By Alibaba Cloud MaxCompute Team
This series details the migration journey of a leading Southeast Asian technology group from Google BigQuery to MaxCompute, highlighting key challenges and technical innovations. This fifth installment analyzes the performance optimization technologies of cross-border data warehouse migration.
Note: The customer is a leading Southeast Asian technology group, referred to as GoTerra in this article.
GoTerra, an Indonesian technology group, is one of the most influential Internet giants in Southeast Asia. GoTerra operates across various sectors, including ride-hailing, e-commerce, food delivery, logistics, and financial payments. Before migrating to MaxCompute, GoTerra utilized BigQuery of Google Cloud Platform (GCP) as its core big data platform. BigQuery offers robust capabilities, including SQL syntax compatibility, automated migration support, streaming ingestion, metadata upgrades, and intelligent resource scheduling.
However, three line-of-business projects of GoTerra demand exceptionally low latency:
1) Business intelligence (BI) reporting: GoTerra's customers rely heavily on BI reports for decision-making, requiring fast and stable query responses, typically within 30 seconds.
2) Ad hoc queries of customer services: In multiple real-time customer service scenarios, customer service representatives need to temporarily trace a large amount of historical data based on different customer requirements to address customer inquiries and resolve issues. Query performance directly impacts service quality and customer satisfaction. The previous BigQuery-based solution achieved an average query response time of approximately 5 seconds.
3) Data pipelines: These automated data processing workflows are critical for core business operations, with downstream processes heavily reliant on their output. Strict performance requirements necessitate sub-30-second timeout thresholds for most jobs to ensure efficient and stable execution.
These demanding performance and stability requirements present a significant challenge during the migration to MaxCompute. Matching BigQuery's has become one of the core challenges of the project.
To meet the demanding latency and stability requirements of MaxCompute users, particularly in matching BigQuery's performance, Alibaba Cloud introduces MaxCompute Query Accelerator (MaxQA), a nearline query solution.
Building upon MaxCompute's core capabilities, MaxQA features significant architectural upgrades and optimizations. By leveraging dedicated control plane components and a query-specific computing resource pool, MaxQA comprehensively optimizes the control plane, connection protocol, query optimizer, execution engine, storage engine, I/O paths, and distributed caching mechanism. These enhancements deliver lower query latency, higher concurrency, and improved system stability, making MaxQA ideal for business scenarios that require faster response speeds and higher concurrency, such as real-time BI report refreshes, interactive ad hoc analysis, and near real-time data warehousing.
Furthermore, MaxQA maintains full compatibility with the MaxCompute SQL dialect. Existing MaxCompute SQL workloads can be seamlessly migrated to MaxQA without code modifications, achieving substantial performance gains. Combined with flexible time-based resource policies and elastic scaling capabilities, MaxQA not only boosts performance but also reduces overall costs, achieving a balance of both.
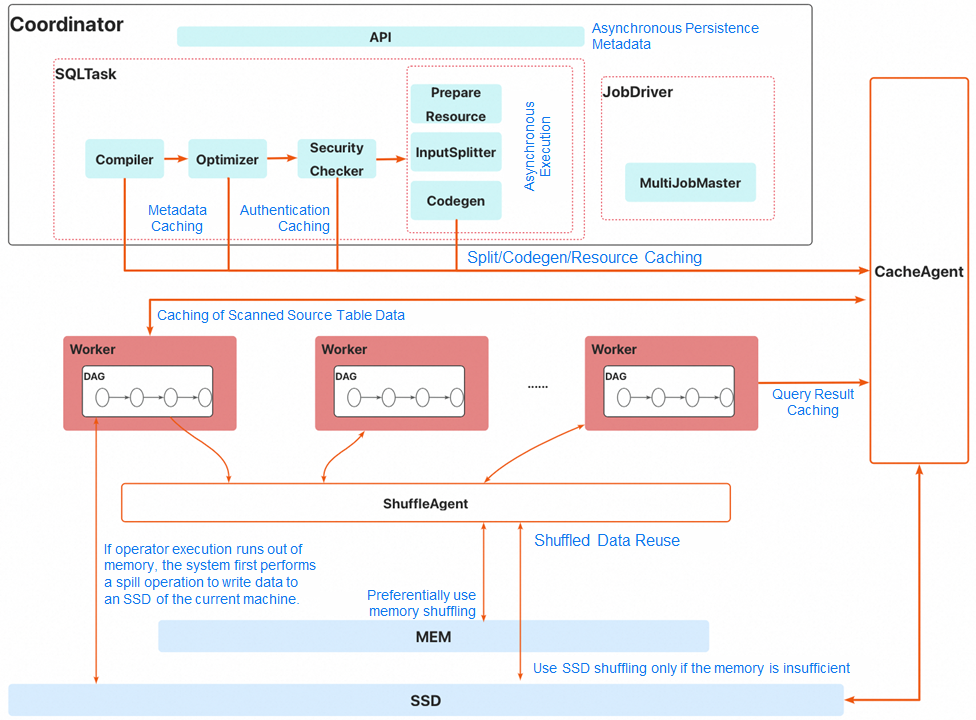
The following figure shows the overall architecture of MaxQA.
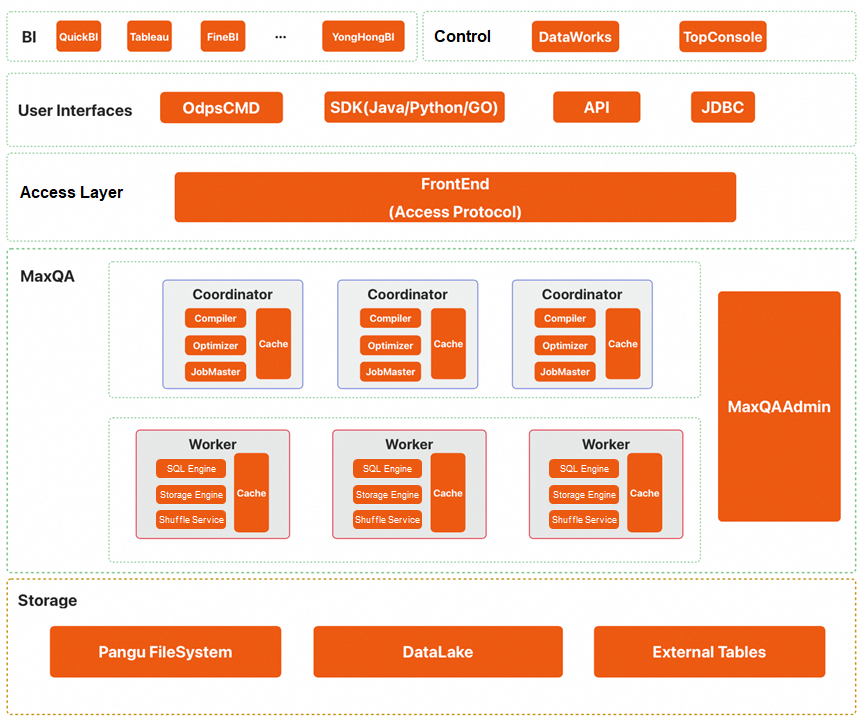
The core modules are described below, from top to bottom:
• BI layer: MaxQA is compatible with various BI tools. For more information, see BI Tools.
• Control layer:
• User interfaces and access layer:
• MaxQA instance layer:
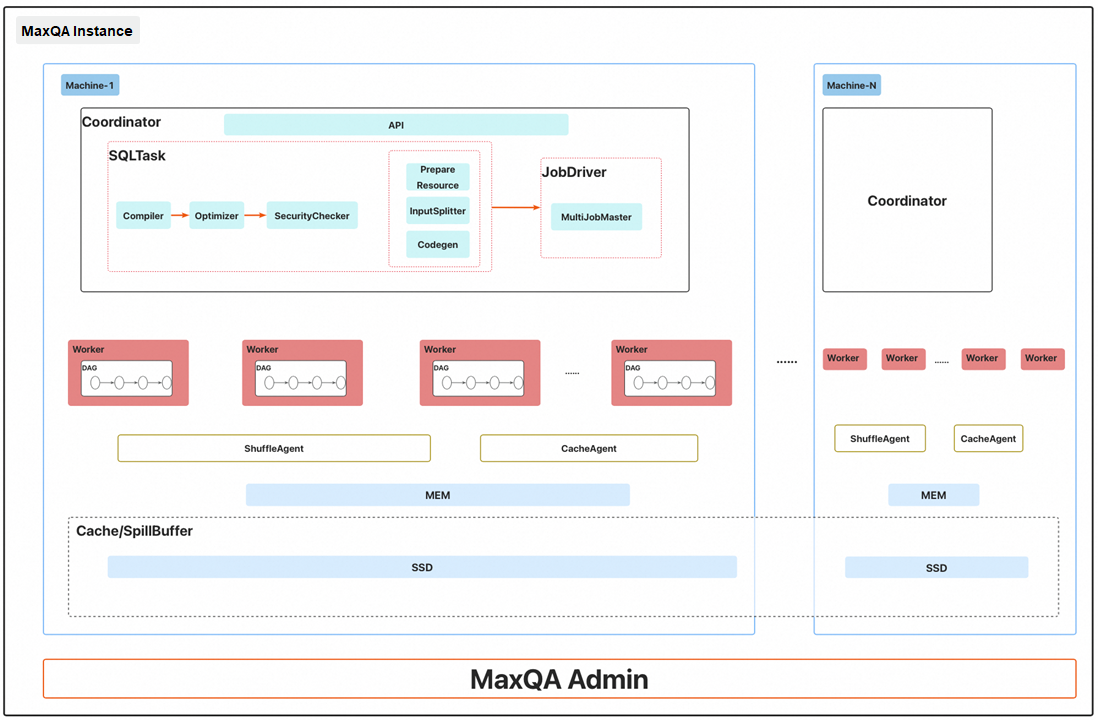
A MaxQA instance consists of several machines. Each machine is equipped with hardware resources such as CPUs, memory, and SSDs. The aggregate CPU and memory resources across all machines in a MaxQA instance correspond to the purchased compute unit (CU) capacity.
The SSDs on each machine contribute to both an instance-level distributed cache layer and a memory spill pool:
• Distributed cache layer:
• Memory spill pool:
A MaxQA instance includes the following core modules:
1. Coordinator:
2. Pre-launched worker pool:
3. MaxQAAdmin:
4. Shuffle agent:
5. Cache agent:
MaxCompute quotas are organized into two levels: Level 1 and Level 2.
• Level 1 quotas: These represent the top-level resource allocation and are categorized by billing method:
• Level 2 quotas: Subscription-based Level 1 quotas can be further subdivided into Level 2 quotas:
The following figure shows the job submission processes for different types of quotas.
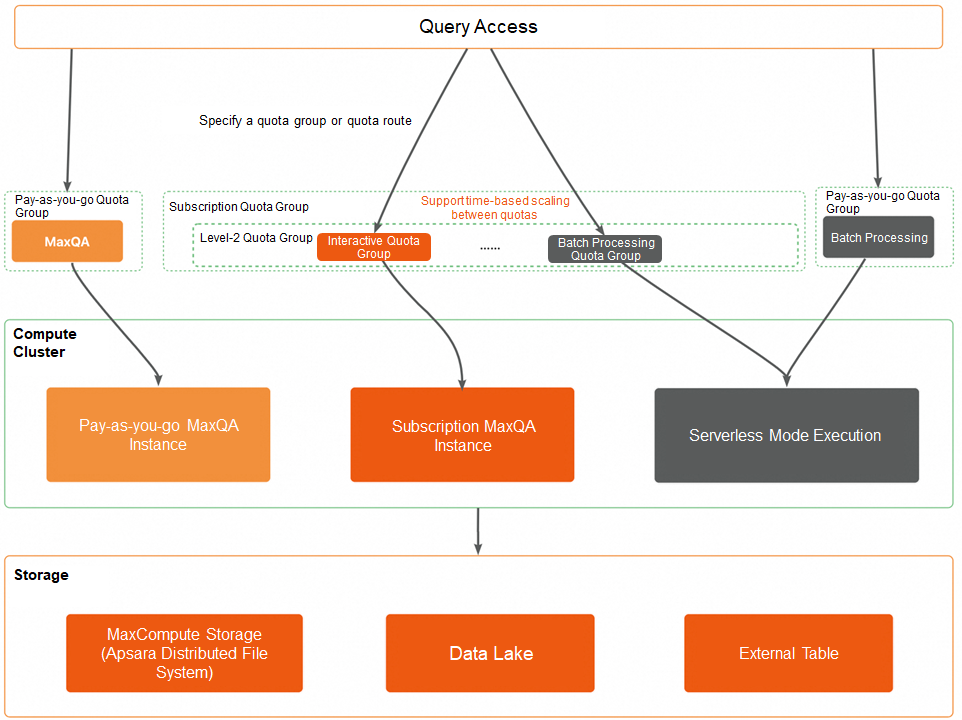
After a job is submitted to the specified quota group, MaxCompute routes it to the appropriate resource pool or instance based on the quota type:
• Subscription quotas:
• Pay-as-you-go quotas:
For more information, see the "MaxQA connection methods" section of the MaxQA Operation Guide topic on the Alibaba Cloud official website.
The following figure shows the differences in job processing between batch processing quota groups and interactive quota groups.
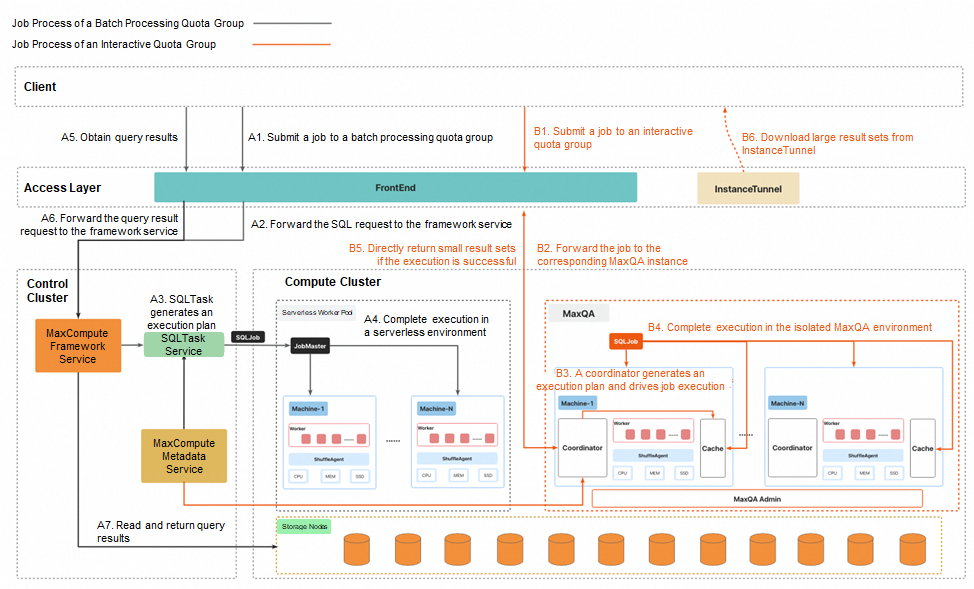
The preceding figure shows the differences in job processing between batch processing quota groups and interactive quota groups within MaxQA, depicted by black and orange lines respectively. The following sections describe the two job processes.
1. Submit an SQL request: After user authentication is complete in the frontend, an SQL request is forwarded to the framework service of the control cluster.
2. Implement request scheduling and throttling: The framework service executes logic such as throttling and queuing, and selects an arbitrary process from the SQLTask service for processing.
3. Generate an execution plan and submit a job: SQLTask parses the SQL request, generates an execution plan, and then submits an SQL deployment to the compute cluster.
4. Start JobMaster to drive job execution: The compute cluster starts JobMaster to apply for worker resources in the serverless environment and drive the job execution.
5. Obtain query results from the client: The client sends a result query request.
6. Return request routing and results: The frontend forwards the result request to the framework service or Tunnel service. Then, the framework service or Tunnel service reads the query results and returns the results to the client.
1. Submit an SQL request: After user authentication is complete in the frontend, an SQL request is directly forwarded to the coordinator module of the corresponding MaxQA instance.
2. Generate an execution plan and drive job execution: The coordinator module generates an execution plan and drives the job execution in the isolated MaxQA environment.
3. Directly return query results (small result set): If the job is a query job and the result set is small, the query results are directly encapsulated in the response of the client and are returned without additional intermediate forwarding steps.
| Process dimension | Batch processing quota (black line) | Interactive quota (orange line) |
|---|---|---|
| Job type | Periodic and large-scale tasks | BI reports and ad hoc queries |
| Resource pool | Serverless resource pool | MaxQA instance (single-tenant isolation) |
| Processing path | Frontend → Control cluster → SQLTask → Compute cluster | Frontend → MaxQA instance |
| Result return | Multiple steps are performed to return results. | Small results are directly returned. |
| Response latency | Higher | Lower |
MaxQA uses the exclusive control layer and computing resource pool for queries to optimize the query access methods, interaction protocol, query optimizer, execution engine, storage engine, I/O paths, and distributed cache mechanism. The following sections describe the core optimization items.
• Single-tenant isolation
An interactive quota group corresponds to an independent MaxQA instance. Each MaxQA instance has an exclusive access layer and a computing resource pool. This implements complete resource isolation in the architecture dimension and prevents mutual interference in multi-tenant environments.
• Query in direct connection mode
Based on single-tenant isolation, MaxQA optimizes query access paths. Requests are directly forwarded from the frontend to the coordinator module of the corresponding MaxQA instance. This greatly reduces the complexity and latency of path queries.
• More simplified interaction protocol
If the execution time of a query is less than 5 seconds and the size of the result set to be queried is 10 MB, only one request needs to be sent to submit the query and return the query result.
• Asynchronization of time-consuming paths
Synchronous write operations on instance metadata and task metadata is optimized to asynchronous write operations, which makes it faster to enter key processing steps. The non-critical operations after a job is successfully run (such as generating a summary and use LogView to display generated results) are optimized to asynchronous processing in the background. This does not occupy end-to-end (E2E) time of queries.
• Better concurrency calculation method
• Memory shuffling mode preferentially used
• SQL operator memory preferentially spilled to I/O of the current machine
• Adaptive execution mode selection
• Downstream read-ahead mode
• Better control layer
• End-to-end caching
If interactive quota groups of users are mainly used to run BI reports and ad hoc query jobs, such tasks usually have obvious time series peaks and valleys. Purchased subscription quota groups are often configured based on the maximum demand of batch jobs. During off-peak hours, idle resources and low utilization often occur.
You can configure time-based scaling to flexibly allocate quotas of interactive quota groups and batch processing quota groups based on different periods of time. This implements dynamic resource scheduling in the time dimension, thereby efficiently utilizing the overall resources, reducing redundancy costs, and improving resource utilization.
As shown in the following figure, the blue line indicates the number of CUs of a purchased subscription level-1 quota group. The orange square indicates the CU quota of an interactive quota group, whereas the green square indicates the CU quota of a batch processing quota group. After time-based scaling is configured, the system automatically adjusts the number of CUs of the interactive quota group and batch processing quota group based on the preset period of time. This realizes intelligent scheduling and efficient utilization of resources within different periods of time.
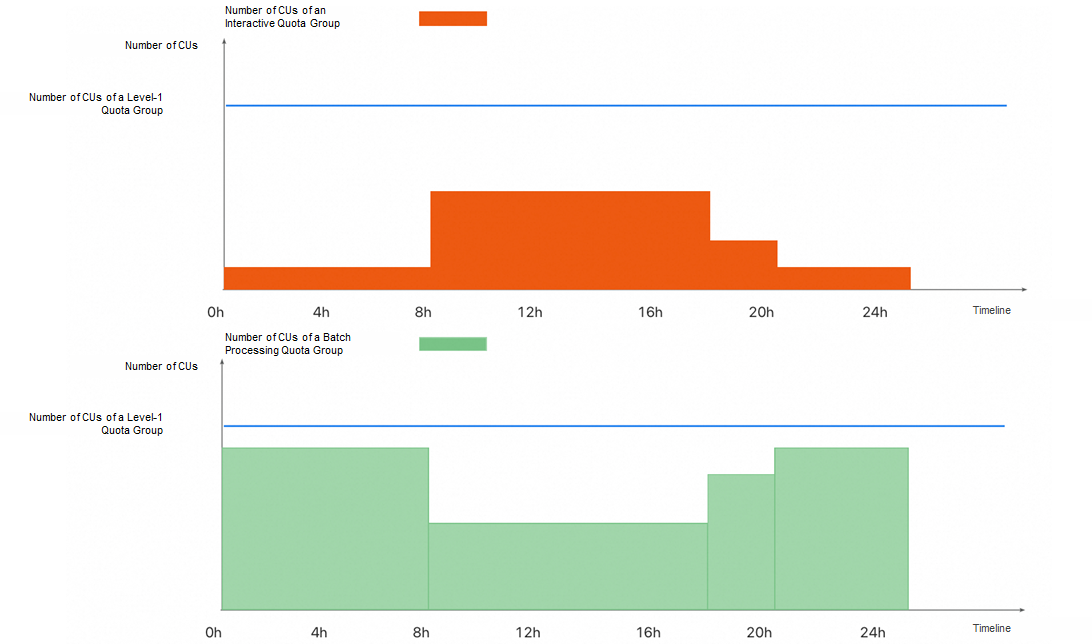
A scheduled scaling plan is suitable for scenarios in which purchased subscription quota groups have sufficient CUs. Flexibly adjusting resource allocation within different periods of time improves the overall resource utilization.
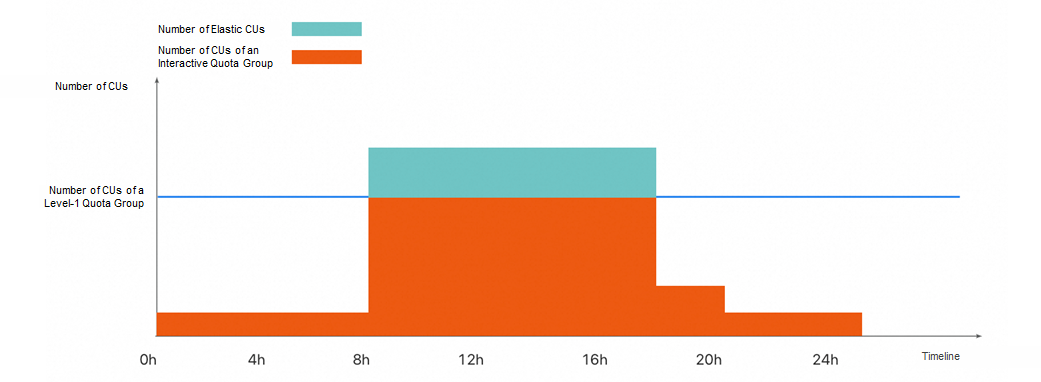
If CUs are insufficient but there are higher resource requirements within specific periods of time, you can use the elastic CU feature. You can use the feature to automatically and dynamically increase CUs within the specified period of time. You are only charged for the temporarily generated CUs. This meets the computing requirements during peak hours without increasing long-term costs as well as balances the flexibility and economy of resource usage.
As shown in the following figure, the blue line indicates the number of CUs of a purchased subscription level-1 quota group. The orange square indicates the CU quota of an interactive quota group, whereas the cyan square indicates the number of elastic CUs. After an elastic scaling policy with a preset period of time is configured, the system automatically generates elastic CUs at the specified point of time and adjusts the overall resource allocation. This implements flexible scheduling and on-demand increase of resources within different periods of time.
Both the scheduled scaling and elastic CU features depend on the effective time period that you configure in advance. Unexpected business growth requirements may fail to be responded in a timely manner due to insufficient reserved resources, resulting in task accumulation and queuing.
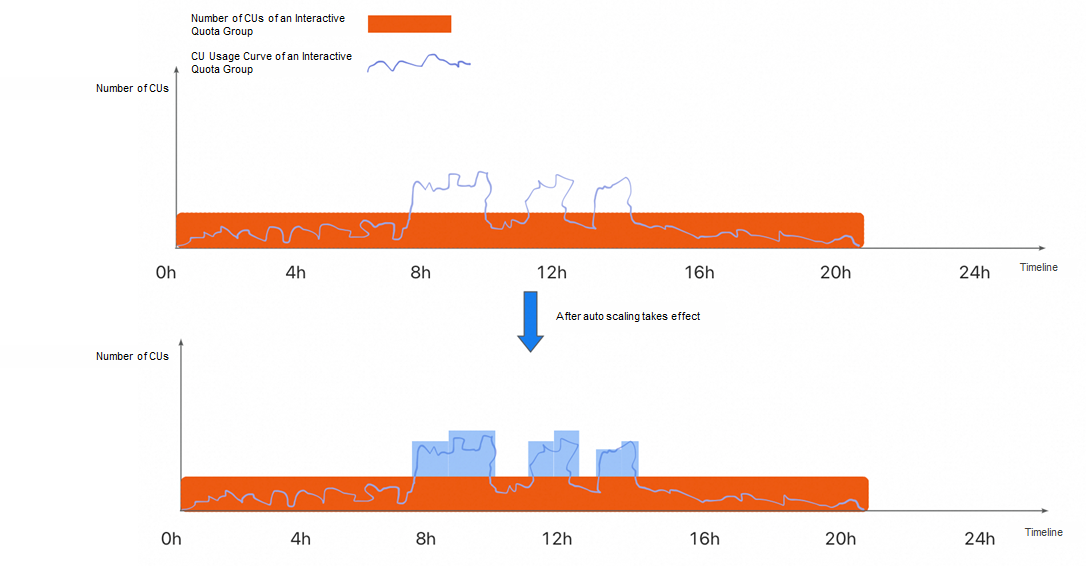
To resolve the preceding issues, the auto scaling feature is introduced. You can use this feature to detect load changes in MaxQA instances in real time and automatically trigger resource scaling based on the preset scaling rule. This helps you quickly respond to unexpected resource requirements. You are charged based on the actual usage duration of CUs. This implements on-demand increase of resources and precise cost control while ensuring the stability and timeliness of job execution.
As shown in the following figure, the CU usage curve does not exceed the maximum CU of the interactive quota within most periods of time. However, within some specific periods of time, the CU usage obviously increases and exceeds the current quota. After the auto scaling feature is used, the system automatically generates CU resources during peak hours to meet unexpected resource requirements.
✅ Note: The auto scaling feature is not available now and will be coming soon.
MaxQA helps GoTerra smoothly migrate multiple business lines from GCP BigQuery to MaxCompute. Throughout the migration process, GoTerra users have zero awareness of underlying architecture changes. Business continuity is not affected by the migration, and the experience remains stable.
After MaxQA is used, the performance of GoTerra's core business scenarios is significantly improved. The overall query efficiency is doubled. This demonstrates the technical advantages of MaxQA in high performance, low latency, and high stability. This also reflects the implementation capabilities and user experience assurance capabilities of MaxQA in large-scale and complex business migration.
In terms of performance improvement, MaxQA will upgrade the multi-threaded pipeline architecture of the execution engine and use parallel processing and pipeline processing of tasks to significantly improve the query efficiency and resource utilization. Scheduling overheads are further reduced. MaxQA better meets the business requirements of high concurrency and low latency.
In terms of stability assurance, MaxQA will build the capability of proactively identifying abnormal jobs and isolate abnormal jobs in a timely manner after they are detected. This prevents the abnormal jobs from affecting the availability of all MaxQA instances. In addition, MaxQA will support the transparent fallback mechanism. If an exception occurs, MaxQA automatically switches the abnormal task to a serverless resource pool. This minimizes the impacts on user business continuity and job performance.
In terms of intelligent optimization, MaxQA will introduce the intelligent data prefetching feature. This feature allows you to load hot data to the cache in advance based on the historical status of jobs in the MaxQA instance. At the same time, the system will improve the recognition accuracy of shuffled data cache and efficiently utilize distributed cache resources to reduce I/O pressure and improve the overall execution efficiency.
With these continuous optimization items, MaxQA will not only improve the query performance and system robustness, but also provide users with more intelligent, efficient, and stable all-in-one big data query experience, thereby helping enterprises achieve more agile data-driven decision-making.

1,333 posts | 466 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - October 17, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - October 20, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - October 17, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - October 17, 2025
Alibaba Cloud MaxCompute - June 25, 2024
Alibaba Cloud MaxCompute - September 30, 2022

1,333 posts | 466 followers
Follow Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Alibaba Cloud provides big data consulting services to help enterprises leverage advanced data technology.
Learn More MaxCompute
MaxCompute
Conduct large-scale data warehousing with MaxCompute
Learn More Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Alibaba Cloud experts provide retailers with a lightweight and customized big data consulting service to help you assess your big data maturity and plan your big data journey.
Learn More Hologres
Hologres
A real-time data warehouse for serving and analytics which is compatible with PostgreSQL.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Community