By Jing Cai, Kun Wu and Yi Chen
In the cloud-native era, an increasing number of users are using multiple Kubernetes clusters to support their business operations. This shift is driven by factors such as global business spread (even reaching the upper limit of a single cluster), the urgent need for disaster recovery, and security compliance requirements. When deploying applications in Kubernetes clusters, administrators usually reserve considerable resource buffers to deal with load fluctuations - a practice aimed at ensuring application reliability. However, this leads to a persistent gap where the requested resources of containers far exceed actual usage, resulting in low cluster resource utilization. In this case, we often run offline tasks across multiple clusters to improve resource utilization. Yet, critical challenges remain, including how to determine which cluster has sufficient resources, the cluster to which the offline task is scheduled, and how to ensure that offline tasks do not affect running online services.
Spark is a widely used distributed computing framework in the big data and AI fields. ACK One's AI job scheduling across clusters supports scheduling and distributing Spark jobs in multiple clusters. Combined with the colocation of ACK Koordinator, it can solve the preceding challenges. On the premise of not disrupting running online services, it intelligently schedules Spark jobs based on the actual available resources in each cluster, maximizing the utilization of idle resources in multiple clusters.
Alibaba Cloud Distributed Cloud Container Platform (ACK One) is an enterprise-class cloud-native container platform that is developed by ACK to meet container management requirements in hybrid cloud, multi-cluster, distributed computing, and disaster recovery scenarios. It provides unified multi-cluster management capabilities. Through ACK One registered clusters, you can connect your Kubernetes clusters from other public cloud service providers and in data centers to the Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes console. Then, the Fleet instance enables unified multi-cluster management for these registered clusters as well as ACK and ACK Edge clusters, including application distribution, traffic management, observable O&M management, and security management.
ACK One multi-cluster AI job scheduling and distribution provides the job distribution feature for multi-cluster and hybrid cloud scenarios, enabling centralized scheduling and distribution of AI workloads. When a single Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster fails to meet the resource requirements for large-scale AI training or inference tasks, or when there are idle resources across multiple ACK clusters, this feature lets you distribute jobs across these clusters to optimize resource utilization. ACK One multi-cluster job distribution offers the following capabilities:
1. Multiple-job type support: Compatible with PyTorchJob, SparkApplication, and TFJob.
2. Multi-cluster gang scheduling: Distribute jobs across clusters through resource pre-allocation or dynamic resource checks, ensuring successful task deployment to sub-clusters and improving overall scheduling efficiency.
3. Multi-tenant quota management: Enforce resource limits per tenant using ElasticQuotaTree-based namespace quotas in multi-tenant environments.
4. Priority-based scheduling: Prioritize important tasks for resource allocation based on PriorityClass defined in PodTemplate for AI jobs.
5. Multiple task queuing policy configuration: Allow for flexible queue policies to support cluster utilization optimization and task priority guarantee modes, supporting both blocking and non-blocking scheduling patterns.
6. Job rescheduling on failure: The Global Scheduler automatically reclaims failed jobs and reschedules them to eligible clusters with sufficient resources.
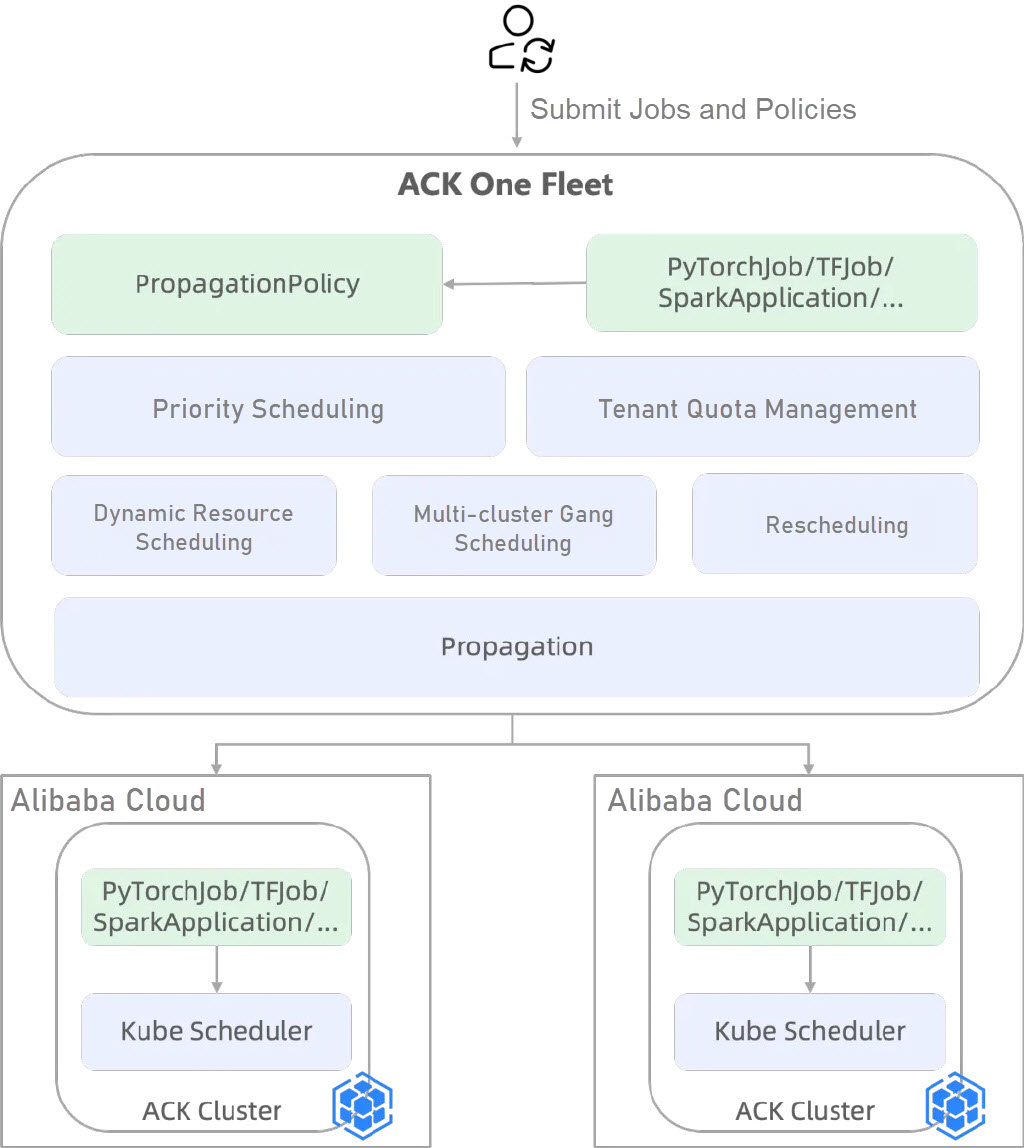
The specific process is as follows:
The following features are required when you use idle resources to schedule and distribute a Spark job in multiple clusters:
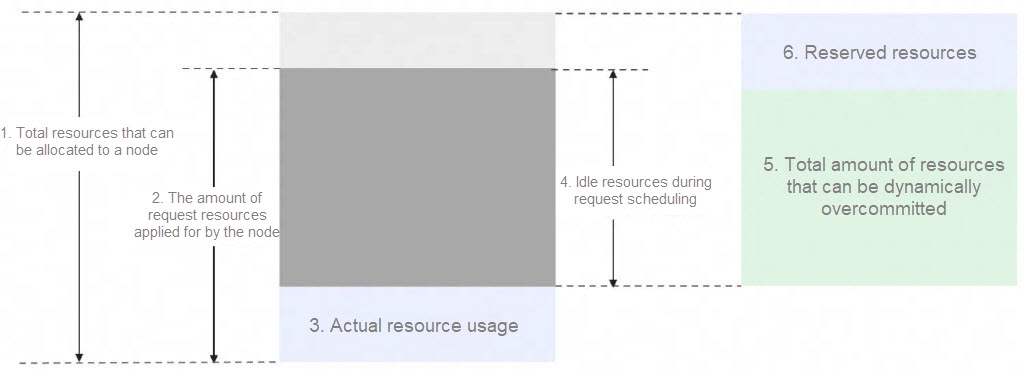
Scheduling based on idle resources in a single ACK cluster is the dynamic resource overcommitment of ACK Koordinator. ACK Koordinator introduces the Batch concept to describe idle resources and records them on nodes through the Extended Resource of Kubernetes. As shown in the following figure, when scheduling with the default Request-based scheduler, area 4 remains idle, and the newly schedulable resources are only the light gray part at the top. However, scheduling based on Koordinator's Batch resources can make full use of idle resources (areas 5 + 6). To improve performance, Koordinator allows configuring a certain percentage of reserved resources. For more information, see Enable dynamic resource overcommitment.
Leveraging ACK Koordinator's colocation capability, ACK Spark Operator allows you to convert the resources required by the SparkApplication driver and executor into Koordiantor's Batch resources based on specific annotations. They are scheduled based on Batch resources when ACK Scheduler schedules pods.
From the multi-cluster perspective, the Global Scheduler of the Fleet instance dynamically monitors idle resources of sub-clusters when scheduling jobs in multiple clusters. The Spark job checks whether the Batch resources of each sub-cluster are sufficient for the resources required by the driver and executor according to the corresponding annotation, and determines the optimal target cluster for job distribution in combination with the multi-cluster gang scheduling of Global Scheduler. For sub-clusters whose Kubernetes version is 1.28 or later, the Fleet instance supports resource preoccupation to improve the success rate of Spark job scheduling. At the same time, the Fleet instance watches the running status of the Spark job in sub-clusters. If the driver cannot be run due to insufficient resources, the Fleet instance reclaims the SparkApplication after a specific period of time and reschedules SparkApplication to other sub-clusters that have sufficient resources.
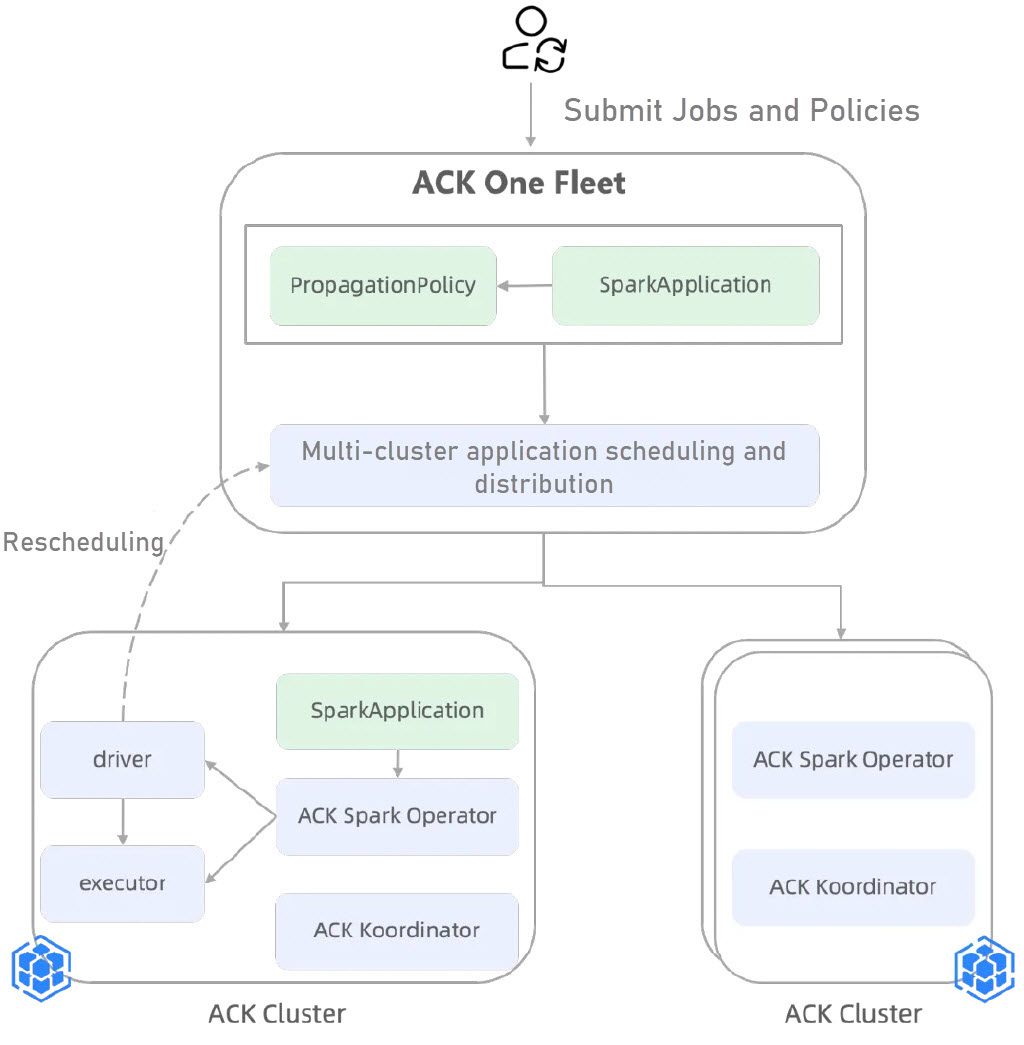
The following steps are required when you use idle resources to schedule and distribute a Spark job in multiple clusters:
1. Prepare the environment.
2. Create SparkApplication and PropagationPolicy for the Fleet instance. The multi-cluster scheduling component (Global Scheduler) of the Fleet instance matches Spark job resource requests based on the remaining resources of each associated sub-cluster. For sub-clusters whose Kubernetes version is 1.28 or later, the Fleet instance supports resource preoccupation to improve the success rate of Spark job scheduling.
3. After the Fleet instance schedules jobs, SparkApplication is scheduled and distributed to the associated clusters.
4. If the job fails, Global Scheduler will reclaim the job and reschedule it to other qualified clusters with sufficient resources.
In addition, through PriorityClass lowering the priority of the Spark job and ACK Koordinator's native QoS capabilities, running the Spark job never compromises the normal operation of online services in the corresponding cluster.
In summary, multi-cluster Spark job scheduling and distribution provided by ACK One helps you break through the resource limits and schedule the Spark job based on the idle resources of each cluster without affecting the online services that are running in the cluster. This maximizes the utilization of idle resources in your multiple clusters. ACK One also supports multi-cluster scheduling for other AI job types such as PytorchJob and TFJob. For more information, see Best practices of multi-cluster Spark scheduling based on idle resources and ACK One multi-cluster AI job scheduling and distribution.

229 posts | 33 followers
FollowAlibaba Container Service - February 25, 2026
Alibaba Container Service - November 21, 2024
Alibaba Container Service - December 5, 2024
Alibaba Container Service - April 8, 2025
Alibaba Container Service - November 15, 2024
Alibaba Container Service - February 25, 2026

229 posts | 33 followers
Follow Container Compute Service (ACS)
Container Compute Service (ACS)
A cloud computing service that provides container compute resources that comply with the container specifications of Kubernetes
Learn More Container Service for Kubernetes
Container Service for Kubernetes
Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes is a fully managed cloud container management service that supports native Kubernetes and integrates with other Alibaba Cloud products.
Learn More EasyDispatch for Field Service Management
EasyDispatch for Field Service Management
Apply the latest Reinforcement Learning AI technology to your Field Service Management (FSM) to obtain real-time AI-informed decision support.
Learn More Conversational AI Service
Conversational AI Service
This solution provides you with Artificial Intelligence services and allows you to build AI-powered, human-like, conversational, multilingual chatbots over omnichannel to quickly respond to your customers 24/7.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Container Service