Today, interactions with large language models (LLMs) are mainly controlled by prompt engineering, but this approach faces several significant challenges:
(1) Missing context leads to frequent hallucinations. To avoid hallucinations, users often have to repeatedly restate historical information during interactions with an AI agent, which results in very poor user experience.
(2) Context overflow can exceed an LLM's context window, raising costs and dramatically degrading the performance of an AI agent.
(3) Very long contexts surface four types of context failures: contamination, interference, confusion, and conflict. These failures directly undermine inference stability and cross-agent transfer.
• Context contamination: Hallucinated content enters the context and produces abnormal outputs.
• Context interference: As the context approaches capacity, knowledge learned during training can be effectively "overwritten," causing the LLM to degrade.
• Context confusion: Redundant or irrelevant context steers outputs away from the intended result.
• Context conflict: Contradictory information in the context, such as previously produced incorrect answers, harms reasoning accuracy.
Context engineering, as proposed by Tobi Lütke and Andrej Karpathy, reframes how we manage information for LLMs. Karpathy compares an LLM to a computer OS, with the context window acting as memory. Context engineering is the memory manager inside that OS. Its role is not simply to fill the memory (the context window) with as much data as possible, but to use sophisticated scheduling policies to decide, at each "clock cycle," which data to load, which to evict, and which to prioritize. By doing so, it preserves smooth operations and improves the accuracy of the final output.
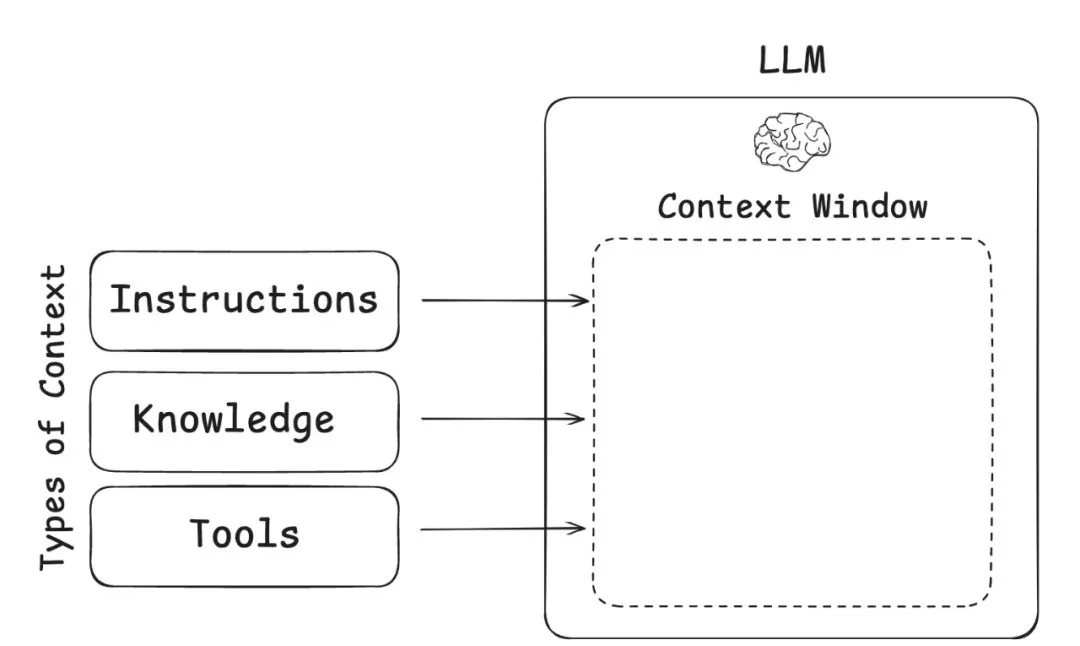
Image source: https://rlancemartin.github.io/2025/06/23/context_engineering/
An AI context typically comprises the following elements:
• Instructions and system prompts: the scenario-setting directives that tell the AI agent what kind of task to perform.
• Long-term memory: the persistent storage used to retain and retrieve extended conversation history or other long-lived information.
• Global states and history: a running, notepad-style record that captures the contextual background for the LLM during interactions.
• Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG): a knowledge-base layer that supplements the AI agent with domain-specific information.
• Tools: the external tools and auxiliary resources that the AI agent can call or consult.
• User prompts: the custom prompts provided by users.
• Structured outputs: the concise, structured data produced as background or constraints for specific tasks.
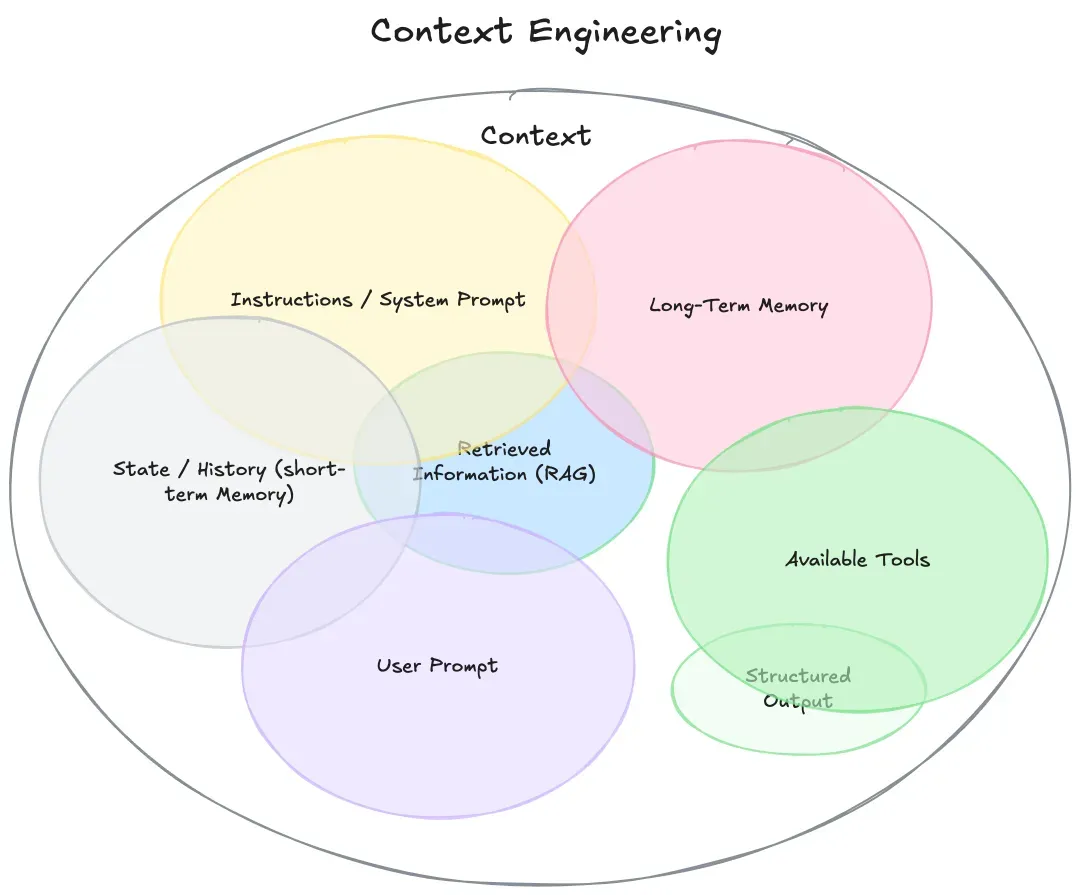
Image source: https://rlancemartin.github.io/2025/06/23/context_engineering/
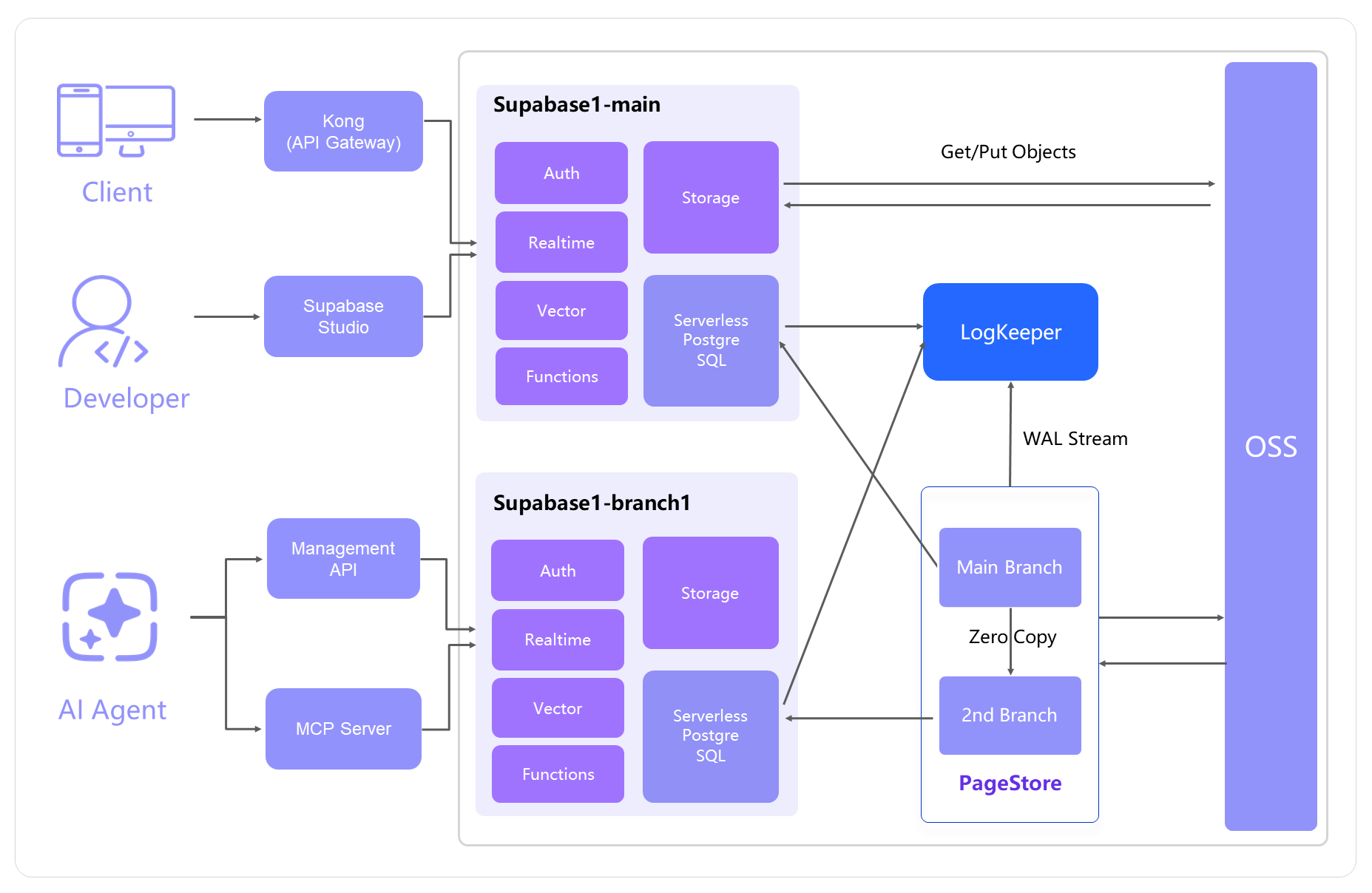
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, part of the Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB ecosystem, is a cloud-native data warehouse built for Data + AI workloads. Even before the rise of LLMs, it already supported vector, scalar, and full-text retrieval. As AI agents have become widespread, AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL has added powerful document parsing, multimodal search, and an enhanced RAG framework that combines knowledge graphs with conventional RAG. These features have enabled more than 30,000 enterprise customers to build production-grade knowledge bases. AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL is also the built-in and officially supported enterprise knowledge-base engine for platforms such as Alibaba Cloud Model Studio, Lingma, Taobao Mobile, and Ant Group Digital Technologies. AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL also provides a long-term memory framework and an all-in-one backend-as-a-service (BaaS) service, Supabase, helping enterprises rapidly deploy AI agents for tasks such as content deduplication, event-chain analysis, similar-event recommendation, sales quality audit, product image search, audio/video analysis, public-opinion monitoring, and review summarization.
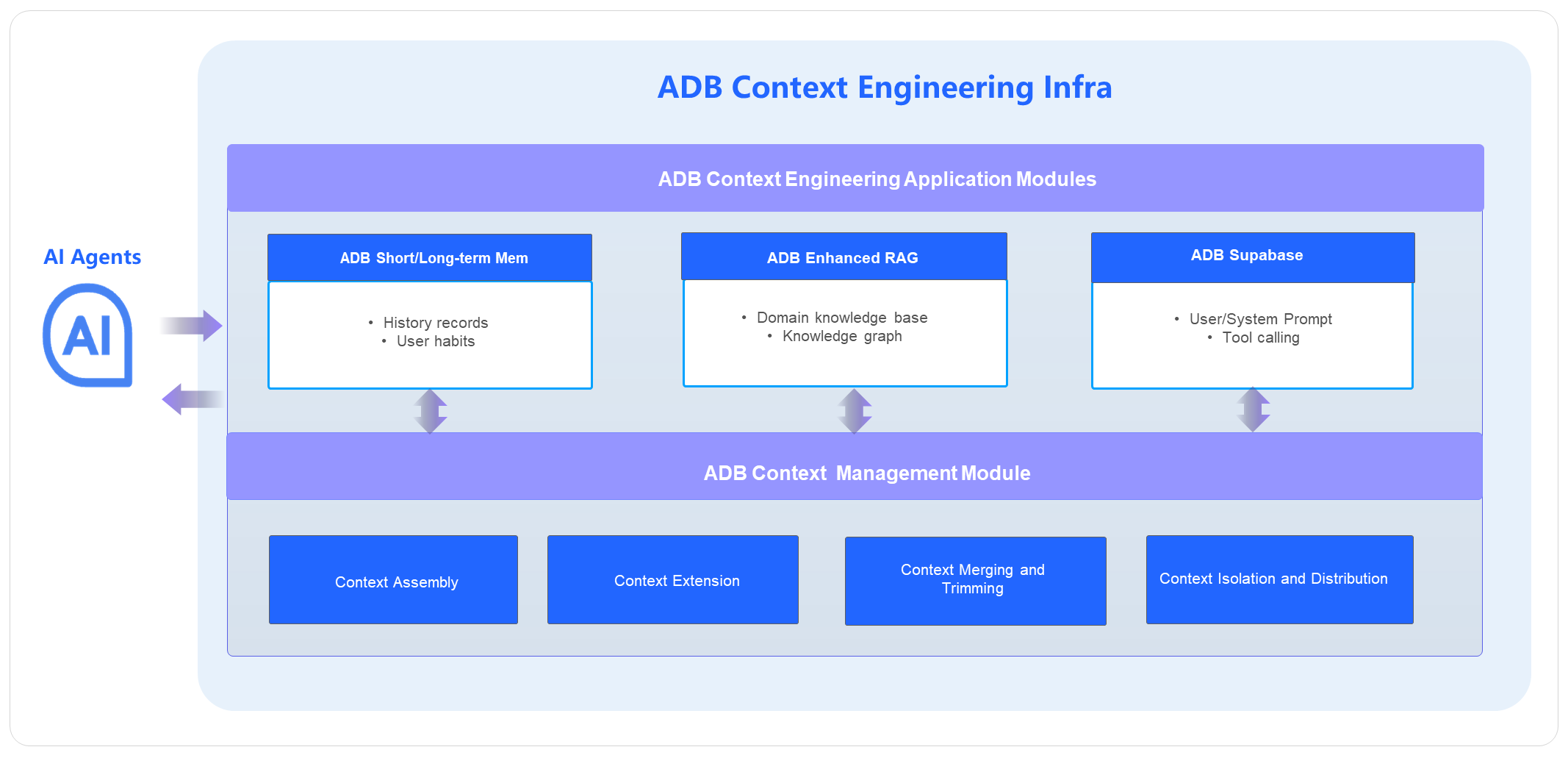
The context produced during AI agent interactions is stored, processed, and assembled into effective contextual information by different application modules within AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL.
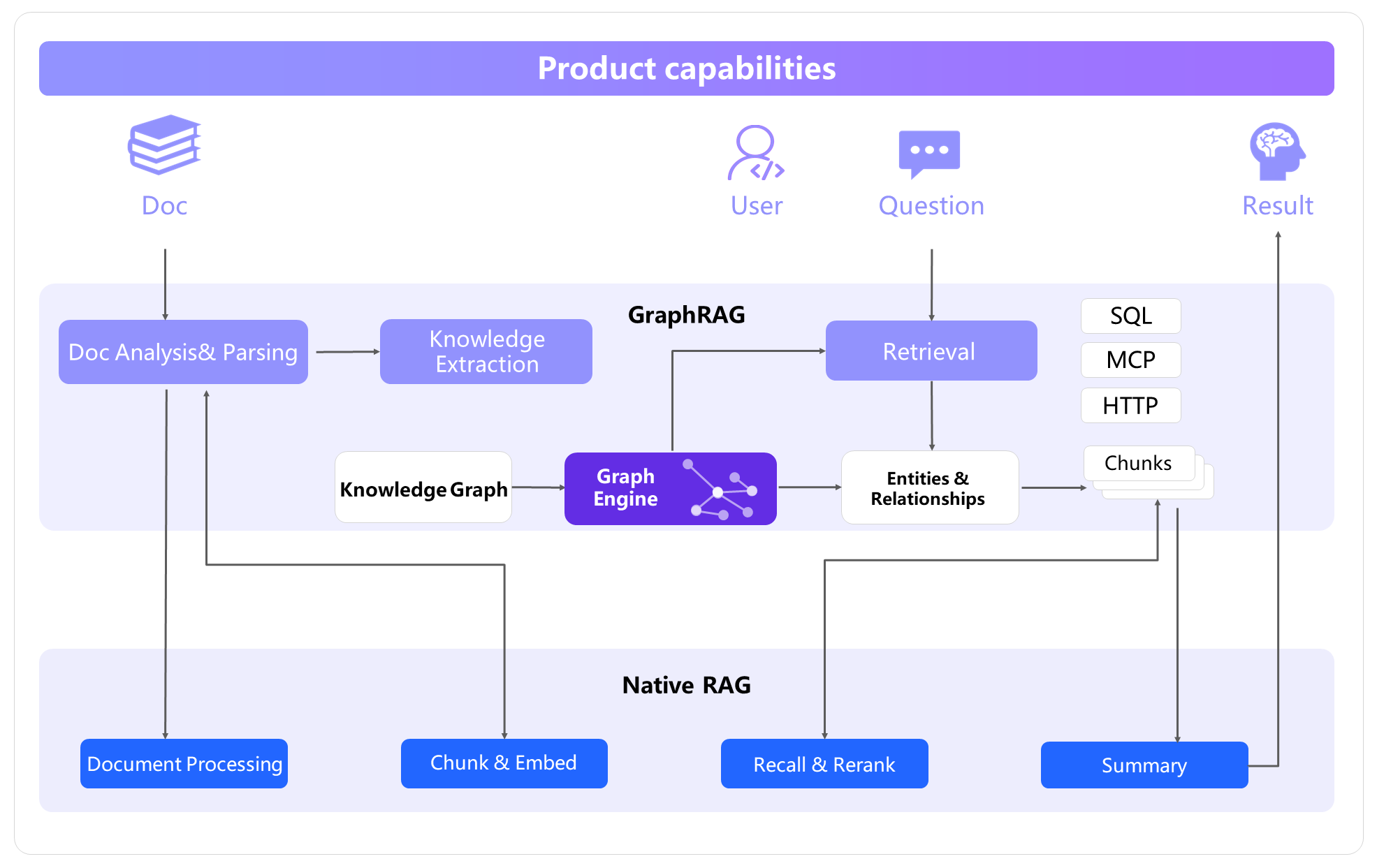
The enhanced RAG module enables AI agents to access vast amounts of domain knowledge without causing an LLM's context window to be exceeded. It typically shortens the response time, compared with direct access to an LLM. The approach decomposes large documents into smaller chunks, stores them in a vector database, and then retrieves the most relevant pieces by using semantic search. AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL further combines knowledge graphs with RAG to form GraphRAG, which preserves domain knowledge and the relationships between knowledge items. In complex scenarios such as comparative inference, relational inference, and summarization inference, this approach can deliver more than a twofold improvement in effectiveness.
The AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL memory module enables AI agents to retain key facts or personal information over extended periods. It also supports memory transfer across multiple AI agents, allowing them to collaborate and form a coordinated knowledge network. Using the high-performance vector and graph engines of AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, the memory module works out of the box and provides a comprehensive suite of capabilities, including automatic memory extraction, summarization, updating, and merging. It mimics how the human brain dynamically updates its understanding as new information is acquired, and recalls key fragments in familiar situations. Moreover, the memory module offers enterprise-grade features such as memory lifecycle management, customizable memory filters, automatic and user-defined memory creation, keyword-based memory retrieval, and intelligent reranking. These features enhance retrieval accuracy, simplify memory management, and reduce both storage and model interaction costs. By maintaining and consolidating memories, the memory module eliminates the need for users to repeatedly restate historical information during interactions and minimizes noise and interference based on continuous memory updates and merging.
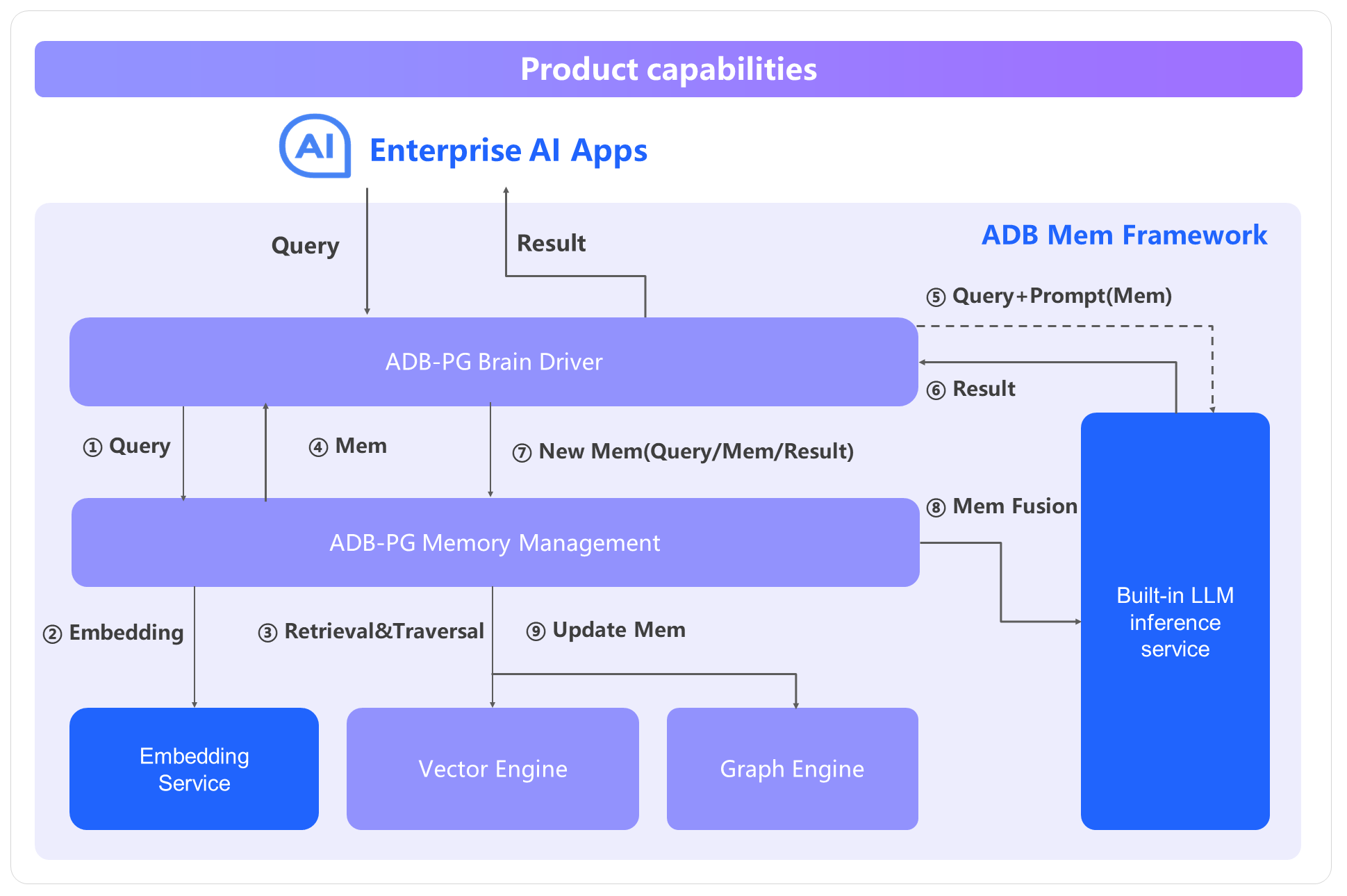
Just as humans take notes while working on tasks, AI agents also need a similar capability. AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL Supabase, an all-in-one BaaS service, provides AI agents with a notebook-like feature for recording information generated during LLM operations, including user and system prompts, instructions, system states, and interaction logs. Unlike long-term memory, the notebook is designed to capture key information that fits within an LLM's context window, ensuring that the most relevant context is readily accessible. Furthermore, AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL Supabase supports edge functions that can call third-party services, enabling AI agents to seamlessly call external tools as part of their workflow.
Effective utilization of context relies on lifecycle and scheduling capabilities, ensuring that the context window is populated with the right information at the right time. The AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL context management module supports context collection, classification, storage (write), retrieval (selection), and processing (merging, trimming, and compression) to generate new context, as well as isolation and distribution mechanisms.
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL delivers end-to-end context engineering services, which integrate with users' AI agents by using API and MCP. Upon receiving context data, the end-to-end service interface classifies and stores the data in the appropriate modules while enforcing access control for context isolation. Built-in models then process the context, including merging and trimming, to produce updated context, which is fed back to AI agents by using the interface. In addition, AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL provides atomic services such as RAG, knowledge graphs, long-term memory, and Supabase. These atomic interfaces can be used independently, allowing users to deeply customize and optimize their AI agent workflows.
As illustrated in the following figure, consider an example workflow orchestrated by AI agents for a beverage brand. The company has deployed a series of AI agents: one AI agent interacts with VIP customers, providing consultation and purchase support, whereas another AI agent assists sales staff in strengthening customer engagement. Within this workflow, a sub-agent is responsible for scheduling dinners with VIP customers. How can context engineering be applied throughout this workflow to maximize overall effectiveness?
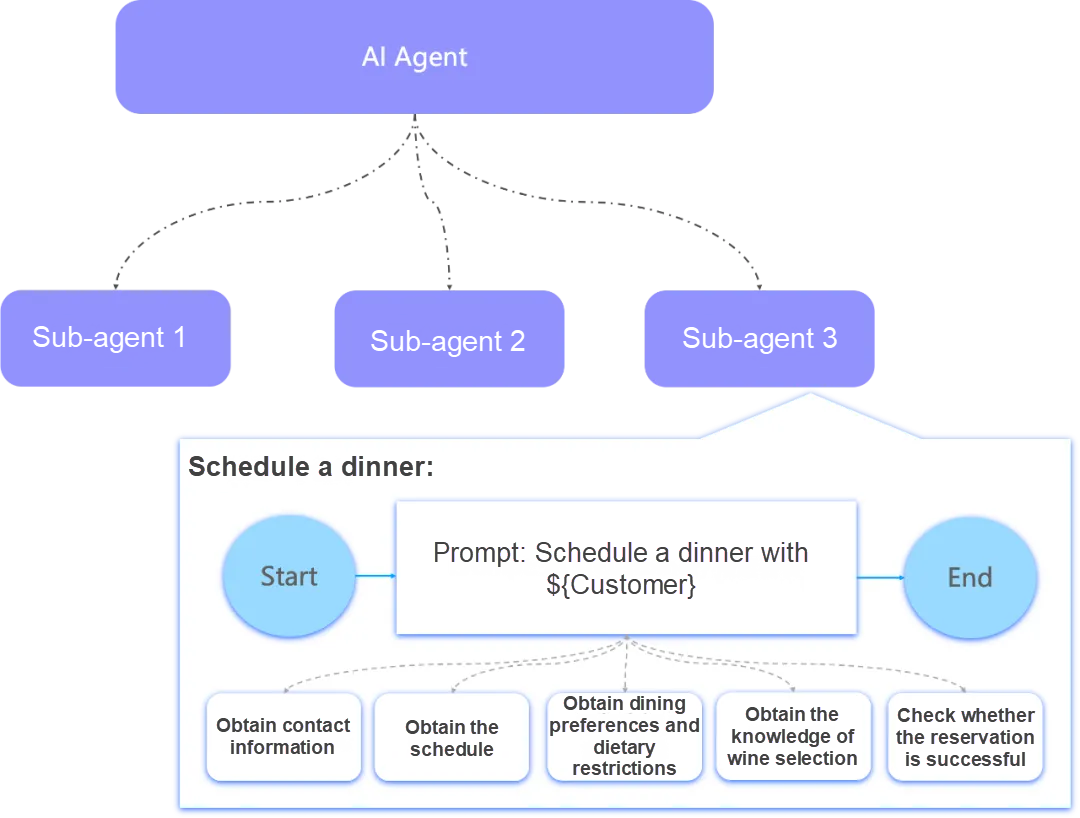
Instructions and system prompts used for interactions with LLMs are stored in a template library. Depending on an AI agent's scenario, appropriate prompts and instructions are selected from the template library to define the tasks to be performed by the AI agent.
Short-term memory is useful for immediate contextual information, but many applications require retaining key facts or personal information over extended periods. In the preceding example, a VIP customer's history captures preferences for food, restaurants, beverages, and any restrictions. The AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL long-term memory framework extracts historical records in batches, summarizes them into customer tags by using built-in models and system settings, and then stores the results in AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL. New incoming records are automatically merged and updated. This framework also supports memory transfer across AI agents, enabling cross-agent knowledge sharing.
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL Supabase retains a limited number of recent messages based on the defined context window size. For example, it may store a VIP customer's annual spending or recent negative reviews. Unlike long-term memory, global states and short-term memory are retained for shorter periods and contain less information, typically serving as initialization data or general context.
The AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL all-in-one RAG engine builds a knowledge base covering all of the brand's beverages, supporting multiple AI agents. The knowledge base may include structured information such as beverage type, vintage, flavor profile (such as sweetness, acidity, tannins, and body), and market reviews, as well as unstructured information such as images and videos. AI agents query this knowledge base based on user preferences and consumption habits from long-term memory to retrieve relevant beverages and descriptions.
AI agents obtain definitions and usage instructions for various tools from AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL. For example, an AI agent may access a contacts directory to retrieve VIP customer information or query a collaboration platform to obtain participants' schedules.
Based on user behavior, corresponding templates from the prompt library are selected and fed as the input to an LLM.
Task context and summaries serve as the input for upstream or downstream AI agents within the workflow.
Context from various sources is retrieved based on an AI agent's requirements and assembled into a unified, consolidated context.
Context can be enriched by using Internet searches or external tool calls. For example, if a user queries domain knowledge that is absent from the internal knowledge base, relevant external sources can be used to supplement the context.
Similar contexts are merged. For example, long-term memory is periodically consolidated and updated. Overly long contexts are trimmed. A direct approach is to limit the text length passed to an AI model. Other strategies include shortening the short-term memory window or restricting the number of blocks returned from vector database queries.
When an AI agent handles numerous tools and tasks, the context window can quickly become overloaded. Context isolation distributes responsibilities across multiple sub-agents, each maintaining its own memory and context management. Certain contexts, such as user identity, VIP level, or global state, need to be shared. Users can configure context sharing and isolation mechanisms within AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL to ensure the proper management and controlled propagation of context.
AI context engineering is a systematic framework for interacting with LLMs. It employs a combination of techniques, including short-term memory, long-term memory, tool call, and RAG, to collect, store, and manage context. Based on context assembly, merging and trimming, and isolation and distribution, it provides LLMs with precise, efficient, and reliable information, thereby improving performance and effectiveness. AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL offers the necessary infrastructure and practical implementations to support AI context engineering, empowering enterprises to build high-quality AI applications.
Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB helps you implement a high-performance and secure AI context engineering solution.
Click the links to learn more.
(1) For more information about the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL all-in-one RAG engine, see https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/analyticdb/analyticdb-for-postgresql/user-guide/rag-service/
(2) For more information about AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL Supabase, see https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/analyticdb/analyticdb-for-postgresql/user-guide/supabase/
Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL 18: The Premier Data Foundation for AI Applications
Solution: Manual Logical Migration from a Self-managed MySQL Database to PolarDB-X Standard Edition
Alibaba Cloud Community - July 29, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - August 22, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - July 24, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - January 4, 2024
5927941263728530 - May 15, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - January 4, 2026
 Container Compute Service (ACS)
Container Compute Service (ACS)
A cloud computing service that provides container compute resources that comply with the container specifications of Kubernetes
Learn More Container Service for Kubernetes
Container Service for Kubernetes
Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes is a fully managed cloud container management service that supports native Kubernetes and integrates with other Alibaba Cloud products.
Learn More AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
An online MPP warehousing service based on the Greenplum Database open source program
Learn More PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB