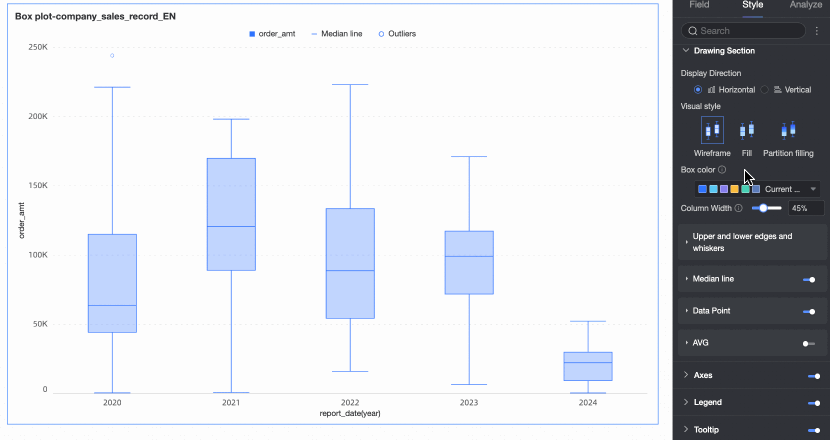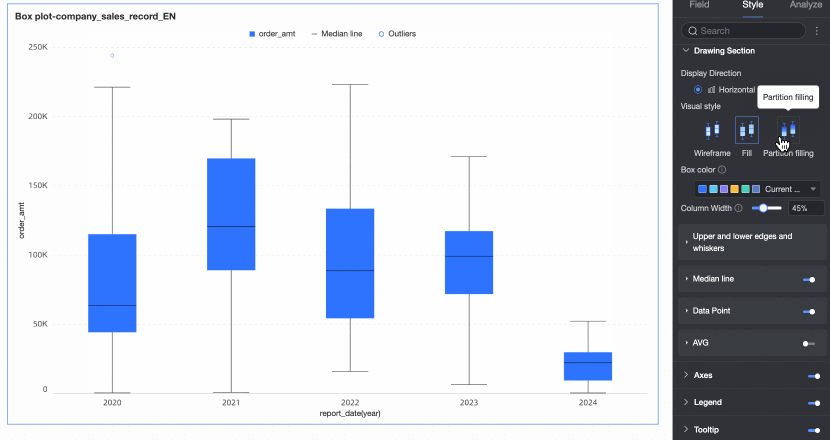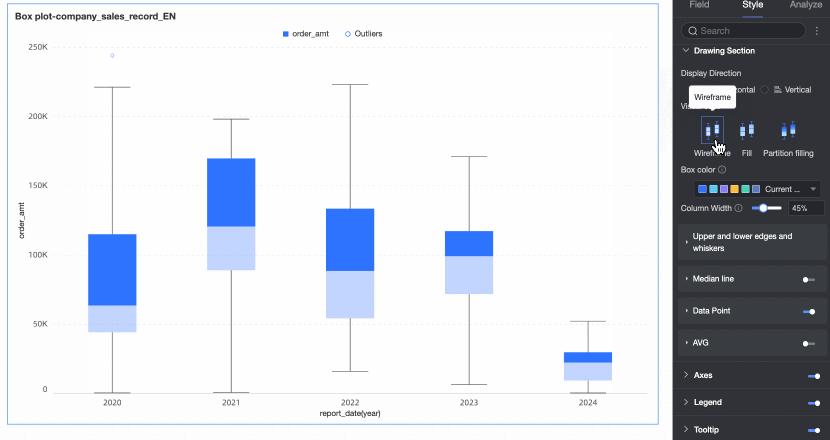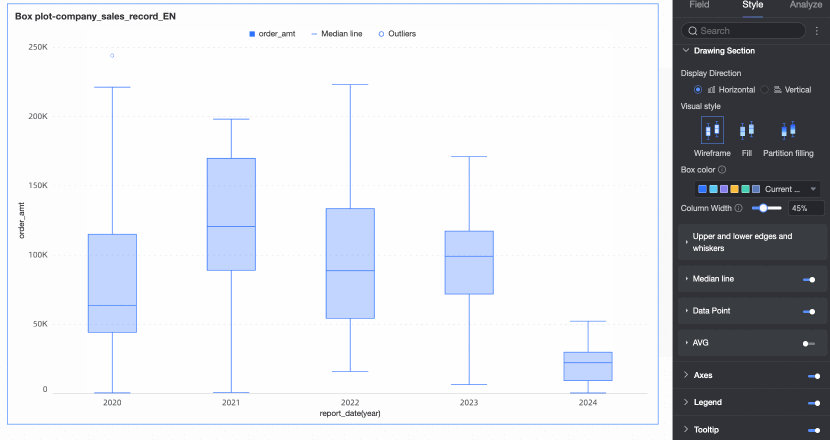
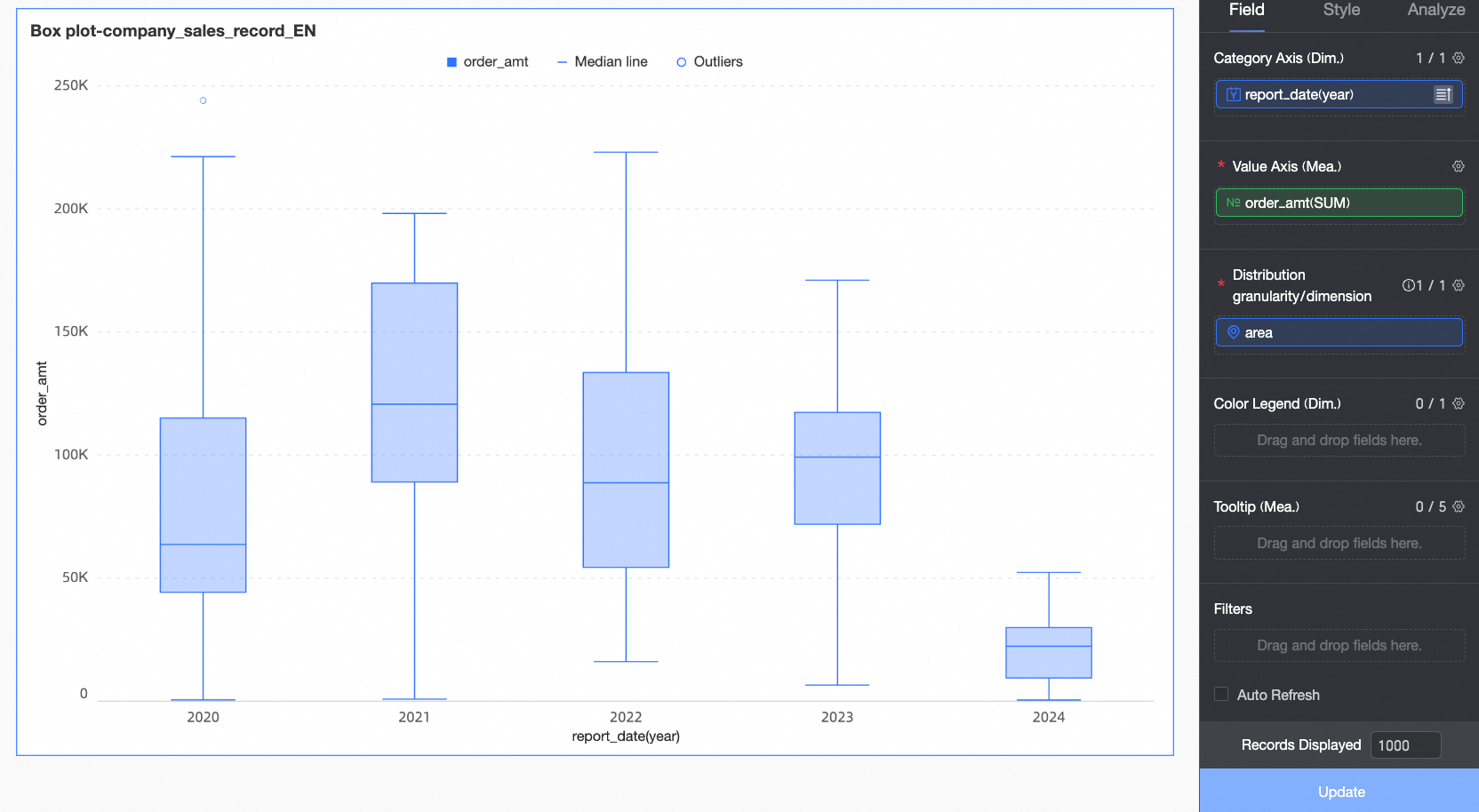
A box plot is a graphical representation used to show the distribution of one or more sets of continuous data. It is effective for visualizing data skewness and identifying outliers. This topic explains how to populate a box plot with data and tailor its appearance.
Prerequisites
You have created a dashboard. For more information, see Create a dashboard.
Overview of the Chart
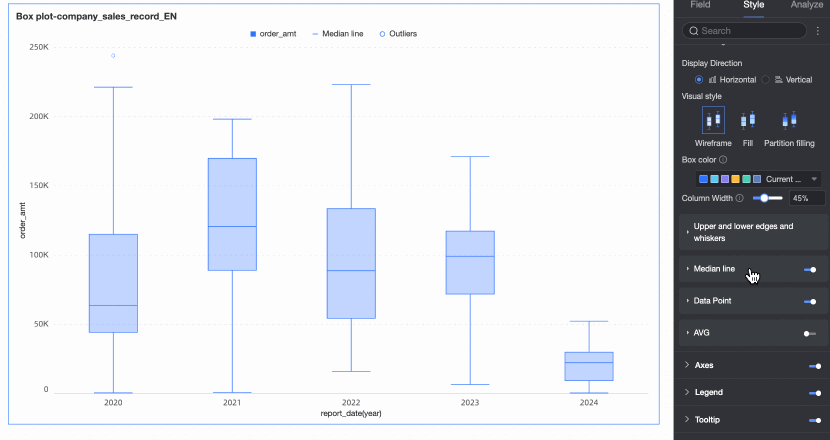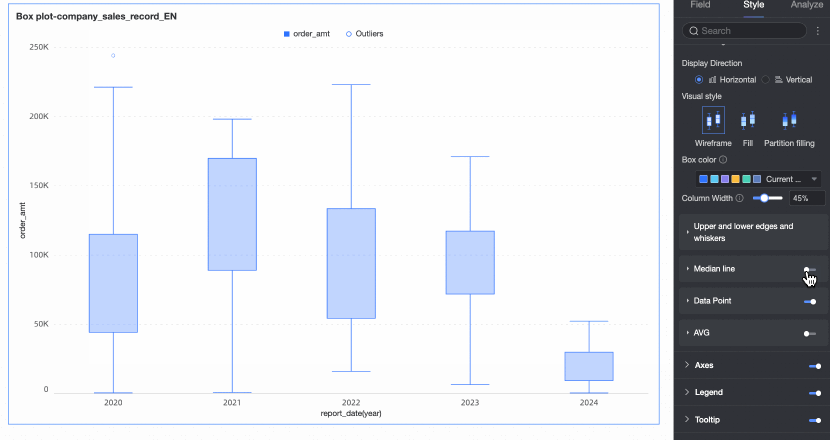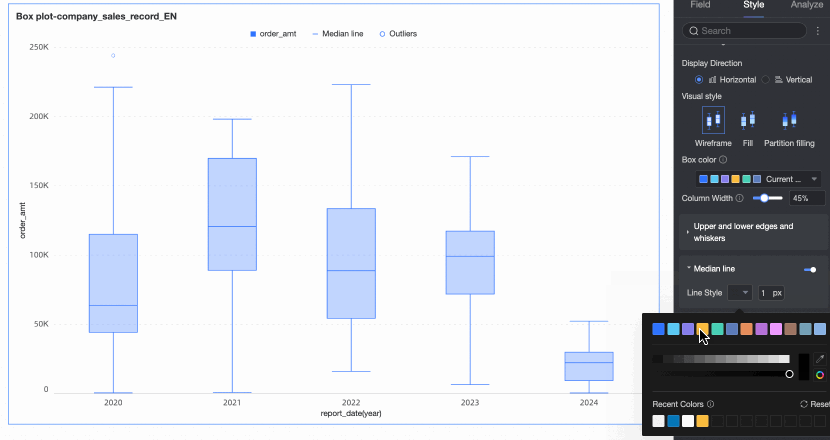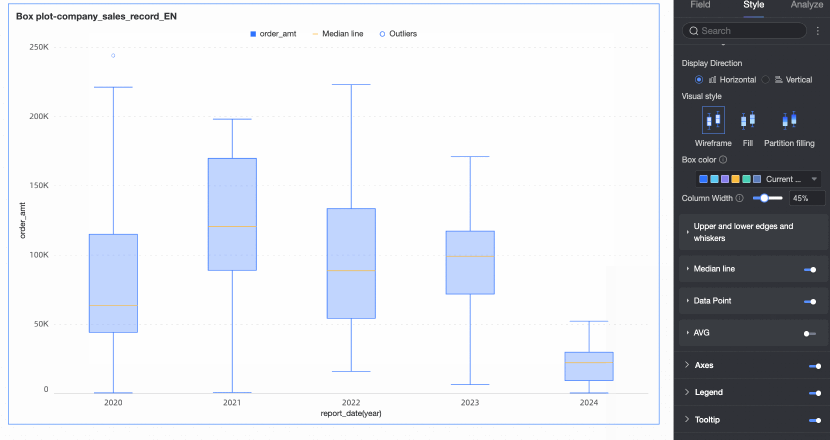
A box plot employs six key elements-upper whisker, upper quartile, median, lower quartile, lower whisker, and outliers-to characterize data distribution. It offers a clear view of data distribution trends. 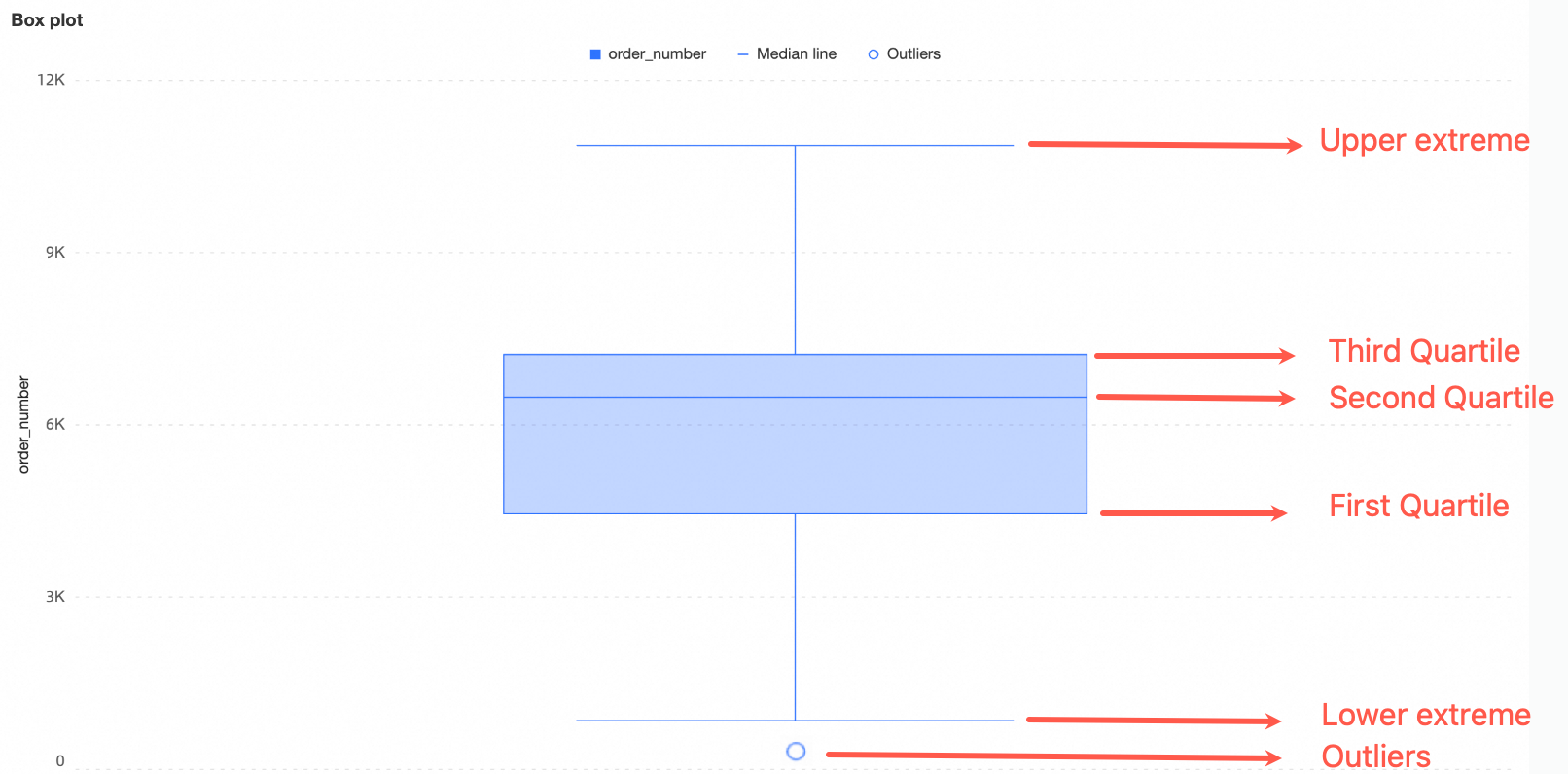
Upper and lower whiskers: Indicate the data distribution range. For details on how these values are calculated, refer to Calculation methods for upper and lower whiskers later in this topic.
Upper quartile (Q3): The value above which lies the top 25% of the data.
Median: The middle value of the dataset, above which lies half of the data.
Lower quartile (Q1): The value above which lies the bottom 25% of the data.
Outliers: Data points below
Q1-1.5IQRor aboveQ3+1.5IQRare considered outliers.
Scenarios
Box plots are commonly used in scenarios such as:
Analyzing data distributions, for example, comparing salary levels across regions or temperature variations in different areas.
Detecting outliers, such as in the audit of monetary transactions to spot anomalies.
Quality control, ensuring product quality consistency by monitoring the distribution of product attributes.
Assessing central tendency and skewness, for example, analyzing regional sales to gauge average performance and variability.
Advantages
Computing power: Offers various methods for calculating whiskers and advanced computational features like cumulative calculations, year-over-year and month-over-month comparisons, TopN analysis, and the addition of intelligent auxiliary lines.
Visualization: Enables style adjustments for enhanced visual clarity, including the addition of legends, thumbnail axes, tooltips, and other auxiliary elements.
Data comparison and annotation: Facilitates comparative analysis across different dimensions and allows for customized annotations and endnotes.
Annotation capability: You can customize remarks and endnote information, and configure jumps to external path links to enable interaction between data and other systems.
Interactive Operations: This encompasses filtering by dimension/measure and within-table filtering.
Example of the Effect
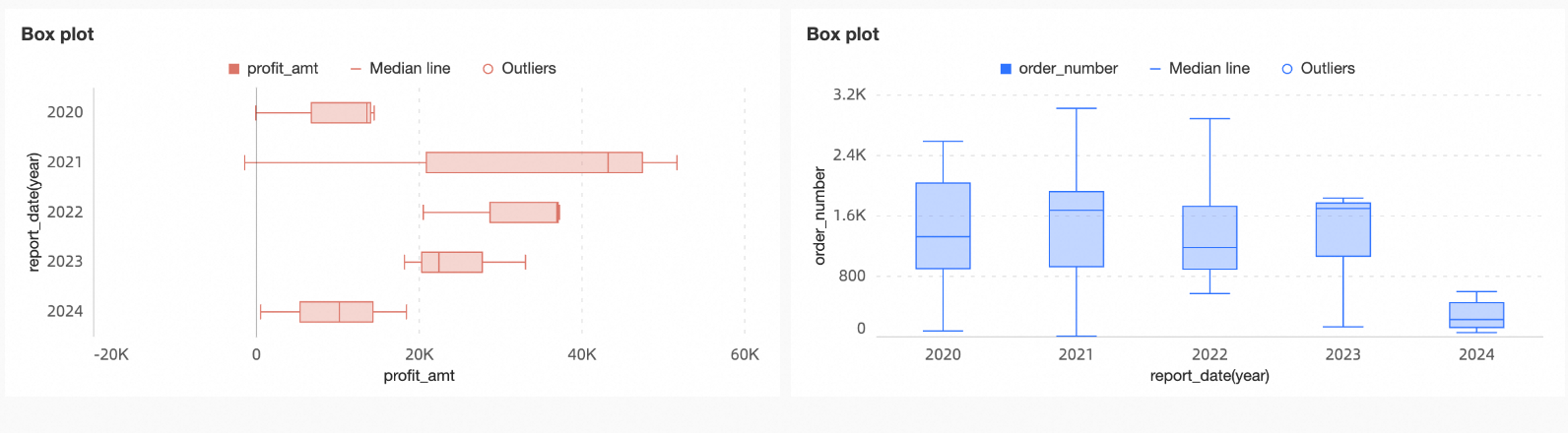
From a box plot, you can discern information such as:
Central tendency: Indicated by the median value in the chart.
Dispersion: Shown by the length of the box, representing the concentration and spread of the data.
Skewness: Evident from the distance between the box and the whiskers, indicating the direction of data skew.
Outliers: Highlighted by the points that fall outside the whiskers.
Range: The span of the whiskers and the distribution of data points show the overall spread of the data.
Configure Chart Fields
This section uses the example of analyzing annual order amounts to illustrate field configuration.
In the Data panel, select the desired dimension and measure fields. Double-click or drag them to the appropriate areas under the Fields tab.
In the Category axis/Dimension section, set the dimensions for data comparison according to your analysis requirements.
For instance, drag the report_date(year) field to compare annual order amounts.
In the Value axis/Measure section, select the primary metric for chart analysis.
Here, drag the Order Amount field as the main metric for analysis.
In the Distribution granularity/Dimension section, set the granularity for analysis, which will determine the data points and form the basis for the box plot calculations.
In this example, drag the Region field to examine order amount distributions across regions.
To further refine comparison dimensions, add additional dimension fields to the Color legend/Dimension section as needed. This will split the chart based on the field's values, allowing for more granular analysis, such as annual profit by product type.
This example does not use this field.
NoteYou can drag the same field into both the Category axis and Color legend areas to assign colors based on different dimension values. The implementation effects in different scenarios are as follows:
When there is only one field in both the Category axis and Value axis, the number of columns equals the number of dimension values on the category axis.
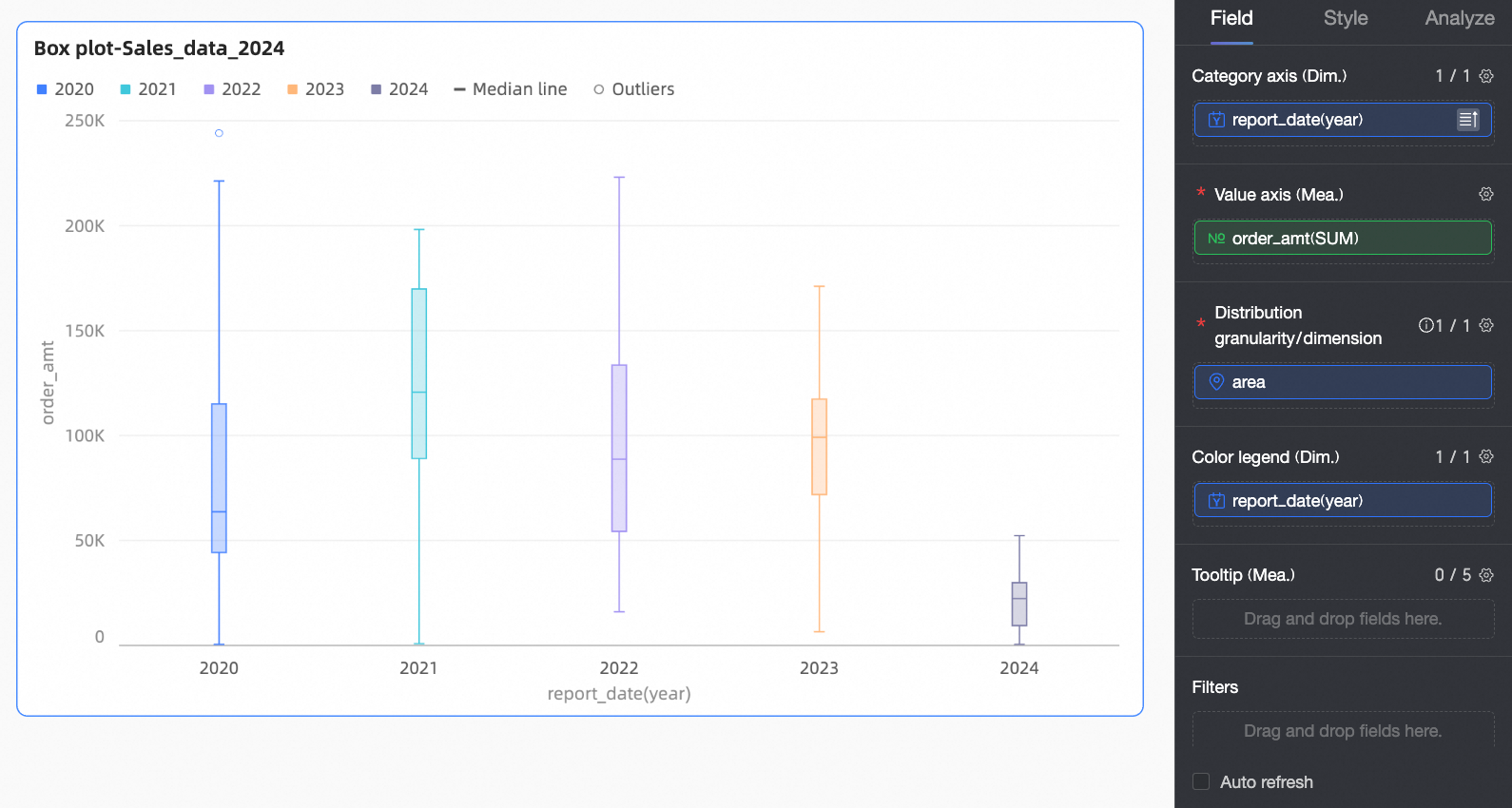
When there are multiple measure fields in the Value axis, the chart displays the first measure by default. You need to manually open the field filter panel to switch to other measures.
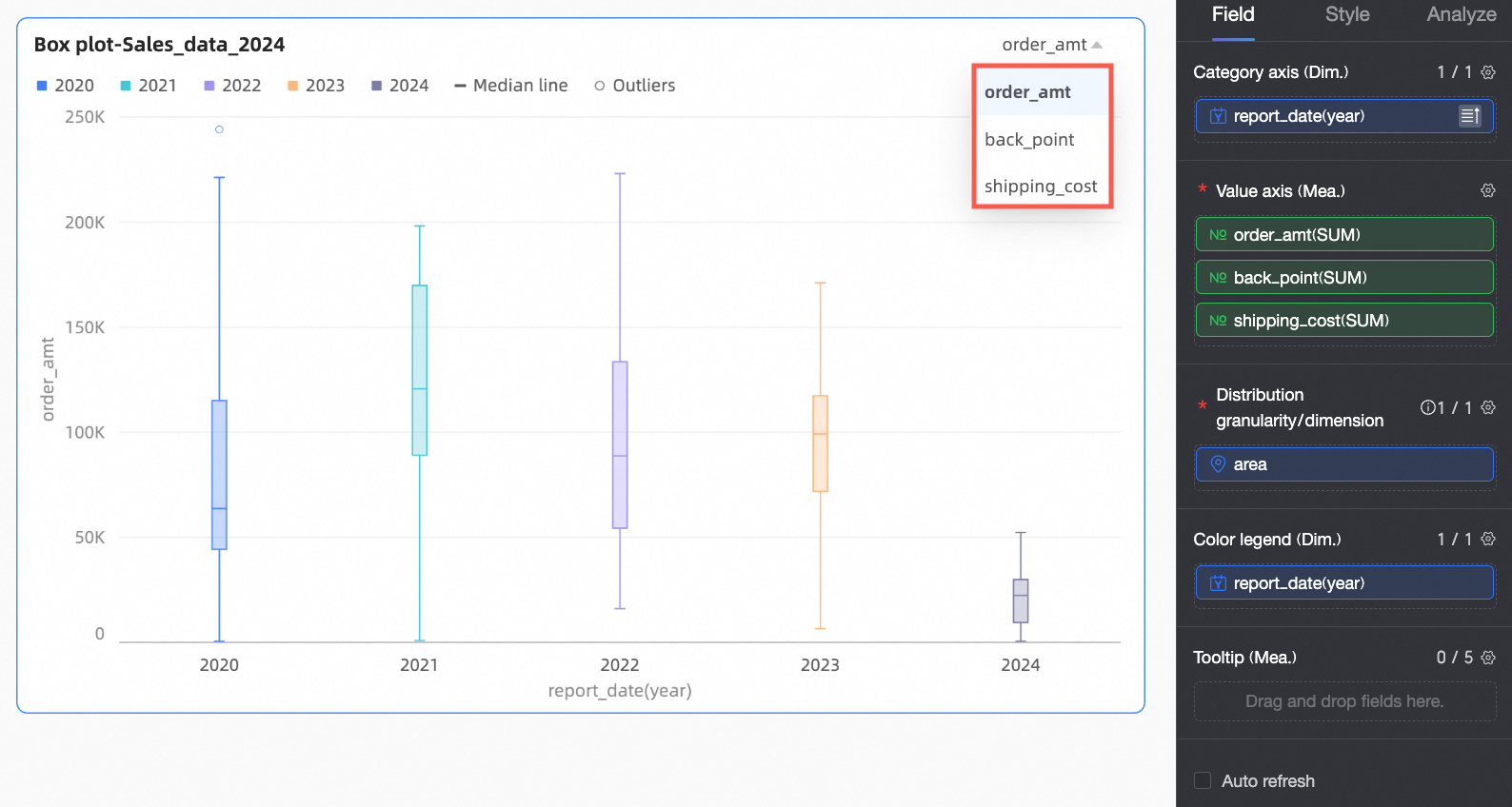
Click Update. The chart will automatically refresh.
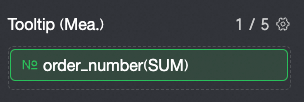
To display specific measure data in the tooltip, add the measure to Tooltip/Measure.
To exclude data from certain regions, drag the Region field to the Filter area. Click the
 icon in the Set Filter window to select the desired data.
icon in the Set Filter window to select the desired data. 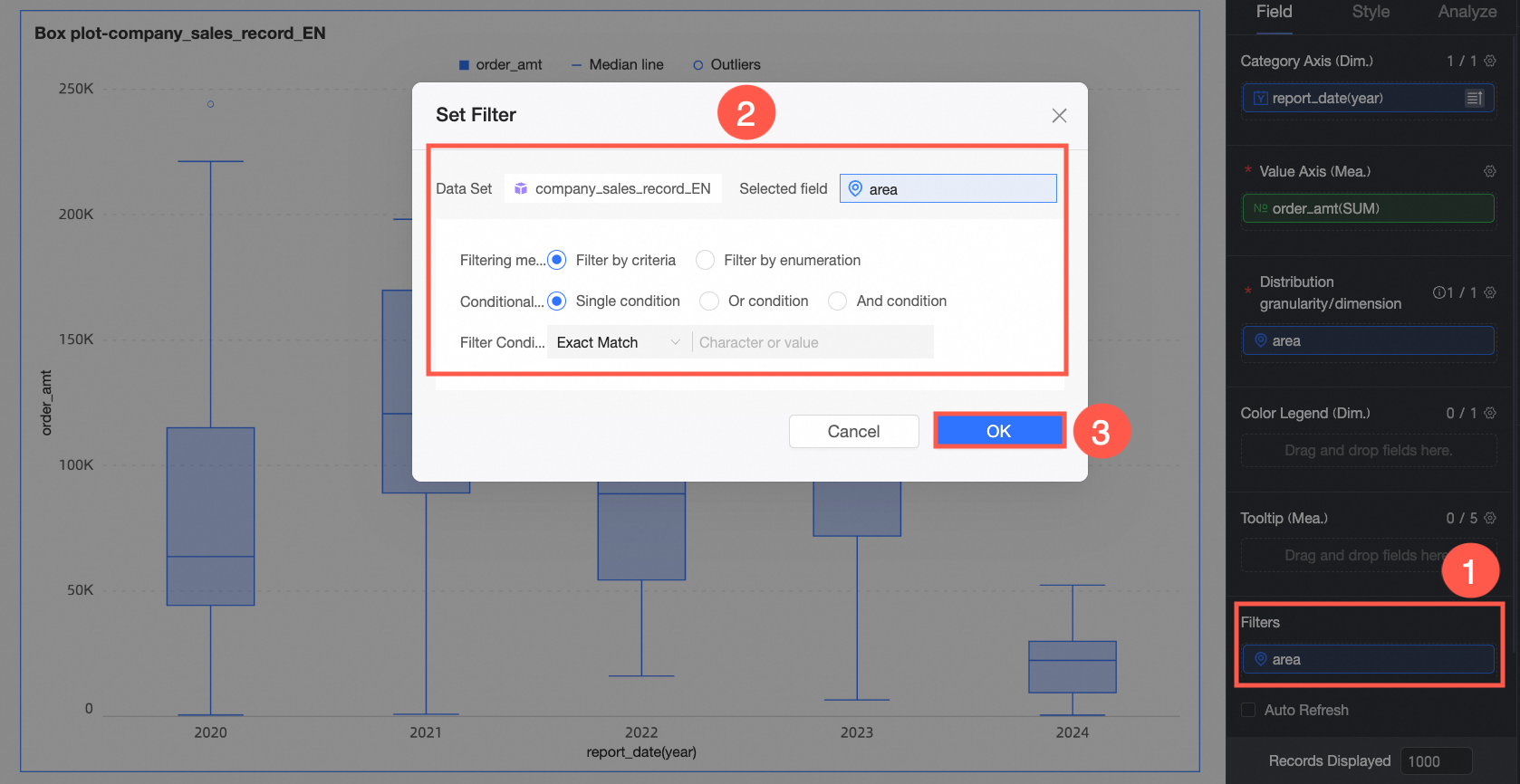
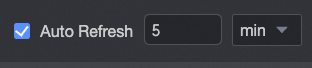
Auto-refresh
Once this option is activated, the system will refresh the chart data automatically. For instance, selecting this option and specifying a duration of 5 with the unit set to Minutes results in the chart data being refreshed every five minutes.
Configure Chart Styles
The following describes how to customize chart styles. For general Title and card settings, see Configure the chart title.
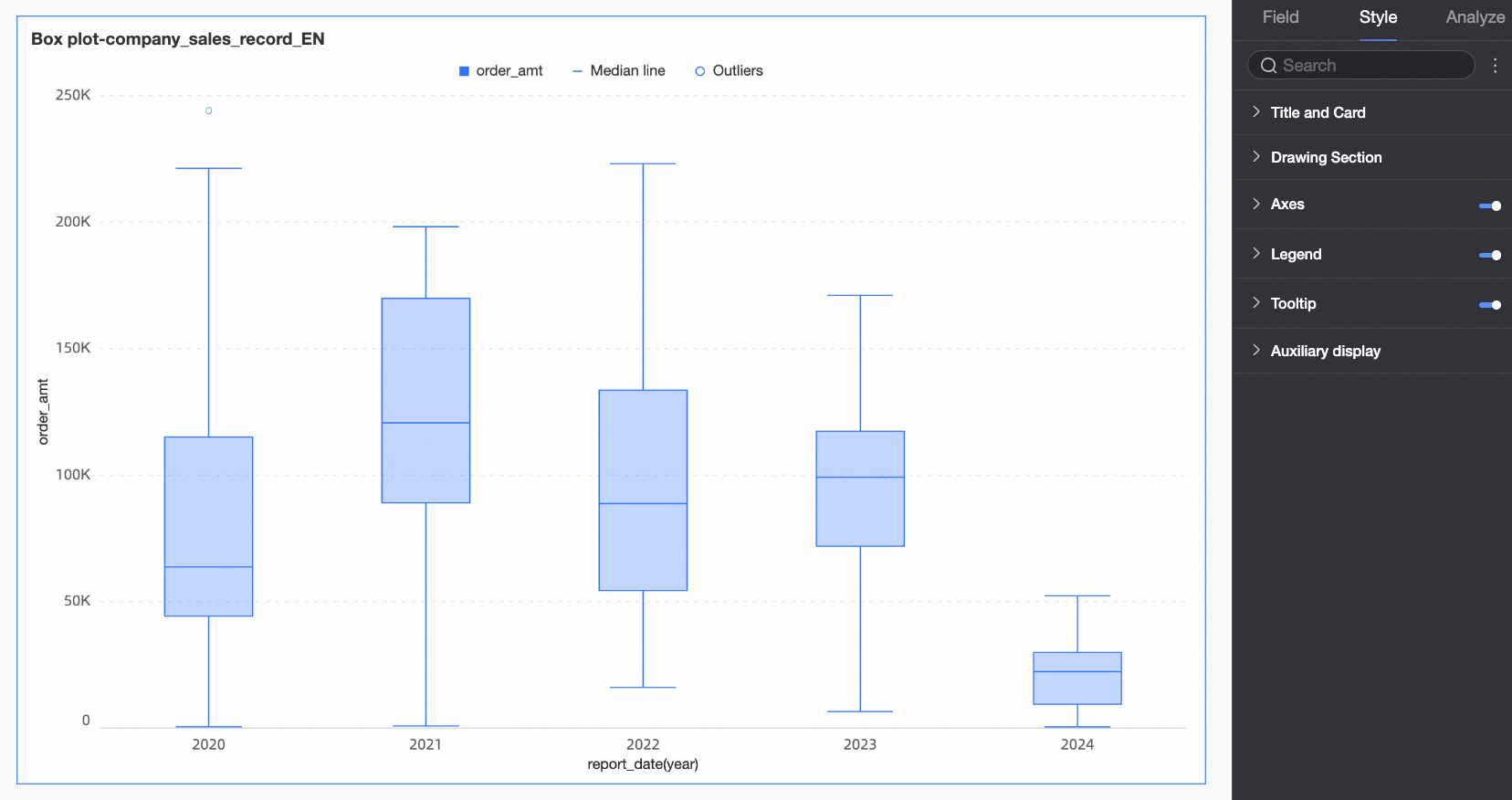
Plot Area
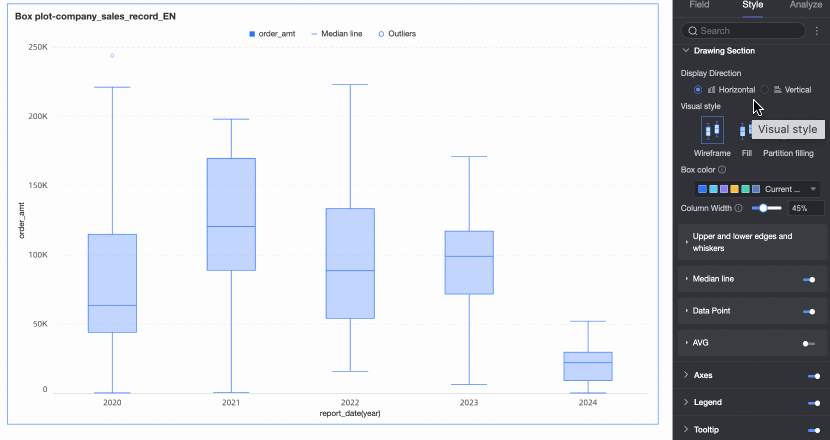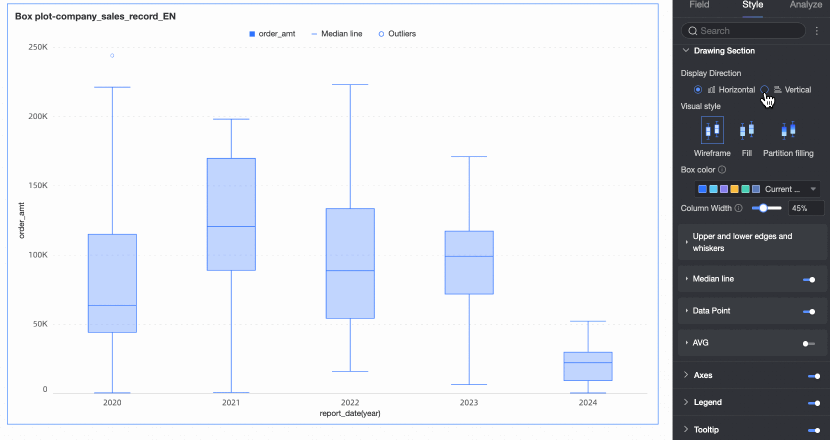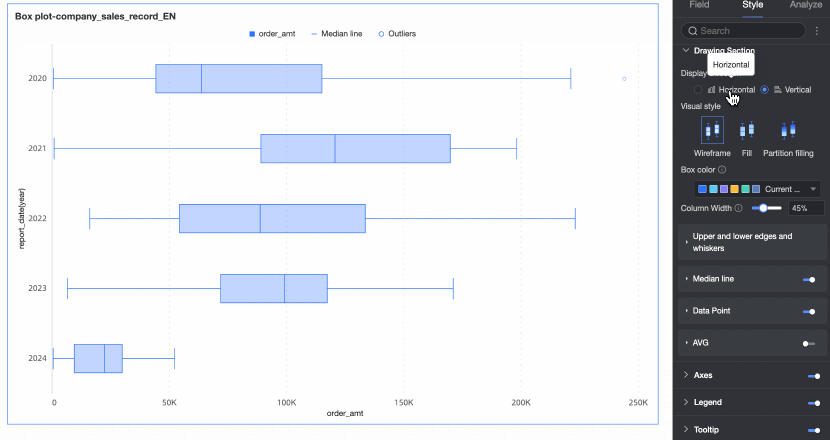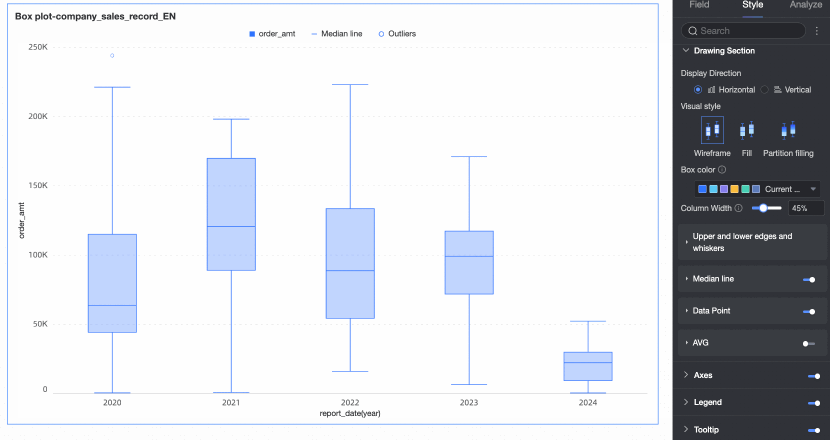
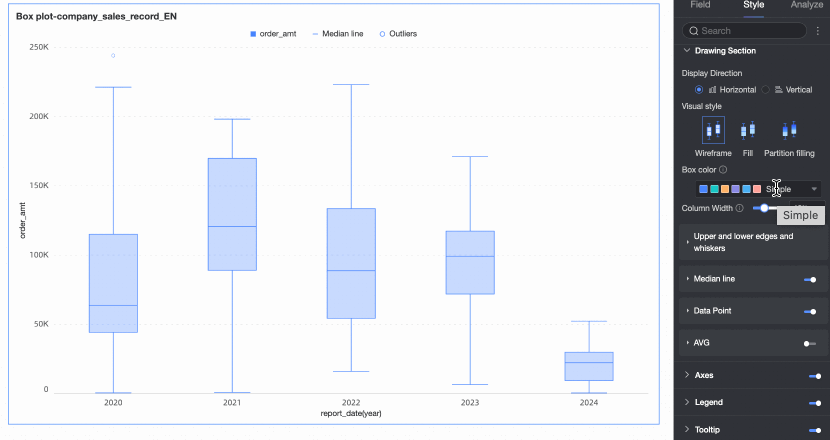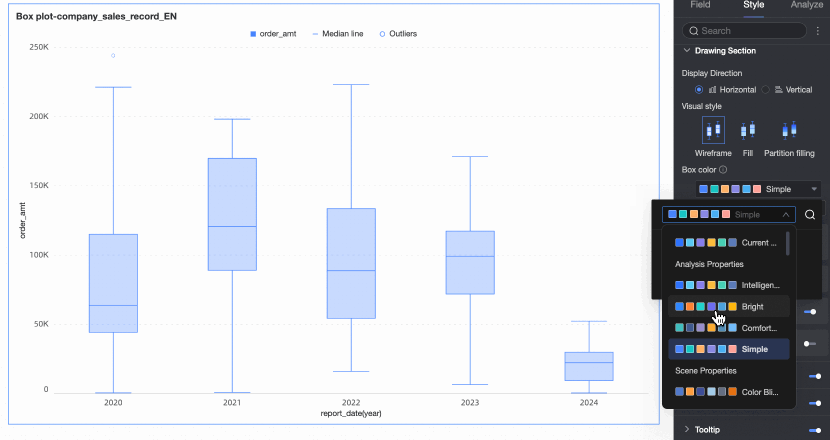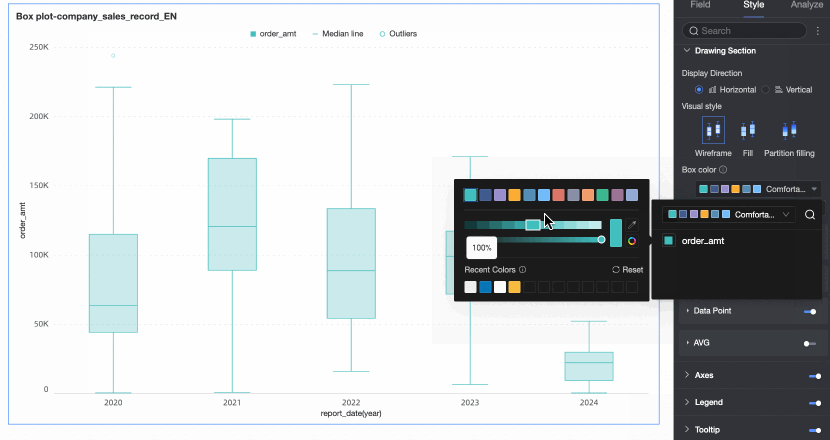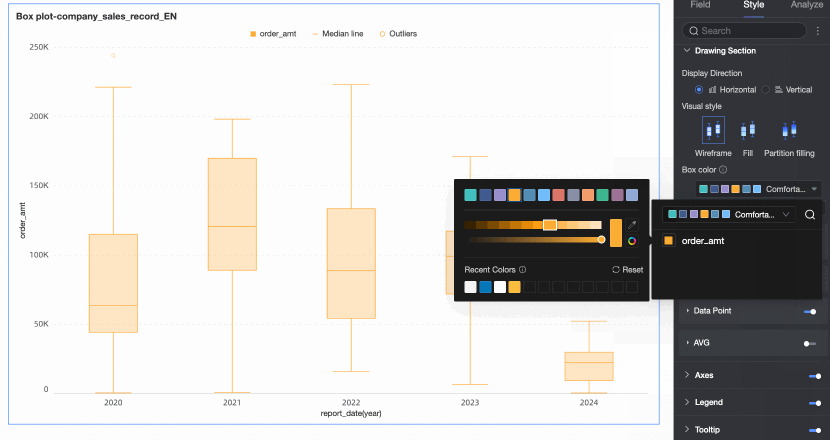
Under the Style tab in the Plot Area section, you can define the box plot's graphic style.
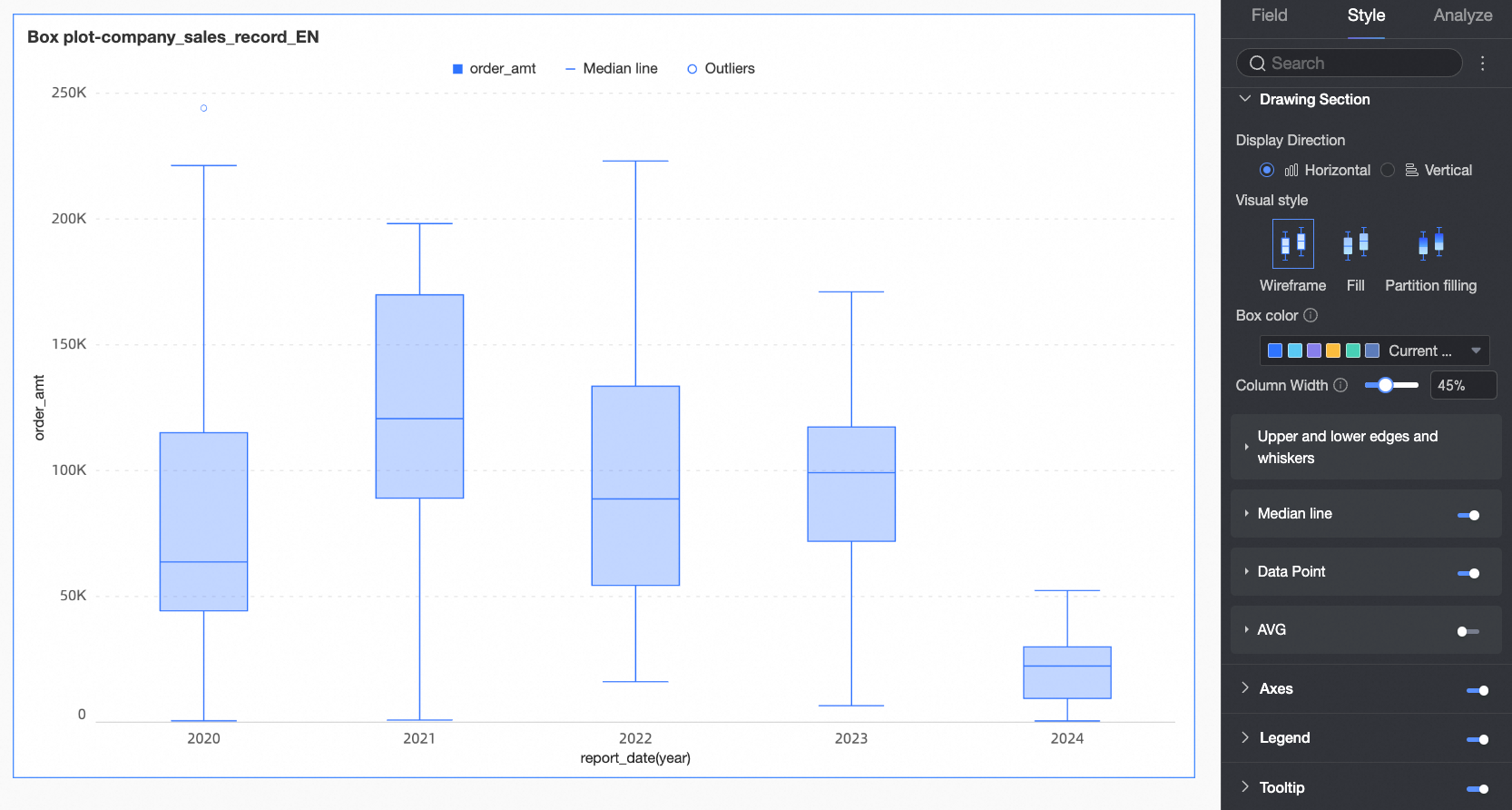
Chart configuration items | Configuration content | Configuration item description |
Chart display orientation | Set the display orientation of the box. Supports horizontal and vertical. | |
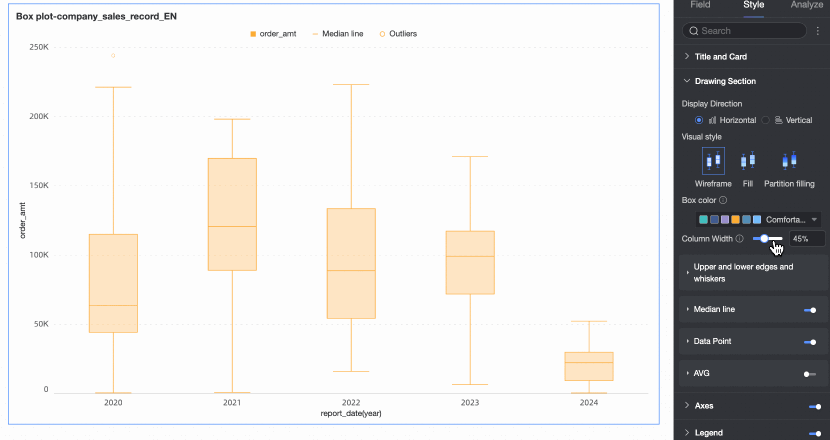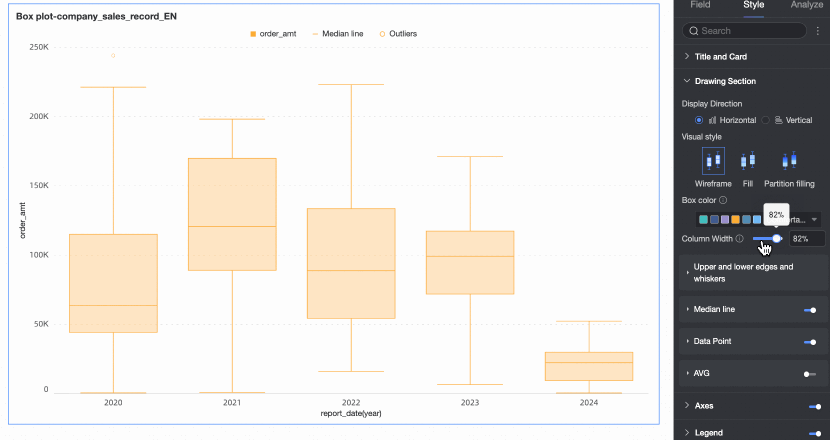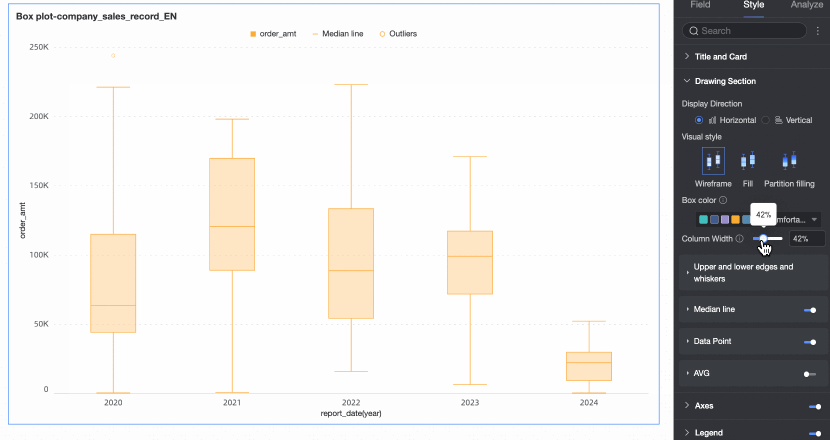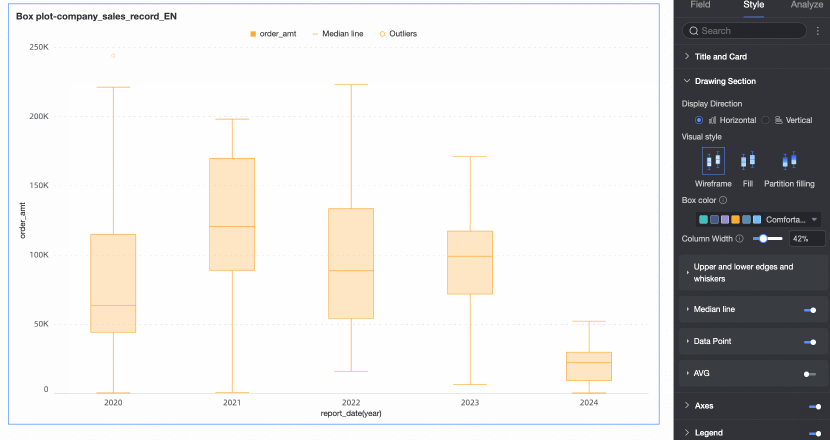
Visualization style | Set the visualization style of the box. You can choose wireframe, fill, or partition fill.
| |
Box color scheme | Set the color style of the box for the fields configured in the value axis/measure. Custom box colors are supported. | |
Column width | Set the width of the box. When the configured width exceeds the maximum width range, this configuration will no longer be effective. | |
Upper and lower edges and whiskers | Upper and lower edge calculation method | Set the calculation method for obtaining the upper and lower edges. The following four calculation methods are supported:
|
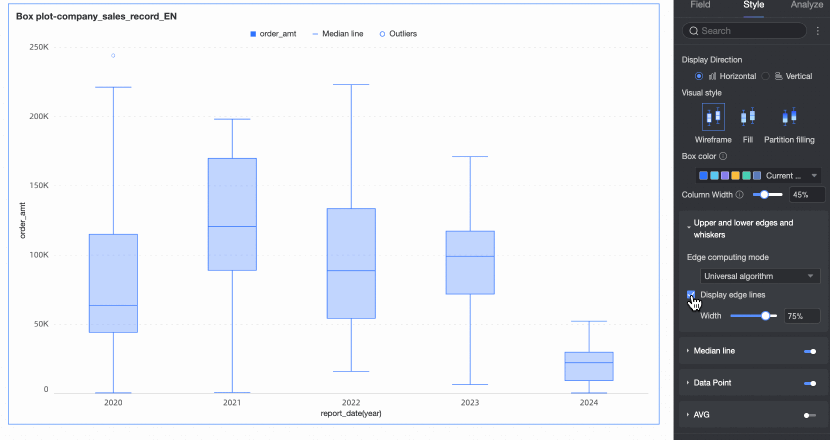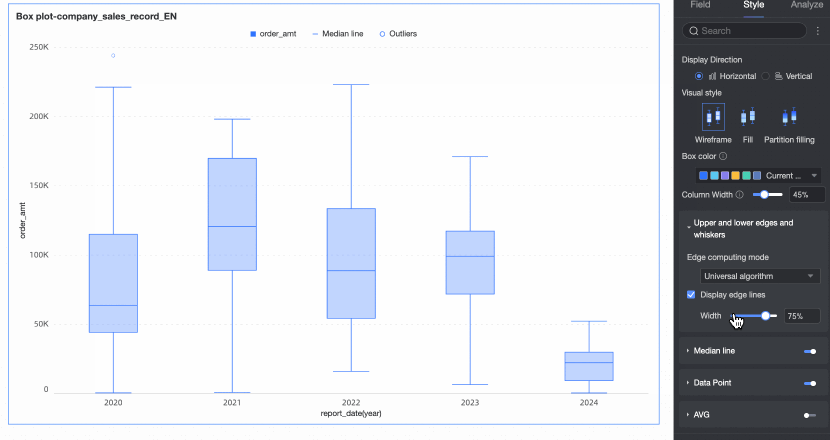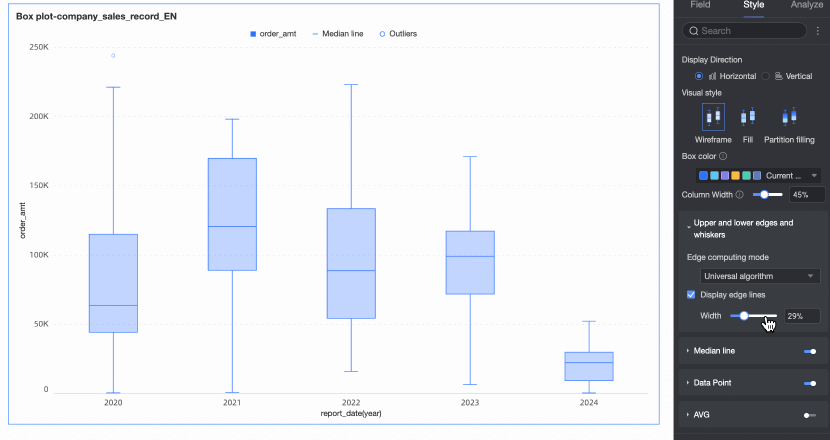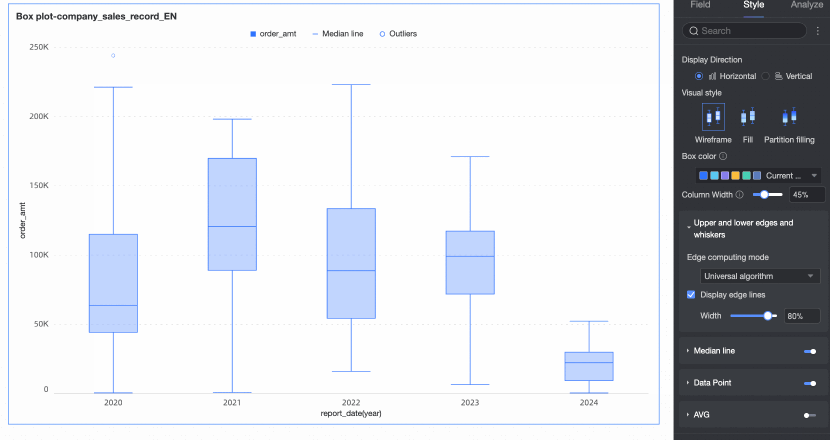
Display upper and lower edges | Set whether to display the upper and lower edge lines of the box plot and, if displayed, set the width of the edge lines. | |
Median line | Set whether to display the median line and the style of the median line. | |
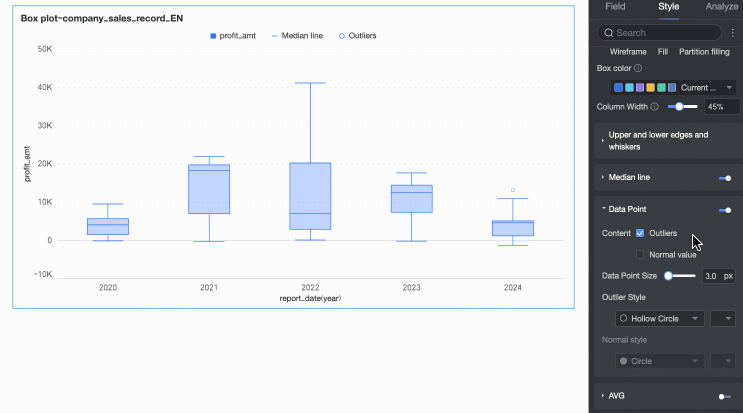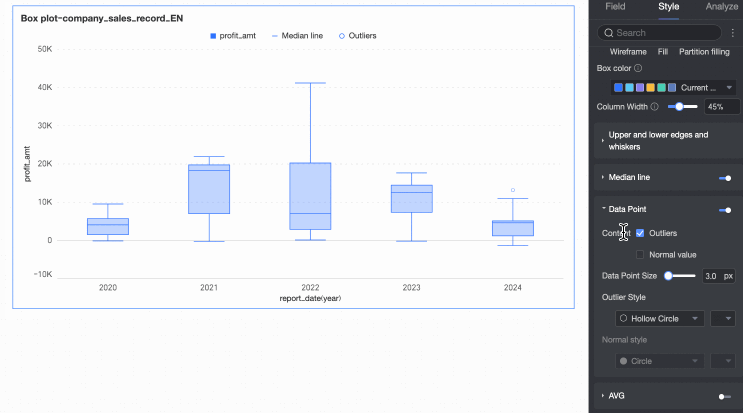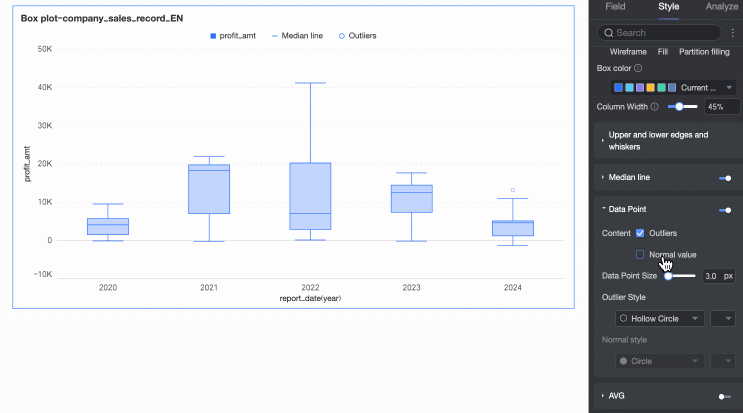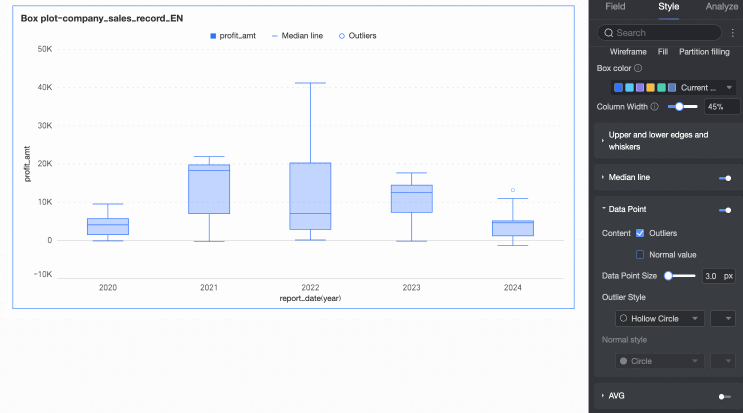
Data points | Content | Set whether to display abnormal values or normal values in the chart. Note Data points only support subsequent style configuration operations when in display status. |
Data point size | Set the size of the data points. | |
Abnormal point style | Set the shape and color of abnormal points. | |
Normal point style | Set the shape and color of normal points. | |
Average value | Average value style | Set the shape and color of the average value when it is in display status. |
Circle size | Set the size of the average value shape. | |
Coordinate Axis
Under the Style tab in the Coordinate Axis section, you can customize the appearance of the coordinate axes. They are displayed by default.
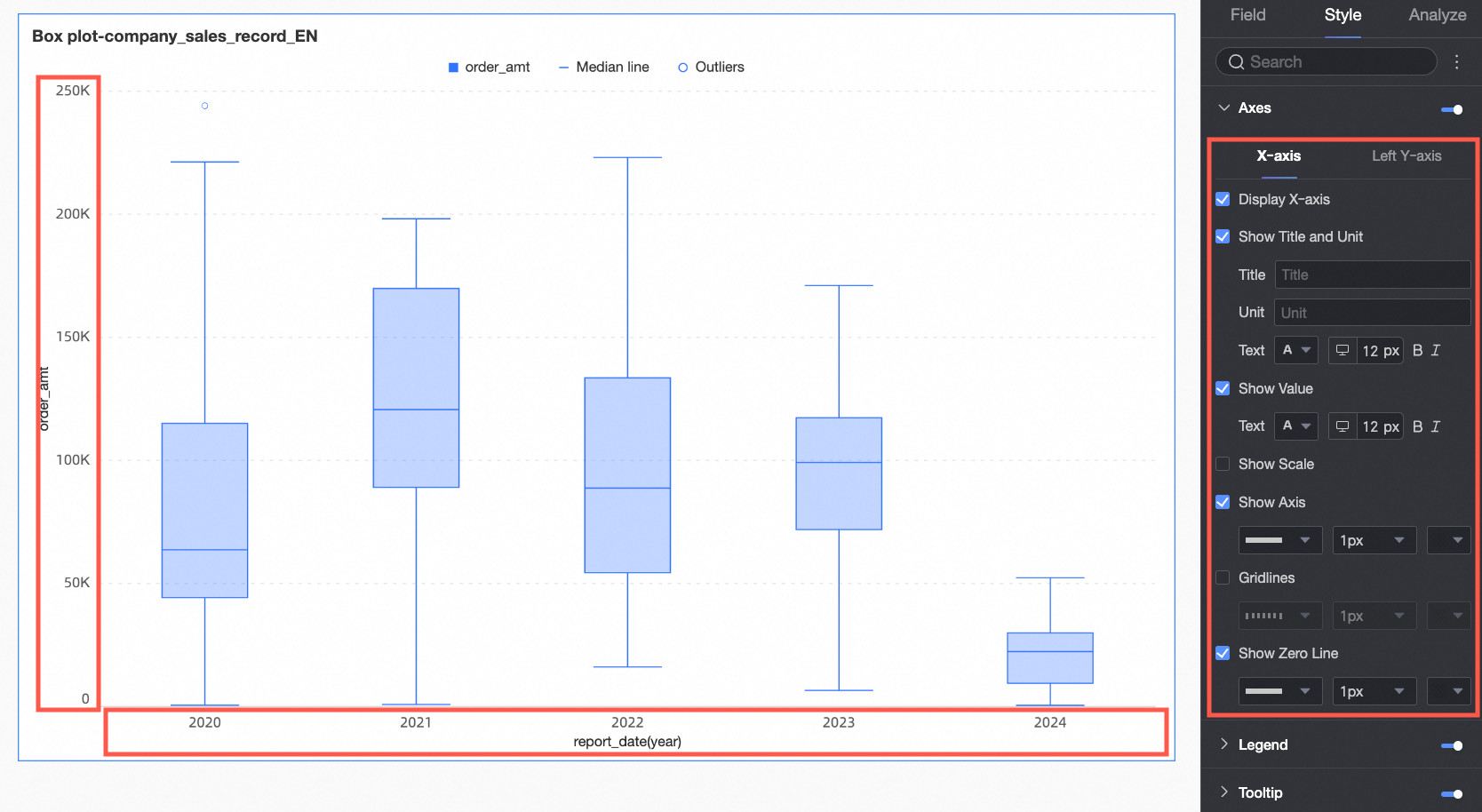
Chart configuration item | Configuration content | Configuration item description |
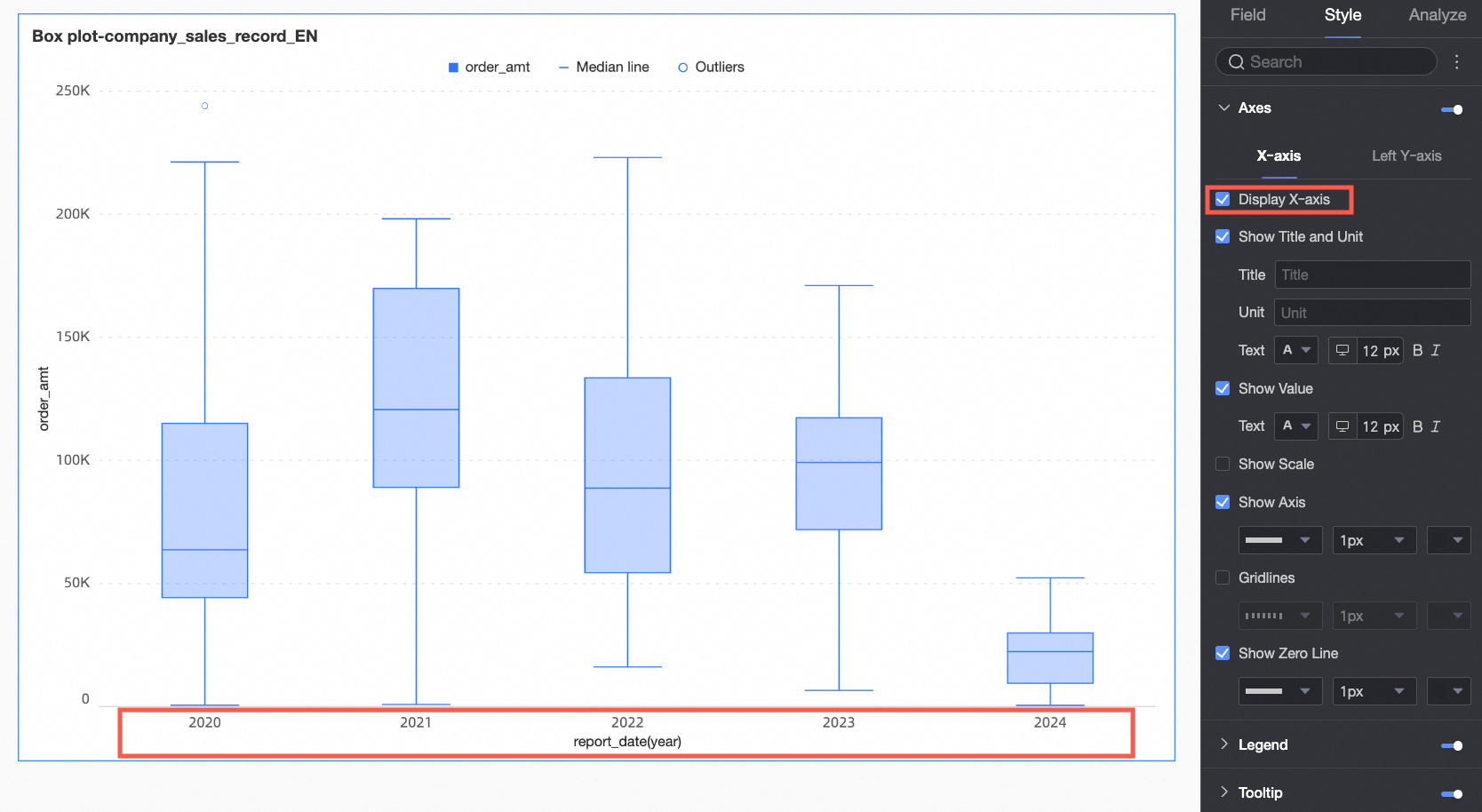
X-axis | Show X-axis | Specifies whether to show the X-axis. |
Show title and unit | Specifies whether to show the title and unit on the X-axis. You can customize the title name and the unit of measurement, and configure the text style. | |
Show axis labels | Specifies whether to show axis labels on the X-axis and the text style of the axis labels. | |
Show scales | Specifies whether to show scales on the X-axis. | |
Show axis | Specifies whether to show the axis line of the X-axis. You can customize the axis style, including line type, line width, and color, when it is shown. | |
Show gridlines | Specifies whether to show gridlines on the X-axis. You can customize the gridline style, including line type, line width, and color, when it is shown. | |
Show zero scale line | Specifies whether to show the zero scale line on the X-axis. You can customize the zero scale line style, including line type, line width, and color, when it is shown. | |
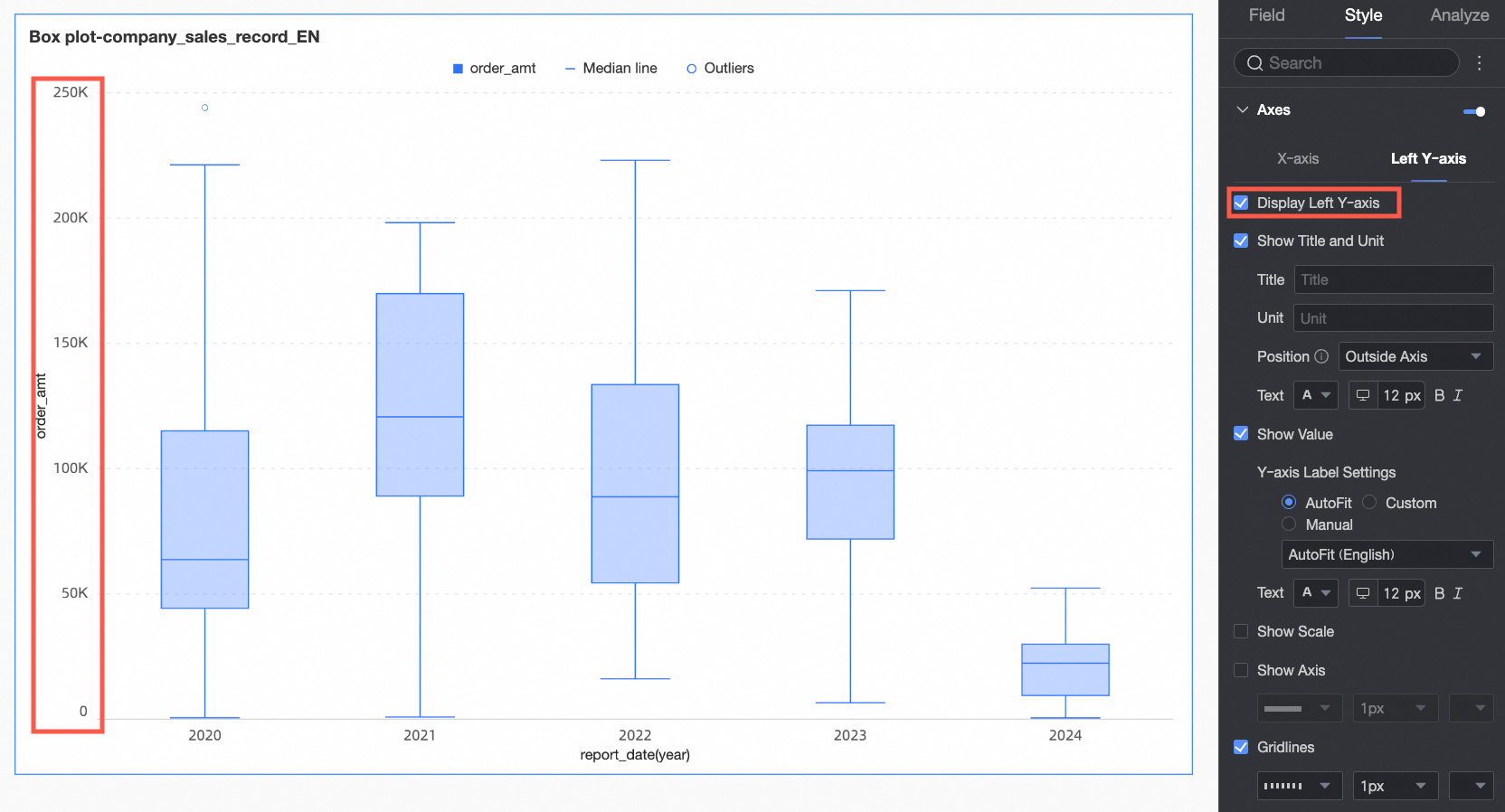
Left Y-axis | Show left Y-axis | Specifies whether to show the left Y-axis. |
Show title and unit | Specifies whether to show the axis title and unit. You can customize the title name and the unit of measurement, and configure the text style. | |
Show axis labels | Specifies whether to show labels on the left Y-axis and the label display format and text style. | |
Show scales | Specifies whether to show scales on the left Y-axis. | |
Show axis | Specifies whether to show the axis line of the left Y-axis. You can customize the axis style, including line type, line width, and color, when it is shown. | |
Show gridlines | Specifies whether to show gridlines on the left Y-axis. You can customize the gridline style, including line type, line width, and color, when it is shown. | |
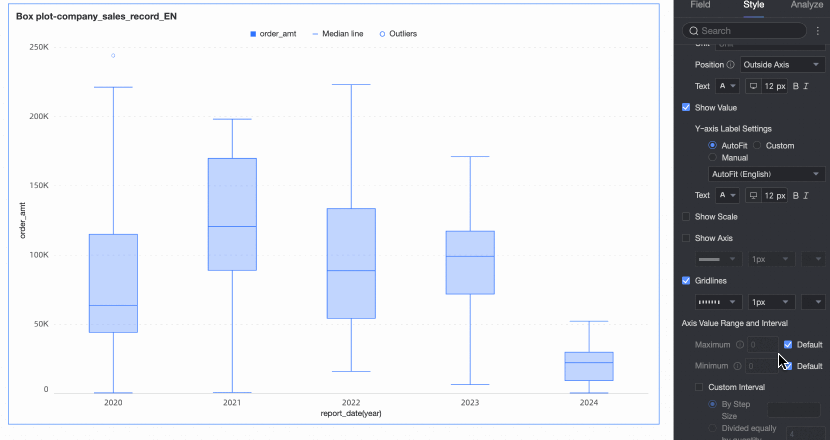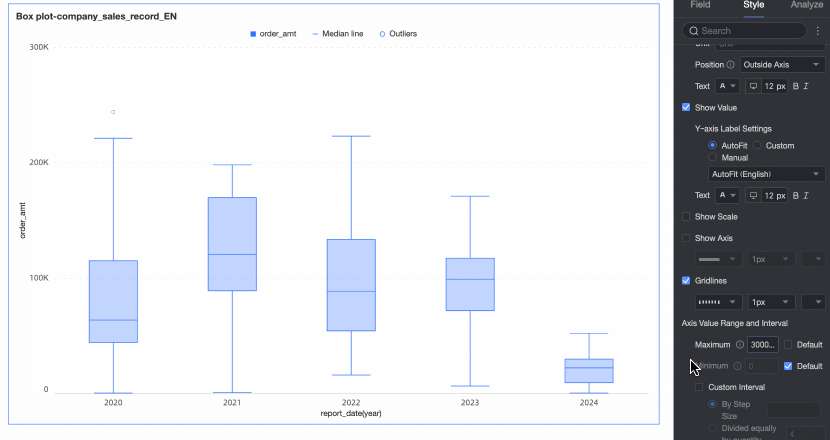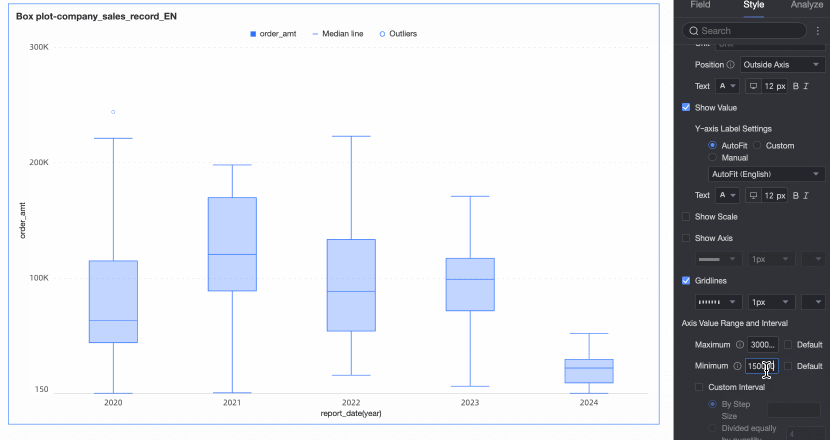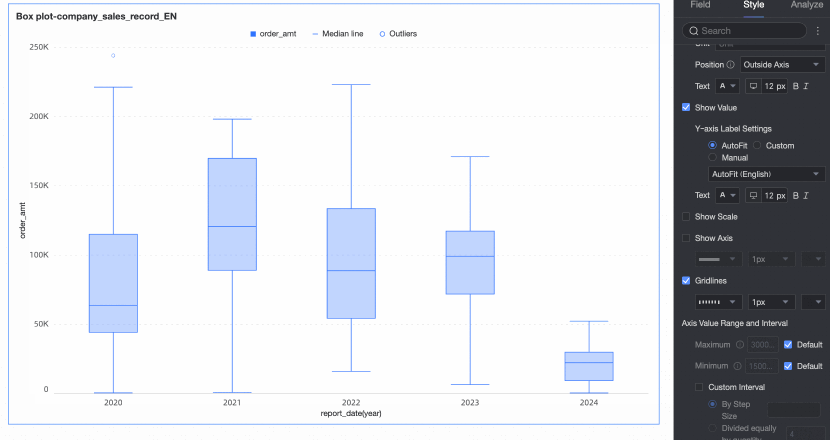
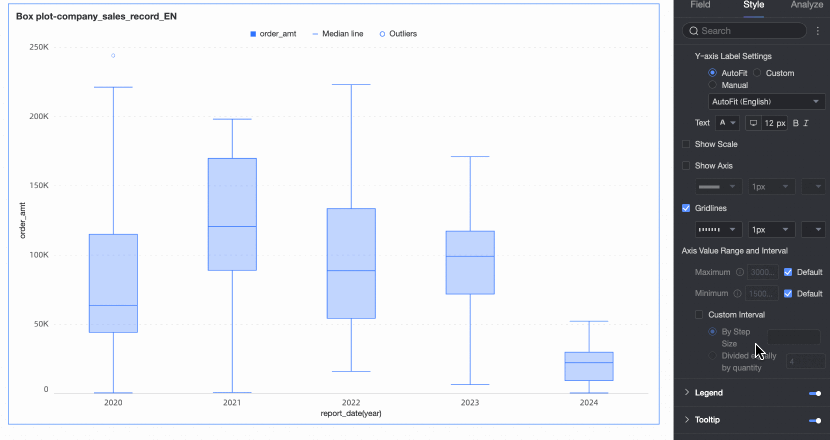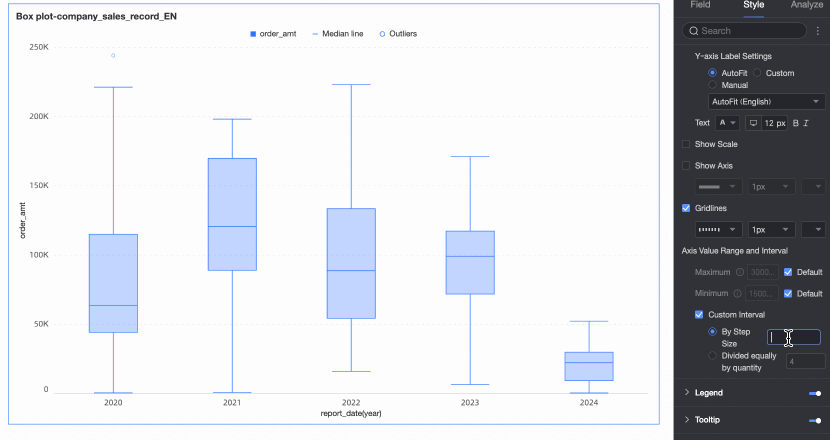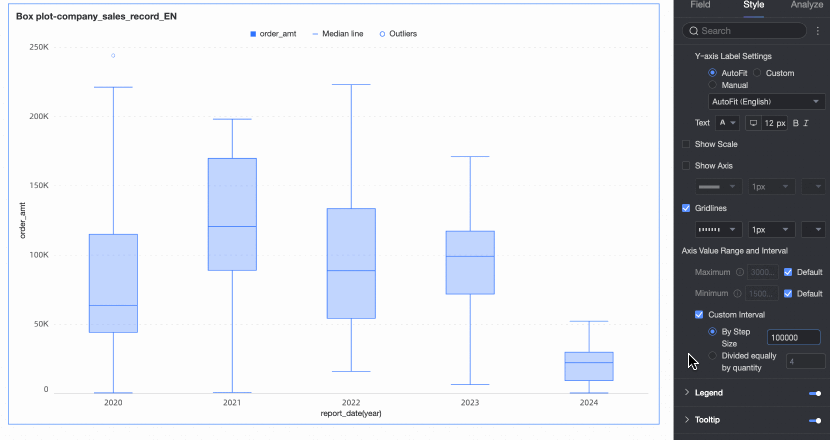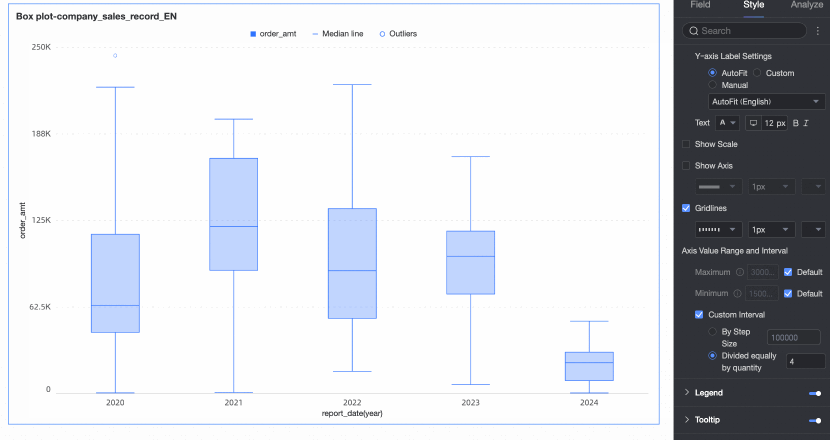
Axis value range and interval | Specifies the maximum and minimum values of the left Y-axis and the interval size between each axis value.
|
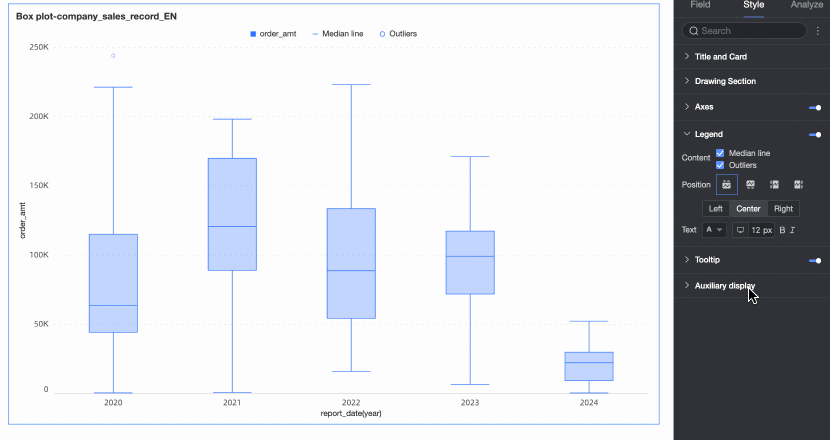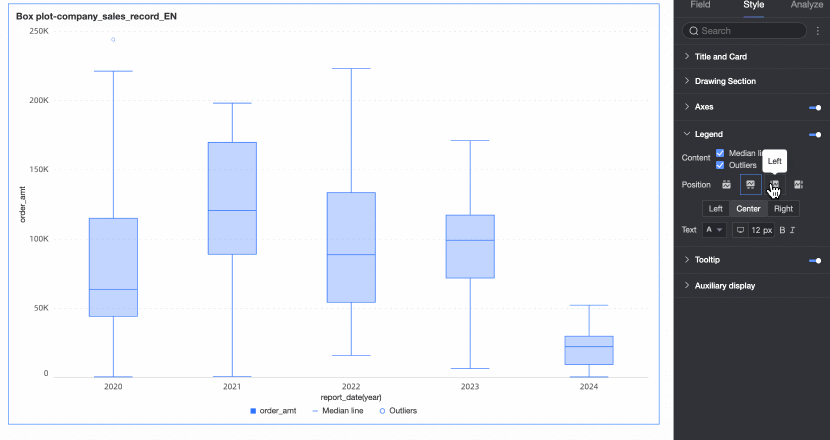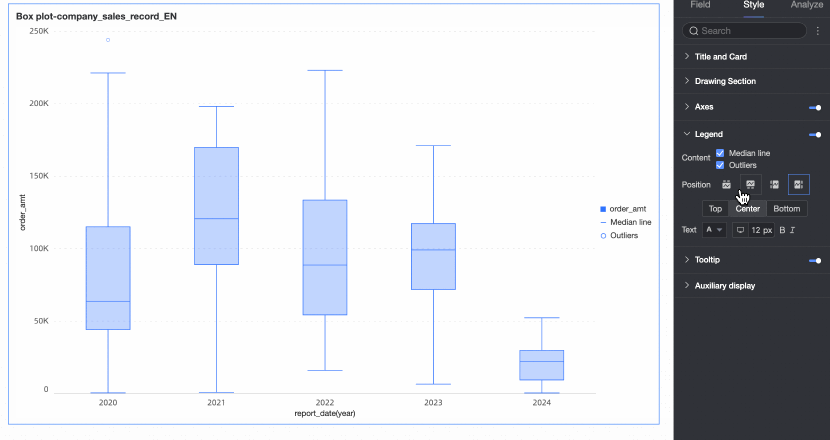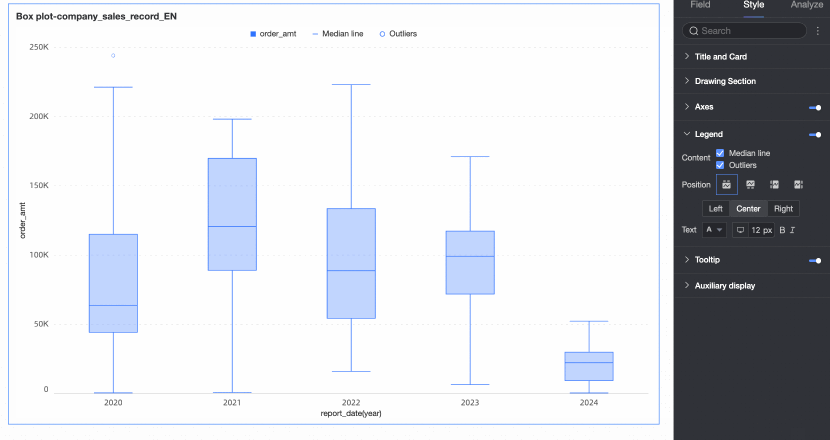
Legend
In the Style tab, configure the chart's legend style. 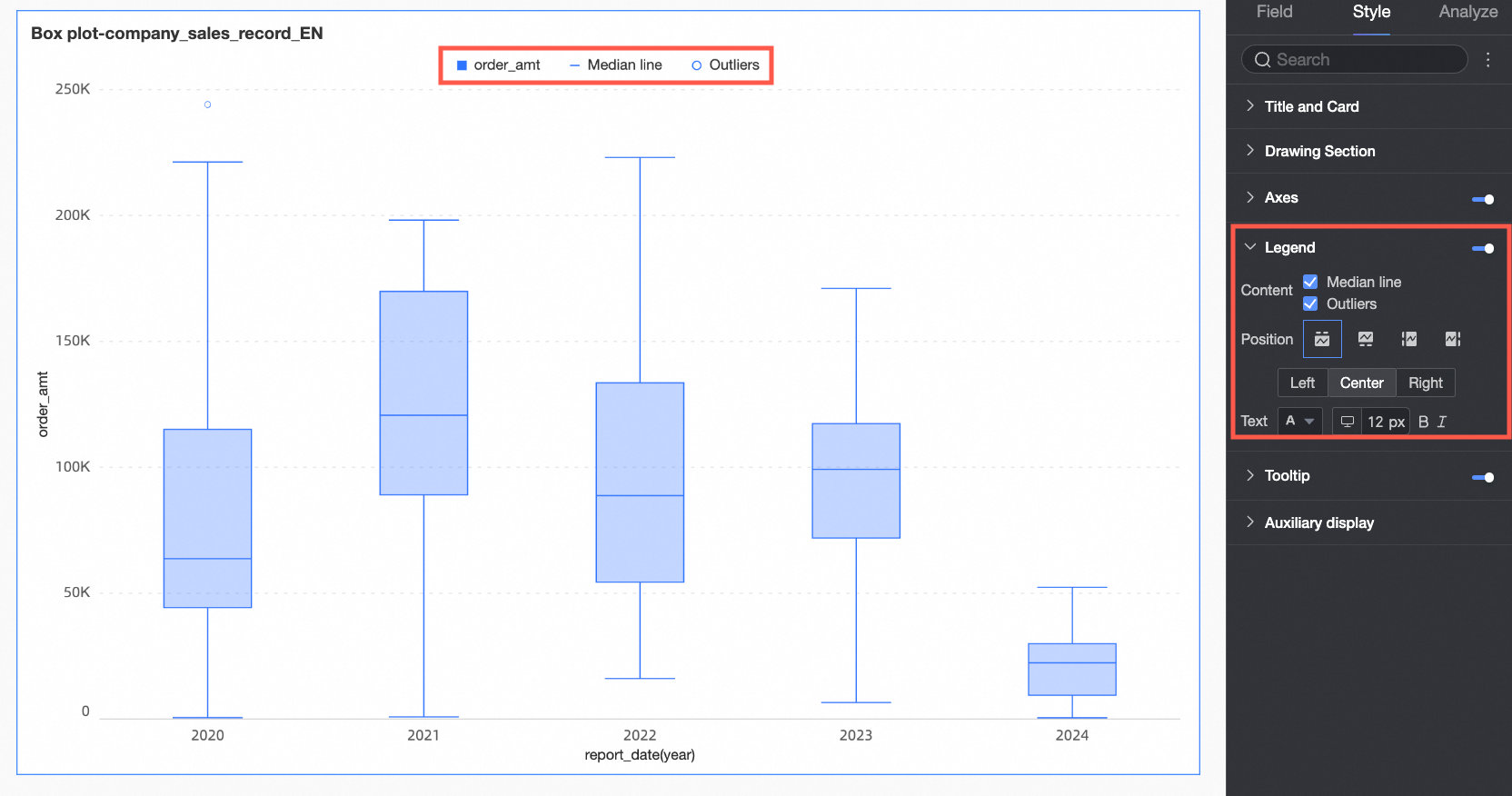
Chart configuration item | Configuration item description |
Content | You can choose whether to display the metrics of the background area in the legend. |
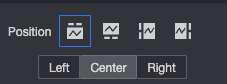
Position | You can set the display position of the legend. The following four legend rendering methods are supported.
|
Text | You can set the text style of the legend. The font size can be set separately for PC and mobile devices, while the rest of the text styles are configured uniformly. |
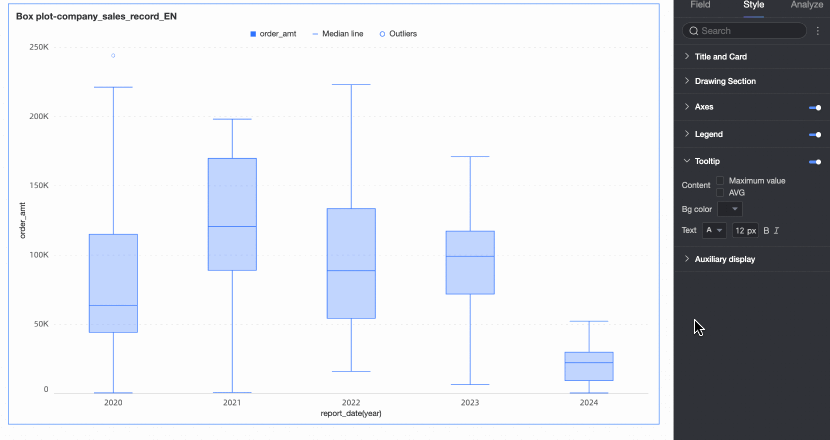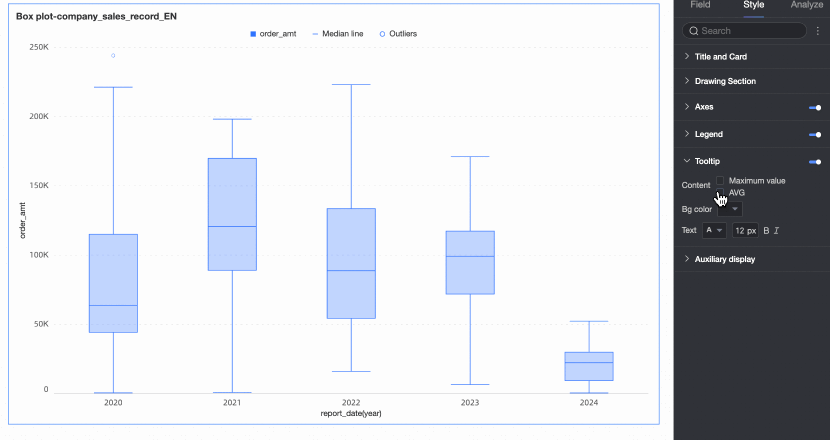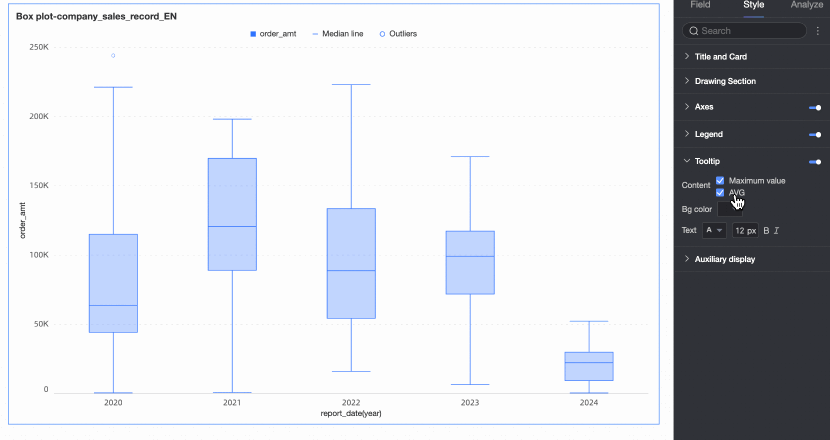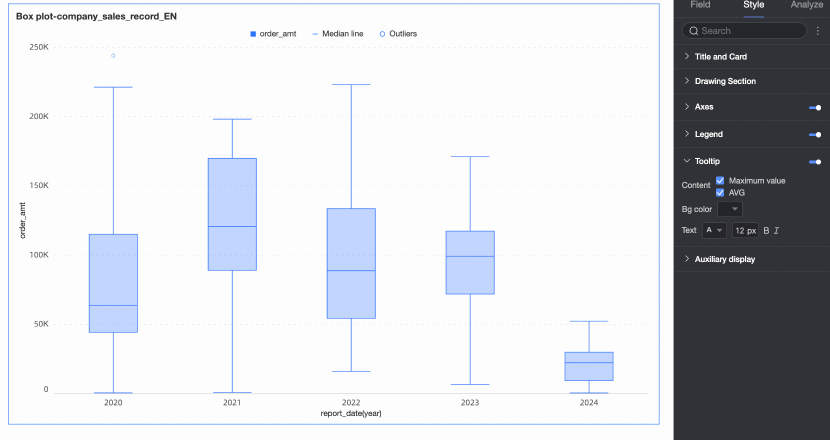
Tooltip
Under the Style tab in the Tooltip section, you can set the tooltip display method.
Tooltips can only be configured on the PC side.
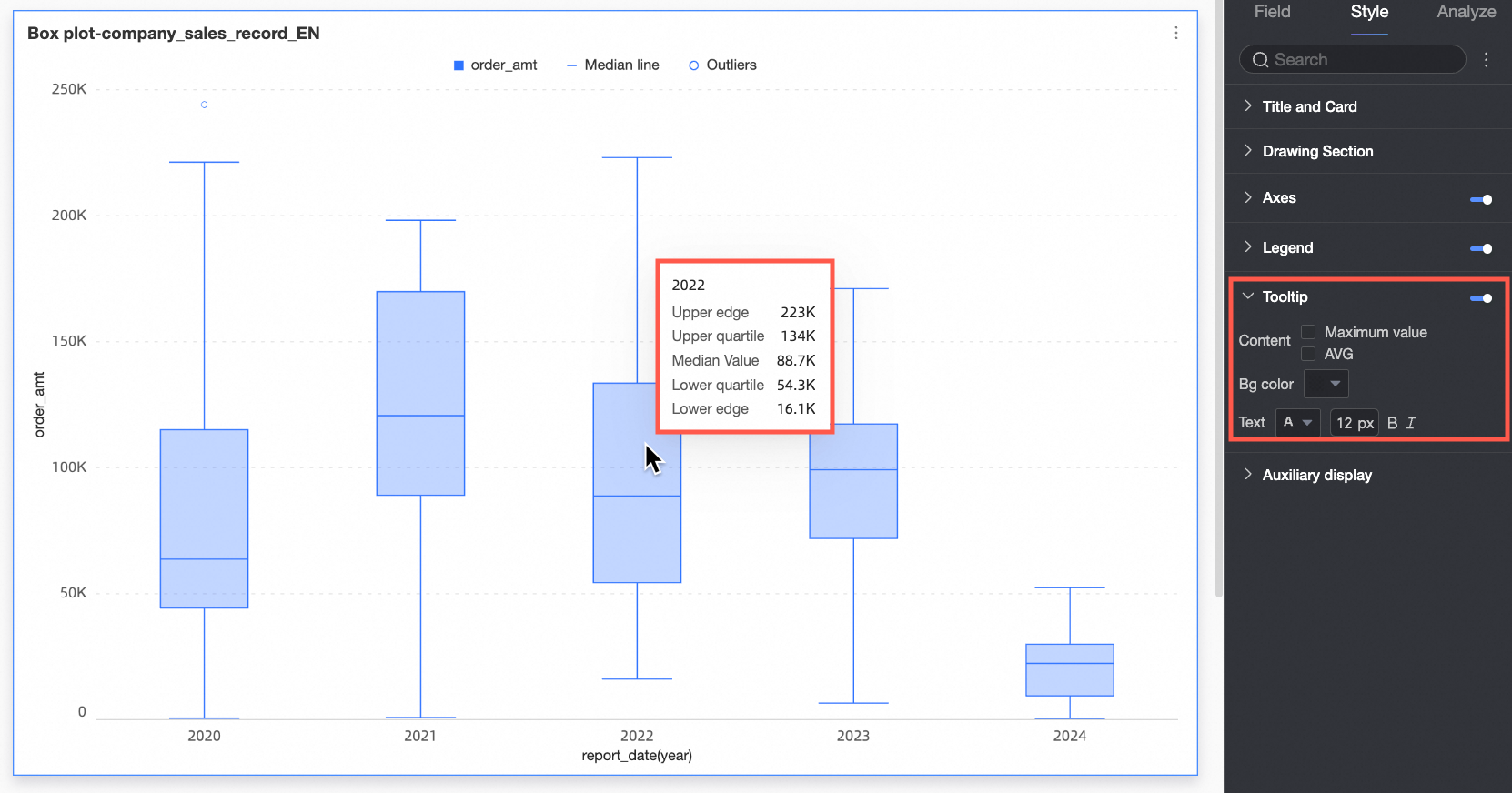
Chart configuration items | Configuration item description |
Content | You can choose whether to display the maximum value, minimum value, and average value in the tooltip. |
Background color | Set the background color of the tooltip box. |
Text | Set the style of the tooltip text. |
Auxiliary Display
In the Style tab, under Auxiliary Display, you can configure the thumbnail axis. 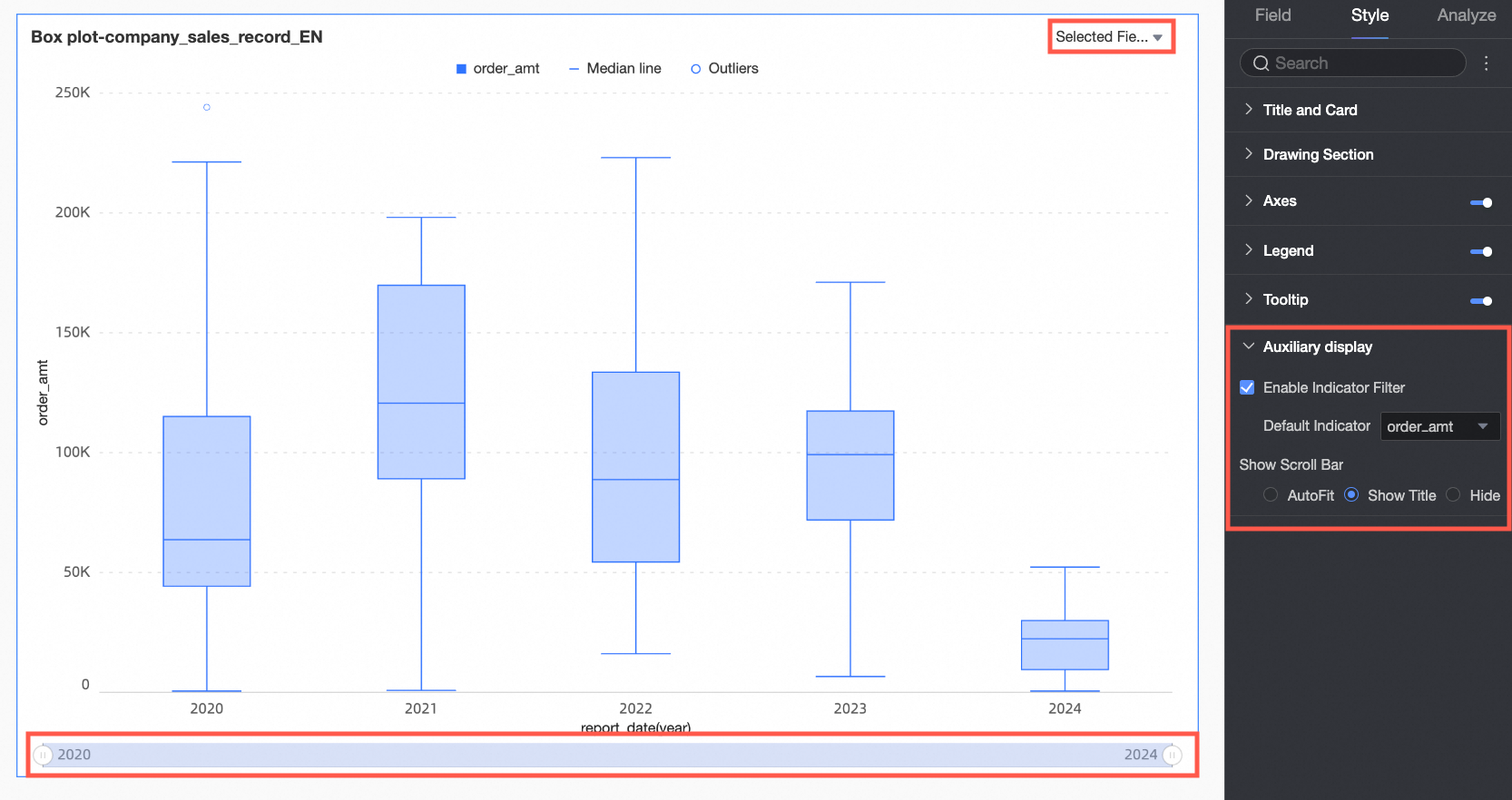
Chart configuration items | Configuration item description |
Enable metric filter display | You can set whether to enable the metric filter display. After enabling, you can configure the default selected fields in the filter. |
Show thumbnail axis | You can set the display mode of the thumbnail axis. |
Chart Analysis Configuration
Chart configuration items | Configuration content | Configuration item description |
Data interaction | Drilling | When you have set the drilling fields in the field panel, you can set the display style of the drilling level here. For more information, see Drilling. |
Filter Interaction | If the data that you want to analyze exists in different charts, you can associate multiple charts to form a linkage for data analysis. For more information, see Filter Interaction. | |
Hyperlink | If the data that you want to analyze belongs to different dashboards, you can associate the dashboards for data analysis. Hyperlink includes three methods: internal product hyperlink, on-page widget, and external link. For more information, see Hyperlink. | |
Analysis Alert | Auxiliary Line | An auxiliary line can be used to show the difference between the value of a measure and the reference value indicated by the auxiliary line. The reference value can be a fixed value or a calculated value. Calculated values include four types: average, maximum, minimum, and median. For more information, see Auxiliary line. |
Annotation | - | When data in a chart is abnormal or requires extra attention, you can use highlighted measures, icons, comments, or data points as labels to help you identify exceptions and take appropriate actions. For more information, see Annotation. |
What to do next
To share the dashboard with others, see Share a Dashboard for more details.
To create a complex navigation menu for thematic analysis, integrate the dashboard into the BI portal. For more information, see BI portal.