A host account grants OS-level access to the underlying Windows host of an ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instance. Use a host account to deploy SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS), SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS), or custom software that requires direct host access.
By default, host account passwords expire after 42 days. Set a password policy in advance to manage password validity. The policy applies to the host account automatically.
Creating a host account removes the instance from SLA coverage. Because the host account has the highest permissions on the host, operations performed with it are beyond the control of ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server. You are responsible for the instance environment. Instances that have never had a host account remain fully covered by the SLA. Normal instance functionality and after-sales service are not affected.
When to use a host account
| Use case | Recommended approach |
|---|---|
| Deploy SSIS, SSAS, or SSRS | Host account |
| Install custom software on the host | Host account |
| Standard database management | Standard database accounts |
| Full OS control with no managed service constraints | Self-managed SQL Server on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) |
ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server is built on the native Microsoft SQL Server kernel and focuses on providing stable, managed database services. If your workload requires SSIS, SSAS, or SSRS, make sure you have the Operations and Maintenance (O&M) capabilities to maintain business continuity.
Supported configurations
The RDS instance must meet all of the following requirements:
Runs RDS Basic Edition, RDS High-availability Edition, or RDS Cluster Edition. For High-availability Edition, the instance must run SQL Server 2012 or later.
Belongs to the general-purpose or dedicated instance family. The shared instance family is not supported.
Uses the subscription or pay-as-you-go billing method. Serverless instances are not supported.
Resides in a virtual private cloud (VPC). To change the network type, see Change the network type.
Was created on or after the following dates:
NoteCheck the Creation Time parameter in the Status section of the Basic Information page in the ApsaraDB RDS console.
Edition Minimum creation date RDS High-availability Edition or RDS Cluster Edition January 01, 2021 RDS Basic Edition September 02, 2022 An Alibaba Cloud account is used to log on to the RDS instance.
Restrictions
Jushita does not support host accounts.
Each RDS instance supports only one host account with System Admin permissions.
The host account name cannot use any reserved keywords.
When the instance is migrated across hosts (such as during a major version upgrade, minor engine version upgrade, specification change with major version upgrade, or zone migration), the host account and any programs or files deployed on the original host (such as SSIS, SSAS, and SSRS) are deleted. Back up or migrate your data before performing these operations.
Actions that may disrupt your instance
The host account has extensive permissions beyond the control of ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server. Follow these guidelines to avoid service disruptions:
| Do not | Reason |
|---|---|
Manage the rdscore database (High-availability or Cluster Edition) | Required for internal service operations |
| Manage system accounts | May break managed service functionality |
| Perform physical backups on your on-premises device | Affects point-in-time recovery (PITR). Use the ApsaraDB RDS backup feature instead. |
Move the instance or manage high-availability objects such as DROP AVAILABILITY GROUP (High-availability or Cluster Edition) | Disrupts the high-availability configuration |
| Store data on drive C (system disk) | Reserved for the operating system |
Modify existing server-level triggers ([_$$_tr_$$_rds_*]) | Required for internal monitoring and control |
| Modify core configurations such as the startup account and port | May cause the instance to become inaccessible |
| Change the Windows administrator password | May disrupt managed service operations |
The server-level triggers that must not be modified are: [_$$_tr_$$_rds_alter_database], [_$$_tr_$$_rds_alter_login], [_$$_tr_$$_rds_create_database], [_$$_tr_$$_rds_create_login], [_$$_tr_$$_rds_drop_database], [_$$_tr_$$_rds_drop_login], and [_$$_tr_$$_rds_server_role].
Step 1: Create a host account
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region of your RDS instance, and then click the instance ID.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Accounts.
Click the Host Account tab, and then click Create Account.
Configure the following parameters.
Parameter Description Host Account Name Lowercase letters, digits, or underscores (_). Must start with a letter and end with a letter or digit. Maximum length: 16 characters. Account Type Standard Account: Creates a standard host account. System Admin Account: Creates a host account with System Admin permissions. Only one System Admin account is allowed per instance. For more information, see Database accounts with SA permissions. New Password 8 to 32 characters. Must contain at least three of the following: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special characters ( !@#$%^&*()_+-=).Confirm Password Re-enter the password. Remarks Optional. Maximum length: 256 characters. Select I Have Read And Agree To The Changes To The RDS Service Level Agreement For Creating A Host Account.
Click OK.
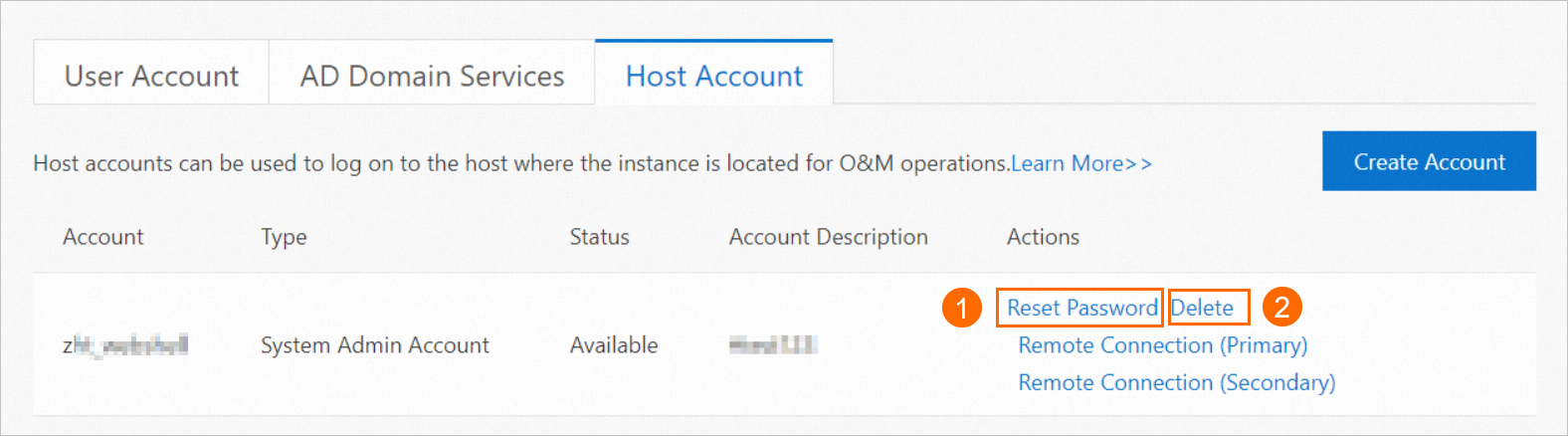
Manage an existing host account
In the Actions column, click Reset Password or Delete to manage the account.
Step 2: Log on to the host
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region of your RDS instance, and then click the instance ID.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Accounts.
Click the Host Account tab. In the Actions column, click Remote Connection (Primary).
In the Remote Connection dialog box, enter the host account password.
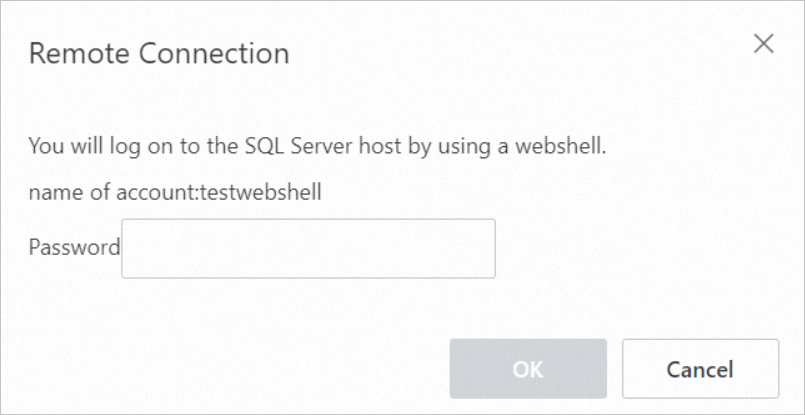
Click OK. The system generates a WebShell URL and opens a new browser tab with the host session. If your browser blocks the pop-up window, allow pop-ups from this site.
FAQ
The error "The specified host information does not exist" appears during remote connection
Host account passwords expire after 42 days by default. In the Actions column, click Reset Password, set a new password, and try again.
To avoid future expirations, set a password expiration policy. The policy applies to the host account automatically.
How do I get the hostname and WebShell URL programmatically?
Call DescribeDBInstanceIpHostname to obtain the IpHostnameInfos (RDS instance hostname), and then call DescribeHostWebShell to obtain the LoginUrl (host WebShell logon URL).
The WebShell URL expires after two minutes. Use it immediately after retrieval. If it expires, call the API again for a new URL.
Next steps
API reference
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| DescribeHostWebShell | Query the WebShell logon information for an RDS for SQL Server instance |
| DescribeDBInstanceIpHostname | Query the hostname of the underlying ECS instance for an RDS for SQL Server instance |
Reserved keywords
The following keywords cannot be used as host account names:
root, admin, eagleye, master, aurora, sysadmin, administrator, mssqld, public, securityadmin, serveradmin, setupadmin, processadmin, diskadmin, dbcreator, bulkadmin, tempdb, msdb, model, distribution, mssqlsystemresource, guest, add, except, percent, all, exec, plan, alter, execute, precision, and, exists, primary, any, exit, print, as, fetch, proc, asc, file, procedure, authorization, fillfactor, public, backup, for, raiserror, begin, foreign, read, between, freetext, readtext, break, freetexttable, reconfigure, browse, from, references, bulk, full, replication, by, function, restore, cascade, goto, restrict, case, grant, return, check, group, revoke, checkpoint, having, right, close, holdlock, rollback, clustered, identity, rowcount, coalesce, identity_insert, rowguidcol, collate, identitycol, rule, column, if, save, commit, in, schema, compute, index, select, constraint, inner, session_user, contains, insert, set, containstable, intersect, setuser, continue, into, shutdown, convert, is, some, create, join, statistics, cross, key, system_user, current, kill, table, current_date, left, textsize, current_time, like, then, current_timestamp, lineno, to, current_user, load, top, cursor, national, tran, database, nocheck, transaction, dbcc, nonclustered, trigger, deallocate, not, truncate, declare, null, tsequal, default, nullif, union, delete, of, unique, deny, off, update, desc, offsets, updatetext, disk, on, use, distinct, open, user, distributed, opendatasource, values, double, openquery, varying, drop, openrowset, view, dummy, openxml, waitfor, dump, option, when, else, or, where, end, order, while, errlvl, outer, with, escape, over, writetext, dbo, login, sys, drc_rds