Alibaba Cloud DataWorks Data Integration introduces an embedding vectorization feature. This feature lets you extract data from disparate data sources, such as OSS, MaxCompute, and Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), and convert it into vectors. You can then write the vectors to destinations that have vector storage capabilities. These destinations include vector databases, such as Milvus, Elasticsearch, and OpenSearch, and Hologres vector tables. This simplifies the extract, transform, and load (ETL) process, efficiently vectorizes knowledge, and helps you implement AI scenarios such as retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
Why use embedding
As large language model (LLM) technology continues to evolve, deeply integrating private knowledge into model systems is key for businesses to apply these models effectively and create value. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has become a key technical approach for this purpose. By encoding data into vector representations and using vector databases for efficient retrieval, RAG provides LLMs with accurate, authoritative, and dynamically updated domain knowledge.
Your business data might be scattered across many disparate data sources, such as OSS, MaxCompute, HDFS, MySQL, Oracle, or message queues. This data must be vectorized using embedding and then written to various destinations that have vector storage capabilities, such as Milvus, OpenSearch, and Elasticsearch vector databases, or Hologres vector tables. This process requires you to write complex ETL scripts and adapt to various source data types. The data goes through multiple stages, including extraction, transformation, vectorization (embedding), and writing. This long and tightly coupled workflow significantly extends the model iteration cycle.
Function introduction
DataWorks Data Integration supports embedding vectorization. It provides a one-stop solution to extract, vectorize, and write data to a vector database within a single data channel, which enables end-to-end automated processing. This capability significantly reduces development complexity, shortens knowledge update latency, and helps you efficiently ingest knowledge for scenarios such as RAG, intelligent customer service, and search and recommendation.
The embedding vectorization feature for offline data synchronization in Data Integration supports two configuration modes:
Codeless UI configuration: You can use a visual interface to quickly configure offline embedding synchronization.
Code editor configuration: The code editor supports more complex and advanced configuration features. You can use the code editor to configure various synchronization pipelines for custom needs.
Limitations
This feature is only available for workspaces where the new version of Data Development is enabled.
Only Serverless resource groups are supported.
This feature is currently available for only some offline synchronization channels.
Billing
For Data Integration tasks that use AI-assisted processing, you incur costs from calling large language models in addition to the costs of the Data Integration task itself. For more information, see Data Integration scenarios.
For information about the billing of Alibaba Cloud DataWorks model services, see Billing of Serverless resource groups - Large language model services.
For information about the billing of Alibaba Cloud Model Studio, see Model inference (call) billing.
For information about the billing of the Alibaba Cloud PAI model marketplace, see Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) billing.
Preparations
Create a workspace with the new version of Data Development enabled.
Create a Serverless resource group and attach it to the workspace.
Prepare the large language model service required for AI-assisted processing. The preparations vary based on the selected large language model service provider:
Alibaba Cloud DataWorks model service: Deploy a model and start the model service in Large Language Model Service Management.
Alibaba Cloud Model Studio: Activate Alibaba Cloud Model Studio and obtain and configure an API key.
Alibaba Cloud PAI model marketplace: Activate Platform for AI (PAI) and obtain a token for the model service.
Create the source and destination data sources required for the offline sync task.
This tutorial uses MaxCompute as the source and Milvus as the destination. Therefore, you must first create a MaxCompute data source and a Milvus data source.
Prepare test data
The table data used in this tutorial comes from a public dataset (E-commerce Product Review Sentiment Prediction Dataset). User reviews of products are vectorized and then synchronized to Milvus for subsequent similarity searches.
On the MaxCompute source side: Create a test table and insert test data.
On the Milvus destination side: Create a destination table to receive the vectorized data. The table schema is as follows:
The destination table has the autoid feature enabled.
Field name
Type
Description
id
Int64
Primary key. Auto-incrementing.
sentence
VarChar(32)
Stores the raw text.
sentence_e
FloatVector(128)
Vector field for similarity search. Uses the COSINE measure.
Codeless UI configuration
This tutorial uses an example in which data is read from a MaxCompute (ODPS) source, vectorized using embedding, and then synchronized to Milvus. It shows how to configure an offline sync task in Data Integration using the codeless UI.
1. Create an offline sync node
Go to the Workspaces page in the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select a desired region. Find the desired workspace and choose in the Actions column.
In the project folder, click . Configure the Data Source and Destination (source: MaxCompute and destination: Milvus for this tutorial) and the node Name. Then, click Confirm.
2. Configure the offline sync task
Configure basic information.
Data Source: Select the data sources for the source and destination.
Resource Group: Select the resource group to run the offline sync task. The resource group must be attached to the current workspace and be able to connect to the data sources.
If no data sources or resource groups are available, make sure that you have completed the preparations.
Configure the Data Source.
The following are the key parameters for the MaxCompute data source in this tutorial. If you use a different data source, the configuration may vary. You can configure the parameters as needed.
Parameter
Description
Tunnel Resource Group
The default value for Tunnel Quota is
Public Transmission Resource, which is the free quota for MaxCompute. For more information about selecting a data transmission resource, see Purchase and use exclusive Data Transmission Service resource groups.ImportantIf an exclusive Tunnel Quota becomes unavailable due to an overdue payment or expiration, a running job automatically switches to
Public Transmission Resource.Table
Select the source table to synchronize.
If no source tables are available, make sure you have prepared the test data.
Filtering Method
Supports Partition Filter and Data Filtering:
If the source table is a partitioned table, you can select the data to sync by partition.
If the source table is a non-partitioned table, you can use a
WHEREclause to select the data to sync.
Click Data Preview to check if the configuration is correct.
Configure Data Processing.
Enable the data processing switch. Then, in the Data Processing List, click to add a Data Embedding processing node.
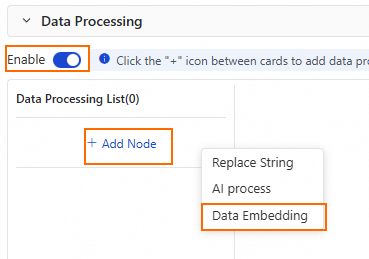
Configure the data vectorization node.
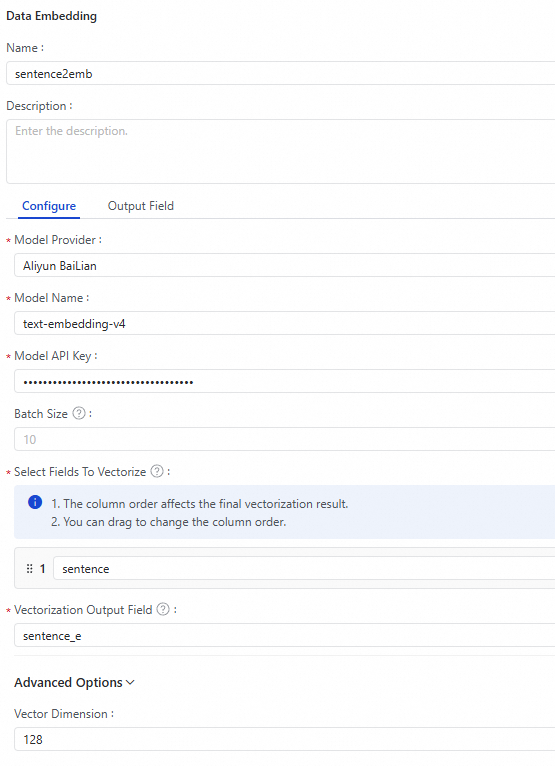 The key parameters are described as follows:Note
The key parameters are described as follows:NoteThe performance of the data vectorization node depends on the performance of the configured model. The QWen model provided by Alibaba Cloud Model Studio has a queries per second (QPS) limit. For the Alibaba Cloud PAI model marketplace, you need to deploy the model on PAI Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS). Its performance depends on the resource specifications used for deployment.
For a given set of parameters, the vectors generated by an embedding model are deterministic. Therefore, DataWorks Data Integration uses a Least Frequently Used (LFU) cache for identical raw data during synchronization. This optimization avoids redundant calls to the embedding model for the same data, which improves processing performance and reduces embedding costs.
Parameter
Description
Model Provider
The large language model provider. The following providers are currently supported: Alibaba Cloud DataWorks model service, Alibaba Cloud Model Studio, and Alibaba Cloud PAI model marketplace.
Model Name
The name of the embedding model. Select one as needed.
Model API Key
The API key to access the model. Obtain this key from the model provider.
Alibaba Cloud Model Studio: Obtain a Model Studio API key.
Alibaba Cloud PAI Model Marketplace: Go to the deployed EAS task and open Online Debugging. Get the value of the Authorization parameter from the headers. Enter this value as the API key.
Model Endpoint
When you set Model Provider to Alibaba Cloud PAI Model Marketplace, you must configure the endpoint (Endpoint API address) to access the model.
Batch Size
The batch size for vectorization. This depends on whether the embedding model supports batch processing. Batch processing helps improve embedding performance and reduce costs. The default value is 10.
Select Fields To Vectorize
Define the columns to vectorize and specify the name of the output field. Data Integration supports vectorizing a single source field or a concatenation of multiple fields.
Vectorization Output Field
The name of the vectorized field defined after vectorizing the source table field.
Vector Dimension
The dimensions of the output vector. The configured embedding model must support the defined vector dimensions. The default value is 1024.
Convert NULL To Empty String
Large language models do not allow NULL data for vectorization. If the source data contains NULL values, you can convert them to empty strings to prevent vectorization errors. This option is disabled by default.
Concatenate Field Name
Specifies whether to concatenate the field name with the text for vectorization. If you select this option, you must also configure the Field Name Delimiter. This option is disabled by default.
Skip Empty Fields
When concatenating multiple fields for vectorization, specifies whether to skip empty fields. By default, this option is selected, and empty fields are skipped.
Preview data output.
Click Data Output Preview in the upper-right corner of the data vectorization node configuration area. Then, click Preview to view the vectorized results and confirm that the configuration is correct.
You can also click Simulate Run at the top of the offline sync edit page to preview the vectorized results.
Configure the Destination.
The following are the key parameters for the Milvus data source in this tutorial. If you use a different data source, the configuration may vary. You can configure the parameters as needed.
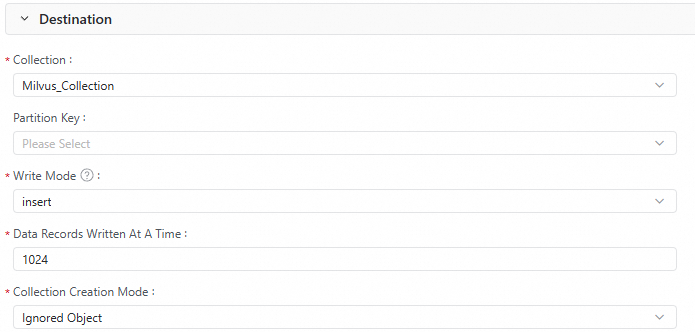
Parameter
Description
Collection
The collection that receives the vector data.
Partition Key
Optional. If the collection is partitioned, you can specify a partition for the received vector data.
Write Mode
upsert:
If autoid is not enabled for the table: Updates an entity in the collection based on the primary key.
If autoid is enabled for the table: Replaces the primary key in the entity with an auto-generated primary key and inserts the data.
insert: Mainly used to insert data into tables with autoid enabled. Milvus automatically generates the primary key.
Using
inserton a table without autoid enabled will cause data duplication.
Configure Destination Field Mapping.
After you configure the data source, data processing, and data destination, the offline sync task automatically generates a field mapping. Because the destination is a data source with no fixed schema, the mapping is performed row by row by default. Click Edit next to a Source Field or Target Field to adjust the mapping order or delete unnecessary fields to ensure that the mapping is correct.
For example, in this tutorial, unnecessary fields are manually deleted. The adjusted mapping is as follows.
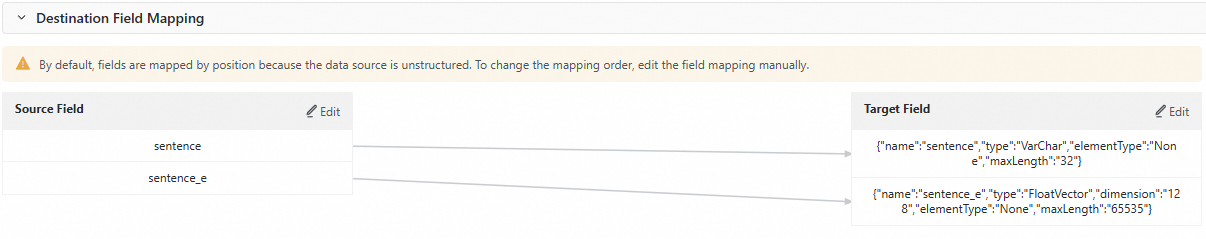
Configure Advanced Configuration.
Click Advanced Configuration on the right side of the node configuration page. You can set parameters such as task concurrency, sync rate, and dirty data policy as needed.
3. Test run
On the right side of the offline sync node edit page, click Run Configuration. Set the Resource Group and Script Parameters for the test run. Then, click Run in the top toolbar to test whether the synchronization pipeline runs successfully.
Go to Milvus and check whether the data in the destination collection is as expected.
4. Configure scheduling and publish
On the right side of the offline sync task, click Scheduling. Set the scheduling configuration parameters for periodic runs. Then, click Publish in the top toolbar. In the publish panel, follow the on-screen instructions to publish the task.
Code editor configuration
This tutorial uses an example in which data is read from a MaxCompute (ODPS) source, vectorized using embedding, and then synchronized to Milvus. It shows how to configure an offline sync task in Data Integration using the code editor.
1. Create an offline sync node
Go to the Workspaces page in the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select a desired region. Find the desired workspace and choose in the Actions column.
In the project folder, click . Configure the Data Source and Destination (source: MaxCompute and destination: Milvus for this tutorial) and the node Name. Then, click Confirm.
2. Configure the sync script
Click
 in the toolbar at the top of the offline sync node to switch to the code editor.
in the toolbar at the top of the offline sync node to switch to the code editor.Configure the offline sync task from MaxCompute to Milvus.
Configure the JSON script for the offline sync task based on Appendix 1: Code editor format description. The script for this example is as follows:
{ "type": "job", "version": "2.0", "steps": [ { "stepType": "odps", "parameter": { "partition": [ "split=dev" ], "datasource": "MaxCompute_Source", "successOnNoPartition": true, "tunnelQuota": "default", "column": [ "sentence" ], "enableWhere": false, "table": "test_tb" }, "name": "Reader", "category": "reader" }, { "category": "flatmap", "stepType": "embedding-transformer", "parameter": { "modelProvider": "bailian", "modelName": "text-embedding-v4", "embeddingColumns": { "sourceColumnNames": [ "sentence" ], "embeddingColumnName": "sentence_e" }, "apiKey": "sk-****", "dimension": 128, "nullAsEmptyString": true }, "displayName": "sentence2emb", "description": "" }, { "stepType": "milvus", "parameter": { "schemaCreateMode": "ignore", "enableDynamicSchema": true, "datasource": "Milvus_Source", "column": [ { "name": "sentence", "type": "VarChar", "elementType": "None", "maxLength": "32" }, { "name": "sentence_e", "type": "FloatVector", "dimension": "128", "elementType": "None", "maxLength": "65535" } ], "writeMode": "insert", "collection": "Milvus_Collection", "batchSize": 1024, "columnMapping": [ { "sourceColName": "sentence", "dstColName": "sentence" }, { "sourceColName": "sentence_e", "dstColName": "sentence_e" } ] }, "name": "Writer", "category": "writer" } ], "setting": { "errorLimit": { "record": "0" }, "speed": { "concurrent": 2, "throttle": false } }, "order": { "hops": [ { "from": "Reader", "to": "Writer" } ] } }For an explanation of the parameters in the Reader and Writer sections, see MaxCompute data source and Milvus data source.
If you use other types of sources and destinations, see Data source list.
The parameters for the data vectorization processing node in the script are described as follows:
Parameter
Description
Required
modelProvider
The large language model provider. The following providers are currently supported:
dataworksModelService: A model service deployed through the DataWorks Large Language Model Service.
bailian: Alibaba Cloud Model Studio. Supports QWen models.
paiModelGallery: Alibaba Cloud PAI model marketplace. Supports BGE-M3 models.
Yes
modelName
The name of the embedding model.
When modelProvider is bailian, you can select
text-embedding-v4ortext-embedding-v3.When modelProvider is paiModelGallery, you can select
bge-m3.
Yes
apiKey
The API key to access the model. Obtain this key from the model provider.
Yes
endpoint
When modelProvider is paiModelGallery, you must configure the endpoint (Endpoint API address) to access the model.
No
batchSize
The batch size for vectorization. This depends on whether the embedding model supports batch processing. Batch processing helps improve embedding performance and reduce costs. The default value is 10.
No
embeddingColumns
Defines which columns to vectorize and specifies the output field name for the vectorized data. Data Integration supports vectorizing a single source field or a combination of multiple concatenated fields.
Example:
{ "embeddingColumns": { "sourceColumnNames": [ "col1", "col2" ], "embeddingColumnName": "my_vector" } }Yes
appendDelimiter
The delimiter used to concatenate multiple field values into a single text for vectorization. The default value is
\n.No
skipEmptyValue
When concatenating multiple fields for vectorization, specifies whether to skip empty fields. The default value is False.
No
dimension
The dimensions of the output vector. The configured embedding model must support the defined vector dimensions. The default value is 1024.
No
nullAsEmptyString
Large language models do not allow NULL data for embedding. If the source data contains NULL values, you can convert them to empty strings to prevent vectorization errors. The default value is
False.No
appendFieldNameEnable
Specifies whether to concatenate the raw data with the field name for vectorization. If enabled, you must also configure appendFieldNameDelimiter. The default value is
False.No
appendFieldNameDelimiter
The delimiter for concatenating field names. This parameter takes effect only when appendFieldNameEnable is enabled.
No
Simulate the run.
Click Dry Run at the top of the offline sync node edit page. Then, click Start Sampling and Preview to view the vectorized results and confirm that the configuration is correct.
Configure Advanced Configuration.
Click Advanced Configuration on the right side of the node configuration page. You can set parameters such as task concurrency, sync rate, and dirty data policy as needed.
3. Test run
On the right side of the offline sync node edit page, click Run Configuration. Set the Resource Group and Script Parameters for the test run. Then, click Run in the top toolbar to test whether the synchronization pipeline runs successfully.
Go to Milvus and check whether the data in the destination collection is as expected.
4. Configure scheduling and publish
On the right side of the offline sync task, click Scheduling. Set the scheduling configuration parameters for periodic runs. Then, click Publish in the top toolbar. In the publish panel, follow the on-screen instructions to publish the task.
Appendix 1: Code editor format description
The basic structure of the code editor is as follows:
{
"type": "job",
"version": "2.0",
"steps": [
{
"stepType": "xxx",
"parameter": {
},
"name": "Reader",
"category": "reader"
},
{
"stepType": "xxx",
"parameter": {
},
"name": "transformer1",
"category": "map/flatmap"
},
{
"stepType": "xxx",
"parameter": {
},
"name": "transformer2",
"category": "map/flatmap"
},
{
"stepType": "xxx",
"parameter": {
},
"name": "Writer",
"category": "writer"
}
],
"setting": {
}
}The steps array defines the operators for each process. It must contain at least one Reader and one Writer. You can include multiple Transformer operators in between. For example, if you set the concurrency to 2, a job will have two parallel data processing streams. Each Reader, Transformer, and Writer is a step in the task configuration.
The steps array defines the type and parameters for each operator. The data synchronization and processing strictly follow the order of each step in the JSON configuration.
For detailed parameter configurations for the read and write channels of various data sources supported by Data Integration, see Supported data sources and sync solutions.
Appendix 2: Example of synchronizing data from OSS to Milvus
This example shows how to synchronize data in JSONL format from OSS, parse the JSON data, vectorize specified fields in the JSON, and finally synchronize the data to Milvus. The complete JSON configuration is as follows:
{
"type": "job",
"version": "2.0",
"steps": [
{
"stepType": "oss",
"parameter": {
"datasource": "${OSS_Data_Source_Name}",
"column": [
{
"name": "chunk_text",
"index": 0,
"type": "string"
}
],
"fieldDelimiter": ",",
"encoding": "UTF-8",
"fileFormat": "jsonl",
"object": [
"embedding/chunk1.jsonl"
]
},
"name": "Reader",
"category": "reader"
},
{
"stepType": "json-extracting",
"parameter": {
"column": [
{
"name": "text",
"fromColumn": "chunk_text",
"jsonPath": "$.text",
"type": "STRING",
"nullOrInvalidDataAction": "DIRTY_DATA"
}
]
},
"name": "jsonextract",
"category": "flatmap"
},
{
"stepType": "embedding-transformer",
"parameter": {
"modelProvider": "bailian",
"modelName": "text-embedding-v4",
"apiKey": "${Your_API_Key}",
"embeddingColumns": {
"sourceColumnNames": [
"text"
],
"embeddingColumnName": "my_vector"
},
"batchSize": 8,
"dimension": 1024
},
"name": "embedding",
"category": "flatmap"
},
{
"stepType": "milvus",
"parameter": {
"schemaCreateMode": "ignore",
"enableDynamicSchema": true,
"datasource": "${Milvus_Data_Source_Name}",
"column": [
{
"name": "my_vector",
"type": "FloatVector",
"dimension": "1024",
"elementType": "None",
"maxLength": "65535"
},
{
"name": "text",
"type": "VarChar",
"elementType": "None",
"maxLength": "65535"
}
],
"collection": "yunshi_vector_07171130",
"writeMode": "insert",
"batchSize": 1024,
"columnMapping": [
{
"sourceColName": "my_vector",
"dstColName": "my_vector"
},
{
"sourceColName": "text",
"dstColName": "text"
}
]
},
"name": "Writer",
"category": "writer"
}
],
"setting": {
"errorLimit": {
"record": "0"
},
"speed": {
"concurrent": 1
}
}
} > Create Node > Data Integration > Batch Synchronization
> Create Node > Data Integration > Batch Synchronization