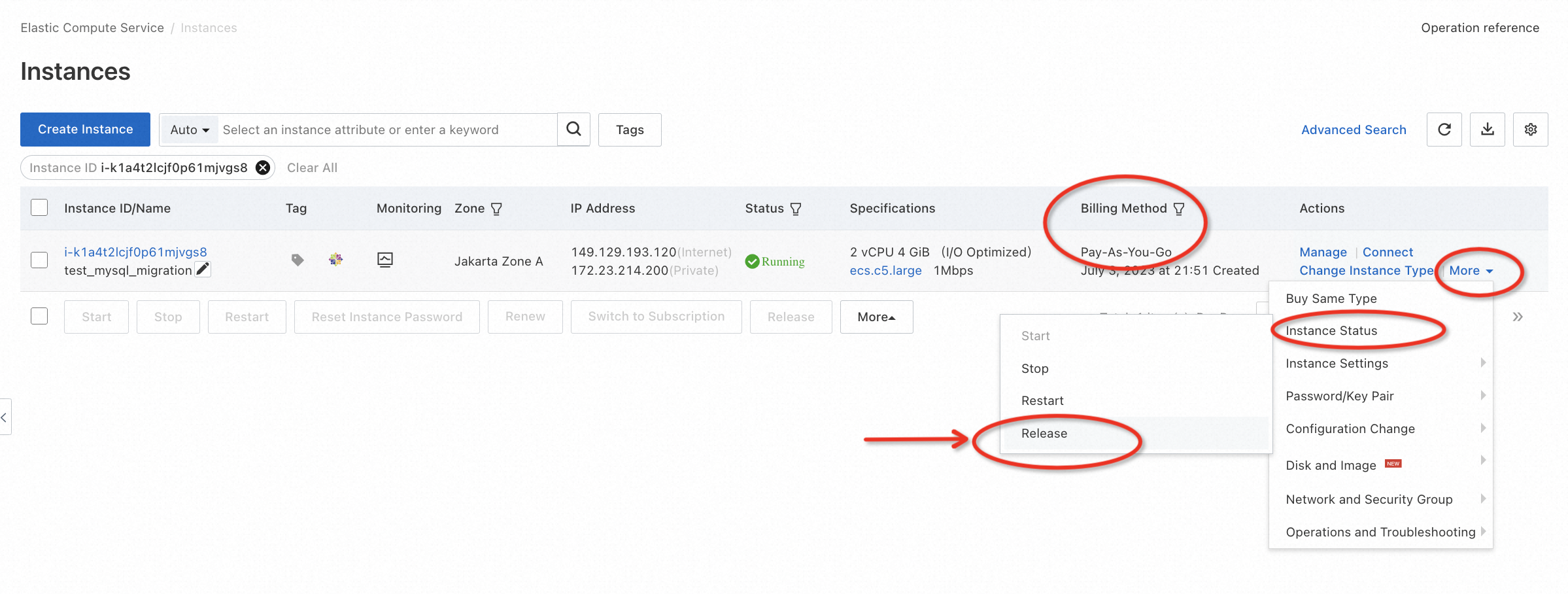
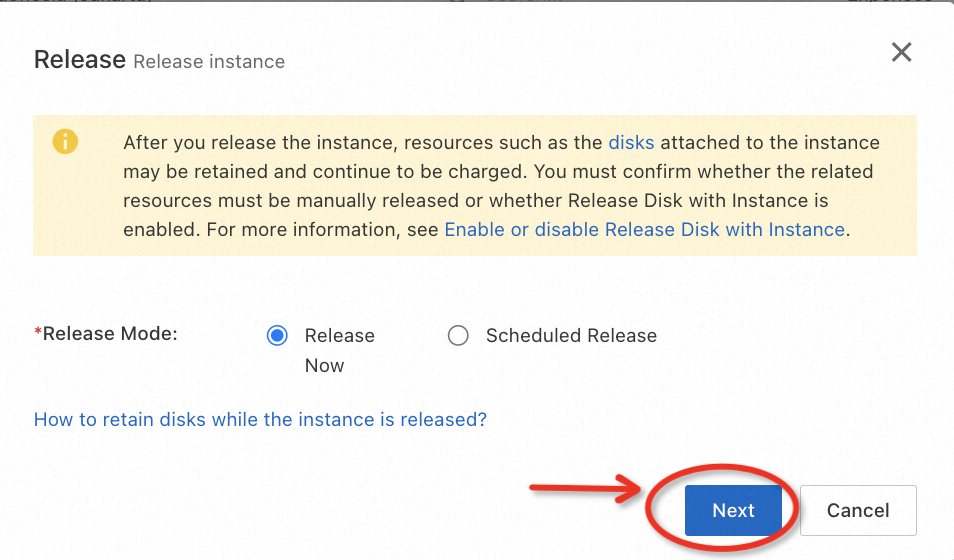
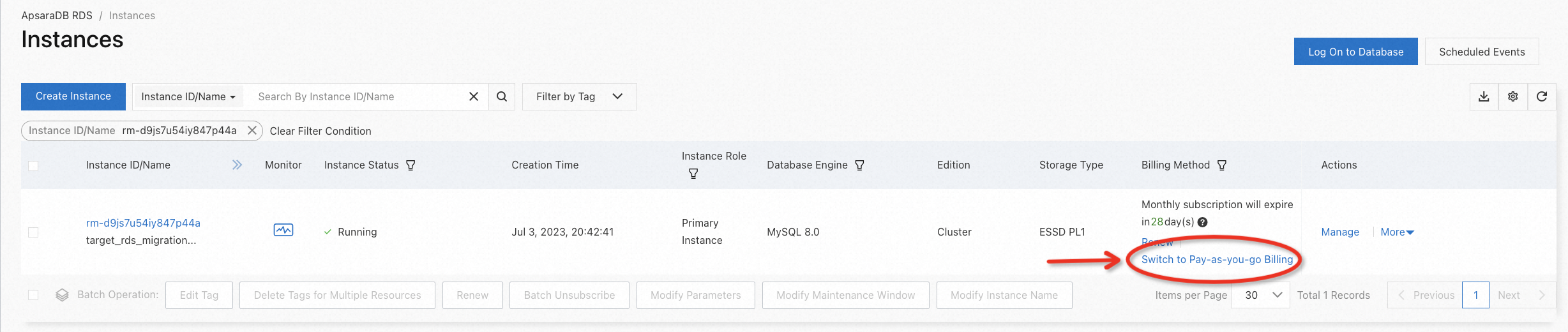
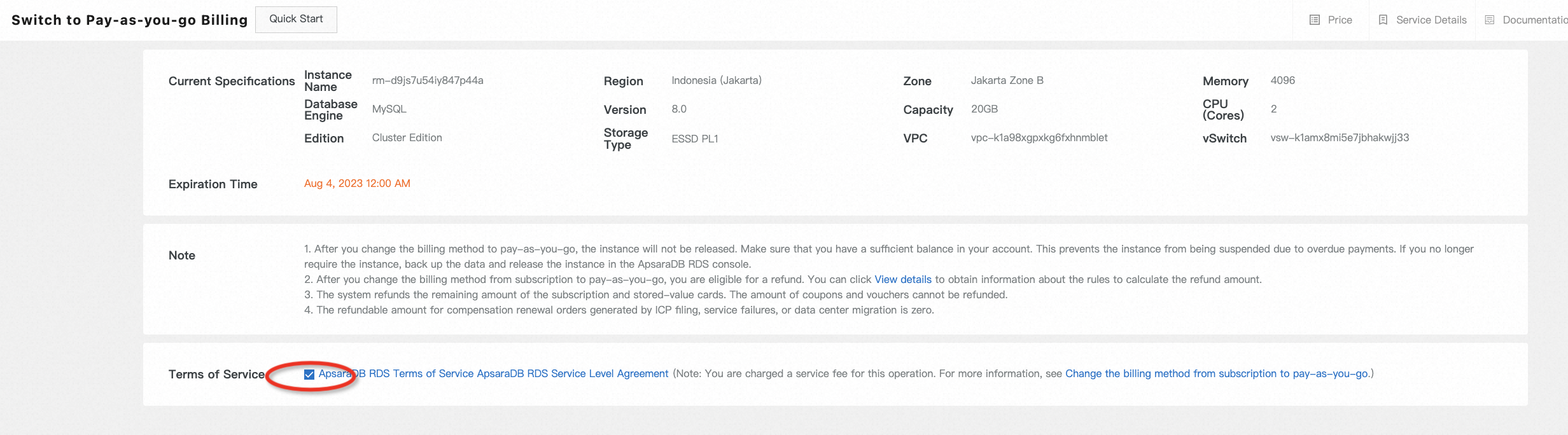
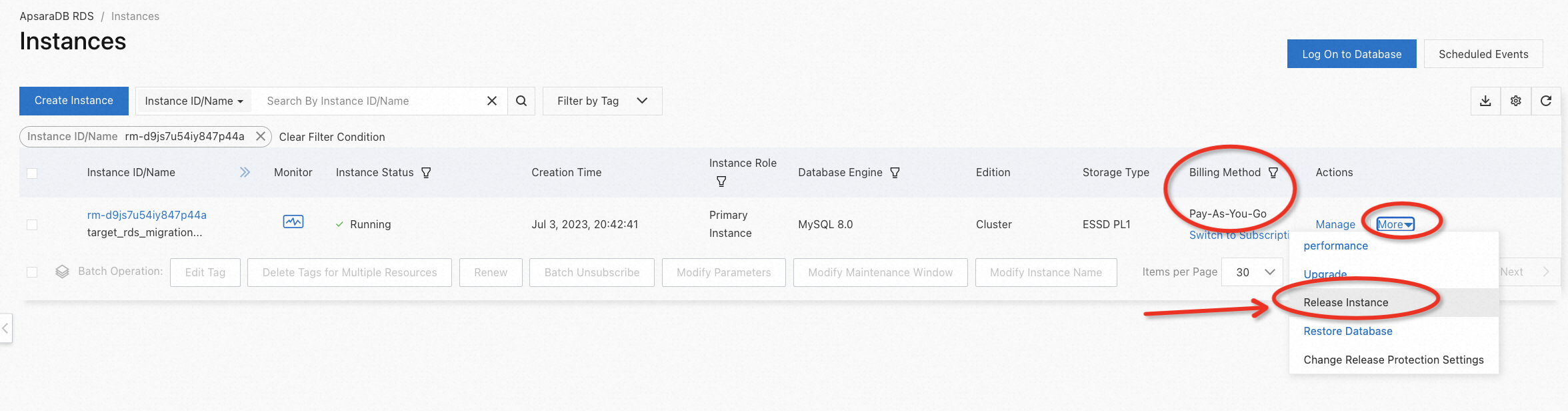
Go to the RDS console, and release the instance step by step according to the example below:
Paper Interpretation | PolarDB Cost-Based Query Transformation
ApsaraDB - July 12, 2023
ApsaraDB - July 13, 2023
Alibaba Clouder - January 27, 2021
ApsaraDB - August 15, 2025
Alibaba Clouder - March 1, 2021
Alibaba Clouder - February 1, 2021
 Database Migration Solution
Database Migration Solution
Migrating to fully managed cloud databases brings a host of benefits including scalability, reliability, and cost efficiency.
Learn More Oracle Database Migration Solution
Oracle Database Migration Solution
Migrate your legacy Oracle databases to Alibaba Cloud to save on long-term costs and take advantage of improved scalability, reliability, robust security, high performance, and cloud-native features.
Learn More ADAM(Advanced Database & Application Migration)
ADAM(Advanced Database & Application Migration)
An easy transformation for heterogeneous database.
Learn More Cloud Migration Solution
Cloud Migration Solution
Secure and easy solutions for moving you workloads to the cloud
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB
Dikky Ryan Pratama July 13, 2023 at 1:34 am
Awesome!