By Nanlong Yu
Large language models (LLMs) have limits in accuracy and real-time responsiveness of generated outputs and are not ideally suitable for direct deployment in customer service or Q&A systems that require precise, up-to-date information. To address the issue, the industry has widely adopted the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) technology to improve the performance of LLMs. RAG significantly improves the performance of natural language processing (NLP) tasks such as Q&A and summarization that require access to external knowledge. RAG integrates LLM models, such as Tongyi Qianwen, with an information retriever to enhance the accuracy and informativeness of the LLM models. When a user query is processed, RAG first uses the information retriever to search a designated knowledge base for contextually relevant documents, passages, or data snippets. Then, the retrieved contents are combined with the original query and fed into the LLM. The LLM then leverages its inherent generative capabilities to produce factually accurate responses based on the latest retrieved information, which eliminates the need to rebuild the model.
PolarDB, a cloud-native database owned by Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB, supports MySQL 9.0 native vector search syntax (The Vector Type [1], Vector Functions [2]). This feature accelerates KNN search by using vectorized execution and parallel scan capabilities of IMCIs. Developers can use PolarDB IMCI as an information retrieval component and use the induction and generation capabilities provided by PolarDB for AI (the integrated Qwen model) to quickly build an RAG system. This effectively overcomes the limitations of LLM in terms of accuracy and real-time performance, and provides accurate and informative responses for various Q&A scenarios.
[1] https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/9.0/en/vector.html
[2] https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/9.0/en/vector-functions.html
The following figure shows the overall process of building and using an RAG system based on PolarDB IMCI and PolarDB for AI.
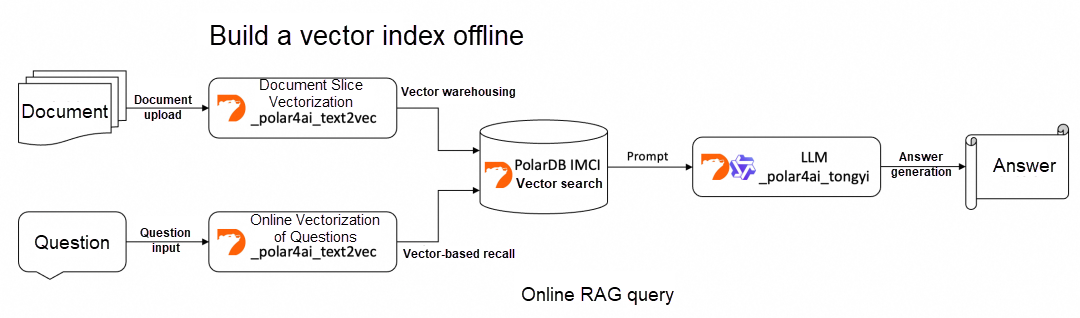
Upload the files to the database, parse the file content, and perform text vectorization.
The following SQL statement is used to upload files to the database.
/*polar4ai*/UPLOAD FILE docfile WITH
( file_id = 'unique_file_id',
file_type = '.docx',
src_file_location = 'your_file_url',
dest_file_name = 'your_file_name.docx',
metadata = '{}',
overwritten = 1
);The following table describes the parameters in the WITH() clause:
| Parameters | Note | Example |
|---|---|---|
| file_id | The unique identifier of the file. | 'Polar4AI' |
| file_type | The file type. | '.docx' |
| src_file_location | The URL of the file. | https://xxx.aliyuncs.com/Polar4AI-Introduction.docx |
| dest_ffile_name | The name of the uploaded file. The name does not need to be unique and cannot be a storage path. | 'Polar4AI-Introduction' |
| metadata | The metadata. You can leave the parameter empty. | '{}' |
To create and update a metadata table for the files uploaded to a database, execute the following SQL statement:
CREATE TABLE file_id_list_rag (
file_id varchar(256) PRIMARY KEY
);
INSERT INTO file_id_list_rag(file_id) VALUES ('unique_file_id');The following table describes the parameters in the preceding SQL statement:
| Parameters | Note | Example |
|---|---|---|
| file_id | The unique identifier of the file specified in the UPLOAD FILE statement. | 'Polar4AI' |
The temporary table that stores the chunks and vectors obtained from the text-to-vector conversion model has fixed parameter names and types. The SQL statement is as follows:
/*polar4ai*/CREATE TABLE file_index_table_rag( chunk_id varchar(265), chunk_content text_ik_smart, file_id varchar(256), file_name varchar(256), vecs vector_768, PRIMARY KEY(chunk_id));The following table describes the parameters in the temporary table.
| Parameters | Note | Example |
|---|---|---|
| file_id | The unique identifier for the source file, which is used to trace the origin of the chunked text. | 'Polar4AI' |
| file_name | The name or title of the file. You can also specify a summary or key phrase related to the content based on your business requirements. | 'Polar4AI-Introduction' |
| chunk_content | The text content of the chunk, which is processed by using a tokenizer. Example tokenizers: text_ik_smart (coarse-grained tokenization) and text_ik_max_word (fine-grained tokenization). | The content of the file. |
| vecs | The vector of the chunk. The _polar4ai_text2vec model converts the text chunk into a vector. | [0.1, 0.2, ...] |
| chunk_id | The ID for each text chunk. The value sequentially increments within the same file. Specify the parameter in the {file_id}-{chunk_order} format. | 'Polar4AI-1' |
Select the file_id to be segmented and vectorized from the document metadata table, parse the document content, and use the predict method of the _polar4ai_text2vec model to convert the document chunks into vectors.
/*polar4ai*/SELECT chunk_id, file_id, file_name, chunk_content FROM predict(model _polar4ai_text2vec, SELECT file_id FROM file_id_list_rag) WITH ( x_cols='chunk_content',
primary_key='file_id',
resource='file',
mode='async',
to_chunk=1,
headers_to_split_on=2,
chunk_size=1024,
chunk_overlap=64,
separator='')INTO file_index_table_rag;The _polar4ai_text2vec model is used to convert text into 768-dimensional vectors. The following table describes the parameters included in the WITH() clause.
| Parameters | Note | Value range or example |
|---|---|---|
| x_cols | The field that stores the text content used as input for the model. | chunk_content |
| primary_key | The primary key of the file list. | id |
| mode | The writing mode of document data. Currently, only the async mode is supported. | async |
| resource | The type of the model. Specify the file model in the file parsing process. | file |
| to_chunk | Specify whether to chunk the file. | 0 and 1 |
| headers_to_split_on | If you set the to_chunk parameter to 1, the file is chunked based on the header level. • To chunk the file based on all header levels, set the headers_to_split_on parameter to -1. •To chunk the file based on the header level x, set the headers_to_split_on parameter to x. |
-1 ≤ x ≤ 6, and the value is an integer. |
| chunk_size | The maximum length of a chunk. | chunk size ≥50 |
| chunk_overlap | The number of overlapping characters between two adjacent chunks. | chunk_overlaps≤chunk_size |
| separator | The delimiter used to separate the chunks. | '' /', ',' etc. |
Use the MySQL native vector type and syntax to create a table that has a vector index and build a column store index.
create table vector_index ( chunk_id varchar(265), chunk_content text, file_id varchar(256), file_name varchar(256), vecs vector(768), PRIMARY KEY(chunk_id)) COMMENT 'columnar=1';First, you need to query the intermediate results of chunks and vectors from the temporary table in the previous section.
/*polar4ai*/select * from file_index_table_rag;Write the intermediate results into the table that has a vector index via the string_to_vector expression.
insert into vector_index (file_name,file_id,vecs,chunk_content,chunk_id)values ("file_name","file_id",string_to_vector("[...]"),'chunk_content',"chunk_id");The SQL statement for the online vectorization of the question is as follows:
/*polar4ai*/SELECT * FROM predict(model _polar4ai_text2vec, SELECT 'question') with();Use distance expressions and accelerate KNN vector search with IMCI to recall the K vectors and text chunks with the highest similarity:
select /*+ SET_VAR(use_imci_engine=forced) */ file_name,chunk_content, distance(string_to_vector("[...]"), vecs, "COSINE") as d from vector_index order by d limit 5;Compose the question and the recalled text chunks into a Prompt, and call the PolarDB for AI's built-in Qwen model for online inference to generate an answer:
"/*polar4ai*/SELECT * FROM PREDICT (MODEL _polar4ai_tongyi, SELECT 'prompt') with ()"You can use PolarDB IMCI and PolarDB for AI to quickly build an RAG system based on the preceding procedure. The appendix of this article provides a sample code. In this example, a document knowledge base is created for some official documents of IMCI. A vector index is built on PolarDB IMCI, and then an RAG system is created by using the PolarDB for AI-integrated Qwen model. A simple Web service is provided as a Q&A interaction. With this RAG system, LLM can correctly answer domain-specific questions related to IMCI.
After the Python environment is correctly installed on the ECS according to requirements.txt, run the following commands in sequence as shown in the figure:
1_upload_file.py Create a document knowledge base2_vectorization.py Perform document segmentation and vectorization and build vector indexes on PolarDB IMCI3_rag.py Start RAG Web services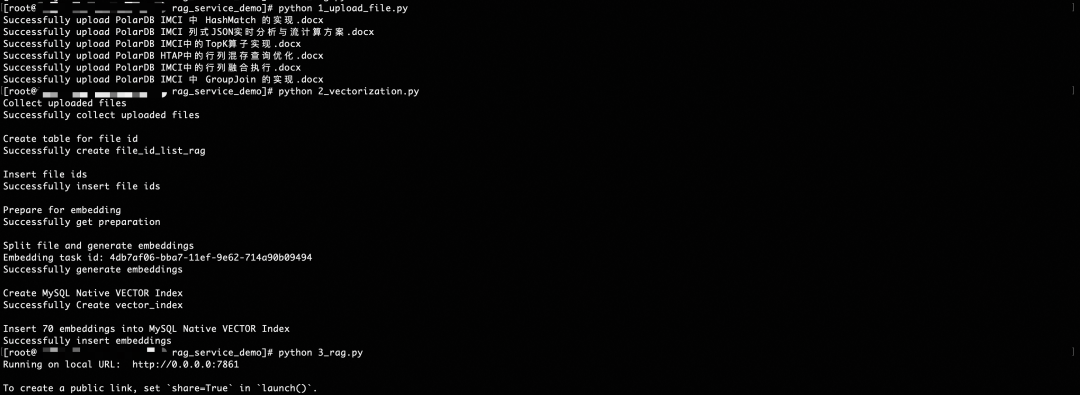
The Hash Match operator is an operator proprietary to IMCI. For the question "What is the Hash Match operator in IMCI", the RAG system can recall similar document chunks from PolarDB IMCI and provide them to LLM as the Prompt. This enables LLM to correctly answer questions about the Hash Match operator.
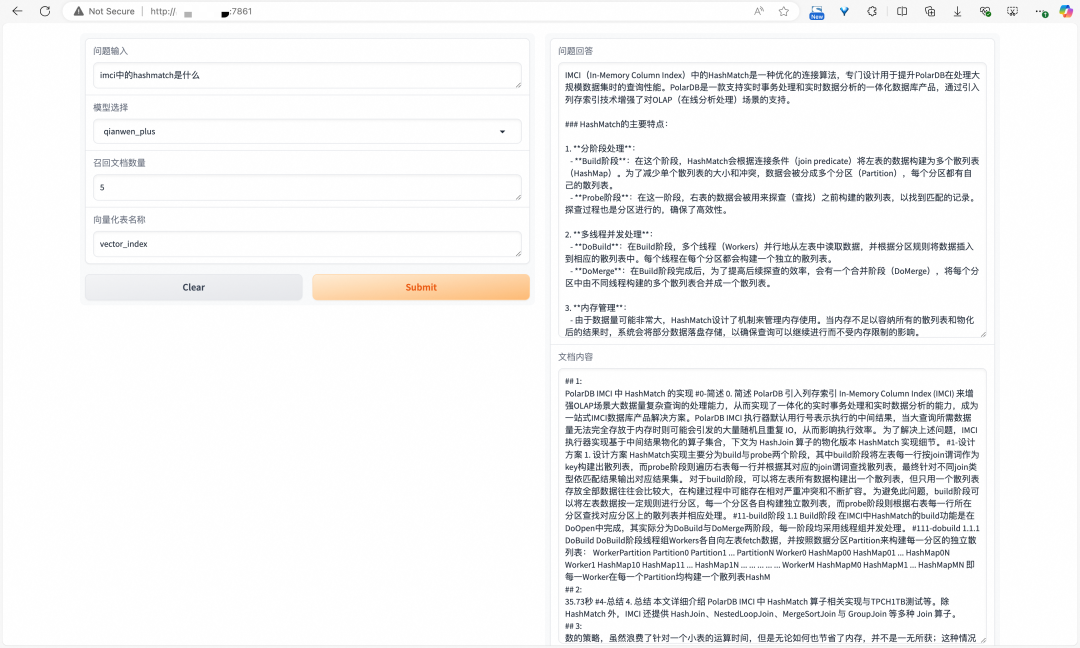
Copy the link below to your browser to get it: https://github.com/nanlongyu/rag_service_demo
Running the sample requires the developer to have the following resources:
Column store nodes are used to build vector indexes, while AI nodes provide text-to-vector conversion and LLM capabilities. The ECS instance runs the RAG system and deploys Web services, and OSS is used to upload knowledge base documents. While the PolarDB cluster and OSS are mandatory, developers may alternatively run the RAG system and deploy Web services in other appropriate environments.
Developers need to update the relevant access configurations of the above resources to 1_upload_file.py, 2_vectorization.py, and 3_rag.py, and then run the RAG system according to the RAG System Example section.
ApsaraDB - October 29, 2024
ApsaraDB - October 16, 2024
ApsaraDB - June 19, 2024
ApsaraDB - January 3, 2024
Morningking - September 26, 2023
ApsaraDB - August 23, 2024
 PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn More PolarDB for Xscale
PolarDB for Xscale
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for Xscale (PolarDB-X) is a cloud-native high-performance distributed database service independently developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More PolarDB for MySQL
PolarDB for MySQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for MySQL is a cloud-native relational database service 100% compatible with MySQL.
Learn More AI Acceleration Solution
AI Acceleration Solution
Accelerate AI-driven business and AI model training and inference with Alibaba Cloud GPU technology
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB