A cluster in a GDN must be of Enterprise Edition and meet the following requirements:
1. Go to the PolarDB cluster buy page. Link: https://polardb-buy.aliyun.com/cusBuy/Prepaid
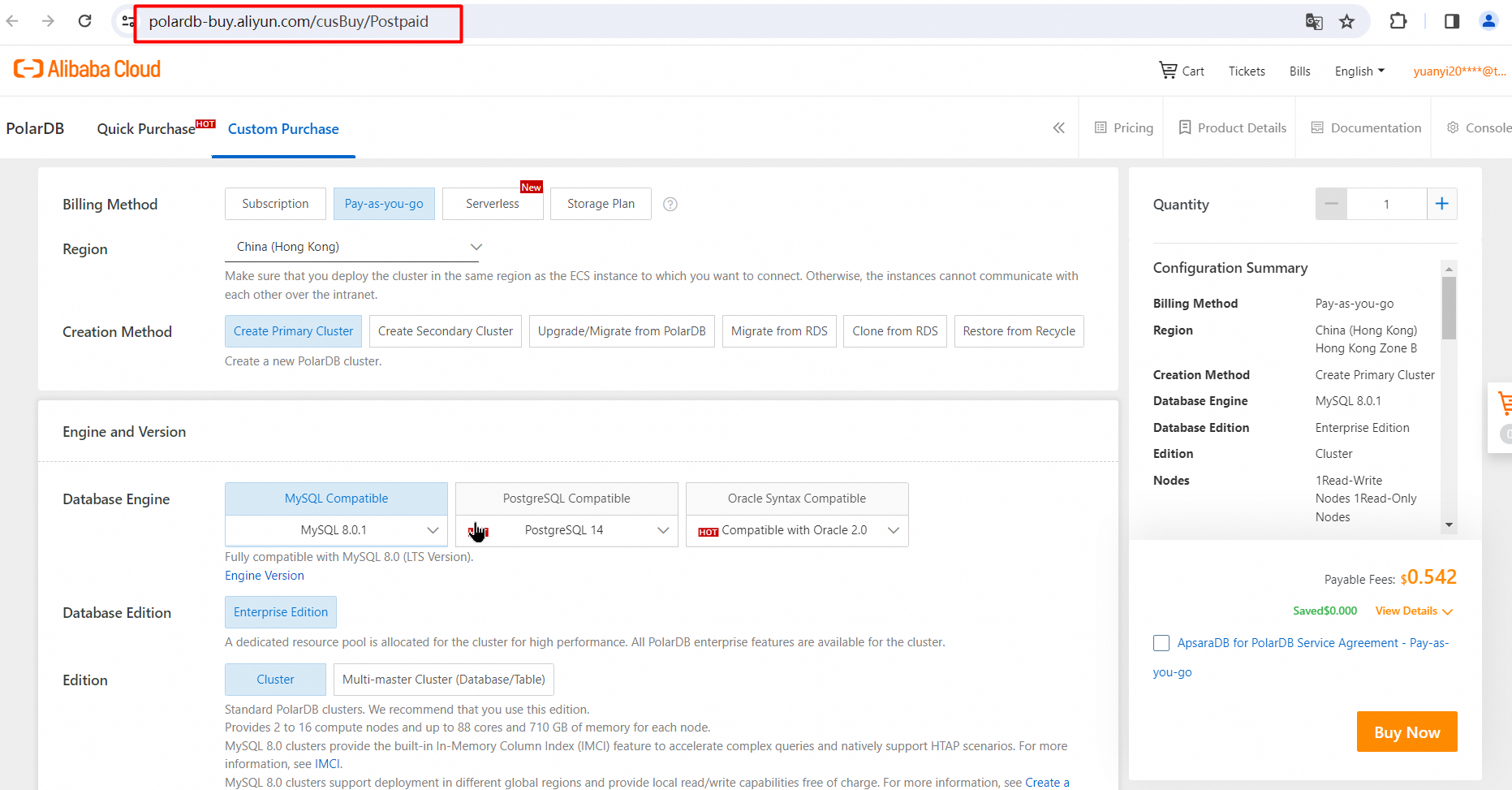
2. Set Billing method to Pay-as-you-go.
3. Select a Region from the drop-down list. Select a region that is closer in proximity to reduce network latency. After a cluster is created, you cannot change the region of the cluster.
4. Set Creation Method to Create Primary Cluster to create a new PolarDB cluster.
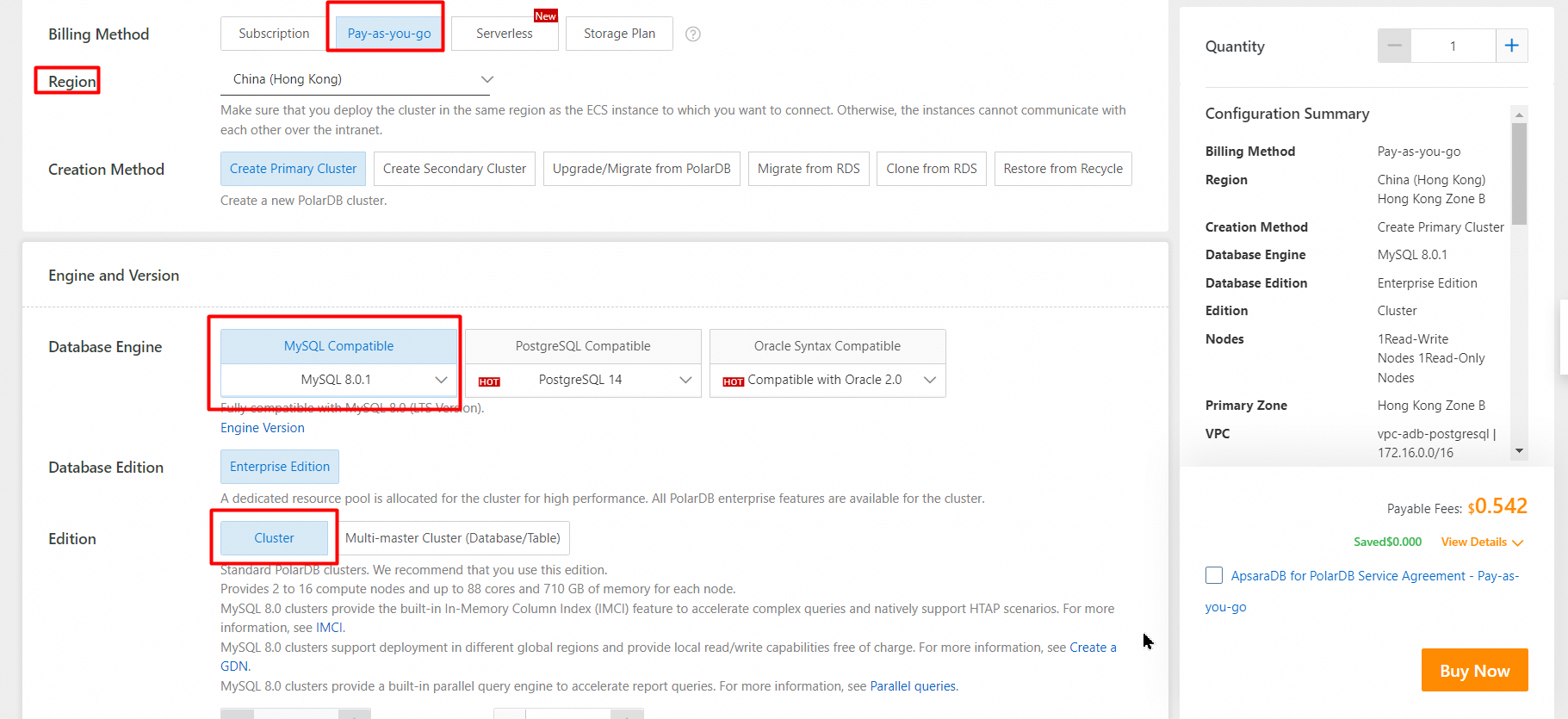
5. Select a Database Engine.
6. Set Database Edition to Enterprise Edition.
7. Select an Edition.
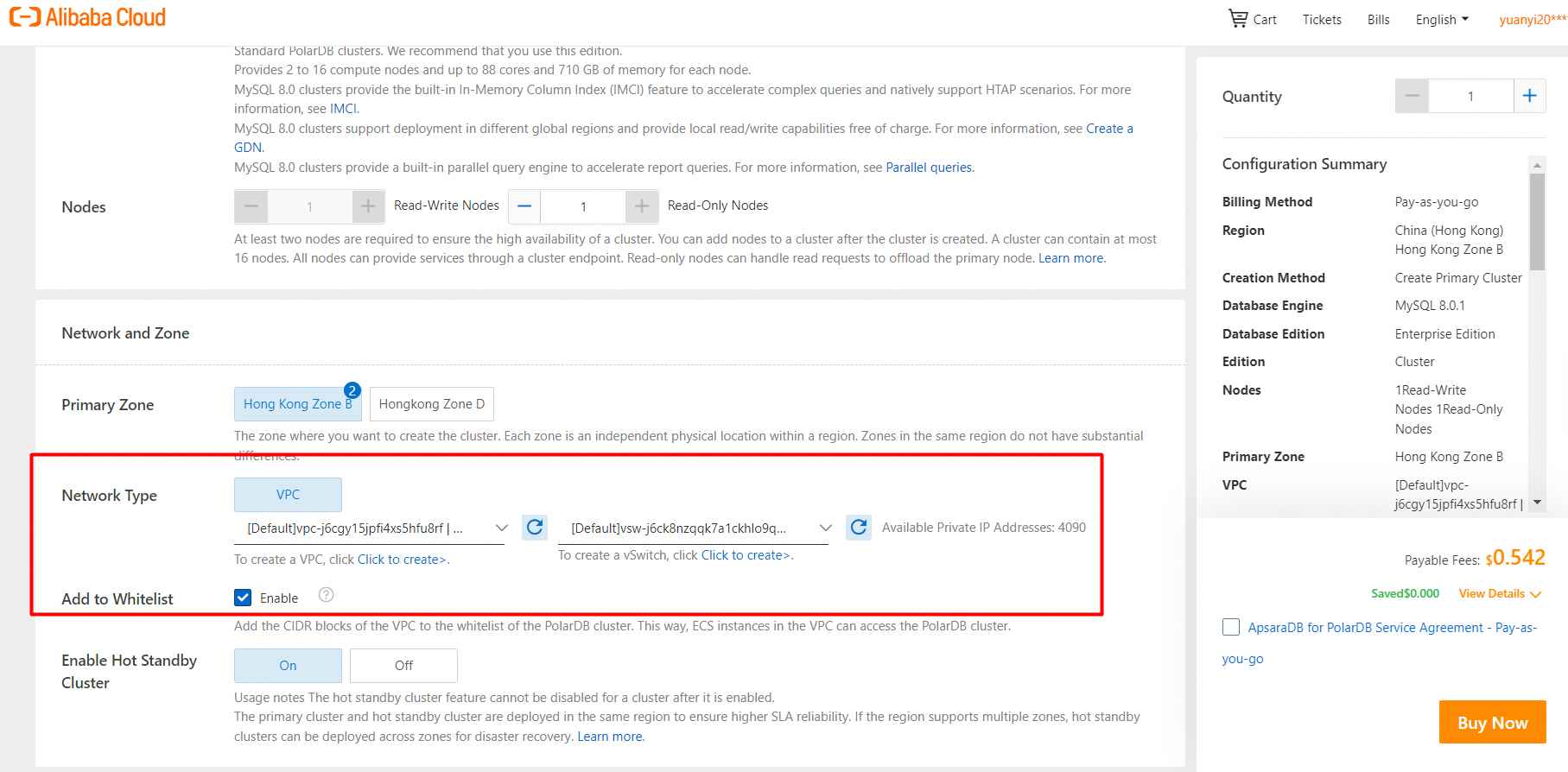
8. Configure the virtual private cloud (VPC) and vSwitch.
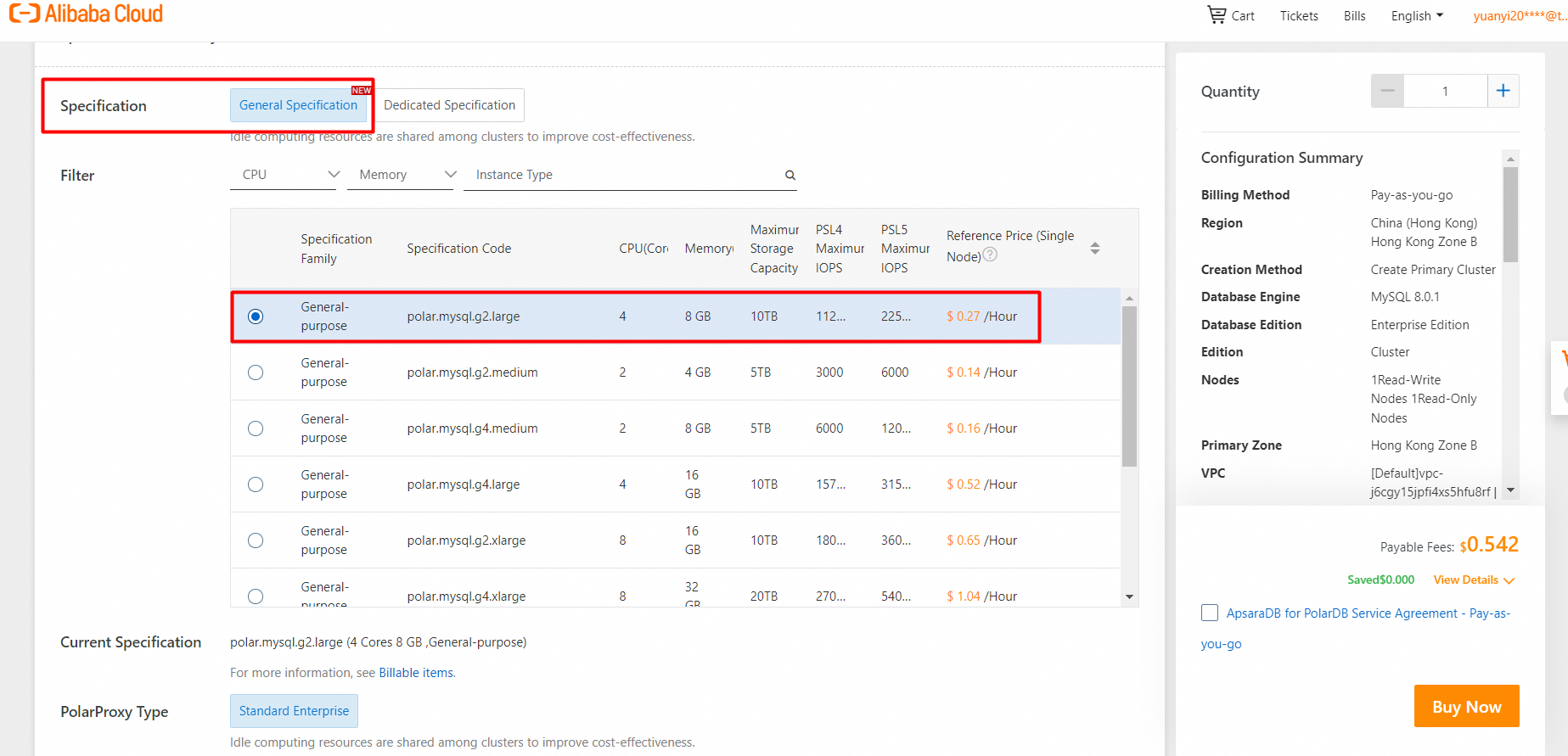
9. Select a Storage Engine.
10. Select specifications for the compute nodes.
11. On the Purchase page, confirm the order and the payment method, and click Purchase.
After you complete the payment, wait 10 to 15 minutes. Then, you can view the new cluster on the Clusters page.
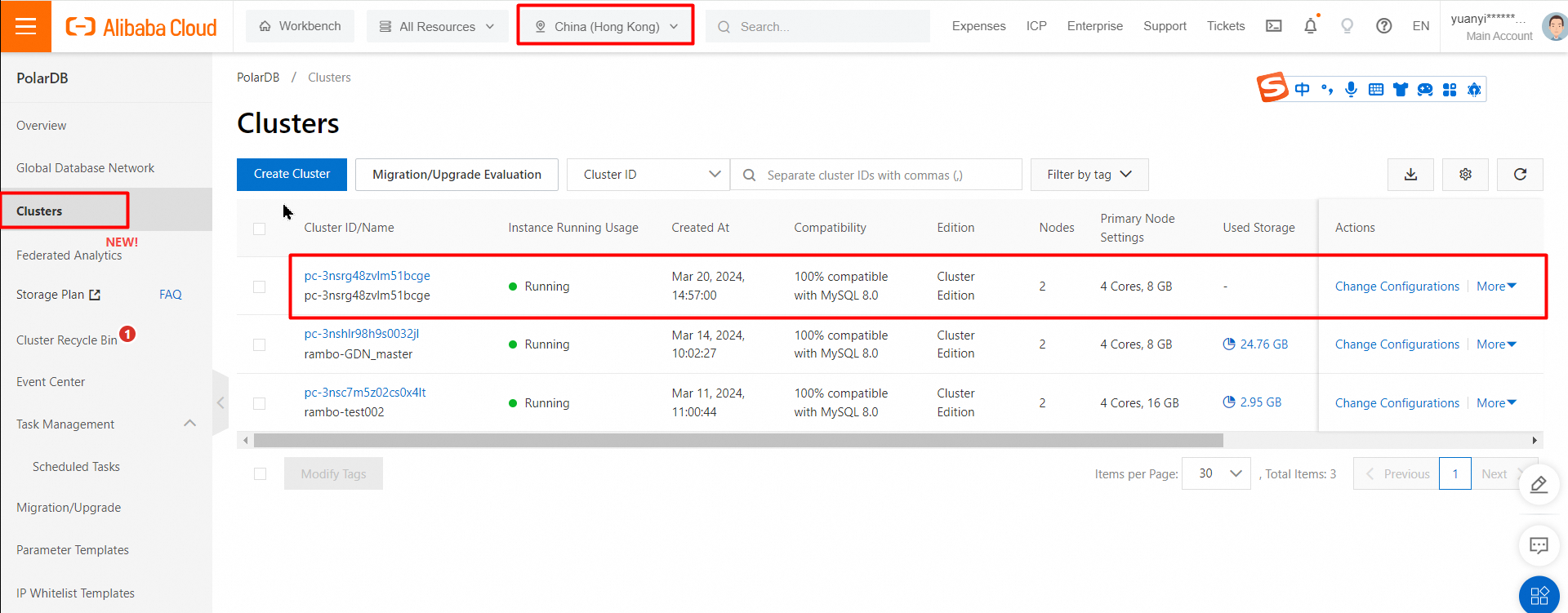
A primary PolarDB cluster is created.
You are not charged for the traffic that is generated during cross-region data transmission within a GDN. You are charged only for the use of PolarDB clusters in the GDN. For more information about the pricing rules of PolarDB clusters, see Billable items overview.
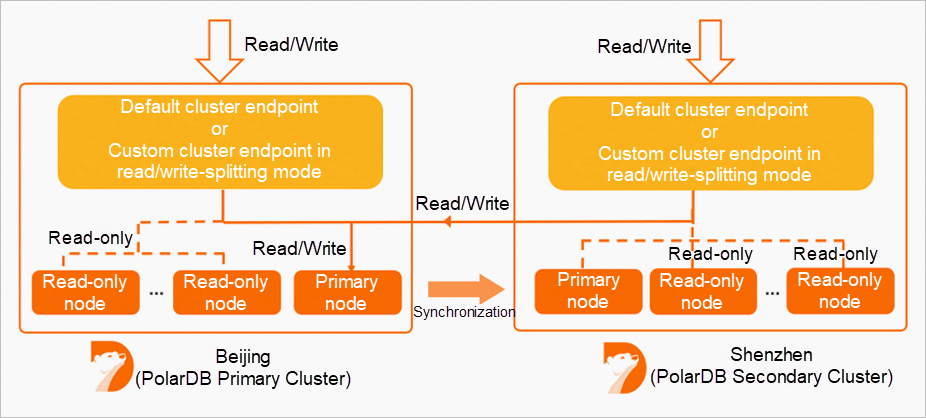
Global Database Network (GDN)
1. Log on to the PolarDB console.
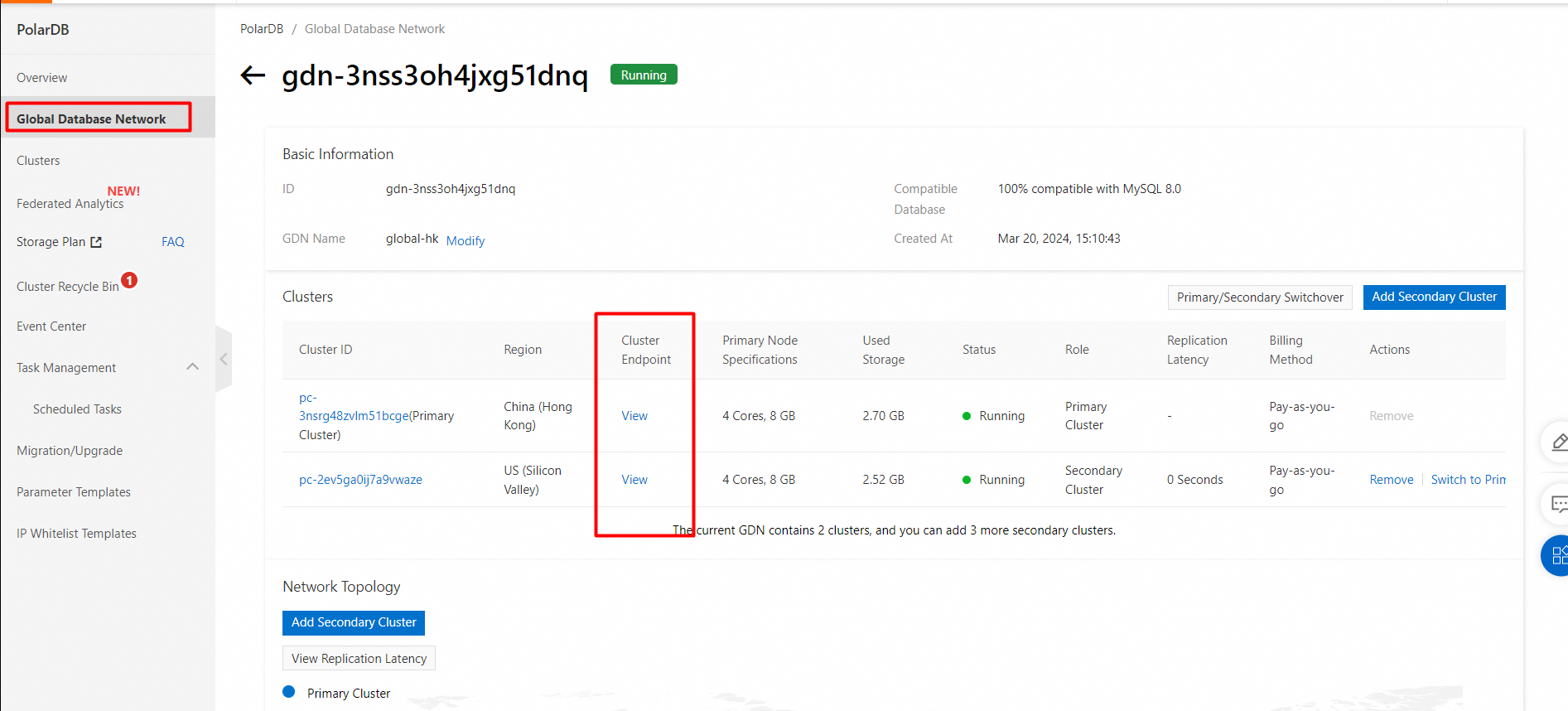
2. In the left-side navigation pane, click Global Database Network.
3. On the Global Database Network (GDN) page, click Create GDN.
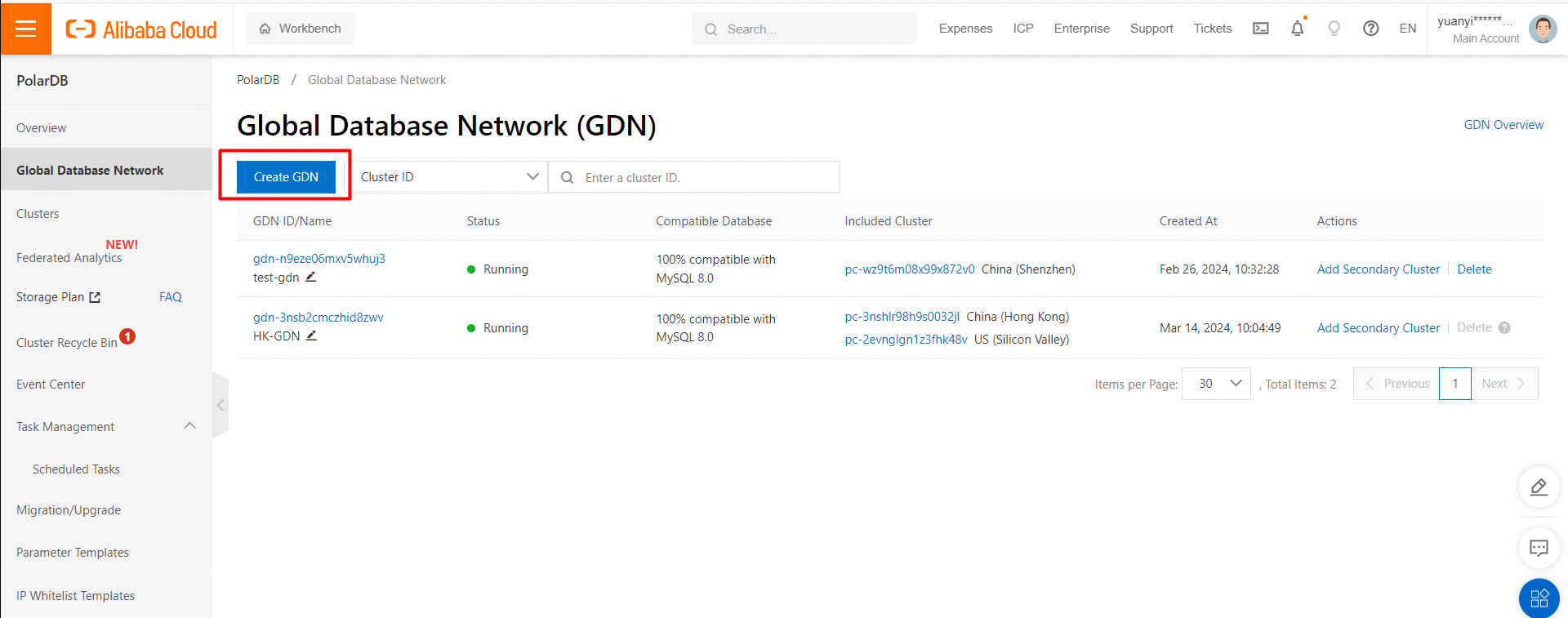
4. In the Create GDN dialog box, configure the following parameters.
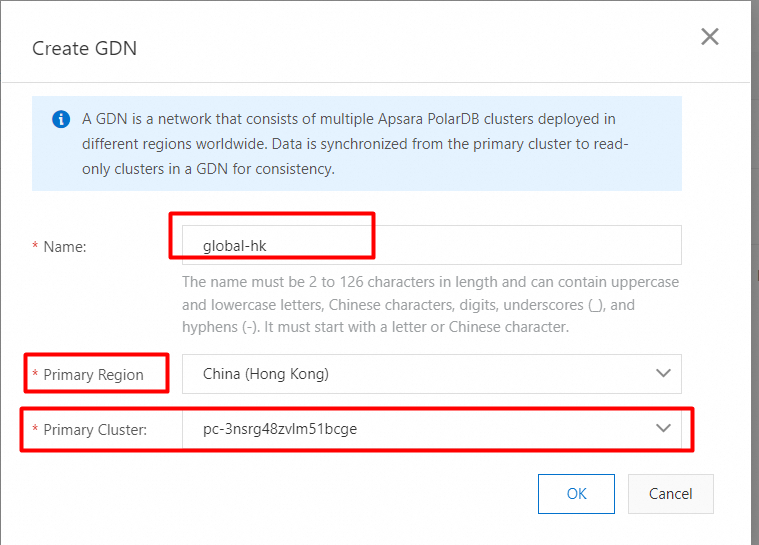
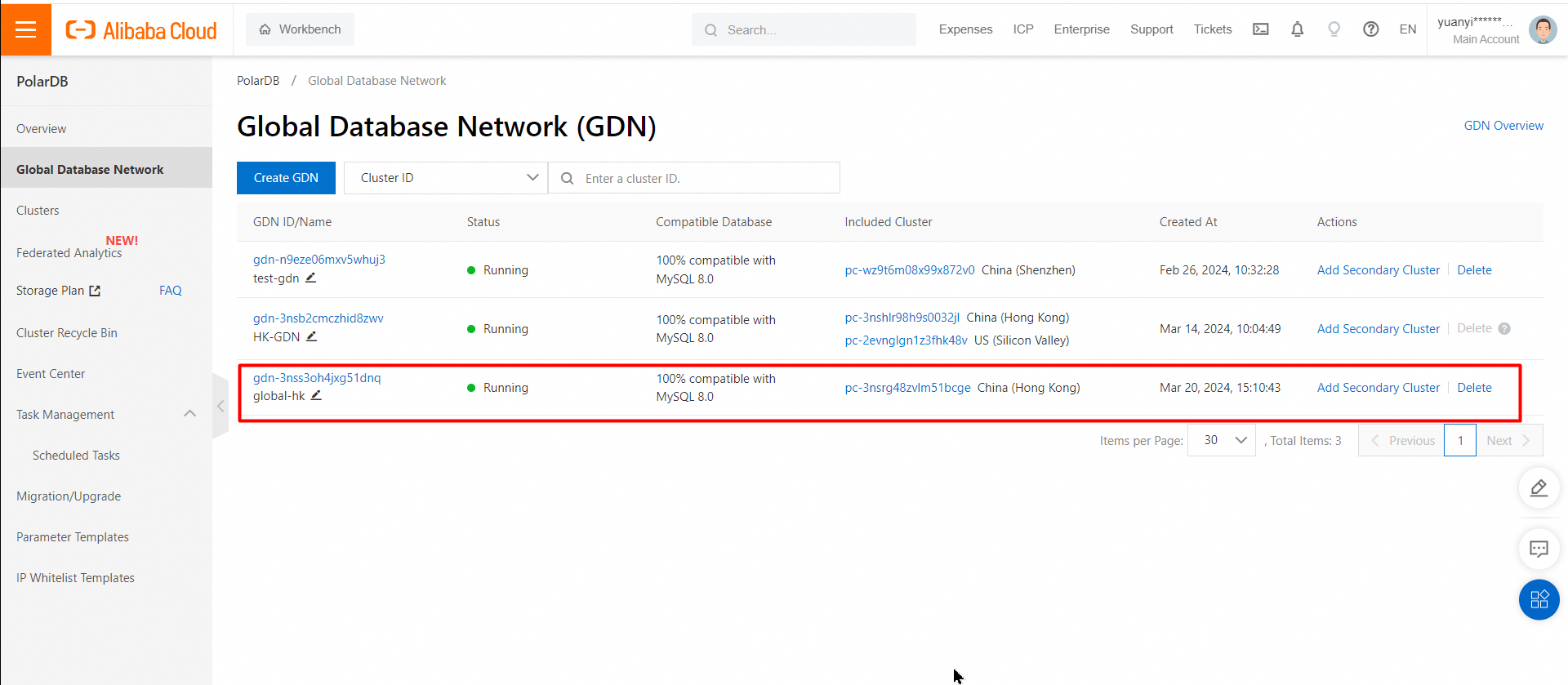
5. Click OK.
6. View the created GDN.
• The primary cluster and secondary clusters must have the same database engine version, which can be MySQL 8.0, MySQL 5.7, or MySQL 5.6.
• You can only create secondary clusters. You cannot specify existing clusters as secondary clusters.
• A GDN uses the physical replication mechanism. Therefore, you do not need to enable binary logging for clusters in a GDN. If you enable binary logging for clusters in a GDN, make sure that the loose_polar_log_bin parameter is set to the same value for the primary and secondary clusters. Otherwise, binary log inconsistency may occur in the event of a primary/secondary cluster switchover.
1. Find the GDN in which you want to add a secondary cluster and click Add Secondary Cluster in the Actions.
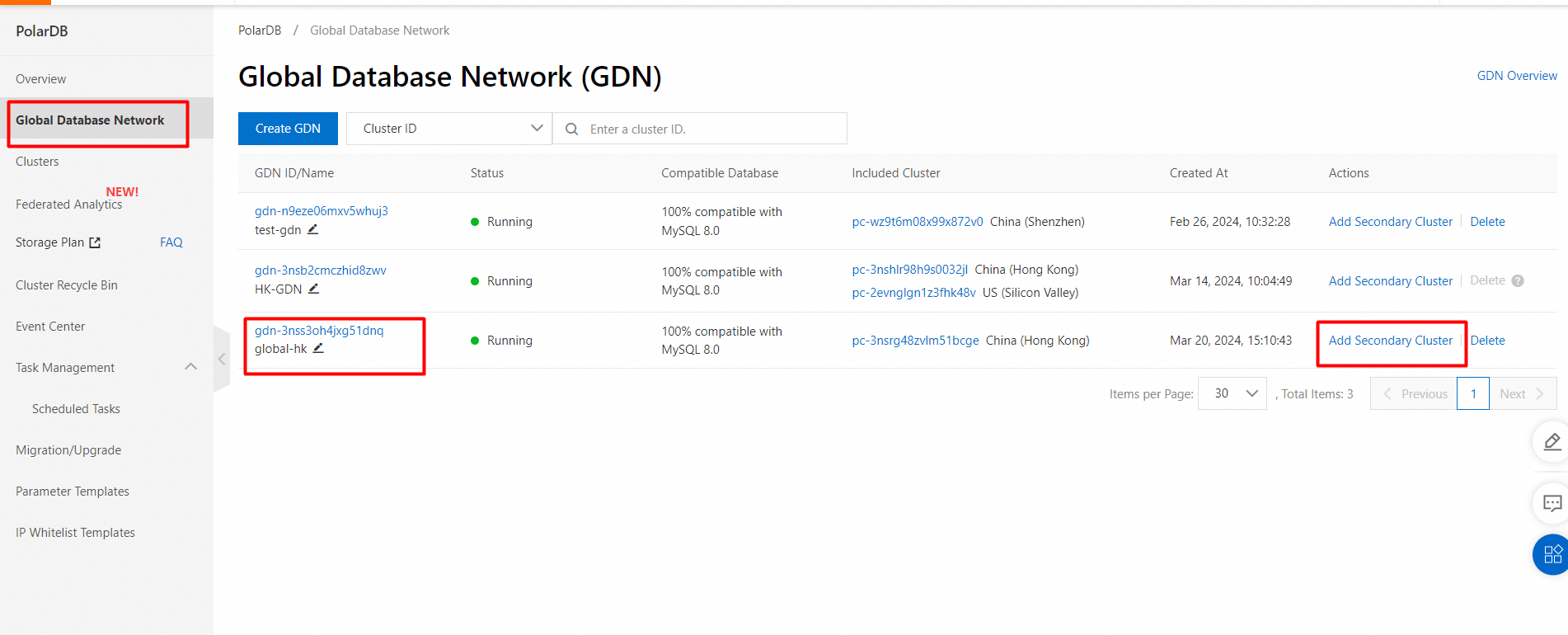
2. On the purchase page, select Subscription or Pay-as-you-go.
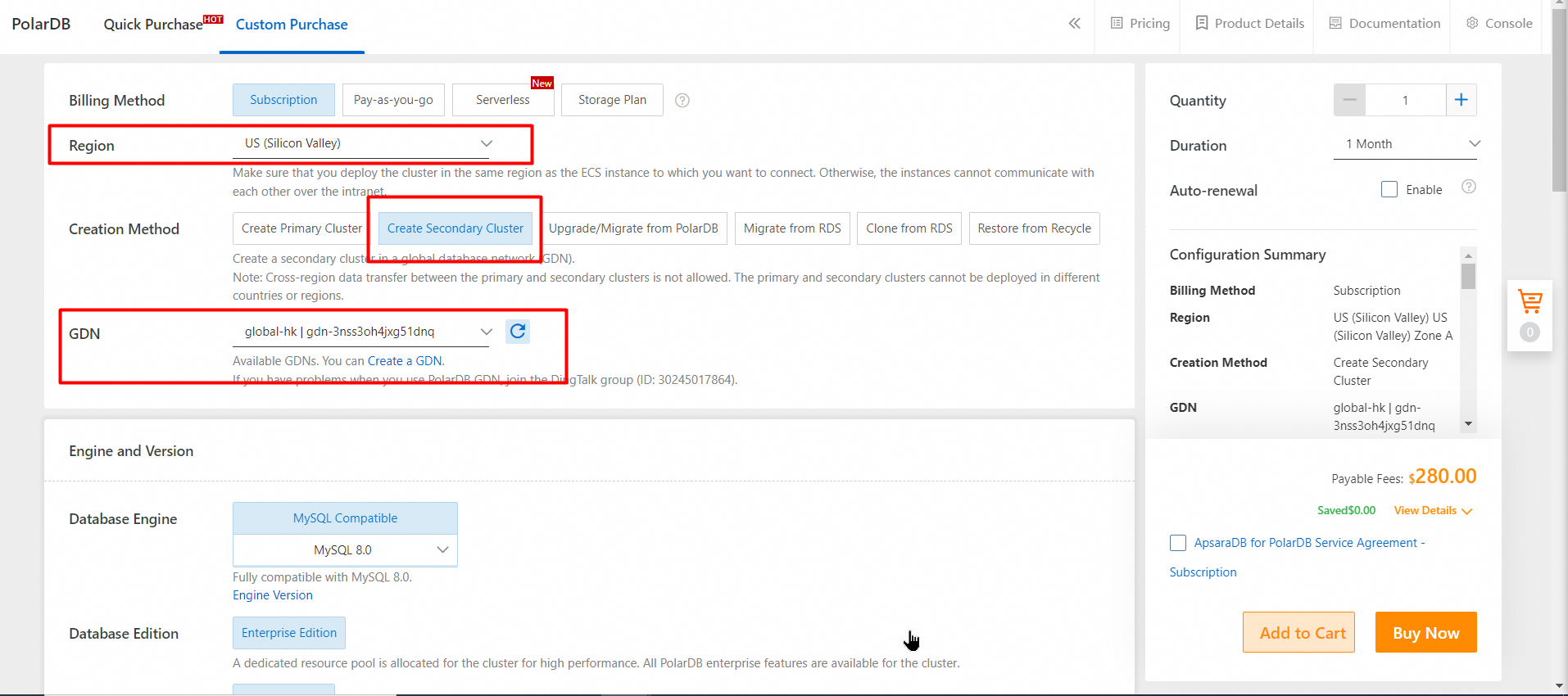
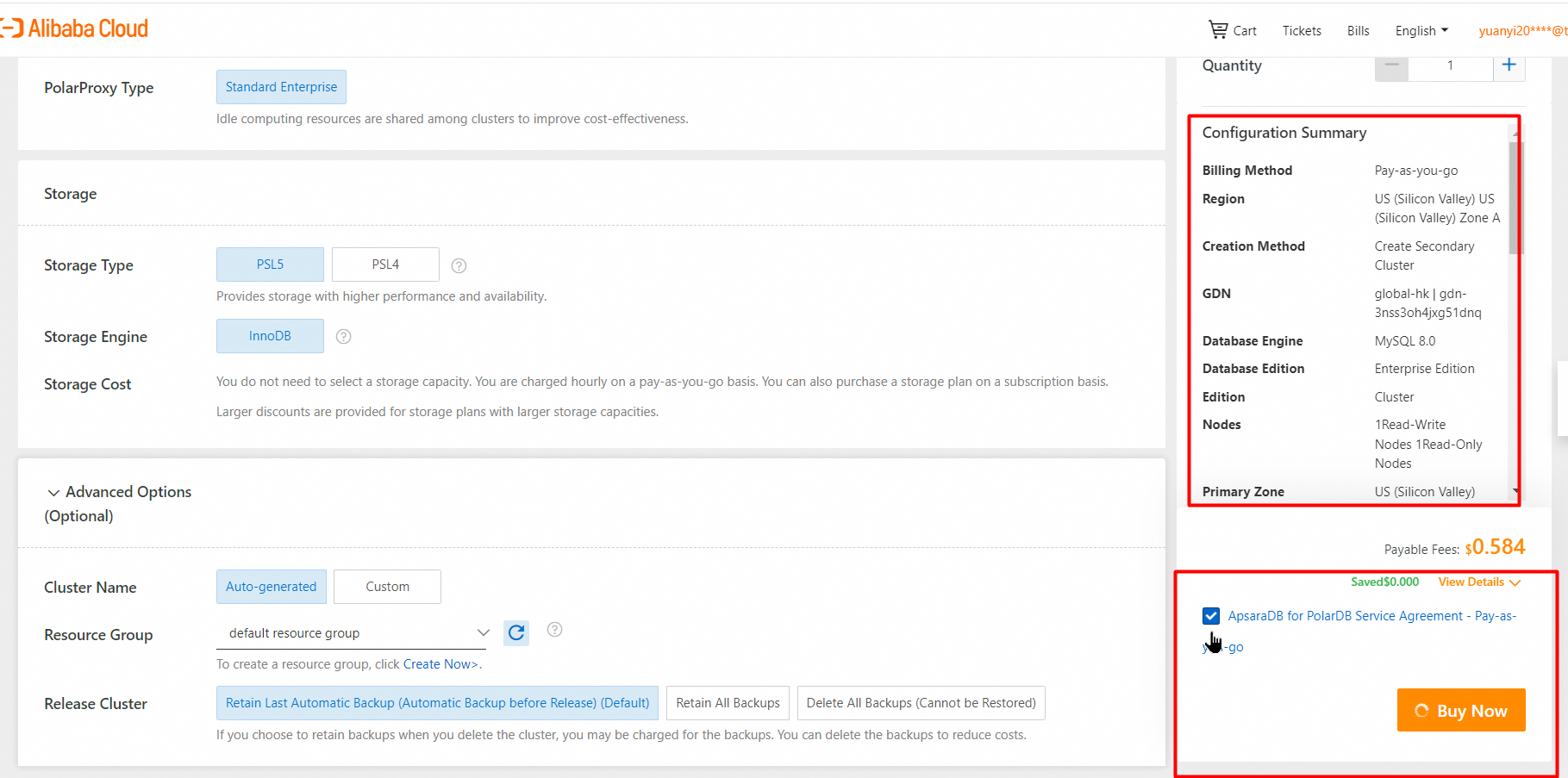
3. Click Next: Confirm Order.
4. On the Purchase page, confirm the order and the payment method, and click Purchase.
5. View the added secondary cluster.
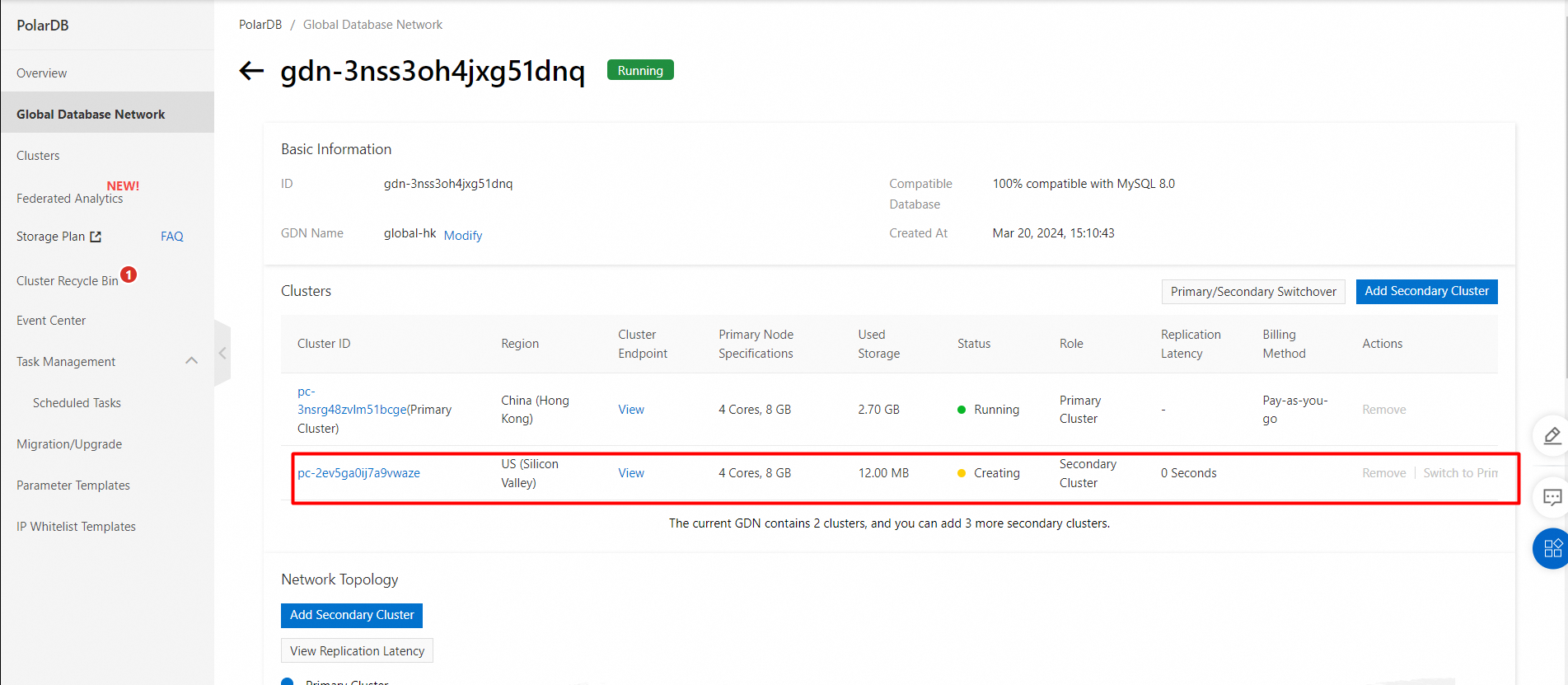
If specific nodes in the cluster are in the Creating state, the cluster is still being created and is unavailable. The cluster is only available when the cluster is in the Running state.
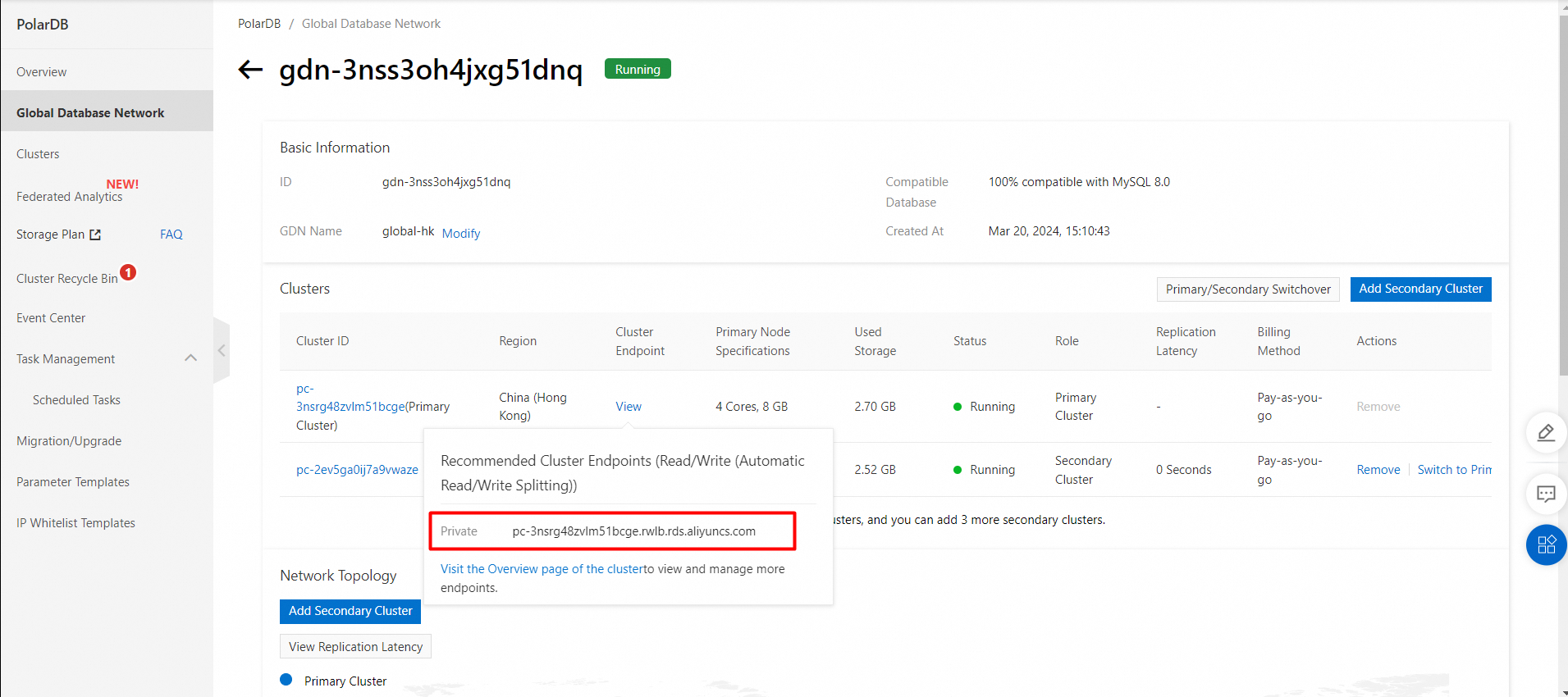
A GDN does not have a unified endpoint. However, each cluster in the GDN, including the primary cluster and secondary clusters, has an individual cluster endpoint. You can use the endpoint of the cluster that is deployed in the nearest region to your application to connect to the GDN. Data is synchronized from the primary cluster to all secondary clusters in a GDN. In most cases, read requests are forwarded to the secondary cluster in the same region, and write requests are forwarded to the primary cluster.
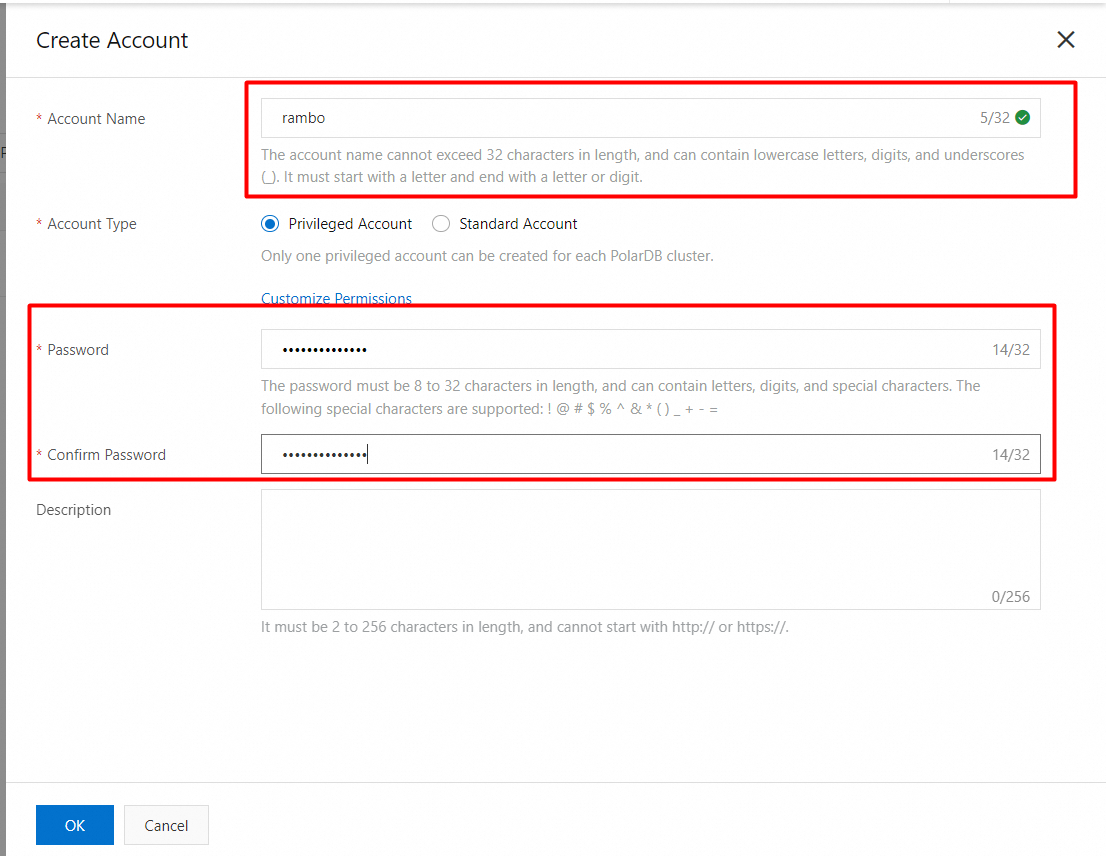
Create a privileged account
1. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Settings and Management > Accounts.
2. On the Accounts page, click Create Account.
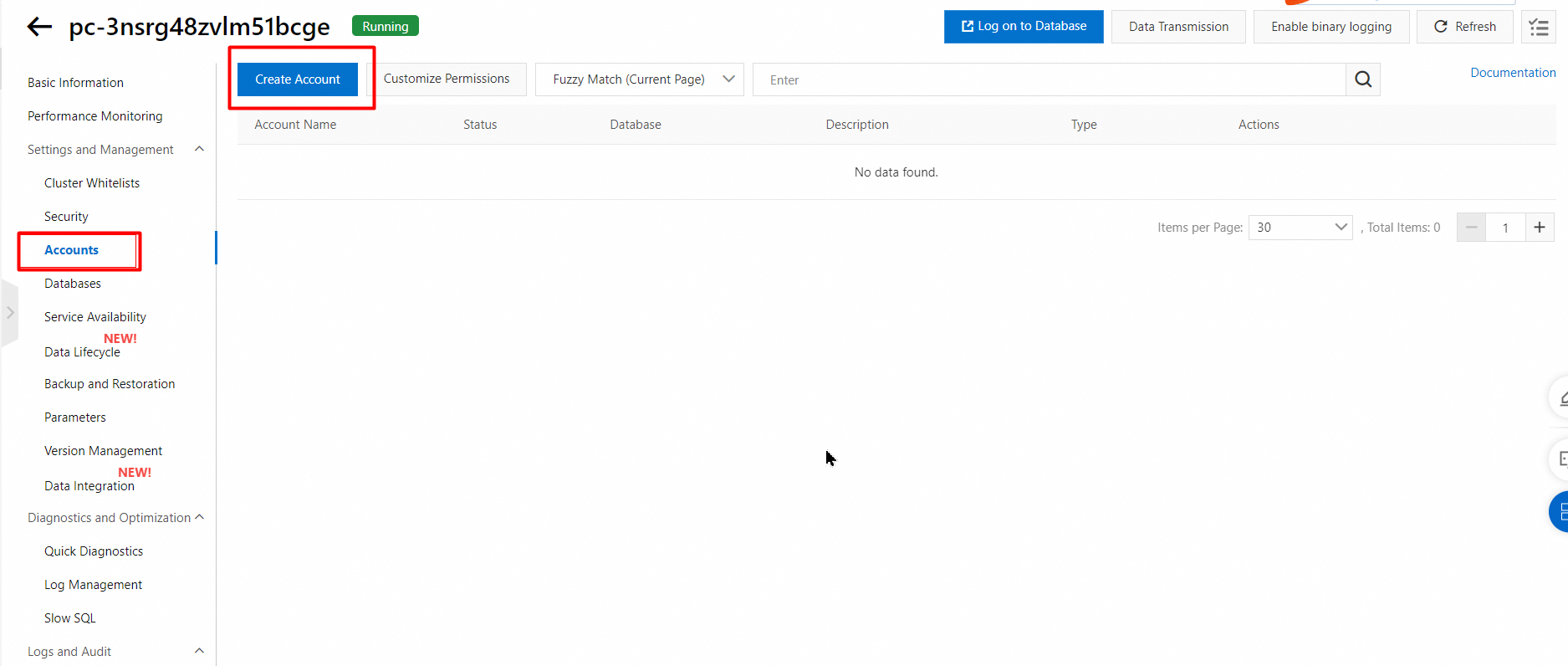
3. In the Create Account panel, configure the following parameters.
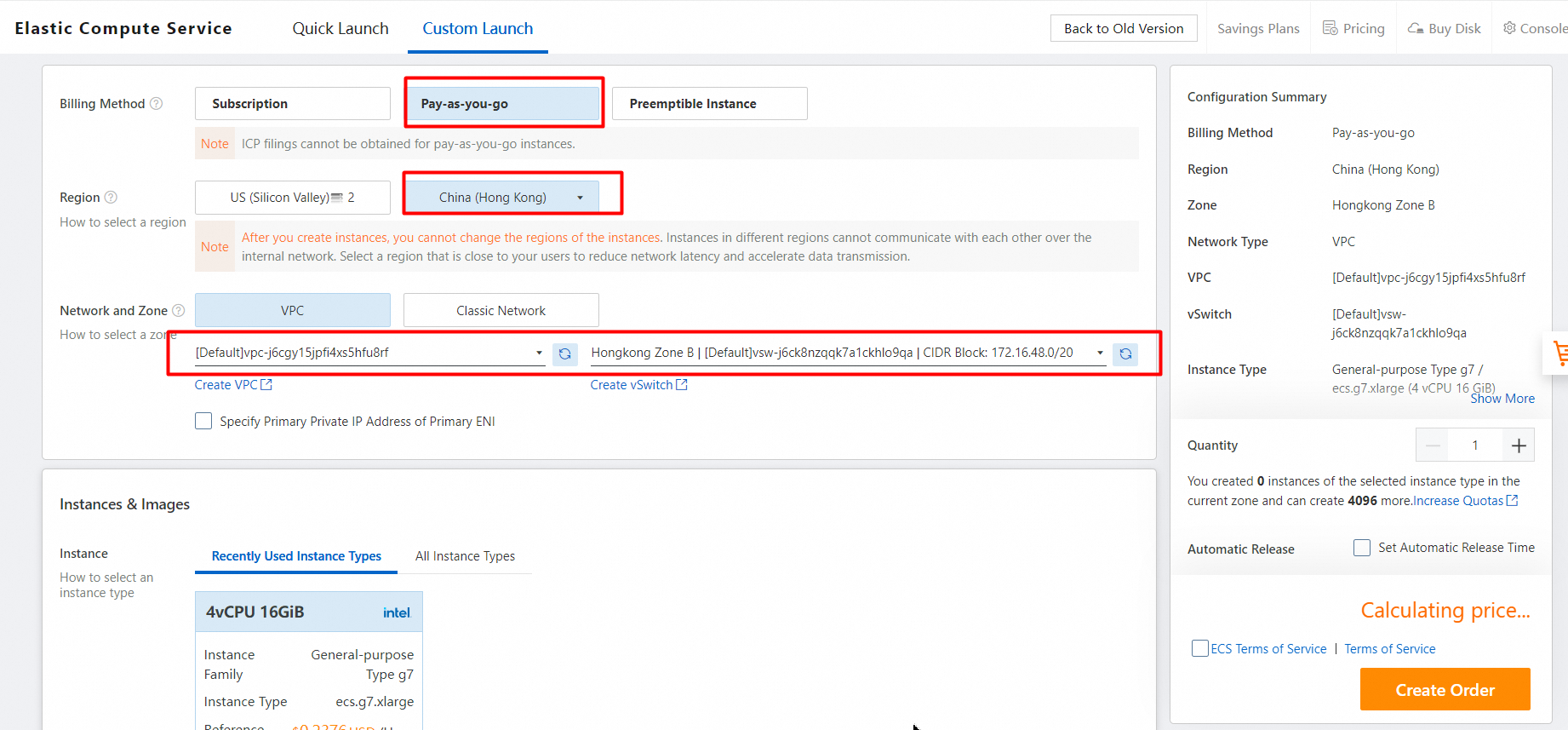
1. Click the Custom Launch tab. Link: https://ecs-buy.aliyun.com/wizard/?spm=a2c63.p38356.0.0.2c7ebdbaoiiMGL#/
2. Select a region that is closer in proximity to reduce network latency.
3. To test the GDN primary cluster, select a vSwitch in the same VPC as the primary cluster.
In this test, the specifications of all ECS instances purchased are:
CPU and memory: 2 vCPUs and 4 GiB of memory
Operating system: CentOS 7.9 64-bit
Instance type: ecs.c7.large that has 2 vCPUs and 4 GiB of memory.
Connect to an ECS instance over a public IPv4
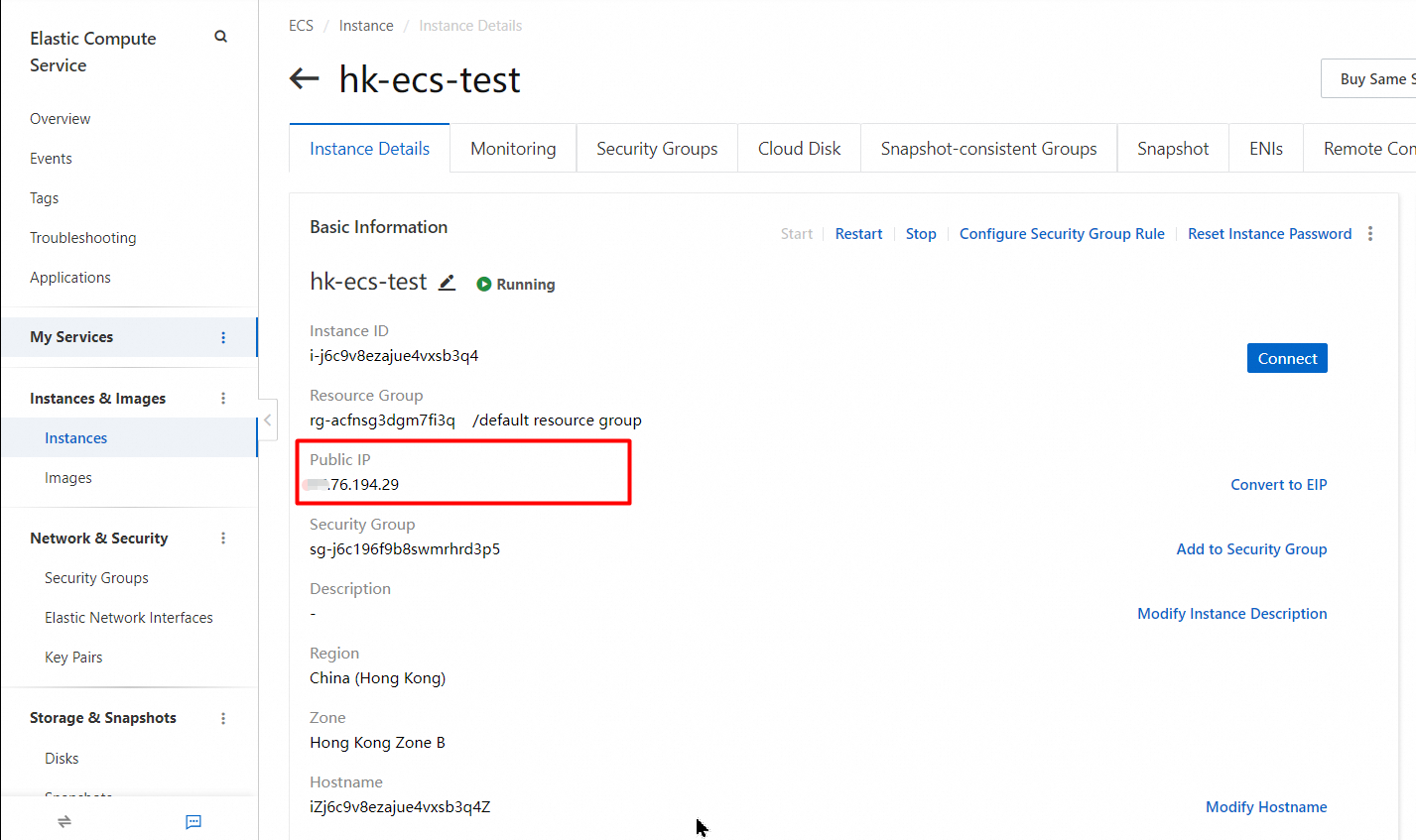
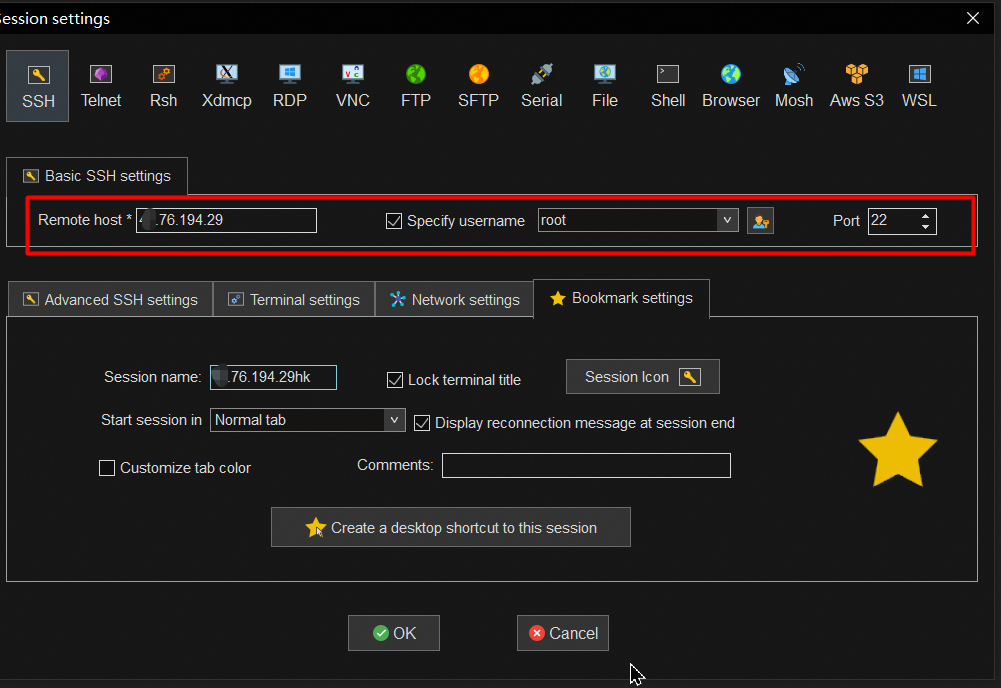
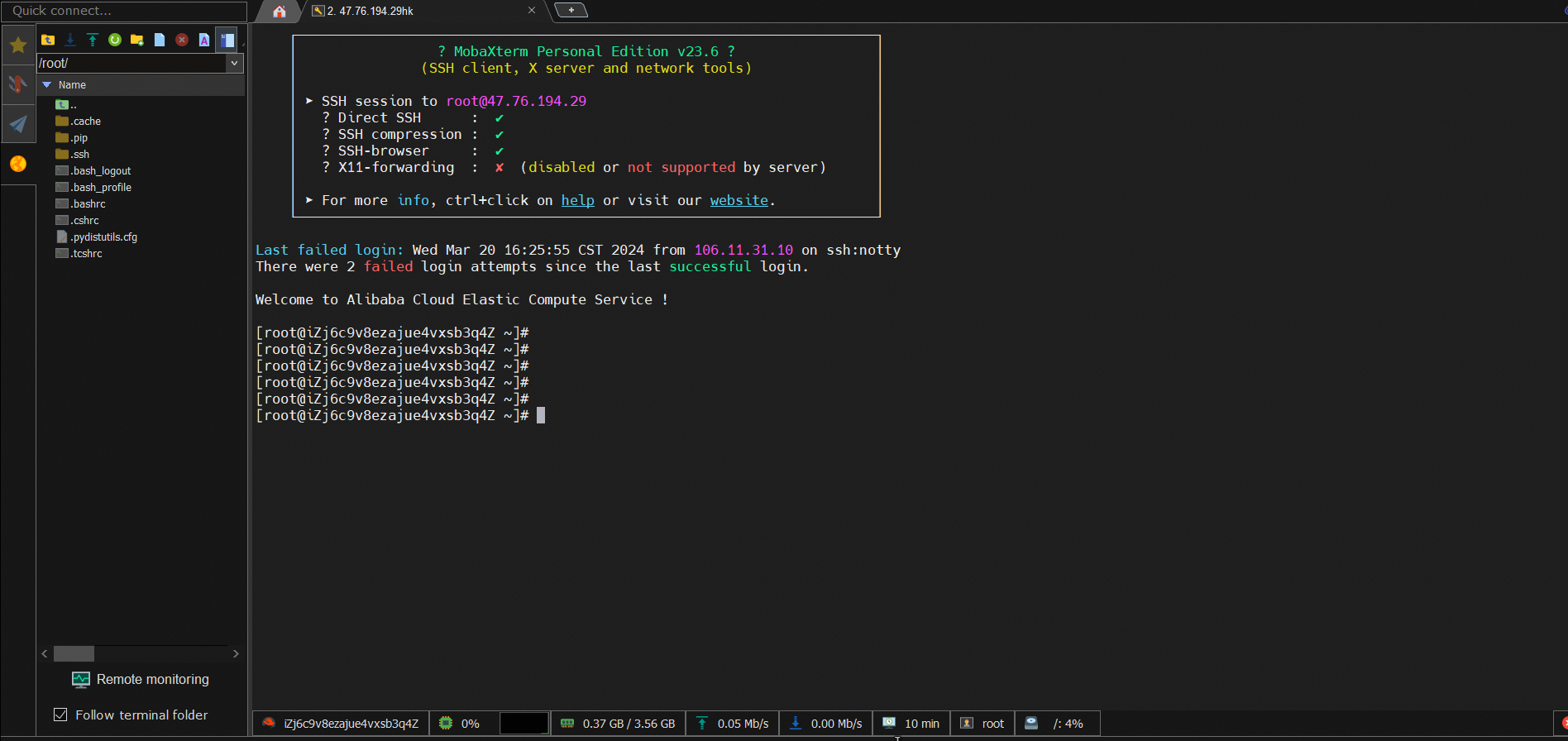
Use an ECS instance to connect to the primary cluster in a GDN by using a private network in the same VPC
1. Download the MySQL client connection tool.
yum install gcc gcc-c++ autoconf automake make libtool bzr mysql-devel git mysql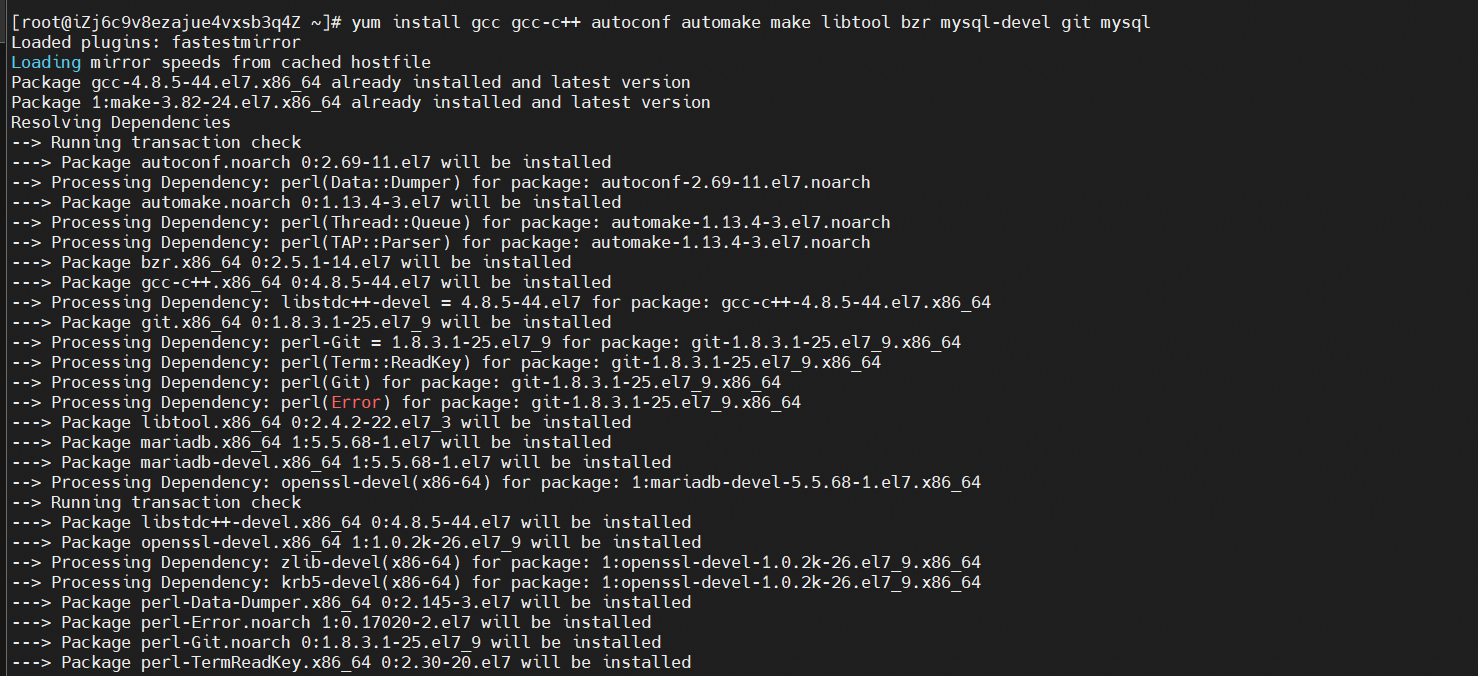
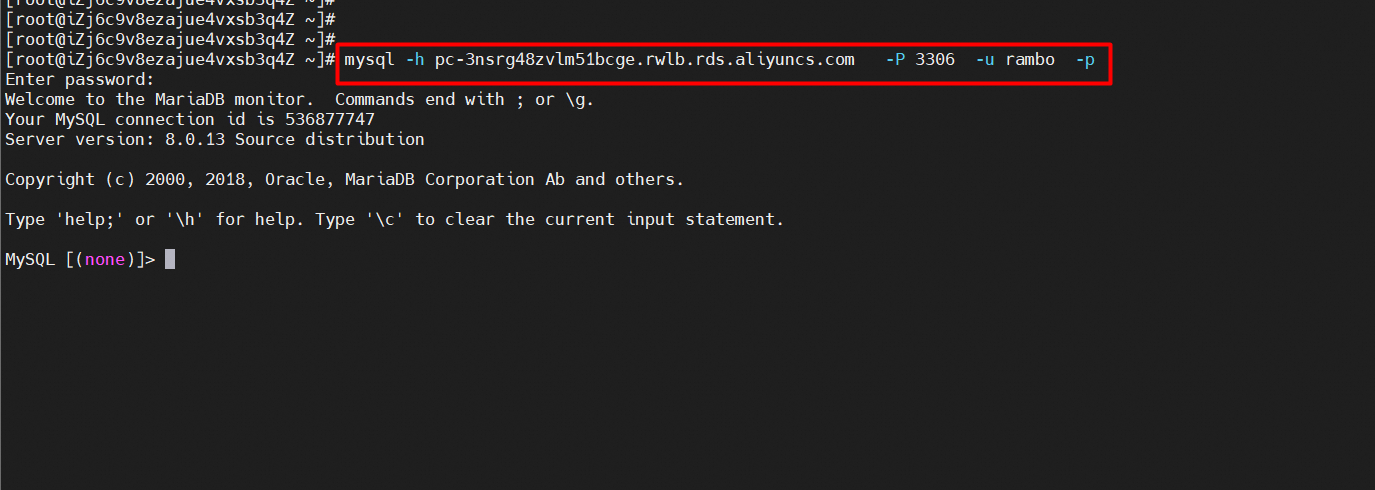
2. Connect to the primary cluster command.
mysql -h<Endpoint> -P<Port> -u<Username> -p<Password>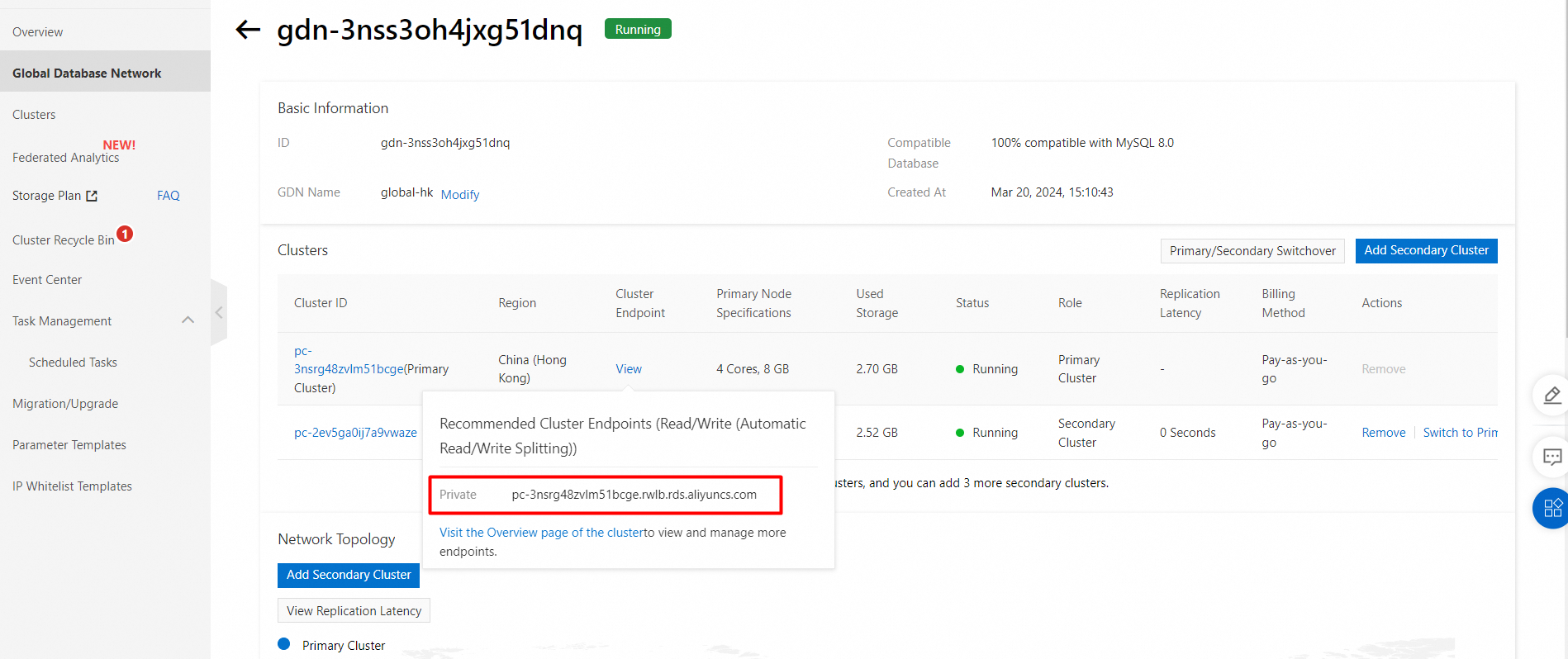
Use an ECS instance to connect to the primary cluster in a GDN via the public endpoint
Apply for a public cluster endpoint or a primary endpoint
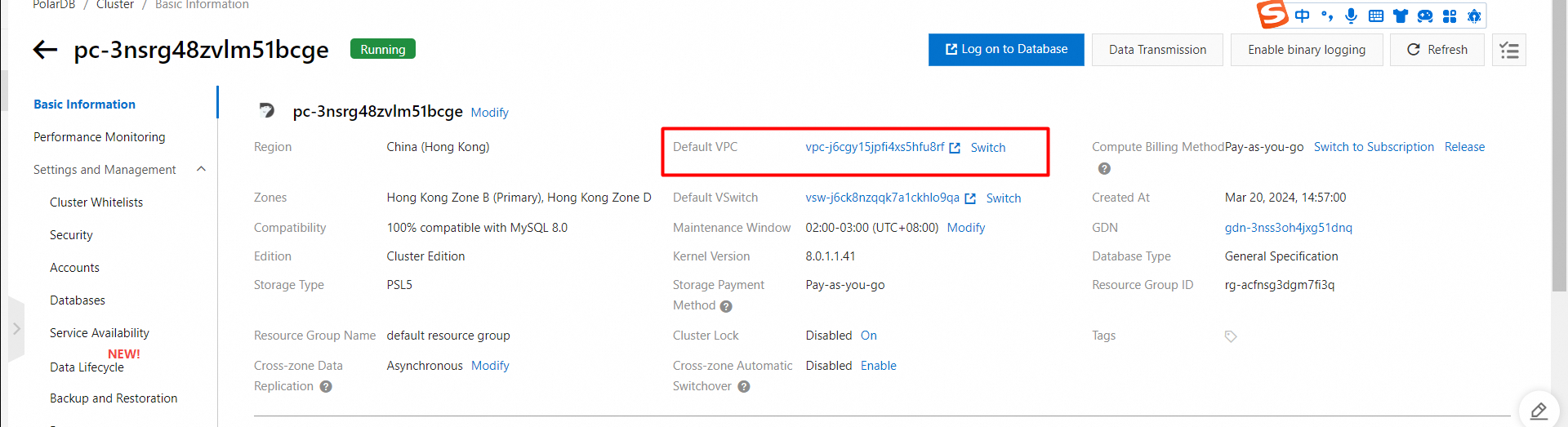
1. Find the target cluster and click the cluster ID.
2. In the Database Connections section of the Basic Information page, find the endpoint and click Apply to the right of the Public parameter.
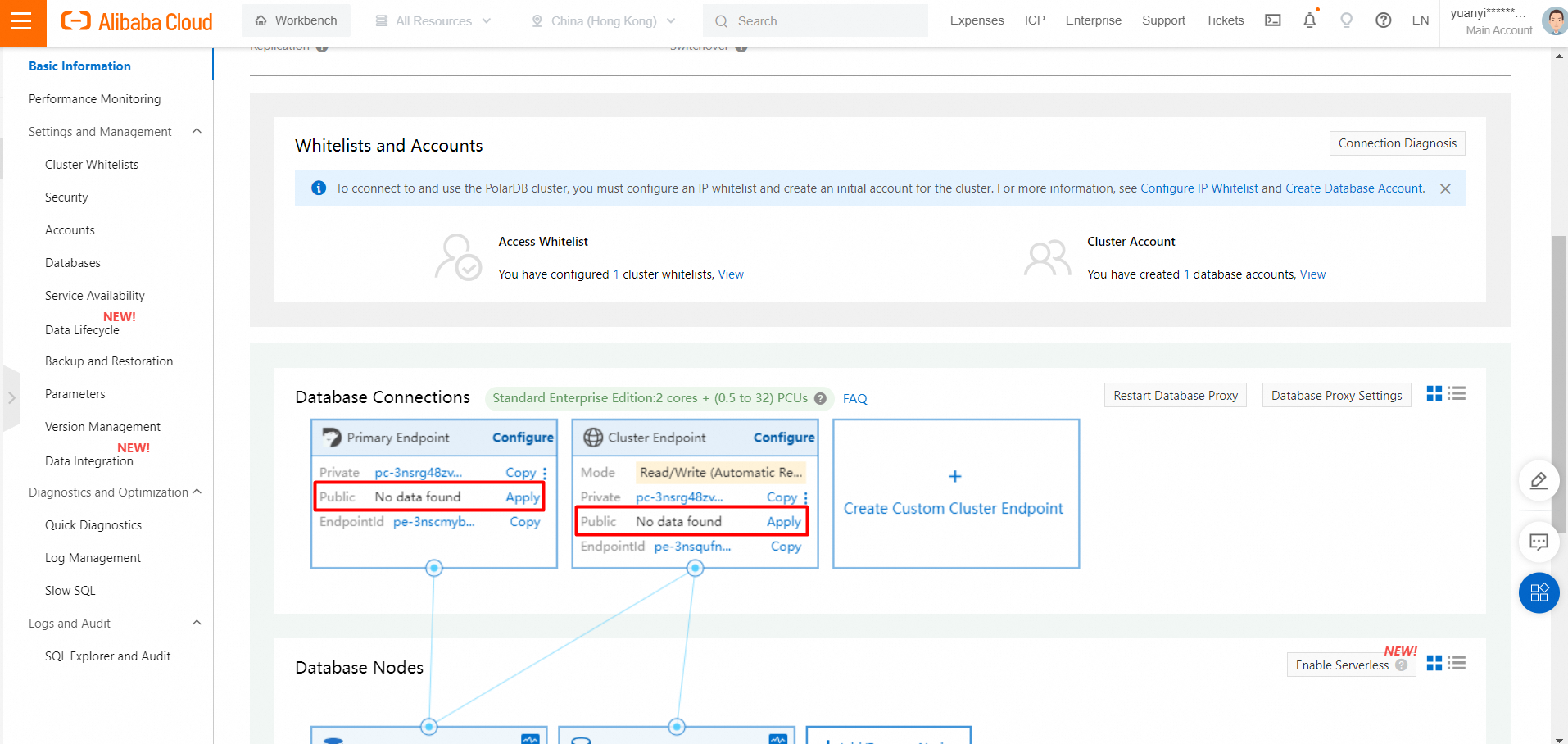
3. In the dialog box that appears, specify a prefix for the required endpoint and click OK.
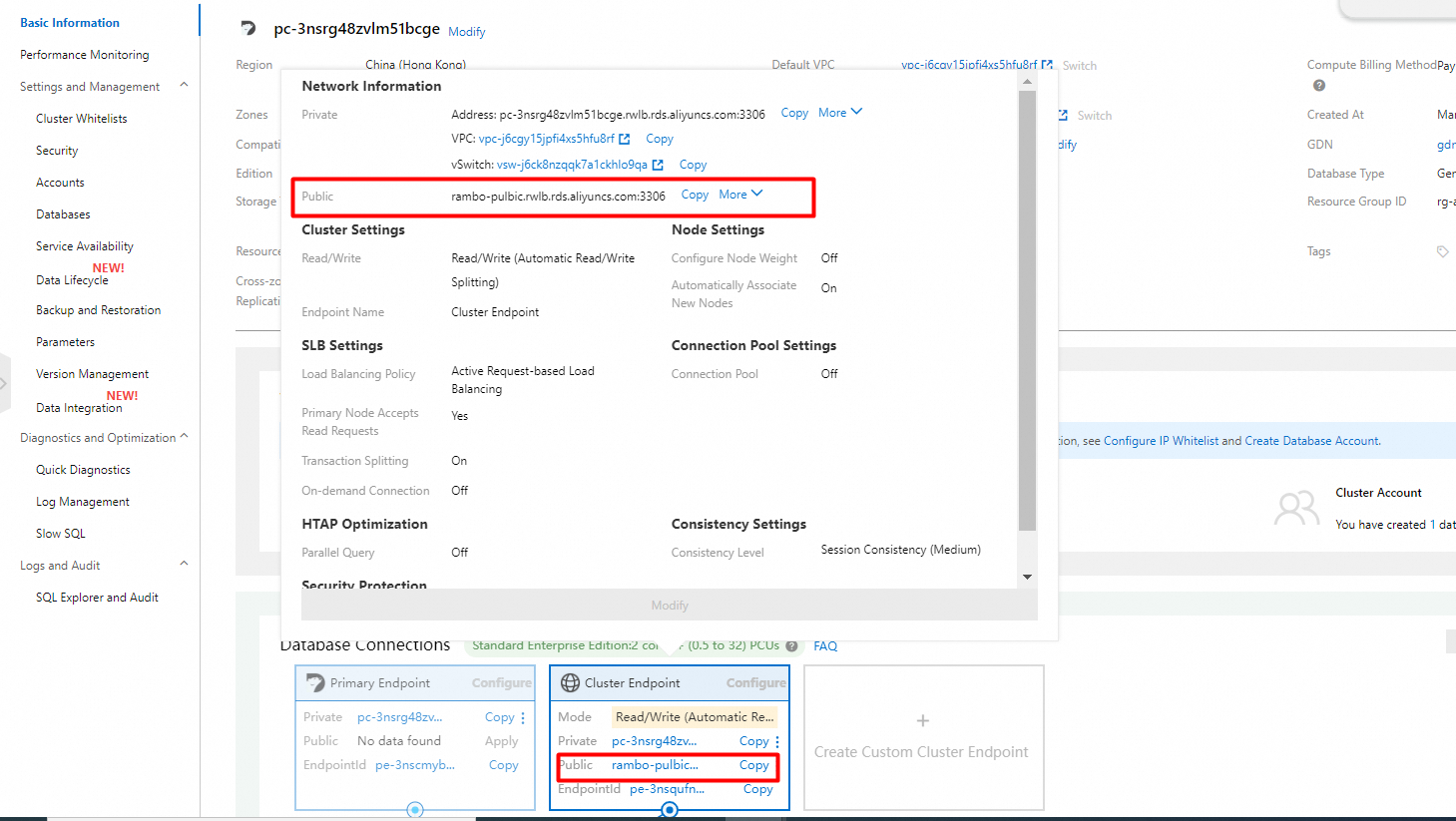
Enable public endpoint access whitelist
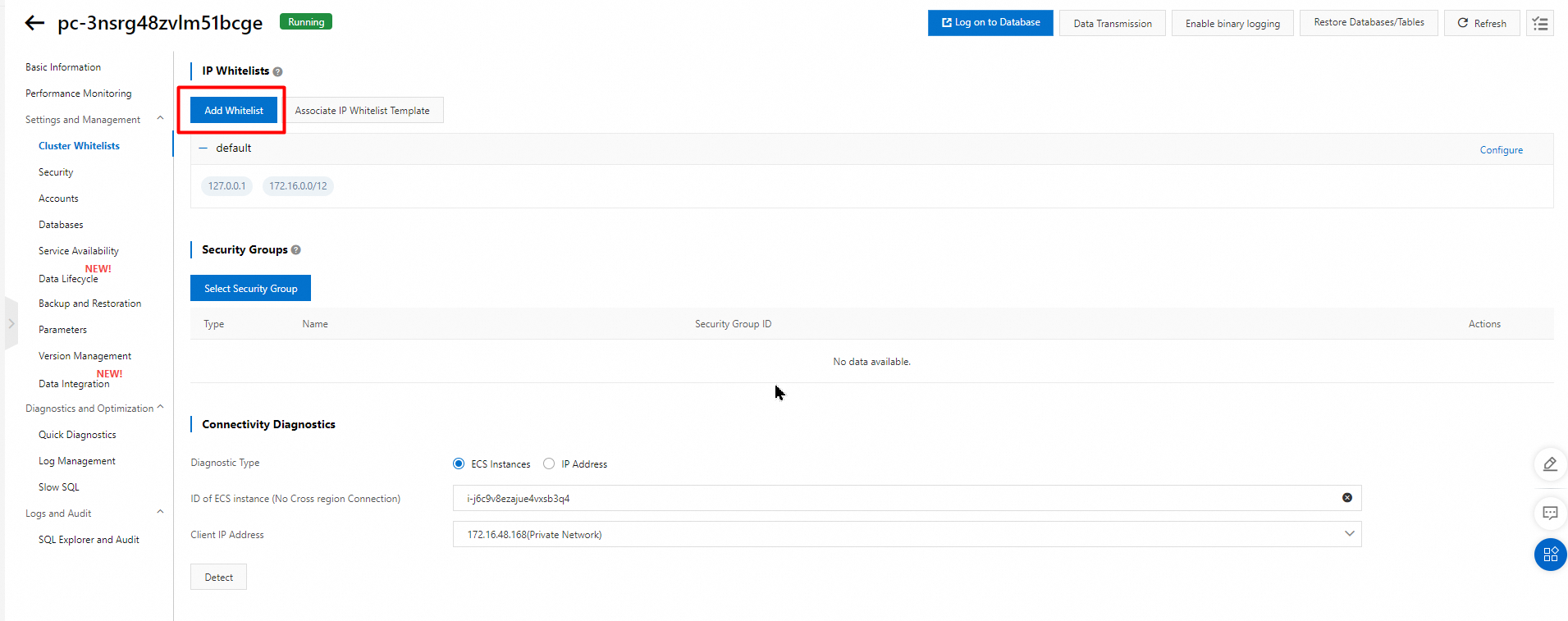
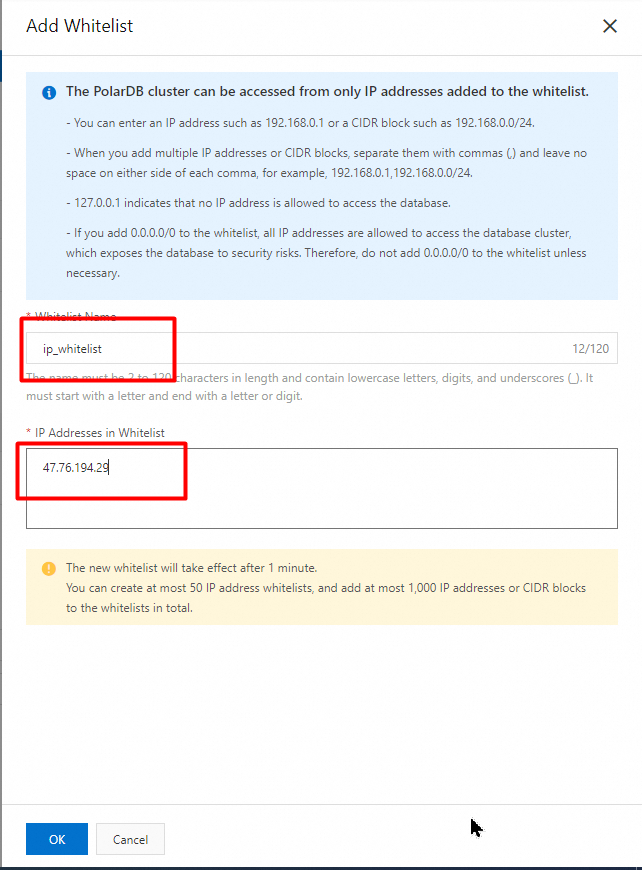
Configure an IP address whitelist
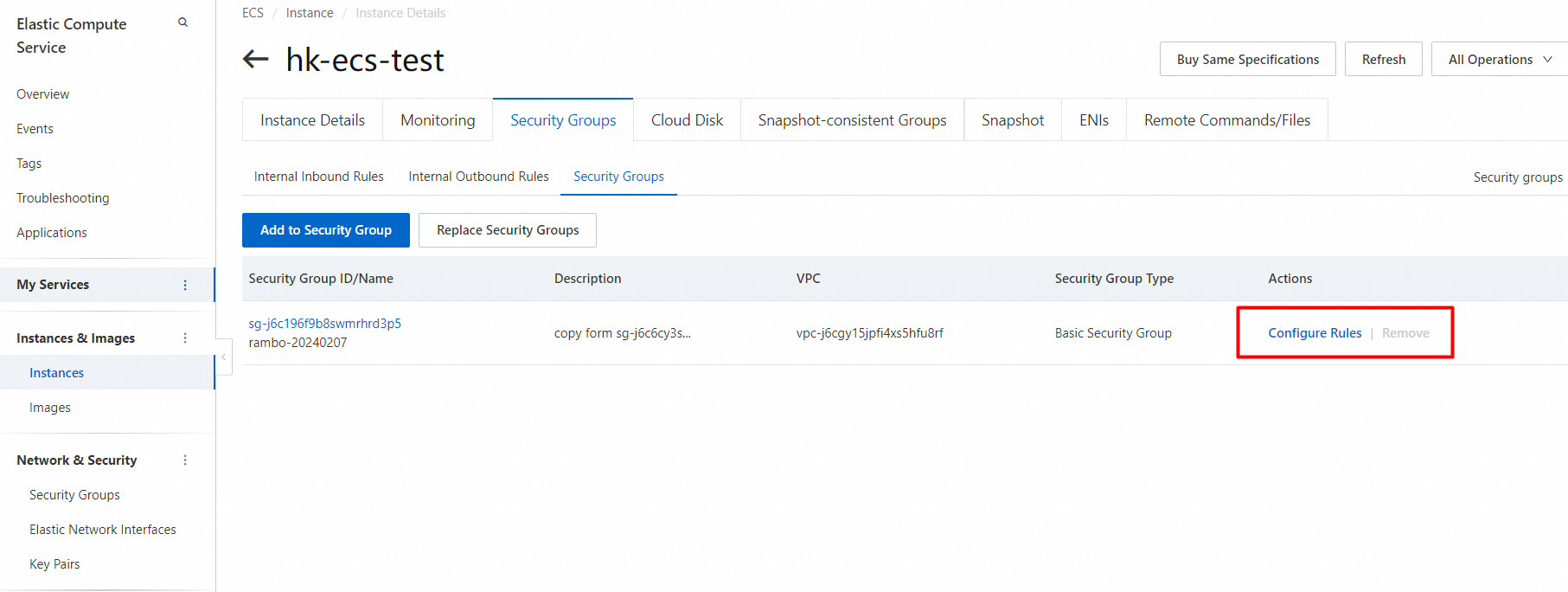
After you create a cluster, you must configure an IP whitelist. Only IP addresses in the IP whitelists or Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances in the security groups of the cluster can access the cluster.
You can configure both IP whitelists and security groups. Both IP addresses in whitelists and ECS instances in security groups are allowed to access the PolarDB cluster.
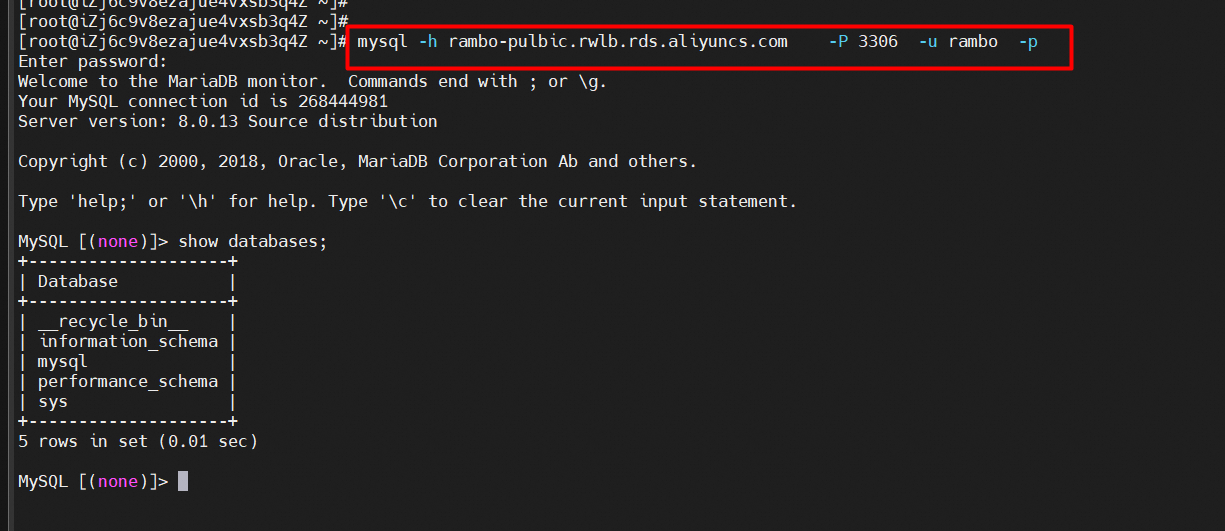
Connect to the primary cluster public endpoint on the ECS instance
1. Connect to primary cluster commands.
mysql -h<Endpoint> -P<Port> -u<Username> -p<Password>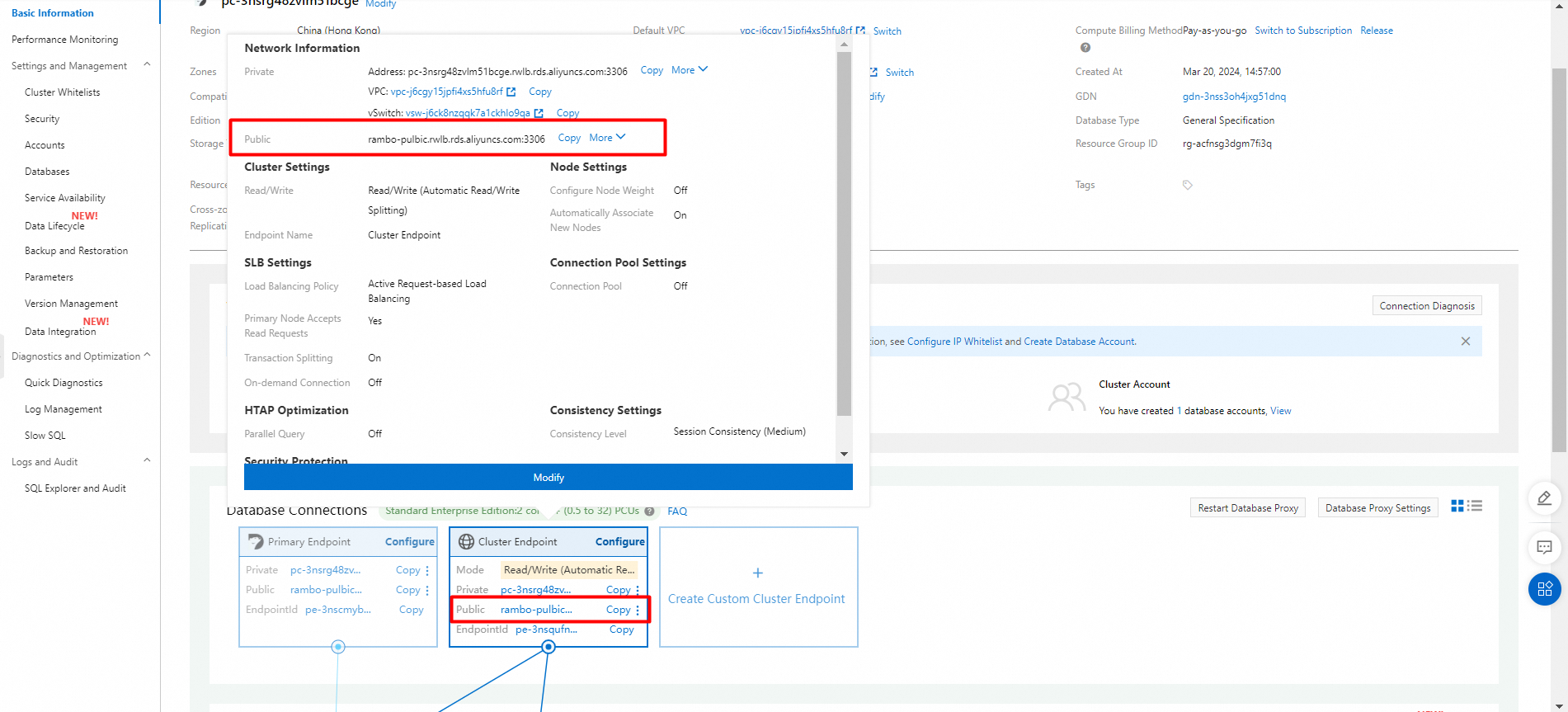
Download the Python installation package, link: https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-3117/

To install Python 3.11.7 on CentOS, you can use the following steps:
1. First, open the terminal.
2. Install the necessary dependencies.
sudo yum groupinstall -y "Development Tools"
sudo yum install -y openssl-devel bzip2-devel libffi-devel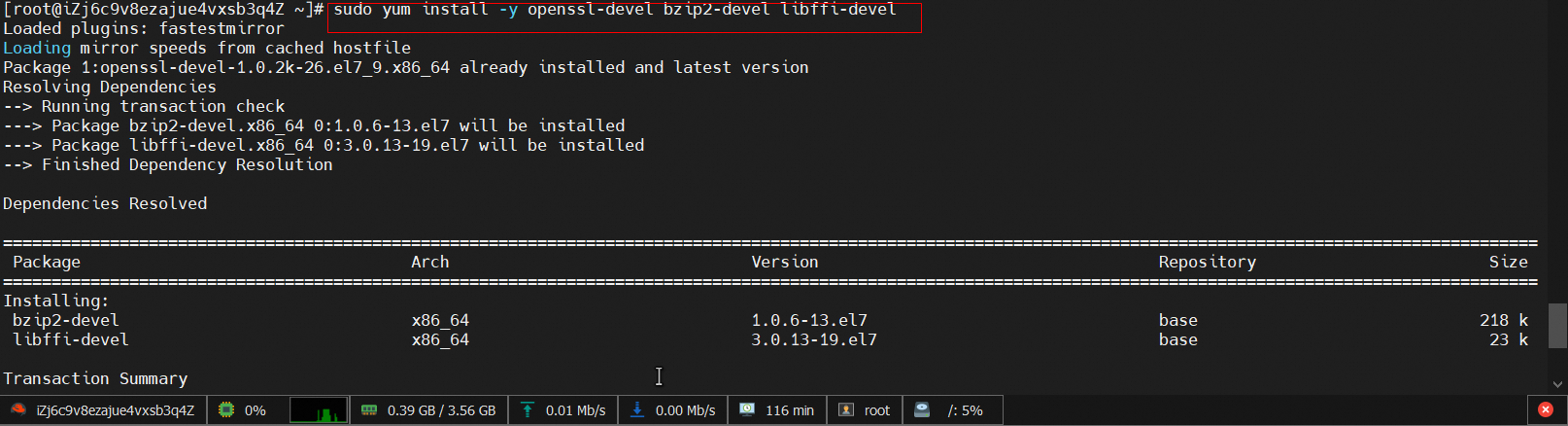
3. Download the Python 3.11.7 source code.
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.11.7/Python-3.11.7.tgz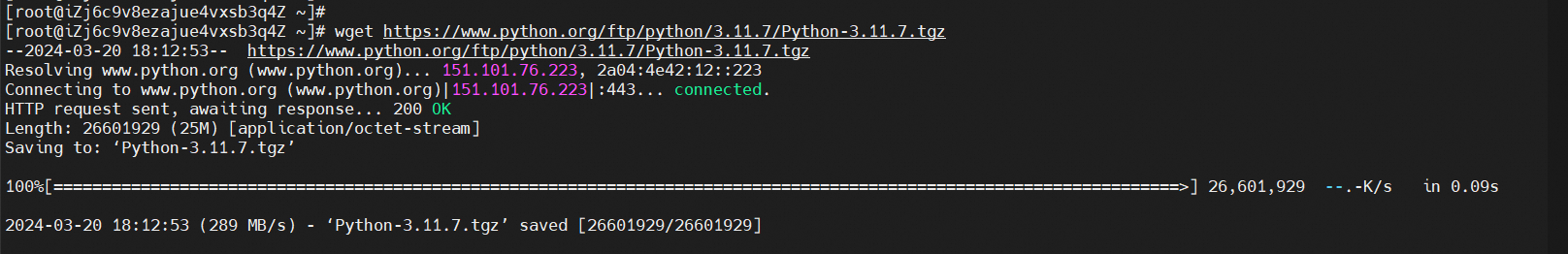
4. Decompress the downloaded source code package.
tar -xvf Python-3.11.7.tar.xz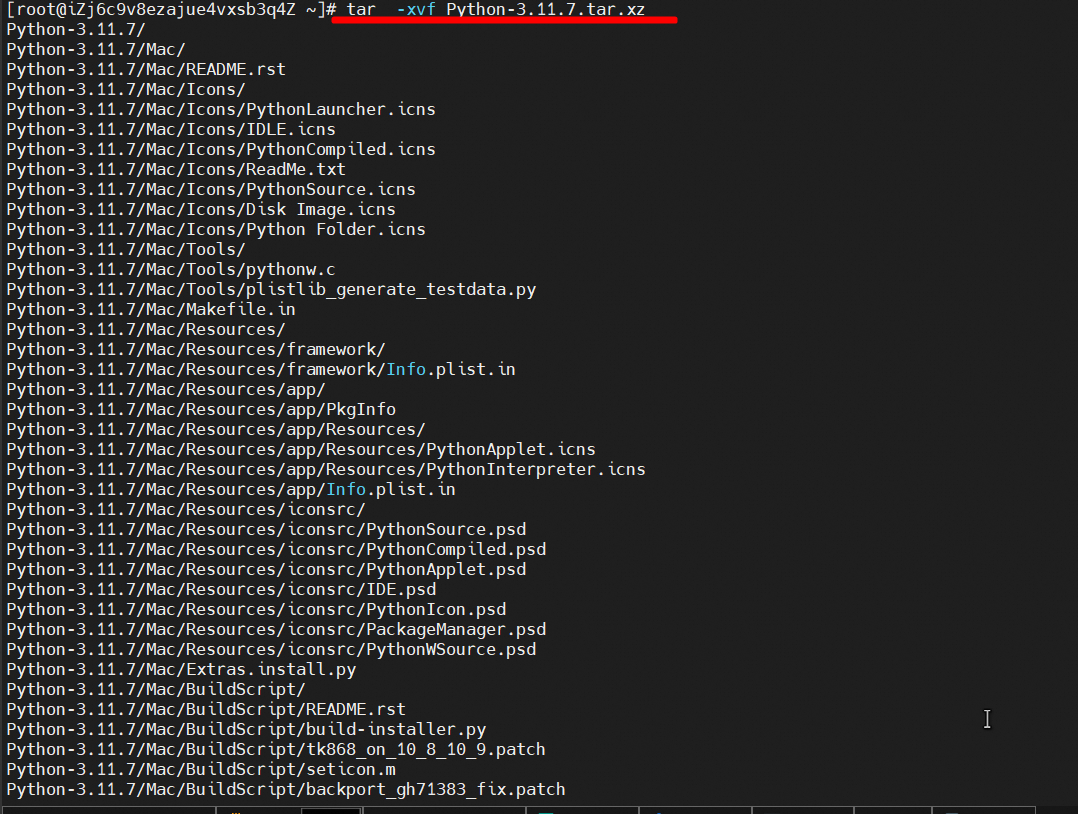
5. Compile and install.
cd Python-3.11.7
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/python
make -j $(nproc) ## Enable multi-core compilation
sudo make install
ln -s /usr/local/python/bin/python3 /usr/bin/python ## link the installed Python version
ln -s /usr/local/python/bin/pip3 /usr/bin/pip3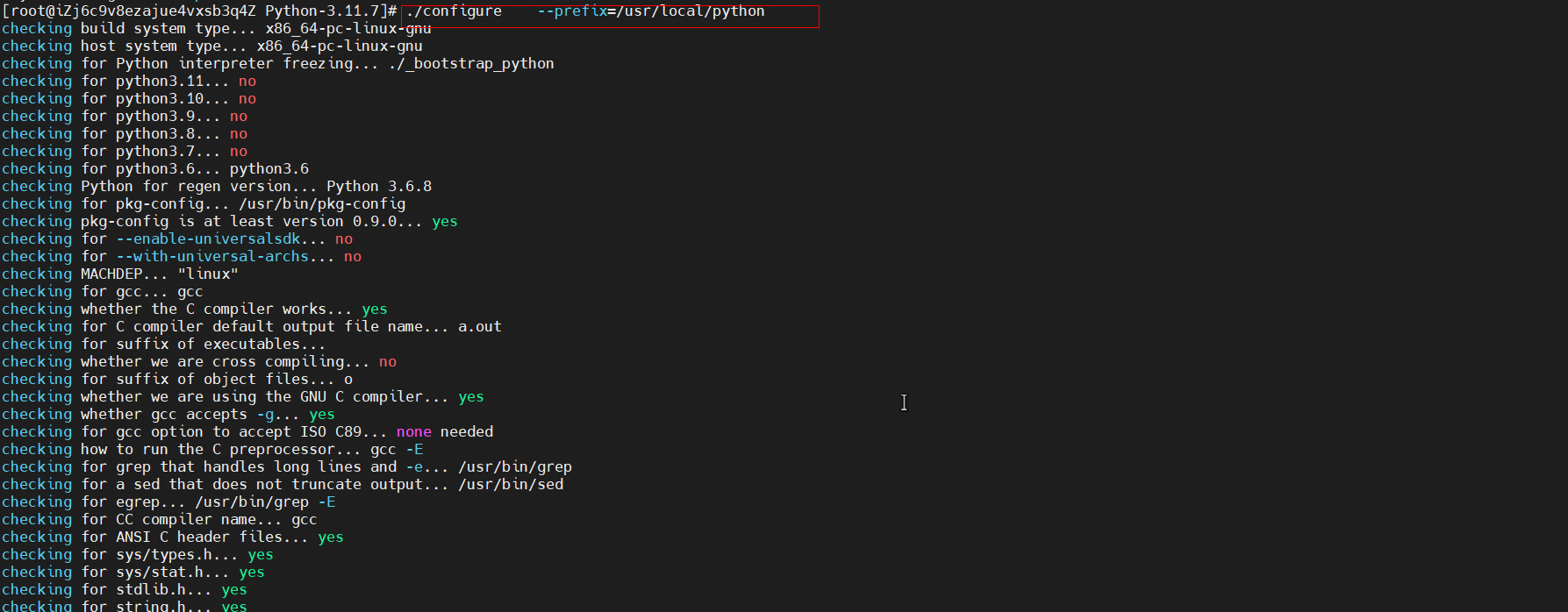
1. Verify the installation.
python --version
pip3 -V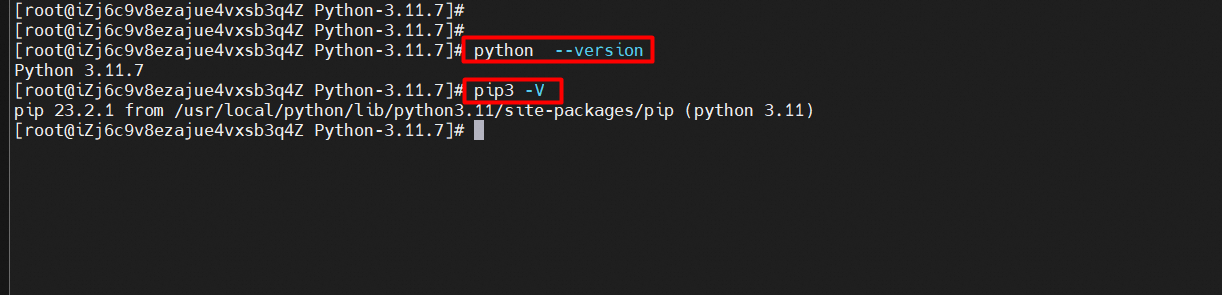
2. To try out the code examples in this tutorial, you should have a MySQL driver to access the MySQL database. We will use the "MySQL Connector" driver, and it is recommended that you use PIP to install "MySQL Connector".
pip3 install mysql-connector-python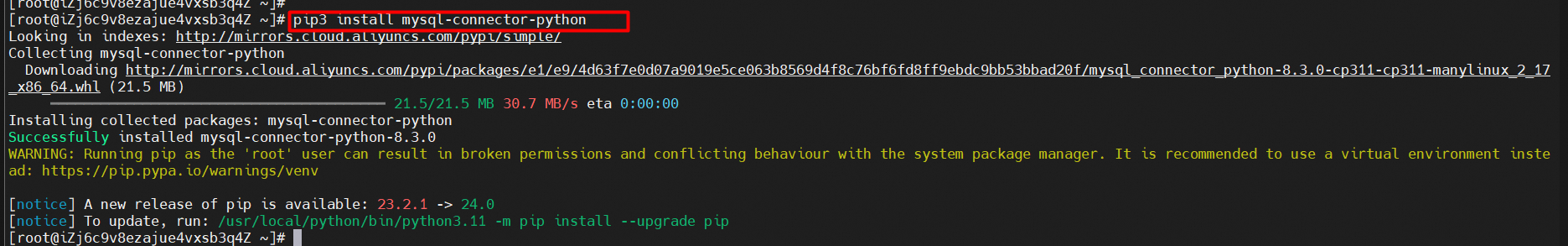
Cloning an instance allows you to quickly create an instance that is the same as or similar to the source instance. This is generally used to replicate a test environment.
1. Log on to the ECS console.
2. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Instances & Images > Instances.
3. In the top navigation bar, select the region where the ECS instance that you want to copy resides.
4. You can clone instances based on your business requirements.
 > Deployment & Elasticity > Clone Instance in the Actions column.
> Deployment & Elasticity > Clone Instance in the Actions column.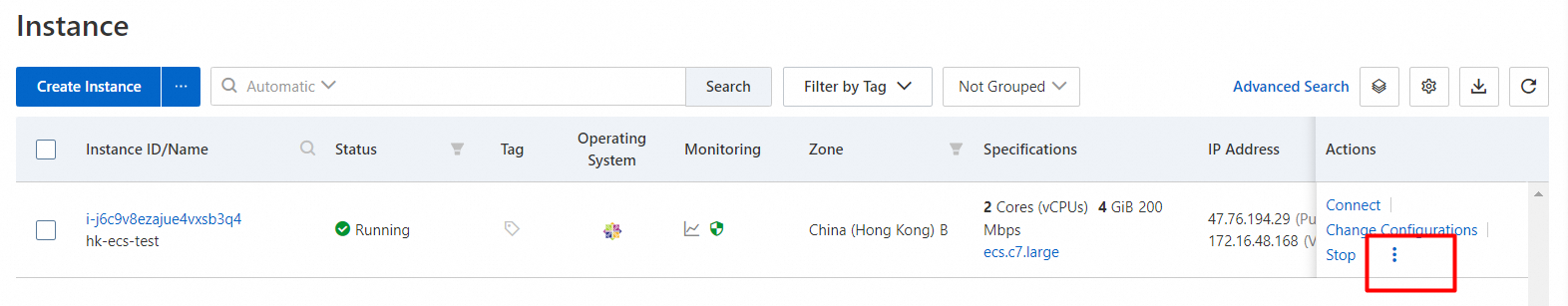
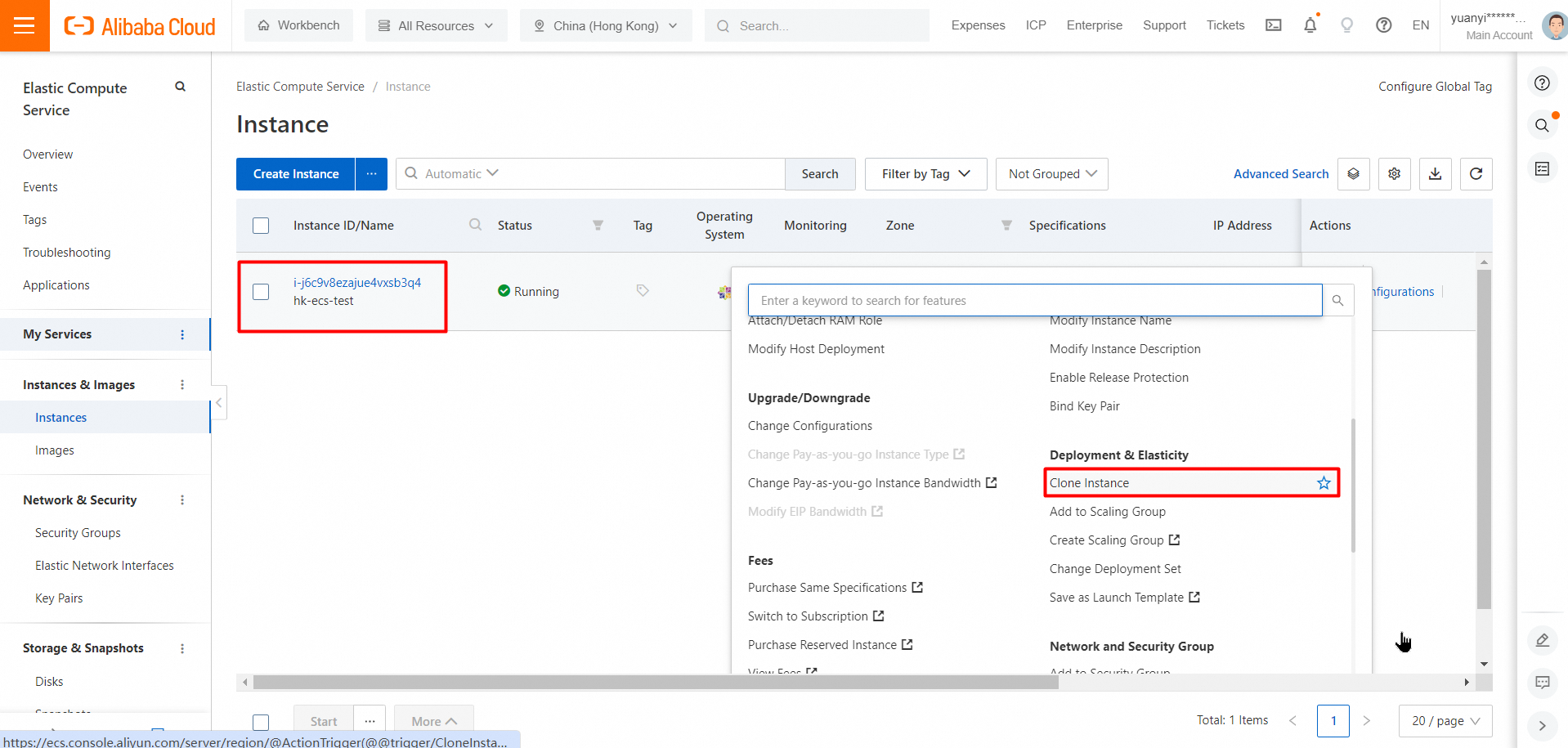
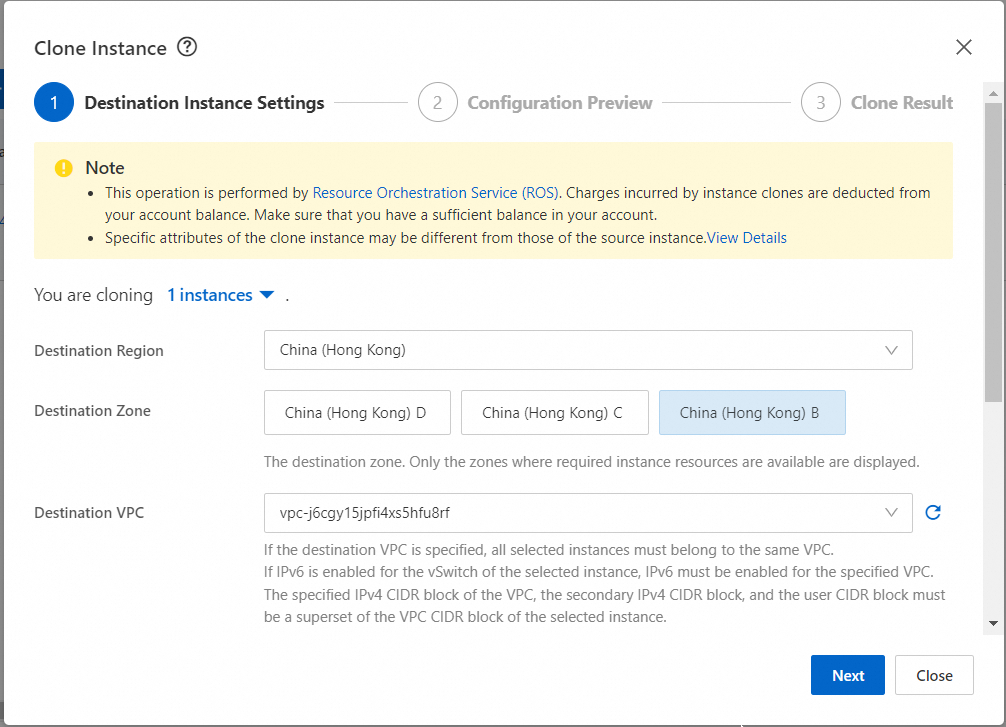
5. In the Clone Instance dialog box, configure parameters and click Next.
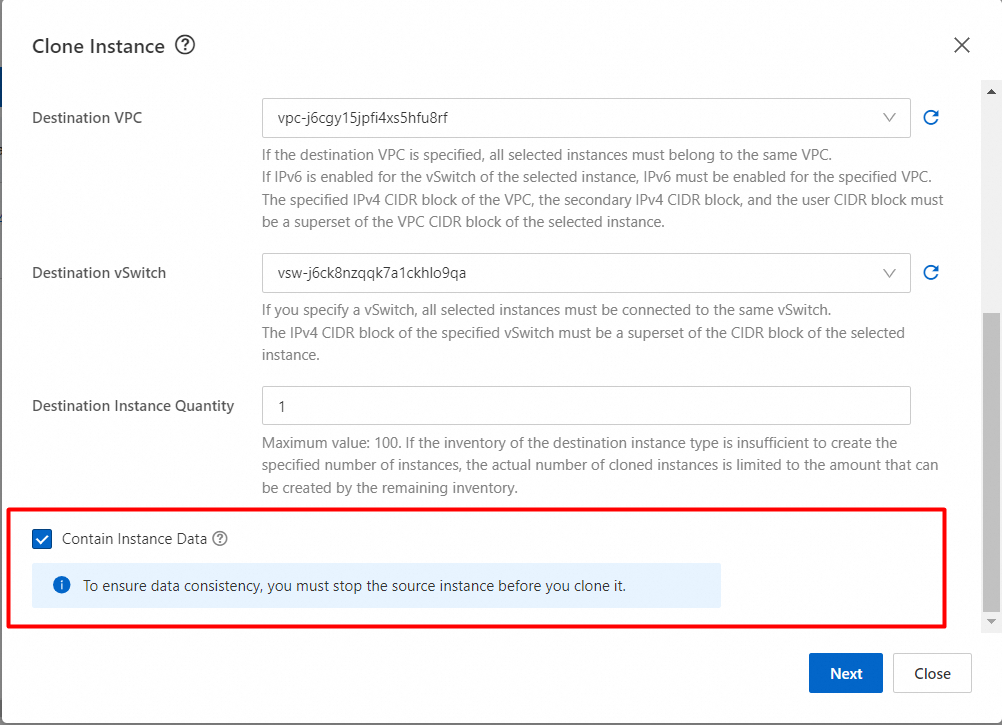
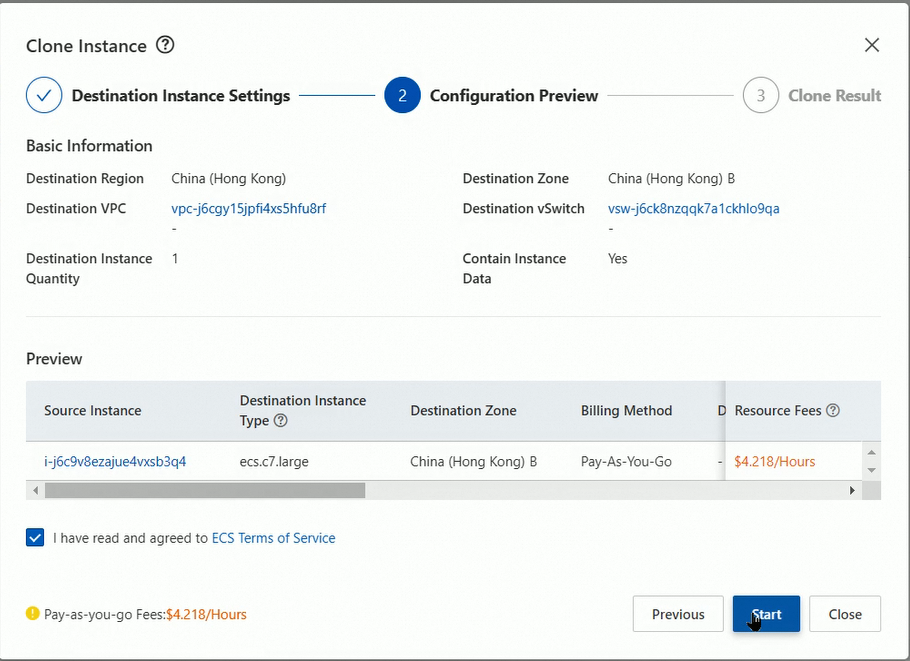
6. The instance is being cloned.
Screen recording for cloning an ECS instance: https://csv-imput.oss-cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com/video/clone%20instance.mp4
• The Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance and the PolarDB for MySQL cluster used in the test are deployed in the same region (Hong Kong).
• The test primary cluster is a Hong Kong node with 4 cores and 8 GB of memory, including one primary node and one read-only node.
• The test secondary cluster is a US Silicon Valley node with 4 cores and 8 GB of memory, including one primary node and one read-only node.
• The endpoint is the private IP address of the primary cluster.
Snapshot of primary and secondary clusters:
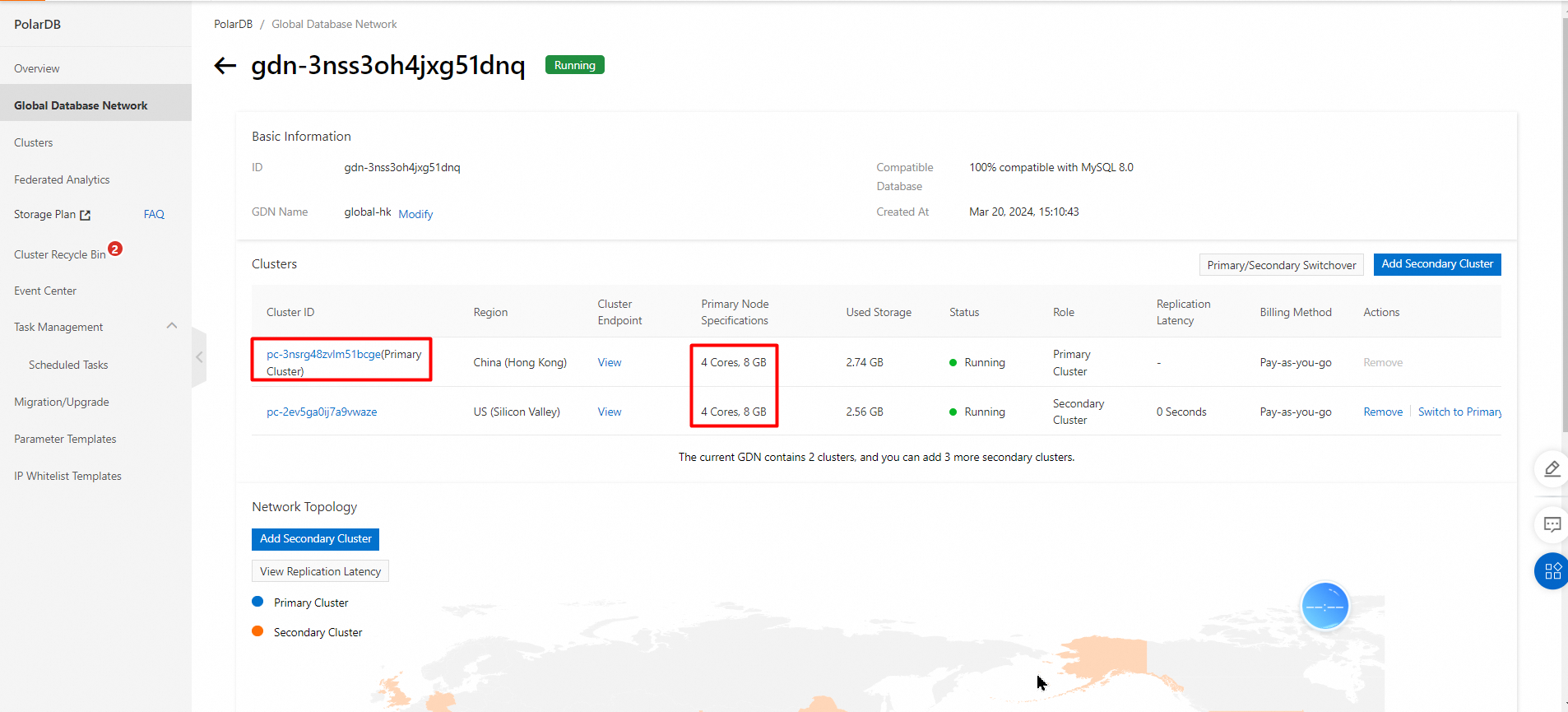
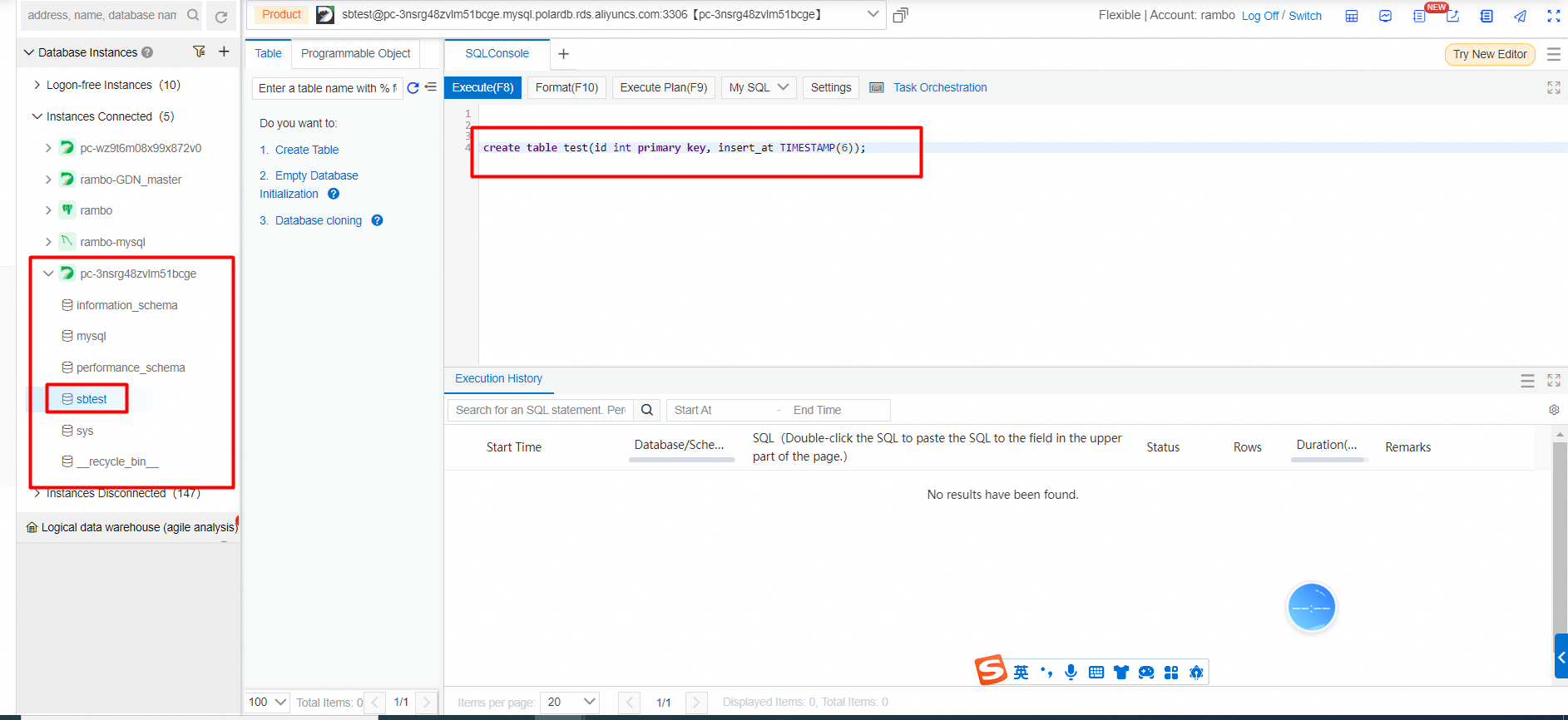
Table creation statement:
create table test(id int primary key, insert_at TIMESTAMP(6));
Command: python Reader.py
The Python script is as follows:
# Read workload
import mysql.connector
import sys
import os
import logging
import time
import datetime
def do_check_time():
conn = mysql.connector.connect(
host='pc-3nsrg48zvlm51bcge.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com',
# host='rambotestip.mysql.polardb.rds.aliyuncs.com',
port=3306,
user='rambo',
password='Tianying12345$')
if not conn:
logging.info("get connect fail")
assert False
i = 1
total_difference = 0
delayed = ''
sum = 0
avg_delayed = ''
print("################################################################################################")
print("\t \t Output as \t hour : minutes : seconds : millisecond")
print("##########################################Reader data###########################################")
print()
with open('delayed.log', 'a') as file:
file.write("################################################################################################\n \t Output as \t hour : minutes : seconds : millisecond" +
"\n##########################################Reader data###########################################\n")
while i <= 100:
sqlstmt = "select insert_at from sbtest.test where id={}".format(i)
cursor = conn.cursor(dictionary=True)
cursor.execute(sqlstmt)
for insert_at in cursor:
total_difference = 0
if len(insert_at) == 0:
print("wait")
else:
i += 1
print("insert_at: ", insert_at)
result = datetime.datetime.now()-insert_at['insert_at']
# sum = result.total_seconds()
sum = sum + result.total_seconds()
delayed = str(result)
avg_delayed = sum/100
avg_delayed = str(avg_delayed)
print('Read delayed:\t' + str(result) + " ms")
print('total_delayed ' + str(sum) + " S")
with open('delayed.log', 'a') as file:
file.write("Read delayed: "+delayed+" ms"+'\n')
print("########################################## Reader data End #####################################")
print()
print('total_delayed :'+str(sum)[0:7]+' S')
print('avg_delayed :'+avg_delayed[0:6] + ' S')
with open('delayed.log', 'a') as file:
file.write("###################################### Reader data End ###############################################"+'\n'
+ '\t'+"Total_delayed: "+str(sum)[0:5]+' S \n' +
'\t' + "avg_delayed: " + str(avg_delayed)[0:5]+' S'+'\n\n')
cursor.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
do_check_time()Command: sh insert.sh
# Insert workload script
#!/bin/sh
HOST=xxxxxxxx.aliyuncs.com
PORT=3306
USER=admin
PASSWORD=xxxxxxx
echo "create table test"
##create table test(id int primary key, insert_at TIMESTAMP(6));
mysql -h$HOST -P$PORT -u$USER -p$PASSWORD -e"use sbtest;"
i=1
while ((i <= 100))
do
CMD="use sbtest;insert into test values($i, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(6));"
echo $CMD
mysql -h$HOST -P$PORT -u$USER -p$PASSWORD -e"$CMD"
((i++))
sleep 1
doneVideo of test results:
https://csv-imput.oss-cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com/video/delayed_demo.mp4
Screen recording for cloning an ECS instance:
https://csv-imput.oss-cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com/video/clone%20instance.mp4
Video of installing Sysbench:
https://csv-imput.oss-cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com/video/sysbench_setup.mp4
Link for downloading the Sysbench tool:
https://github.com/akopytov/sysbench.git
Video of Sysbench performance testing:
https://csv-imput.oss-cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com/video/sysbench_stress_testing.mp4
ApsaraDB - June 19, 2024
ApsaraDB - January 6, 2023
ApsaraDB - May 29, 2023
ApsaraDB - November 12, 2024
ApsaraDB - July 17, 2025
ApsaraDB - May 29, 2025
 PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn More PolarDB for Xscale
PolarDB for Xscale
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for Xscale (PolarDB-X) is a cloud-native high-performance distributed database service independently developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More PolarDB for MySQL
PolarDB for MySQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for MySQL is a cloud-native relational database service 100% compatible with MySQL.
Learn More Time Series Database (TSDB)
Time Series Database (TSDB)
TSDB is a stable, reliable, and cost-effective online high-performance time series database service.
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB