This topic describes how to use the host account of an RDS instance to log on to the RDS SQL Server instance host. After you log on to the host, you can use SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) to manage and operate the SQL Server database.
Background information
RDS SQL Server provides the WebShell feature that allows users to log on to the operating system of an RDS SQL Server instance through a web interface and execute commands, upload and download files, and perform other operations in the operating system. The WebShell feature facilitates the management and maintenance of RDS SQL Server instances, especially when SSH clients cannot be used, providing a convenient and quick remote management method.
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) is a Microsoft enterprise-level reporting service that helps users generate various types of reports from SQL Server databases and other data sources, such as tabular reports, chart reports, cross reports, and multidimensional data reports. The SSRS service can connect to an RDS SQL Server database and use it as a data source to generate various types of reports. This combined use allows enterprises and users to manage and analyze data more efficiently and generate various types of reports to support business decisions and management.
Scenarios
Assume that you are a database administrator for a small or medium-sized enterprise and are responsible for managing the company's SQL Server database. As the company's business volume continues to increase, the database access volume also increases. To better manage and optimize the database, you need to use the SSRS service to analyze and monitor the database. However, because the company's server host is not local, you cannot directly log on to the host to perform operations.
Based on the preceding situation, you can create a host account in the RDS console and use the account to log on to WebShell and then to the RDS SQL Server instance host. After you log on to the host, you can use the SSRS service to easily manage and operate the SQL Server database, keep track of the database status in a timely manner, and better support the company's business development.
Prerequisites
The RDS instance must meet the following requirements:
Instance edition: Basic Edition, High-availability Edition (SQL Server 2012 and later), or Cluster Edition
Instance type: General-purpose, Dedicated (The Shared type is not supported)
Billing method: Subscription or pay-as-you-go (Not supported for Serverless ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instances)
Network type: virtual private cloud (VPC). To change the network type, see Change the network type.
Instance creation time:
High-availability Edition and Cluster Edition instances must be created on or after January 1, 2021.
Basic Edition instances must be created on or after September 2, 2022.
NoteYou can view the Created At in the Basic Information page under Status.
You must log on with an Alibaba Cloud account.
A System Admin account is created on the User Account tab.
A host account with the account type set to System Admin Account is created on the Host Account tab.
Impact
The System Admin account used in this tutorial has the highest permissions for the SQL Server database, and the host account has the highest permissions for the host. Because the operations that can be performed by a System Admin account or a host account are beyond the control scope of RDS SQL Server, RDS SQL Server instances for which such accounts have been created are no longer covered by the SLA guarantee. The instance running environment belongs to the user, but the normal use of the instance and after-sales service are not affected. RDS SQL Server instances for which such accounts have not been created are still covered by the complete SLA guarantee.
Step 1: Log on to the RDS SQL Server host through WebShell
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Accounts.
Click the Host Account tab and click Remote Connection (Primary) in the Actions column of the target account.
In the Remote Connection dialog box that appears, enter the host account password.
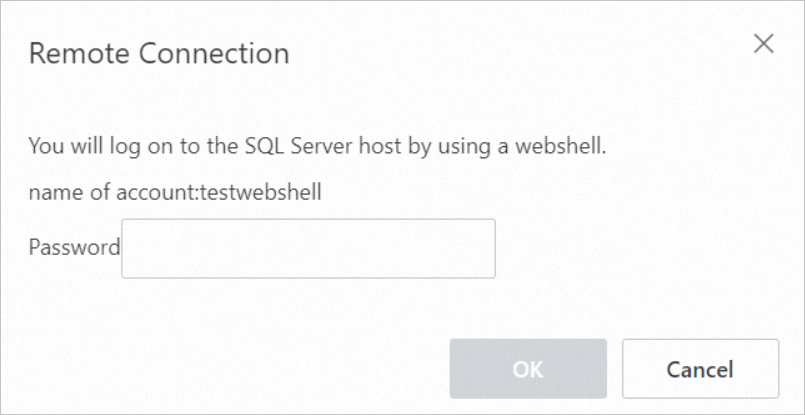
Click OK.
After you click OK, the system generates a WebShell logon URL and automatically logs on to the SQL Server instance host. The system opens a new WebShell page in a pop-up window. The browser may block the pop-up window. If this occurs, configure the browser to always allow pop-up windows to ensure that the page is properly displayed. The page is displayed as follows:
Step 2: Configure and use the SSRS service
Prerequisites
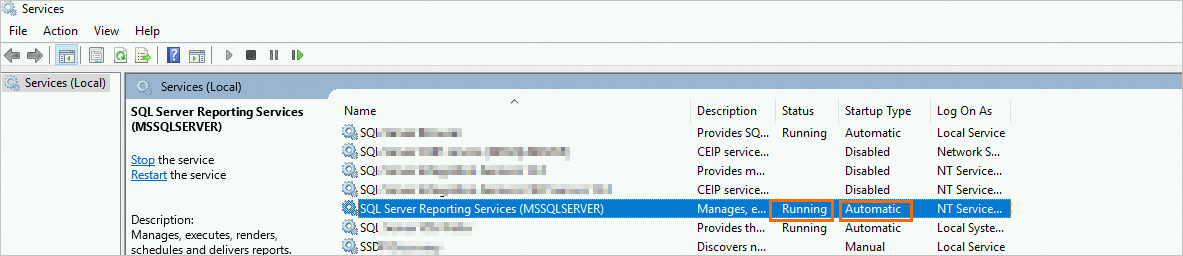
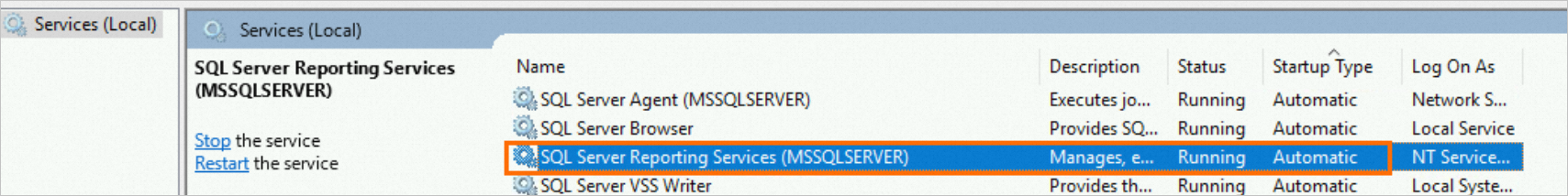
Before you configure the SSRS service on the SQL Server host, make sure that the SQL Server Reporting Services (MSSQLSERVER) service status is enabled and running. For information about how to view or modify the SSRS service status, see View or modify the SSRS service status.
Precautions
When the RDS SQL Server instance series is High-availability Edition or Cluster Edition, the SSRS service configuration may fail because the database is in a mirroring or Always On availability group state. If this problem occurs, use a System Admin account to log on to the SQL Server instance and execute the following commands:
Because RDS instances regularly set up mirroring or availability groups, multiple configuration errors may occur when you configure the SSRS service. To resolve this problem, each time a configuration error occurs, you need to use a System Admin account to log on to the SQL Server instance and execute the following commands.
-- High-availability Edition instance (disable database mirroring)
ALTER DATABASE [ReportServer] SET PARTNER OFF;
ALTER DATABASE [ReportServerTempDB] SET PARTNER OFF;
-- Cluster Edition instance (remove databases from the ag-rds availability group)
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [ag-rds] REMOVE DATABASE [ReportServer];
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [ag-rds] REMOVE DATABASE [ReportServerTempDB];The purpose of the preceding operations is to ensure that the SSRS service can be properly configured and run. For Cluster Edition instances, to ensure high availability of data and normal database backup and recovery, after the SSRS configuration is complete, use a System Admin account to log on to the SQL Server instance and execute the following commands to add the databases back to the availability group.
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [AG-RDS] ADD DATABASE [ReportServer]
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [AG-RDS] ADD DATABASE [ReportServerTempDB]Procedure
Log on to the SQL Server instance using a privileged account and execute the following command.
DISABLE TRIGGER [_$$_tr_$$_rds_alter_database] ON ALL SERVER;NoteFor information about how to connect to an SQL Server instance, see Connect to an SQL Server instance.
Click
 > Reporting Services Configuration Manager.
> Reporting Services Configuration Manager.
In the dialog box that appears, confirm the report server name and click Connect.
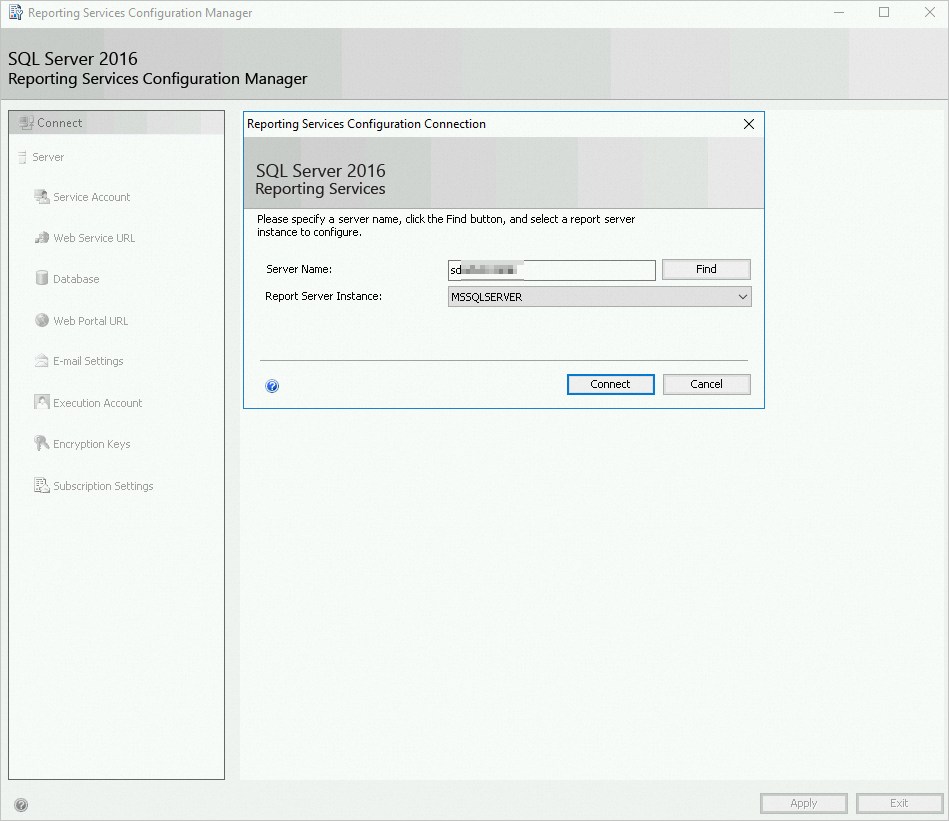 Note
NoteIf your RDS SQL Server instance series is High-availability Edition or Cluster Edition, the connection to the report server may fail due to database mirroring or availability groups. If this problem occurs, see Precautions in this topic for solutions.
In the navigation pane on the left, configure Service Accout and Web Service URL as needed.
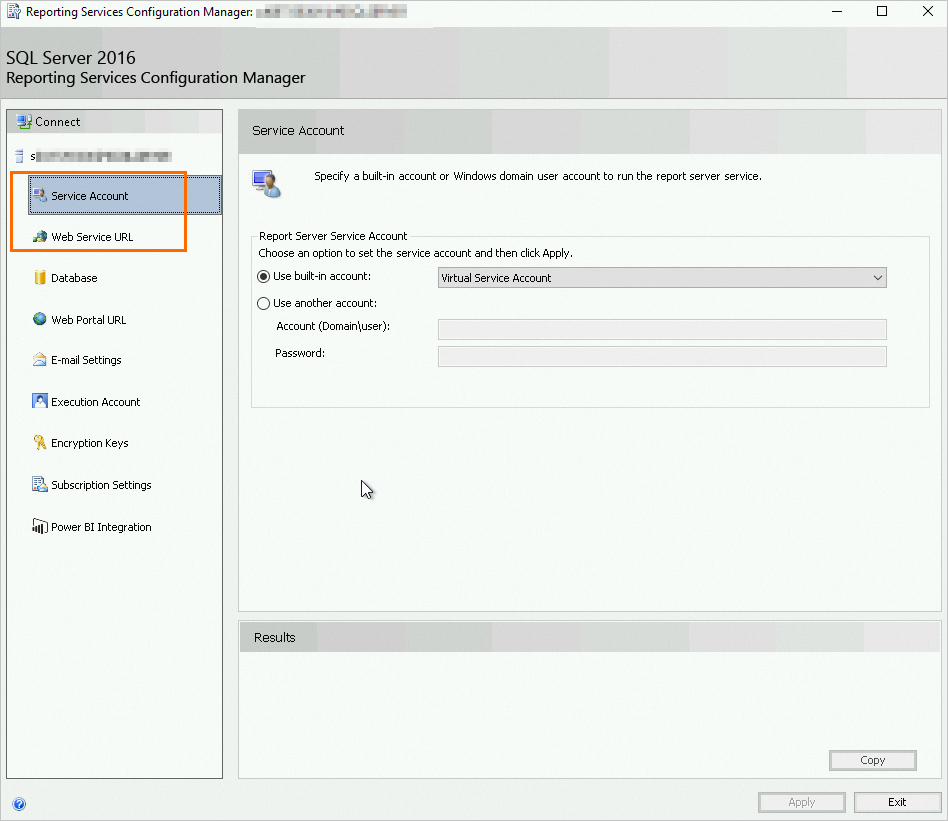 Note
NoteFor information about the configuration method, see the official documentation.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Database, and then click Change Database on the right to create a new report server database on the host.
Select Create a new report server database and click Next.
Confirm the server name, configure the following parameters, and click Next.
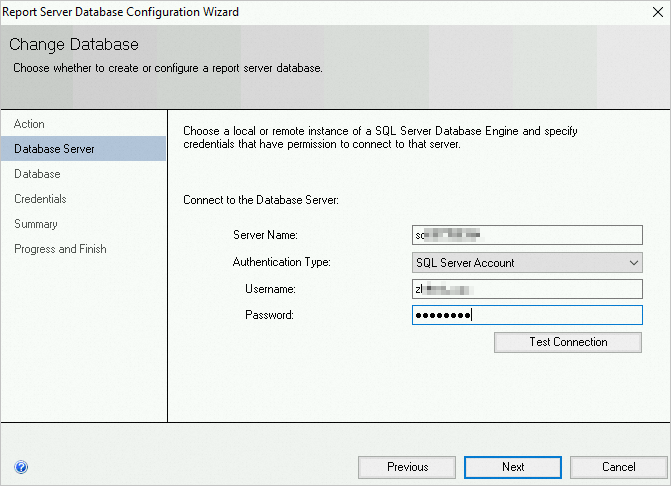
Configuration item
Description
Server Name
The server name. This is a fixed configuration and does not need to be modified.
Authentication Type
The authentication type. Select SQL Server Account.
Username
Enter the System Admin account that is created on the User Account tab of the RDS SQL Server instance.
Password
Enter the password of the System Admin account on the User Account tab of the RDS SQL Server instance.
Enter the report server database name, select the language for the script, and click Next.
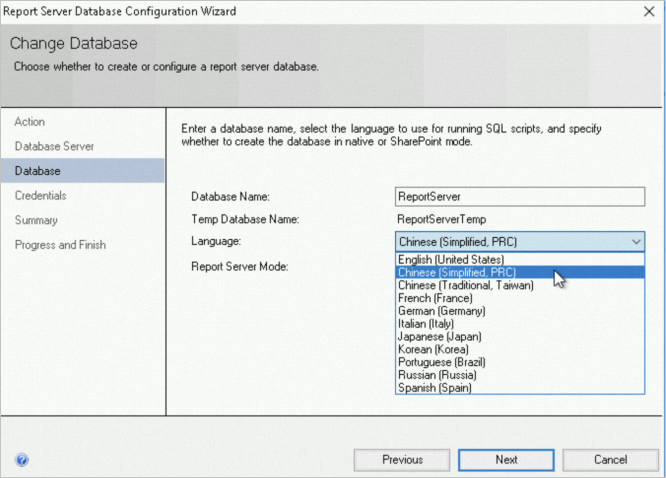
Set the credentials for the account to connect to the report server and click Next.
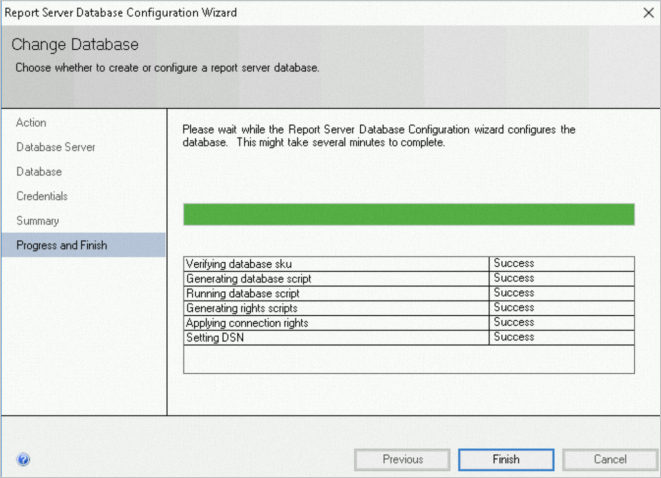
Confirm the summary, click Next, wait for the report server database to be created, and then click Finish.
Use a System Admin account to log on to the SQL Server instance and execute the following commands.
USE [master] GO -- Change the recovery model of the database to FULL, using the NO_WAIT parameter to make the change take effect immediately ALTER DATABASE [ReportServer] SET RECOVERY FULL WITH NO_WAIT GO ALTER DATABASE [ReportServerTempDB] SET RECOVERY FULL WITH NO_WAIT GO -- Enable a specific trigger on all databases on the server ENABLE TRIGGER [_$$_tr_$$_rds_alter_database] ON ALL SERVER;Subsequent operations such as creating data sources depend on your business requirements. For specific operations, see Steps 5 to 8 or the official documentation.
View or modify the SSRS service status
Log on to the SQL Server host and enter
services.mscin the search box to open the Services window.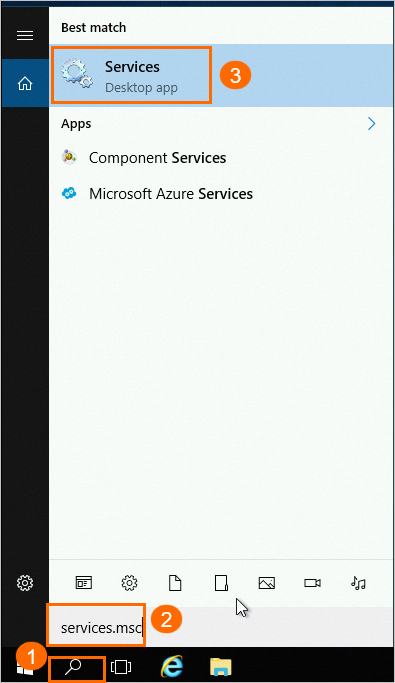
In the local services window, check the Status of
SQL Server Reporting Services (MSSQLSERVER).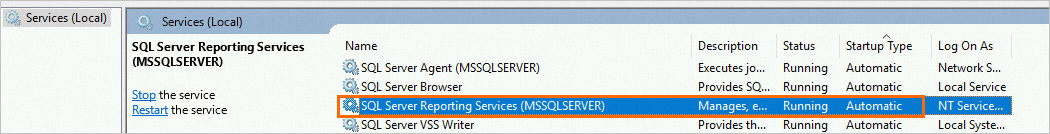 Note
NoteThe SSRS service startup types are described as follows:
Manual: The service needs to be started manually and is not automatically started when the system starts.
Automatic: The service is automatically started when the system starts.
Automatic (Delayed Start): The service is automatically started after the system has been running for a period of time.
Disabled: The service is disabled and cannot be started.
(Optional) Modify the SSRS service running status and start the service.
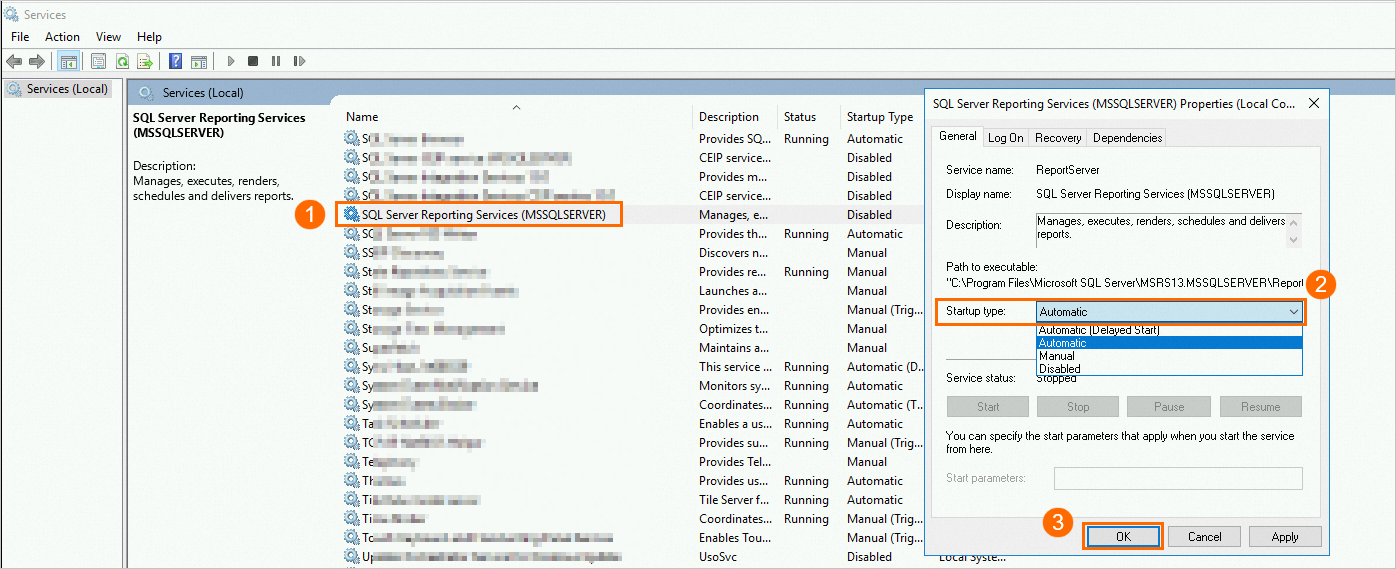
Double-click the service. In the dialog box that appears, modify the Startup type property.
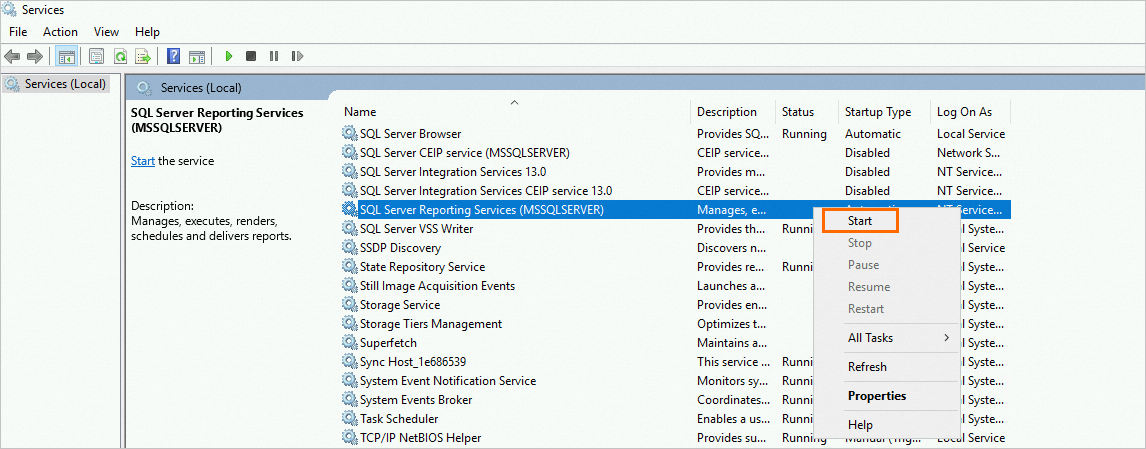
Right-click the service. In the dialog box that appears, click Start.
View the modified SSRS service running status.