This topic provides answers to frequently asked questions about the database proxy feature of ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL. If you encounter problems when using the database proxy feature, you can refer to this topic.
Contents
What are the differences between general-purpose database proxies and dedicated database proxies?
Does a database proxy consume the QPS or TPS of my primary RDS instance?
Is a database proxy endpoint the same as a regular endpoint?
Which architecture do database proxies use? Does this architecture provide a failover mechanism?
Does the number of database proxy endpoints depend on the number of database proxies?
Can I modify a database proxy endpoint or a read/write splitting endpoint?
After I enable the database proxy feature for my RDS instance, how do I verify read/write splitting?
Does the nearest access feature become unavailable after you migrate proxy nodes across zones?
Can I change the zone of a proxy node when I modify the proxy node configuration?
Are the IP addresses resolved from database proxy endpoints fixed?
How do I determine whether a session is connected through a database proxy endpoint?
Why can't I retrieve the data that I just wrote when I query through a database proxy endpoint?
What are database proxies?
A database proxy serves as a network proxy that resides between your database system and your application and forwards all requests from your application. The database proxy provides advanced capabilities, such as automatic read/write splitting, transaction splitting, connection pooling, and persistent connections. Database proxies are easy to use and maintain, and deliver high availability and high performance.
What are the differences between general-purpose database proxies and dedicated database proxies?
General-purpose: This type of database proxy shares physical CPU resources and is provided free of charge. The highest specification of this database proxy type is 16 CPU cores that are provided by eight proxy nodes.
Dedicated: This type of database proxy exclusively occupies physical CPU resources and is charged based on the pay-as-you-go billing method. The highest specification of this database proxy type is 64 CPU cores that are provided by 32 proxy nodes. This type of database proxy delivers more stable performance.
For more information, see Database proxy types, Relationship between the number of database proxies and the database proxy specification, Billing rules for the database proxy feature.
Does a database proxy consume the QPS or TPS of my primary RDS instance?
No, it will not.
Is a database proxy endpoint the same as a regular endpoint?
No.
A regular endpoint forwards all requests that are sent only to the RDS instance.
A database proxy endpoint automatically forwards write requests to the primary RDS instance and read requests to the read-only RDS instances based on the SQL statements that are executed. This helps reduce the loads on the primary RDS instance.
After I enable the database proxy feature, does the system reclaim the original endpoints of the primary RDS instance and its read-only RDS instances?
It will not be reclaimed.
Is the internal network type of a database proxy the same as the internal network type of its primary RDS instance?
Yes, the internal network types of a database proxy and its primary RDS instance are virtual private clouds (VPCs).
Which architecture do database proxies use? Does this architecture provide a failover mechanism?
Database proxies use a high availability architecture with two primary nodes. Connections are distributed to the two nodes at a ratio of 1:1. If one node fails, the other node takes over the faulty node and the system automatically triggers a restoration task on the faulty node to ensure high availability of database services.
For more information about the database proxy deployment architecture, see Deployment architecture of proxy nodes.
What is the relationship between the specification of a database proxy and the specifications of proxy nodes?
Specification of a database proxy = Total specifications of all proxy nodes.
For example, four dedicated database proxy nodes are deployed in Zone A and Zone B and the number of CPU cores for a single proxy node is 1 in Zone A and is 2 in Zone B. The specification for the database proxy is 6 CPU cores. The value is obtained based on the following calculation: 1 × 2 + 2 × 2 = 2 + 4 = 6.
What is the relationship between the number of database proxies and the specification of the database proxy?
Number of proxies = Proxy specification / Unit proxy specification, where the unit proxy specification is 2 CPU cores.
For example, if the specification of a database proxy is 6 CPU cores, the number of proxy nodes is 3. The value is obtained based on the following calculation: 6/2 = 3.
What are the limits on the specifications of proxy nodes?
A general-purpose proxy node can have up to 8 CPU cores, and a dedicated proxy node can have up to 16 CPU cores.
The specifications of proxy nodes that are deployed in the same zone must be the same.
In the dual-zone deployment mode that involves two proxy nodes, the specifications of the proxy nodes must be the same.
The specifications of the proxy nodes that are deployed in different zones can be different. If you deploy general-purpose proxy nodes in different zones, we recommend that the proxy nodes use the same specifications.
Is there a relationship between the number of proxies and the number of proxy addresses?
No.
Each RDS instance with the database proxy feature enabled supports up to seven database proxy endpoints. You can apply for one internal endpoint and one public endpoint for each database proxy endpoint. For more information, see Create a database proxy endpoint.
Is the performance of database proxies improved if I increase the number of database proxy endpoints?
No.
If your RDS instance runs RDS High-availability Edition, the performance of the database proxy feature for the RDS instance is related to the number of read-only RDS instances, the number of database proxies, and the database proxy specification. If your RDS instance runs RDS Cluster Edition, the performance of the database proxies for the RDS cluster is related to the number of secondary nodes, the number of database proxies, and the database proxy specification. An RDS instance that runs RDS Cluster Edition is referred to as an RDS cluster.
If you increase the number of read-only RDS instances for RDS instances that run RDS High-availability Edition or the number of secondary nodes for RDS clusters, the database proxies can process more read requests.
If you increase the number of database proxies or add the database proxy specification, the performance of the database proxies is improved.
Is the number of connections to a database proxy limited?
The maximum number of connections that can be established to a database proxy is unlimited. The maximum number of connections varies based on the specifications of the primary RDS instance and read-only RDS instances in your database system.
What do I do if a timeout error occurs when I use a database proxy endpoint to connect to my RDS instance?
We recommend that you increase the value of the wait_timeout parameter and try again. For more information about how to modify instance parameters, see Configure instance parameters.
Can I modify a database proxy endpoint or a read/write splitting endpoint?
Yes, it is.
For more information about how to modify a database proxy endpoint or a read/write splitting endpoint, see Manage database proxy endpoints.
If my primary RDS instance processes a small number of write requests, can read requests also be sent to my primary RDS instance?
Yes, it is.
You need only to specify a proper read weight for your primary RDS instance. For more information about how to set a read weight for your primary RDS instance, see Enable the database proxy feature.
Does read/write splitting support hints?
Yes, the read/write splitting feature supports hints. You can use hints to forcibly route requests to the primary RDS instance. For more information about supported hint formats, see the section about using hints to specify SQL statements to be sent to the primary RDS instance or read-only RDS instances in Rules of read weight allocation by the system.
After I modify the read weights of my primary RDS instance and read-only RDS instances, the new read weights do no take effect. Why?
The new read weights take effect only on new connections. The new read weights do not take effect on existing connections because the existing connections are not re-established.
Why do the loads on the primary RDS instance and read-only RDS instances not comply with the read weights of the instances?
If the load on each node does not match its configured read weight, check the following two aspects:
Requests contain transactions. All requests that contain transactions are forwarded only to the primary RDS instance. To offload the requests from the primary RDS instance, you can enable transaction splitting. For more information, see Use the transaction splitting feature on an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
The endpoints of the primary RDS instance and the read-only RDS instances are used to connect to your database system. As a result, requests are not forwarded to the primary RDS instance and read-only RDS instances based on the read weights of the instances. In this case, you can use a database proxy endpoint to connect to your database system.
If I disable the database proxy feature for my RDS instance, can I assign read weights to its read-only RDS instances?
No, you cannot assign read weights to read-only RDS instances if you disable the database proxy feature for your RDS instance. You can configure the endpoints of the primary RDS instance and its read-only RDS instances in different applications to implement read/write splitting and load balancing.
If a read-only RDS instance becomes faulty, new connections are established only to other healthy read-only RDS instances. In this case, does the current connection to the faulty read-only RDS instance fail over to another healthy read-only RDS instance?
No, the current connection to the faulty read-only RDS instance does not fail over to another healthy read-only RDS instance. You must wait until the current connection times out. Then, a new connection is established to another healthy read-only RDS instance.
After I enable the database proxy feature for my RDS instance, how do I verify read/write splitting?
For more information about how to verify read/write splitting, see Verify read/write splitting on an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
After I purchase a read-only RDS instance to implement read/write splitting, is the historical data of my primary RDS instance automatically synchronized to the read-only RDS instance?
Yes, after you enable the database proxy feature and complete the configurations for read/write splitting, the historical data of the primary RDS instance is automatically synchronized to the read-only RDS instance.
What is the difference between the connection pool in a database proxy and the connection pool in an application? How do I use the connection pools together?
The connection pooling feature of a database proxy in ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL does not affect the connection pooling feature of the client. If the client provides a connection pool, you can disable the connection pooling feature of the database proxy. For more information about the connection pooling feature of a database proxy in ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, see Set the connection pool type of an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
Why are garbled characters returned when I query data?
The character sets that are used on the primary RDS instance may be different from the character sets that are used on the read-only RDS instances. You can execute the following statement to check whether the primary RDS instance and the read-only RDS instances use the same character sets:
select
@@global.character_set_results,
@@global.character_set_client,
@@global.character_set_connection,
@@global.character_set_server;If the primary RDS instance and the read-only RDS instances use different character sets, you can modify the character sets of the primary RDS instance or read-only RDS instances to ensure that these instances use the same character sets. For more information about how to modify the character set of an RDS instance, see Character set description for ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL.
Are DDL operations automatically synchronized from the primary RDS instance to the secondary RDS instance?
All DDL operations such as creating and deleting databases and tables, changing table schemas, and changing permissions are automatically synchronized from the primary RDS instance to the secondary RDS instance.
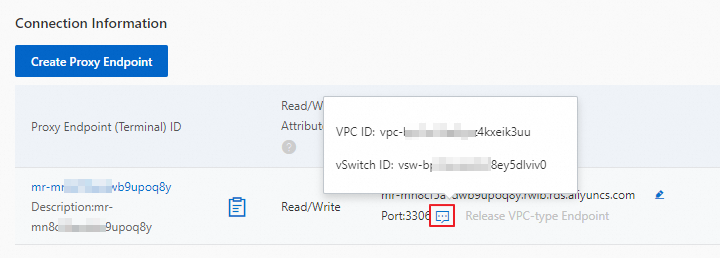
How do I view the VPC ID and vSwitch ID parameters of a VPC-type internal endpoint?
In the Database Proxy page of the instance, in the Connection Information section, move the pointer over the icon to the right of Port, as shown in the following figure.
Does the cross-zone migration of database proxies affect the connection to my primary RDS instance?
The cross-zone migration of database proxies affects your workloads only if you use a database proxy endpoint to connect to your RDS instance. If your RDS instance runs RDS High-availability Edition and you use the endpoint of the primary RDS instance or a read-only RDS instance to connect your application to the RDS instance, your workloads are not affected. If your RDS instance runs RDS Cluster Edition and you use the read/write endpoint, read-only endpoint, or direct node connection endpoint to connect your application to the RDS instance, your workloads are not affected. We recommend that you connect your application to the RDS instance using the preceding endpoints and migrate database proxies across zones during off-peak hours.
What are the impacts of the cross-zone migration of database proxies?
When you migrate database proxies across zones, a transient connection that lasts for approximately 30 seconds occurs during the migration. The duration of the transient connection varies based on your business. We recommend that you use the endpoints that are not affected by the migration to connect to your RDS instance and migrate database proxies across zones during off-peak hours. For more information about the impacts, see Migrate database proxies across zones.
Does the nearest access feature become unavailable after you migrate proxy nodes across zones?
This may become invalid.
After the cross-zone migration, the new nearest zone can be accessed by default. The original nearest zone can no longer be accessed. If you change the zone of a proxy endpoint to a zone that is different from the default zone, the nearest access to the new zone fails. The following table describes example scenarios.
Scenario | Original proxy node information | New proxy node information | |||||
Current zone of the proxy node | Proxy endpoint | Nearest access | New zone of the proxy node | Default zone of the proxy endpoint | New zone of the proxy endpoint | Nearest access | |
Scenario 1:
| Zone A | Proxy endpoint a | Zone A | Zone A | Zone A | Zone A | Zone A |
Zone C | Invalid | ||||||
Zone B | Proxy endpoint b | Zone B | Zone C | Zone C | Zone C | Zone C | |
Zone D | Invalid | ||||||
Scenario 2:
| Zone A | Proxy endpoint a | Zone A | Zone C | Zone C | Zone C | Zone C |
Zone E | Invalid | ||||||
Zone B | Proxy endpoint b | Zone B | Zone D | Zone D | Zone D | Zone D | |
Zone E | Invalid | ||||||
Can I change the zone of a proxy node when I modify the proxy node configuration?
Not supported.
For more information about how to migrate proxy nodes across zones, see Migrate database proxies across zones.
When I change the deployment mode from dual-zone deployment to single-zone deployment, an error message indicating that the vSwitch IDs of database proxy endpoints are not in the specified zone is displayed. What do I do?
If you change the deployment mode from dual-zone deployment (Zone 1+Zone 2) to single-zone deployment (Zone 1), you must delete the database proxy endpoint in Zone 2. For more information, see Manage database proxy endpoints.
Are the IP addresses resolved from database proxy endpoints fixed?
No, the IP addresses are not fixed. You must use the database proxy endpoint (for example, d3pswqe3jk9xwc5d****-rw4rm.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com) to connect to your RDS instance. Do not use the resolved IP address.
How do I determine whether a session is connected through a database proxy endpoint?
You can determine whether a session is connected through a database proxy endpoint based on the session ID. If the session ID is less than 16777215, the session is connected through a View and manage instance endpoints and ports. Otherwise, the session is connected through a database proxy endpoint.
You can view the session ID using the Session Manager feature.
Why can't I retrieve the data that I just wrote when I query through a database proxy endpoint?
Common cause: The database proxy endpoint routes the request to a read-only RDS instance, but the read-only RDS instance has not yet applied the corresponding binary log. As a result, you cannot query the latest data.
Solution:
Use hint syntax to route queries that require strong consistency to the primary RDS instance using
/*FORCE_MASTER*/.Set transaction splitting and encapsulate queries that require strong consistency in transactions.
Set the consistency level to global consistency.
All of the preceding methods route more query requests to the primary RDS instance. Therefore, you must evaluate the capacity of your primary RDS instance. We recommend that you use hint syntax to route only queries that require strong consistency to the primary RDS instance.