Transit routers can be used to establish network communication between network instances and forward network traffic within a region or across regions. Transit routers support a range of routing features. You can configure routes to define how traffic is forwarded between network instances.
How Enterprise Edition transit routers work
Connect network instances
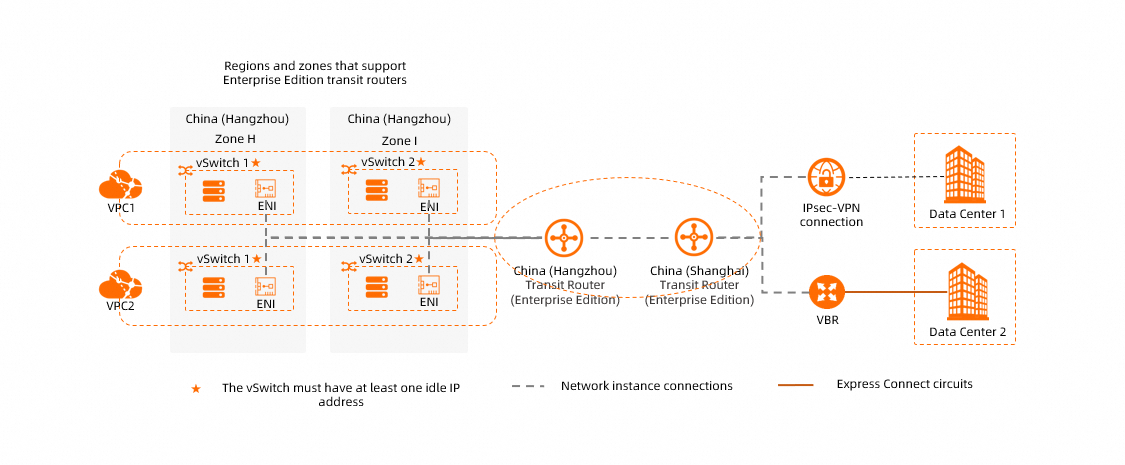
You can connect the following network instances to an Enterprise Edition transit router:
One or more virtual private clouds (VPCs)
In regions where Enterprise Edition transit routers are available in only one zone, such as China (Nanjing - Local Region), make sure that the VPC to be connected has at least one vSwitch in the zone and that the vSwitch has at least one available IP address. When you connect the VPC to the Enterprise Edition transit router, an elastic network interface (ENI) is created in the vSwitch. The ENI occupies one IP address in the vSwitch and forwards network traffic between the VPC and Enterprise Edition transit router.
In regions where Enterprise Edition transit routers are available in more than one zone, such as China (Hangzhou), make sure that the VPC to be connected has at least two vSwitches. The vSwitches need to be located in different zones, with each having an available IP address. When you connect the VPC to the Enterprise Edition transit router, an ENI is created in each of the vSwitches. Each ENI occupies one IP address in the vSwitch and forwards network traffic between the VPC and Enterprise Edition transit router. The two vSwitches support zone-disaster recovery to ensure uninterrupted data transmission between the VPC and the transit router.
NoteFor information about the regions and zones that support Enterprise Edition transit routers, see What is CEN?.
If your Enterprise Edition transit router is deployed in a region that supports multiple zones, we recommend that you create a vSwitch in each of the zones for VPC connections. Make sure that each vSwitch has at least one idle IP address. This way, the network latency is reduced and the network performance is improved due to shorter data transmission distance. For more information, see VPC connection routing principles.
Routing
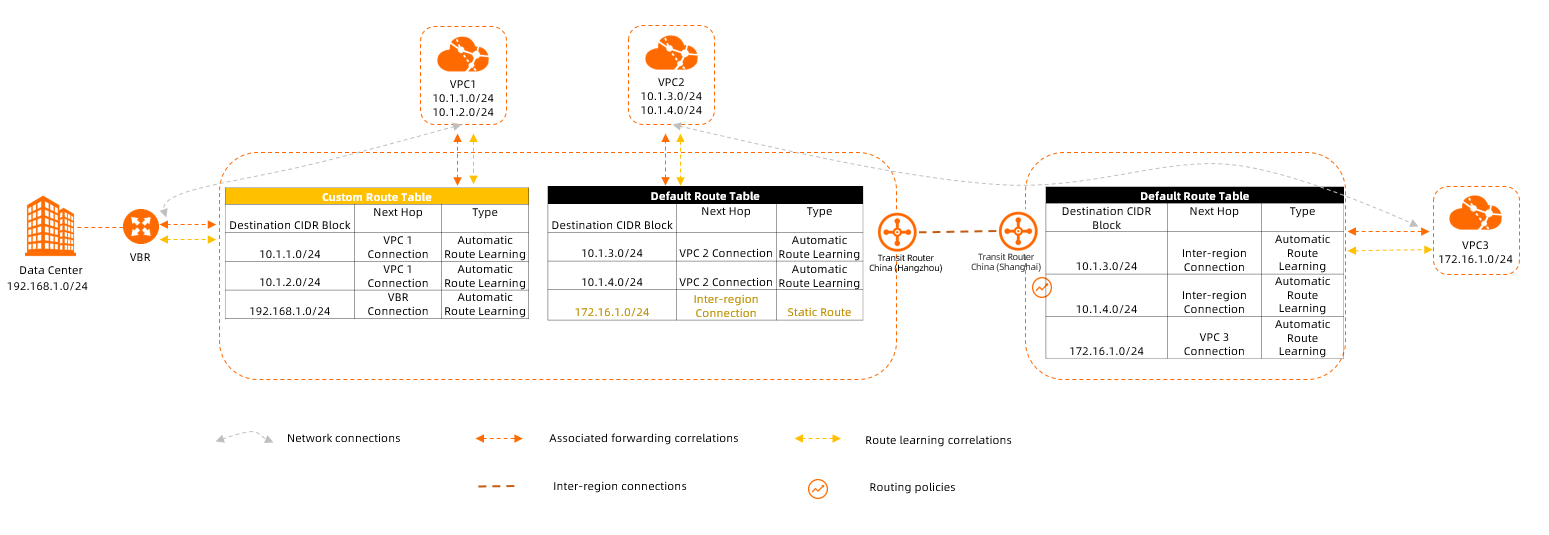
After network instances are connected to an Enterprise Edition transit router, routes of the network instances are stored in route tables. The Enterprise Edition transit router forwards traffic of the network instances based on the routes in the route table.
Each Enterprise Edition transit router has a default route table. You can also create custom route tables for Enterprise Edition transit routers. Default route tables are isolated from custom route tables for access control.
Associated forwarding controls how network traffic is forwarded. An Enterprise Edition transit router can forward network traffic for a network instance by querying routes only after the network instance connection is associated with the route table.
Each network instance connection can have an associated forwarding correlation with the route tables of only one Enterprise Edition transit router.
Route learning controls how a network instance advertises routes. The routes of a network instance can be advertised to an Enterprise Edition transit router only after you enable route learning between the network instance connection and the route tables of the transit router.
You can enable route learning between the network instance connection and the route tables of one or more Enterprise Edition transit routers. Then, routes can be advertised from the network instance to the route tables.
You can add custom routes to the route tables of an Enterprise Edition transit router to manage traffic forwarding.
Default route behavior
After a network instance is connected to an Enterprise Edition transit router, no routes are advertised to the network instance by default. You can enable route synchronization to turn on the feature. For more information, see Route synchronization.
Route priority
Traffic that enters Enterprise Edition transit routers is routed based on the Longest Prefix Match principle. In cases where there are multiple routes to the same destination CIDR block, the routing is determined in the following order of priority:
If there is a static or dynamic route entry in the route table with the VPC connection as the next hop, any learned route entries from other network instances with the same destination will be marked as conflicting.
If there is a dynamic route entry sourced from a VPC, any learned route entries from other network instances with the same destination will be marked as conflicting.
If there is a static or dynamic route entry that is not sourced from a VPC, any learned route entries from a VPC with the same destination will be marked as conflicting.
NoteVPCs and on-premises networks host different services. There should be no active-standby or Equal-Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) relationships between overlapping CIDR blocks across VPCs or hybrid clouds.
To prevent conflicts, a transit router uses route conflict rules. When receiving a duplicate route from another service, it blocks connectivity between the new and existing networks without disrupting traffic for existing services. This ensures no impact on production workloads.
For route entries that point to a data center and do not cause routing conflicts, the route priority will be determined by comparing the following items in order:
Static routes in route tables: Static routes manually configured in the route table have the highest priority, including custom route entries and entries of prefix lists. When both are configured, they automatically form ECMP routes.
Dynamic routes: If route entries are automatically learned, the priority is determined in the following order of priority:
Type of source instance: The priority is in the descending order: VBR instances > Express Connect Router (ECR) instances > Cloud Connect Network (CCN) instances > IPsec connections (VCO).
Type of route entry in source route table: BGP route entries take precedence over custom route entries.
As-Path: Routes with shorter BGP AS_PATH length are preferred.
Next hop: Intra-region connections are prioritized over inter-region ones.
Routing policy: Select a route entry based on priority specified by the routing policy. A lower value indicates a higher priority.
If none of the above rules determine the route priority, the following applies:
For intra-region next hops: ECMP routing is enabled.
For inter-region next hops: If the transit router route table has multi-region ECMP Routing for VBRs enabled and the source instance is a VBR or ECR, ECMP is enabled. If disabled, priority is determined by comparing the region IDs of the next-hop transit routers. Entries with alphabetically earlier region IDs are prioritized.
IPv6 Description
Enterprise Edition transit routers are capable of learning and propagating IPv6 routes as well as forwarding IPv6 traffic. By connecting VPC, ECR, and VBR instances to the transit router, you can enable IPv6 communication for the associated local networks in the same region or across regions.

Network instances supported by IPv6
Network instance | Description |
Enterprise Edition transit router | Enterprise Edition transit routers have IPv6 network communication enabled by default upon creation. |
VPC | IPv6 network communication is supported. To facilitate IPv6 communication through an Enterprise Edition transit router, the following prerequisites need to be met:
|
ECR | ECR instances have IPv6 network communication enabled by default upon creation. |
VBR | IPv6 network communication is supported. To enable IPv6 communication through an Enterprise Edition transit router, the VBR instance needs to have IPv6 enabled. For more information, see Create a VBR. |
IPsec-VPN connection | IPv6 network communication is not supported. |
Cloud Connect Network (CCN) | IPv6 network communication is not supported. |
Limits
The multicast feature does not support IPv6 network communication.
IPv6 route entries consume the route table entry quota of the transit routers.
For example, if the maximum number of route entries for a transit router is 10,000, the combined total of IPv4 and IPv6 entries must be lower than the quota.
IPv4 and IPv6 traffic and routing behaviors are aligned for all features of transit routers, with the exception of the following scenarios.
When you select IPv Automatically Create Route That Points to Transit Router and Add to All Route Tables of Current VPC upon creating a VPC connection, the system automatically adds three custom route entries of 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16 to all route tables, directing IPv4 traffic to the transit router. However, IPv6 routes are not added automatically.
To enable IPv6 communication through the transit router for a VPC instance, activate route synchronization after creating a VPC connection, or manually add IPv6 route entries in the VPC route tables. This step is necessary for routing IPv6 traffic to the transit router. For more information, see Establish inter-region IPv6 communication with transit router
How Basic Edition transit routers work
Beginning March 31, 2022, Basic Edition transit routers are supported only in CCN areas. They are not available for purchase in Alibaba Cloud regions. By default, only Enterprise Edition transit routers are available for purchase in Alibaba Cloud regions. If your Basic Edition transit routers reside in regions that no longer support Basic Edition transit routers, we recommend that you upgrade to Enterprise Edition, which supports more features and greater networking capacity. For more information, see Upgrade Basic Edition transit routers.
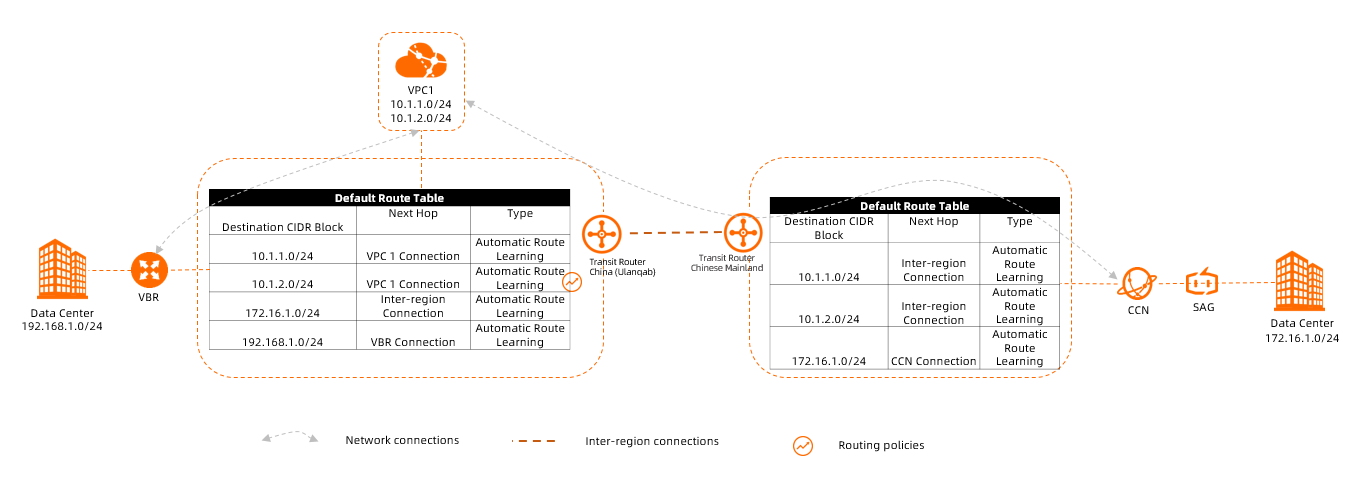
Connecting network instances
You can connect the following network instances to a Basic Edition transit router:
Manage routes
After network instances are connected to a Basic Edition transit router, routes of the network instances are stored in route tables. The Basic Edition transit router forwards traffic of the network instances based on the routes of the route table.
Each Basic Edition transit router has one default route table. You cannot create custom route tables for Basic Edition transit routers.
After network instances are connected to a Basic Edition transit router, all routes of the network instances are advertised to the default route table of the Basic Edition transit router. Then, the Basic Edition transit router advertises the routes to all network instances that are also connected to the transit router to enable communication among the network instances.
You can configure routing policies to control route advertisement for the route tables of a Basic Edition transit router. You can configure routing policies to specify whether to advertise the routes in the route table of a Basic Edition transit router to the network instances connected to the transit router. You can also configure routing policies to modify the attributes of the routes in the route table of a Basic Edition transit router.
If both VBRs and CCN instances are connected to a Basic Edition transit router, the system automatically creates a routing policy whose priority is 5000, action is Reject, and direction is Egress Regional Gateway. This routing policy forbids the VBRs and CCN instances from communicating with other VBRs and CCN instances that are also connected to the Basic Edition transit router. For more information, see Default routing policy.