The System Admin (SA) role is the most powerful role in SQL Server. This role completely bypasses all security checks and can perform any operation in SQL Server. You can create a database account with System Admin permissions (privileged account) in RDS SQL Server to quickly adapt on-premises software to the cloud.
Prerequisites
The RDS instance must meet the following requirements:
Instance edition: Basic Edition, High-availability Edition (SQL Server 2012 and later), or Cluster Edition
Instance type: General-purpose, Dedicated (The Shared type is not supported)
Billing method: Subscription or pay-as-you-go (Not supported for Serverless ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instances)
Network type: virtual private cloud (VPC). To change the network type, see Change the network type.
Instance creation time:
High-availability Edition and Cluster Edition instances must be created on or after January 1, 2021.
Basic Edition instances must be created on or after September 2, 2022.
NoteYou can view the Created At in the Basic Information page under Status.
You must log on with an Alibaba Cloud account.
Notes
If your instance meets the prerequisites but you cannot see the entry for creating a System Admin account in the console, you can perform a zone migration operation on the instance. After the operation is complete, refresh the Accounts page to create a System Admin account.
You can create only one database account with System Admin permissions for each instance. You can delete this account from the console after it is created.
Apsara Stack does not support creating System Admin accounts.
The System Admin account name cannot be any of the following:
root|admin|eagleye|master|aurora|sysadmin|administrator|mssqld|public|securityadmin|serveradmin|setupadmin|processadmin|diskadmin|dbcreator|bulkadmin|tempdb|msdb|model|distribution|mssqlsystemresource|guest|add|except|percent|all|exec|plan|alter|execute|precision|and|exists|primary|any|exit|print|as|fetch|proc|asc|file|procedure|authorization|fillfactor|public|backup|for|raiserror|begin|foreign|read|between|freetext|readtext|break|freetexttable|reconfigure|browse|from|references|bulk|full|replication|by|function|restore|cascade|goto|restrict|case|grant|return|check|group|revoke|checkpoint|having|right|close|holdlock|rollback|clustered|identity|rowcount|coalesce|identity_insert|rowguidcol|collate|identitycol|rule|column|if|save|commit|in|schema|compute|index|select|constraint|inner|session_user|contains|insert|set|containstable|intersect|setuser|continue|into|shutdown|convert|is|some|create|join|statistics|cross|key|system_user|current|kill|table|current_date|left|textsize|current_time|like|then|current_timestamp|lineno|to|current_user|load|top|cursor|national|tran|database|nocheck|transaction|dbcc|nonclustered|trigger|deallocate|not|truncate|declare|null|tsequal|default|nullif|union|delete|of|unique|deny|off|update|desc|offsets|updatetext|disk|on|use|distinct|open|user|distributed|opendatasource|values|double|openquery|varying|drop|openrowset|view|dummy|openxml|waitfor|dump|option|when|else|or|where|end|order|while|errlvl|outer|with|escape|over|writetext||dbo|login|sys|drc_rds$
Impact
Because a System Admin account has excessive permissions that are beyond the control of RDS SQL Server, if you have created a System Admin account in an RDS SQL Server instance, the instance is no longer covered by the Service-Level Agreement (SLA). The instance runtime environment belongs to you, but the normal use of the instance and after-sales service are not affected. RDS SQL Server instances for which no System Admin account has been created are still fully covered by the SLA.
Usage recommendations
Because a System Admin account has excessive permissions that are beyond the control of RDS SQL Server, you must follow these recommendations when you use this account:
Do not operate the
rdscoredatabase of High-availability Edition or Cluster Edition RDS SQL Server instances.Do not operate system accounts. For more information, see System account description.
Do not perform physical backup operations in the local environment. These operations affect the point-in-time recovery (PITR) capability of the instance. We recommend that you use the backup feature of RDS. For more information, see Back up SQL Server data.
Do not remove or operate high availability-related objects for High-availability Edition or Cluster Edition RDS SQL Server instances, such as executing the
DROP AVAILABILITY GROUPoperation.Do not store any data on drive C (system disk).
Do not modify existing server-level triggers in the RDS instance, including
[_$$_tr_$$_rds_alter_database],[_$$_tr_$$_rds_alter_login],[_$$_tr_$$_rds_create_database],[_$$_tr_$$_rds_create_login],[_$$_tr_$$_rds_drop_database],[_$$_tr_$$_rds_drop_login], and[_$$_tr_$$_rds_server_role].Do not modify core configurations of SQL Server, such as the startup account and port.
Do not modify the Windows Administrator password.
Procedure
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Accounts.
Click Create Account, set the following parameters, and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Database Account
The account name can contain lowercase letters, digits, and underscores (_). It must start with a letter and end with a letter or digit. The account name can be up to 64 characters in length.
Account Type
Select System Admin Account, read and select I have read and agree to changes to the ApsaraDB RDS Service Level Agreementcaused by the creation of a system admin account.
NoteIf you cannot find this account type, check whether your instance meets the prerequisites.
For information about other account types, see Standard and privileged accounts and Host account.
New Password
Set the account password. The password must meet the following requirements:
The password must be 8 to 32 characters in length.
The password must contain at least three of the following character types: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special characters.
Special characters include
!@#$%^&*()_+-=.
Confirm Password
Enter the password again to confirm it.
Apply Password Policy
When you create an account, you can choose whether to apply a password policy to control the validity period of the account password and enhance account security. Before you apply a password policy, you must configure the password policy.
Description
Enter a description of the account. The description can be up to 256 characters in length.
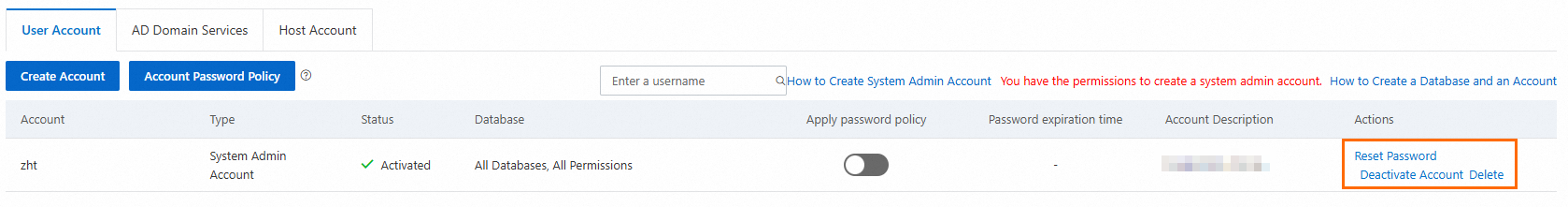
(Optional) Reset the account password or disable the account.
You can click the Reset Password, Deactivate Account, or Delete button in the Actions column to manage an account. For more information, see Reset a password.
References
You can also create a database account with System Admin permissions or other permissions by calling an API operation. For more information, see CreateAccount - Create a database account.
To create a standard account or privileged account in the console, see Create a standard or privileged account.