This topic describes how to create an ACK Serverless cluster in the Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) console. This topic also describes how to create an application from an image and view the containers in an ACK Serverless cluster.
Prerequisites
ACK is activated and authorized to access Alibaba Cloud services.
Elastic Container Instance is activated in the Elastic Container Instance console.
Step 1: Create an ACK Serverless cluster
This section describes only the key parameters that are required to create an ACK Serverless cluster. You can configure other parameters and install components based on your business requirements. For more information, see Create an ACK Serverless cluster.
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, click Create Kubernetes Cluster.
On the page that appears, click the ACK Serverless tab and configure the following parameters.
The following list describes some of the parameters:
Parameter
Description
Example
Cluster Name
Enter a custom name for the cluster.
ask-hangzhou
Cluster Specification
Select a cluster type. You can select Pro or Basic. We recommend that you use Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) Pro clusters in the production environment and test environment. ACK Basic clusters can meet the learning and testing needs of individual users only.
Standard edition
Region
The region of the cluster. The closer the selected region is to the user and the deployed resources, the lower the network latency and the faster the access speed.
China (Hangzhou)
VPC
Configure the VPC of the cluster. You can specify a zone to automatically create a VPC. You can also select an existing VPC in the VPC list.
Select Existing VPC
Configure SNAT for VPC
When using VPC sharing, do not select this option.
After you select this check box, ACK performs the following operations on the newly created or selected VPC:
If the VPC does not have a NAT gateway, a NAT gateway will be automatically created and switch-level SNAT rules will be configured for all switches used by the cluster.
If the VPC already has a NAT gateway:
If there are no VPC-level SNAT rules, switch-level SNAT rules will be configured automatically for all switches used by the cluster.
If VPC-level SNAT rules already exist, no action will be taken.
If you do not select this check box, you can manually configure a NAT gateway and configure SNAT rules after creating the cluster to ensure that instances in the VPC can access the Internet. For more information, see Create and manage an Internet NAT gateway.
Configure SNAT for VPC
vSwitch
Select an existing vSwitch from the vSwitch list or click Create vSwitch to create a vSwitch. The control plane and the default node pool use the vSwitch that you select. We recommend that you select multiple vSwitches in different zones to ensure high availability.
vsw-uf6x420ebylcwqclw****,
vsw-uf6qbh0tfvfuco0q7****
Security Group
When VPC is set to Select Existing VPC, you can select the Select Existing Security Group option.
You can select Create Basic Security Group, Create Advanced Security Group, or Select Existing Security Group.
By default, automatically created security groups allow all outbound traffic. When you modify the security group for business purposes, make sure that traffic destined for
100.64.0.0/10is allowed. This CIDR block is used to access other Alibaba Cloud services to pull images and query basic ECS information.If you select an existing security group, the system does not automatically configure security group rules. This may cause errors when you access the nodes in the cluster. You must manually configure security group rules. For more information, see Configure security groups for clusters.
Create Advanced Security Group
Service CIDR
Specify the CIDR block of Services in the cluster. The Service CIDR block must not overlap with the CIDR block of the VPC, the CIDR blocks of the ACK clusters in the VPC, or the pod CIDR block. The Service CIDR block cannot be modified after it is specified. For more information about how to plan CIDR blocks for a cluster, see Network planning of an ACK managed cluster.
172.21.0.0/20
Access to API Server
By default, an internal-facing Server Load Balancer (SLB) instance is created for the Kubernetes API server of an ACK Serverless cluster. You can modify the specification of the SLB instance. For more information, see Specification.
ImportantIf you delete the SLB instance, you cannot access the Kubernetes API server of the cluster.
Select or clear Expose API Server with EIP. The Kubernetes API server provides multiple HTTP-based RESTful APIs, which can be used to create, delete, modify, query, and monitor resources, such as pods and Services.
If you select this check box, an elastic IP address (EIP) is created and associated with the SLB instance by the ACK Serverless cluster. In this case, the Kubernetes API server of the cluster is exposed to the Internet through port 6443 of the EIP. You can use kubeconfig files to connect to and manage the cluster over the Internet.
If you clear this check box, no EIP is created. You can connect to and manage the cluster by using kubeconfig files only from within the VPC.
For more information, see Expose the API server to the Internet.
Expose API Server with EIP
After you configure the cluster, click Next:Component Configurations in lower-right part of the page to configure components.
Parameter
Description
Example
Service Discovery
Configure service discovery for the cluster. You can select Disable, PrivateZone, or CoreDNS.
PrivateZone is a DNS resolution service for private domain names within VPCs. You can use PrivateZone to resolve private domain names to IP addresses in one or more VPCs.
CoreDNS is a flexible and scalable DNS server that serves as a standard service discovery component in Kubernetes.
Disable
Ingress
Specify whether to install an Ingress controller. You can select Do Not Install, Nginx Ingress, ALB Ingress, or MSE Ingress.
Nginx Ingress: The NGINX Ingress controller is optimized based on open source ingress-nginx and provides flexible and reliable routing services based on Ingresses.
ALB Ingress: The Application Load Balancer (ALB) Ingress controller is compatible with the NGINX Ingress controller, and provides improved traffic routing capabilities based on ALB instances. The ALB Ingress controller supports complex routing, automatic certificate discovery, and HTTP, HTTPS, and QUIC protocols. The ALB Ingress controller meets the requirements of cloud-native applications for ultra-high elasticity and balancing of heavy traffic loads at Layer 7.
MSE Ingress: An Ingress is an API object that provides Layer-7 load balancing to manage external access to Services in a Kubernetes cluster. To better support cloud-native scenarios, Alibaba Cloud provides Microservices Engine (MSE) Ingress gateways that are developed based on deep integration and optimization of MSE cloud-native gateways and ACK. MSE Ingress gateways help you manage ingress traffic of clusters in an efficient manner.
Do Not Install
Monitoring Service
You can view predefined dashboards and performance metrics by using Managed Service for Prometheus. For more information, see Managed Service for Prometheus.
You can also install the metrics-server component. The metrics-server component is an offline monitoring data component that is modified and enhanced based on open source monitoring components. The component allows you to view the offline monitoring data of clusters.
Install metrics-server
Log Service
Specify whether to Enable Log Service. You can select an existing project or create a project.
Create Project
Knative
Specify whether to Enable Knative. Knative is a Kubernetes-based serverless framework that supports request-based auto scaling, scaling to zero, version management, and canary release.
Enable Knative
After configuring components, click Next:Confirm in the lower-right part of the page.
On the Confirm wizard page, read the Term of Service and click Create Cluster.
After cluster creation, view your ACK Serverless cluster on the Clusters page. Locate the newly created cluster, click Details in the Actions column, then click the Basic Information and Connection Information tabs for cluster details.
Step 2: Create an application from an image
This section describes only the key parameters that are required to create an application from an image. For more information, see Create a stateless application from an image.
Configure basic information
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page, choose .
In the upper-right corner of the Deployments page, click Create from Image.
On the Basic Information wizard page, configure the basic settings of the application.
Parameter
Description
Example
Name
Enter a name for the application.
serverless-app-deployment
Type
Specify the type of resource object. Valid values include Deployment and StatefulSet.
Deployment
Click Next.
Configure container settings
In the General section of the Container wizard page, configure the basic settings of containers.
Parameter
Description
Example
Image Name
To select an image, click Select Image. In the Select Image dialog box, select an image and click OK.
You can also enter the address of an image that is stored in a private registry. The image address must be in the following format:
domainname/namespace/imagename:tag.In this example, an image that is stored on a Container Registry Personal Edition instance is used. The instance is deployed in the China (Hangzhou) region.
Image Version
Click Select Image Version and select an image version. If you do not specify an image version, the latest image version is used.
In this example, no image version is specified.
In the Ports section, click Add to configure one or more container ports.
Parameter
Description
Example
Name
Enter a name for the container port.
nginx
Container Port
Specify the container port that you want to expose. The port number must be from 1 to 65535.
80
Protocol
Valid values: TCP and UDP.
TCP
Click Next.
Configure advanced settings
In the Access Control section of the Advanced wizard page, configure a Service to expose the backend pod.
Click Create on the right side of Services. In the Create Service dialog box, configure the following parameters.
Parameter
Description
Example
Name
Enter a name for the Service.
serverless-app-svc
Type
The type of Service. This parameter determines how the Service is accessed.
Select Server Load Balancer. Then, select Public Access and Create SLB Instance. You can click Modify to change the Server Load Balancer (SLB) instance specification based on your business requirements.
In this example, the default specification Small I (slb.s1.small) is used.
Port Mapping
Specify a Service port and a container port. The container port must be the same as the one that is exposed in the backend pod.
In this example, the Service port is set to 8080 and the container port is set to 80.
You can find the created Service in the Access Control section. You can click Update or Delete to change the configurations.
Click Create.
Access the NGINX application
On the Complete wizard page, click View Details. You can find serverless-app-deployment on the Deployments page.

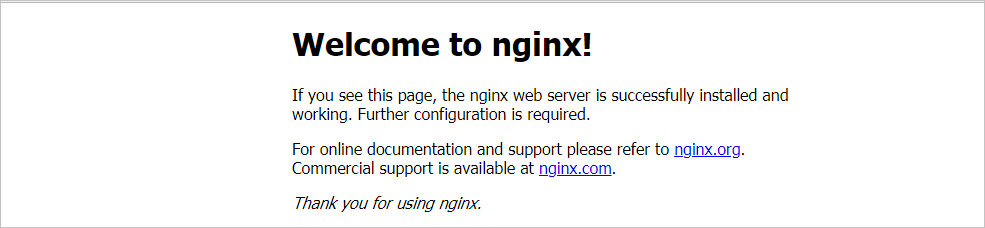
Access the NGINX application.
In the left-side navigation pane of the cluster details page, choose . On the Services page, you can find the serverless-app-svc Service.

Click the address in the External Endpoint column to access the NGINX application by using a browser.
 Note
NoteFor more information about how to access an application by using an Ingress, see Access Services by using an ALB Ingress.
Step 3: View the pod
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page, choose .
Select the pod that you want to view and click Details in the Actions column.
NoteYou can modify or delete the pod based on your needs. We recommend that you use templates to manage pods that are created by using templates. Do not directly modify or delete these pods.
On the details page of the pod, you can view the detailed information about the pod.