When monitoring the running status of the system and troubleshooting complex issues, logs have long served as an indispensable observability method. Scientific local log management strategies not only retain more complete historical records locally and minimize performance overhead but also facilitate log collection and subsequent analysis. However, in actual O&M, we often encounter counterexamples. The collection problems caused by such management defects cannot be perfectly solved by mainstream collection tools such as LoongCollector (formerly iLogtail), Filebeat, FluentBit, Vector, and OpenTelemetry Collector. The best practice is to solve the root cause. Here we summarize our experience, hoping to provide some inspiration and collectively enhance log utility for all.
The principle of using the copy truncate mode of Logrotate to rotate logs is to first copy the original log file and then truncate it. This method raises the following issues:
Therefore, the copy truncate mode may lead to issues like duplicate log collection, content loss, or inconsistency.
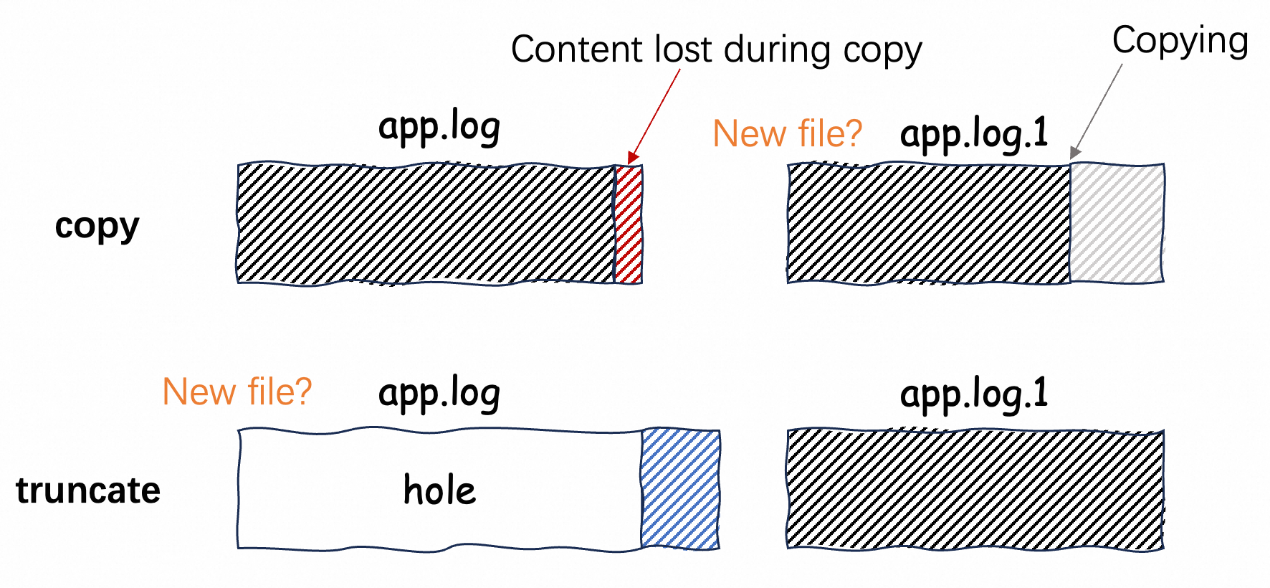
It is recommended to use the create mode for log rotation, that is, to create a new file and rename the old file, which ensures file integrity and continuity. If unavoidable, use the exact path name when configuring the collection settings.
Network-attached storage (NAS) typically employs an eventual consistency model, which is a common design in distributed systems. In real-time collection scenarios, this may cause the following issues:
These issues may cause the collected data to be inconsistent with the final content.
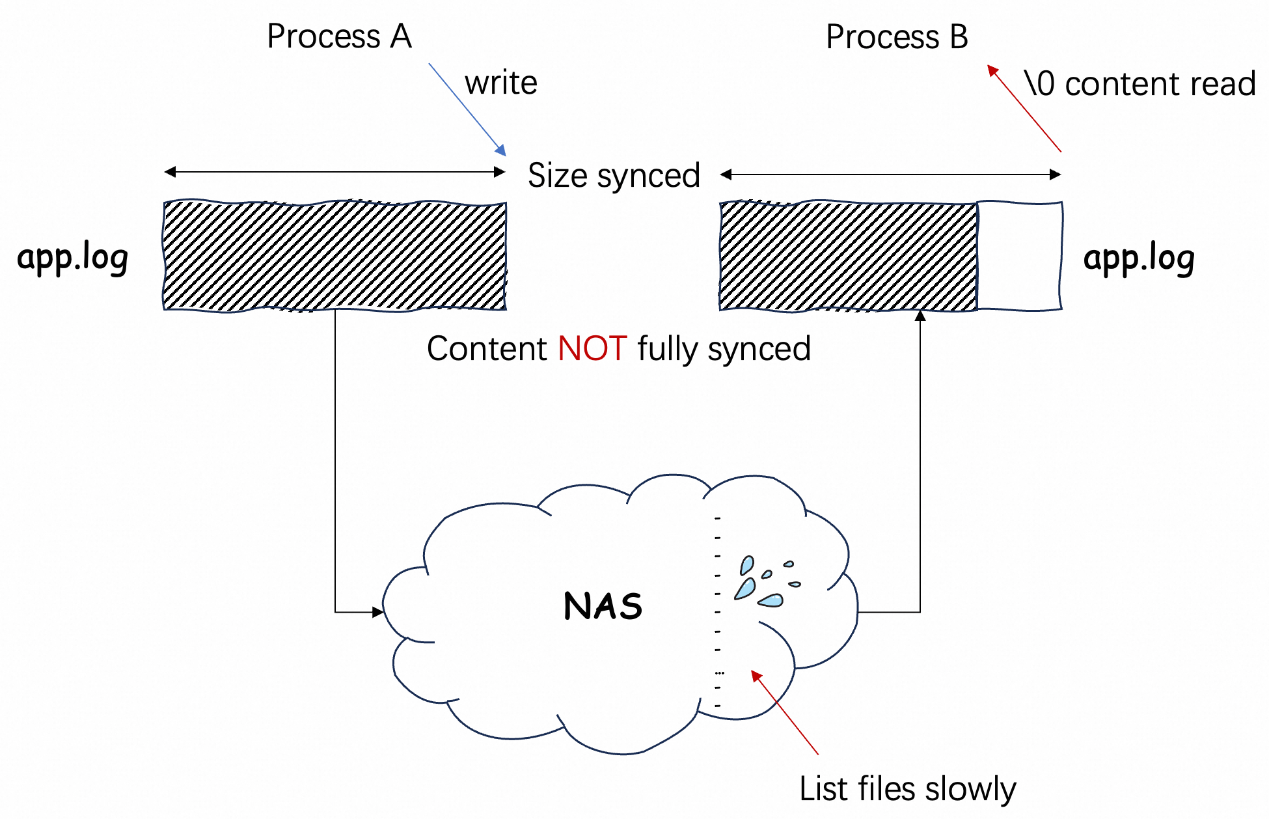
It is recommended to use EBS and use local disks for on-premises servers to ensure the efficiency and consistency of log reading and writing. If unavoidable, implement the compatibility logic for exception logs on the consumer.
It is a common but not recommended practice for multiple processes to write to the same log file concurrently, which may lead to the following problems:
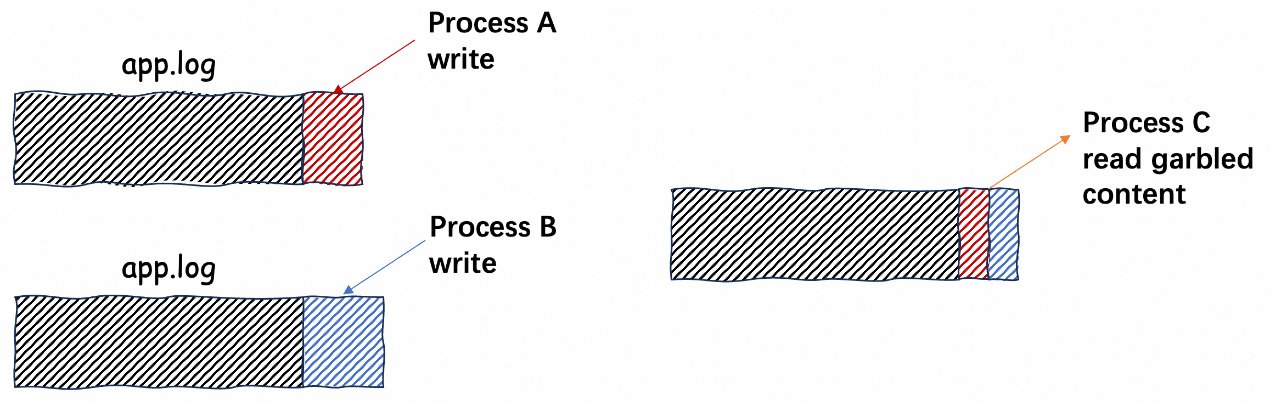
It is recommended that multiple processes write their respective files to ensure log integrity and order. If unavoidable, implement the compatibility logic for exception logs on the consumer.
Releasing log file space by creating holes in the file header is a risky practice for the following reasons:
This practice may result in duplicate data collection and loss of historical data.
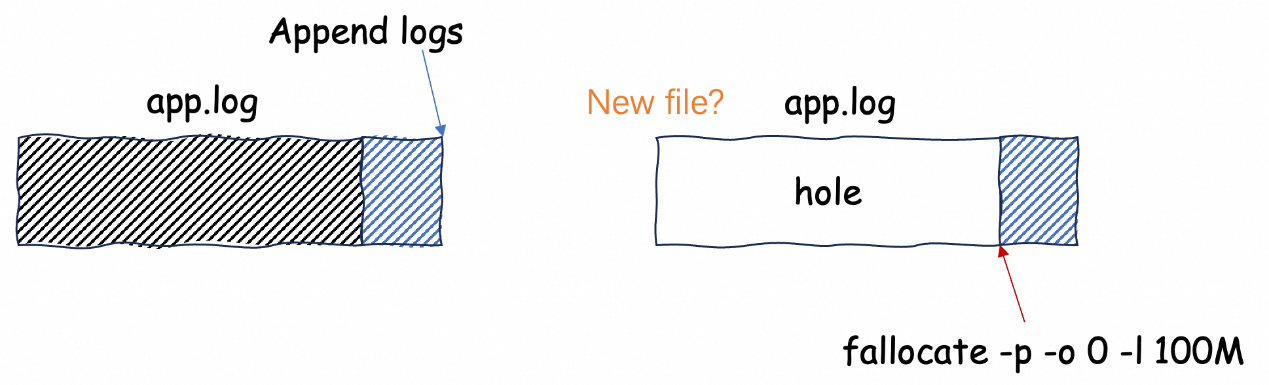
It is recommended to use the standard log rotation mechanism to manage log file size, such as using the Logrotate tool for regular log rotation, which ensures log integrity and traceability. If unavoidable, we recommend that you use fallocate instead of truncate or dd, and implement compatibility logic for exception logs on the consumer.
Frequently overwriting the entire log file is an insecure log management method. It may cause the following issues:
This practice may result in inconsistency between the collected content and the final file content, or complete loss of file content.
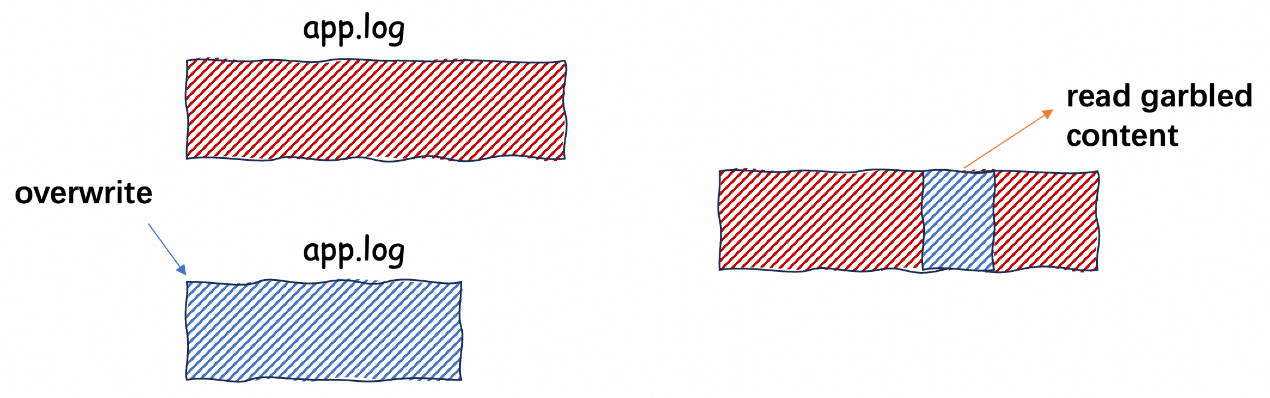
It is recommended to record logs in append mode and use the log rotation mechanism to manage the file size. If unavoidable, implement the compatibility logic for exception logs on the consumer.
When you use Vim to edit and save a file, its saving mechanism can cause the following issues:
This editing mode may lead to duplicate log collection or data loss.
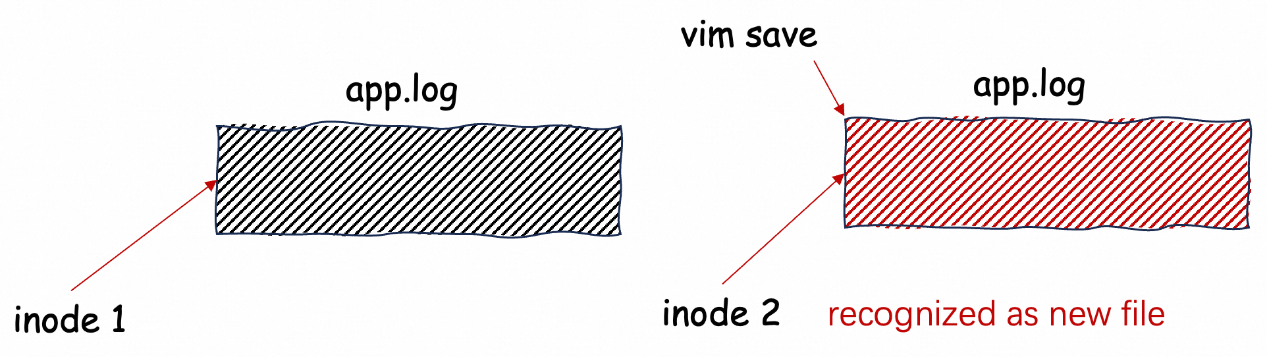
If you only need to view logs, we recommend that you use read-only tools such as less and grep. If unavoidable, implement deduplication and exception handling logic on the consumer.
Log is the "black box" of system operations, and its management quality directly affects the troubleshooting efficiency and system reliability. By avoiding the anti-patterns mentioned in this article and following the best practices, such as using Logstore rotation, local disk writing, and single-threaded appending, you can significantly lower log collection risks and improve observability. It is hoped that this article can provide practical references for teams to build a robust and efficient log management system.
Best Practices for Gin Framework Observability Without Cumbersome Manual Instrumentation

664 posts | 55 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native Community - August 13, 2025
Alibaba Developer - April 2, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - August 7, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - January 4, 2026
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - August 8, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - September 8, 2025

664 posts | 55 followers
Follow OSS(Object Storage Service)
OSS(Object Storage Service)
An encrypted and secure cloud storage service which stores, processes and accesses massive amounts of data from anywhere in the world
Learn More Apsara File Storage NAS
Apsara File Storage NAS
Simple, scalable, on-demand and reliable network attached storage for use with ECS instances, HPC and Container Service.
Learn More Hybrid Cloud Distributed Storage
Hybrid Cloud Distributed Storage
Provides scalable, distributed, and high-performance block storage and object storage services in a software-defined manner.
Learn More Storage Capacity Unit
Storage Capacity Unit
Plan and optimize your storage budget with flexible storage services
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Native Community