This topic describes how to connect a Spring Boot application to SchedulerX, including how to create a SchedulerX application, configure the necessary connection parameters, configure an agent within a Spring Boot project, and verify the connection. This ensures that your Spring Boot application runs as expected in SchedulerX and implements automatic scheduling and precise management of jobs.
Prerequisites
Optional. A namespace is created. If your Spring Boot application requires high security, you can create a namespace to isolate the resources and services of the application from other applications. For more information, see the "Create a namespace" section of the Namespace management topic.
A Spring Boot project is created.
Overview
To connect a Spring Boot application to SchedulerX, perform the following steps:
Create a SchedulerX application: Create an application in SchedulerX, obtain the parameters for connecting to SchedulerX, and implement centralized job management and configuration.
Connect your Spring Boot application to SchedulerX using an agent: In the .properties or .yml file of your Spring Boot project, configure the parameters required by SchedulerxWorker and create a JobProcessor class to connect the Spring Boot application to the specified SchedulerX application.
Verify the result: Verify that the Spring Boot application is connected to SchedulerX and runs as expected.
Step 1: Create a SchedulerX application
1.1 Basic configuration
Log on to the MSE SchedulerX console, and select a region in the top navigation bar.
On the Application Management page in the left navigation bar. Select the target Namespace, and click Create Application. Enter the Application Name and Application ID, select the Application Type, configure advanced settings as needed, and click Next.
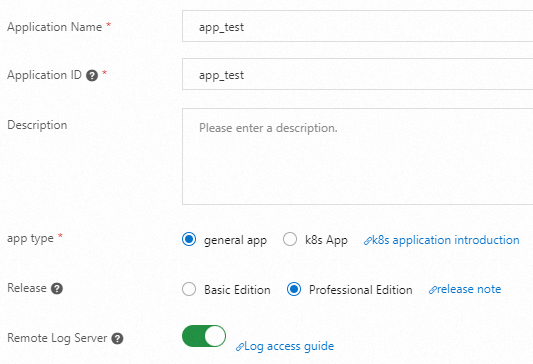 Important
ImportantMake sure that resources are created in the selected region and namespace and the resource information is valid.
Configuration item
Description
Default value
Application Name
Customize the application name.
None
Application ID
The Application ID is the GroupID for application access. It must be unique within the same namespace. Otherwise, the creation fails. It can be the same as the Application Name.
None
Application Type
Regular App: Select this option if the application is not deployed in a Kubernetes cluster or does not require Kubernetes jobs.
k8s App: Select this option if you want to deploy the application in a Kubernetes cluster and require Kubernetes jobs.
Regular App
Edition
Select an edition based on your requirements.
Professional Edition
Simple Log Service
If you enable this feature, add a Log4j or Logback configuration. Then, you can view the scheduling logs of jobs, including distributed jobs, in the console for troubleshooting.
Off
load5
The value cannot be greater than the number of CPU cores available on the client machine.
0
Memory Usage
If the average memory usage within the previous 5 minutes exceeds the threshold that is specified by this parameter, the worker is considered busy.
90%
Disk Usage
If the disk usage exceeds the threshold that is specified by this parameter, the client machine is considered busy.
95%
Trigger Busy Machine
Specify whether to continue to trigger job execution when the machine is busy.
On
Advanced Configuration
Maximum Number Of Jobs
Specify the maximum number of jobs that are supported in a group.
1000
Automatic Scale-out
Specify whether to enable automatic scale-out. If you enable this feature, you need to set Global Job Count.
Off
Traffic Throttling
Specify whether to enable traffic throttling. If you enable this feature, you need to set Task Instance Concurrency.
Off
Calendar
You can select Financial Day or Workday from the drop-down list to schedule the application.
Financial day: a trading day for financial business.
Workday: a day of normal work or operations for a society, organization, or individual.
0
1.2 Notification configuration
On the Notification Configuration wizard page, enter the relevant information, select a Notification Channel, and set Contacts.
The Notification Channel supports Text Message, Email, Webhook, and Phone.
For more information about Webhook configuration, see Webhook configuration description.
Notification Contacts supports two methods: contact groups and contacts.
Contact Group
All contacts in the contact group can receive notifications. For more information about how to create a contact group, see Create a notification contact or notification contact group.
Contact
Added contacts can receive notifications. You can add multiple contacts at a time. After you Add Contact, click Go To Create Contact.
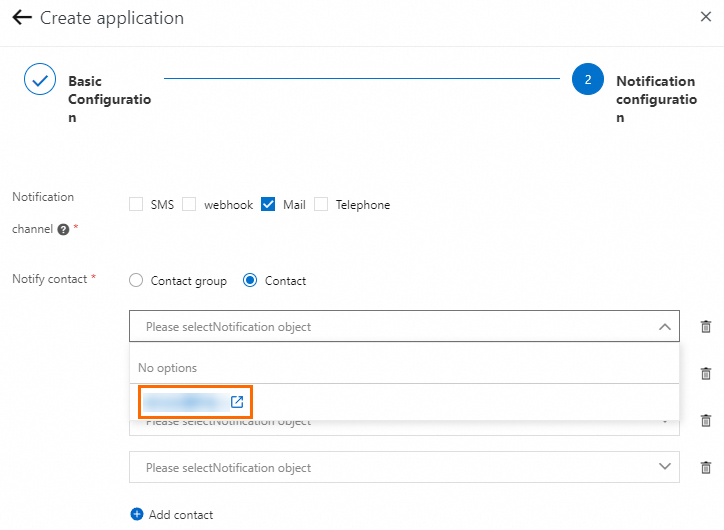
In the dialog box that appears, click Create Contact, and enter the contact information.

Configuration item
Description
Notification Channel
The following notification channels are supported: Text Message, Email, Webhook, and Phone.
Email
Enter the email address of the contact.
Webhook
Enter the webhook URL that you want to use. WeCom, Lark, and DingTalk are supported. You can also specify multiple webhook robots at a time. Separate multiple robot links with commas (,).
You need to add the keyword "SchedulerX" (case-sensitive) to the DingTalk robot. Otherwise, you cannot receive alert information.
For more information about how to obtain a webhook URL, see DingTalk Developer Documentation, WeCom Developer Documentation, and Lark Developer Documentation.
Mobile Phone Number
Enter the mobile phone number of the contact.
Verification
Refresh the page and select the specified region and namespace. Then, view the information about the created application.
Step 2: Connect a Spring Boot application to SchedulerX using an agent
Add the required dependency to the pom.xml file.
Add the required SchedulerxWorker dependency to the pom.xml file of your Spring Boot application to allow the Spring Boot application to use the features provided by SchedulerX.
NoteSchedulerX supports Spring Boot 2.x and 3.x applications.
<dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun.schedulerx</groupId> <artifactId>schedulerx2-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>${schedulerx2.version}</version> <!-- If you use Logback, you must exclude Log4j and Log4j 2. --> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId> </exclusion> <exclusion> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId> </exclusion> <exclusion> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>ImportantReplace <version>${schedulerx2.version}</version> with the latest agent version. Example: <version>1.11.5</version>. For more information, see Agent release notes.
Configure parameters.
In the application.properties configuration file of the Spring Boot application, add the parameters required by SchedulerxWorker, such as connection information and authentication information. Such parameters are required for the Spring Boot application to connect to the SchedulerX application.
spring.schedulerx2.endpoint=${endpoint} spring.schedulerx2.namespace=${namespace} spring.schedulerx2.groupId=${groupId} # The appKey parameter is supported only in versions 1.2.1 and later. spring.schedulerx2.appKey=${appKey} # If you do not use an appKey, you can use an Alibaba Cloud AccessKey and SecretKey, or an STS token. #spring.schedulerx2.aliyunAccessKey=${aliyunAccessKey} #spring.schedulerx2.aliyunSecretKey=${aliyunSecretKey} #spring.schedulerx2.stsToken=${aliyunStsToken}Parameter sources:
Log on to the SchedulerX console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Applications. On the Applications page, find the application that you want to manage and click AccessConfig in the Operation column. In the AccessConfig panel, select Spring Boot from the drop-down list.
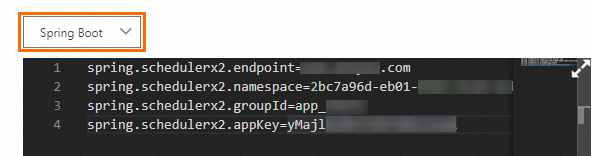 Important
ImportantCheck whether SchedulerX and the agent are in the same region. If not, the agent fails to connect to SchedulerX.
If your Spring Boot application runs on a non-Alibaba Cloud server or in an on-premises environment, make sure that you have enabled Internet access to the Spring Boot application and created a SchedulerX application in the Internet region. For more information, see Connect to SchedulerX over the Internet from an on-premises environment.
NoteIf your client application contains multiple services or you need to isolate scheduled tasks for permission management, you can create multiple applications in the console to achieve fine-grained management. For example, for a client application named
animals, you can create two applications in the console: animals.dog and animals.cat. You do not need to request separate workers for these two applications. You only need to configurespring.schedulerx2.groupId=${groupId}in the application.properties configuration file and list the application names separated by commas. For example:spring.schedulerx2.groupId=animals.dog,animals.cat.Parameter description:
endpoint: the endpoint of SchedulerxWorker. The value of this parameter must match the endpoint of the region in which your application is deployed. For more information, see Endpoints.
namespace: the ID of the namespace to which the application belongs. You can view the namespace ID on the Namespaces page of the SchedulerX console.
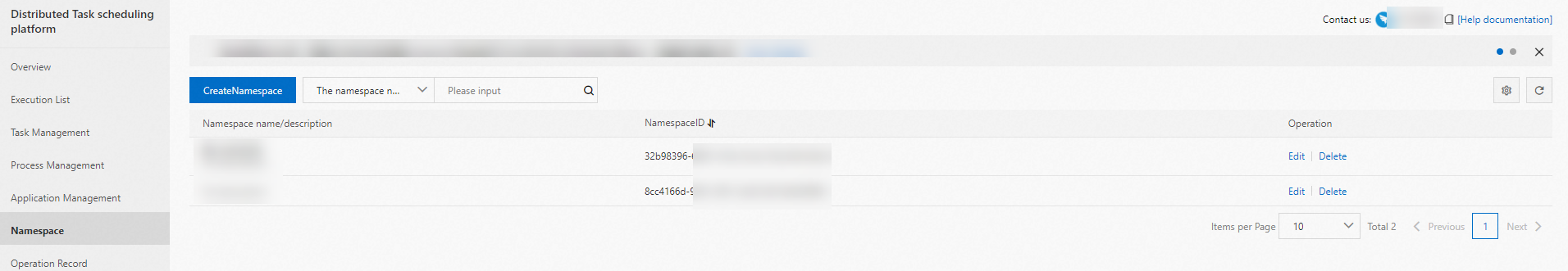
groupId and appKey: the ID and key of the application. You can view the values on the Applications page of the SchedulerX console.
aliyunAccessKey and aliyunSecretKey: the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of your Alibaba Cloud account. You can view the AccessKey pair on the Security Management page of the User Management console.
The following table describes the parameters that you can configure as needed.
key
Description
Value
Initial version
spring.schedulerx2.enabled
Specifies whether to enable the starter of SchedulerX 2.0. Default value: true. You do not need to configure this parameter.
true
false
0.1.7
spring.schedulerx2.endpoint
The endpoint of the specified region. For more information, see Endpoints.
N/A
0.1.7
spring.schedulerx2.namespace
The UID of the namespace. You can view the namespace UID on the Namespaces page of the SchedulerX console.
N/A
0.1.7
spring.schedulerx2.groupId
The ID of the application. You can view the application ID on the Applications page of the SchedulerX console.
N/A
0.1.7
spring.schedulerx2.appKey
The key of the application. You can view the application key on the Applications page of the SchedulerX console.
N/A
1.2.1
spring.schedulerx2.host
The actual IP addresses if multiple IP addresses exist. Multiple IP addresses may exist if the agent uses a VPN or multiple network interface cards (NICs).
N/A
0.1.7
spring.schedulerx2.port
The port on which the agent listens. If you do not specify a port, the system randomly selects an available port.
N/A
0.1.7
spring.schedulerx2.blockAppStart
Specifies whether to block the startup of the application if SchedulerX fails to complete the initialization. Default value: true.
true
false
1.1.0
spring.schedulerx2.shareContainerPool
Specifies whether to allow all jobs on agents to share the thread pool. Default value: false.
true
false
1.2.1.2
spring.schedulerx2.sharePoolSize
The size of the thread pool if you allow all jobs to share the pool. Default value: 64.
N/A
1.2.1.2
spring.schedulerx2.label
The labels. You can add labels to agents so that you can use labels to specify workers for job management. This feature is suitable for canary release and stress testing scenarios.
N/A
1.2.2.2
spring.schedulerx2.enableCgroupMetrics
Specifies whether to use the cgroup to collect the metrics of an agent. Default value: false. You must manually enable this feature in a Kubernetes environment.
true
false
1.2.2.2
spring.schedulerx2.cgroupPathPrefix
The path of the cgroup in the container.
The default path is /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/. If the path already exists, you do not need to configure this parameter.
1.2.2.2
spring.schedulerx2.enableHeartbeatLog
Specifies whether to display heartbeat logs in the ${user.home}/logs/schedulerx/heartbeat.log file.
Default value: true.
true
false
1.2.4
spring.schedulerx2.mapMasterStatusCheckInterval
The interval at which SchedulerX checks whether all tasks are complete in the Map model. Unit: milliseconds. If you want to increase the scheduling frequency of second-granularity jobs, configure this parameter.
3000
1.2.5.2
spring.schedulerx2.enableSecondDelayCycleIntervalMs
Specifies whether to enable millisecond precision for second-granularity jobs. Default value: false. If you set this parameter to true, the scheduling interval specified in the console for second-granularity jobs is interpreted in milliseconds instead of seconds. This increases the scheduling frequency of your jobs.
true
false
1.2.5.2
spring.schedulerx2.broadcastMasterExecEnable
Specifies whether the primary node is required to run a broadcast job. Default value: true.
true
false
1.8.13
spring.schedulerx2.broadcastDispatchRetryTimes
The maximum number of retries after broadcasting fails. By default, no retry is performed. The retry interval is fixed to 2 seconds.
3
1.8.13
spring.schedulerx2.enableSecondDelayStandaloneDispatch
Specifies whether to enable dispatching of second-granularity standalone jobs. Default value: false.
true
false
1.8.13
Create a JobProcessor class
Create a JobProcessor class in the Spring Boot application to enable job scheduling.
The following sample code shows how to schedule a simple JobProcessor class to periodically display a message. In this example, the message
hello schedulerx2.0is displayed.package com.aliyun.schedulerx.test.job; import com.alibaba.schedulerx.worker.domain.JobContext; import com.alibaba.schedulerx.worker.processor.JavaProcessor; import com.alibaba.schedulerx.worker.processor.ProcessResult; @Component public class MyHelloJob extends JavaProcessor { @Override public ProcessResult process(JobContext context) throws Exception { System.out.println("hello schedulerx2.0"); return new ProcessResult(true); } }
Step 3: Verify the result
Log on to the Microservices Engine (MSE) console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Task Scheduling > SchedulerX Version. On the SchedulerX Version page, click Applications in the left-side pane. Then, find the application that you want to manage and click View instances in the Operation column.

If the Total number of instances column displays 0, the application fails to connect to SchedulerX. Check and modify the on-premises application.
If the Total number of instances column displays an integer other than 0, the application is connected to SchedulerX.
What to do next
After the Spring Boot application is connected to SchedulerX, you can create jobs in the SchedulerX console. For more information, see the "Create a job" section of the Job management topic.
FAQ
For more information about how to handle alerts when you use SchedulerX, see FAQ about alerts.
For more information about how to connect Spring jobs to SchedulerX, see FAQ about Spring jobs.
For more information about the permission and connection issues of SchedulerX, see FAQ about permissions and FAQ about connections.
References
For more information about other methods for connecting an application to SchedulerX using an agent, see Connect an agent to SchedulerX.