Microsoft has officially launched SQL Server 2025, marking the database's entry into the "AI era" with a brand-new logo. Alibaba Cloud RDS for SQL Server 2025 is now officially live and available for a free trial! This article takes a user-centric perspective to provide a deep dive into the five core upgrades of SQL Server 2025. We will also explore how these advancements, combined with Alibaba Cloud's cloud-native and enterprise-grade capabilities, empower businesses to achieve "Data as Intelligence."

7-Day Free Trial of RDS SQL Server 2025 Enterprise Edition. Open to both new and existing users (Limit: 1 instance per user).
Driven by the dual forces of digital transformation and the explosion of Large Language Model (LLM) technologies, databases have evolved beyond mere "data storage" tools to become the core engines of enterprise intelligence.
The launch of Alibaba Cloud RDS for SQL Server 2025 marks our leadership in integrating the innovative features of SQL Server 2025 into a cloud-native architecture. This release provides enterprises with out-of-the-box AI capabilities, an ultimate development experience, and a high-availability architecture.
Why Choose Alibaba Cloud?
• Deep Cloud-Native Optimization: Leveraging storage-compute decoupling to unleash the full performance potential of SQL Server 2025.
• One-Click Upgrade: Seamlessly upgrade older RDS SQL Server instances to the 2025 major version with a single click.
• Fully Managed Service: A comprehensive end-to-end solution—including database management, backup and recovery, high availability/disaster recovery, monitoring/alerting, and deep diagnostics—to simplify O&M and reduce costs.
Tips
Starting with the 2025 version, the Web Edition will no longer be provided.
SQL Server 2025 introduces significant updates across the following five aspects:
Vectors are the cornerstone of the AI era. They assign “semantic coordinates” to text, images, audio, and video—the language AI uses to understand the world. Traditionally, computing semantic similarity in business systems has meant introducing an external vector database, which leads to duplicated data, an extra network hop, a separate O&M stack, and more complex security and consistency. As the saying goes, “Any problem can be solved by adding another layer,” but every extra layer increases architectural complexity, cost, latency, and failure risk.
If “vector storage + nearest-neighbor search” are built directly into the database engine, can we eliminate that extra layer? In practice, yes. The figure contrasts architectures with and without native vector support: Without built-in vectors, even a simple RAG application must pull data from SQL Server, call an external model to chunk text and generate embeddings, then store those vectors in a separate system (e.g., Milvus) before running vector queries—while also handling data synchronization, permissions, and consistency. With SQL Server 2025’s native vector capabilities, all of these steps can be completed inside a single database, dramatically simplifying the architecture.
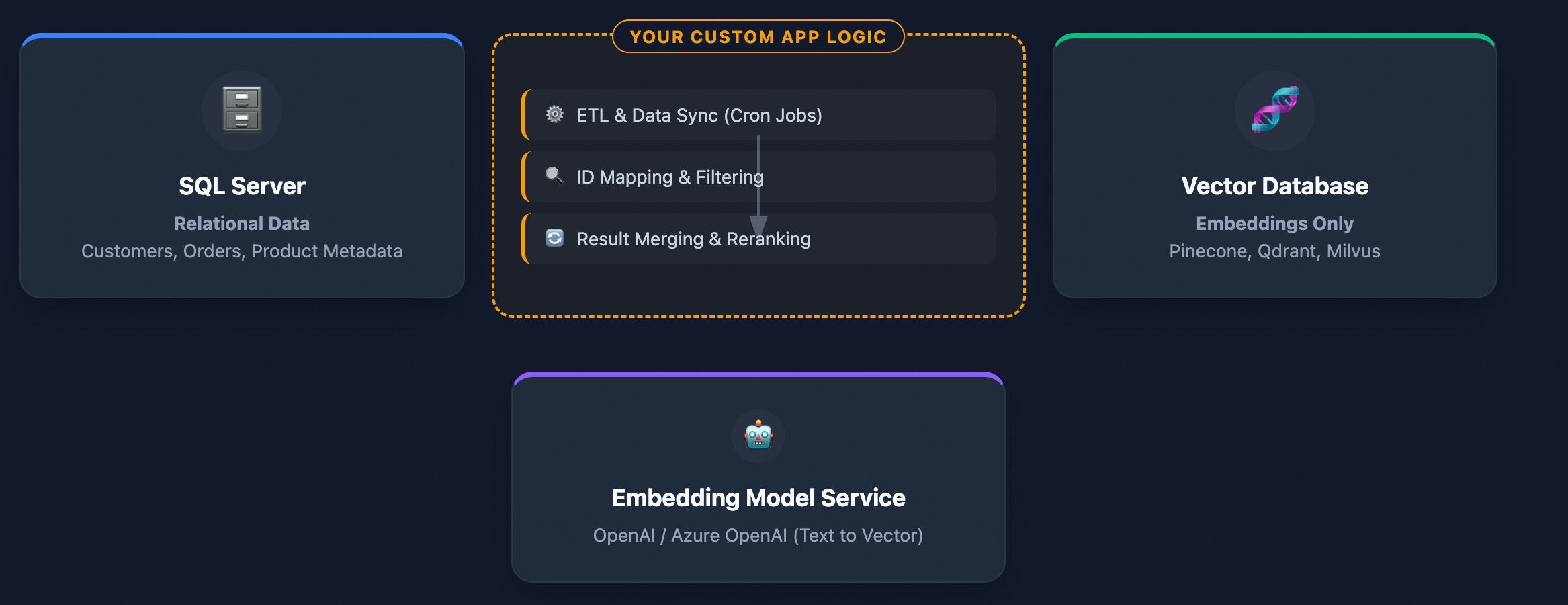
Figure: Application without vector support
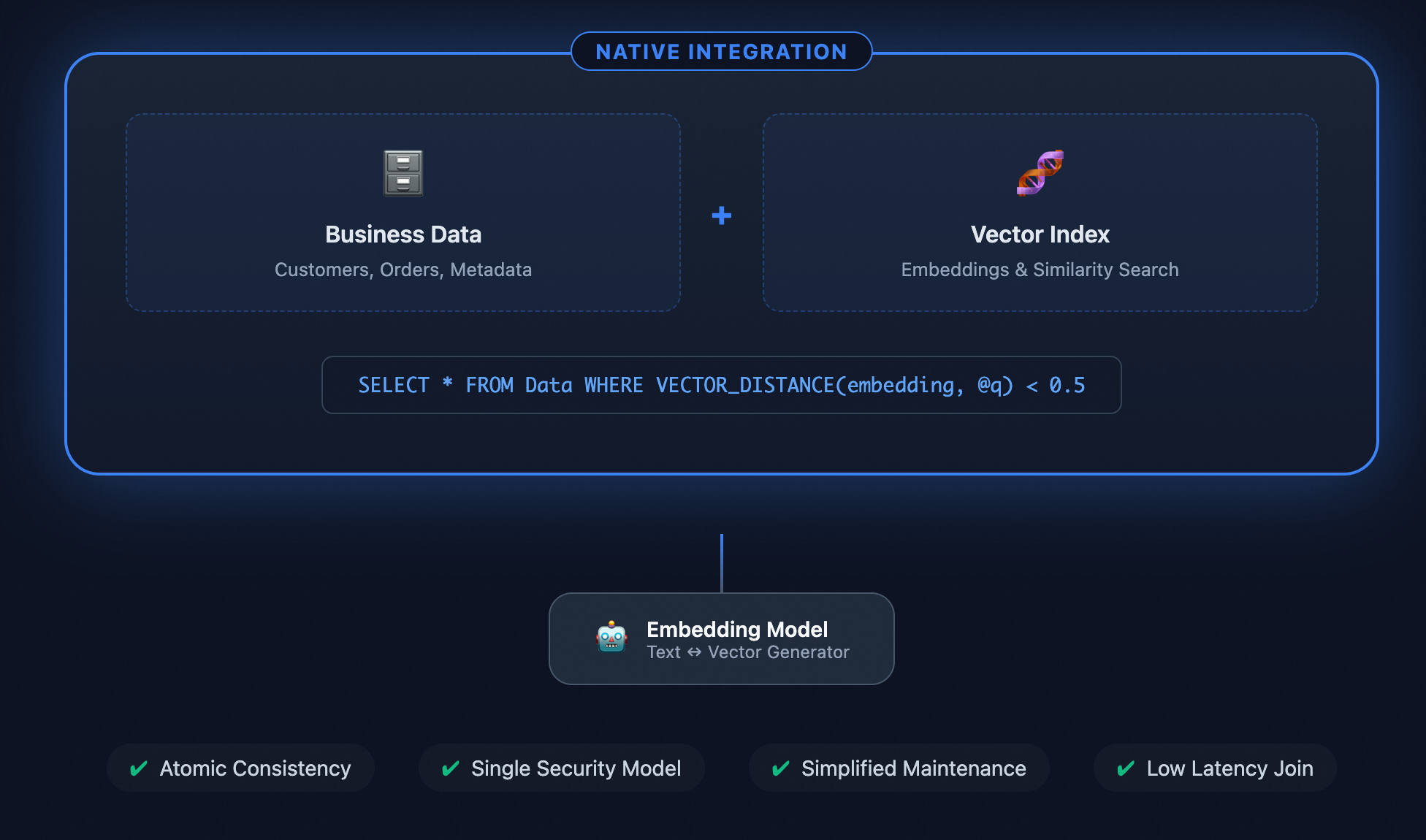
Figure: SQL Server 2025 with vector support
SQL Server 2025 introduces a VECTOR(n) data type, an array of n floating-point numbers. For example, VECTOR(3) represents a 3 D vector like [0.1, 2, 30].
Vectors are stored on disk in a compact binary format, avoiding text parsing overhead and significantly reducing storage footprint.
To enable efficient approximate vector search, SQL Server 2025 incorporates Microsoft Research’s DiskANN algorithm.
The large graph index resides on SSDs while only minimal navigation data stays in memory, enabling nearest-neighbor lookup with very few random disk reads.
Although slightly slower than pure in-memory approaches, DiskANN delivers over 90% memory savings while keeping query latency in the millisecond range.
Combined with Alibaba Cloud ESSD disks (high IOPS, low latency), DiskANN on the cloud can achieve retrieval performance close to local NVMe—offering excellent cost-performance.
SQL Server provides built-in functions for similarity and search, such as VECTOR_DISTANCE to compute distances between vectors and VECTOR_SEARCH to run nearest-neighbor queries over tables—making vector operations straightforward for developers.
Current limitation
When a vector index is created on a table, INSERT/UPDATE operations are currently not supported (the table becomes read-only). To modify data, the index must be dropped first. This limitation is expected to be lifted in the future.
Usage example
Create a DiskANN index on the Embedding column of an article repository, then issue a single SQL query to find the articles most similar to a given vector—all executed entirely within the database.
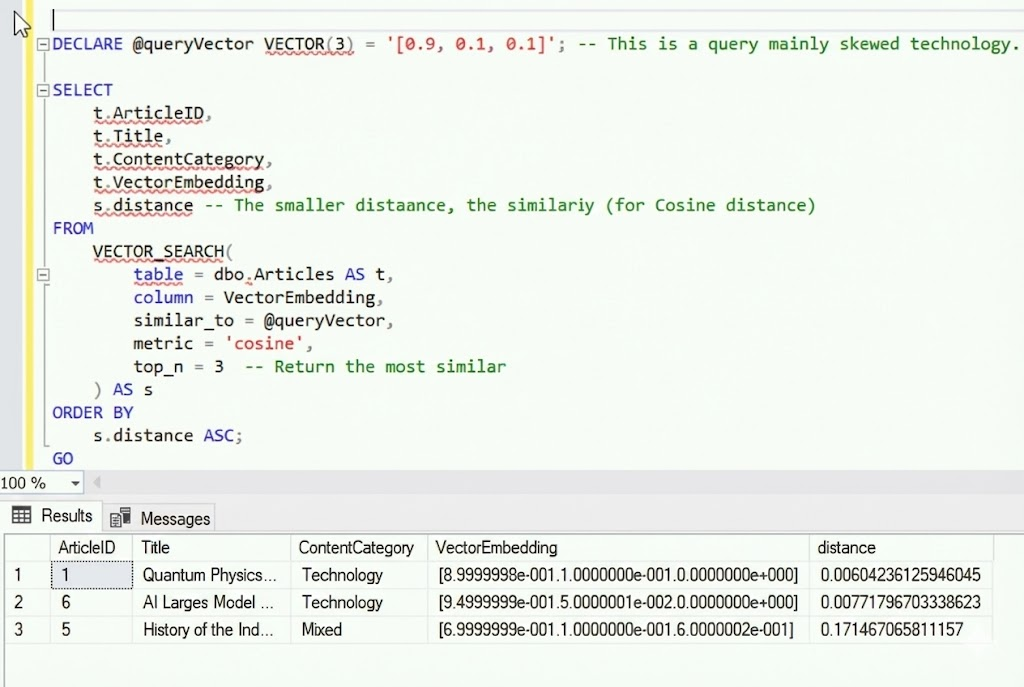
Figure: Perform a similarity search based on a vector index
SQL Server 2025 features built-in capabilities for calling external services via HTTP (through the sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint stored procedure), allowing the database to directly access external REST APIs.
This means we can now call AI model interfaces directly within T-SQL scripts to process data—for example, requesting a text embedding API to generate vectors or calling external services to perform specific computations and retrieve the results. Similarly, we can even trigger DingTalk Robot Webhooks directly from the database to send notifications, enabling truly database-driven automation workflows.
The following figure demonstrates examples of calling an AI interface in T-SQL to obtain text embeddings and sending notifications via DingTalk:
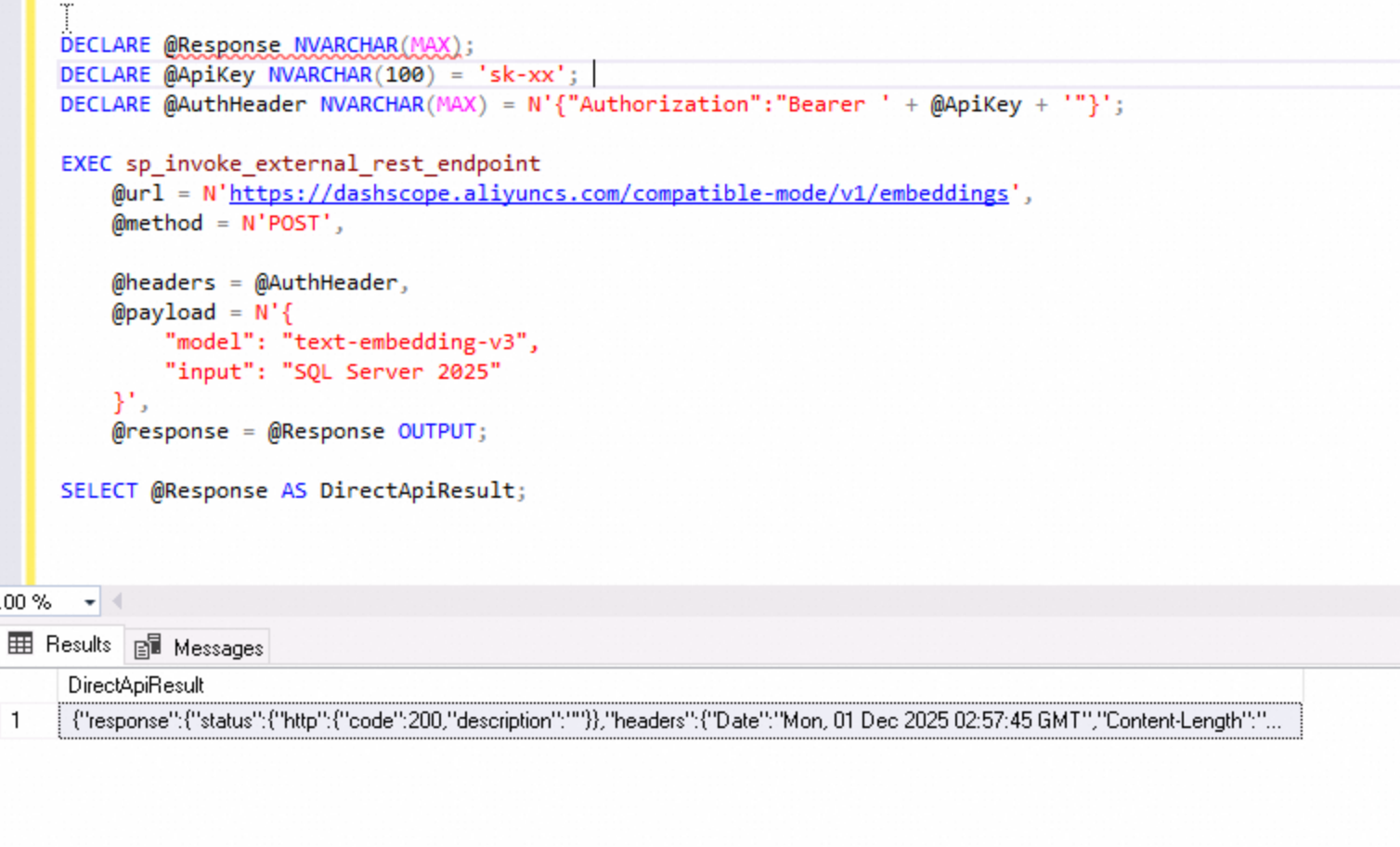
Figure: Call an external model service
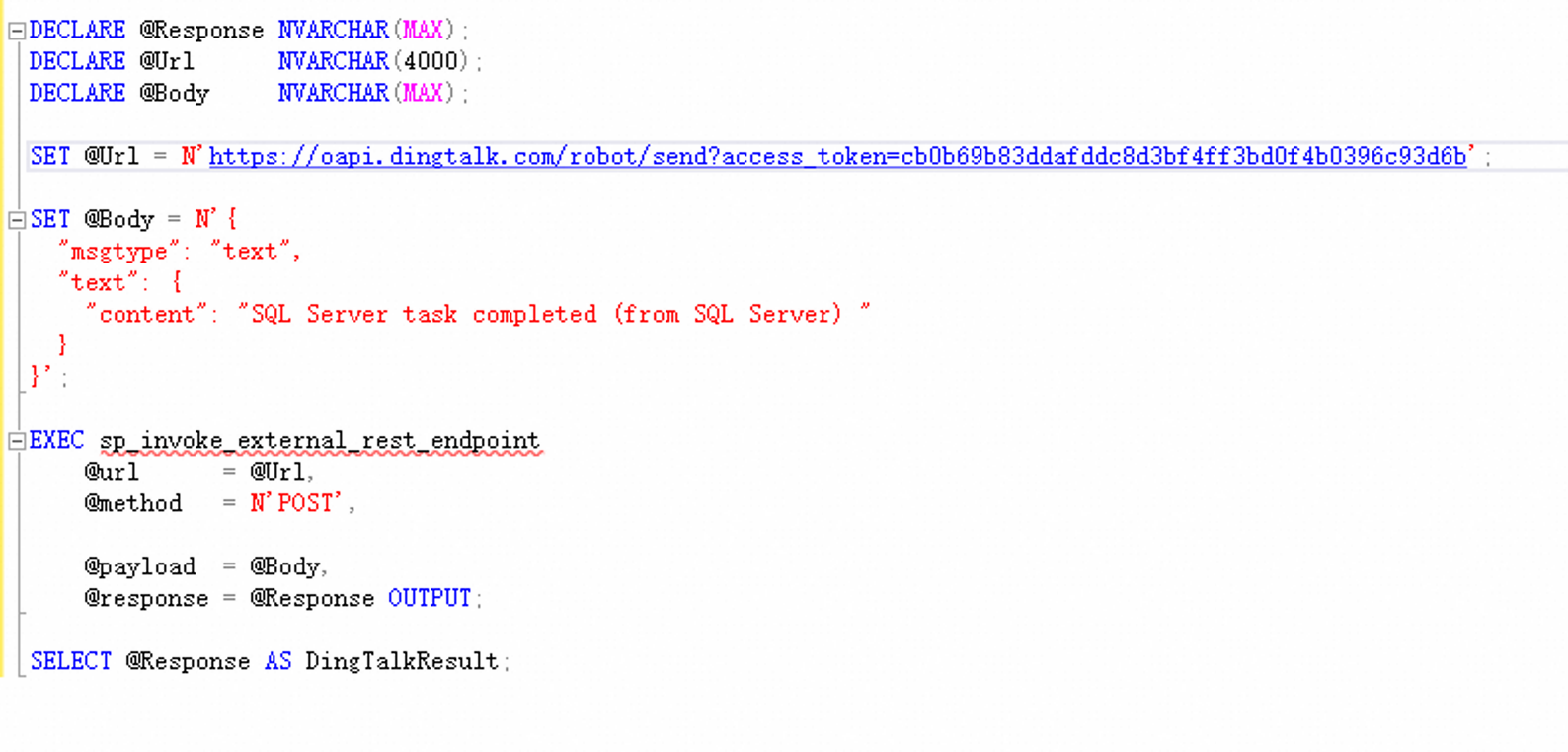
*Figure: Send DingTalk notification through T-SQL
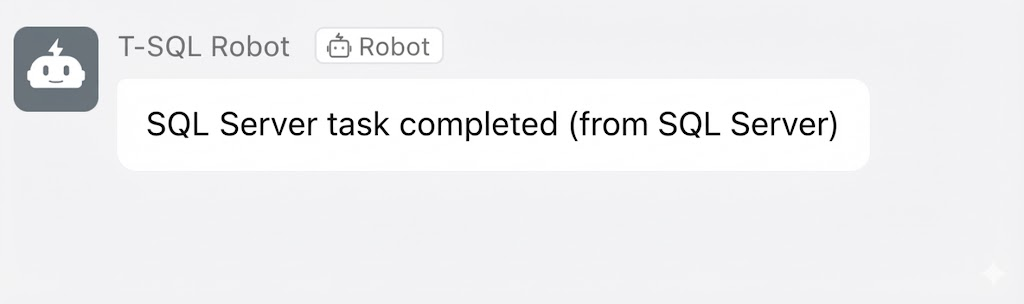
Figure: DingTalk message
In addition, SQL Server 2025 provides the CREATE EXTERNAL MODEL statement, which makes it easy to register third-party AI models and invoke them through built-in functions. For example, we can register OpenAI’s Embeddings endpoint as an external model and then directly use functions such as AI_GENERATE_CHUNKS and AI_GENERATE_EMBEDDINGS to segment long text and generate vectors. However, this capability currently only allows calls to OpenAI’s official domain (api.openai.com), so domestic large-model services cannot be used directly for now—you still need to call them at a lower level via sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint.
Cloud integration practice: For Alibaba Cloud users, SQL Server 2025 can be used to build a unified data layer that combines the operational database and the vector database. At the storage layer, choose high-performance ESSD cloud disks to support fast DiskANN retrieval. Within a VPC, connect to Alibaba Cloud Qwen and other model services via Function Compute or API Gateway, so that the entire workflow—from text chunking and embedding generation to final Q&A inference—runs on the cloud’s internal network. Compared with the traditional architecture of “operational DB + external vector DB + public-internet AI service,” this approach is simpler and more efficient, with greatly reduced link risk and latency.
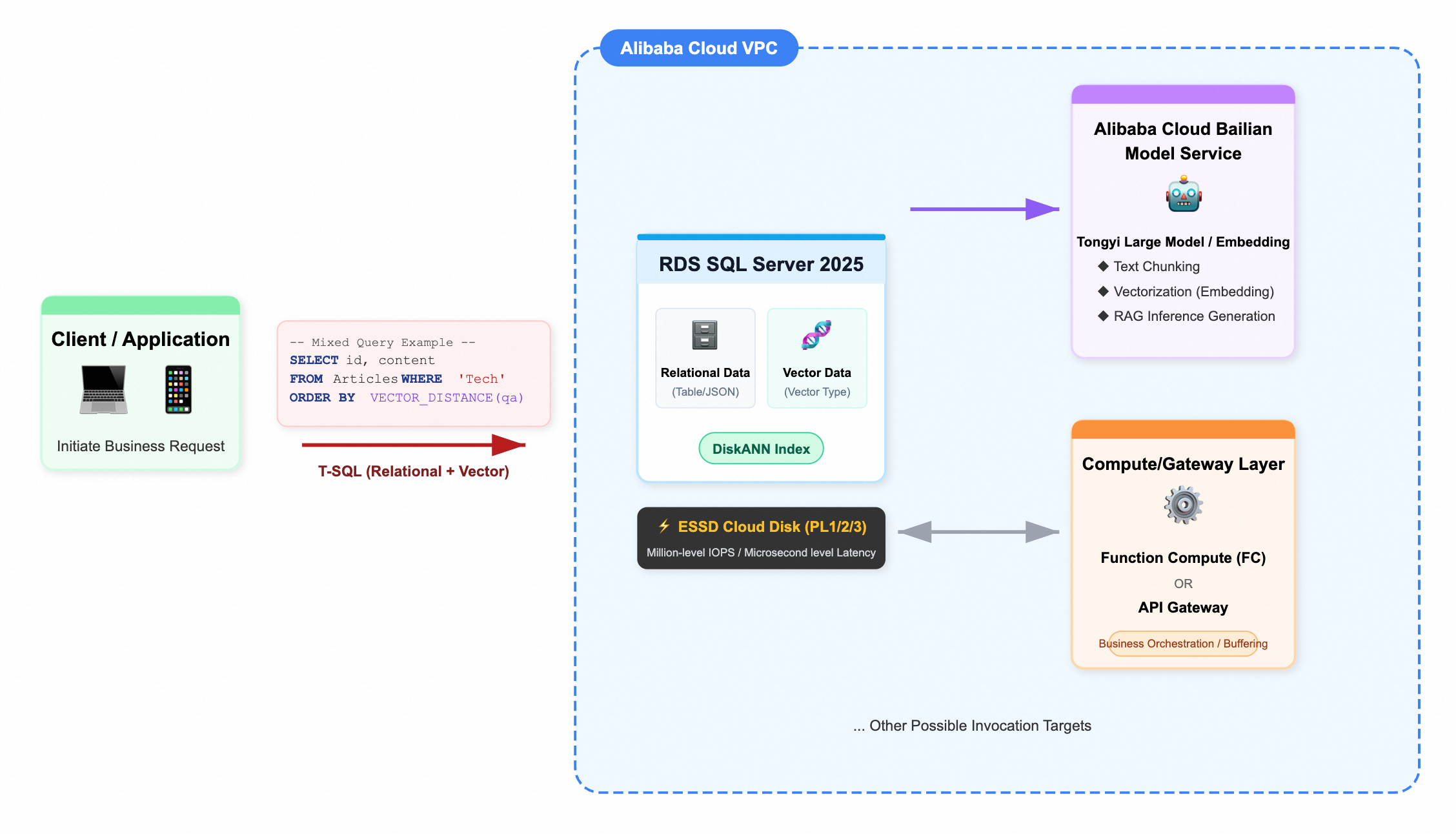
Architecture Diagram: Integration of Alibaba Cloud RDS Vector Database and Internal LLMs
SQL Server 2025 introduces tempdb space quota controls: DBAs can set upper limits on tempdb usage for different workload groups, and any query that exceeds its quota is immediately terminated (error 1138), protecting tempdb from being exhausted. I find this feature a bit “meh”—today a single instance usually serves a specific workload, so few people need such fine grained tempdb management. That said, it does add an extra safeguard for cloud multi tenant isolation or to prevent “bad SQL” from consuming all resources.
In addition, tempdb now supports Accelerated Database Recovery (ADR). This means that even if tempdb contains large uncommitted transactions, after an unexpected crash and restart the database can complete recovery within minutes, rather than getting stuck for a long time (I’ve seen tempdb recovery take an entire night in my career). This enhancement greatly improves SQL Server’s availability during abnormal recovery.
SQL Server 2025 introduces a native JSON data type (stored internally in a binary format) rather than just treating JSON as simple strings. This significantly enhances storage efficiency—reducing space consumption by approximately 50% while providing automatic schema validation. More importantly, it supports partial in-place updates, allowing specific parts of a JSON document to be modified without replacing the entire string, which drastically improves the performance and efficiency of JSON field updates.
Furthermore, a suite of new JSON processing functions and indexing capabilities has been added. For example, JSON_ARRAYAGG and JSON_OBJECTAGG can aggregate query results directly into JSON arrays or objects, while JSON_CONTAINS can verify if a specific value exists at a given path. These operations can be further accelerated using dedicated JSON indexes. In essence, this native support embeds a lightweight, high-performance NoSQL engine within SQL Server, ensuring JSON data is "easy to store and fast to modify." In my view, this is a major boon for JSON-heavy scenarios—such as IoT telemetry and game configurations—as well as for handling AI model inputs and outputs.
SQL Server 2025 finally introduces native Regular Expression (Regex) support (based on the Google RE2 library). New functions like REGEXP_LIKE, REGEXP_REPLACE, REGEXP_SUBSTR/INSTR, and REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_TABLE enable complex string matching, replacement, extraction, and splitting directly within the database. For instance, you can use REGEXP_LIKE to validate email formats or REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_TABLE to parse log strings into multiple records based on regex delimiters.
This feature significantly bolsters SQL Server’s capabilities in log analysis and data cleansing. However, since regex matching can be resource-intensive, I view this more as an "icing on the cake" feature that closes the gap with other databases like Oracle and PostgreSQL. While highly useful for specific tasks, its impact on daily high-concurrency OLTP workloads remains limited.
The 2025 release brings two major improvements via ADR. First, lock escalation is eliminated: no matter how many rows a transaction modifies, it retains only a minimal set of versioned row locks and does not escalate to a table lock (greatly reducing the blocking impact of long transactions on other queries). Second, LAQ (lock after qualification): during UPDATE, rows are first filtered to determine exactly which ones need to be changed, and only then are locks acquired to perform the updates (avoiding interference from locking irrelevant rows while scanning the table). Together, these optimizations noticeably reduce blocking in high concurrency write workloads.
The new OPTIMIZED_SP_EXECUTESQL option ensures that parameterized queries with the same structure are compiled only once and share execution plans under high concurrency. This prevents "compilation storms" that lead to CPU spikes. Combined with PSPO (Parameter Sensitive Plan Optimization) introduced in SQL 2022, the database can now cache multiple plans for different parameter values and intelligently select the best one, solving the "one-size-fits-all" plan issue.
OPPO (optional parameter optimization) generates different plans for queries where parameters are sometimes supplied and sometimes omitted, avoiding full table scans caused by empty parameters. In addition, a more intelligent cardinality estimation feedback mechanism can learn actual row counts for common filter/join patterns across queries and adjust estimates accordingly, reducing performance issues caused by statistical bias.
Query Store now supports the ABORT_QUERY_EXECUTION hint, allowing you to tag specific queries so that each execution is immediately terminated by the engine (returning error 8778). For queries that are noncritical but abnormally resource hungry, this provides an emergency stopgap (though it’s not a root cause fix and is intended mainly for firefighting).
Nonclustered columnstore indexes (NCCI) now support specifying a sort key, and both create and rebuild support ONLINE operations. This means that when you attach a columnstore index to an OLTP table for analytics, you can leverage ordering to boost query performance and maintain the index without downtime—very beneficial for HTAP scenarios. Columnstore indexes already excel at compression and analytic performance; these improvements further lower the barrier to adoption.
SQL Server 2025 introduces the ZSTD compression algorithm, which delivers higher compression ratios and faster speeds at the same compression level. Alibaba Cloud RDS will make it the default for 2025 backups, resulting in noticeably smaller backup files and improved backup/restore efficiency.
Full and differential backups are now supported on Always On secondary replicas, so backups no longer have to run on the primary. This reduces load on the primary and makes backup scheduling more flexible.
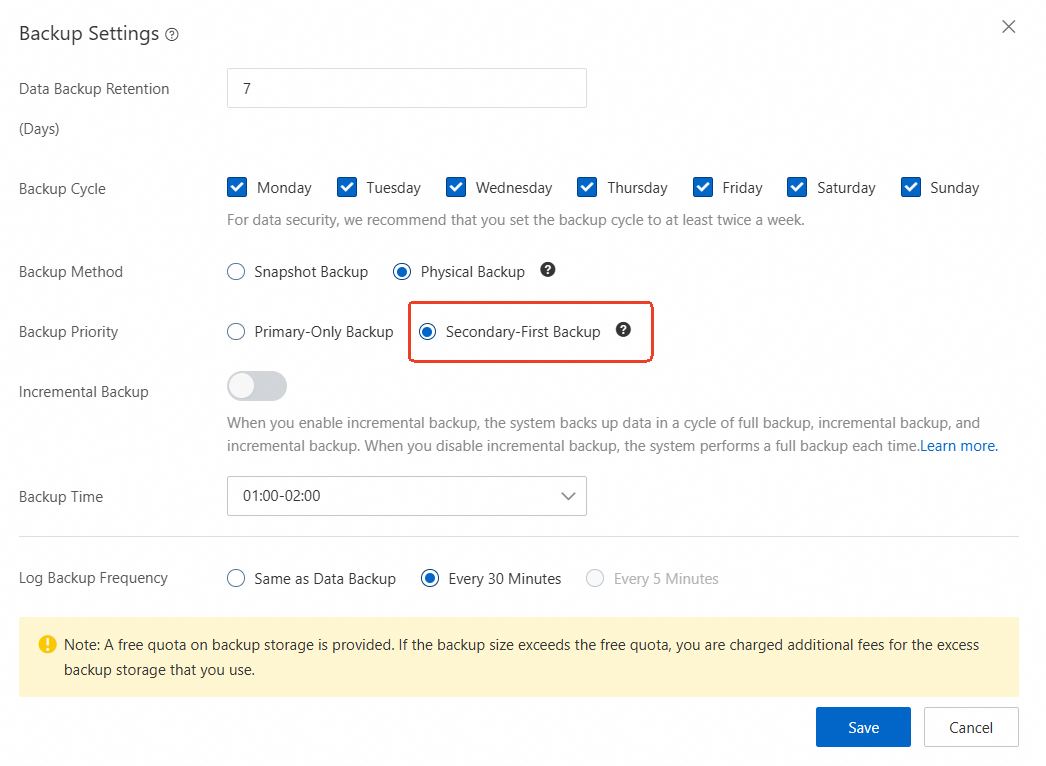
Figure: ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server Cluster Edition supports backup from secondary databases
In addition, the 2025 release enables Query Store by default on read-only replicas and improves statistics synchronization, making execution plans on read-only replicas more consistent with the primary and preventing identical queries from inexplicably slowing down on replicas.
• External data querying: Without installing PolyBase, you can use OPENROWSET in T-SQL to query Parquet, CSV, and other files directly on OSS/S3, treating object storage as part of the database. This enables hot–cold data separation and zero ETL ad hoc analytics, further integrating SQL Server with the data lake.
• Memory-optimized offload: You can now remove filegroups for In-Memory OLTP. The previous limitation that prevented dropping memory-optimized filegroups after enabling the feature has finally been lifted, making operations easier.
SQL Server 2025 is undoubtedly a leap forward, marking the evolution of the database from traditional relational storage to a comprehensive AI-ready data platform. Native vector data types, highly efficient DiskANN vector indexing, and support for external AI model calls enable semantic vector retrieval and AI inference to run directly inside the database, greatly simplifying architectures for applications like RAG. At the same time, native JSON support, regex functions, and kernel-level upgrades such as improved lock mechanisms and parameterized queries address many long-standing pain points and significantly enhance performance and usability.
Alibaba Cloud RDS for SQL Server already supports these new features and provides a one-click upgrade capability to help users adopt the power of SQL Server 2025 at minimal cost. Coupled with cloud advantages such as DAS intelligent diagnostics and Always On high-availability architecture, and through integration with Alibaba Cloud Model Studio to access the Qwen large language model, the SQL Server 2025 instance on RDS will unleash greater potential and value.
If you would like to seamlessly introduce vector databases and AI capabilities into your existing architecture, you are welcome to participate in the free trial of the new product.

ApsaraDB - January 27, 2026
Alibaba Cloud Community - December 17, 2025
ApsaraDB - January 15, 2026
Alibaba Cloud Community - February 3, 2026
ApsaraDB - December 28, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - July 3, 2025
 ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server
ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server
An on-demand database hosting service for SQL Server with automated monitoring, backup and disaster recovery capabilities
Learn More AI Acceleration Solution
AI Acceleration Solution
Accelerate AI-driven business and AI model training and inference with Alibaba Cloud GPU technology
Learn More Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline SDKs for visual production, such as image segmentation, video segmentation, and character recognition, based on deep learning technologies developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Top-performance foundation models from Alibaba Cloud
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB